

Lecture outline
•Simple principles in carcinogenesis
•Features of transformed cells
•The sequence of events in normal cell
growth
•Four groups of normal regulatory genes
are involved in carcinogenesis
•Transformation of proto-oncogenes to
oncogenes
•Tumour suppressor genes
•Viruses and cancer

Lecture Objectives
By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to:
•Enumerate the features of transformed cells
•Define the sequence of events in normal cell
growth
•Understand the meaning of clonality
• Know that four groups of normal regulatory
genes are involved in carcinogenesis
•Describe how proto-oncogene becomes an
oncogene (with examples)
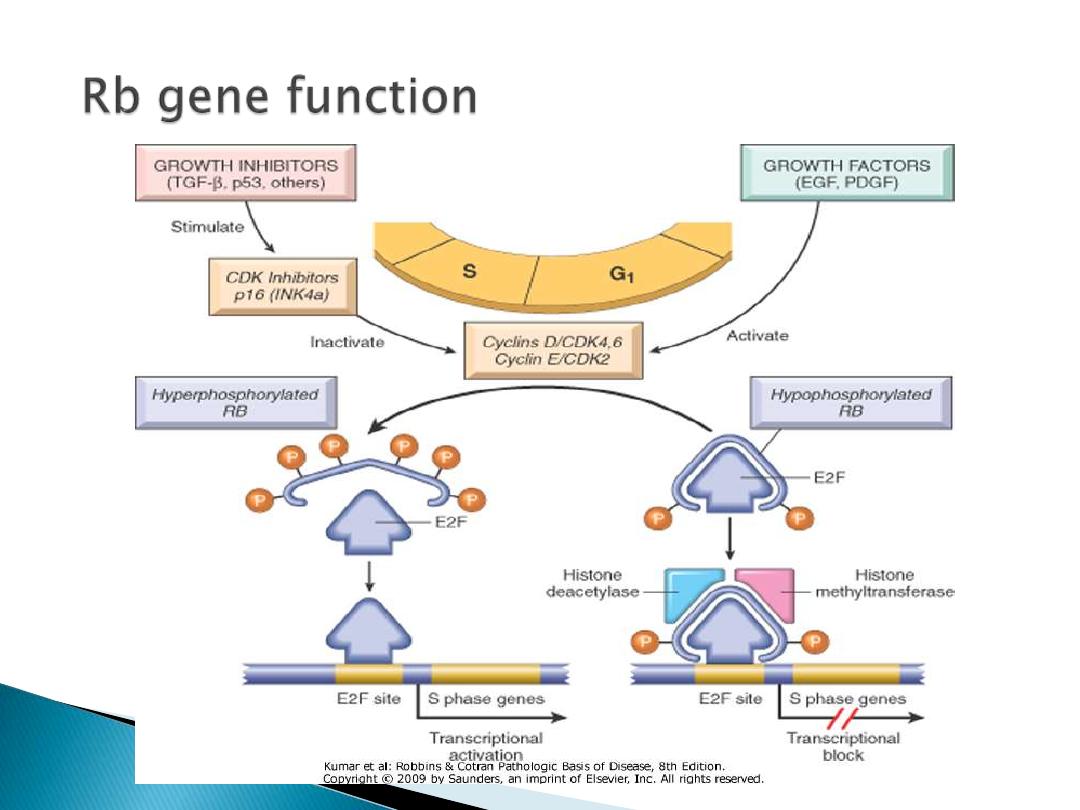
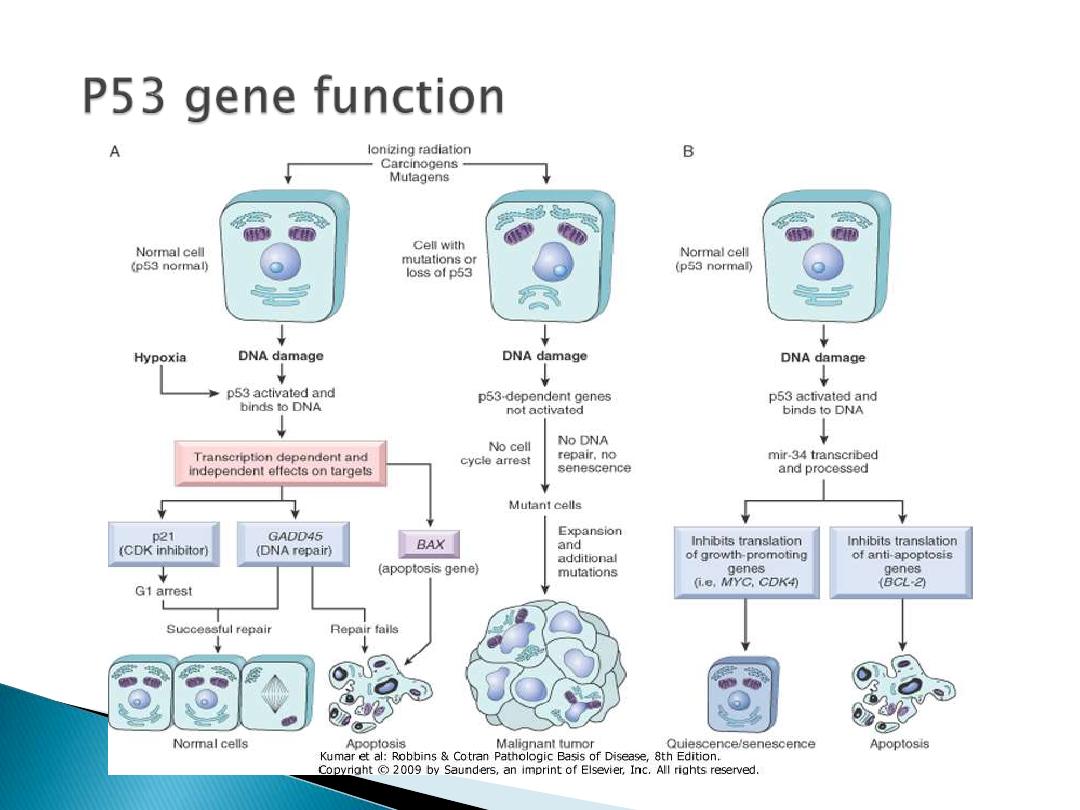
•Understand the role of Rb and P53 in the control
of normal cell growth
•Enumerate viruses that play role in cancer
development

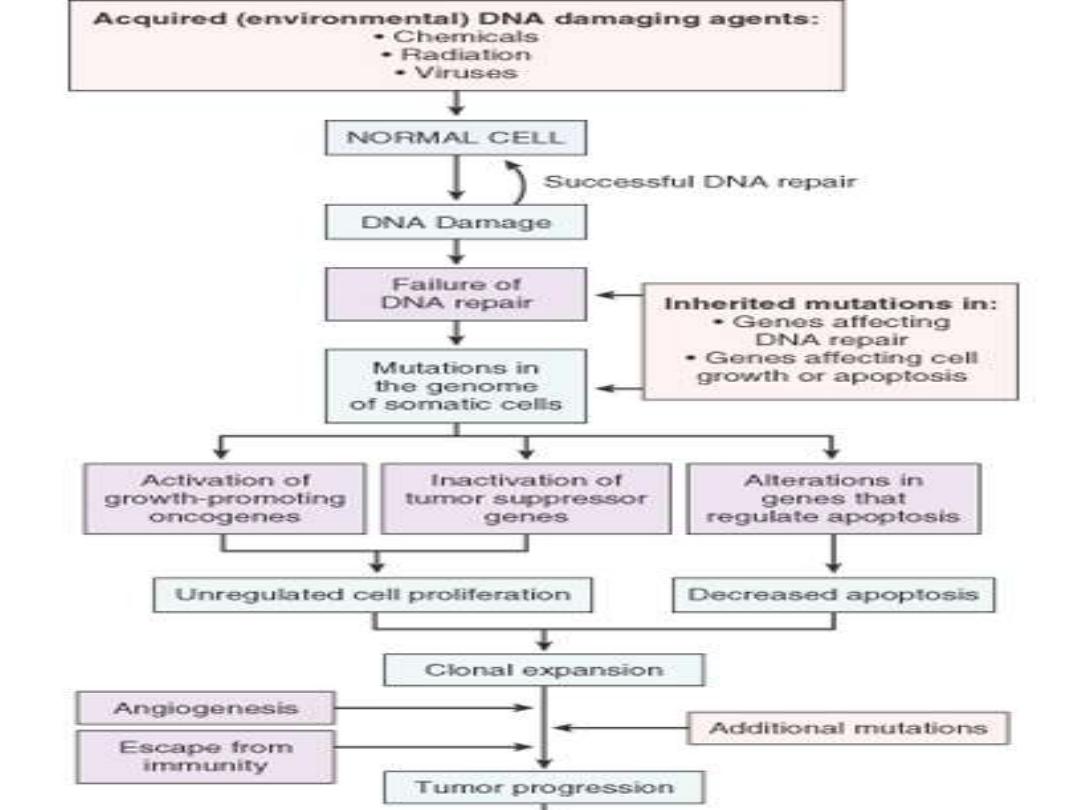
1-Inherited cancer syndromes (autosomal
dominant type): Familial adenomatous polyps
2-Familial cancers.
-early age.
- two or more relatives.
- sometimes multiple or bilateral
3-Autosomal recessive syndromes of defective
DNA repair (Xeroderma pigmentosum).
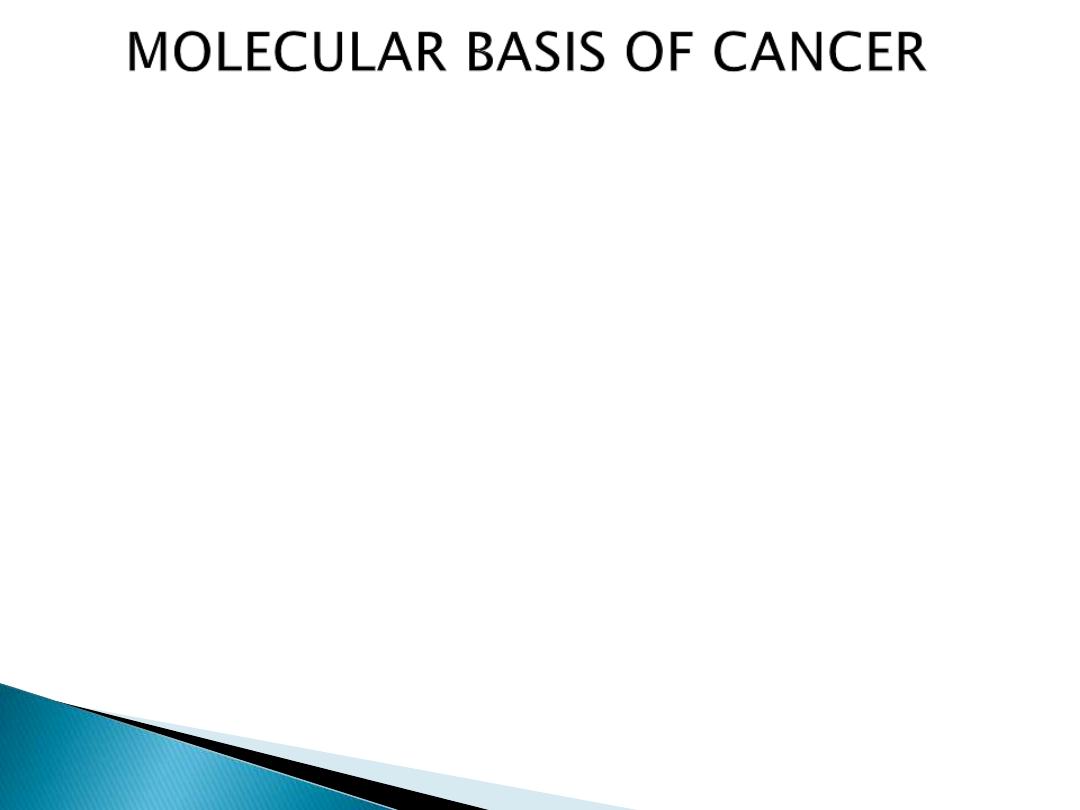
some fundamental principles
:
1-Non-lethal genetic damage (mutation)
2- The tumor is the result of clonal expansion
of a single precursor cell
3- Carcinogenesis is a multi-step process:
Phenotypic (tumor progression)
genetic ( accumulation of mutations)
4- Involvement of normal regulatory genes

1.
Density independent growth.
2. Anchorage independent growth.
3. Immortality.
4. Decreased dependence on exogenous
growth factors.
5. In-vivo tumorigenicity.
6. Angiogenesis.
7. Metastasis.

1-Non-lethal genetic damage (mutation)
A. Acquired through the action of
environmental factors: radiation, chemicals or
viruses.
e.x HPV associated with cancer of the cervix
B. Inherited in germ line cells.
e.x Familial adenomatous polyps (APC gene,
autosomal dominent disorder)
Familial adenomatous polyps
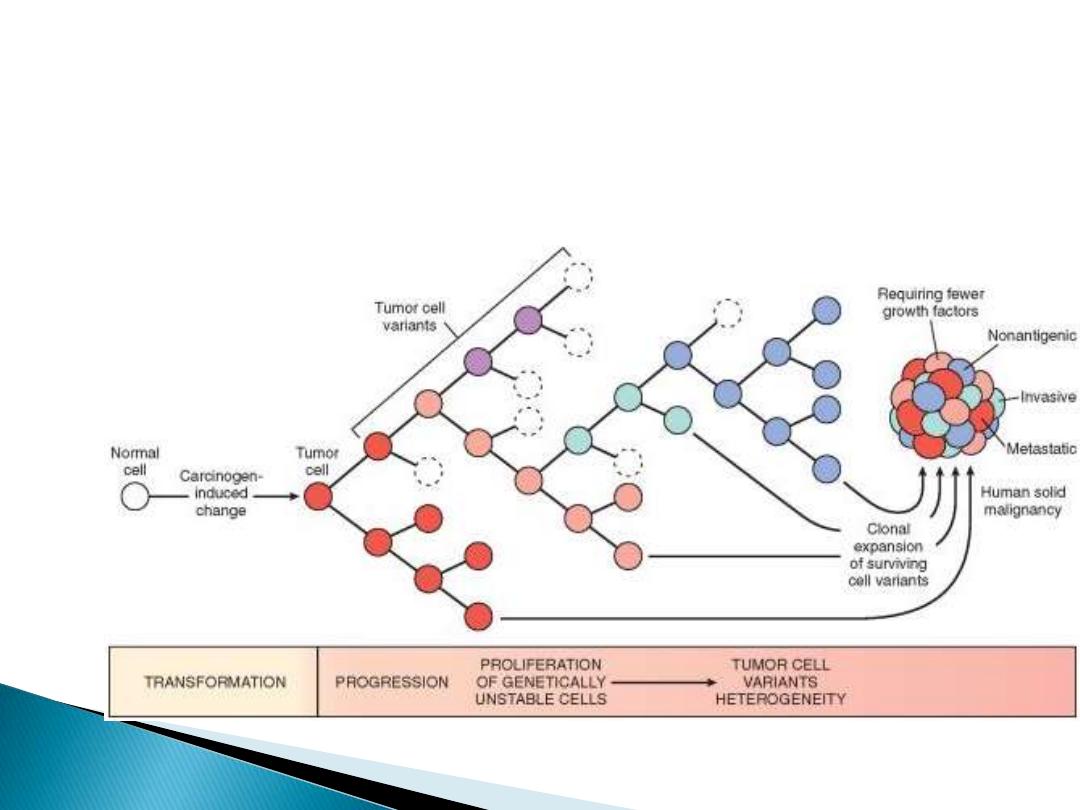
2- The tumor is the result of clonal expansion of
a single precursor cell.
3-Multistep carcinogenesis
: Phenotypic (tumor
progression), genetic (accumulation of
mutations)

The most commonly used method to determine
tumor clonality involves the analysis
of methylation
patterns adjacent to the highly polymorphic locus of
the human androgen receptor gene,
AR
. The
frequency of such polymorphisms in the general
population is more than 90%, so it is easy to
establish clonality by showing that all the cells in a
tumor express the same allele. For tumors with
acquired cytogenetic aberrations of any type (e.g., a
translocation)
their presence can be taken as
evidence that the proliferation is clonal.
Immunoglobulin receptor and T-cell receptor gene
rearrangements
serve as markers of clonality in B-
and T-cell lymphomas, respectively.

4- Involvement of normal regulatory
genes:
A: The growth promoting genes (proto-
onco-genes).
B: The growth inhibiting (cancer
suppressor ) genes.
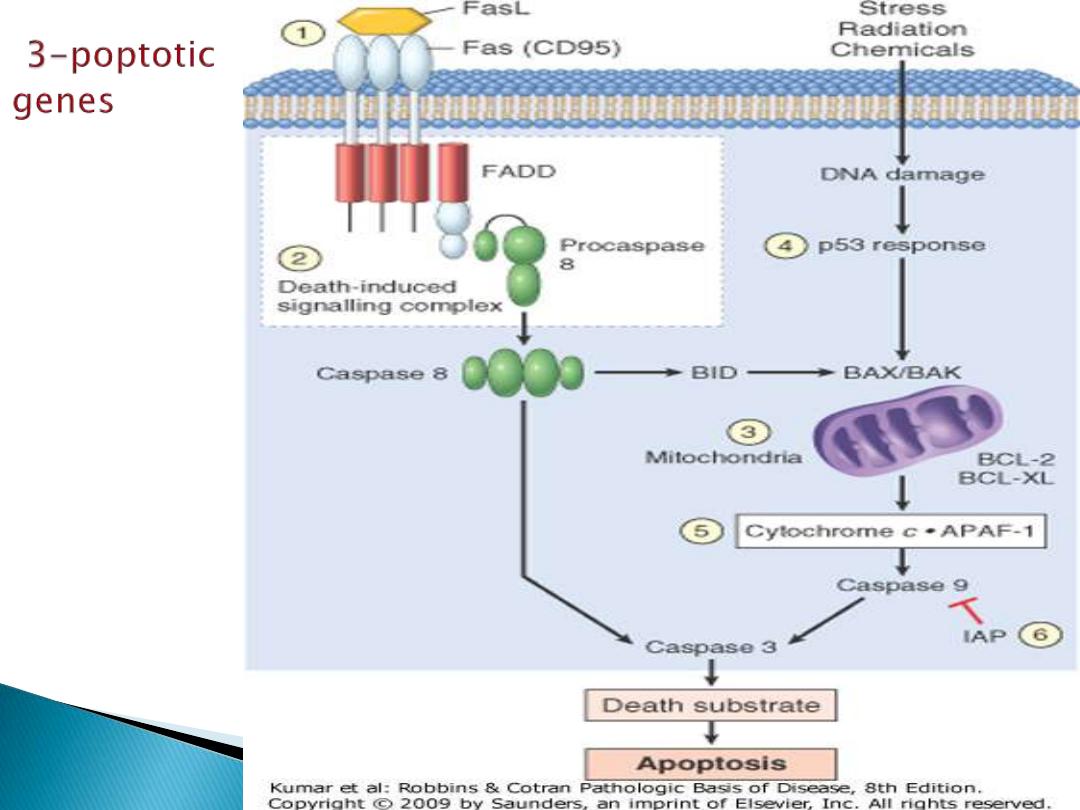
C: Genes that control programmed cell
death (apoptosis).
D: DNA repair genes.
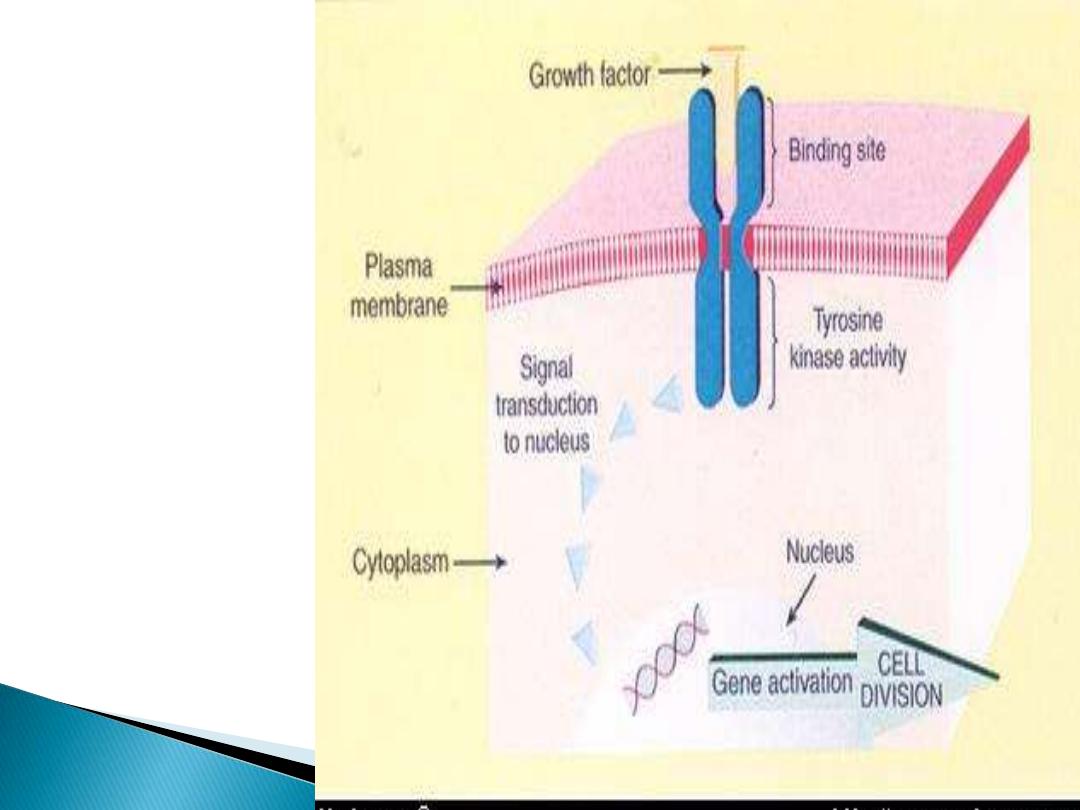

1
. The binding of growth factor to its receptor.
2. transient & limited activation of this complex
leads to activation of signal trasducing proteins.
3. Transmission of the signal via second
messengers.
4. Induction & activation of nuclear regulatory
factors that initiate transcription.
5. Entry & progression in the cell cycle.
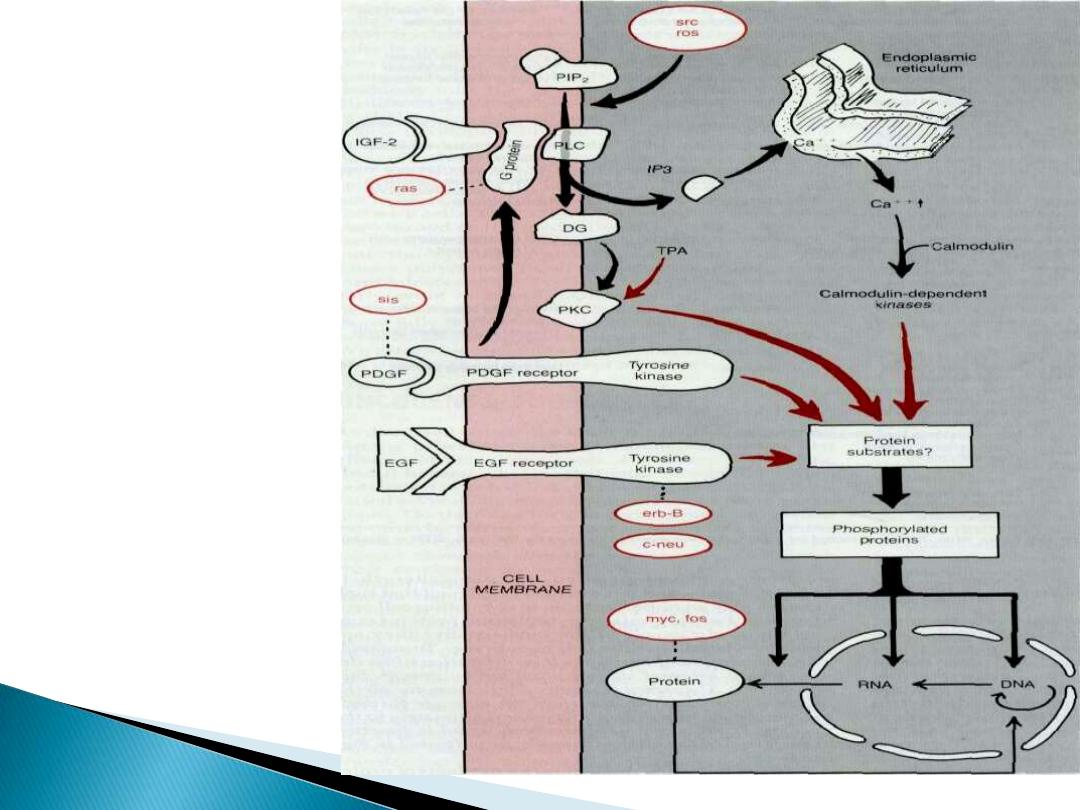
proto-onco-genes
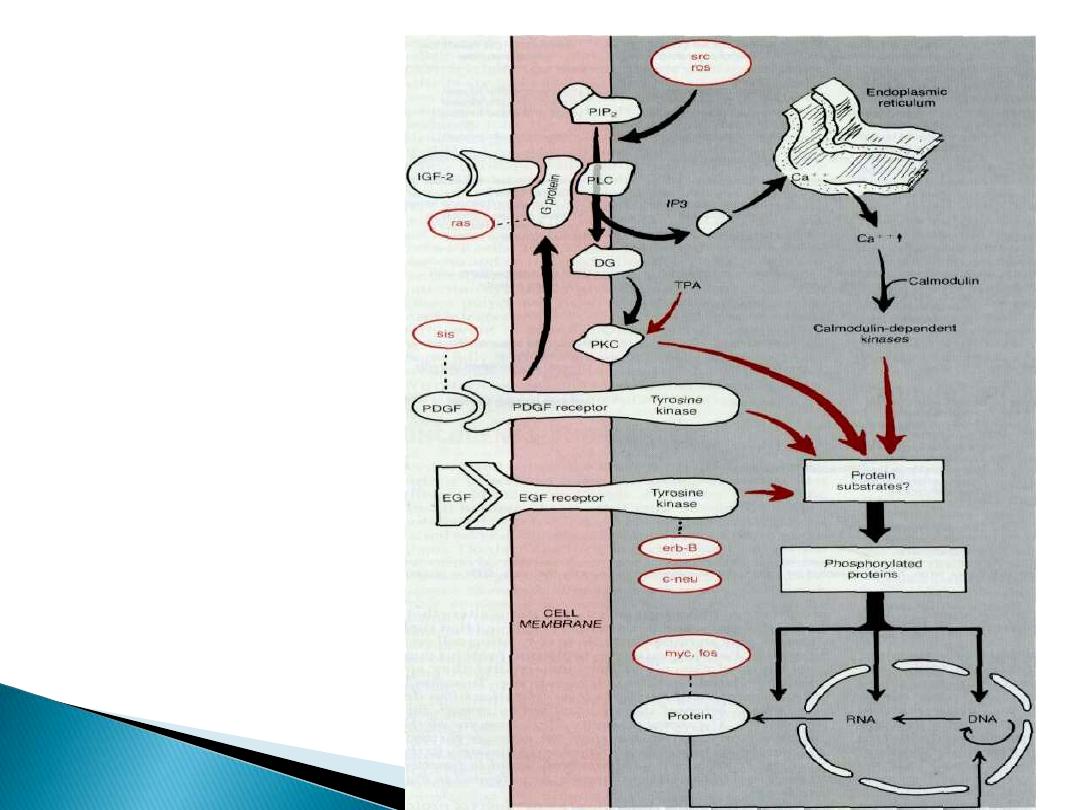
proto-oncogenes may
function as:
growth factors or
their receptors,
signal transducers,
transcription factors, or
cell cycle components

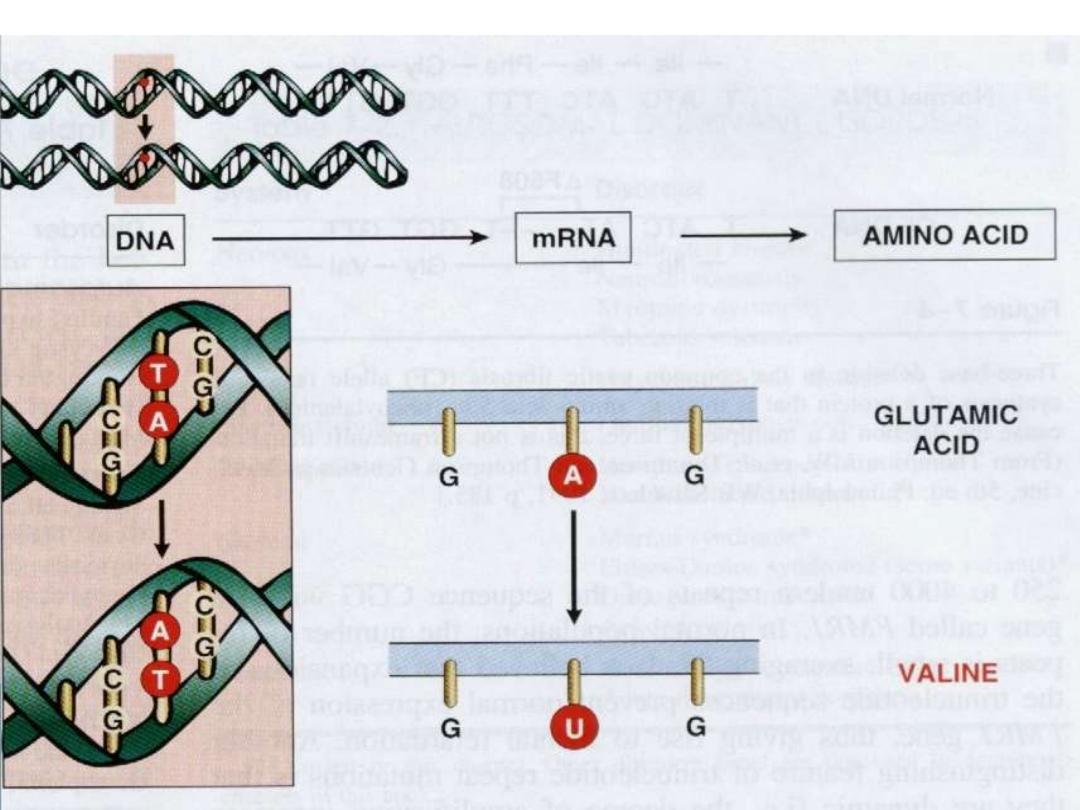
Transformation of proto-oncogenes to oncogenes:
-
point mutation
-Chromosomal translocation (philadelphia
chromosome in chronic myeloid leukaemia)
-Amplification (myc gene, HER2 gene)
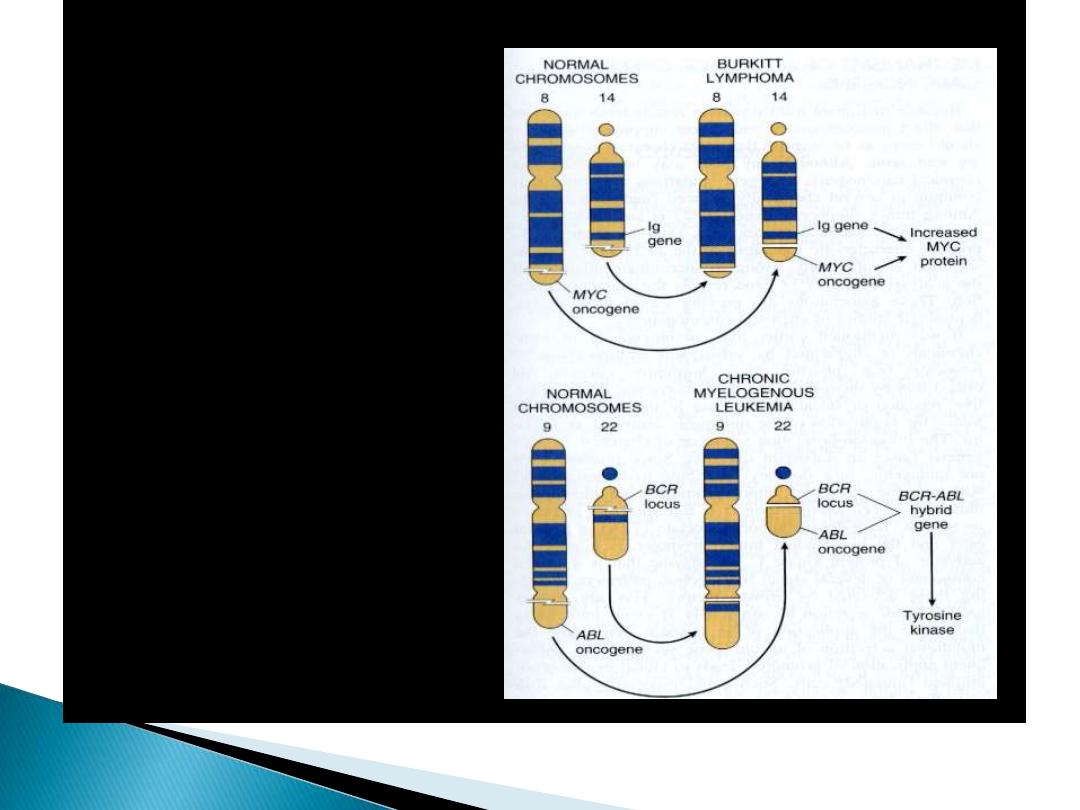
Chromosomal translocations
The chromosomal
translocations and
associated oncogenes
in Burkitt’s lymphoma
and chronic myelogenous
leukemia
Pheladelphia chromosome
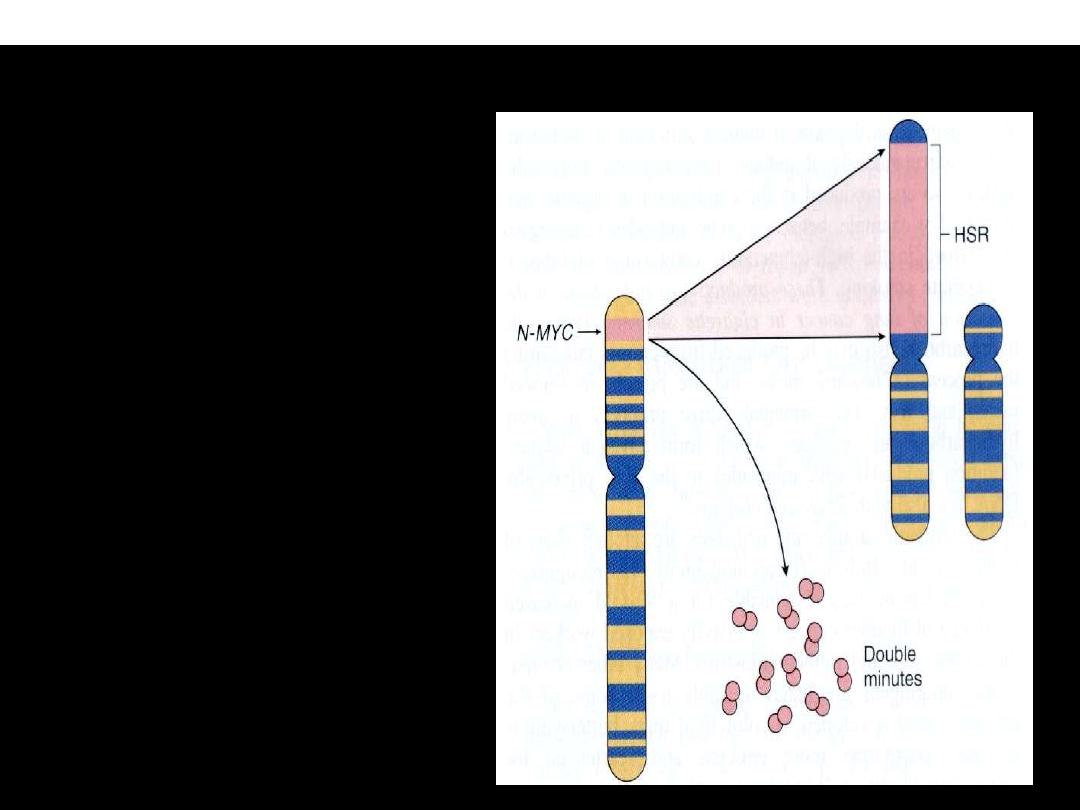
N-MYC gene amplification in neuroblastoma
The N-MYC gene,
present normally on
chromosome 2p,
becomes amplified
and
is seen either as extra-
chromosomal double
minutes or as a
chromosomal integrated
homogeneous-staining
region (HSR).
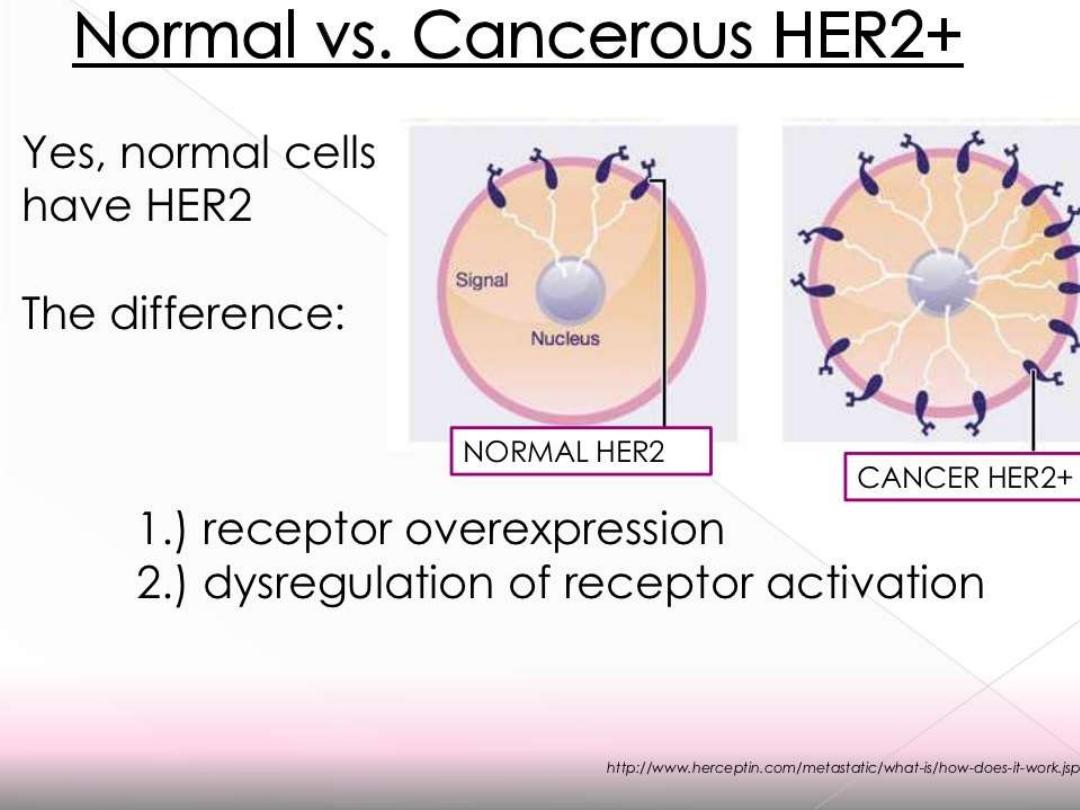
Proto oncogene
HER2/neu: epidermal growth factor receptor
overexpressed in 30% of breast cancer cases

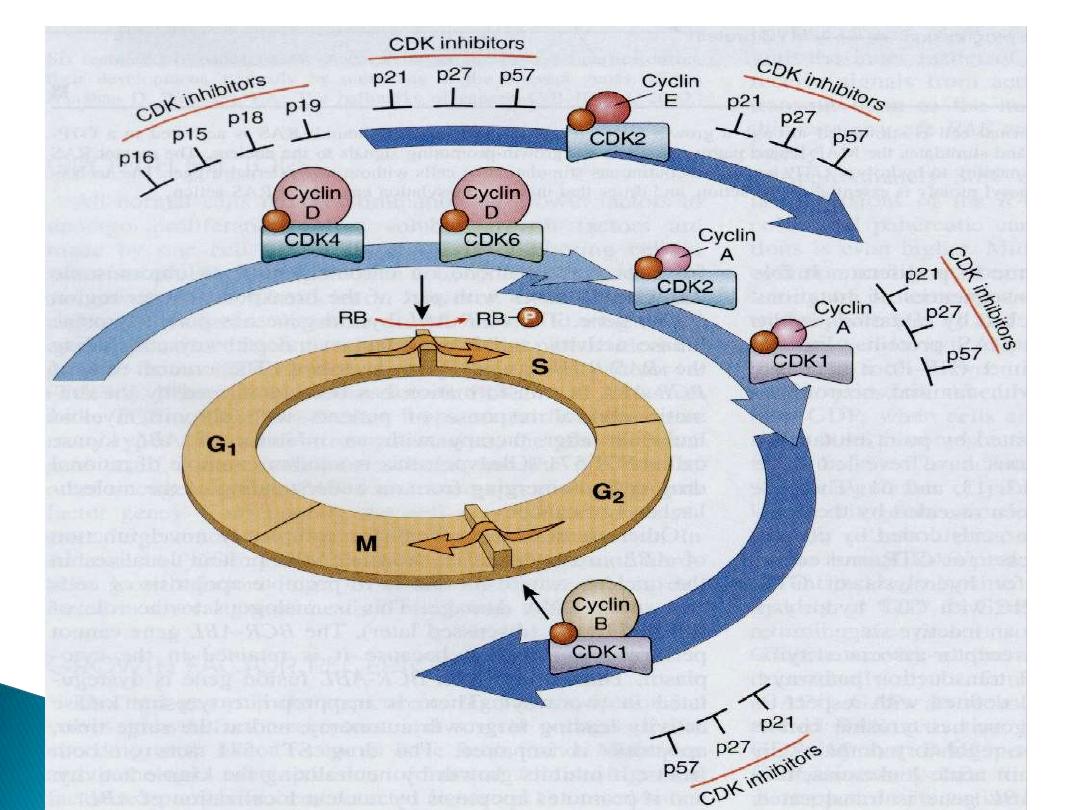
Rb gene
P53 gene
TGF-beta
APC-beta-catenin
NF-1
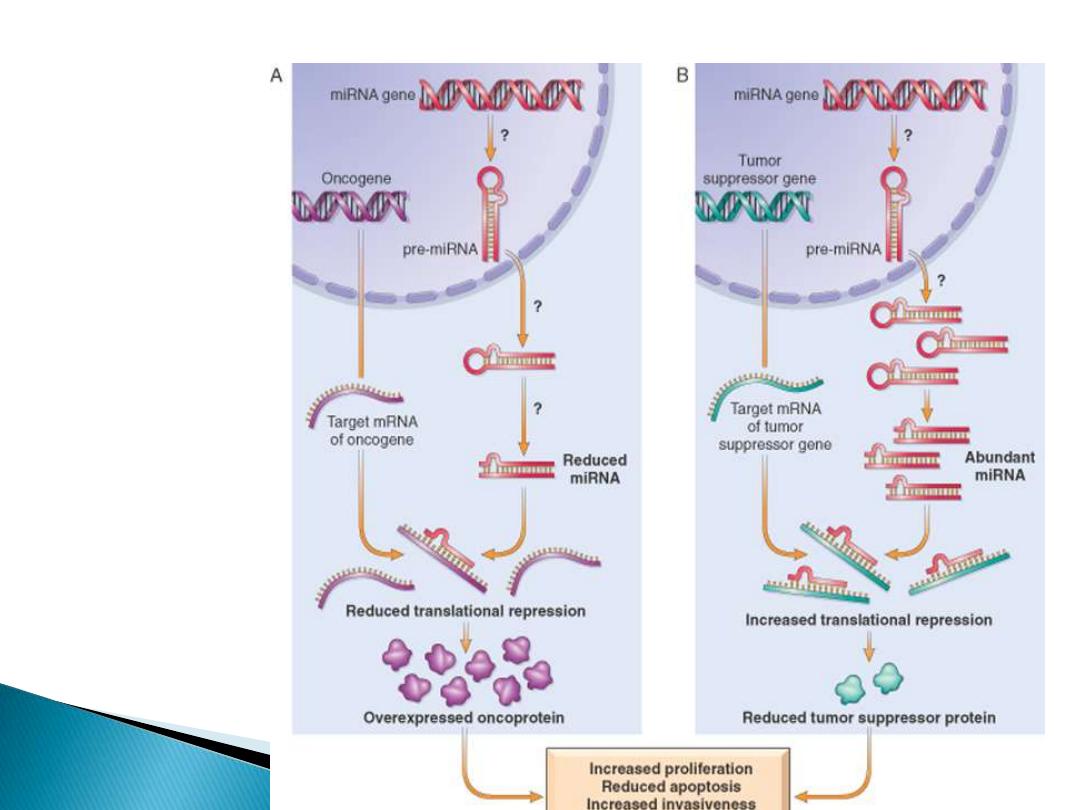
1000 genes in humans that encode miRNAs
miRNAs can
participate in
neoplastic
transformation
either by
increasing the
expression of
oncogenes or
by reducing the
expression of
tumor
suppressor
genes
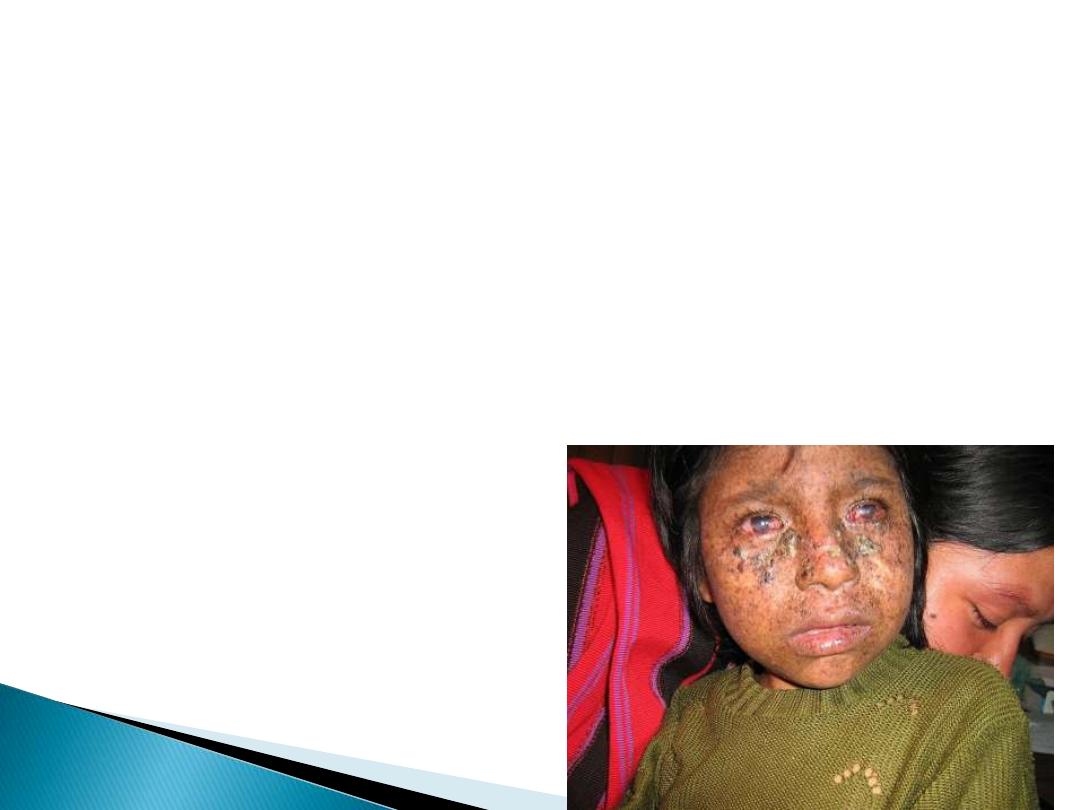

4-DNA repair genes
Xeroderma pigmentosum, or XP,
is genetic
disorder of nucleotide excision repair mechanism
ability to repair damage caused by ultraviolet (UV)
light is deficient
Children of the Night
Photosensitivity
Skin lesions & changes
skin cancer at early age

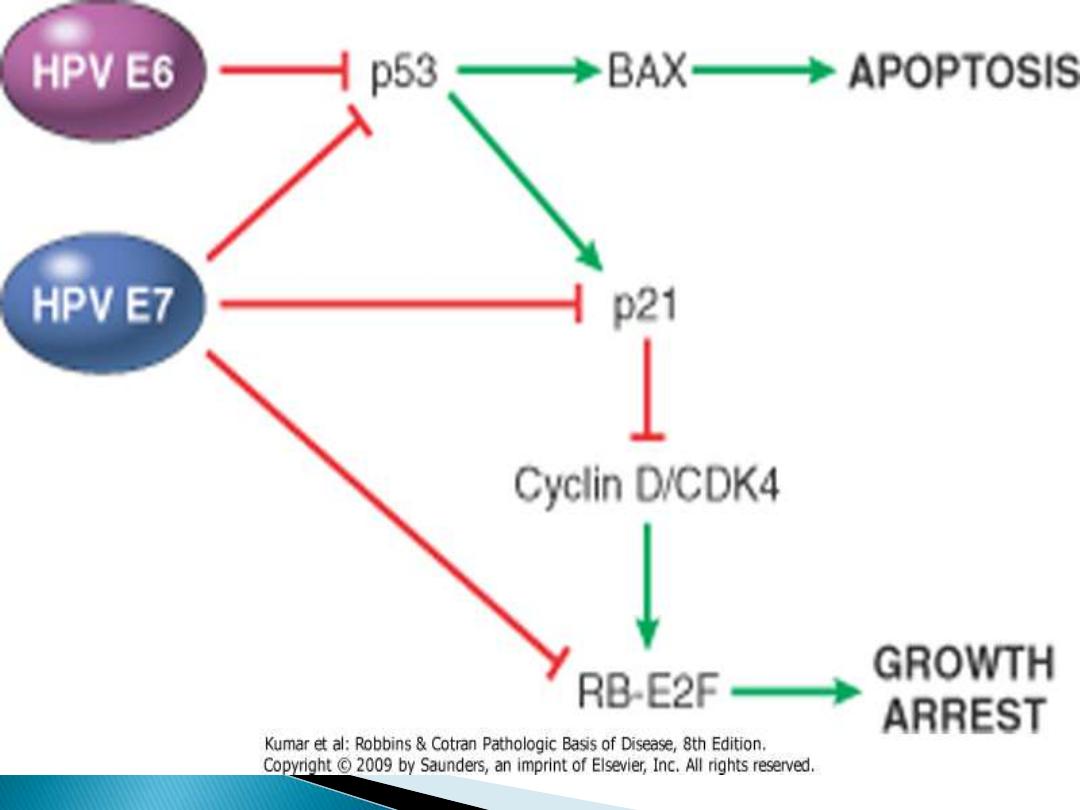
DNA viruses:
HPV, HBV, EBV, Herpes, Adenovirus.
RNA viruses:
.1
HTLV-1 (gag, pol, env,
tax
genes)
HCV

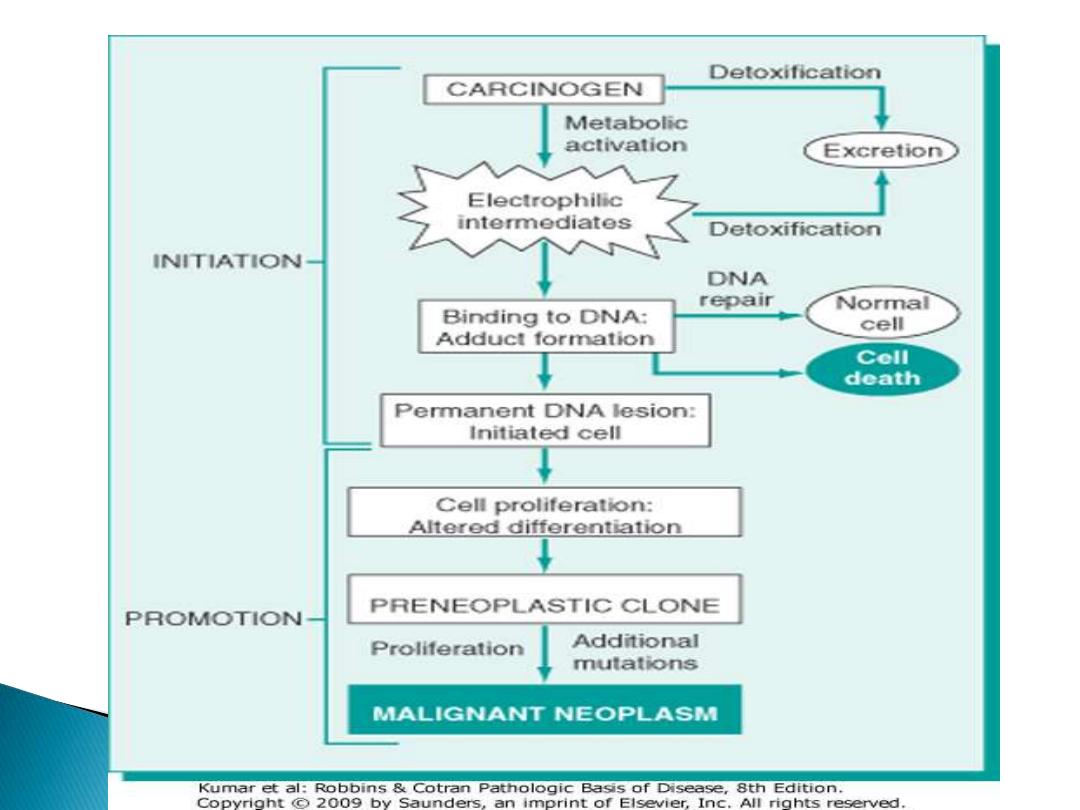
Initiation
DNA damage
- Direct acting
- Indirect acting
Promoters

Summary
•Cancer results from clonal expansion
•Carcinogenesis is a multistep process
•Four groups of normal regulatory genes are
involved in carcinogenesis
•Tumour suppressor gene (P53 & Rb) play important
role in the control of cell growth
•Some viruses are linked to cancer

THANK YOU
