
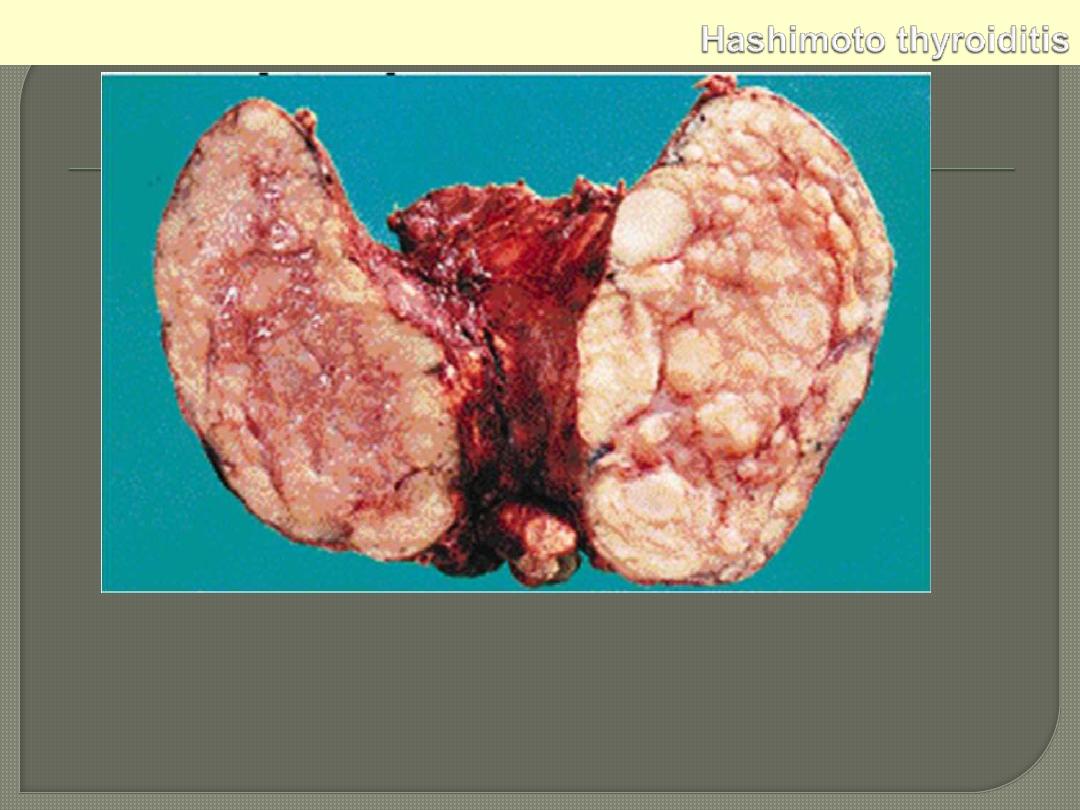
Grossly the thyroid is usually symmetrically enlarged and firm,
with a bosselated surface. As a result of disappearance of brown
(iodine-rich) colloid, and its replacement by lymphocytes, the cut
surface is whitish rather than normal brown color.
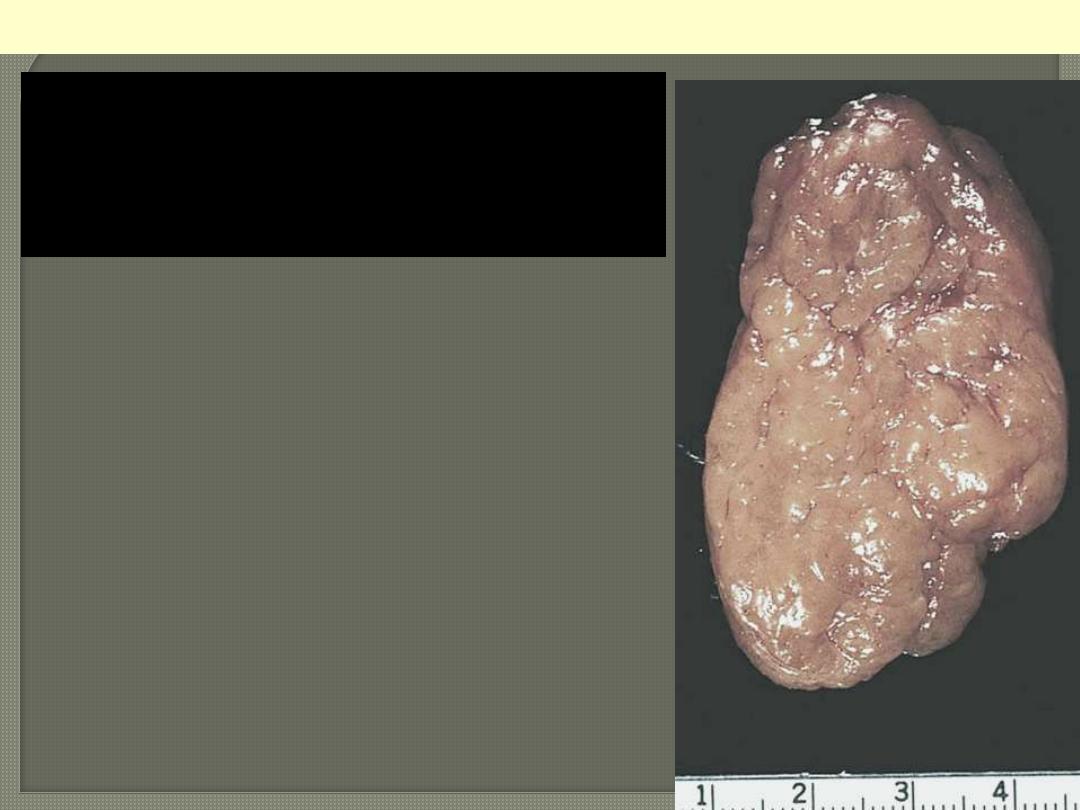
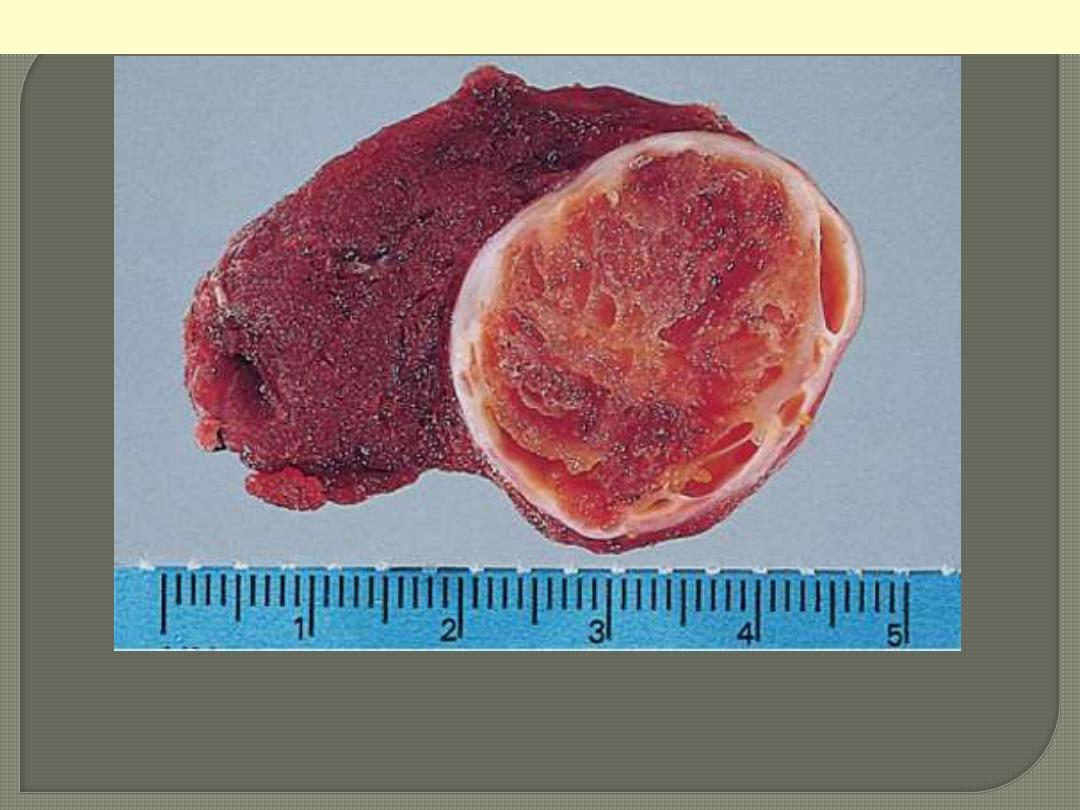
Cut surface of thyroid involved by
Hashimoto's thyroiditis. The
appearance is reminiscent of a
hyperplastic lymph node.
Hashimoto thyroiditis
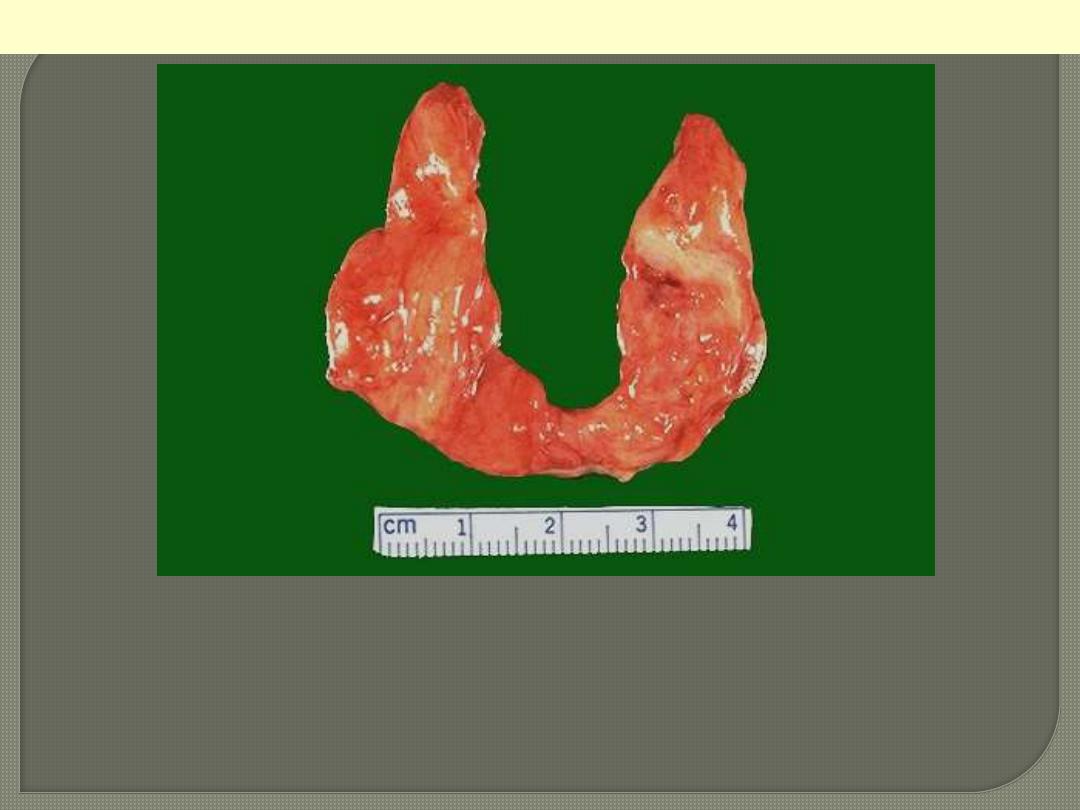
This symmetrically small thyroid gland demonstrates atrophy. This
patient was hypothyroid. This is the end result of Hashimoto's
thyroiditis. Initially, the thyroid is enlarged and there may be transient
hyperthyroidism, followed by a euthyroid state and then hypothyroidism
with eventual atrophy years later.
Hashimoto thyroiditis
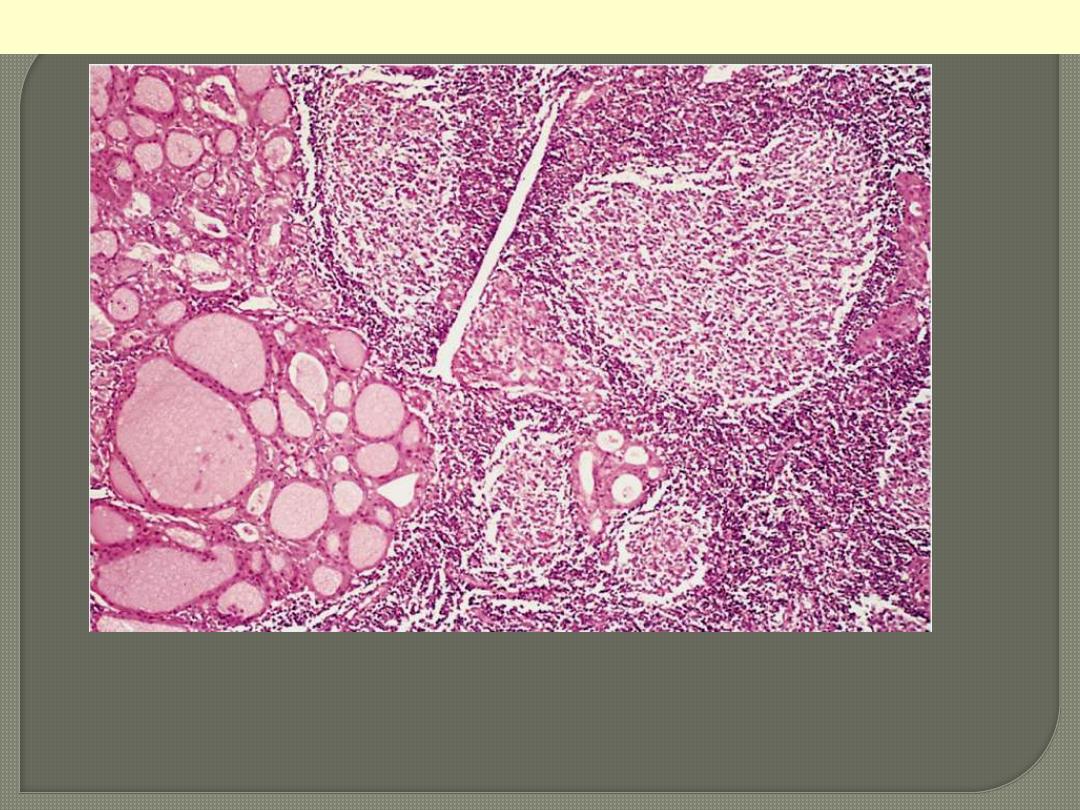
The thyroid parenchyma contains a dense lymphocytic infiltrate
with germinal centres. Residual thyroid follicles lined by deeply
eosinophilic Hürthle cells are also seen.
Hashimoto thyroiditis
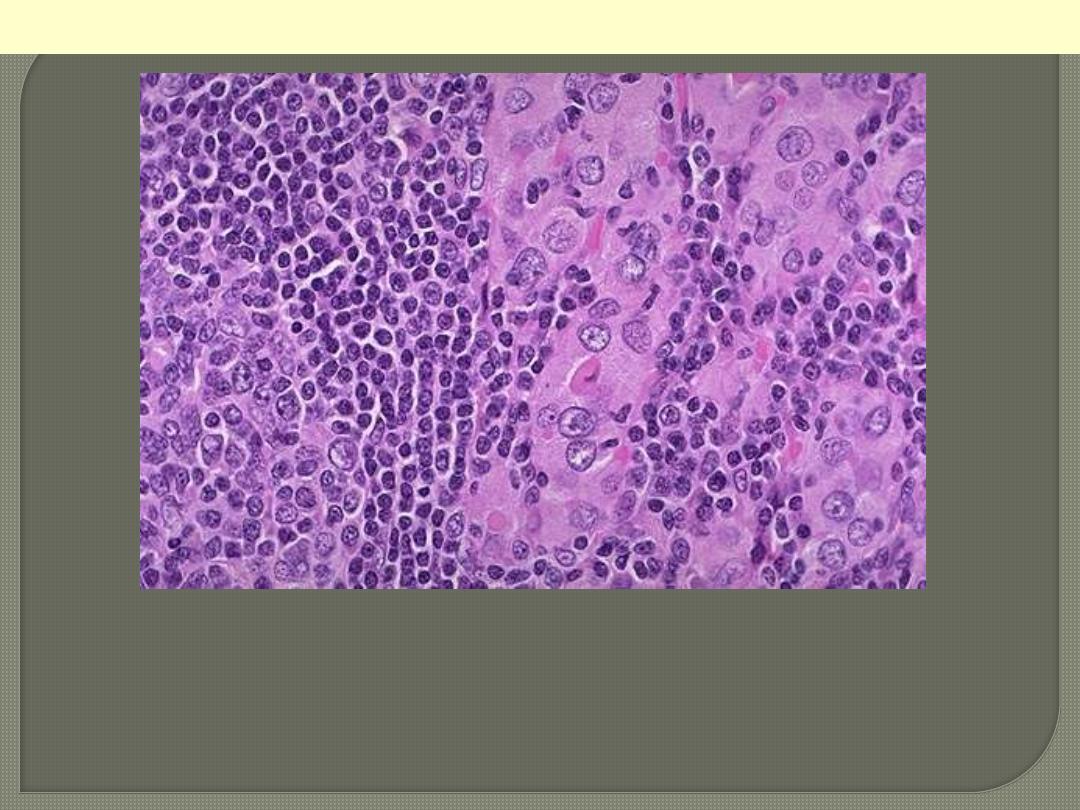
Hashimoto's thyroiditis demonstrates the pink Hurthle cells at the
center and right. The lymphoid follicle is at the left. Hashimoto's
thyroiditis initially leads to painless enlargement of the thyroid,
followed by atrophy years later.
Hashimoto thyroiditis

A solitary, well-circumscribed, encapsulated nodule is seen.
Follicular adenoma thyroid

Follicular adenoma G
Here is another follicular adenoma that is surrounded by a thin white
capsule. It is sometimes difficult to tell a well-differentiated follicular
carcinoma from a follicular adenoma. Thus, patients with follicular
neoplasms are treated with thyroidectomy just to be on the safe side.
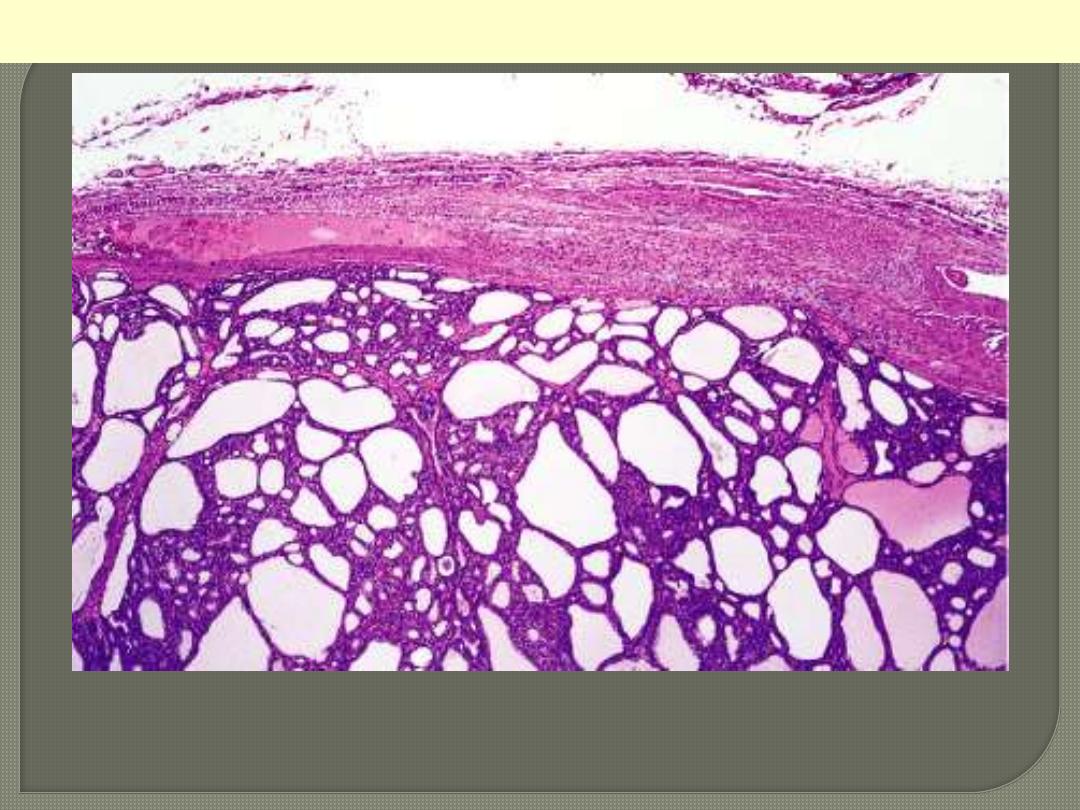
Follicular Adenoma thyroid
Intact fibrous capsule around a follicular adenoma
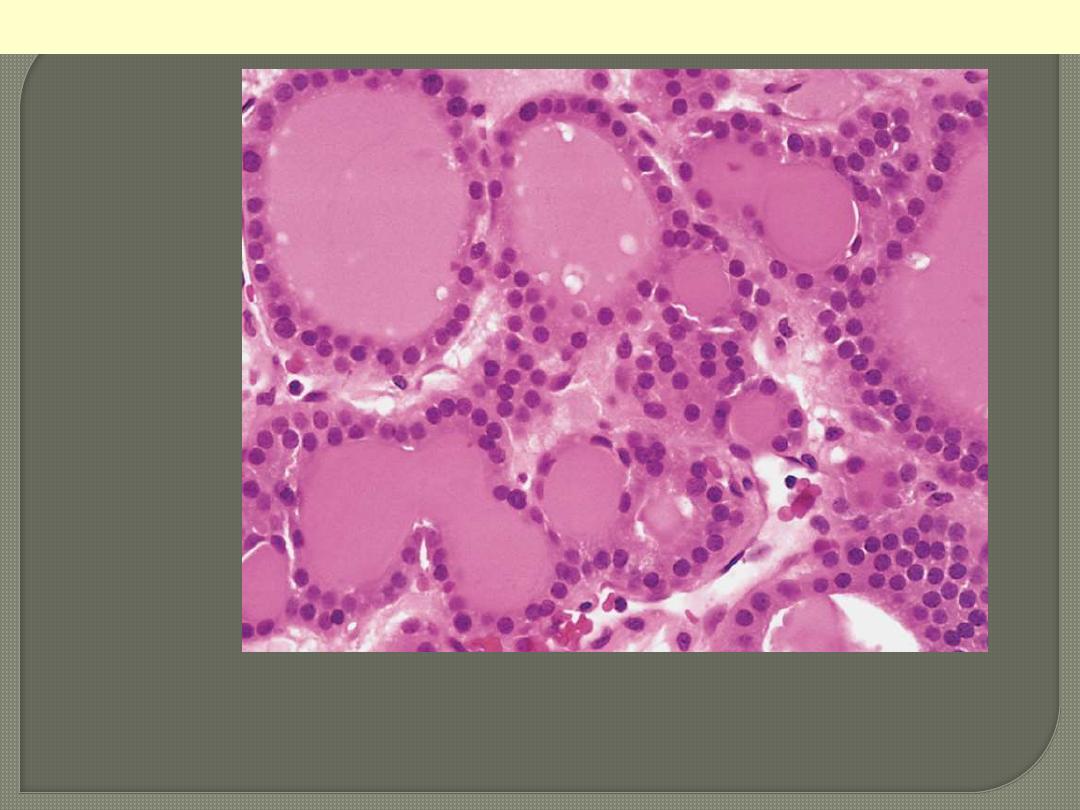
Well-differentiated follicles resemble normal thyroid
parenchyma.
Follicular adenoma thyroid
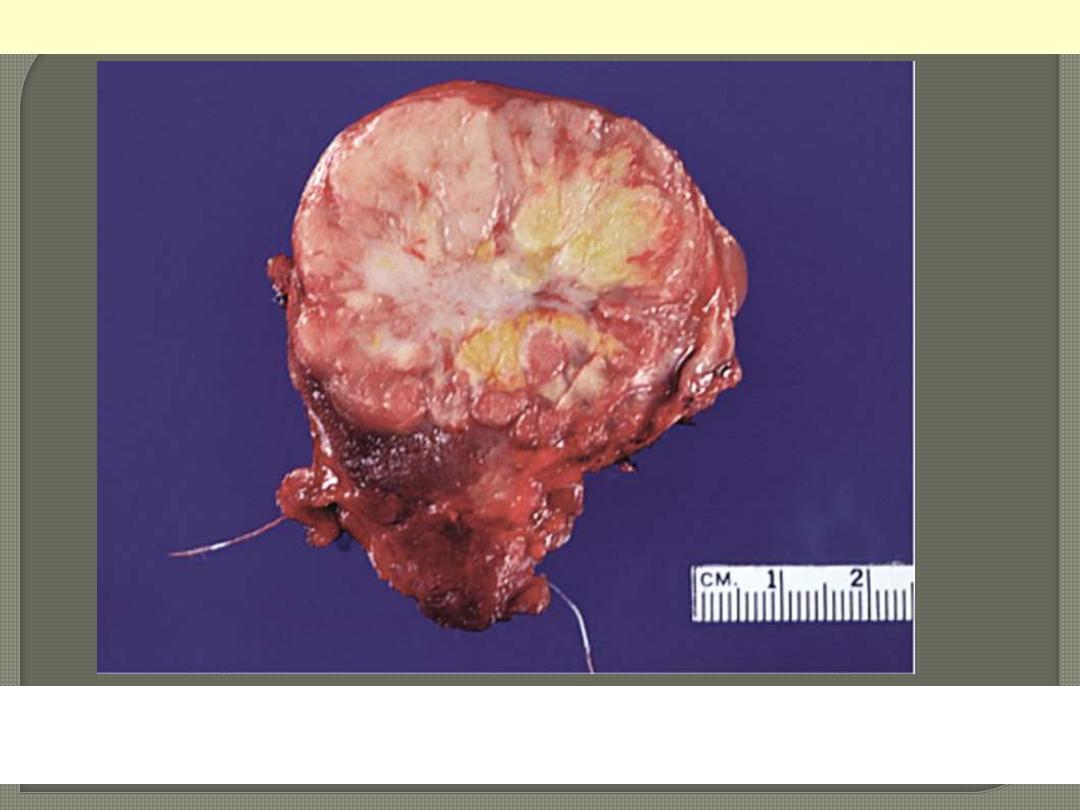
Most cases are solid, whitish, firm & clearly invasive. The tumor
shown exhibits a central area of fibrosis
Papillary ca thyroid central fibrosis
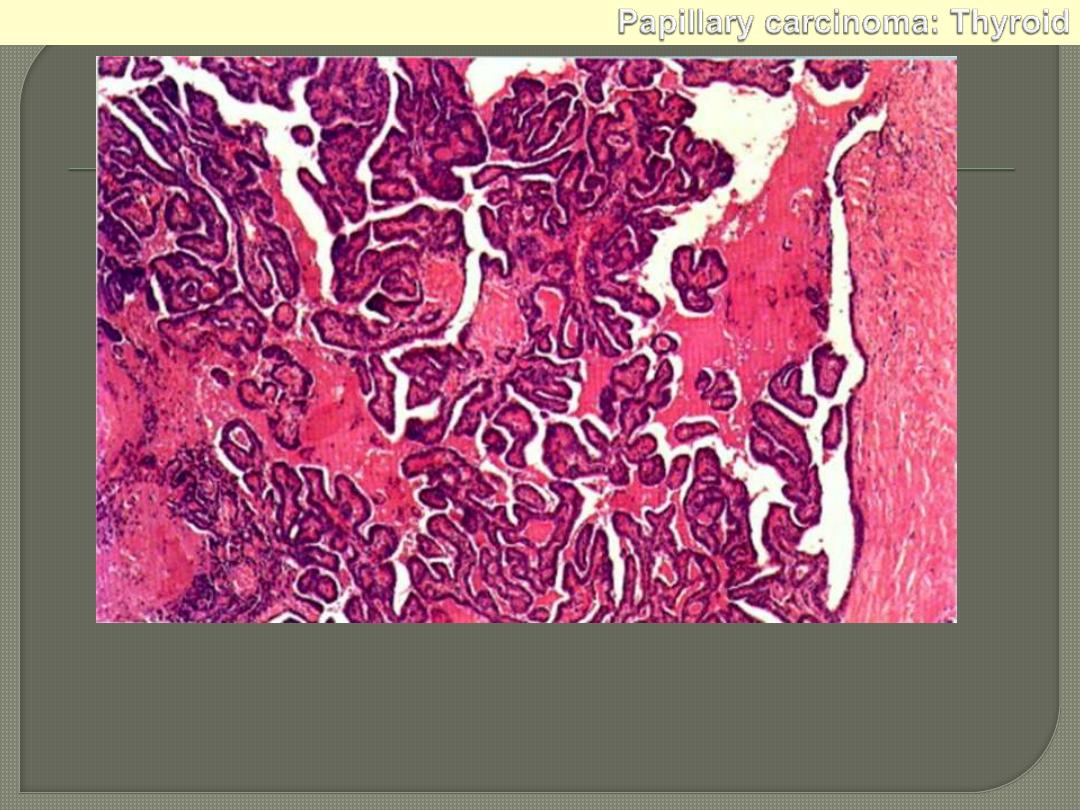
Papillary adenocarcinoma: thyroid. It is a well-differentiated papillary lesion,
lying within a cystic space. The fibrous capsule is on the right. The papillae
have a core of vascular connective tissue and are covered with cuboidal
epithelium.
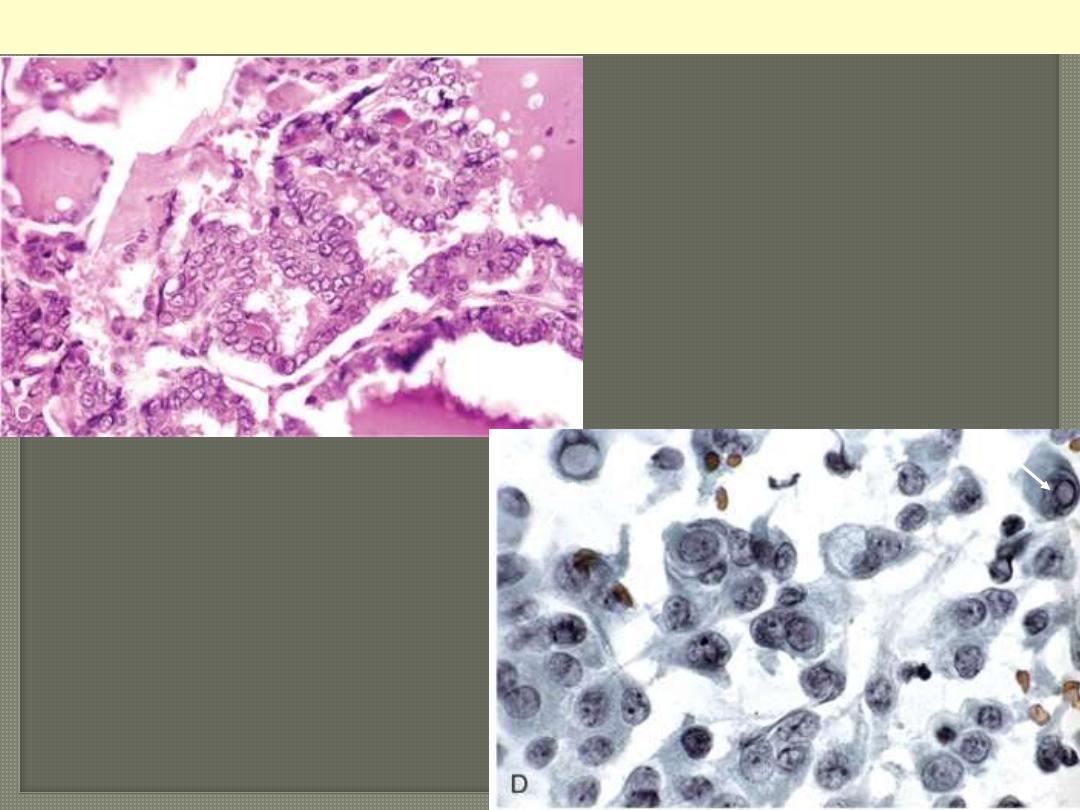
The papillae are lined by cells with
characteristic empty-appearing
nuclei, (ground glass or "Orphan
Annie eye" nuclei) (C). D, Cells
obtained by fine-needle aspiration of
a papillary carcinoma.
Characteristic intranuclear
inclusions are visible in some of the
aspirated cells.
Papillary carcinoma nuclear features
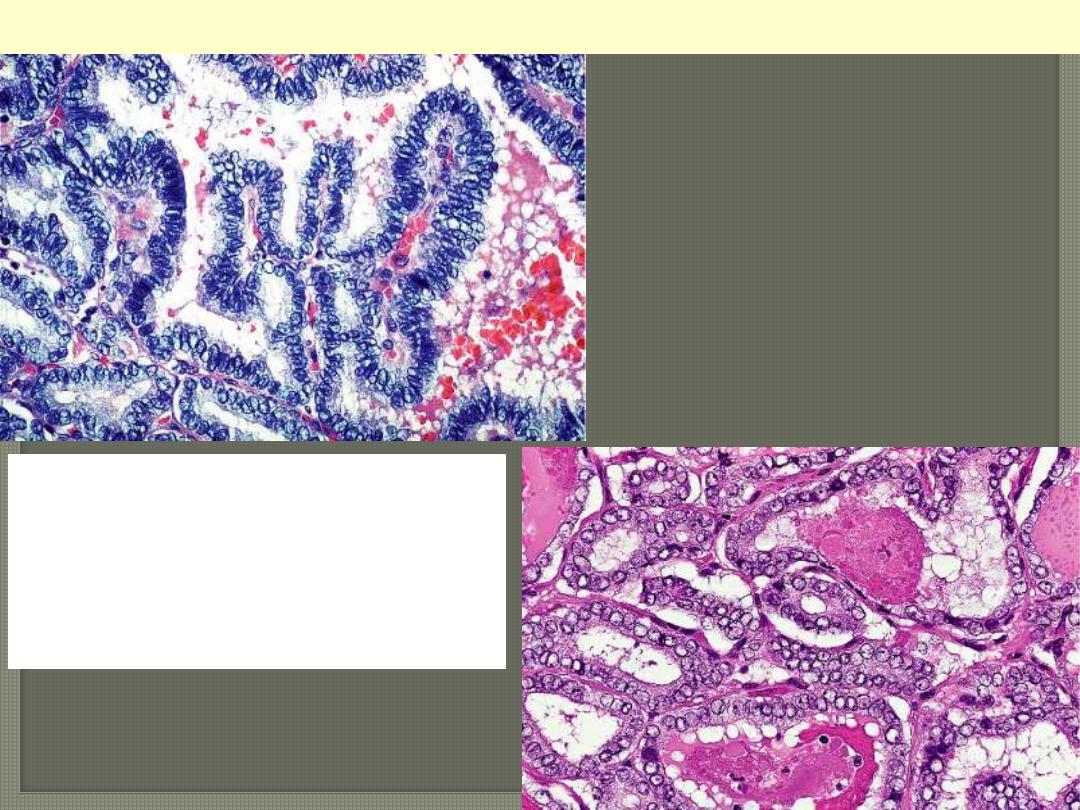
Nuclear features of
papillary carcinoma:
optically clear (ground
glass) nuclei
Papillary carcinoma thyroid ground glass nuclei
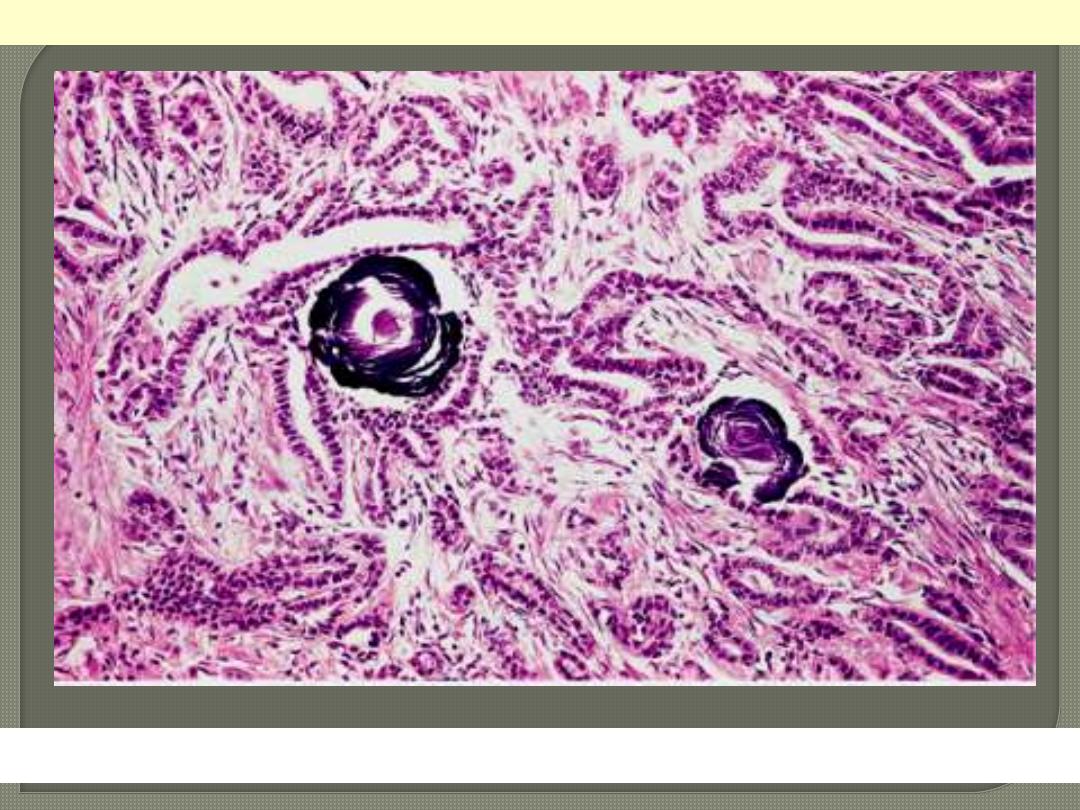
Psammoma body formation within the stroma of the tumor.
Papillary carcinoma: Thyroid
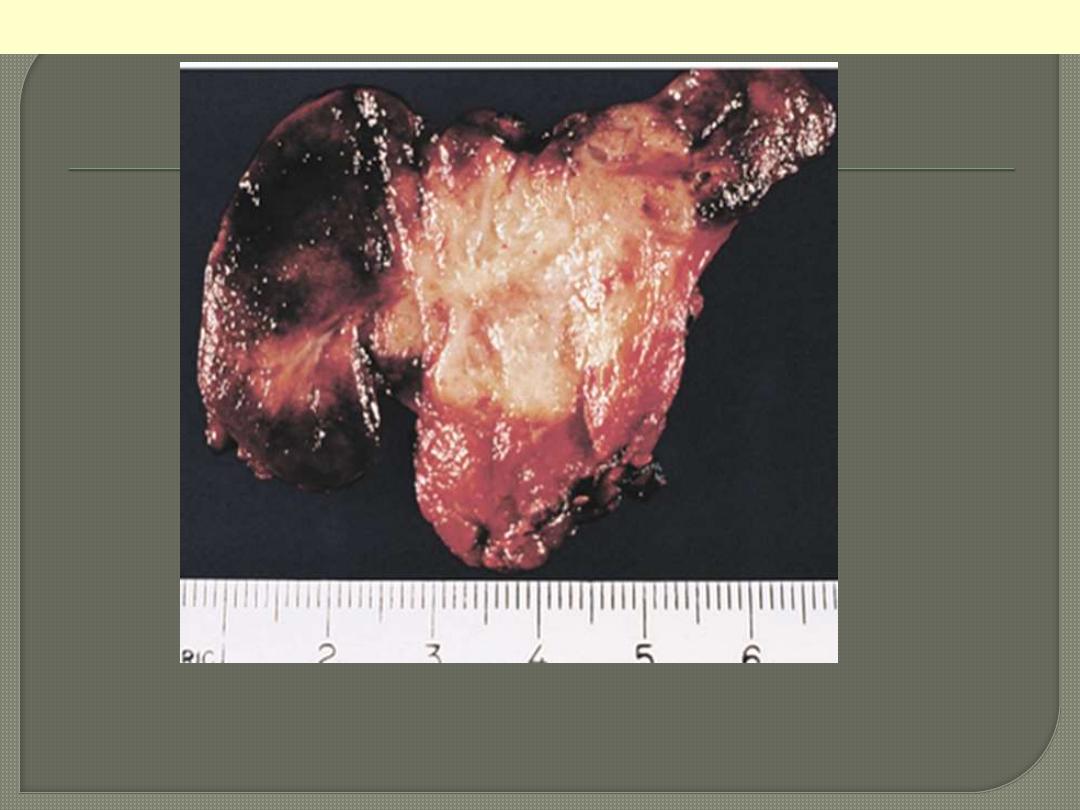
Note its unencapsulated quality, solid appearance, and
yellowish tan color
Medullary carcinoma thyroid
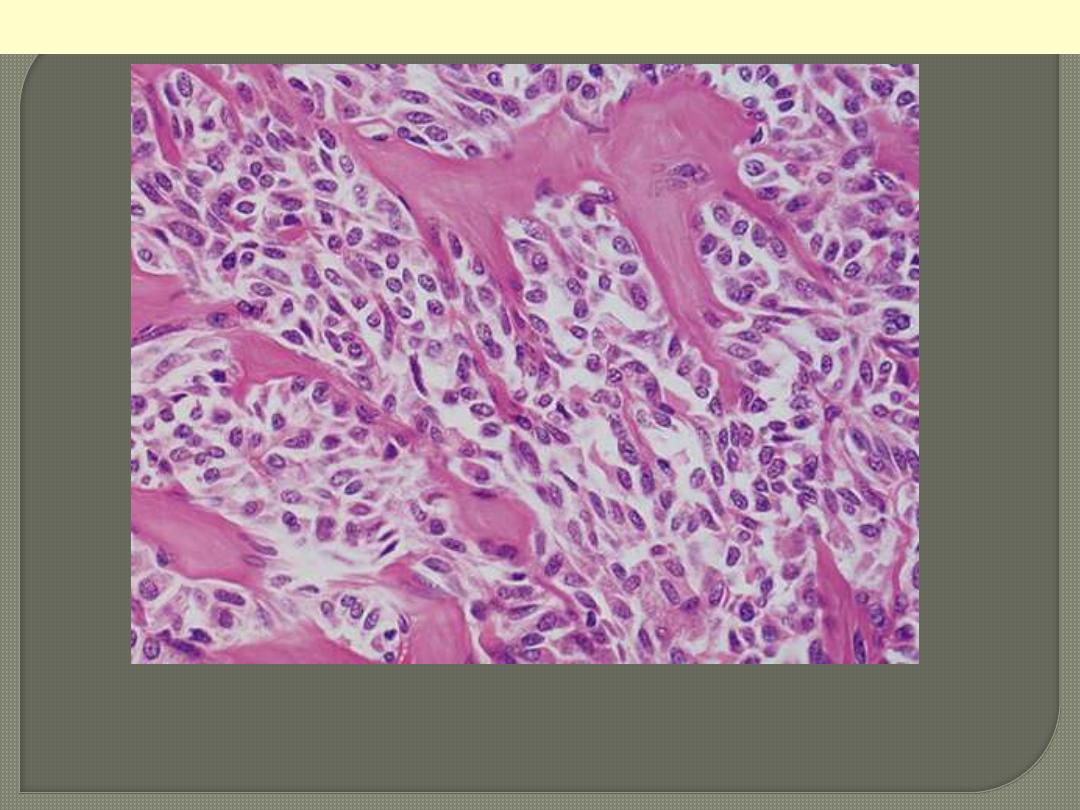
Solid pattern of growth with round & spindle cells
associated with deposition of pinkish amyloid.
Medullary carcinoma thyroid
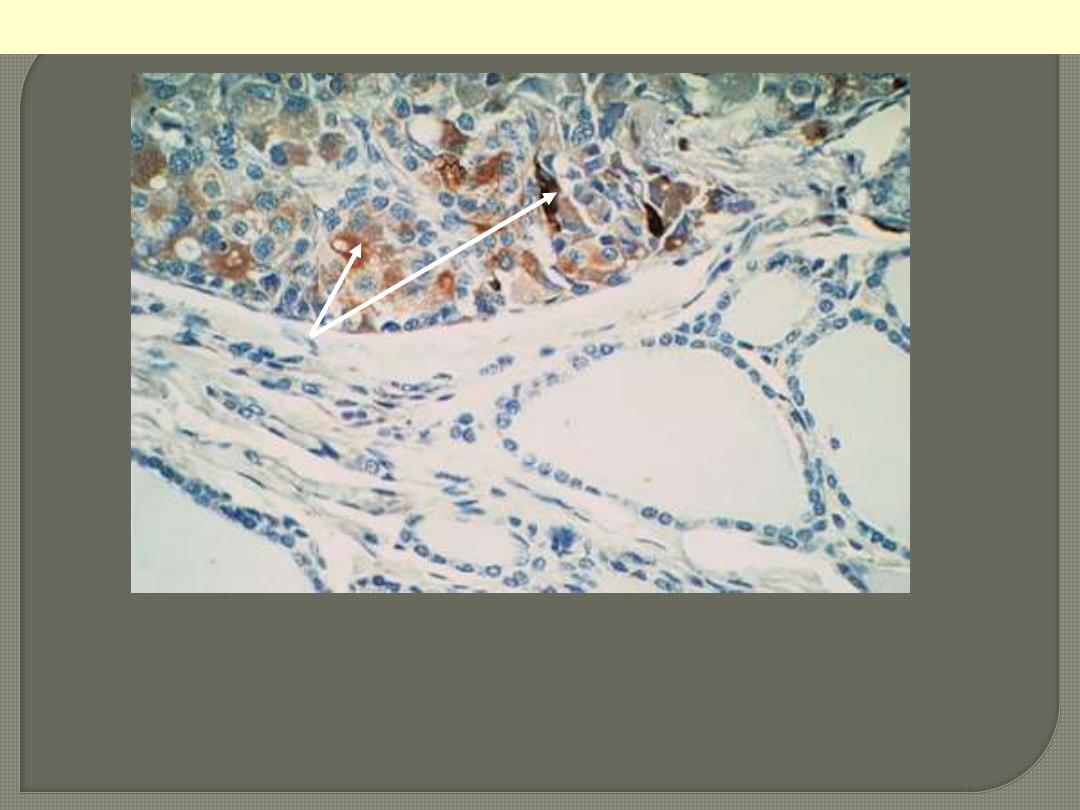
c
Medullary carcinoma
Immunocytochemical positivity for calcitonin. The
adjacent nonneoplastic thyroid follicles are negative.
