
Roots of psychology
psychology can be defined as a scientific investigation
of behavior has a long history of 100year
Although psychology is relatively new science but it
has roots in philosophy and natural science as these
study the human behavior ,ancient people tended to
explain behavior ,natural disaster ,accidents to the
idea of (animism ) spirit that is independent this is no
longer valid ideas ,objectivity started to play a role in
the up growing field of psychology

Psychology as a discipline
•
Ethnology is the study of animal behavior
•
Observing people behavior by single or group of
psychologists
•
Experiments on animal
•
Theories
•
Developmental
•
Socibiological
•
Anthropology and cross cultural
•
Clinical neuropsychological testing like IQ
personality

Concepts of normality
•
As WHO
stated ; normality is a state of physical
mental and social well being
•
Normality in psychology is a pattern of behavior
or personality trait that are typical or that
conform to some standards of proper and
acceptable ways of behaving and being
•
Also it is a successful performance of mental
functions in term of thoughts ,mood ,behavior
that results in productive activities ,fulfilling
relationships with other and the ability to accepts
others and any type of adversity

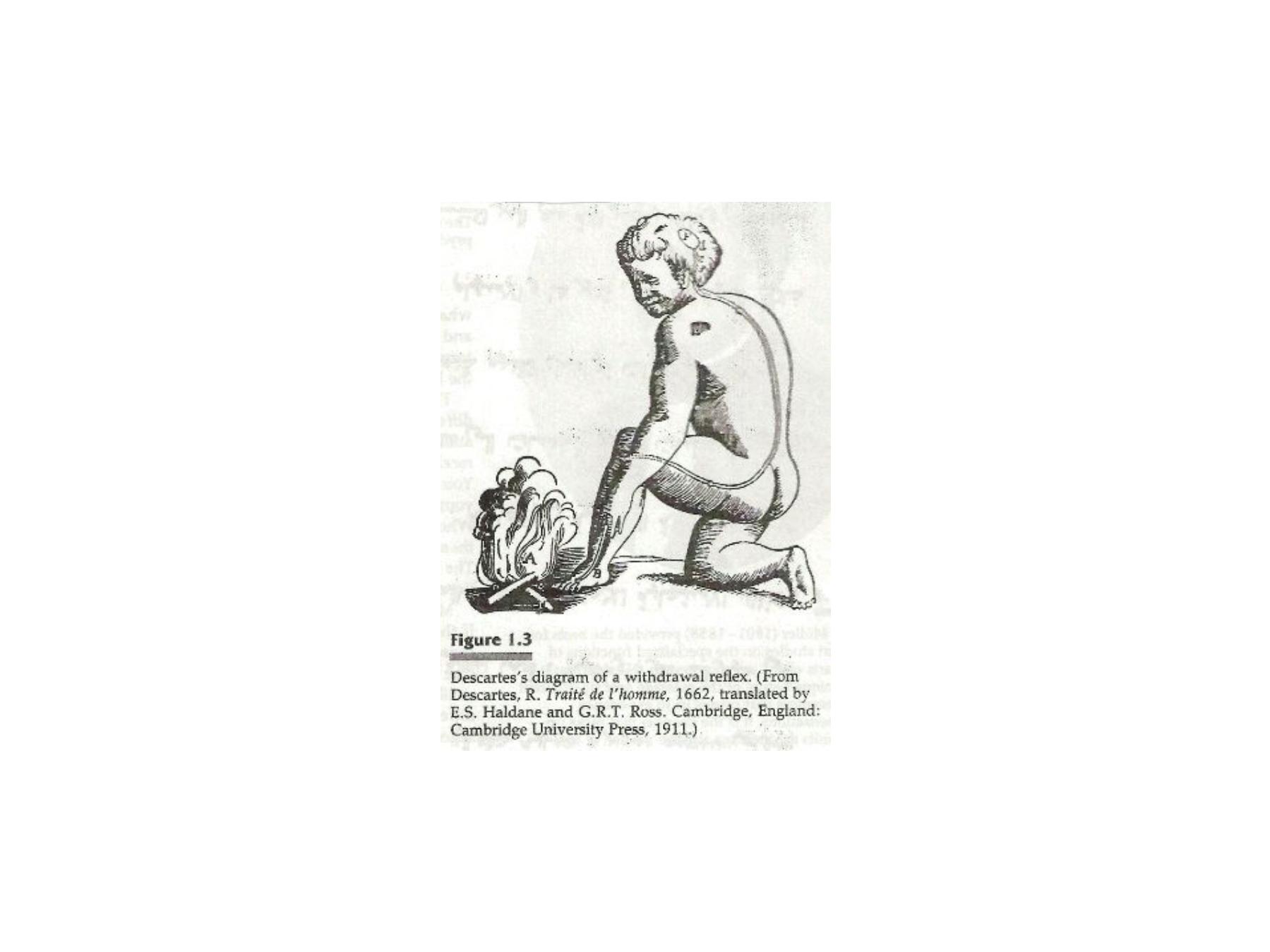


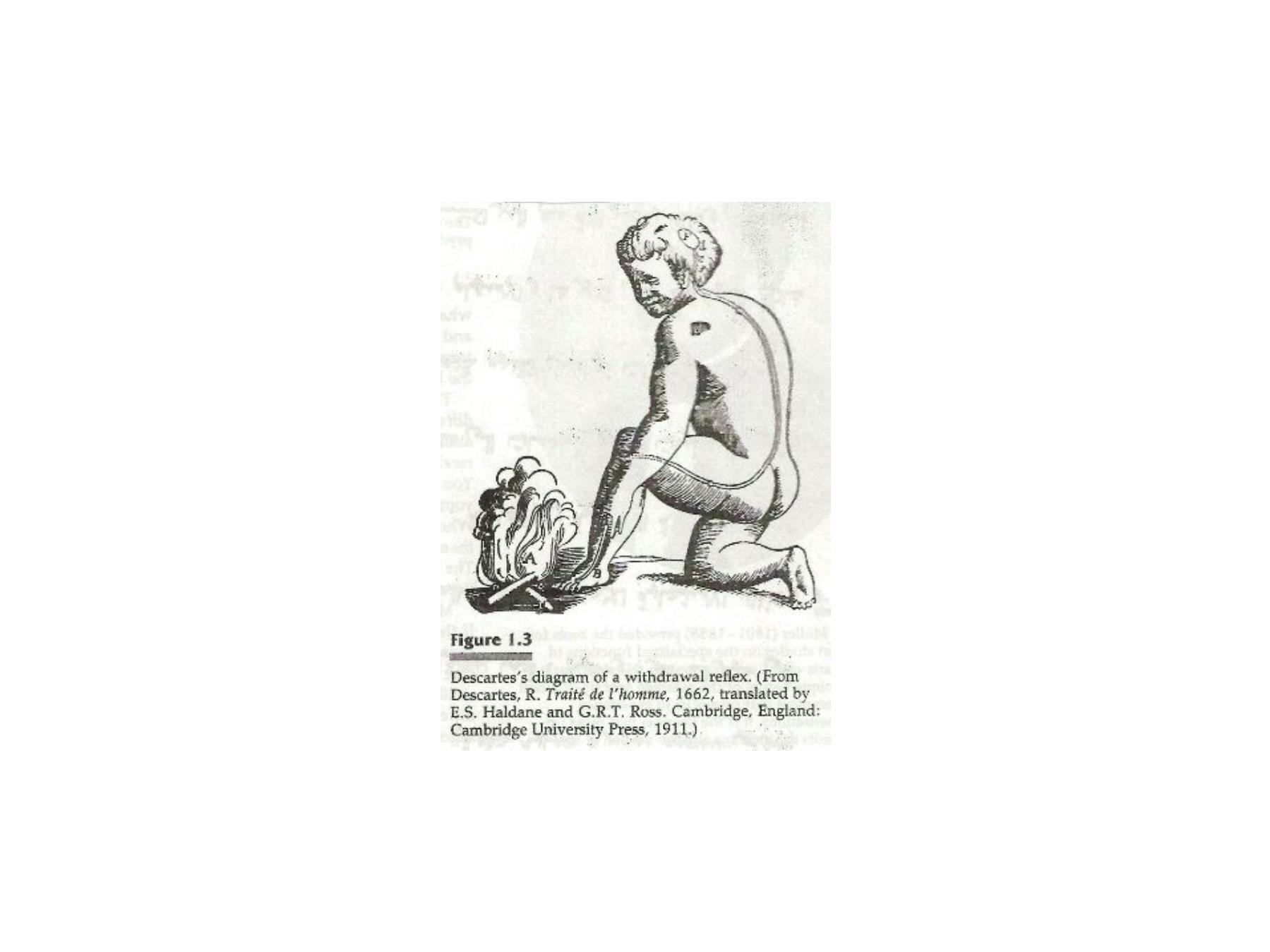
•
Decaretes(1596-1650)
was the first to w rite about scientific
theories and methodology considered the father of
physiological psychology based on biological tradition ,he
assessed the interaction between body and mind (dualism);
mind and matter
•
The scientific method :
•
Discover relation among events, consist of 4 steps
•
1-Identify the problem and formulate hypothetical cause and
effect relations among variables .
•
2-classifying (different factors like physiological ,environmental)
•
3-cause –effect relationship
•
4-manipulate the theory and work with ethical codes


Sigmund Freud 1856 in vienna ,neurology
,neurophysiology ,psychoanalysis

Major trends in development o psychology
•
The actual beginning of modern psychology started at 18
century ,Wilhelm wundt (1832-1920)founded the
psychological laboratory in Leipzig in 1879 based on
direct observation and scientific experiments
,
his
book (The principles of physiological psychology
)was the first text book in psychology ,the German
university system was well established .
•
William James (1842-1910)established a functional
point of view in psychology .he treated thinking and
knowledge as instruments in the struggle to live
assimilating mental science to biological disciplines.

He associated thinking reading with doing experiments 1-
mental operation was more important than structure
(functional psychology)
2-mental processes are not studied as isolated and
independent events but part of biological activity of the
organism
3-functional psychology studies –the relation between the
environment .

Psychodynamic theory
•
S
iggmund Freud(1856-1939) began his career as a
neurologist but soon became interested in behavior and
emotional problems and began formulating his
psychodynamic theories about personality ,and was the
first to employ psychoanalytical methods in his treatment
of patient ,he treated illnesses that seemed to have no
apparent organic explanation ,to treat the patient one
had to bring to conscious level the facts and
circumstances of earlier ,repressed experiences and
feelings .his theory of mind included structure but his
structures different from Wundts theory

Types of Psychologists
•
Classification of psychologist
according to different
kinds of explanation to human behavior ,causal events
•
Looking to the individual from physiological causes like
activity of nerve cells or secretion of glands give the
psychologists their title
•
Other psychologists look inside the individual in
philosophical sense, explaining behavior in term of
potential mental states such as anger ,fear ,need to
achieve .still others look only for environmental events
that cause behaviors .
•

Types of psychologists
•
Physiological psychologists
; study almost all
behavioral phenomena that can be observed in
human and animals , topics involved are ;thinking
,memory ,sensory processes ,emotional
drives,motivation,sexual behavior ,sleep , nervous
system is the base line for knowledge.,
•
Comparative psychologists ;they study the behavior
of animals other than humans .They explain in term of
adaptation to the environment ,their main interest was
to study inherited behavioral pattern known as
species-typical behaviors such as courting ,predation
,defensive behavior ,parenting

Experimental psychologists
•
Groups of psychologists interested in the general
principles of learning ,perception ,motivation, by
experments on animals for the ethical purposes ,the
cause effect may be all environmental in origin .
•
Cognitive psychologists ;
•
They study human behavior exclusively ,the causal
events consist of function of the human brain in
response to environmental events most of them don’
t
study physiological mechanisms. Language
,perception ,attention

PIONEERS IN PSYCHOLOGY
CHARLES Darwin 19 -20 century

Developmental psychology
•
1-john lock 1632-1704 ; he promoted the philosophy of reasoning in
child development
•
2-charles darwin 1809-1882 ; he established a baby biography and
study his own child
•
3-Alfred Binet 1844-1924 ; developed the first intelligence test and
encouraged the movement to study individual difference .
•
4-James Baldwin 1857-1911 ; developed one of the first
comprehensive theories of development
•
5-Sigmund Freud 1856-1939 ; formulated a psychodynamic theory
of personality development
•
6-Jean Piaget 1896-1980 ; proposed an influntial broad theory of
cognitive development

Means of study
•
Researchers in developmental psychology gathered information by;
•
1-structured interview
•
2-questionnaire
•
Or combination of both ,psychologists may make a group study for
behavior observation either during childhood or in adulthood ,the
idea of observing behavior is to compare it with others that form the
majority and analyze the motives and drives behind each gesture ,or
they may go back to animal psychology to associate human
behavior with comparative animals specially studies related to
instincts and emotions ,aggression ,parenthood

Integration of psychology and psychiatry
•
Study of psychology ; behavioral sciences was
introduced to medical colleges by psychiatrists and was
supervised by academics in psychiatry
•
-the apparent similarity of psychology and psychiatry
;abnormal behavior ,predisposing factors ,precipitating,
marinating factors for abnormal behavior may be
psychological in nature or genetically determined or
environmental I;e man with excessive drinking
•
After trauma
•
Genetic predisposition for addiction
•
Exposure to environment ?certain jobs?

Ethologic
It’
s the study of animal behavior its roots lies in the natural
science of biology it has relevant relationship to medicine
and psychiatry
Konard Lorenz 1903-1989 established the theory of
imprinting ,young animal is highly sensitive to a certain
stimulus that then provokes a specific behavior pattern
also known for his study on aggression between the
same species and different species can be applied on
human kind by the theory of selection ,that human when
aggregate in small groups become more likely to defend
them selves and be aggressive ,the phenomena of fight
and flight being strongest in center of territory with
competition with neighboring groups

•
Nikolass Tinbergen 1907-1988 described the
innate releasing mechanism (releaser)is a
specific environmental stimuli that triggers the
animal behavior ,he applied his theories on
studying the autistic children their hypothesis
stated that in certain predisposed children fear
can be provoked by stimuli that normally have
positive social value for most children .

Anthropology and cross cultural psychiatry
•
It’
s the study of human beings
its related to cultural psychiatry,
the cultural differences may explain certain abnormal
behavior ,
the continuous feed back between normal and
maladaptive behavior ,biological theories in causation
of
psychiatric illnesses
has changed many concepts of
psychopathology and gave more importance to anthropology rather
than child ear least experiences focusing on similarity of human
beings they emphasized that people cant be independent of their
culture and attempt to study cross-cultural behavior is culture bound
•
Margaret mead 1901-1978she was the first to attract attention to
cultural differences and its effects on the normal and abnormal
behavior ,she published her famous book in 1928 after spending
years studying and observing primitive cultures in Many countries

Cross cultural psychiatry
•
Culture is a complex concept that includes the behavior pattern and
lifestyle of a society a group of persons share a system of action
that last longer than the human life it provide overall consistency of
society pattern and component over the generation symbol ,beliefs
,values ,attitudes ,manifested in rituals ,costume, religion ,mating
preference, diet ,child rearing practice ,art, entertainment
•
Societies are not static .Access to printed media ,internet travel
geopolitical changes ,migrants or refugees who change their culture
and adopt a new one are called assimilated
•
All cultures develop adjustment and conflict resolution and pressure

History of psychoanalysis
•
Before 20 th century it’
s the fundamental relationship between
psychology and psychiatry ,it’
s the basic knowledge of
understanding psychodynamic ,created by Freud1856-1939 still has
his influence
•
Psychic determination ,unconscious mental activity ,and role of
childhood experience in shaping the adult personality ,childhood
experiences are repeated throughout life and critical in determining
adulthood relationship
•
Resistance, transference and counter transference are the core of
psychoanalysis s a treatment, Freud also focused on (parapraxes )
slip of the tongue which reveal unconscious intent that is outside the
individual awareness
•
Also this is seen in dreams and many nonverbal behaviors these
theories were reinforced by the neuroscience investigations

•
During the early 1890 he focused on treatment of
hysteria ,he was convinced that childhood sexual
seduction played a major role in causing neurosis which
acted like repressed memories
•
He started dream analysis in his book –interpretation of
dreams he stated that a dream is a hidden unconscious
childhood wish ,displacement, condensation, and
symbolic representation ,physical stimuli during sleep
also play a role in dream formation like sensory stimuli
like pain ,hunger ,thirst ,urgency

Schools derived from Freud
•
Karl Abraham 1877-1925 was the first psychoanalysis in
Germany he elaborated Freud psychosexual stages and
gave it more explanations, he also worked on
psychological theories in explaining obsessive
compulsive neurosis and its relation to fixation to anal
sadistic stage
•
Alfred Adler 1870-1937 Austria apposed the sexual origin
of neurosis ,his theory concerned about thinking to
overcome inferiority ,and his definition for organ
inferiority also he studied the rank of siblings in the
family
•
Erick Fromm 1900-1980he worked on the 5 types of
personality

Schools after Freud
•
1-the receptive personality –passive
•
2-the exploitative personality –manipulative
•
3-the marketing personality-opportunistic
•
4- the hoarding personality –save –preservative
•
5-the productive personality –mature ,sincere
•
Anna Freud 1895-1982 –daughter she elaborated her
fathers work on defense mechanisms she also
developed modern ego psychology and founded the field
of child psychanalysis

