
MOTIVATION
PROFESSOR MAHA S YOUNIS

•
Definition Of motivation
•
Motivation is
•
Qualities Of Motivation
•
Process of motivation
•
Six c’s of motivation
•
Basic model of motivation
•
Theory of motivation
•
Case study
Definition of motivation
:
* The driving force within individuals by which they
attempt to achieve some goal in order to fulfill some
needs or expectation.
* The degree to which an individual wants to choose
in certain behavior.

Motivation is…
Complex
Psychological
Physical
Unique to each and every person
Context sensitive
Not fully understood

Qualities of Motivation:
Energizes behavior
Directs behavior
Enable persistence towards a goal
Exists in varying details

MOTIVATION AS A
PROCESS:
It is a process by which a person’s efforts are
energized, directed and sustained towards attaining
the goal.
*Energy- A measure of intensity or drive.
*Direction- Towards organizational goal.
*Persistence- Exerting effort to achieve goal
DIRECTION
PERSISTENCE
ENERGY
Six C’s of Motivation..
Choices
collaboration
Constructing meaning
Consequences
Control
Challenges
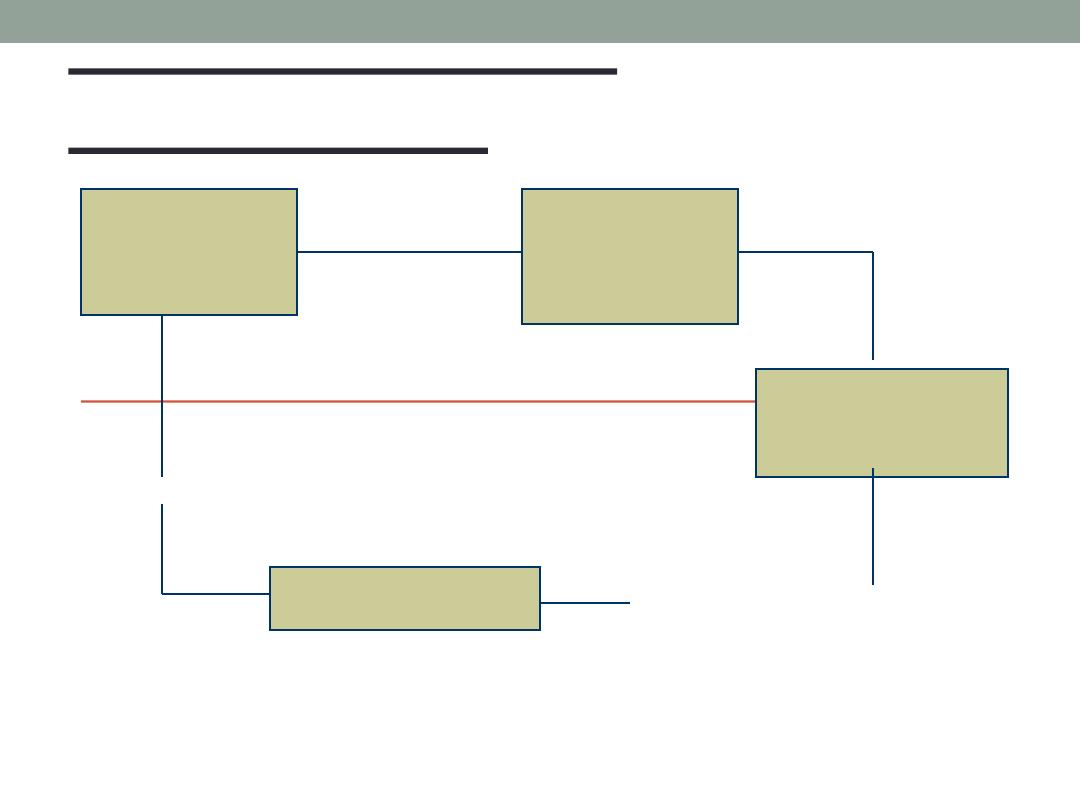
BASIC MODEL OF
MOTIVATION
Needs or
expectations
Result in Drive force
(Behavior or
Action)
To Achieve
Desired Goals
Which Provides
fulfillments
Feedback

Early Theories of Motivation:
Content Theories:
Emphasis on what motivates
individuals.
Maslow’s need Hierarchy
Macgregor's Theories X & Y
Herzberg’s two factors theory

Process Theories of Motivation:
Emphasis on actual process of motivation
.
Three needs Theory ( McClelland)
Goal-setting Theory
Reinforcement Theory
Designing Motivating theory
Equity Theory
Expectancy Theory

Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs theory
Needs were categories as five levels of lower-higher-order
needs.
*Individual must satisfy lower-level needs before they can
satisfy higher order needs.
*Satisfied needs will no longer motivate.
*Motivating a person depends on knowing at what level
that a person is on the hierarchy.
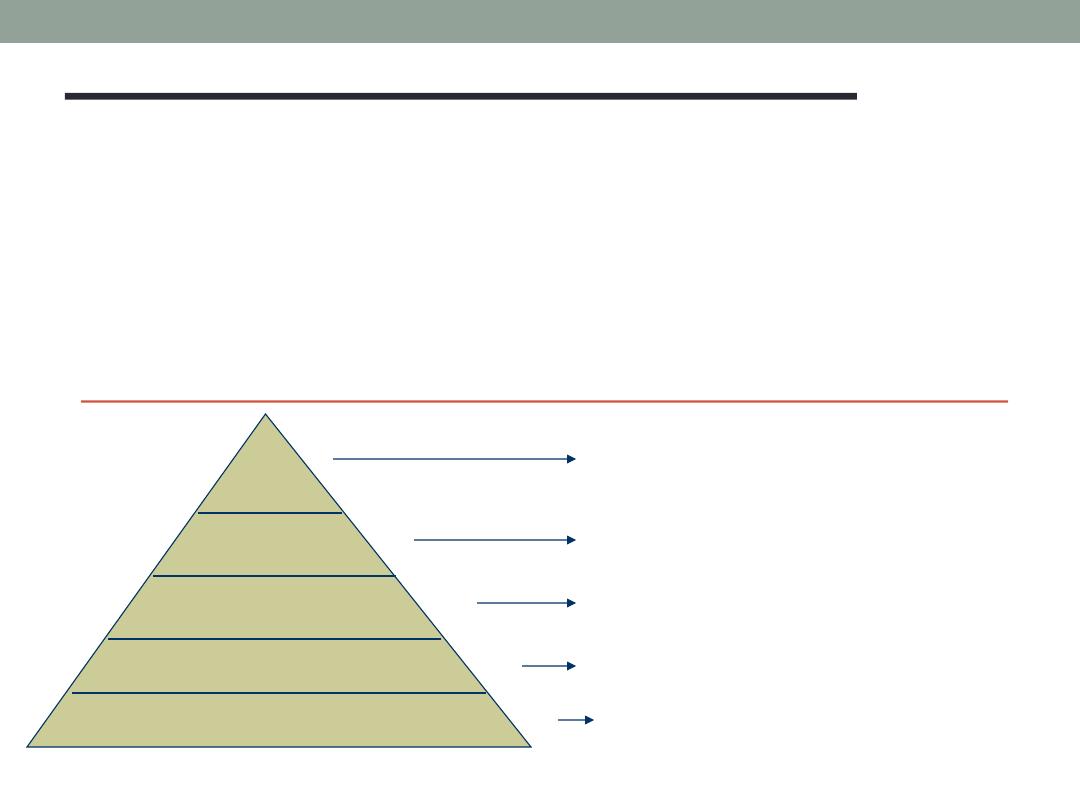
HIERARCHY OF NEEDS
*Lover order ( External ) : Physiological and safety needs
*Higher order ( Internal ) : Social, Esteem, and Self-
actualization
Physiological needs
Safety Needs
Social Needs
Esteem Needs
Self-Actualization Needs

McGregor’s Theory X and Y
Theory X
Assume that workers have little ambition, dislike
work, avoid responsibility, and require close
supervision.
Theory Y
Assumes that workers can exercise self-direction,
desire, responsibility, and like to work.
Assumption
Motivation is maximized by participative decision
making, interesting jobs, and good group relation.
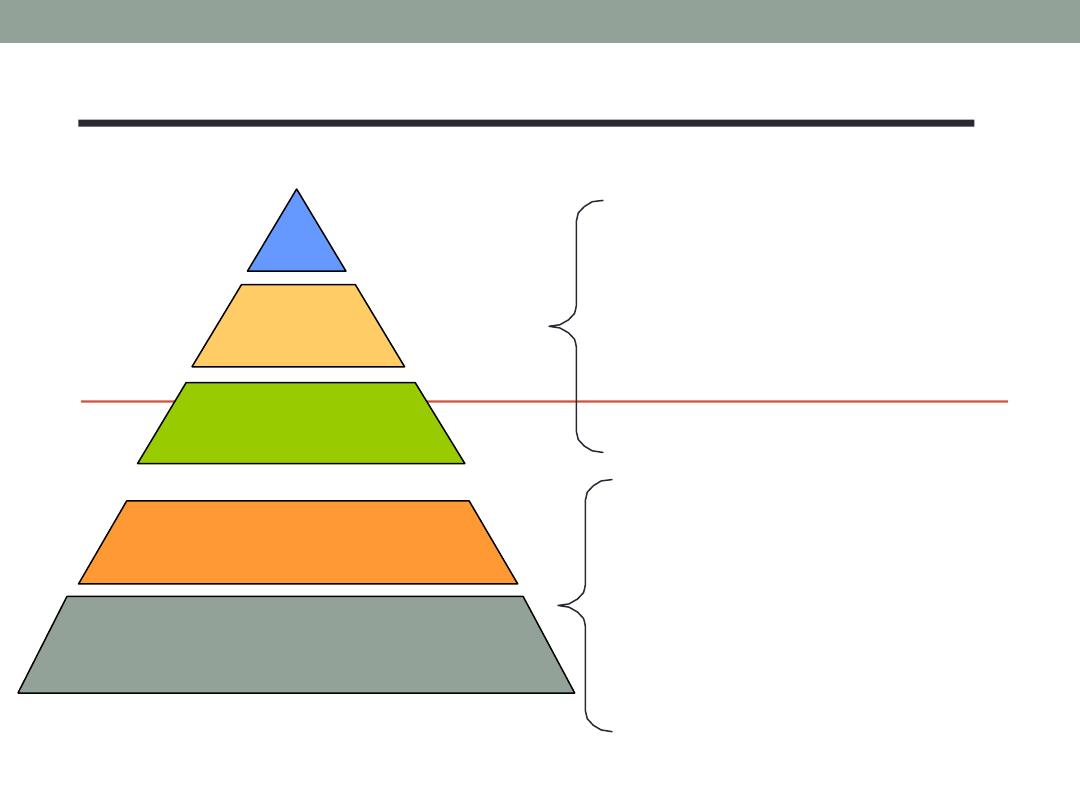
Motivational Theories X & Y
Physiological
Safety & Security
Esteem
SA
Theory Y - a set of
assumptions of how to
manage individuals
motivated by higher
order needs
Social
Theory X - a set of
assumptions of how to
manage individuals
motivated by lower order
needs

McClelland’s Need Theory: Need
for Achievement
Need for
Achievement
The desire to excel and
succeed

McClelland’s Need Theory: Need
for Power
Need for Power –
The need to influence the
behavior of others.

McClelland’s Need Theory: Need
for Affiliation
Need for Affiliation –
The desire for interpersonal
relationship

Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene
Theory
Job satisfaction and job dissatisfaction are created y different
factors.
Hygiene factors-
Extrinsic ( Environmental ) factors that
create job dissatisfaction.
Motivation Factors-
Intrinsic ( Psychological ) factors that
create job satisfaction.
Attempted to explain why job satisfaction does not result in
increased performance
The opposite of satisfaction is not dissatisfaction but rather
no satisfaction
.
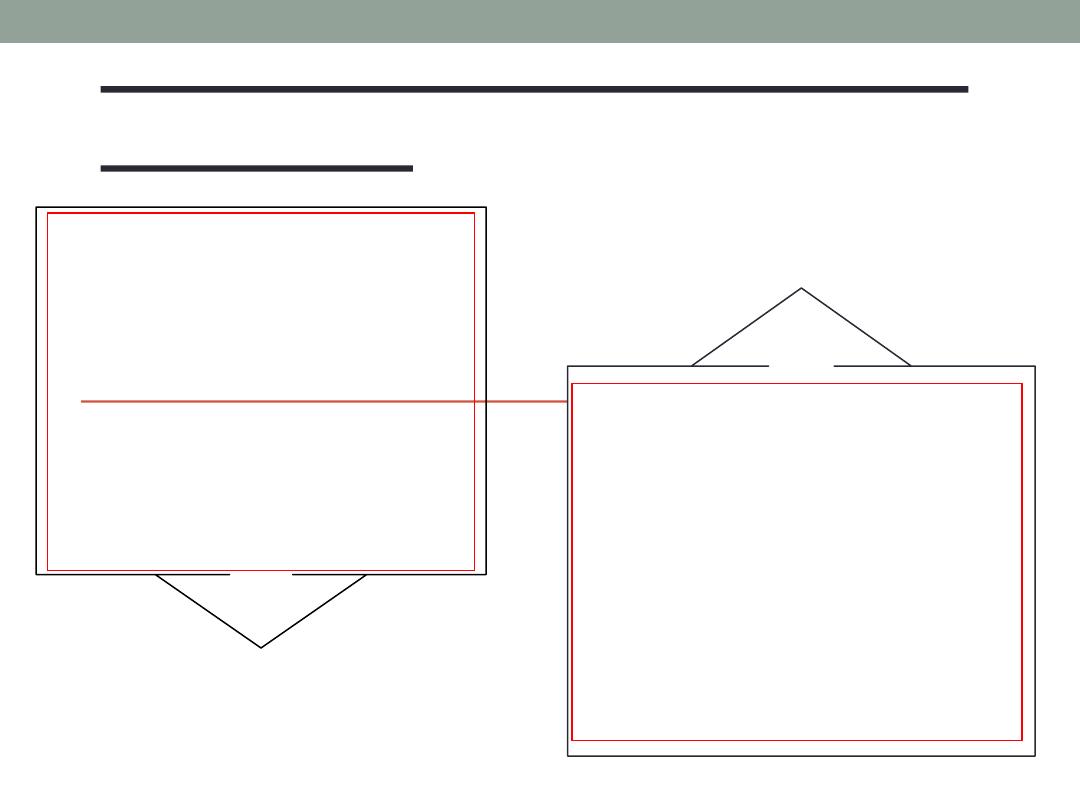
Motivation–Hygiene Theory of
Motivation
Hygiene factors avoid
job dissatisfaction
•
Company policy &
administration
• Supervision
• Interpersonal relations
• Working conditions
• Salary
• Status
• Security
•
Achievement
• Achievement recognition
• Work itself
• Responsibility
• Advancement
• Growth
• Salary?
Motivation factors
increase job satisfaction
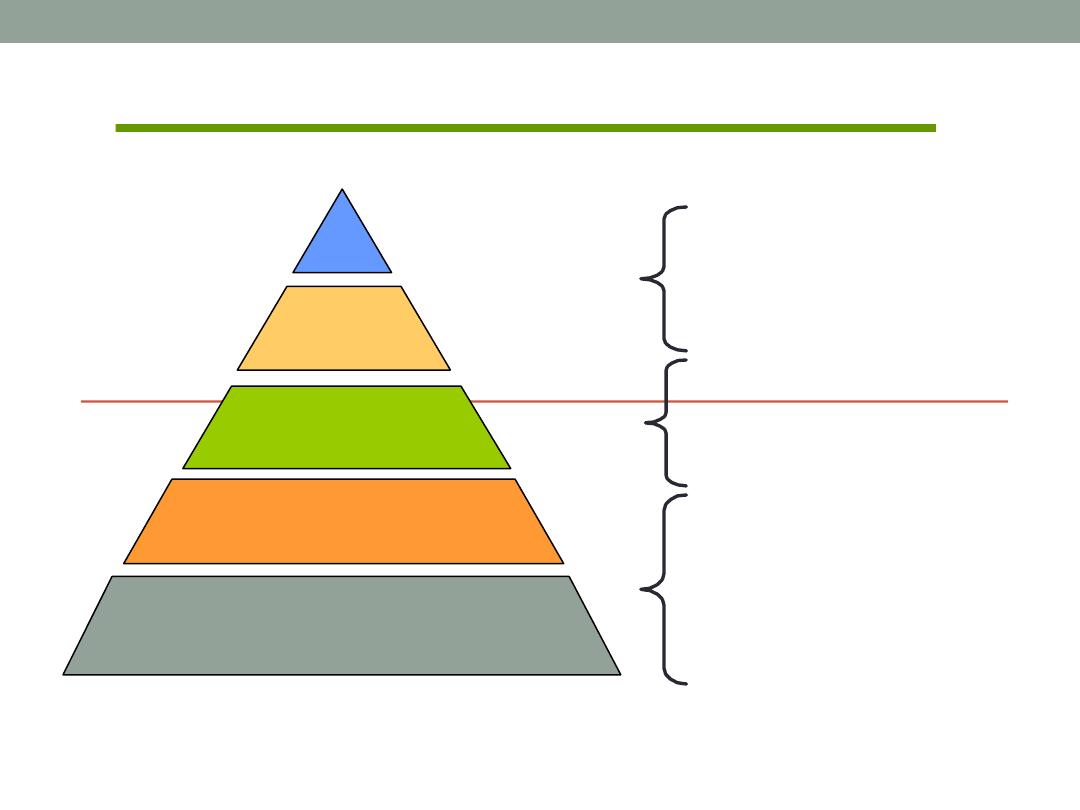
Alderfer’s ERG Theory
Physiological
Safety & Security
Love (Social)
Esteem
SA
Existence
Relatedness
Growth
Self-actualization
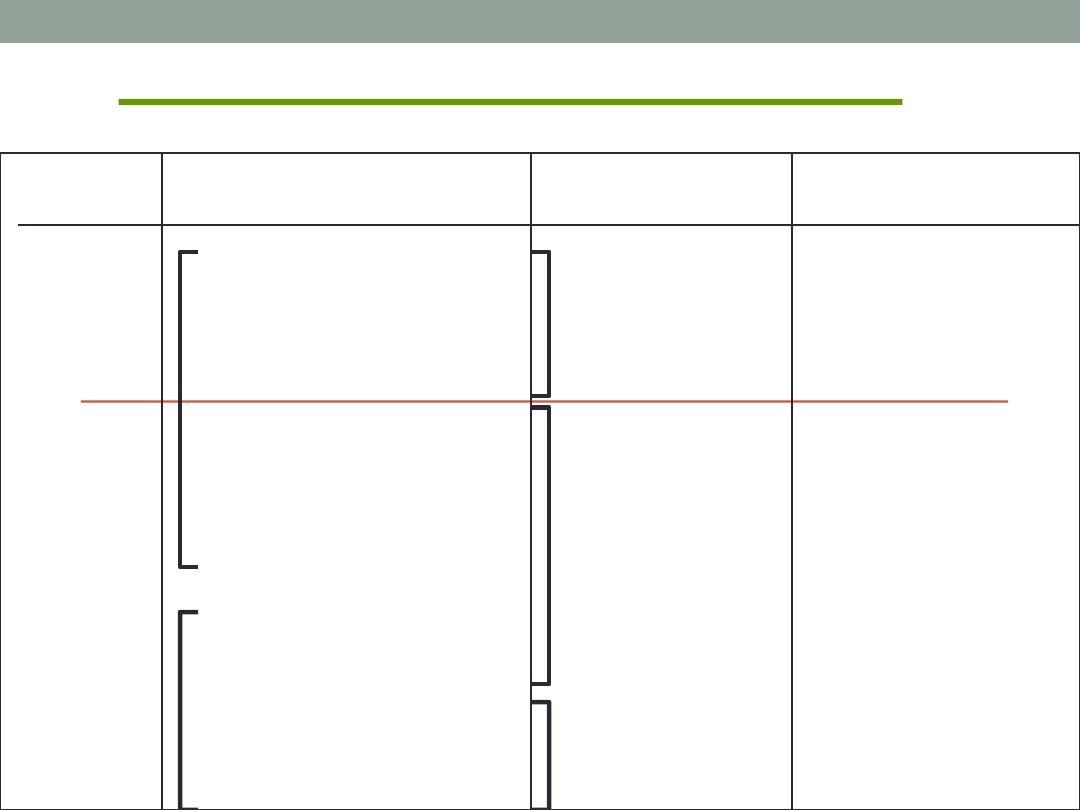
Motivational Need Theories
Maslow
Alderfer
McClelland
Higher
Order
Needs
Lower
Order
Needs
Esteem
self
interpersonal
Safety & Security
interpersonal
physical
Need for
Achievement
Need for
Power
Relatedness
Need for
Affiliation
Existence
Growth
Belongingness
(social & love)
Physiological

Case Study

