







Psychoanalytic Theory
Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theory
Sigmund Freud, M.D.,a Viennese physician who thought his patients’
problems were more emotional than physical.
Freud began his work by using hypnosis and eventually switched to
psychoanalysis.
Freud had many followers: Jung and Adler, to name a few.
More than 100 years later, his work is still influential and very
controversial
The Id, Ego, and Superego
Id: Innate biological instincts and urges; self-serving & irrational
•
Totally unconscious
•
Works on Pleasure Principle: Wishes to have its desires
(pleasurable) satisfied NOW, without waiting and regardless of the
consequences
Ego: Executive; directs id energies
•
Partially conscious and partially unconscious
•
Works on Reality Principle: Delays action until it is practical
and/or appropriate
The Id, Ego, and Superego, continued
Superego: Judge or censor for thoughts and actions of the ego
•
Superego comes from our parents or caregivers; guilt comes from
the superego
•
Two parts
-
Conscience: Reflects actions for which a person has
been punished (e.g., what we shouldn’t do or be)
-
Ego Ideal: Second part of the superego; reflects
behavior one’s parents approved of or rewarded
(e.g., what we should do or be)
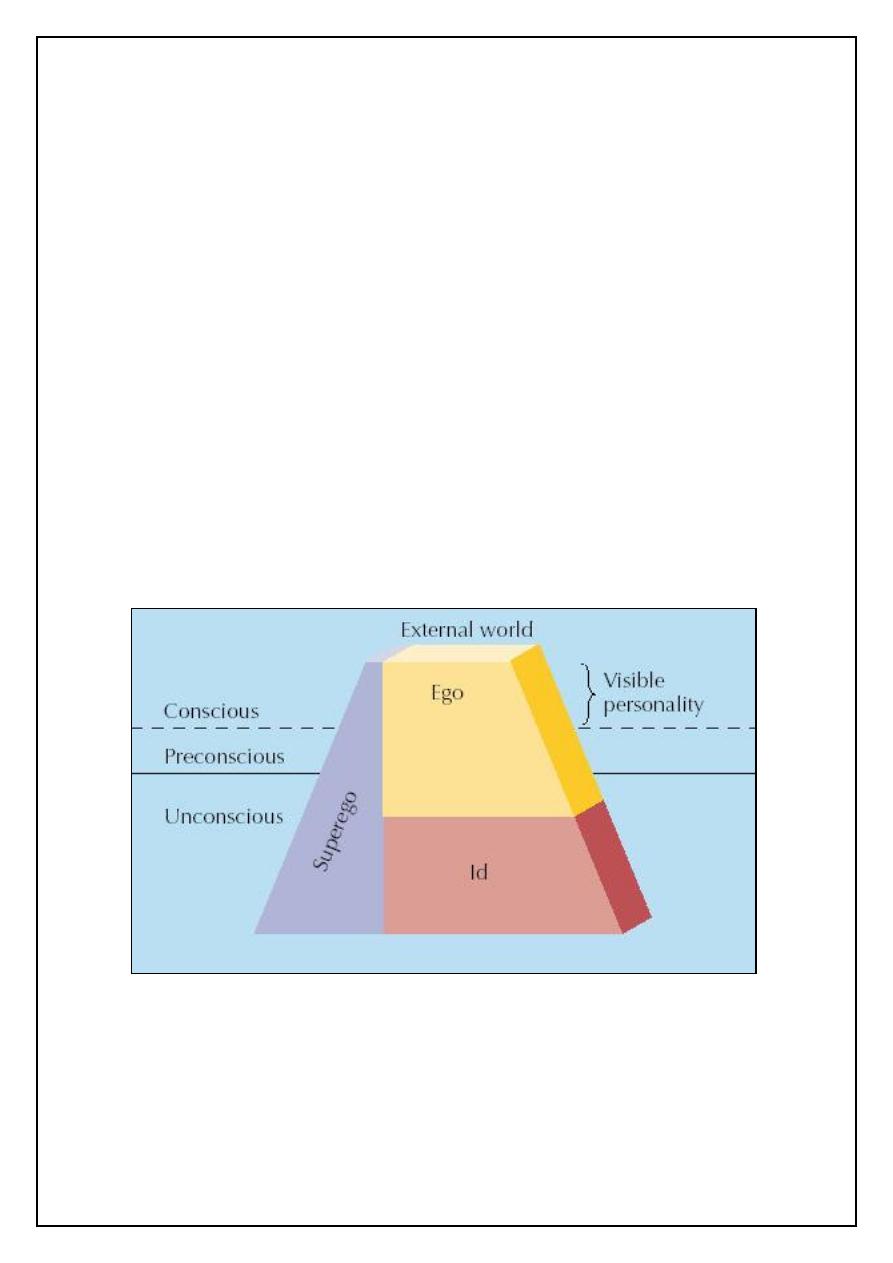
Levels of Awareness:
.
Conscious: Everything you are aware of at a given moment
Preconscious: Material that can easily be brought into awareness
Unconscious: Holds repressed memories and emotions and the id’s
instinctual drives
Graphic: Levels of Awareness
Cause of Anxiety:
Ego is always caught in the middle of battles between superego’s desires
for moral behavior and the id’s desires for immediate gratification
Neurotic Anxiety: Caused by id impulses that the ego can barely control
Moral Anxiety: Comes from threats of punishment from the superego
Defense mechanism: a process used by the ego to distort reality and
protect a person from anxiety
Examples of Defense Mechanisms
Regression: Ego seeks the security of an earlier developmental period in
the face of stress.
Displacement: Ego shifts unacceptable feelings from one object to
another, more acceptable object.
Sublimation: Ego replaces an unacceptable impulse with a socially
acceptable one
Reaction Formation: Ego transforms an unacceptable motive or feeling
into its opposite.
Projection: Ego attributes personal shortcomings, problems, and faults
to others.
Rationalization: Ego justifies an unacceptable motive by giving a false
Border lines:
1-unstabile mode
2-unstabile relationship
3-unstabile identify with brief dissociated state and brief psychiatrical
episode + suicidal ideation.
