
1
P
P
H
H
C
C
–
–
2
2
n
n
d
d
L
L
e
e
c
c
t
t
u
u
r
r
e
e
S
S
t
t
r
r
a
a
t
t
e
e
g
g
i
i
e
e
s
s
&
&
E
E
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
s
s
Assistant Professor
Dr. Batool A li Ghalib Yassin
Department of Community & Family M edicine
College of M edicine –University of Baghdad
October, 2015

O
O
b
b
j
j
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
s
s
1. Numerate the essential strategies for implementing
PHC.
2. Discuss the concept of burden of diseases &
determinants of health and how they apply to
practice.
3. Verify
the
two
specific
forms
of
food
supplementation & identify population at risk of
malnutrition
4. List & describe the globally important nutritional
problems; Vit A deficiency, Iron deficiency anaemia
& Iodine deficiency.
5. Have an overview on the importance & types of
Health Education
2

3
1. The development of a basic health infra-
structure,
2. A competent two-way referral system between
the various health service delivery levels,
3. Development of human resources for health,
4. Incorporating the traditional medical system.
5. Ensuring inter-sectoral cooperation,
6. Empowering
the
community
with
health
education.
7. Relevance
of
the
programs
to
the
community health problems.
8. Cost-effectiveness.
T
T
h
h
e
e
P
P
H
H
C
C
a
a
p
p
p
p
r
r
o
o
a
a
c
c
h
h
w
w
a
a
s
s
b
b
a
a
s
s
e
e
d
d
o
o
n
n
t
t
h
h
e
e
f
f
o
o
l
l
l
l
o
o
w
w
i
i
n
n
g
g
s
s
t
t
r
r
a
a
t
t
e
e
g
g
i
i
e
e
s
s

4
I
I
n
n
t
t
e
e
r
r
v
v
e
e
n
n
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
s
s
t
t
r
r
a
a
t
t
e
e
g
g
i
i
e
e
s
s
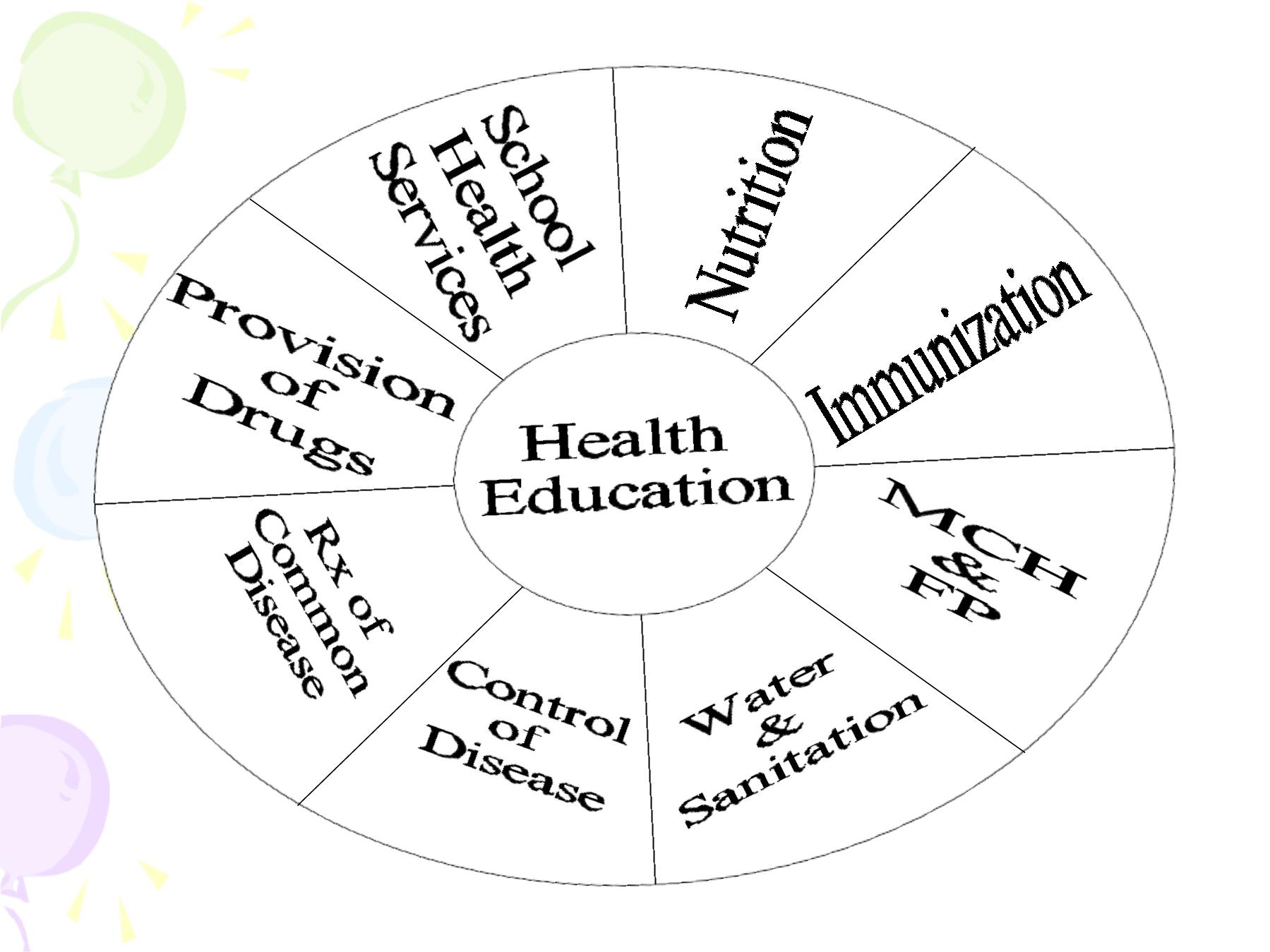
Interventions are actions to improve health.
There are different types of intervention:
1. Interventions
aimed
at
prevention
(immunization)
2. Interventions that promote changes in lifestyle (
stop smoking , using bed nets, physical activity)
3. Interventions may improve Dx & Rx which
reduces the duration or severity of disease
(correct sputum Dx of TB, correct use of ORS)
4. Population based interventions (reduction of
diarrhoeal diseases are often multisectoral)
5. Individual based interventions : they could be
Personal preventive services (screening for
cervical cancer) or Basic clinical services
(ORS for diarrhea, antibiotics for pneumonia)

5
I
I
n
n
t
t
e
e
r
r
v
v
e
e
n
n
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
s
s
t
t
r
r
a
a
t
t
e
e
g
g
i
i
e
e
s
s
Some interventions have more than one
effect.( to individuals & community)
•
EPI is a population- based programme with the
aim to reduce the incidence (& hence mortality and
morbidity) of certain infectious diseases. It also acts
as a personal preventive service for the individual
child who is vaccinated.
•
What
about
systematically
improving
clinical
services to treat TB &STDs ?

6
Burden of Disease
Clinician-patient
Public Health - problem
Facts= history, examination &
investigations
Facts = Statistics &
Epidemiology
Treat the patient
Plan public health
intervention
W hich diseases cause the most illness or death
in a population?
We are concerned with both mortality & morbidity.
M orbidity=Disability (few days or yrs)
M ortality=can be measured in terms of yrs of life lost.
Disability-adjusted life year (DALY);
Is a measure of the yrs of life lost following death together with
the time spent suffering from disability as compared with a full lifespan.
7
D
D
e
e
t
t
e
e
r
r
m
m
i
i
n
n
a
a
n
n
t
t
s
s
o
o
f
f
D
D
i
i
s
s
e
e
a
a
s
s
e
e
Disease can be caused by many factors,
some are direct causes & others more
indirect or underlying causes.
Clinician-young child w ith diarrhea & severe dehydration
Direct= bacterial or viral infection
Indirect= underfeeding, recurrent infections, bottle-feeding
(poor nutritional status +inappropriate home treatments
Underlying causes = lack of access to medical care, no
clean water, no sanitation, low education, large family size,
lack of land, income

8
L
L
e
e
v
v
e
e
l
l
s
s
o
o
f
f
p
p
r
r
e
e
v
v
e
e
n
n
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
P rimary prevention: aims to prevent the condition starting
through environmental control of agents, change in personal
behavior or immunization
Secondary prevention: aims to detect disease at earliest stage
& prevent the condition progressing (screening , early treatment)
Tertiary prevention: aims at damage limitation in those with
established disease (Rx , surgery, rehabilitation to restore
function)
Preventive programmes & clinical services reduce the
burden from disease through prevention at primary,
secondary & tertiary levels
9

10
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
S
S
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
There are tw o specific forms of food supplementation :
I. Food Supplements:
These are directed to two target groups
:
1. P regnant w omen at risk of delivering LBW infants:
Extra
food supplements are given during the third trimester which is
the period of rapid foetal growth. The aim is to reduce the risk of
LBW. The amount given is 500 cal + 10 g protein/day. This will
result in an additional average weight gain of 1.5 Kg, which will
be reflected in an average increase of BW by 300g.
How to identify w omen at risk:
•
Women whose weight is 90% or less of the standards weight
for height.
•
Women with mid-upper arm circumference of <22.5cm.
•
Women who fail to have a regular weight gain of 1.5Kg/month
during the last 6 months of pregnancy.
Much of maternal malnutrition can be prevented through
the training of elderly women & TBAs to provide nutrition
information & to promote beliefs and customs favourable to
pregnant and lactating women, as well as young children.

11
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
S
S
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
2. Children:
High protein food supplements for
malnourished children are a major component of
many health care programs. These programs are of
two types:
•
Take home distribution system:
Where the
rations are distributed at regular intervals with the
expectation that the food will be eaten by the
beneficiary at home. Problems are substitution of
other foods and sharing by other members of the
household.
•
Central feeding:
where the beneficiaries are
assembled at a single place & fed together. The
problems which face these programs are travel cost
and cross infections.
•
Maternal education
is a critical component of most
feeding
programs
aiming
at
the
correction
of
inappropriate feeding habits.

12
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
S
S
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
I I . Food Fortification:
It is defined as the process whereby micronutrients
are added to food to maintain or improve the quality
of the diet of a population or a community.
•
The
program
aims
at
dealing
with
specific
micronutrient deficiencies & is typically used in
conjunction with staple foods.
•
The three major specific micronutrient deficiencies
are: iodine, vitamin A and iron.
•
Vitamin A and iron deficiency, even in mild forms,
may exacerbate the duration and severity of other
diseases, sometimes causing death, which may have
been otherwise avoidable.
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
S
S
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
;
;
1
1
)
)
I
I
o
o
d
d
i
i
n
n
e
e
D
D
e
e
f
f
i
i
c
c
i
i
e
e
n
n
c
c
y
y
:
:
13

14

15
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
S
S
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
1
1
)
)
I
I
o
o
d
d
i
i
n
n
e
e
D
D
e
e
f
f
i
i
c
c
i
i
e
e
n
n
c
c
y
y
:
:
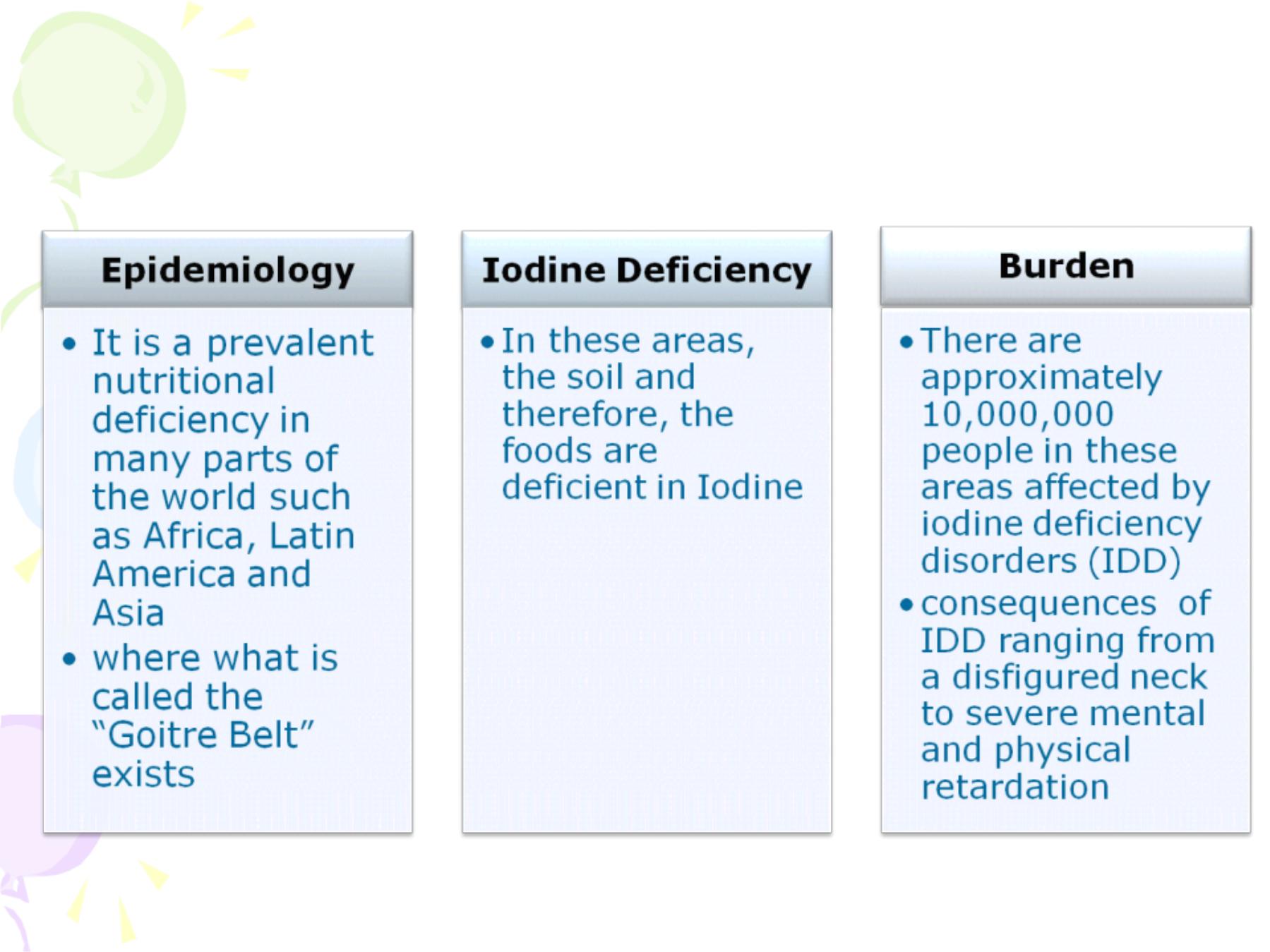
-This problem is very easily prevented
through fortifying salt with iodine.
- For people living in remote areas and not
consuming the fortified salt, long term
release iodine injections are given, which
release iodine slowly over years.
-The amount added is 30g of iodine to one
tonne of salt (iodine loss may take place due
to humidity).
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
S
S
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
2
2
)
)
I
I
r
r
o
o
n
n
D
D
e
e
f
f
i
i
c
c
i
i
e
e
n
n
c
c
y
y
:
:
16

17
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
S
S
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
2
2
)
)
I
I
r
r
o
o
n
n
D
D
e
e
f
f
i
i
c
c
i
i
e
e
n
n
c
c
y
y
:
:
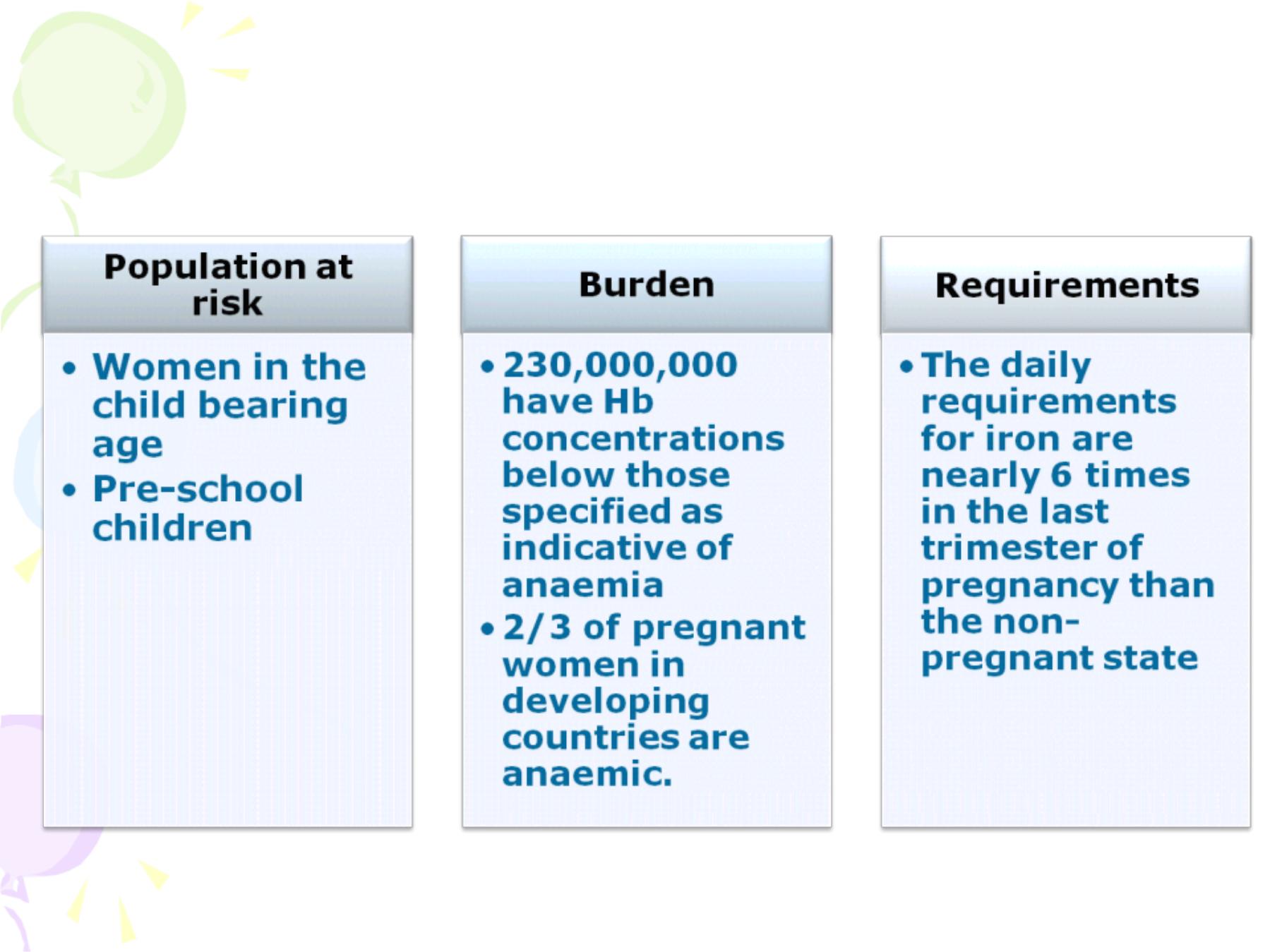
This need is covered by iron from the diet
and from iron stores, w hich if inadequate,
anaemia w ill result.
In infants, iron stores are exhausted
around the fourth month of life, especially w hen
w eaning is delayed or the w eaning diet is mainly
starchy.
Anaemia may not lead directly to death,
but it has a profound effect on learning and
problem solving capacities, psychological and
physical behaviour, development of fatigue,
reduction of w ork capacity and increased risk of
maternal and foetal morbidity.

18
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
S
S
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
2
2
)
)
I
I
r
r
o
o
n
n
D
D
e
e
f
f
i
i
c
c
i
i
e
e
n
n
c
c
y
y
:
:
IDA is prevented by
- Changing dietary habits (increase
animal protein and vegetables rich in
iron),
- Iron supplementation to pregnant
and lactating women, and
- Fortifying foods with iron salts (flour,
sugar, salt and spices).

19
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
S
S
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
3
3
)
)
V
V
i
i
t
t
a
a
m
m
i
i
n
n
A
A
D
D
e
e
f
f
i
i
c
c
i
i
e
e
n
n
c
c
y
y
:
:
Annually, 5-10 million children develop mild
xerophthalmia & nearly 250,000 are blinded by this
condition. VAD is related to other health problems as
well. Studies have shown that child death rates almost
triple with each increase in the degree of VAD. These
excessive deaths are due to diarrhoeal diseases and
respiratory infections
.
•
Children are supplemented with Vitamin A capsules
or drops once every 6 months
•
In Iraq they receive 50,000 IU at 9 months of age
and 100,000 IU at 18 months of age.
•
This had reduced deaths rates in children over 1 year
of age by 1/3.
•
It also helps to add green leafy vegetables and yellow
fruit and vegetables as well as fats and oils to the child’
s weaning foods.

20
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
S
S
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
3
3
)
)
V
V
i
i
t
t
a
a
m
m
i
i
n
n
A
A
D
D
e
e
f
f
i
i
c
c
i
i
e
e
n
n
c
c
y
y
:
:
•
Vitamin A deficiency also causes
-
anaemia and impaired growth.
- Survival of children with measles can be
increased
by
giving
vitamin
A
supplementation
.
•
Breast feeding is protective against vitamin A
deficiency in infants if the mother’
s vitamin A
levels are adequate.
•
Postnatal lactating women are supplemented
with 200,000 IU of vitamin A.
•
Vitamin A can also be added to milk and
sugar.

21
H
H
e
e
a
a
l
l
t
t
h
h
E
E
d
d
u
u
c
c
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
•
is the part of health care that is
concerned
with
promoting
healthy
behaviour
.
•
A person's behaviour may be the main
cause of a health problem, but it can
also be the main solution. (smoking,
poorly nourished kid, Butcher’
s habits)
•
Health education
does not replace
other health services, but it is needed to
promote
the
proper
use of
these
services. (immunization)

22
H
H
e
e
a
a
l
l
t
t
h
h
E
E
d
d
u
u
c
c
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
&
&
P
P
H
H
C
C
The truth is that ;
I ndividuals & families, not doctors
& other health workers, make most of the
important decisions that affect their health.
Mothers decide what food to give to
their families & how to prepare it. Families
decide when to go to a doctor, where to go
& whether or not to follow the instructions
they receive from a health worker.
people need to be equipped with the
knowledge & skills necessary to exercise
individual & community responsibility

23
M
M
a
a
j
j
o
o
r
r
o
o
b
b
j
j
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
s
s
o
o
f
f
e
e
d
d
u
u
c
c
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
f
f
o
o
r
r
h
h
e
e
a
a
l
l
t
t
h
h
a
a
r
r
e
e
t
t
o
o
e
e
n
n
a
a
b
b
l
l
e
e
p
p
e
e
o
o
p
p
l
l
e
e
:
:
1. To define their own problems &
needs.
2. To understand what they can do
about these problems with their own
resources combined with outside
support.
3. To decide on the most appropriate
action to promote healthy living &
community well-being.

24
C
C
h
h
a
a
n
n
g
g
e
e
s
s
i
i
n
n
B
B
e
e
h
h
a
a
v
v
i
i
o
o
u
u
r
r
Favourable behaviour must be encouraged,
unfavourable ones must be stopped.
•
Natural change: in response to the change in
the community around us. Example: we wear
different clothes for different seasons.
•
Planned change: we change behaviour to
improve our lives. Example: stop smoking, eat
healthier diets.
Note: not all people are ready to change, some
may change quickly, and others may change
slowly.

25
H
H
e
e
l
l
p
p
i
i
n
n
g
g
p
p
e
e
o
o
p
p
l
l
e
e
t
t
o
o
l
l
e
e
a
a
d
d
h
h
e
e
a
a
l
l
t
t
h
h
i
i
e
e
r
r
l
l
i
i
v
v
e
e
s
s
•
Using Force;
It gives a temporary change in
behaviour
•
Giving Information;
it is needed but the success is not
always there.
•
Discussing & Participating;
This is the most vital part to help
through community full participation.

26
H
H
e
e
a
a
l
l
t
t
h
h
E
E
d
d
u
u
c
c
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
;
;
T
T
y
y
p
p
e
e
s
s
1.
Health Education w ith Individuals; Counselling.
2.
Health Education w ith groups
The advantages of group education:
Ø
Provides support & encouragement
Ø
Permits sharing of experience & skills
Ø
Makes it possible to pool the resources of all members
3.
Health Education w ith Communities
•
get the support of influential people in the community.
•
Make sure that all people in the community are informed
about the problem & that their information on plans &
progress is updated. For this purpose, we need to use all
available methods of communication.
•
Get the maximum number of people involved, in order to
strengthen the capacities of the community to solve its
problems.
