
C
C
H
H
I
I
L
L
D
D
H
H
E
E
A
A
L
L
T
T
H
H
C
C
A
A
R
R
E
E

O
O
b
b
j
j
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
s
s
•
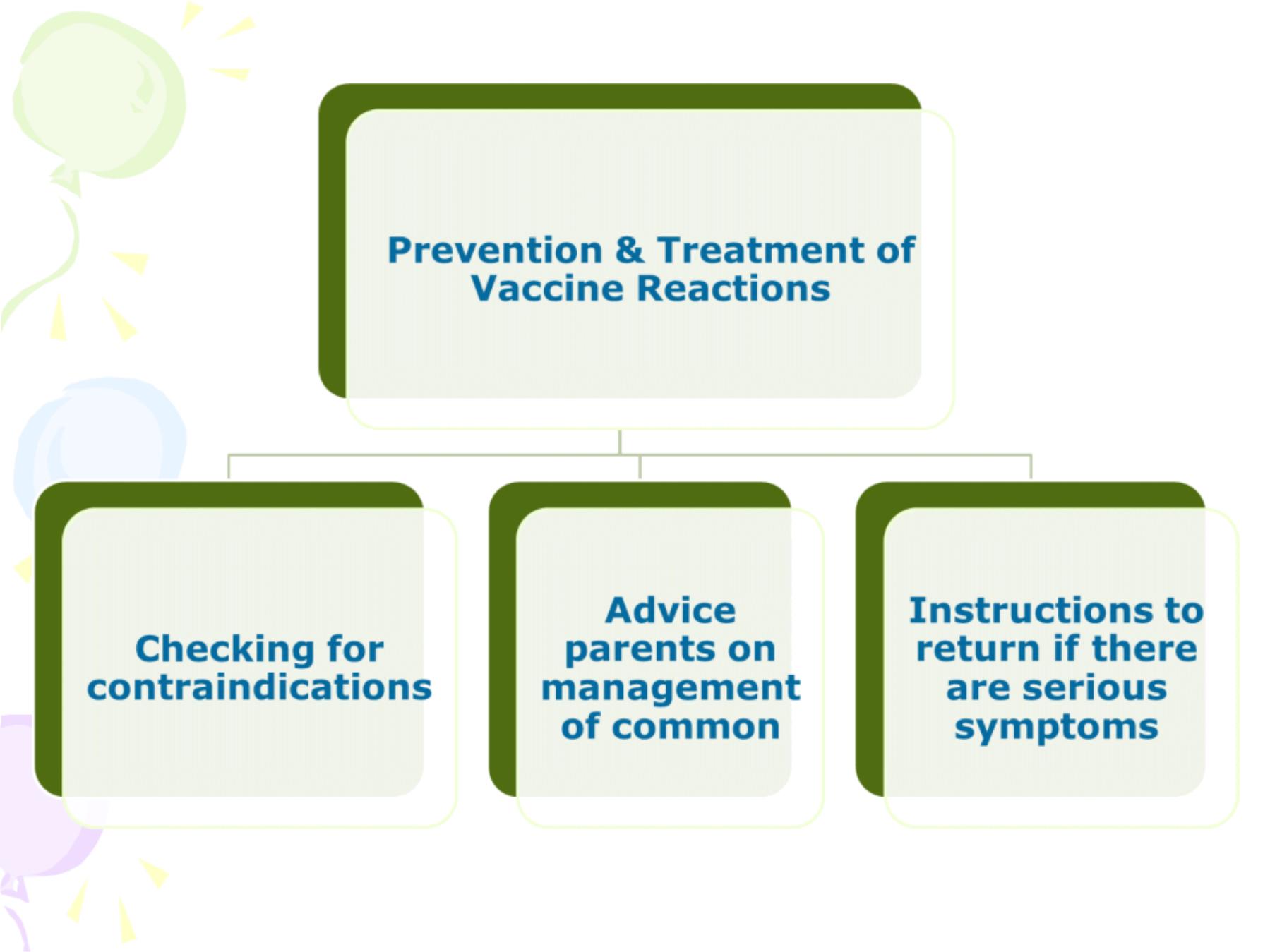
Recog nize the importance of CHC & list the most
important preventive programmes.
•
Understand the p rinciples of A pgar’
s Score
•
State the ob jectives of EP I .
•
Recog nize the scientific principles of immunization .
•
Outlines the schedule of compulsory immunization I n
Iraq.
•
List the sid e effects & contraindicatio ns to
vaccination.
•
Exp lain the four strategies for the vaccine delivery.
•
Define the cold chain.
•
Discuss the three components of the cold chain.
•
Interp ret the to ols for the cold chain monitoring.

C
C
h
h
i
i
l
l
d
d
H
H
e
e
a
a
l
l
t
t
h
h
C
C
a
a
r
r
e
e
P
P
r
r
e
e
v
v
e
e
n
n
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
s
s
e
e
r
r
v
v
i
i
c
c
e
e
s
s
a
a
r
r
e
e
n
n
e
e
e
e
d
d
e
e
d
d
f
f
o
o
r
r
c
c
h
h
i
i
l
l
d
d
r
r
e
e
n
n
f
f
o
o
r
r
t
t
h
h
e
e
f
f
o
o
l
l
l
l
o
o
w
w
i
i
n
n
g
g
r
r
e
e
a
a
s
s
o
o
n
n
s
s
:
:
1.
M
M
a
a
n
n
y
y
c
c
a
a
u
u
s
s
e
e
s
s
o
o
f
f
m
m
o
o
r
r
b
b
i
i
d
d
i
i
t
t
y
y
a
a
n
n
d
d
m
m
o
o
r
r
a
a
l
l
i
i
t
t
y
y
a
a
r
r
e
e
a
a
v
v
o
o
i
i
d
d
a
a
b
b
l
l
e
e
,
,
2.
E
E
x
x
i
i
s
s
t
t
e
e
n
n
c
c
e
e
o
o
f
f
a
a
s
s
o
o
c
c
i
i
o
o
e
e
c
c
o
o
n
n
o
o
m
m
i
i
c
c
g
g
r
r
a
a
d
d
i
i
e
e
n
n
t
t
3 .
V
V
u
u
l
l
n
n
e
e
r
r
a
a
b
b
i
i
l
l
i
i
t
t
y
y
o
o
f
f
c
c
h
h
i
i
l
l
d
d
r
r
e
e
n
n
a
a
n
n
d
d
t
t
h
h
e
e
i
i
r
r
p
p
a
a
r
r
e
e
n
n
t
t
s
s
d
d
u
u
r
r
i
i
n
n
g
g
t
t
h
h
e
e
e
e
a
a
r
r
l
l
i
i
e
e
r
r
y
y
e
e
a
a
r
r
s
s
o
o
f
f
t
t
h
h
e
e
i
i
r
r
l
l
i
i
f
f
e
e

C
C
h
h
i
i
l
l
d
d
H
H
e
e
a
a
l
l
t
t
h
h
C
C
a
a
r
r
e
e
P
P
r
r
e
e
v
v
e
e
n
n
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
c
c
a
a
n
n
b
b
e
e
p
p
r
r
i
i
m
m
a
a
r
r
y
y
,
,
s
s
e
e
c
c
o
o
n
n
d
d
a
a
r
r
y
y
o
o
r
r
t
t
e
e
r
r
t
t
i
i
a
a
r
r
y
y
t
t
h
h
r
r
o
o
u
u
g
g
h
h
m
m
a
a
n
n
y
y
P
P
r
r
o
o
g
g
r
r
a
a
m
m
s
s
l
l
i
i
k
k
e
e
:
:
ü
G
G
r
r
o
o
w
w
t
t
h
h
M
M
o
o
n
n
i
i
t
t
o
o
r
r
i
i
n
n
g
g
,
,
ü
C
C
o
o
n
n
t
t
r
r
o
o
l
l
o
o
f
f
D
D
i
i
a
a
r
r
r
r
h
h
o
o
e
e
a
a
l
l
D
D
i
i
s
s
e
e
a
a
s
s
e
e
s
s
,
,
ü
B
B
r
r
e
e
a
a
s
s
t
t
F
F
e
e
e
e
d
d
i
i
n
n
g
g
,
,
ü
E
E
x
x
p
p
a
a
n
n
d
d
e
e
d
d
P
P
r
r
o
o
g
g
r
r
a
a
m
m
o
o
n
n
I
I
m
m
m
m
u
u
n
n
i
i
z
z
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
,
,
ü
F
F
a
a
m
m
i
i
l
l
y
y
P
P
l
l
a
a
n
n
n
n
i
i
n
n
g
g
,
,
ü
F
F
o
o
o
o
d
d
F
F
o
o
r
r
t
t
i
i
f
f
i
i
c
c
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
a
a
n
n
d
d
s
s
u
u
p
p
p
p
l
l
e
e
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
,
,
ü
F
F
e
e
m
m
a
a
l
l
e
e
E
E
d
d
u
u
c
c
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
ü
C
C
o
o
n
n
t
t
r
r
o
o
l
l
o
o
f
f
A
A
c
c
u
u
t
t
e
e
R
R
e
e
s
s
p
p
i
i
r
r
a
a
t
t
o
o
r
r
y
y
I
I
n
n
f
f
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
s
s
.
.
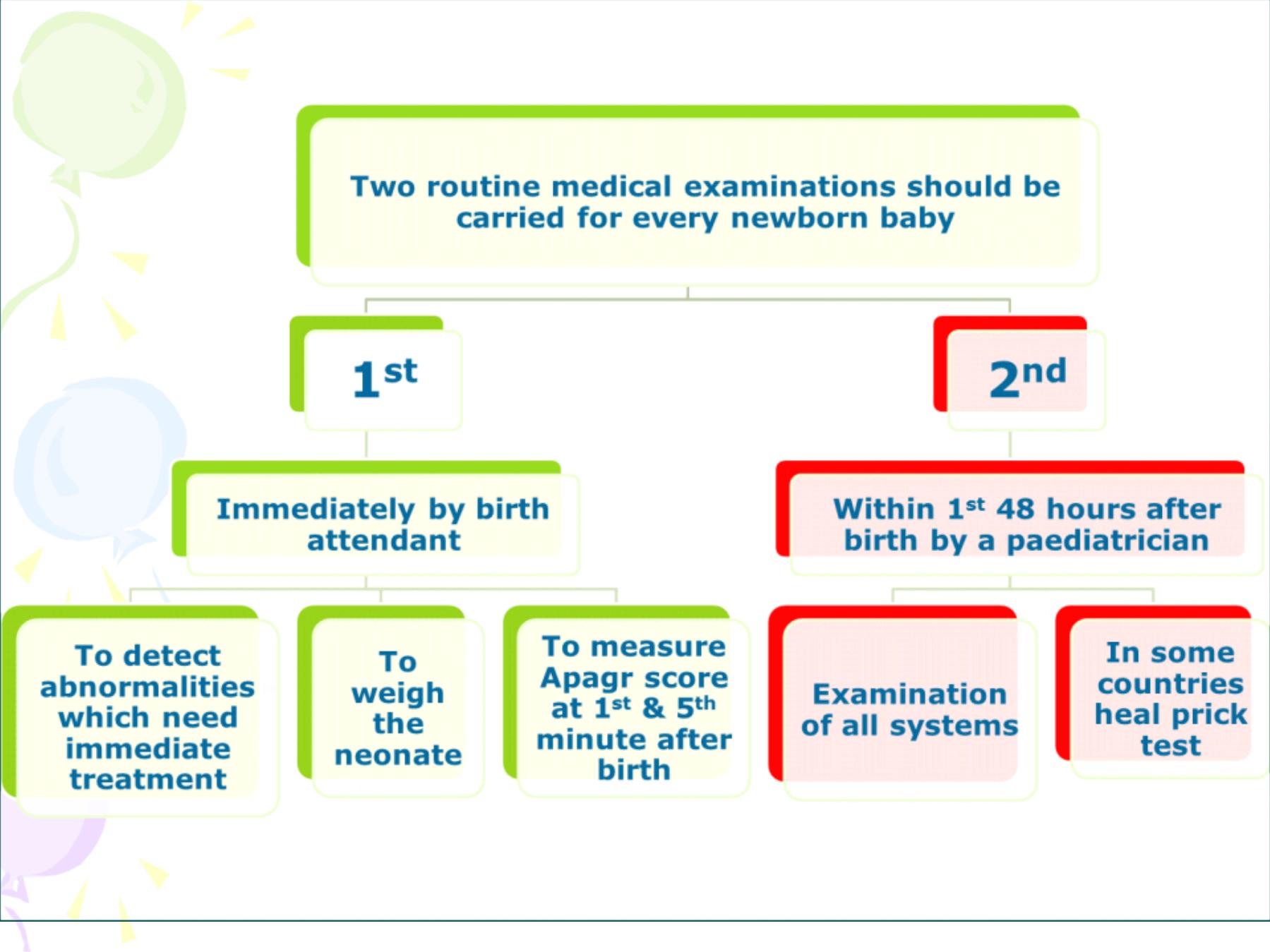
A
A
p
p
g
g
a
a
r
r
’
’
s
s
S
S
c
c
o
o
r
r
e
e
•
measures 5 signs, each is given a score of 0, 1 or
2 depending on the state of the newborn.
Sign
Score
0
1
2
Heart Rate
Absent
Slow (100/minute)
>100/minute
Respiratory effort
Absent
Slow irregular
Regular, crying
Muscle Tone
Limp
Some flexion of the
extremities
Active movement
Response to catheter in
nostril
No reaction
Grimace
Cough and Sneeze
Skin color
Pale or blue
Pink body, pale
extremities
Pink all over
Apgar Score Measurement
•
The range is between zero which means a dead infant to 10
which is very rare at the first minute.
•
Apgar score
3 at 5 minutes:
the infant is at a higher
risk of
neonatal death
, or of having
respiratory and/or cerebral
complications
during the neonatal period and need urgent referral
to the neonatal intensive care unit.

T
T
h
h
e
e
E
E
x
x
p
p
a
a
n
n
d
d
e
e
d
d
P
P
r
r
o
o
g
g
r
r
a
a
m
m
o
o
n
n
I
I
m
m
m
m
u
u
n
n
i
i
z
z
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
(
(
E
E
P
P
I
I
)
)
Most of the vaccines used currently were introduced in the
1960s. During the early 1980s the EPI was introduced in
most countries.
What determines a high immunization coverage rate?
1
.
Integrity of the health services (vaccine availability on
regular basis, functional cold chain system)
2.
Awareness of the parents of the availability of the vaccines
and the program and their motivation to vaccinate their
child.
3.
Motivation and dedication of the health workers.
Note: If we attain 90-95% vaccine coverage of children
against a certain disease we are virtually attaining a 100%
protection of children, & this is the concept of “
Herd
immunity”which means that those who are vaccinated will
protect those who are not through cutting the cycle of
transmission.

E
E
P
P
I
I
o
o
b
b
j
j
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
1 .
Reduce morbidity and mortality of
EPI targeted diseases.
2.
Promote EPI services in all PHC.
3
.
Achieve 95% coverage rate at
district level by vaccines
(a. BCG. b. Polio3. c. DPT3.
d.
HepB 3.
e. measles
)

S
S
t
t
r
r
a
a
t
t
e
e
g
g
i
i
e
e
s
s
1.
Routine
2.
Campaigns
3.
Surveillance
4.
Health promotion and education
5.
RED ( Reach Every District) approach
I
I
m
m
m
m
u
u
n
n
i
i
t
t
y
y
Specific defenses
Immunity
Passive immunity
Active immunity
Following clinical infection
Following subclinical infection
Following vaccination
Following administration of
Immunoglobulin or antiserum
Transfer of maternal
Antibodies Through milk
Transfer of maternal
Antibodies Through placenta
natural
acquired
B
B
a
a
s
s
i
i
c
c
D
D
a
a
t
t
a
a
o
o
n
n
E
E
P
P
I
I
V
V
a
a
c
c
c
c
i
i
n
n
e
e
s
s
Vaccine
against
Nature
F orm
Dose
Route
Heat
Stability
Type of
Immunity
Diphtheria
Toxoid
Fluid
0.5ml
IM*
High
IgG
Tetanus
Toxoid
Fluid
0.5ml
IM*
High
IgG
Hepatitis B
HBs Ag**
Fluid
0.5ml
IM
High
IgG
Pertusis
Whole killed Bac.
Fluid
0.5ml
IM*
Medium
IgG,A,M
Measles
Attinuated live V.
Freeze-
Dried
0.5ml
S.C.
High/dri
Low/reco
IgG,A,M
T.B.
Attinuated live
BCG
Freeze-
Dried
0.1ml
I.D.
Medium/dried
–
Low/reco
T cell Mediated
Polio-
myelitis
Attinuated live V.
Fluid
3 drops
oral
Low
IgG,A,M intestinal
+ circulating
Polio-
myelitis
Killed V.
Fluid
IM
Medium
Same only
circulating
Rubella
Attinuated live V. Freeze-
Dried
0.5m
S.C.
High/ Low
IgG,A,M

T
T
h
h
e
e
N
N
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
a
a
l
l
I
I
m
m
m
m
u
u
n
n
i
i
z
z
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
S
S
c
c
h
h
e
e
d
d
u
u
l
l
e
e
i
i
n
n
I
I
r
r
a
a
q
q
A ge/ Po pulatio n Group
Vaccine
0-one week
BCG, OPV0 , HBV1(HBV1:within 24 hrs after birth)
2 months
P enta
(DPT1, HIB1 , HBV2) +Rota Virus 1+ OPV1
4 months
Tetra
(* DPT2, HIB2)+ Rota Virus 2 + OPV2
6 months
P enta
(DPT3, HIB3 , HBV3) +Rota Virus 3+ OPV3
9 months
Measles + Vitamin A (100,000 IU)
15 months
( Measles, Mumps, Rubella) MMR1
B oo sters
18 months
Ø
(1st booster); Tetra (* DPT, HIB)+ OPV
Ø
Vitamin A (200,000 IU)
School entry age (4-6 ys)
DPT + OPV (2nd booster)+ MMR 2
Every 10 years
Td (full dose of tetanus toxoid and a reduced dose of
diphtheria toxoid after the age of 6 years)
* If the infant develops a severe reaction to a prior dose, give DT
not DPT, because the pertussis component is responsible for this
severe reaction

T
T
h
h
e
e
N
N
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
a
a
l
l
I
I
m
m
m
m
u
u
n
n
i
i
z
z
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
S
S
c
c
h
h
e
e
d
d
u
u
l
l
e
e
i
i
n
n
I
I
r
r
a
a
q
q
;
;
E
E
x
x
p
p
e
e
c
c
t
t
e
e
d
d
M
M
o
o
d
d
i
i
f
f
i
i
c
c
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
s
s
Regarding P olio Vaccine;
•
By January 2016 the injectable Killed
Bivalent Polio Vaccine will be used in three
doses instead of the oral trivalent polio
vaccine that is used till now.
•
The zero dose will remain from the OTPV
•
The Hexa vaccine will be used which include;
Dephtheria, Acellular Pertusis, Tetanus
Toxoid, HBV, Hib and injectable polio
T
T
e
e
t
t
a
a
n
n
u
u
s
s
T
T
o
o
x
x
o
o
i
i
d
d
f
f
o
o
r
r
P
P
r
r
e
e
g
g
n
n
a
a
n
n
t
t
W
W
o
o
m
m
e
e
n
n
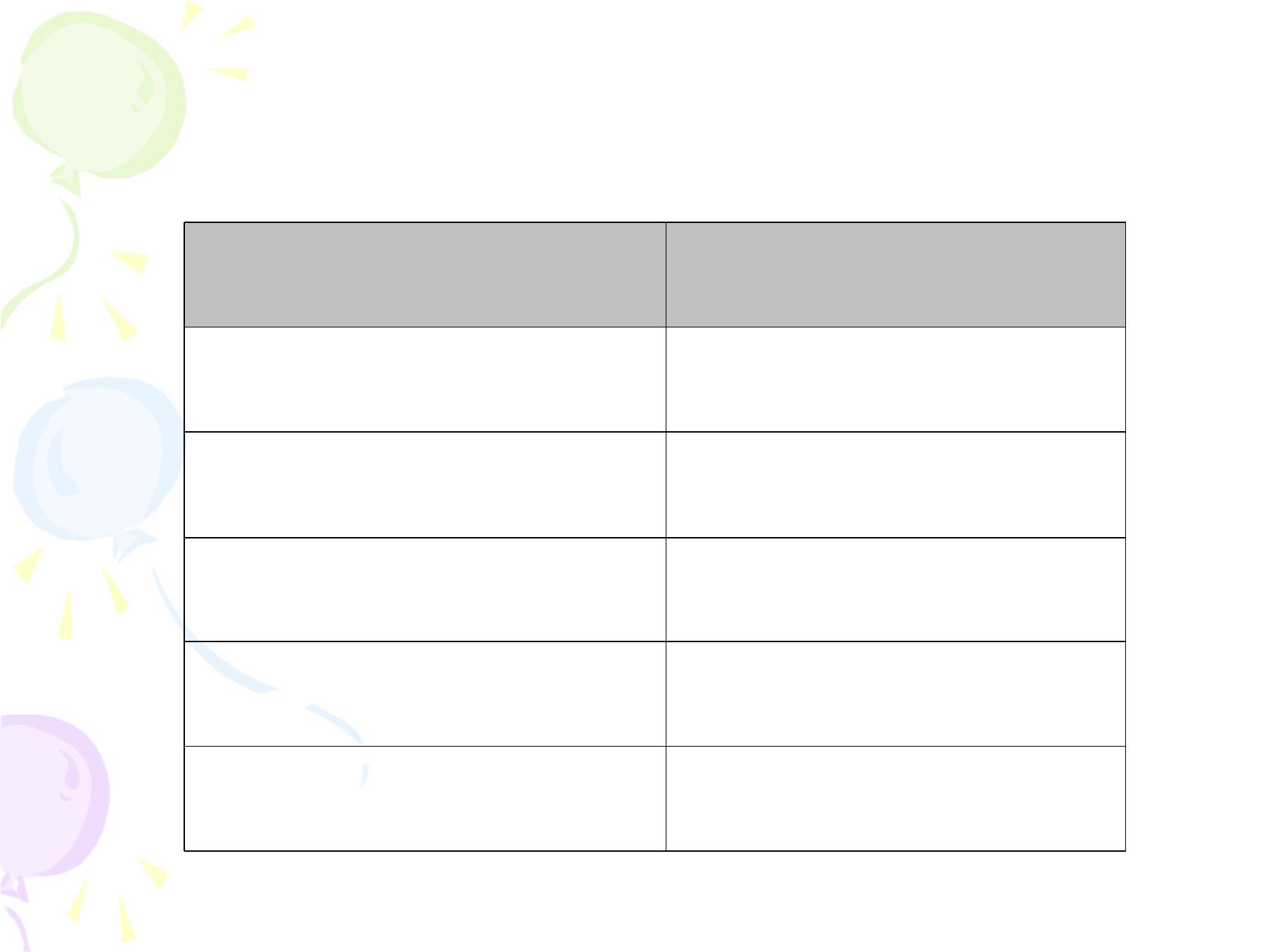
Date of vaccination
Dose
4
th
month of pregnancy
1
st
5
th
month of pregnancy
2
nd
dose
6 month after the 2
nd
dose
3
rd
dose
1 year after the 3
rd
dose
4
th
dose
1 year after the 4
th
dose
5
th
dose
T
T
e
e
t
t
a
a
n
n
u
u
s
s
T
T
o
o
x
x
o
o
i
i
d
d
f
f
o
o
r
r
C
C
h
h
i
i
l
l
d
d
B
B
e
e
a
a
r
r
i
i
n
n
g
g
A
A
g
g
e
e
W
W
o
o
m
m
e
e
n
n
(
(
C
C
B
B
A
A
W
W
)
)
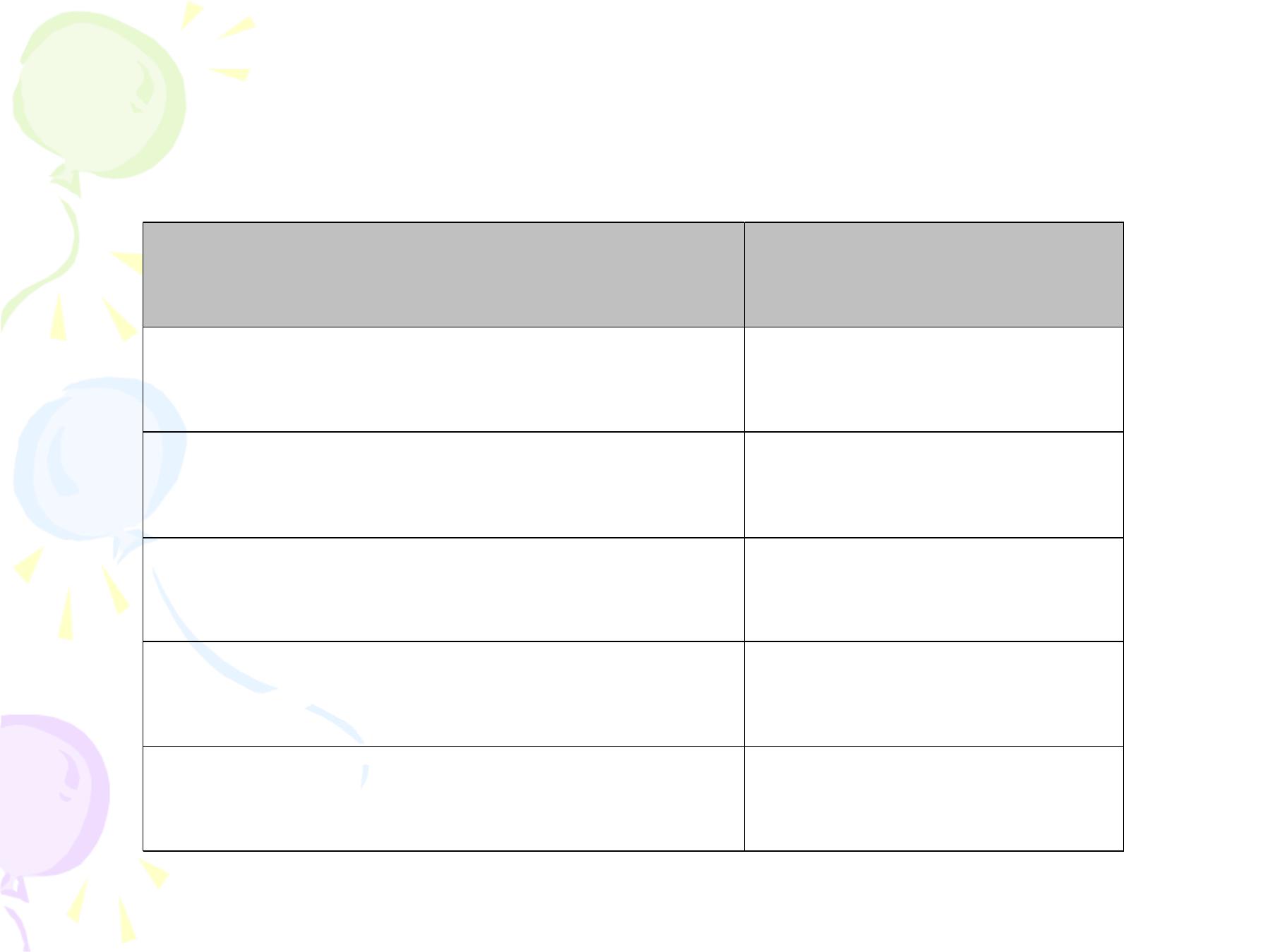
Date of vaccination
Dose
1
st
visit
1
st
dose
1 month from date of 1
st
dose
2
nd
dose
6 month from date of 2
nd
dose
3
rd
dose
1 year from date of 3
rd
dose
4
th
dose
1 year from date 4
th
dose
5
th
dose

Diphtheria:
full dose to children over 6 years of age
P ertusis
-
Any abnormality of the CNS e.g. Spina bifida
-
Acute febrile illness
-
Severe local or general reaction to a previous
dose (give DT)
-
History of convulsions in a child
-
Family history of convulsions (controversial)
Contraindications to Killed Vaccines &
Toxoids

General
-
Pregnancy
-
Acute febrile illness
-
Immunological dysfunction e.g. hypo-gamma-globulinaemia
-
Malignant disease, e.g. Leukaemia, Hodgkin’
s disease
-
Steriod therapy, immuno-suppressants & radiotherapy
Specific
-
Oral Poliomyelitis: diarrhoea & vomiting
-
Measles: Active TB, allergy to polymyxin & neomycin, family
history of convulsions.
-
BCG: Local septic condition, premature & LBW baby, chronic
skin disease
-
Rubella: pregnancy, allergy to neomycin & polymyxin,
thrombocytopenia.
Contraindications to Live Vaccines

C
C
h
h
a
a
r
r
a
a
c
c
t
t
e
e
r
r
i
i
s
s
t
t
i
i
c
c
s
s
o
o
f
f
V
V
a
a
c
c
c
c
i
i
n
n
e
e
s
s
;
;
B
B
C
C
G
G
It has an efficacy of 60-90% which can be lower when the
infection is due to an antigenic variant. BCG prevents the forms
of TB developing through haematogenous spread of bacteria (TB
meningitis & miliary TB). Efficacy is particularly high in high
incidence situations where protection may last for up to 20 y.
Side Effects
1. Small Red papule at the site of injection, which appears 6 - 8
weeks after vaccination, and progresses to a scar after 12 w.
2. If given subcutaneously (instead of the usual intra-dermal
route) it will lead to abscess formation & regional
lymphadenopathy.
3. If the child is Tuberculin positive, it will lead to a severe
reaction.
Storage: Sensitive to sunlight & heat. It should be stored at
refrigerator temperature (4-8
0
C) for up to 2 years.
Note: Physiological neonatal jaundice is not a contraindication to
BCG vaccination.


C
C
h
h
a
a
r
r
a
a
c
c
t
t
e
e
r
r
i
i
s
s
t
t
i
i
c
c
s
s
o
o
f
f
V
V
a
a
c
c
c
c
i
i
n
n
e
e
s
s
;
;
D
D
P
P
T
T
•
Efficacy is 90% (after 3 doses).
Side Effects & Adverse reactions
-Swelling, tenderness & redness develop at the site of injection
with fever lasting for about 24 hours.
-Increase in frequency and severity with increasing age, so we
give Td (full dose of Tetanus & reduced dose of Diphtheria
toxoids) after the age of 6 years.
-Severe Side effects include screaming attacks, convulsions,
collapse, and brain damage.
-The incidence of such complications is about 1/180,000 doses,
which is much rarer than the complications of the diseases
targeted by these vaccines.
-Pertussis vaccine is a killed vaccine the components of which
may cause a reaction.
-Currently, an acellular vaccine is being developed to
minimize these side effects.
Storage: Refrigerator temperature.

C
C
h
h
a
a
r
r
a
a
c
c
t
t
e
e
r
r
i
i
s
s
t
t
i
i
c
c
s
s
o
o
f
f
V
V
a
a
c
c
c
c
i
i
n
n
e
e
s
s
;
;
P
P
o
o
l
l
i
i
o
o
m
m
y
y
e
e
l
l
i
i
t
t
i
i
s
s
V
V
a
a
c
c
c
c
i
i
n
n
e
e
s
s
There are tw o types of poliomyelitis vaccine, Salk and Sabin
Comparison Betw een Salk and Sabin Poliom yelitis Vaccines
Salk (I P V )
Sabin ( OP V)
1
Inactivated (killed)
Live attenuated
2
Injectable
Oral
3
In developed countries
In developing countries
4
Prevents spread of wild polio
virus to the nervous system
through blood
Limits multiplication of wild poliovirus in
the intestine and therefore reduces faecal
transmission.
5
No shedding of vaccine virus in
the stool
Shedding of vaccine leading to passive
immunity of close contacts
6
Expensive (needles & syringe)
Cheap & Easy
7
No side effects
Side effects: vaccine associated paralysis
(1/3,000,000 doses)
Storage:
OPV: -20
o
C (up to 2 years), 0 –8
o
C (up to 1 year), 37
o
C (1 day).
IPV: 0 - 8
o
C (18 months), 37
o
C (4 weeks).

E
E
r
r
a
a
d
d
i
i
c
c
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
o
o
f
f
P
P
o
o
l
l
i
i
o
o
V
V
i
i
r
r
u
u
s
s
Global eradication of poliomyelitis is possible because the virus can only
survive in humans. The principle for eradication is that we need 3 years to pass by
from the last case registration in order to announce eradication. The last case
reported in Iraq was on the 28th of January 2000, yet because of unlimited threats
another case appear during 2014.
Strategies
1. Routine Im munization: We must have a coverage rate of at least
90% at both national & district level.
2. P olio National Immunization Days (NI Ds): Two round of
vaccination (one month apart) are done nationwide during the low
transmission season (spring and autumn)
The aim is to interrupt the circulation of poliovirus by immunizing every
child. A child can take up to 15 doses of OPV without side effects. These
campaigns can be implemented at the same time in neighbouring
countries (cross-border), so that virus transmission is cut between
countries.
3. Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP ) Surveillance: Any case with Acute &
Flaccid paralysis in children under the age of 15 years must be reported
& checked by taking two stool samples to detect the presence of the wild
polio virus in the stool. The case is followed up for 60 days (if the child
dies, lost for follow up or remains paralyzed for more than 60 days then
this is assumed to be a case of Poliomyelitis). There should be at least
one case detected per 100,000 children under the age of 15 years to
ensure good and reliable surveillance.
4. M opping Up (cleaning up): When even one case occurs in a
previously polio clean area, or in high risk areas, we implement door-to-
door immunization in limited areas.

Measles:
ü
Two factors are considered when determining the age at
which the vaccine is given; age incidence and maternal
antibody interference.
ü
Maternal antibodies disappear at the age of 6 months and
cases start to appear at the age of one year, so the best age to
give the vaccine in Iraq is 9 months. The vaccine is 95%
effective when given at the age of 9 months & provides a
longer lasting immunity.
Storage:
Being a live attenuated virus it must be kept in deep
freeze at a temperature of -20
o
C, while if it is in a powder form
we can store it at room temperature for 4 weeks. Once diluted
it must be used within 24 hours. When diluted, the diluent
should be kept at the same cold temperature as the vaccine to
prevent vaccine inactivation by high temperatures.

Measles:
S
S
i
i
d
d
e
e
E
E
f
f
f
f
e
e
c
c
t
t
s
s
Mild
q
Pain and tenderness within 24hrs
q
Fever
5% on day 8 last 1-2 days
q
Rash
2% on 7-10days last 2 days
Severe
1.
Urticaria
2
.
Anaphylaxis 1-1 million dose and not due to residual egg
portions due to gelatine used as stabilizer in vaccine production
3.
Encephalopathy / encephalitis;
q
The risk of encephalitis 1/10
6
but natural measles virus infection
causes post-infections encephalomyelitis in 1-1000 infected
persons so by vaccinating children, we have diluted the incidence
of encephalitis by 1000 times.
q
About 50% of those affected are left with permanent CNS
impairment This syndrome is considered to be immunologically
mediated.
q
Encephalopathy study 10 years follow-up did not identify an
increase risk of permanent neurological abnormality following
Measles vaccination .

Measles:
S
S
i
i
d
d
e
e
E
E
f
f
f
f
e
e
c
c
t
t
s
s
Other severe but rare AEAV
4.
Sub acute sclerosing panencephlitis (SSPE)
5.
Guillan-Barre syndrome
6.
Seizures
7.
Thrombocytopenia 1-400.000 dose
8.
Inflammatory bowel diseases
9.
Autism

HB Vaccine:
-
Three doses are effective.
-
Side effects: local reaction, with no
contraindications. It should be stored at
refrigerator temperature.
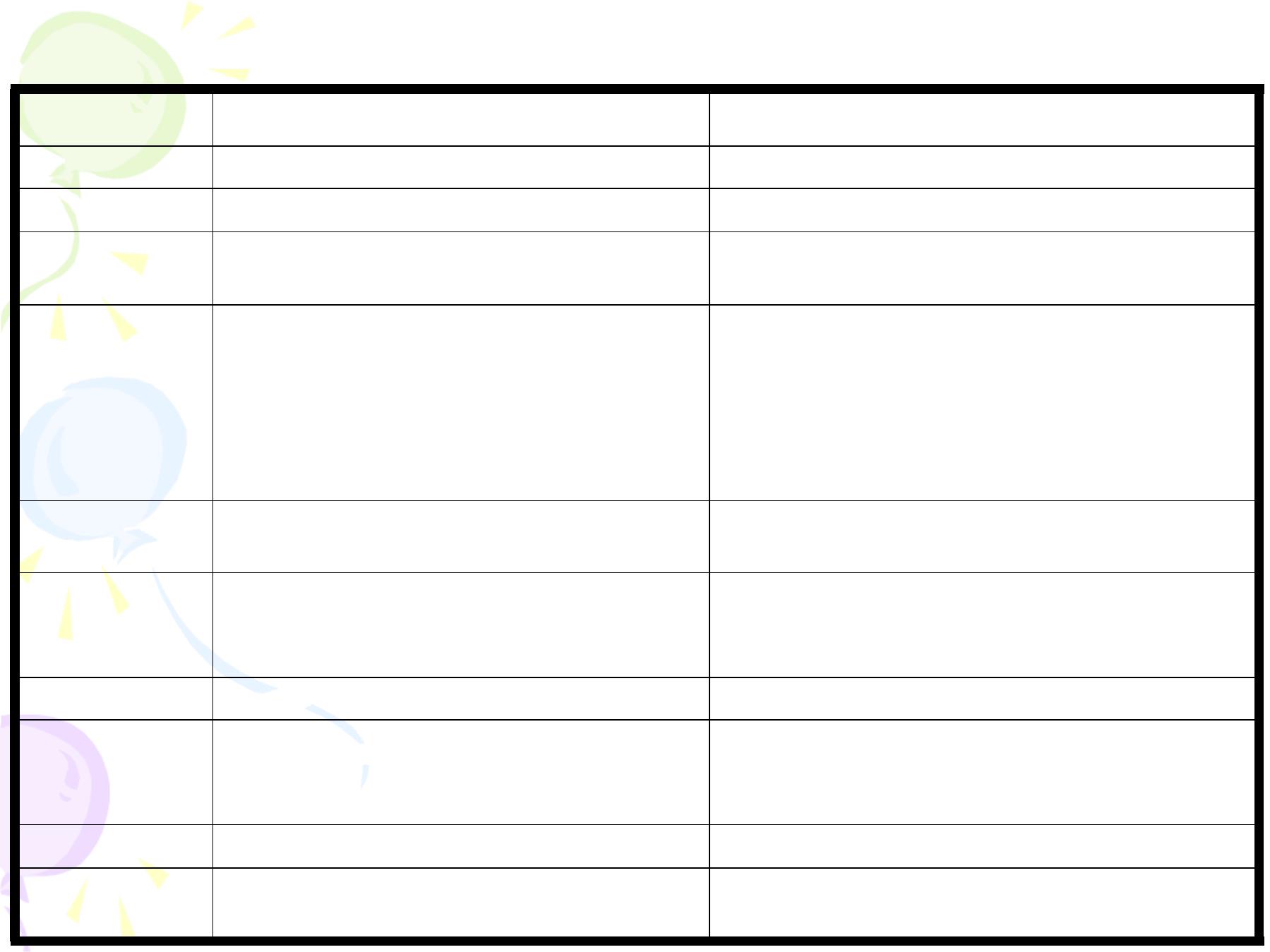
Adve rse Events Following Va ccination
Vaccine
Mild
Se ve re
BCG
Axilla ry, cervical, Ly mph adenitis
Oste itis TB me ning itis
Diphtheria
Redne ss, pain, fever
Urticaria, pruritis a naphylaxis
Te tanus
Pa in, ery thema sterile - abscess, fe ve r
Urticaria, bra chial neuritis Gullian- Barre
a naphylaxis
Pe rtussis
Pa in, te nderness, Nodule e rythema, oedema
fe ve r, irritation, loss appetite, vomiting
* persistant inconsolable cry
* unusual screams
* convulsion
* fe ve r 4 0+
o
C
* hy potonic- hyporesponsive e pisode s
* ence phalopathy
Hepatitis B
Fe ve r, pain, swelling ery thema , headache
Anaphy laxis Gullian- Barre Ha ir- loss
Diabete s ty pe 1
Measle s
Pa in, te nderness, fe ve r , ra sh
Urticaria, encephalopa thy, encephalitis, SSPE,
se izures Gullian- Ba rre thrombocytopenia,
Autism inflamma tory bowel dise ase
Mumps
Pa in, te nderness, fe ve r parotitis
Ase ptic mening itis
Rubella
Pa in, te nderness, fe ve r
rash, lymphade nopathy he adache
Arthalg ia
Arthritis
a rthropathy
MMR
Fe ve r, rash, parotitis lymphade nopathy
OPV
VAPP, Gullian- Barre ascptic me ning itis,
transve rse my elitis

T
T
h
h
e
e
C
C
o
o
l
l
d
d
C
C
h
h
a
a
i
i
n
n
q
Vaccines are effective only if maintained at the
recommended temperatures throughout their journey
from the manufacturer to the consumer.
q
Exposure to high temperatures w ill lead to the
damage of these vaccines.
q
To keep them cold we need equipment (freezer,
refrigerator, cool boxes, vaccine carriers,
thermometers & cold rooms) & people who know how
to keep the vaccines at the recommended temperature.
Methods used for detecting heat exposure:
1
.
CCM (Cold Chain Monitor) : there is a colour
index with the vaccine that changes its colour when
exposed to higher temperatures than recommended.

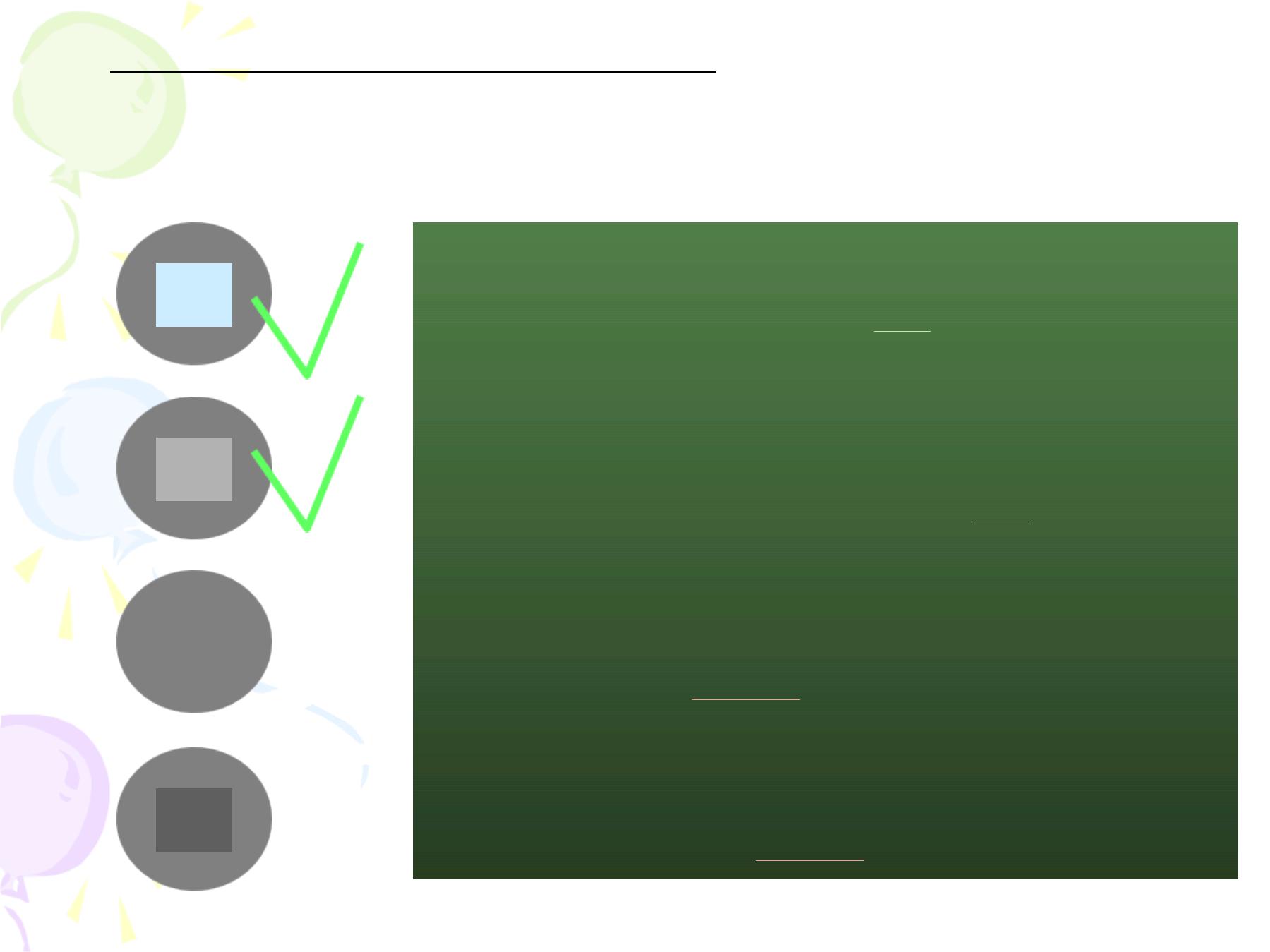
inner square still lighter than outer ring
;
if the expiry date is not passed, use the vaccine
inner square lighter than outer ring
;
if the
expiry date is not passed, use the vaccine
inner square matches the colour of outer ring;
discard point - do not use the vaccine
inner square darker than outer ring; beyond
the discard point - do not use the vaccine
x
x
Ö
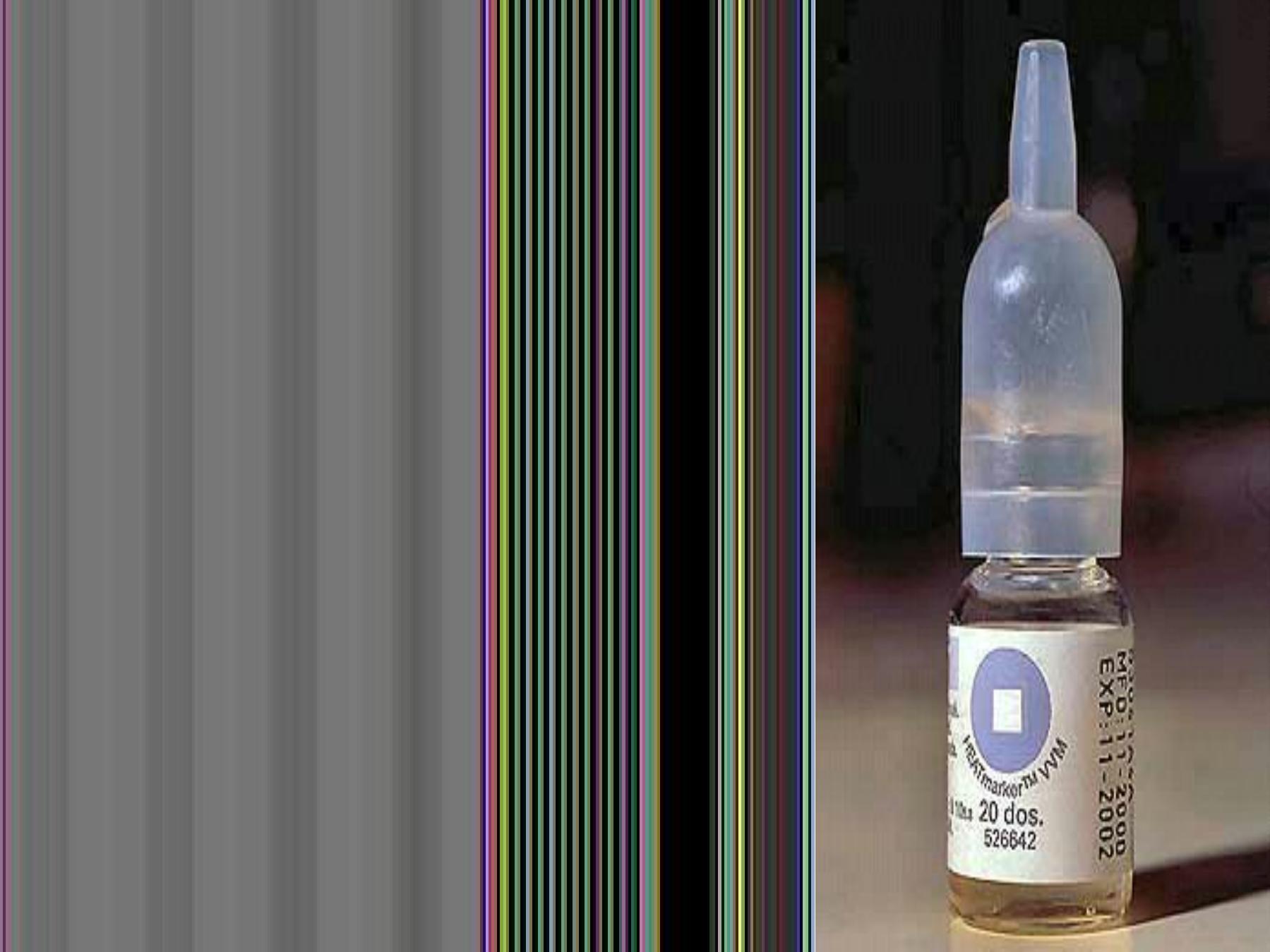
2. VVM (Vaccine Vial Monitor): used only in polio vaccine
vials, where each one has a sticker (a square & a circle in it)
one is purple & one is white, and when exposed to high temp
both the circle & the box become purple.

D
D
e
e
s
s
t
t
r
r
u
u
c
c
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
o
o
f
f
U
U
n
n
u
u
s
s
e
e
d
d
V
V
a
a
c
c
c
c
i
i
n
n
e
e
s
s
:
:
q
When vaccines are not used, because
they were kept at room temperature
during a vaccination session, and can not
be re-refrigerated, they should be
destroyed.
q
This is done by incineration.
q
If thrown with the wastes, or into the
sewerages, they may regain their
potency and cause an epidemic.

L
L
a
a
s
s
t
t
c
c
o
o
n
n
f
f
i
i
r
r
m
m
e
e
d
d
p
p
o
o
l
l
i
i
o
o
c
c
a
a
s
s
e
e
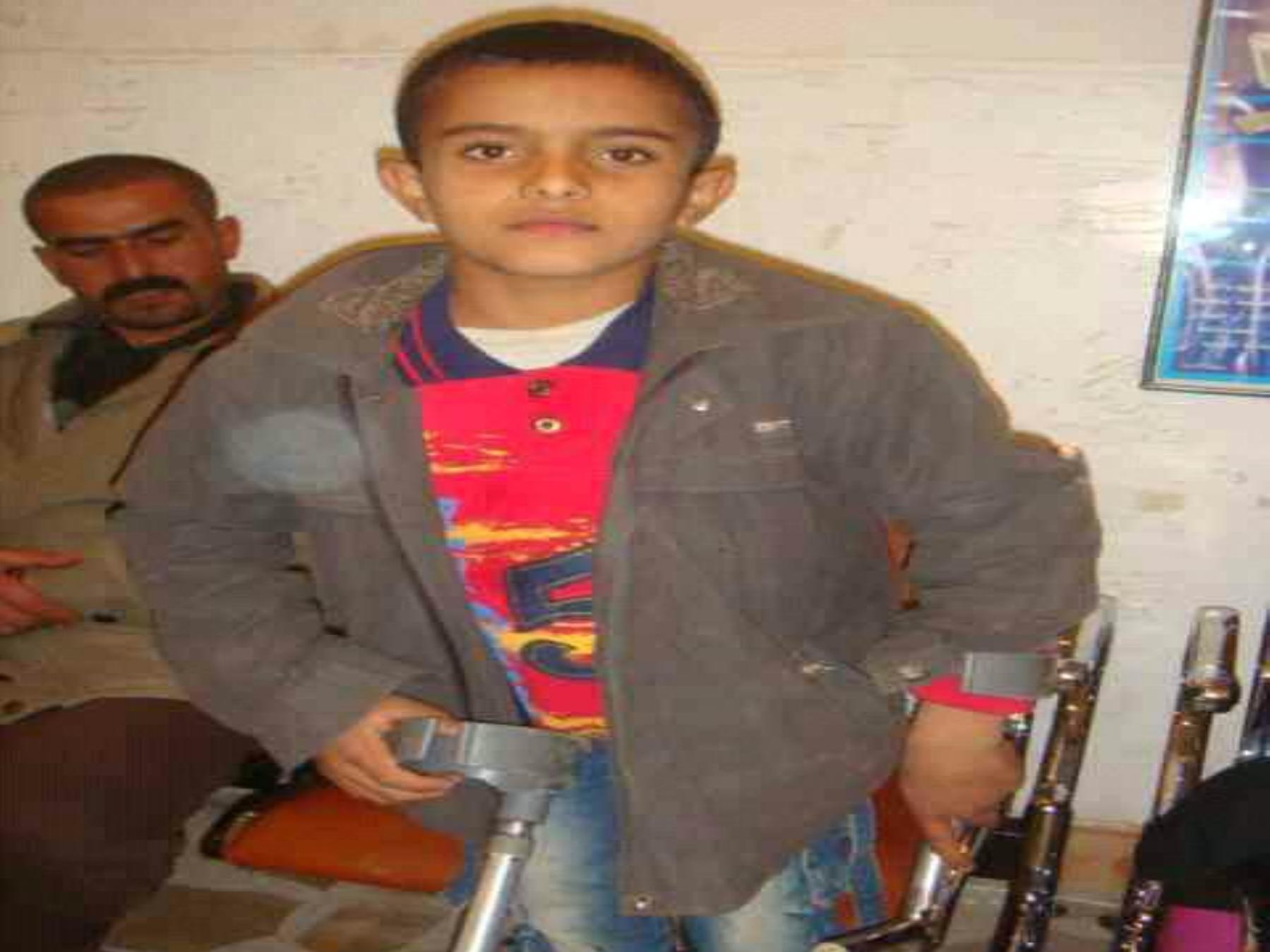
D
D
i
i
a
a
l
l
a
a
2
2
8
8
/
/
1
1
/
/
2
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
P lease no more
polio cases
Forgive
us


M
M
o
o
b
b
i
i
l
l
e
e
I
I
m
m
m
m
u
u
n
n
i
i
z
z
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
T
T
e
e
a
a
m
m
D
D
i
i
a
a
l
l
a
a



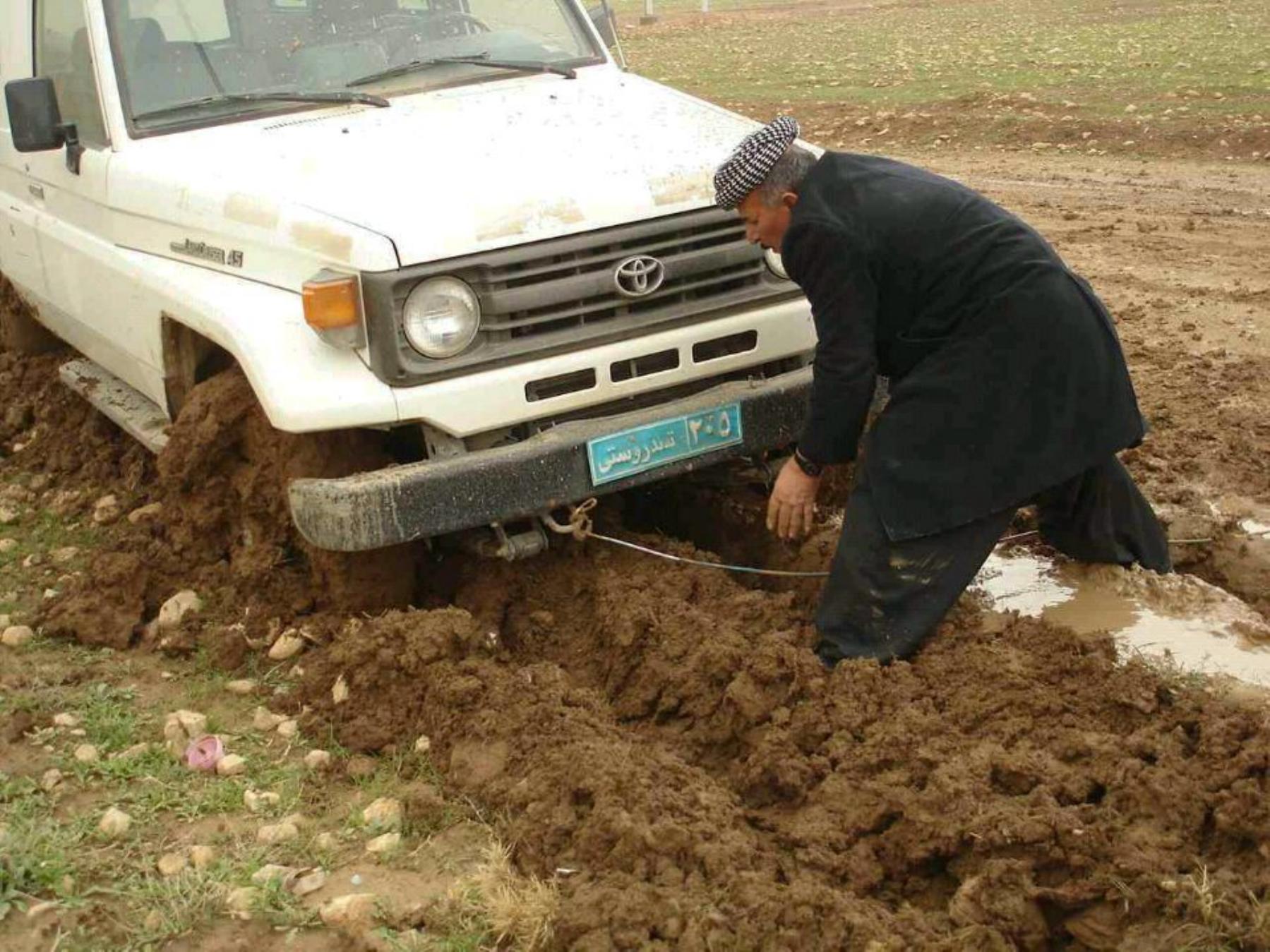
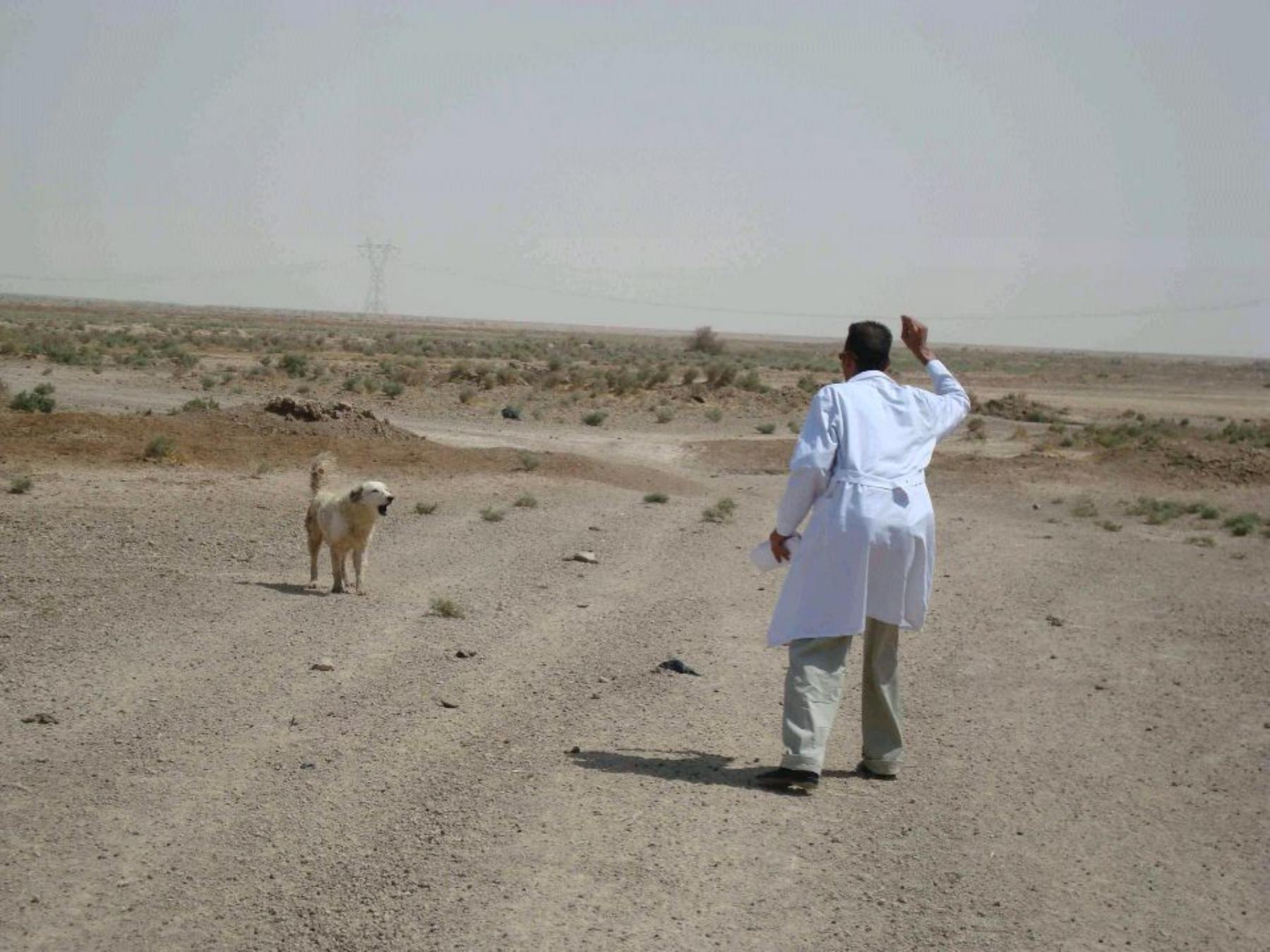
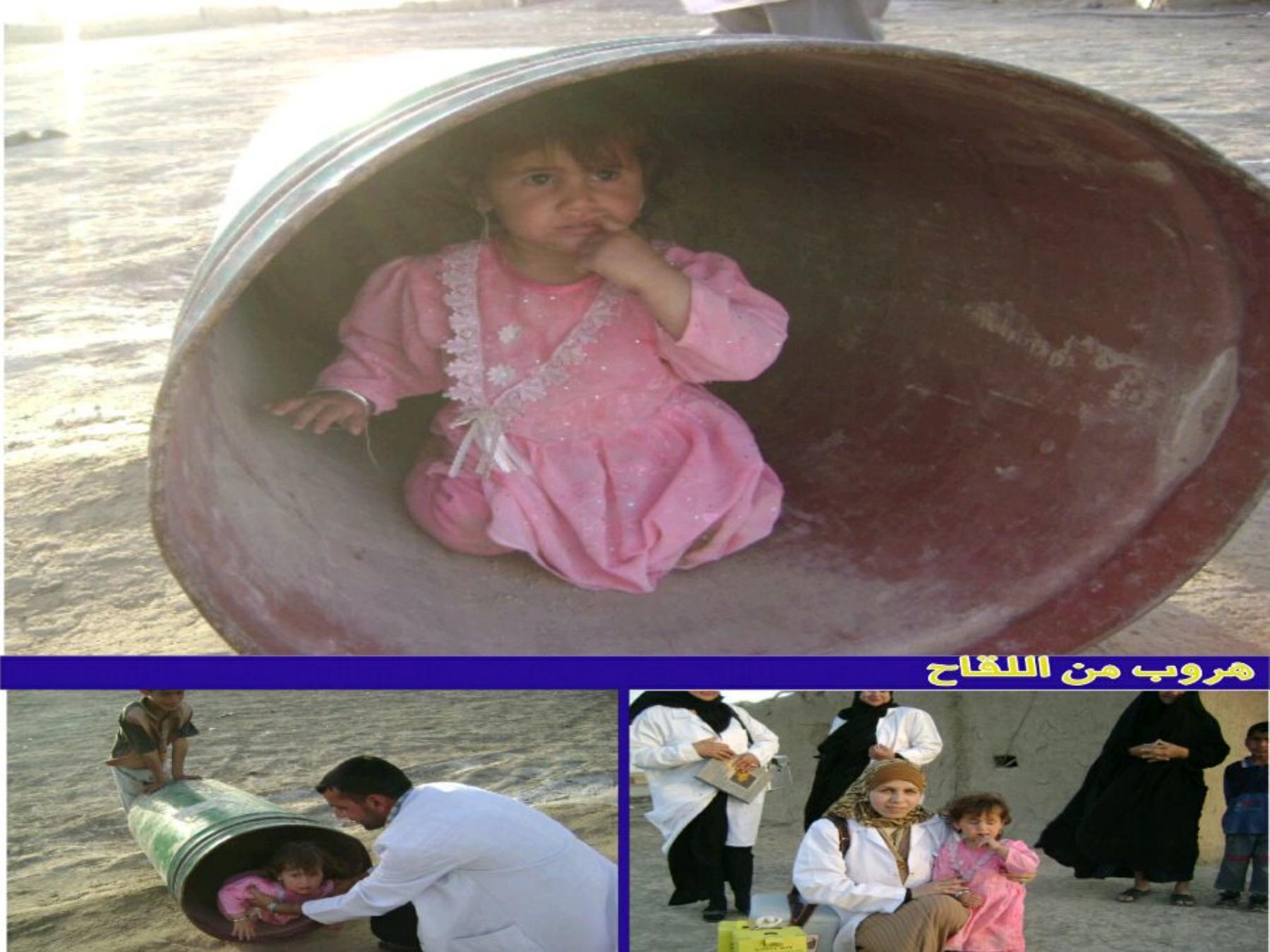
10 millions doses of
Polio vaccine
distributed through
this small opening
Isolation wall
surround main
vaccine
warehouse

PHC destroyed by terrorist
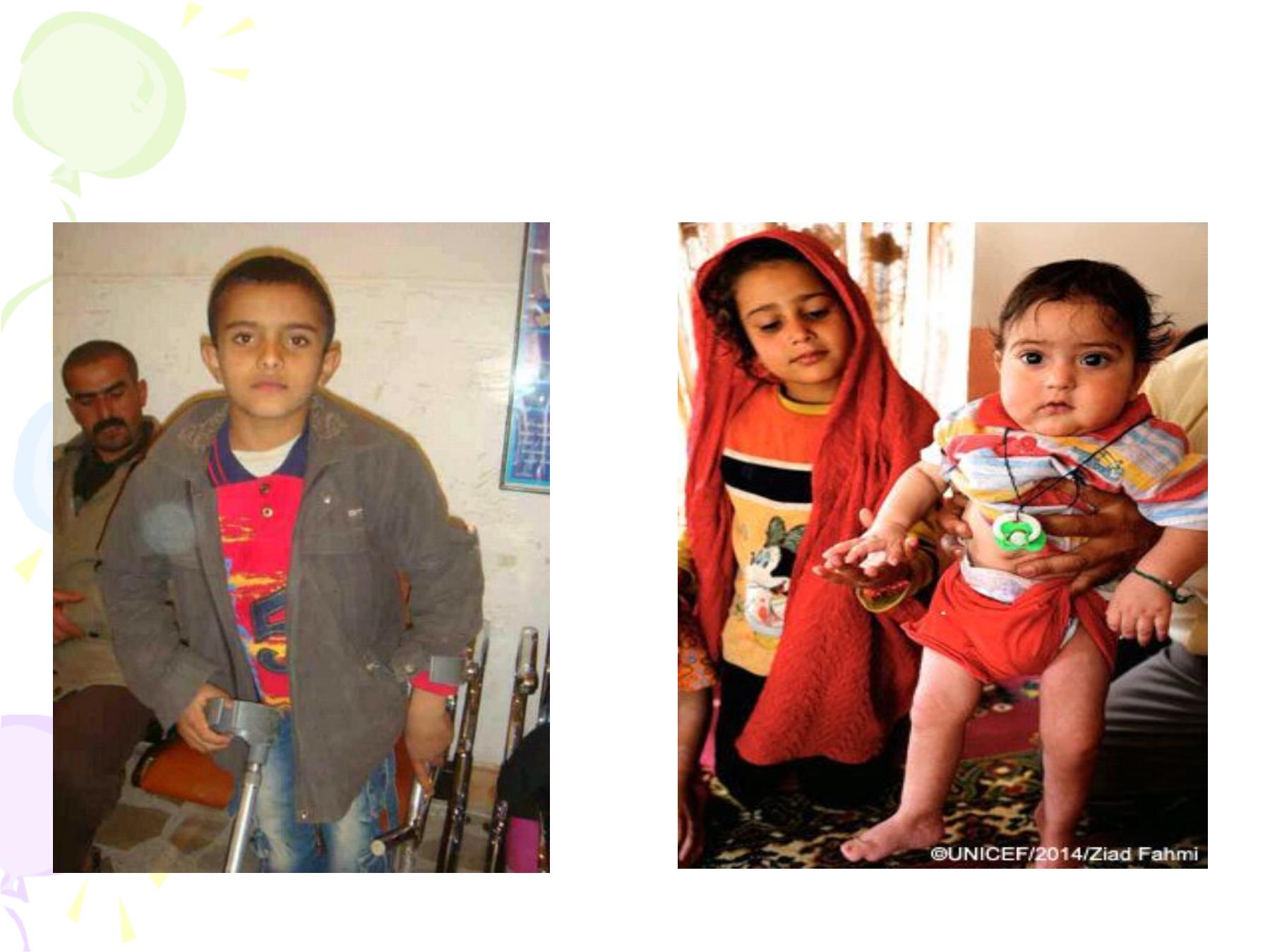




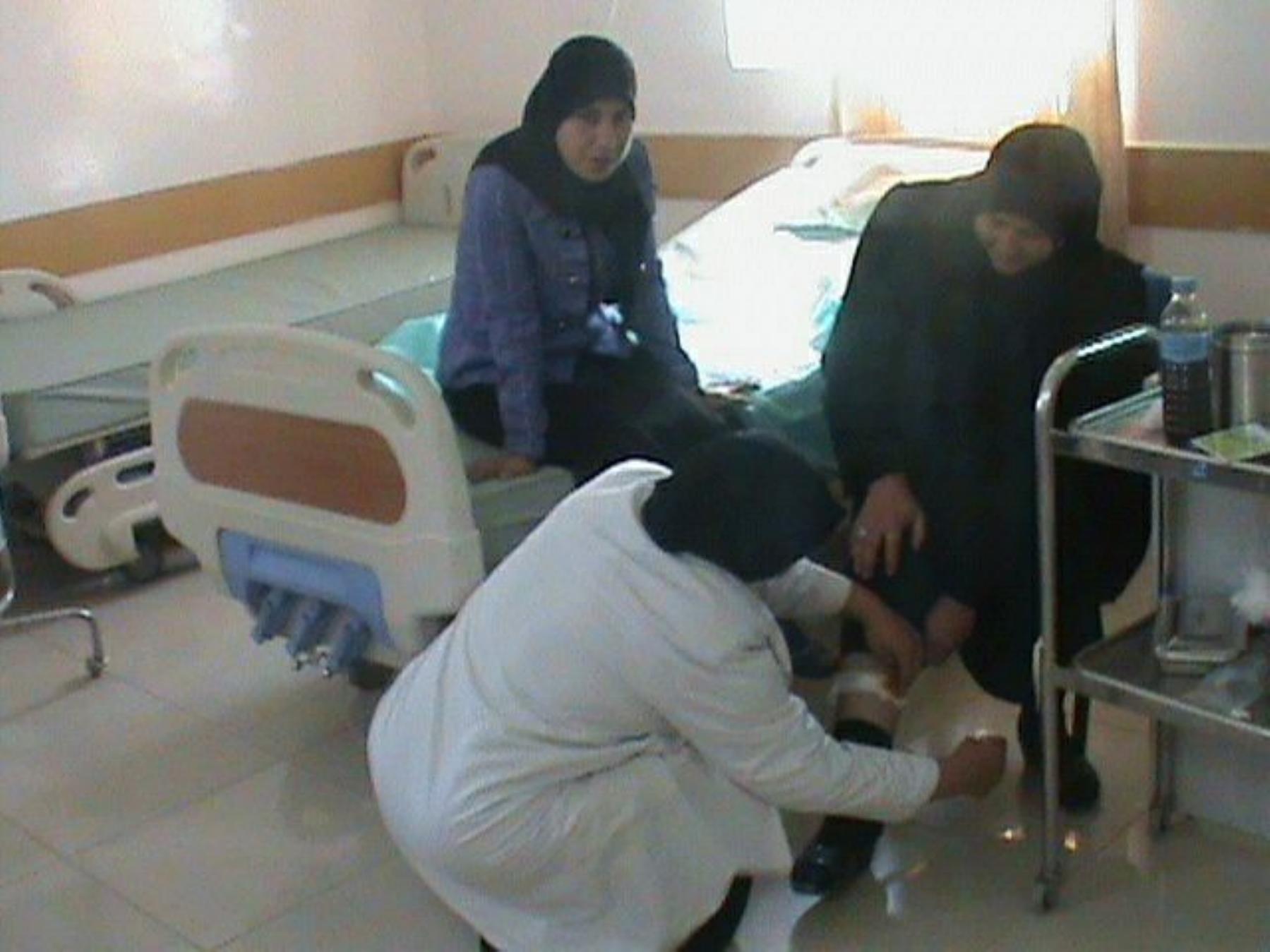


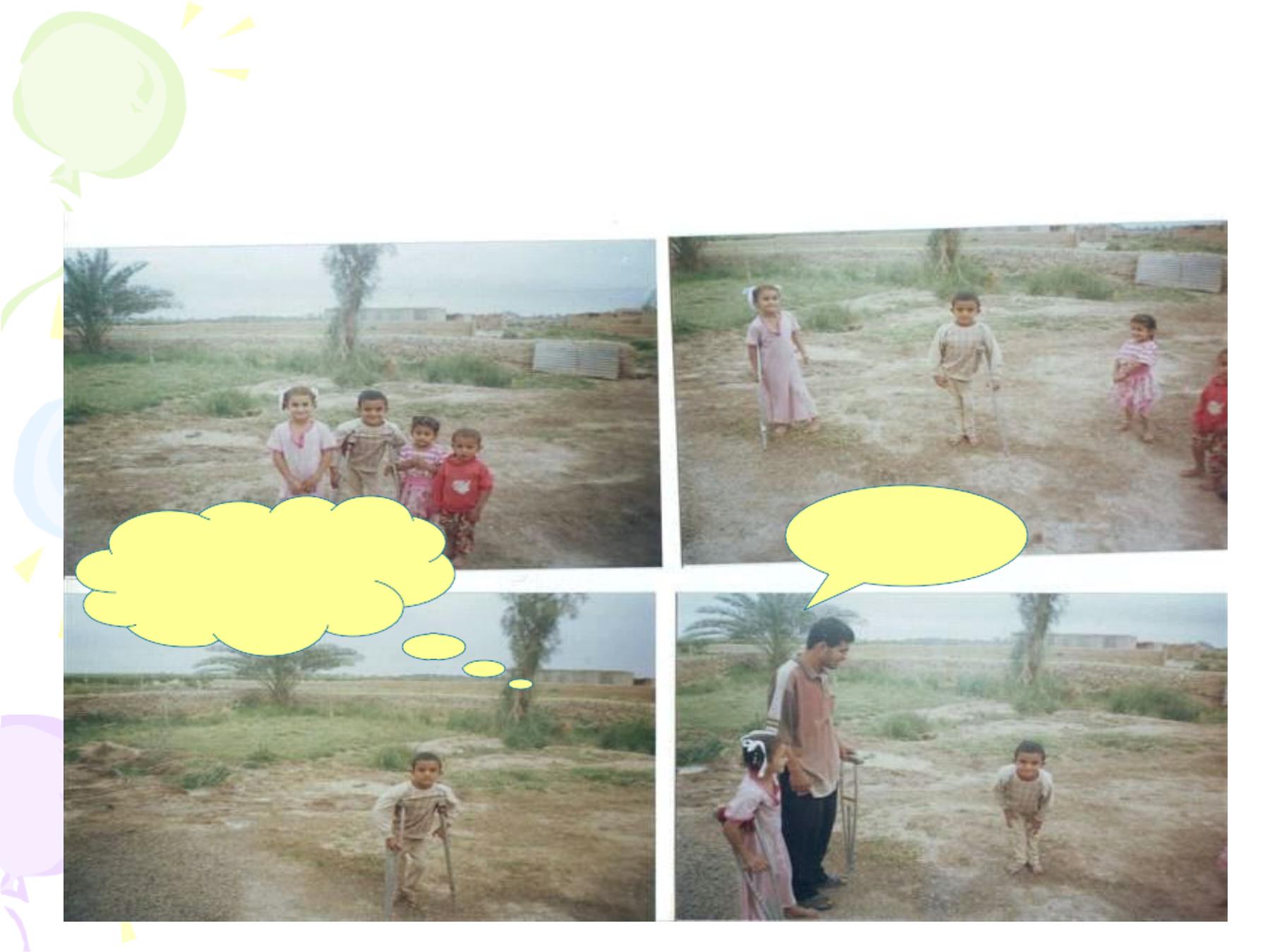
This boy w as the last
case of polio since 2001
During 2014 another
baby w as the victim
