
Family Planning and
Contraception

Goal of Family Planning
To assist the clients with reproductive
decision making, enabling the client to
have control of the number of
pregnancies, spacing the time between
children, and to prevent pregnancy if
desired

Decision to use a
contraceptive
May be made by the individual man or
woman or jointly as a couple

Legal Issues related to Family
Planning and Contraception
May vary from state to state concerning
sterilization,and abortions.
Informed consent-need to document
information provided and understanding
of client -the nurse should use
(BRAIDED)when counseling client on
contraceptive methods
decision about contraception should be
made voluntarily with informed consent

BRAIDED
B- Benefits/Advantages
R-Risks/Disadvantages
A- Alternatives/Other methods available
I-Inquiries/ Allow time for questions
D-Decisions/opportunity to decide or
change mind
E-Explanation/about method/how to
use
D-Documentation /everything taught

What to teach about each
method
What it is, How it is used , or How it
works?
advantages
disadvantages
effectiveness
side effects
risks
contraindications
long term effects

Assessment
Obtain a history to identify the client’s
past and current health status and
potential risks factors.
Sexual history
Reproductive health
Future plans for childbearing
Psychosocial data- lifestyle, motivation,
religious beliefs,cultural
influences,

Assessment
Financial factors
these factors may affect the
selection,access,and use of aparticular
method
Don’t assume anything….ask.
Knowledge of and concern about
contraceptive methods need to be
determined to identify deficits and need

Assessment
For accurate and additional information
Identify actual or potential problems
from the assessment.
Provide privacy for assessment and
discussion about contraceptive methods

Methods of Family Planning or
Contraception
Natural methods-
abstinence
Coitus interruptus -(withdrawal)
Fertility awareness methods-calendar
method,basal body temperature (BBT),
cervical mucus method

Methods of Family Planning
and Contraception
Mechanical methods-
Barrier methods-
Condoms- Male/Female
Diaphragm
Spermicides
Intrauterine device(IUD)

Methods of Family Planning
and Contraception
Chemical Methods-
Oral Contraceptives(birth control pills)
Subdermal implants(Norplant)
Long-acting progestin injections
Postcoital contraception
Surgical Methods-Vasectomy
Tubal ligation

Natural methods
Safe
Situational methods requiring increased
self awareness
Self control
to be effective

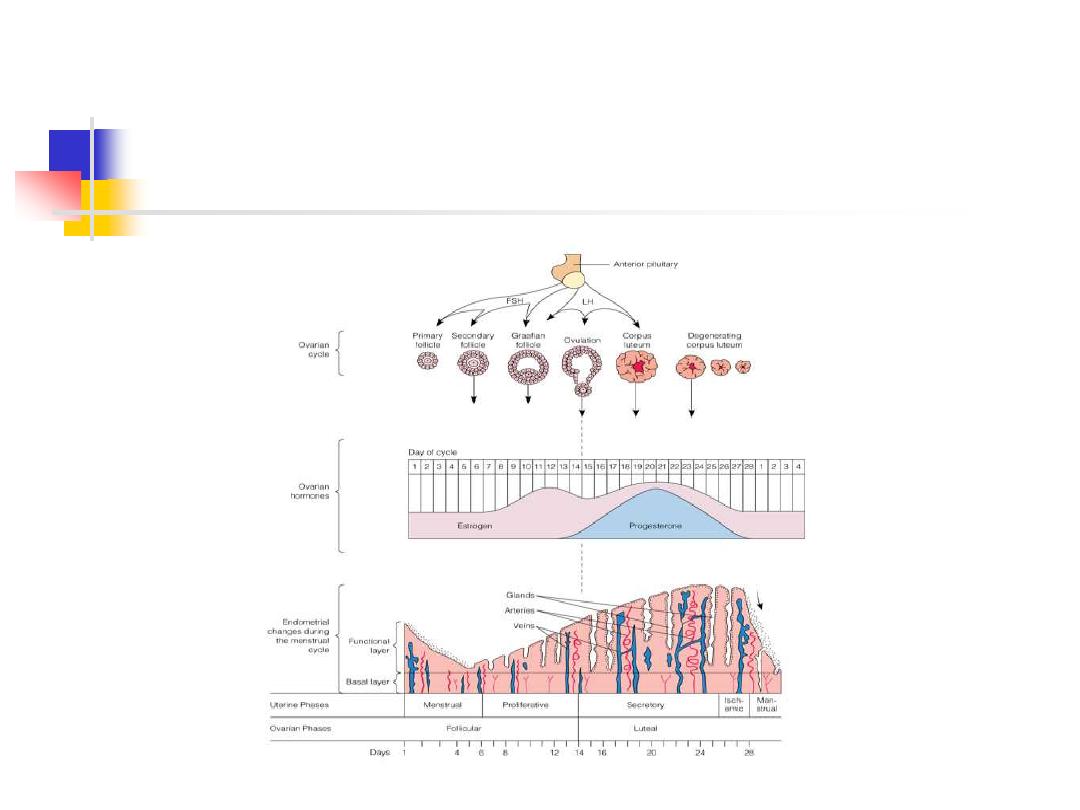
Fertility Awareness Methods
Based on an understanding of the
woman’s ovulation cycle and the timing
of sexual intercourse
All methods attempt to identify the
female fertility and to avoid unprotected
intercourse during that time period
Free,safe,and acceptable to couple’s
religious beliefs prohibit other methods
Female Reproductive Cycle

Cont.
Increases awareness of the woman’s
body
encourages communication
can be used to prevent or plan a
pregnancy
Requires extensive counseling and
education
difficult with irregular cycles
no protection for STI’s

Calendar method
Rhythm method
75-91% effective
shortest and longest cycles
18days from shortest cycle
11days from longest cycle
avoid sex during fertile period

BBT
Based on the thermal shift in the
menstrual cycle
75-97% effective
drop prior to ovulation then raises0.5-1
degree with ovulation
Avoid intercourse when temperature
drops and for 3 days after.

Cervical mucus
Ovulation or Billing’s Method
Based on the cervical mucus changes
that occur during the menstrual cycle
75-97% effective
Cervical mucus changes in response to
levels of estrogen and progesterone
Assess for amount, color,consistency,
and viscosity

Symptothermal Method
Incorporates the assessment of multiple
indicators of ovulation-BBT, and cervical
mucus,increased libido,abdominal
bloating,mittelschmerz ,breast
tenderness,pelvic tenderness,pelvic or
vulvar fullness,softer cervix located
higher in the vagina
75-97% effective

Mechanical Methods
Male condom-86-97 % effective
water based lubricants
proper technique to apply
protection from pregnancy and Std’s
Female condoms-79-95% effective
Proper technique to apply

Diaphragm
80-94% effective
Dome- shaped appliance made of
rubber with flexible rim that fits over
cervix
used with spermicidal jelly or cream
physician will assess for size
reassessment after birth of baby or
weight loss or gain.
Proper technique to apply

Spermicides
Chemical barrier to prevent pregnancy
by killing sperm or neutralizing vaginal
secretions
74-94% effective
creams,jelly,melting suppositories,
foaming tablets,foam,and films

Intrauterine device-IUD
A device placed in the uterus to prevent
pregnancy
98.5-99.2 % effective
Placed and removed by health
professional
check for side effects

Oral Contraceptives-Birth
control pills
Act by inhibiting the release of an
ovum,blocking the cyclical release of
gonadotropin-releasing hormones and
changing cervical mucus
95-99.5% effective
combined oral contraceptives-estrogen
and progestin
progestin-only pill-minipill

Subdermal implant(Norplant)
Consist of 6 silastic capsules containing
levonorgestrel-progestin
98.5-99.5% effective
placed and removed by health care
provider

Long-acting Progestin injection
Depo-Provera
long-acting progestin that blocks lh
surge,suppresses ovulation and thickens
cervical mucus
97.7% effective
Repeat every 80-90 days


Postcoital contraception
Emergency method-not to be used on a
frequent or regular basis
reduces pregnancy rates by 75-85%
oral contraceptives-MAP (morning after
pill)
insertion of IUD
abortions

Vasectomy
Male sterilization
the vas deferens is resected through
small incision in the scrotum resulting in
blockage of the passage of the sperm
Health care provider must do in
clinic,office or hospital
sperm count to check for sterility
99.5%effective

Tubal ligation
Surgical procedure done in hospital
cuts, tied ,or cauterized the fallopian
tubes preventing sperm from fertilizing
ovum
99.2-99.6% effective
