بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم

Measles
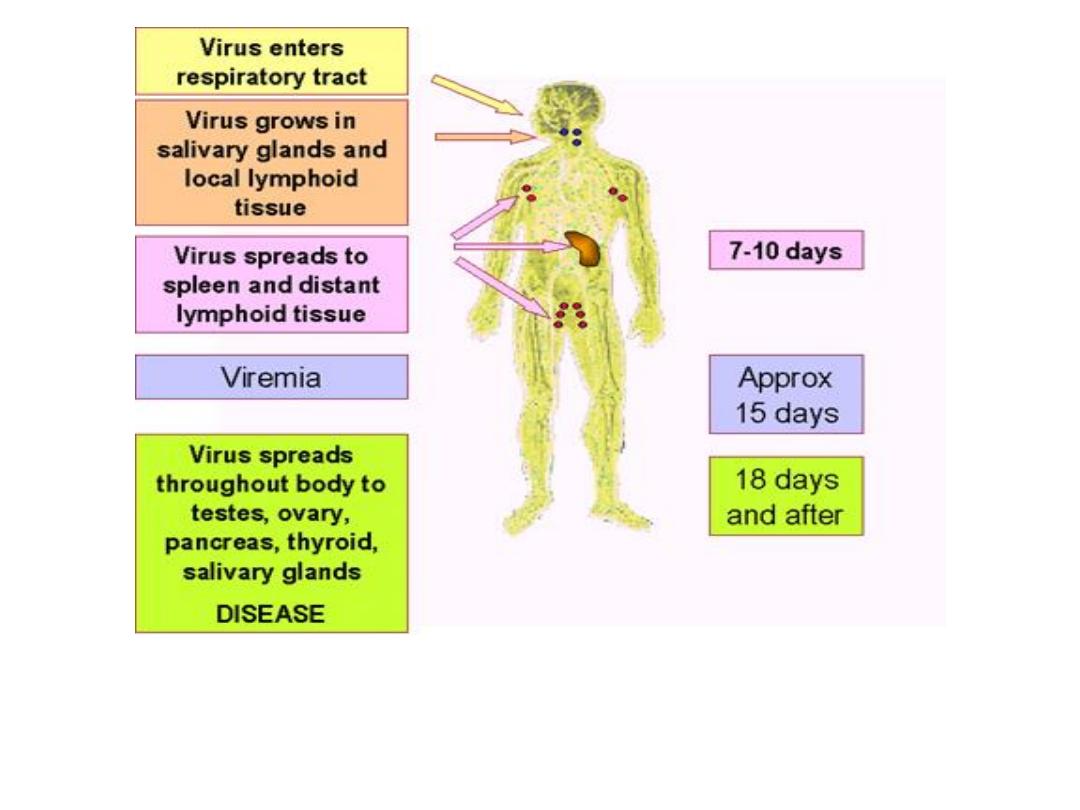
Agent- RNA virus
( Paramyxo virus family,
genus Morbillivirus )

Environmental factor
• Winter season, over crowding
• Transmission – Droplet infection,
direct contact with nasal or throat
secretions of infected persons,
• 4 days before and 4 days after rash.
• Incubation period- about 10 days (7
to 18 days)…

Clinical features
• 3 Cs (Cough, Coryza & Conjunctivitis)
• Koplik spots
• Four days fever (40
0
c)
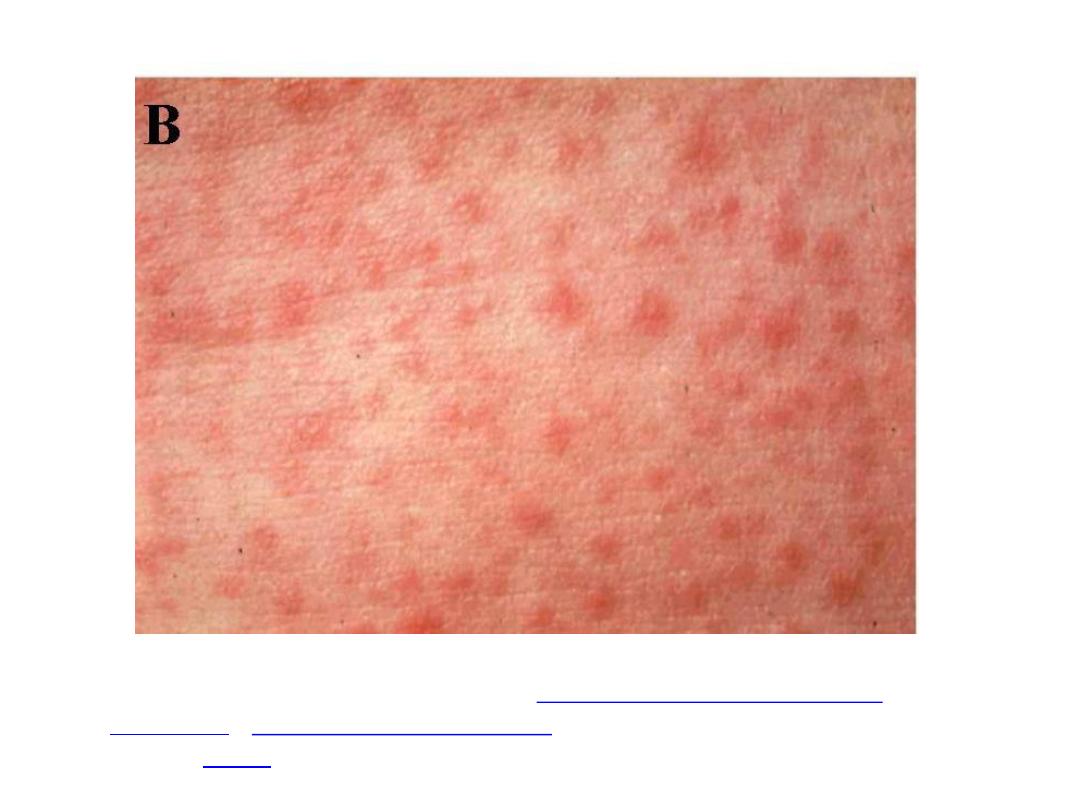
• Generalized maculopapular,erythematous
rash.
The rash begins on face then becomes
generalized, lasts for 4-7 days.
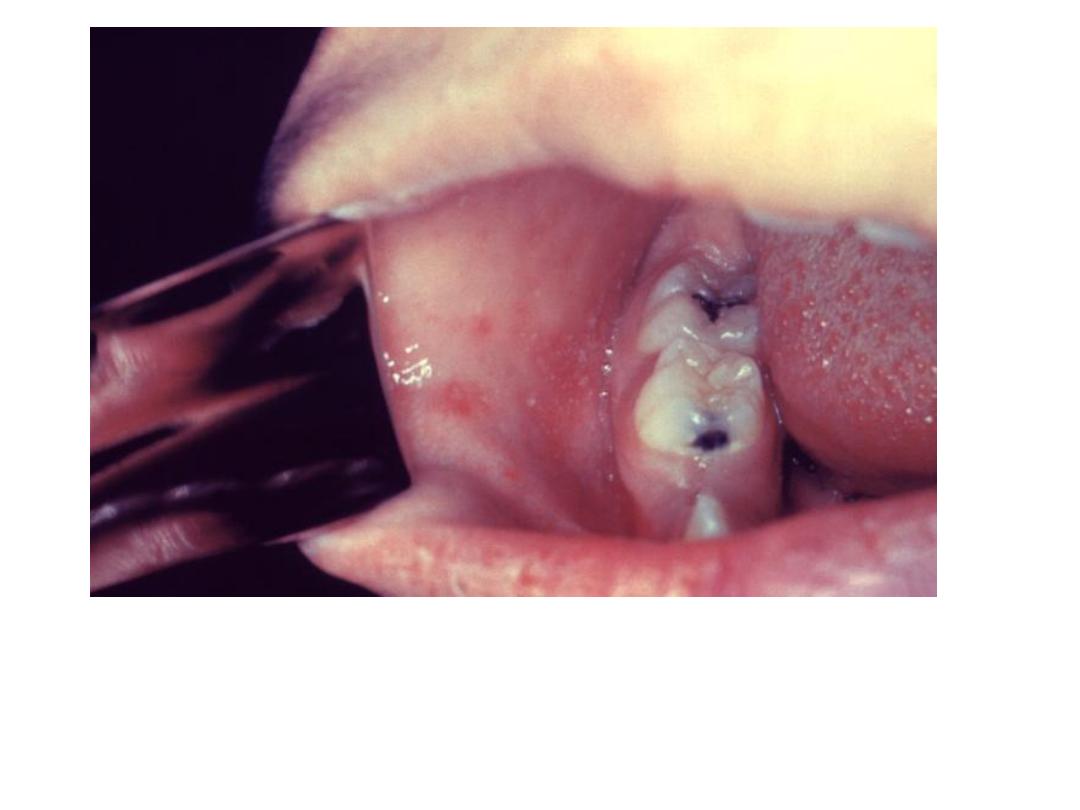
KOPLIK SPOT
Source:
http://phil.cdc.gov/PHIL_Images/20040908/4f54ee8f0e5f49f58aaa30c1bc6413ba/6111_lo
res.jpg

Complication
• Diarrhea,
• Pneumonia
• Laryngotracheobronchitis
• Otitis media
• Convulsions,
• Encephalitis,
• SSPE
(
sub acute sclerosing panencephalitis)
(rarely)

Diagnosis of Measles
• Ask questions about:
• Symptoms
• Current medical conditions
• Current medications
• Family history of medical conditions
• Serology- detect the presence of antibodies
against a microorganism
• certain microorganisms stimulate the body
to produce antibodies during an active
infection
9

Mumps
(Infectious parotitis)

Mumps
Acute viral diseases..
Myxovirus parotidis –RNA virus.
The name comes from the British word
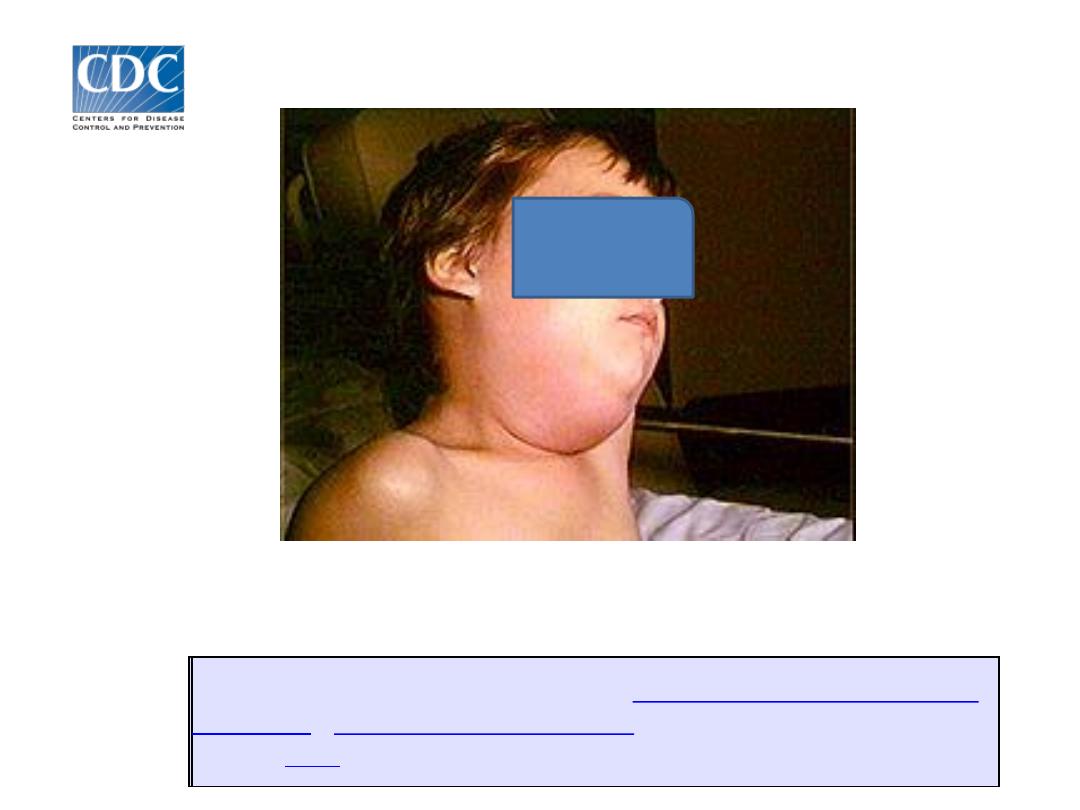
"to mump", that is grimace or grin.
The appearance of the patient as a result
of parotid gland swelling seems to be in
grin.
Courtesey: This media comes from the
Centers for Disease Control and
(PHIL), with identification
Content Providers: CDC/NIP/Barbara Rice

• Immunity - life long
• Environmental factor – winter and
spring are peak seasons.
• Reservoir : Humans.
• Mode of transmission – airborne
transmission, droplet spread , direct
contact with salivary of infected
person.

• I.P - 16-18 days.
• Period of communicability: Virus has
been isolated from saliva (7 days before
to 9 days after the onset of parotitis ) and
from urine (6 days before to 15 days after
the
onset
parotitis).
Maximum
infectiousness occurs between 2 days
before, 4 days after onset of illness.

Clinical features
• Fever
• Swelling & tenderness of one
or more salivary glads, usually
parotid.
• Orchitis
most
commonly
unilateral (postpubertal males)
Courtesy : Adapted from Mims et al.
Medical Microbiology, 1993, Mosby

Complications
• Orchitis
• Oophoiritis
• Spontaneous abortion.
• Sensory neural hearing loss, (uni- or bilateral).
• Mild form of meningitis.
• Encephalitis.
• Pancreatitis usually mild , 4% of cases
• Symptomatic aseptic meningitis up to 10 % of
cases

• Acute mumps infection can be confirmed
by :
- A positive serological test for specific-
mumps IgM.
- A significant ( at least 4 folds ) rise in
serum mumps IgG.
- Isolation of mumps virus.

Rubella (German measles)

• Agent – RNA virus (Togo virus family), Genus
Rubivirus.
• Source of infection – Respiratory secretion
• Reservoir : Human
• Immunity –life long
• Environmental factors –winter and spring
season
• Transmission – droplet, direct contact with
patient, vertical transmission
• I.P 14-17 days.
• Period of communicability 1 week before and
at least 4 days after onset of rashes.

Clinical feature:
• Low-grade fever
• Conjunctivitis
• Mild coryza.
• Tender lymphadenopathy (particularly
posterior auricular and ooccipital , posterior
cervical lymph nodes).
• Leukopenia is common .
• Body rashes, Maculo-papular rashes

Complications
• Encephalitis
• Intrauterine death
• Spontaneous abortion
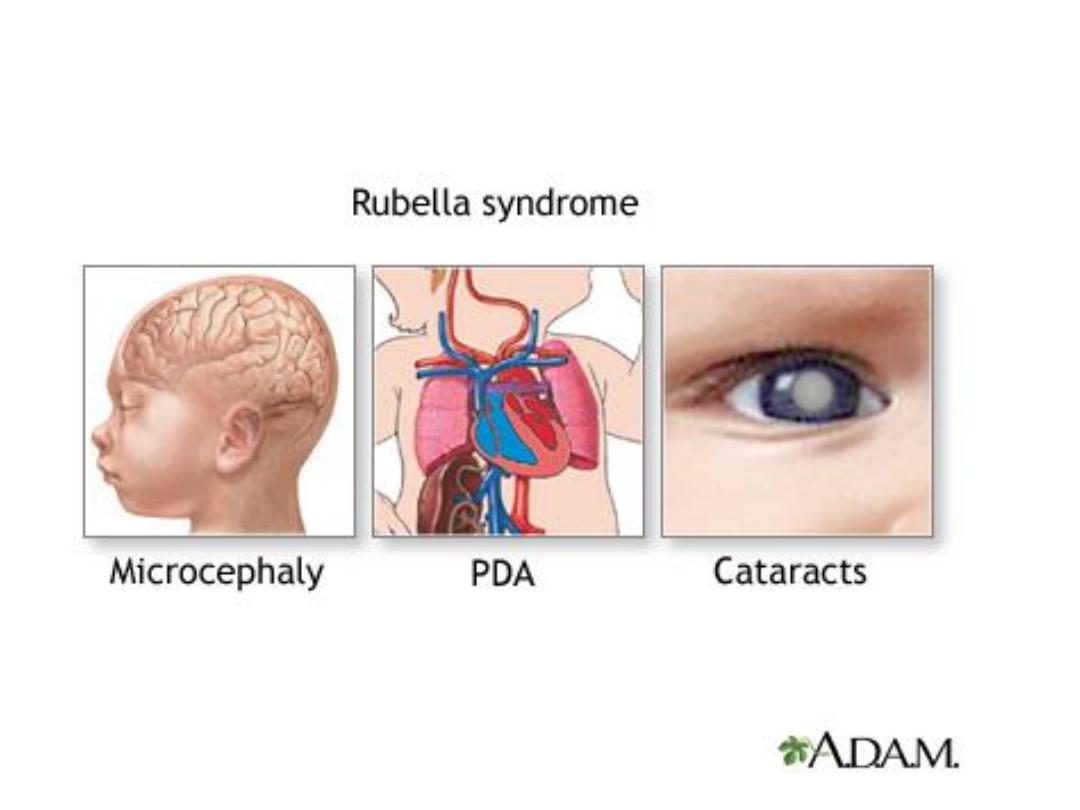
• Congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) up to 90%
of infants born to infected mothers. Include :
- Deafness , cataract , congenital glaucoma,
microcephaly,
meningoencephalitis,
mental
retardation, patent ductus arteriosis, arterial
septal defect, hepatosplenomegaly.
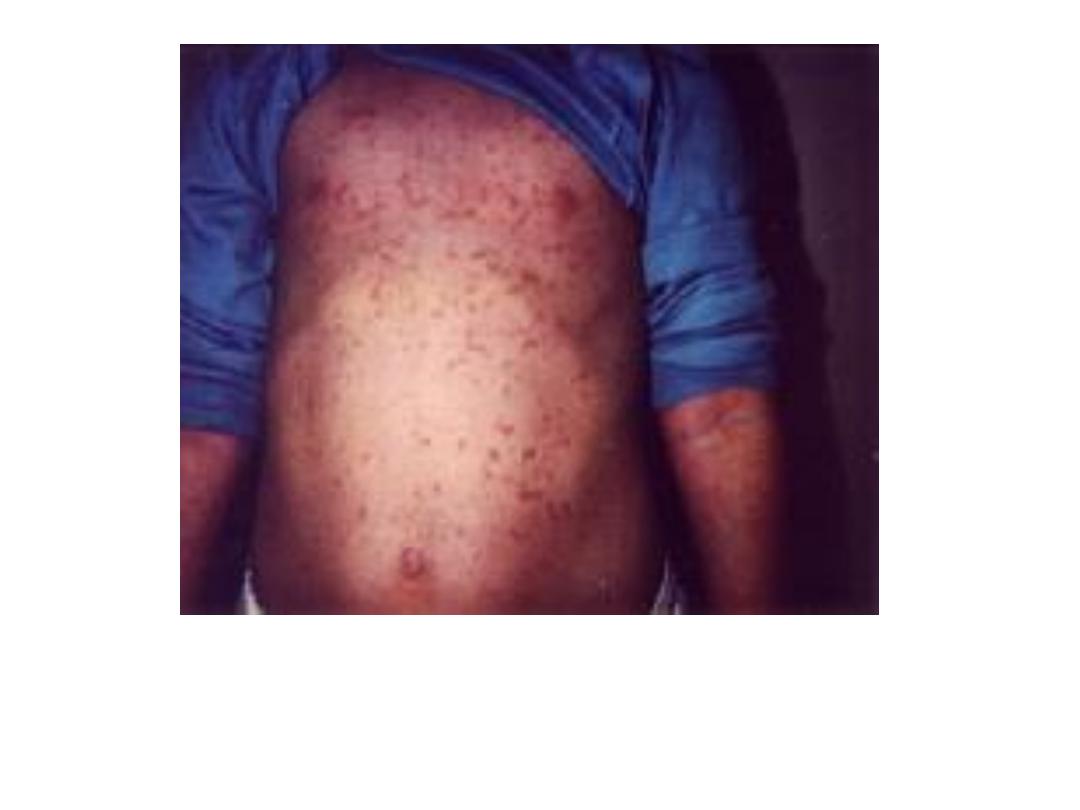
Image in a 4-year-old girl with a 4-day history of low-grade fever,
symptoms of an upper respiratory tract infection, and rash.
Courtesy of Pamela L. Dyne, MD.
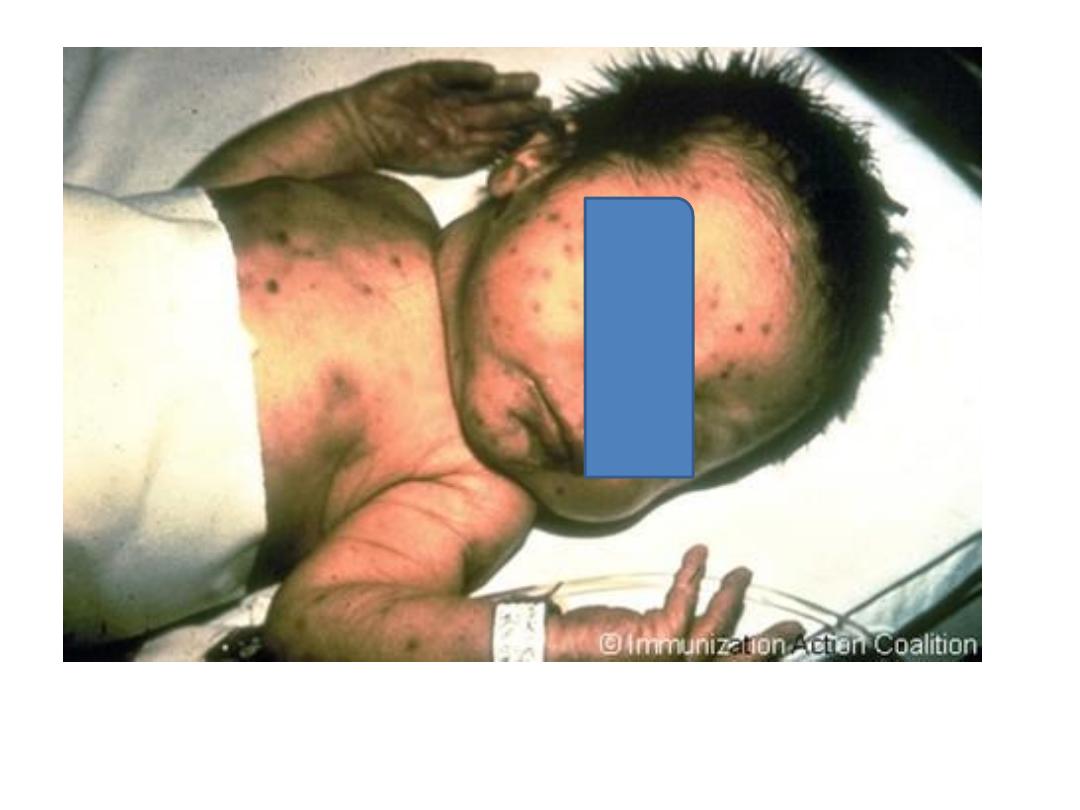
Photo source: U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
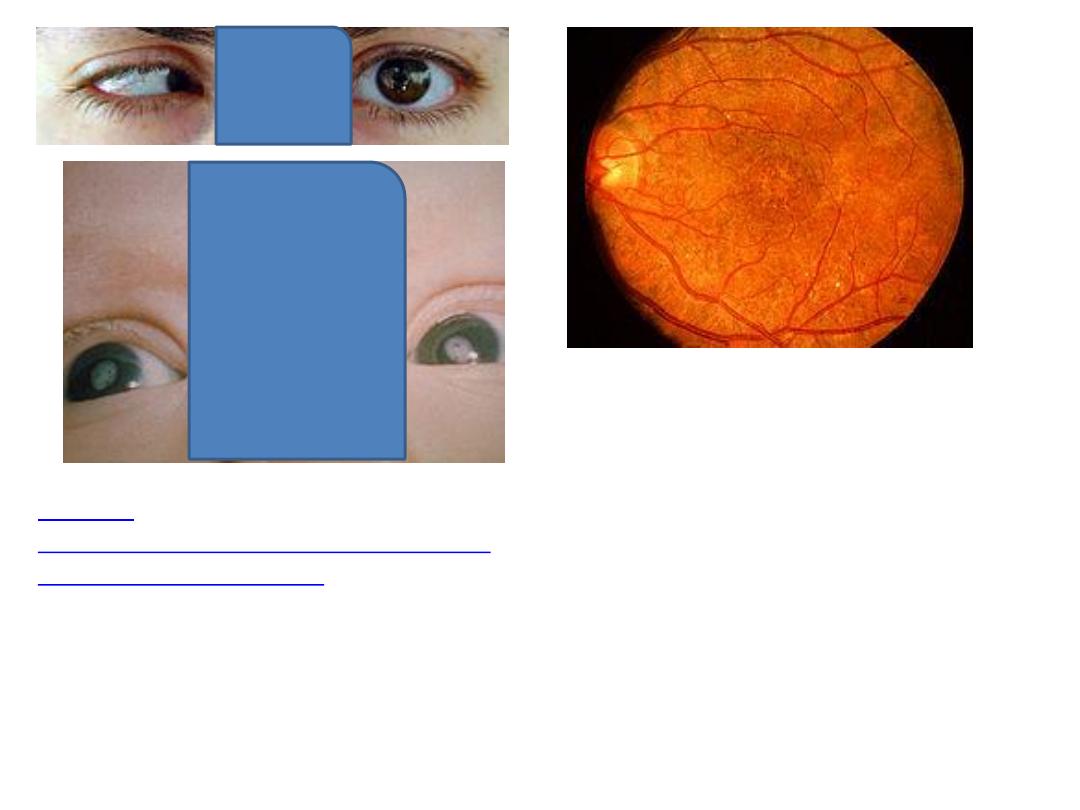
Salt and pepper retinopathy
Content Providers(s): CDC Creation
Date: 1976
Courtesy
http://phil.cdc.gov/phil_images/2003072
4/28/PHIL_4284_lores.jpg
http://www.kellogg.umich.edu/theeyeshave
it/congenital/retinopathy.html
Courtesy: Jonathan Trobe, M.D. - University
of Michigan Kellogg Eye Center

Prevention
• Public education by health departments and
physicians for encouraging immunization.
• MMR vaccine:
Live attenuated virus vaccine
helps prevent measles, mumps, and rubella.
Children 1 year of age and older get dose given
between ages 15 and 18 months and again
between ages 4 and 6 years
• Taking serum immune globulin 6 days after being
exposed to the measles virus can reduce the risk
in contacts, or can make the disease less severe
U.S. Dept. of Health & Human Services,
27

• Vitamin A supplements: reduce the
risk of death and complications in
children in less developed countries
• People who lack vitamin A are more
likely to get infections, including
measles.
Prevention
28

Control of patients and contacts
- Report to local health authority..
- Respiratory Isolation for known
cases..
- Concurrent disinfection …
- Investigation of contacts and source
of infection…

Isolation Precautions
• Respiratory isolation- airborne precautions- are
used for those patients who have or are
suspected of having infections transmitted by the
airborne route
• This means that the bacteria or virus causing
their disease is so small that it can be suspended
in the air for periods of time
• Examples of diseases: tuberculosis (TB),
varicella (chickenpox), zoster (shingles), and
measles
• Children with measles should kept out of
school
30
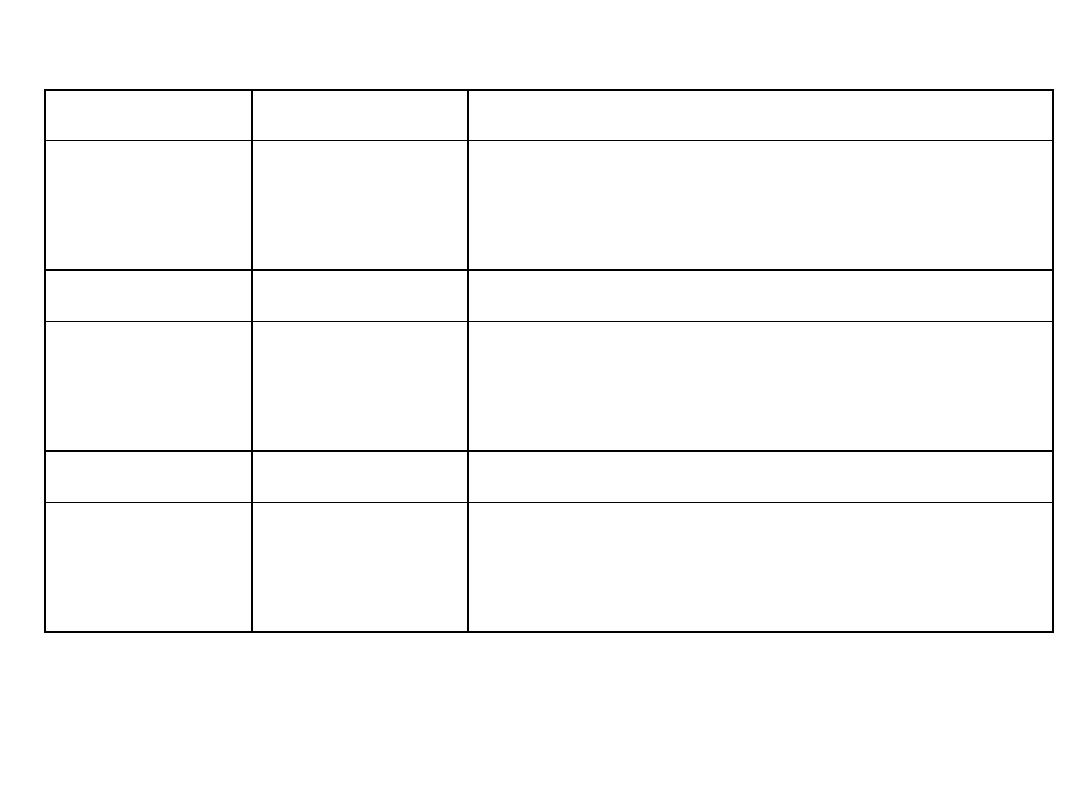
Age
Vaccines Note
9 months Measles
Deep subcutaneous injection
into the upper arm.
12-15
months
MMR -1
Deep subcutaneous injection
into the upper arm.
5 years
MMR -2
Deep subcutaneous injection
into the upper arm.

Contraindication for live virus
vaccine
- Patient with primary immune deficiency: e.g.
lymphoma, leukemia..
- Patient with sever acute illness: e.g. upper
respiratory disease.
- Patient with anaphylactic hypersensitivity.
- Vaccine should be given at least 14 days
before IG or blood transfusion.

Chicken pox
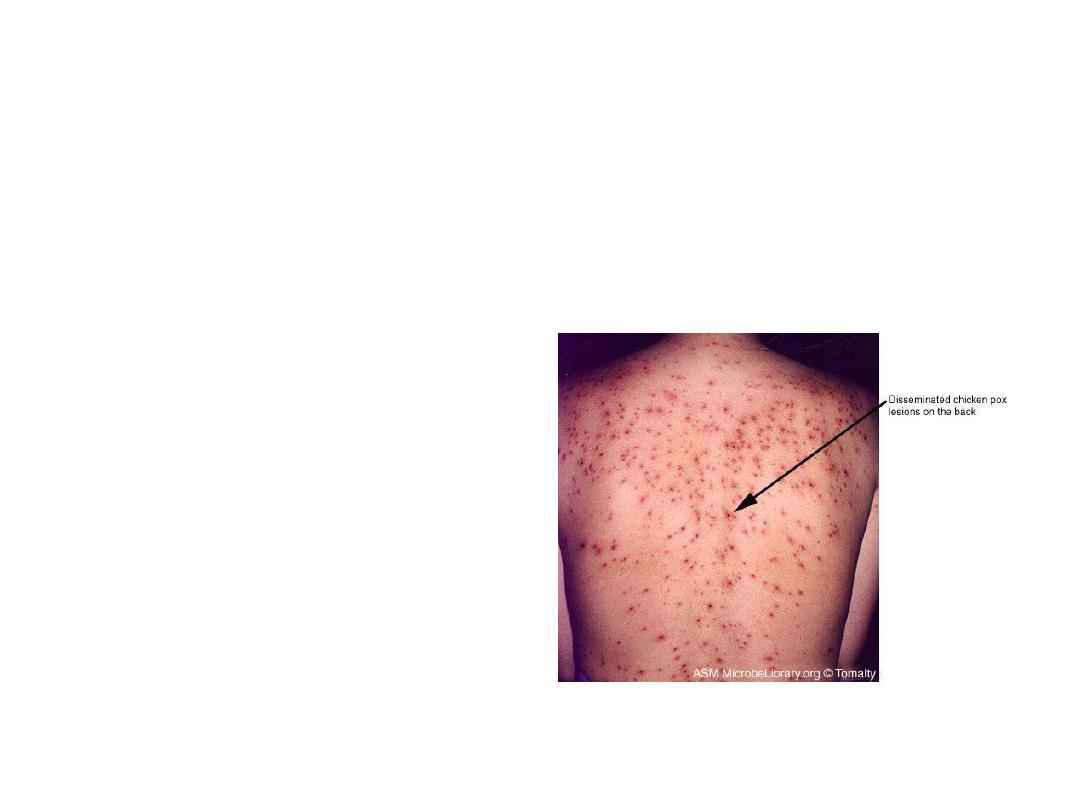
• Chicken pox is acute , generalized disease
caused by a virus called varicella zoster.

Varicella Zoster Virus
• Herpes virus (DNA)
• Primary infection results in varicella
(chickenpox)
• Recurrent infection results in herpes
zoster (shingles)
• Short survival in environment

Varicella Pathogenesis
• Respiratory transmission of virus
• Replication in nasopharynx and regional
lymph nodes
• Repeated episodes of viremia
• Multiple tissues, including sensory
ganglia, infected during viremia

Varicella Clinical Features
• Incubation period 14-16 days (range 2-3
weeks)
• Mild prodrome for 1-2 days
• Generally appear first on head; most
concentrated on trunk
• Successive crops (2-4 days) of pruritic vesicles

Varicella Epidemiology
• Reservoir Human
• Transmission Air droplet , Direct
contact with lesion.
• Communicability 1-2 days before,
to 4-5 days after onset of rash..

Varicella Vaccine
• Composition
Live virus (Oka-Merck strain)
• Efficacy
95% (Range, 65%-100%)
• Duration of
>7 years
Immunity
• Schedule
1 Dose (<13 years of age)
May be administered simultaneously with measles-
mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine
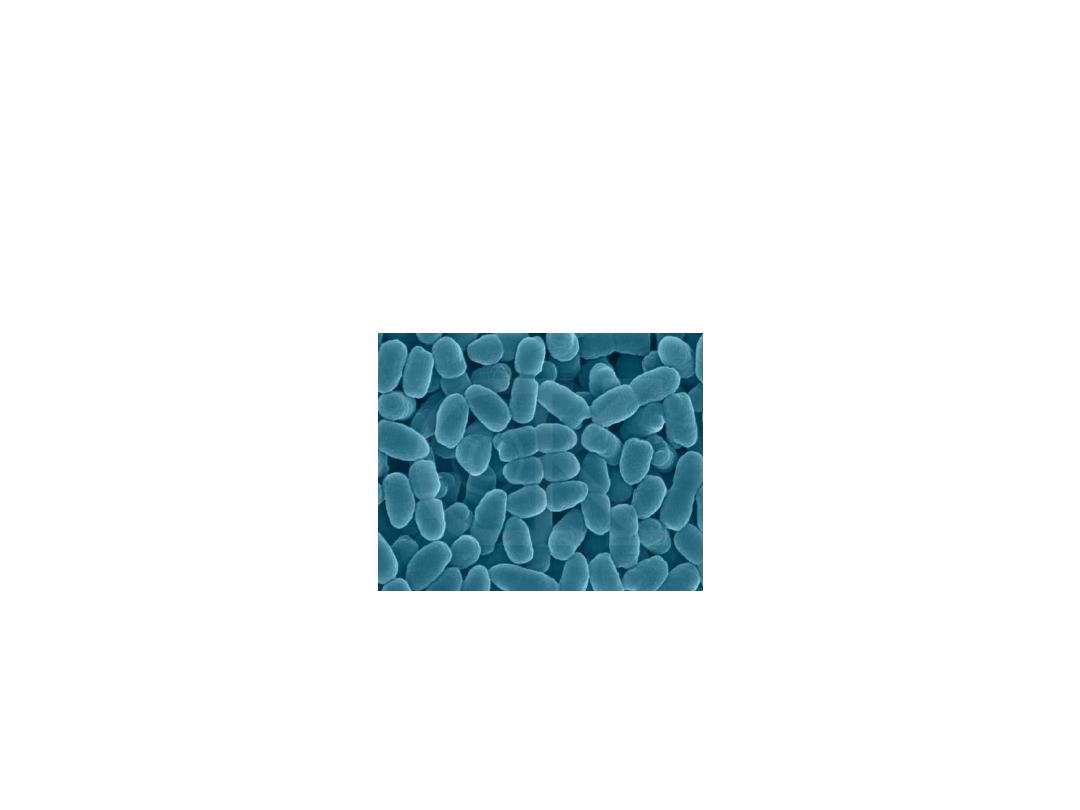
Whooping cough
(Bordetella pertussis)
http://www.hhmi.princeton.edu/sw/2002/psidelsk/Microlinks.htm

Whooping Cough (Pertussis)
• Acute bacterial infection of respiratory
tract…
• Bordetella pertussis, aerobic, gram
negative coccobacillus ….
• Specific to Humans…
• Colonizes the respiratory tract
http://microvet.arizona.edu/Courses/MIC420/lecture_notes/bordetella_pertussis/
gram_pertussis.html

Clinical Features
• Incubation period 9-10 days (range 6-20days)
• 3 Stages
– 1
st
Stage- Catarrhal Stage insidious onset
with an irritating cough…
– 2
nd
Stage- Paroxysmal Stage repeated
violent cough…
– 3
rd
Stage- Covalescent Stage weeks-months
http://www.cdc.gov/nip/publications/pertussis/chapter1.pdf

Transmission
• Very Contagious
• Transmission occurs via respiratory
droplets
• Reservoir Human
• Period of communicability
Highly during catarrhal stage
& at beginning of paroxysmal stage(1-2
weeks)
http://www.ratbags.com/rsoles/history/2000/12december.htm
http://www.universityscience.ie/imgs/scientists/whoopingcough.gif
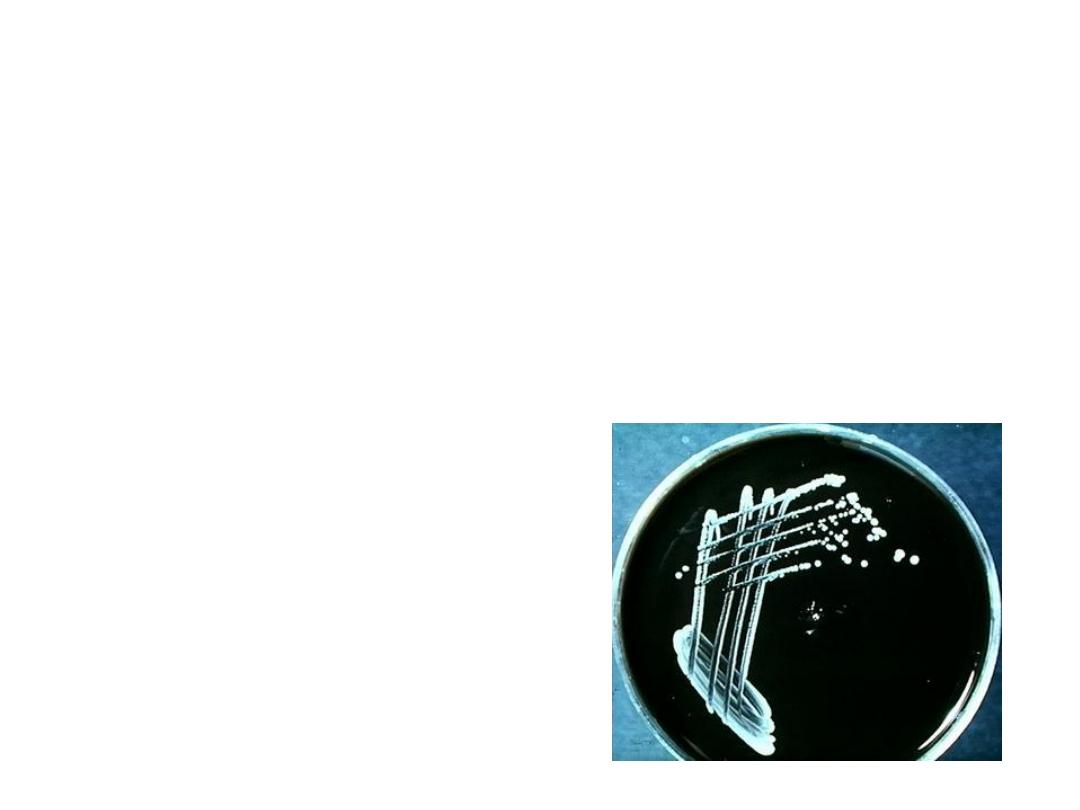

Diagnosis
• Isolation by culture
• PCR
• Serological testing
http://medinfo.ufl.edu/year2/mmid/bms5300/images/d7053.jpg

Pertussis Vaccine
• 1st Pertussis vaccine- whole cell
• A cellular vaccine now used (contain 1-5
different component of bacteria…
http://www.nfid.org/publications/clinicalupdates/pediatric/pertussis.html
http://www.tdh.state.tx.us/immunize/providers.htm

Control of patients and contacts
- Report to local health authority..
- Respiratory Isolation for known
cases..
- Concurrent disinfection …
- Investigation of contacts and source
of infection…

THANK YOU