
Dr. Nadia Aziz Nasir
C.A.B.C.M
Department of Community Medicine
Baghdad Medical college

Objectives
Define Radiation & Ionizing Radiation
Describe types & sources of Ionizing Radiation
Understand measurement of Ionizing Radiation
Describe biological & clinical effects
Describe preventive measures

Radiation
Definition
: Energy emitted from a source e.g.
heat or light from the sun
microwaves from an oven
X rays from an X-ray tube
gamma rays from radioactive elements

Ionizing Radiation
Radiation with
enough energy
so that during
an interaction with an atom, it can remove
tightly bound electrons from the orbit of an
atom, causing the atom to become charged or
ionized.
Occurs in two forms -
waves
or
particles
.

Ionizing Radiation
Forms of electromagnetic radiation differ only in
frequency
and
wave length
.
Heat waves
Radio waves
Infrared light
Visible light
Ultraviolet light
X rays
Gamma rays

Ionizing Radiation
Longer wave length, lower frequency waves (heat
and radio) have less energy than shorter wave
length, higher frequency waves (X and gamma rays).
Not all electromagnetic (EM) radiation is ionizing.
Only the
high frequency
portion of the
electromagnetic spectrum which includes X rays

Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing Radiation occurs in two forms :
waves
particles
.

Ionizing Radiation
Waves
Most of the types of electromagnetic radiation (e.g.
visible light, radio waves) exhibit “wave-like” behavior
in their interaction with matter.
Photons are
chargeless
bundles of energy that travel in
a vacuum at the velocity of light, which is 300 000
km/sec.

Ionizing Radiation
Particulate
Particulate radiation, consisting of
atomic
or
subatomic
particles
(electrons, protons, etc.) which carry energy in
the form of
kinetic energy
.
Alpha
particles and
beta
particles are considered
directly ionizing
because they
carry a charge
and can,
therefore, interact directly with atomic electrons

Ionizing Radiation
2-
Electromagnetic
type of ionizing radiation includes
gamma
and
X rays
. These are indirectly ionizing because
they are
electrically neutral
(as are all electromagnetic
radiations) and do not interact with atomic electrons
Ionizing Radiation
Atoms
, in their normal state, are
electrically neutral
because the negative charge of electrons outside the
nucleus equals the positive charge of the nucleus.

Isotopes
Are atoms with the
same number of protons
and
different number of neutrons
. An isotope may be
one or more forms of the same element having the
same
atomic
number,
differing mass
numbers.
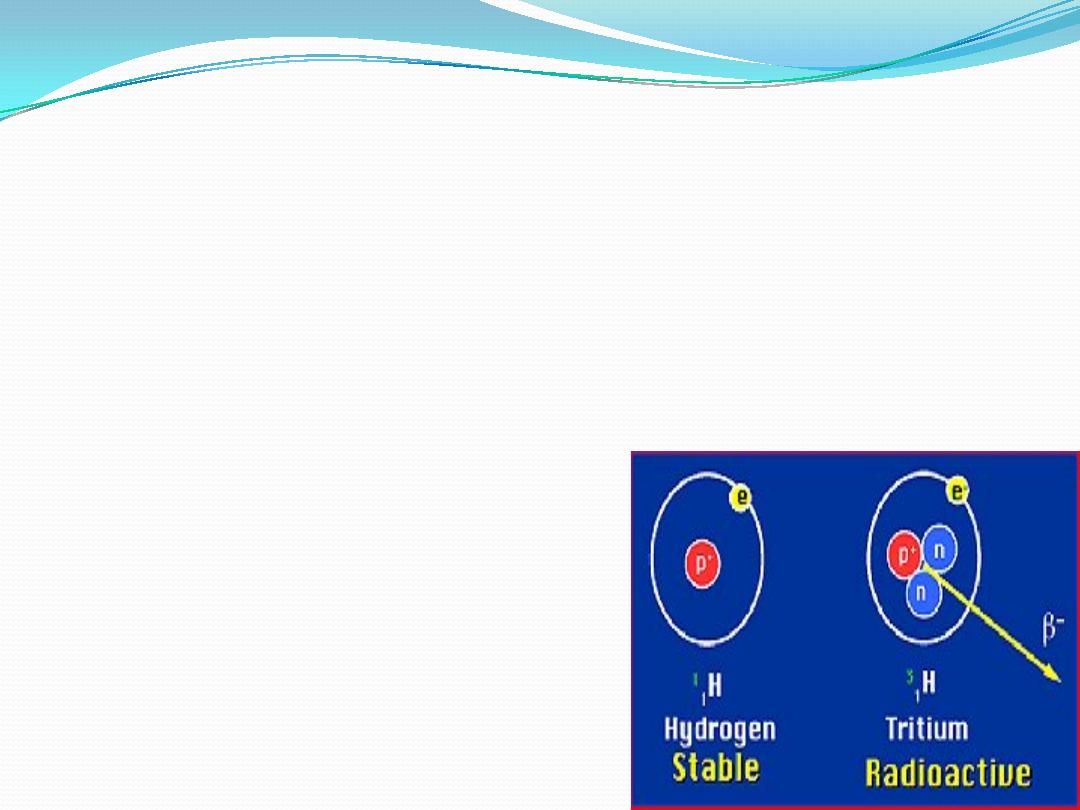
Isotopes
The different forms of an element may be
stable
or
unstable
(radioactive).
Since they are forms of the same element, they possess
identical
chemical
and
biological
properties.

Isotopes
Activity of a radioisotope
Is measured by how many atoms
undergo radioactive
decay
per a unit of time.
Only the amount of energy of ionizing radiation that
absorbed
by the human body can cause
harm to health
.

Measures of Ionizing Radiation
The
international (SI) unit
of measure for absorbed dose
is the
gray
(Gy)
The
gray
is defined as
1 joule of energy deposited in 1
kilogram of mass.
The old unit of measure for this is the
rad
, which stands
for "
radiation absorbed dose
."
1 Gy = 100 rad.

Measures of Ionizing Radiation
Equivalent dose :
the biological effect depends on:
The amount of the
absorbed
dose
The
intensity
of ionization in living cells caused by
different type of radiations.
The unit of equivalent dose is the
sievert
(Sv).
The old unit of measure is the
rem
. 1 Sv = 100 rem.

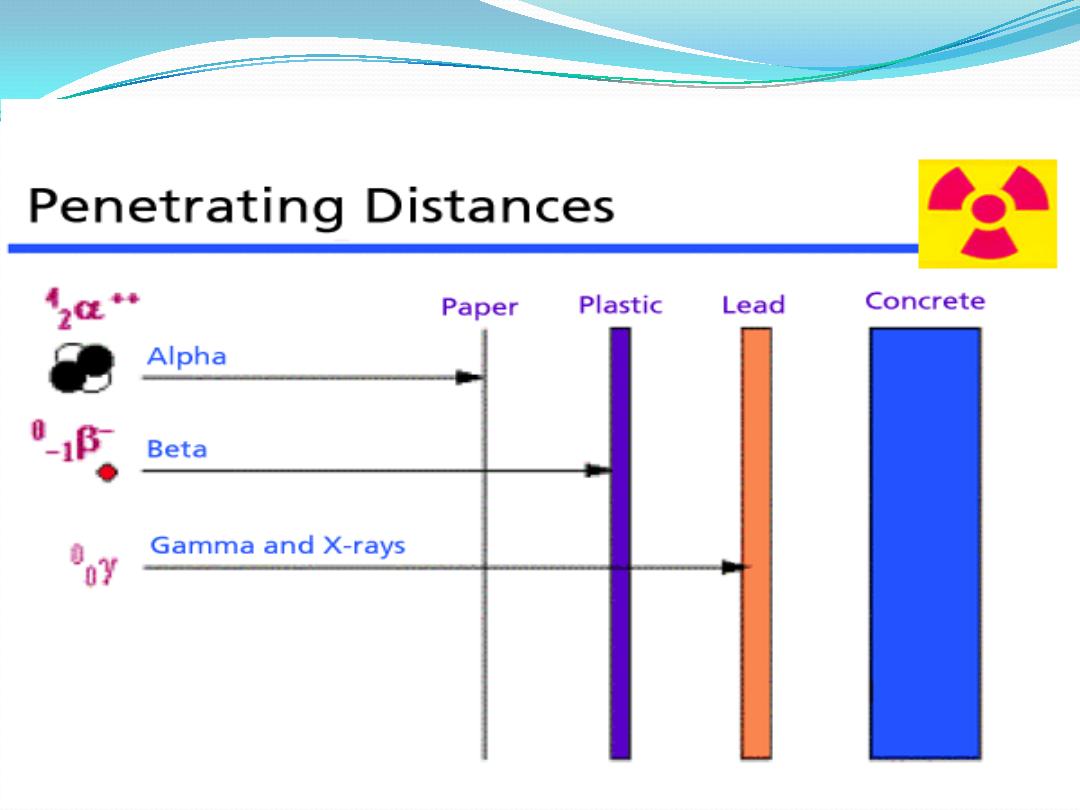
Alpha particles
Are identical to a
helium
nucleus.
They are a
highly ionizing
form of particle radiation
have
low penetration
depth.
They can be
stopped
by a few centimeters of air, or by
the skin.

Beta particles
Are
high-energy
& high-speed
electrons
Emitted by certain types of radioactive nuclei, such
as
potassium-40.
The production of beta particles is termed beta
decay.

Gamma radiation
It’s a type of
electromagnetic
radiation of extremely
high
frequency.
Shielding
from gamma rays requires
large amounts of mass
,
in contrast to alpha particles which can be blocked by paper
or skin, and beta particles which can be shielded by foil.
Lead shield is better
as a gamma shield, than an equal mass
of another shielding material such as aluminum, concrete,
water or soil.

X-rays
Due to their
penetrating
ability, X-rays are widely
used to image the inside of objects, e.g. in
medical
radiography
and
airport security

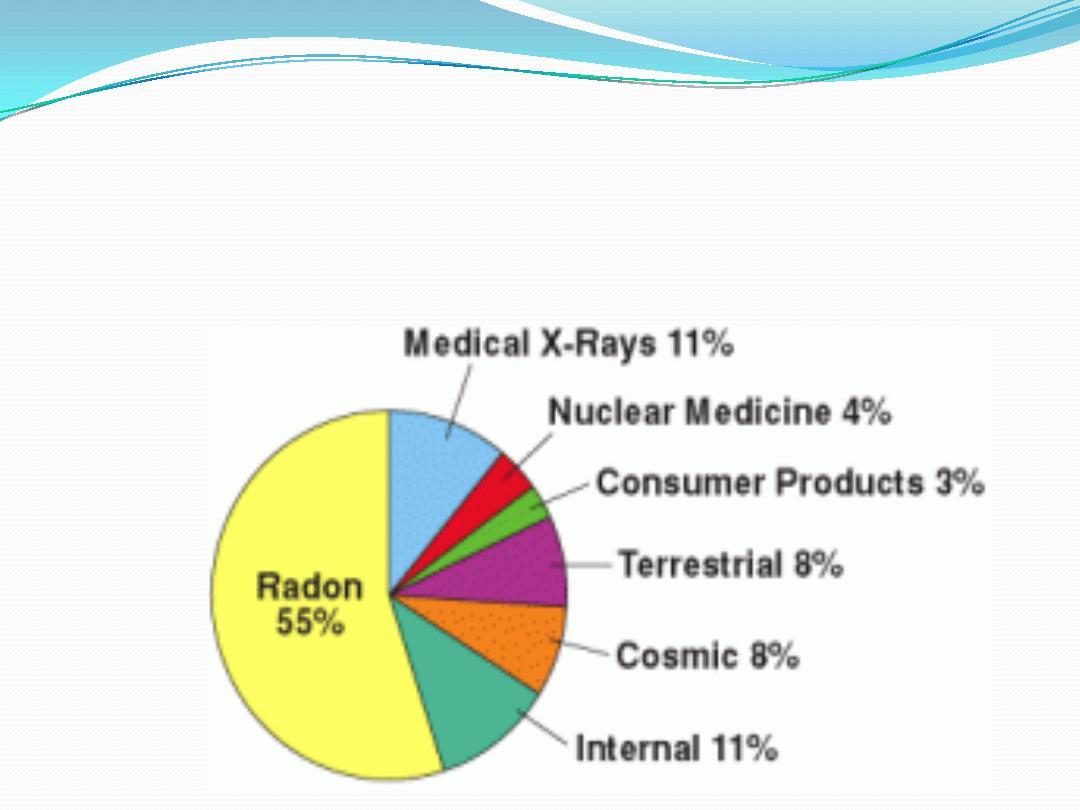
Sources of Radiation
Large proportion of the average annual radiation dose
received by people results from
natural environmental
sources (air, water, food & soil).
Each member of the world population is exposed, on
average, to
2.4 mSv/yr
of ionizing radiation from
natural sources.
In some areas, the natural radiation dose may be 5 to
10-times higher to large number of people

Sources of Radiation
a-
cosmic rays
, which originate in outer space are
higher in mountains & much higher at aircraft altitudes.
b-
Terrestrial radiation
, which emanate from thorium,
uranium, radium & other radioactive constituents of
the earth crust

Sources of Radiation
c-
internal radiation
, which is emitted by the
potassium-40, carbon-14, radium and other
radionuclides normally present in living cells
d-
radon
& its daughter elements, which are inhaled
in indoor air.

Sources of Radiation
On average,
80%
of the annual dose that a person
receives is due to
naturally
occurring terrestrial and
cosmic radiation.
Human exposure to radiation also comes from
human-
made
sources ranging from nuclear power generation to
medical uses of radiation diagnosis or treatment.
The most common human-made sources of ionizing
radiation are
X-ray
machines and other medical devices.
Sources of Radiation

Radiation exposure
may be
1- Instantaneous (atomic bomb)
2-chronic (uranium miners)
3-fractionated (radiotherapy)
4-partial-body

Radiation exposure
The whole-body exposure is
more harmful
than
partial-body exposure for a given dose.
Radioisotopes decay with time into stable elements
and have physical half- lives of various lengths, from
fractions of a second to millions of years.

Biological & clinical
effects
Atoms or molecules that become ionized attain stability
again by forming substances that may
alter molecular
processes
within a cell or its environment.
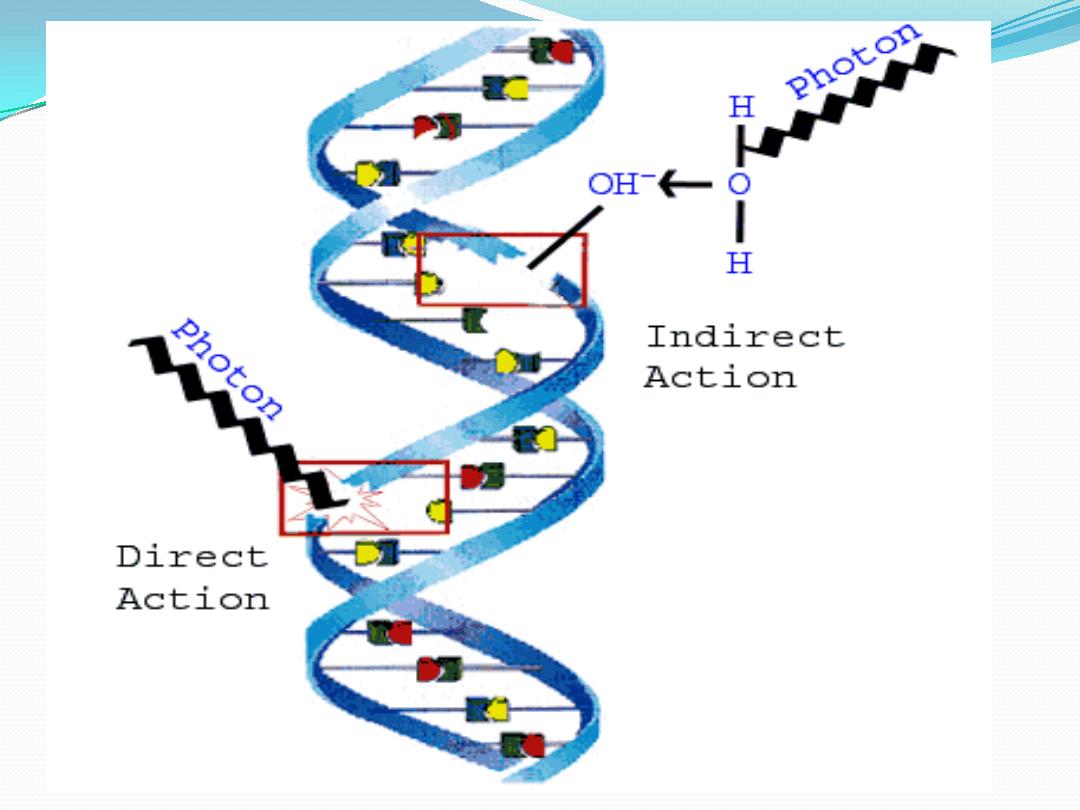
Ionizing radiation, in colliding with a cell, can cause
changes in its constituents, including
deoxyribonucleic
acid(DNA).
Such damage, if unrepaired, may
disable
or
kill
the cell.

Biological & clinical
effects
The most sensitive:
Blood forming organs
Reproductive organs
Skin
Bone and teeth
Muscle
Least sensitive: nervous system

Biological & clinical
effects
Developing
embryo
is most sensitive to radiation
during the
early stages of differentiation
, and an
embryo/fetus is more sensitive to radiation
exposure in the
first trimester
than in later
trimesters.

Acute Effects
All ionizing radiation causes
similar damage
at a
cellular level
Alpha and Beta particles cause only
localized damage
,
e.g. radiation burns to the skin.
Gamma rays are more penetrating, causing
diffuse
damage
throughout the body (e.g. radiation sickness,
cell's DNA damage, cell death& increasing incidence of
cancer).

Acute radiation syndrome
The onset and type of symptoms depends on the
radiation exposure.
smaller
doses result in
gastrointestinal
effects such as
nausea and vomiting and symptoms related to
falling
blood counts
such as infection and bleeding.
larger
doses can result in
neurological
effects and
rapid
death.

Delayed effects
Largely are due to
1- Mutagenesis
2- Teratogenesis
3- Carcinogenesis
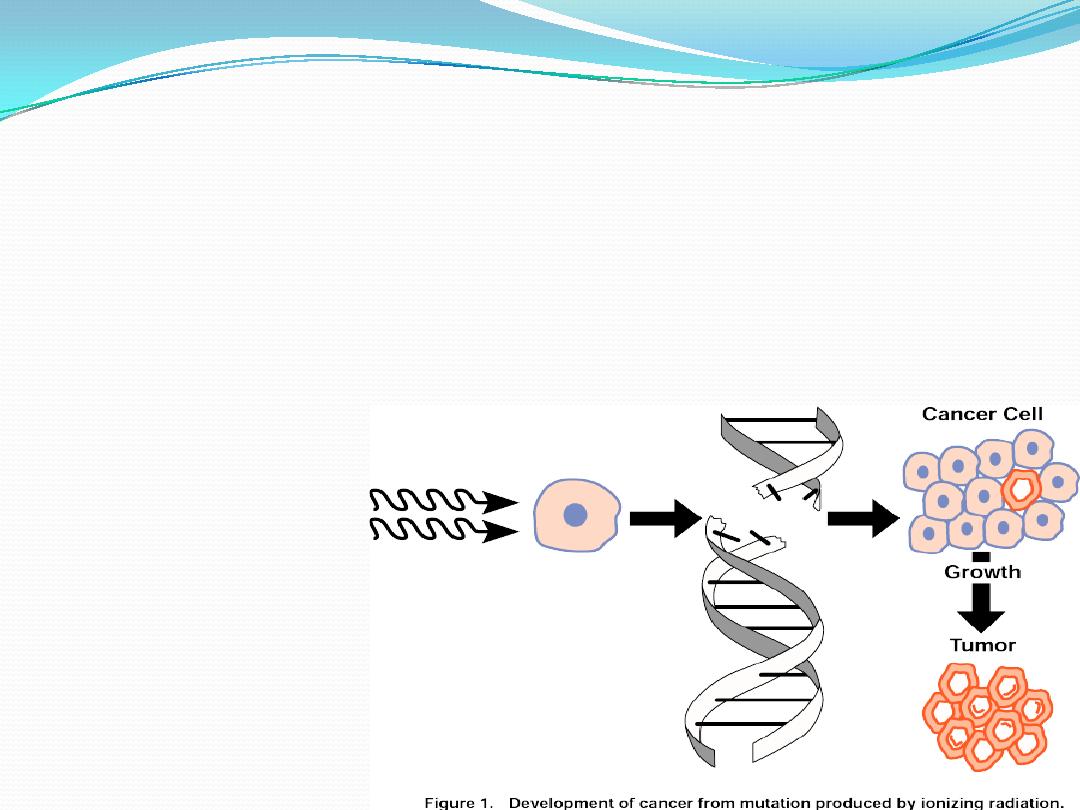
Mutagenesis
Ionizing radiation is a
germ- cell mutagen
&causes
chromosome breaks in somatic cells
.

Teratogenesis
Intrauterine exposure
to ionizing radiation may
cause
small head size
alone or with
severe mental
retardation
.
Susceptibility to severe mental retardation is
greatest at
8 to 15 weeks
of gestational age.

Carcinogenesis
The maternal exposure to
diagnostic x-rays
during
pregnancy was associated with
1.5 fold
excess of
almost every type of cancer in children younger than 10
years.
Its believed that
leukemia
is associated with
in utero
exposure to radiation and an increase in
thyroid cancer
occurred in children exposed to the atomic bomb

Radon
Accounts for
55%
of background radiation. Radon gas
comes from radioactive decay of radium, a product of
ubiquitous uranium deposits in rocks & soil.
Radon enters homes through
cracks in the foundation
&
granite walls. Thus radiation exposures in basement may
be higher than those on the first floor level.

Prevention of exposure
External Radiation
The
risk of cancer
associated with most diagnostic
radiation is
low
, and use of radiation should
not be
restricted
when needed for correct diagnosis.
Limitation of radiation
,
shielding sensitive
body parts
such as the thyroid, and ensuring a
non pregnant
state
are components of good medical practice.

Prevention of exposure
External Radiation
Computed tomography(CT) scan require radiation
exposures that
induce cancer
later in life, so more
active
reduction in CT exposure
setting was
recommended.

Prevention of exposure
RADON
Radon exposure can be reduced by
1-
Increasing
ventilation
2-
Reducing the influx
of radon in the home, by sealing
cracks in the foundation, creating negative pressure
under the basement floor, and prohibiting the use of
building materials containing excessive radium.

Prevention of exposure
Fallout(Internal Emitters)
Radioiodines
are expected to be released after a
malfunction
or
terrorist
event occurring at a nuclear
power plant or after the detonation of a nuclear
weapon.
Potassium iodide
(KI) should be administered promptly
to protect the thyroid from radioiodines.

Good Luck
