Physiological
changes in
pregnancy
Dr. ISHRAQ MOHAMMED

Early pregnancy
·
In e arly pregnancy , the de veloping fe tus, corpus lute um
and place nta produce and re le ase increasing quantitie s of
hormone s, growth factors and othe r substances in to
maternal circulation which trigge rs a cascade of eve nts.
· C hange s in all body syste ms to pre pare the mothe r to
support fe tal growth
· F ollowing implantation, the mate rnal adaptation to
pre gnancy can be cate gorize d base d on following functions:
1
1. Incre ased availability of pre cursors for hormone production
and fe tal-placental me tabolism.
2.I mprove d transport capacity.
3.M aternal-fe tal e xchange .
4. Re moval of additional waste products.
·
Incre ased availability of me tabolic substrate s is achie ved by
incre ase s in die tary intake.
· T ransport capacity is enhanced by incre ase s in cardiac
output.
· T he place nta re gulate mate rnal-fe tal e xchange by 10-12
we eks ge station.
·
Disposal of waste product occurs through pe riphe ral
vasodilatation and by incre ases in ventilation and re nal
filtration.
Volume homeostasis
·
Maternal blood volume e xpand during pre gnancy to allow
ade quate perfusion of vital organs including the place nta
and fe tus, and to anticipate blood loss associate d with
de live ry.
2
· T he rapid e xpansion of blood volume be gins at 6-8 we e ks
ge station and plate aus at 32-34 we e ks gestation.
·
The most marke d e xpansion occurs in extracellular fluid
volume e spe cially circulating plasma volume , this
accounts for be twee n 8 and 10 kg of ave rage mate rnal
we ight gain during pre gnancy.
·
The factors contributing to fluid re tention are :
1.S odium re te ntion.
2.R e se tting of osmostat.
3.D e crease thirst thre shold.
4.D e crease plasma oncotic pressure.
· C onse que nce s of fluid re tention:
1.D e crease in hae moglobin conce ntration.
2.D e crease in hae matocrit.
3.D e crease in se rum albumin concentration.
4.I ncre asing in stroke volume .
5. Incre asing in re nal blood flow.
3
Blood
·
Haematology
· M aternal Hb le ve ls are de cre ases because of discre pancy
be twe e n incre ases in plasma volume &the incre ases in
e rythrcyte mass.
· T he me an Hb conce ntration falls from 13gm/ dl in non-
pre gnant state to10,9gm/ dl at 36 we eks of normal
pre gnancy.
· T he hae matocrit is also re duced 32-34pe r cent.
· P re gnancy without iron supple me ntation le ad to de pletion of
iron stores.
· R e nal cle arance of folic acid incre ase leads to fall in plasma
folate conc. Howe ve r re d ce ll folate conc. Do not fall to the
same e xte nt. Folate supple me ntation in wome n e ating
ade quate diet & carrying a single fetus is not routinely
indicate d.
· P late le t count may be lower than the non-pre gnant state
due to increase d aggre gation.
·
Erythrocyte sedime ntation rate is inre ase d in pre gnancy
4
Haemostasis &coagulation
·
Pre gnancy is a hype rgoagulable state & re turn to normal
around 4 wee ks afte r de live ry.
· A lmost all procoagulant factor including factor 7,8,9,10&11&
fibrinogen are incre ased during pregnancy
· F ibrinoge n is incre ase d by 50 pe r ce nt 300mg/ dl to
450mg/ dl in pre gnancy
· L e ve l of von Willebrand factor incre ase in pre gnancy
· T he incre ase in procoagulant, pote ntial for vascular damage
& incre ase ve nous stasis particularly in the lower
e xtre mitie s, e xplain why the incide nce of ve nous
thromboe mbolic complications is five time s gre ate r during
pre gnancy but this is to prote ct wome n from ble e ding afte r
de live ry
· A ctivate d prote in c re sistance is increase d in pregnancy
·
D-dime rs incre ase d in pre gnancy
5
Biochemistry
·
Plasma prote in conce ntration particularly albumin, are
de cre ased during normal pre gnancy , which not only affects
the plasma oncotic pre ssure , but also affe cts the pe ak
plasma conce ntration of drugs that are highly protein bound.
· S erum cre atinine, uric acid & ure a conce ntration are
re duce d during normal pre gnancy.
·
Alkaline phosphatase le vels incre ases thoughout pre gnancy.
In contrast SGOT & SGPT show lower leve l in uncomplicated
pre gnancy
The immune response
·
The pre se nce of the fetus is analogous to the grafting
of tissue s or organs be twe en two individuals of the
same spe cies who are gene tically dissimilar.
· P ropose d me chanisms for the succe ss of the fe tal
allograft:
1- mate rnal/ syste mic: none ( normal ce ll me diate d
immunity).
2-fe tal:
6
· a -ute rus & local lymphatic syste m:
· - uterus has bee n considered as privile ge d
immunological site.
· - localize d, non spe cific suppression induce s tole rance &
ge ne rate suppre ssor T cells.
· b -place nal:
· - se paration of the maternal-fe tal circulations, including
tight local barrie rs.
· - lack of e xpre ssion of class 2 HLA at the mate rnal-fe tal
inte rface.
· - limite d immune re sponse of cytotoxic T lymphocyte s
to trophoblasts.
·
c-syte mic : unidentifie d hume ral &ce llular
immunosuppre ssive elements.
The maternal brain & the senses
·
De cline in memory in the third trime ste r, the unde rlying
me chanisms are le ss cle ar. Proposed cause s include lack
of oe strogen or ele vate d leve l of oxytocin, which has an
7
amnesic e ffe ct while proge ste rone has a se dative e ffe ct.
· P re gnant wome n appe ar to have gre ate r tolerance for
pain, which is bioche mically me diate d by incre ase d se rum
le ve l of B-e ndorphins
· T HE SENSES
· C hange s in pe rce ption of odours during pre gnancy
,olfactory se nsitivity & odour thre sholds are significantly
de cre ased during the third trime ster.
·
Corneal se nsitivity decre ase s inmost pre gnant wome n &
this can be re late d to an incre ase in corne al thickne ss
cause d by oe dema & a de cre ase in te ar production
occurs in around 80 per ce nt of pre gnant wome n.
Respiratory tract
·
Airway: the ne ck, oropharynge al tissues, bre ast & che st wall
are all affe cte d by we ight gain, breast e ngorge me nt & air
way e dema, can compromise the airway le ading to difficulty
with visualization of the larynx during trache al intubation.
·
Ve ntilation: this begins to increase significantly at around 8
we eks ge station in re sponse to proge sterone se nsitization
of
the respiratory centre to CO2.the diaphragm is e levate d
4cm
8
by the enlarging uterus& the lowe r che st circumfe re nce
e xpand by 5cm.
· I ncre ase minute ventilation
· I ncre ase tidal volume
· D e crease re sidual volume
· D e crease d functional re sidual capacity
·
Vital capacity unchange d or slightly incre ase d
·
Oxyge nation: during pre gnancy the re is an increase in 2,3-
diphosphoglyce rate conce ntration within mate rnal
e rythrocyte s. This le ad incre ase availability of oxyge n within
the tissues(shifts the oxyge n-hemoglobin dissociation curve
to the right).
· D e crease d Pco2
· I ncre ased pO2
· P Halters little
· I ncre ased bicarbonate excre tion
Cardiovascular system
·
Sign & symptoms of pregnancy mimics those of he art
dise ase such as bre athle ssne ss, ede ma in the e xtre mitie s,
palpitation
9
are common & usually re present sinus tachycardia, which is
normal in pre gnancy.
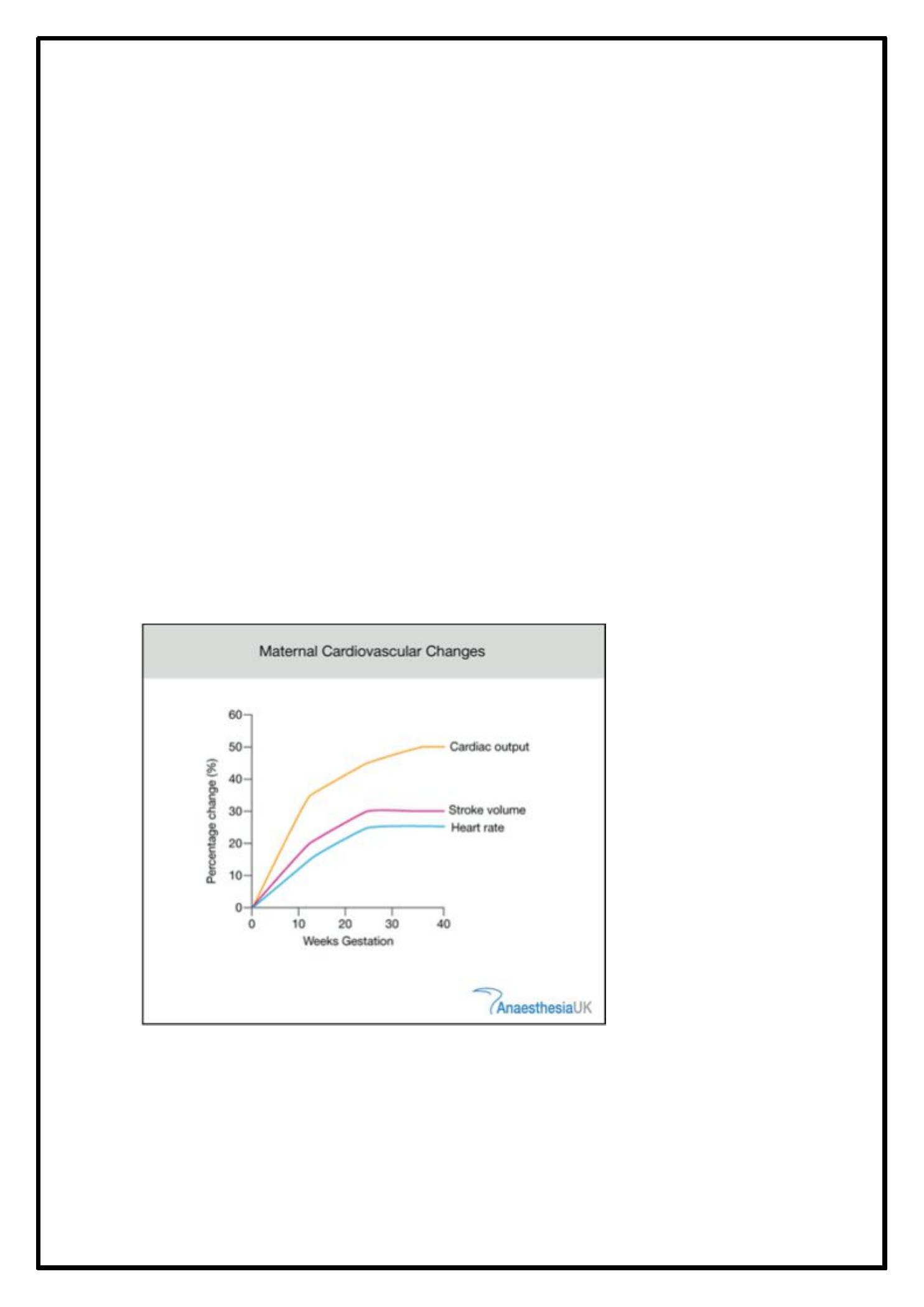
· I n normal pre gnancy, cardiac output incre ase s as e arly as5
we eks ge stations
· N on pre gnant adult fe male 4.5L/ min
· 2 0we e ks pre gnant6.3L/ min 40pe r cent rise
· E arly labour17 pe r cent rise 7.3
· A ctive labor 7.7 L/ min
· 2
nd
stage of labor 8.4
· M ost increase in cardiac output is contributed to raise of
stroke volume
·
De crease s in diastolic blood pre ssure are more marke d than
the de crease in systolic pre ssure le ad to increase in pulse
pre ssure . Late r, diastolic blood pre ssure increase s to le ve l
that are at le ast e quivale nt to those found in the non-
pre gnant state. The be st measure me nt are obtaine d when
the fifth Korotkoff sound is use d
·
A 70 pe r ce nt re duction in pe ripheral vascular resistance
has bee n de monstrated by 8 we eks ge station due to
alte ration in the production vasoconstrictor& vasodilator
age nt that pe ripheral arte rial tone .
· 1
st
heart sound is loud , wide splitting of the 2
nd
heart sound,
3
rd
he art sound is audible in 84 pe r ce nt of the pre gnant
wome n by 20 we eks ge station, an e jection systolic murmur
can be heard in 96 per ce nt of normal pregnant wome n,
diastolic murmur occur transie ntly in only 20 pe r ce nt of
pre gnant wome n &10 pe r cent de ve lop continuous murmur
due to increase d mammary blood flow.
Gastrointestinal changes
·
Oral: pre gnancy gingivitis, e de ma, hype rplasia & incre ased
ble eding of gingival tissue & dental caries &increase tooth
mobility.
10
· G ut: the ute rus displace the stomach & inte stine upwards,
incre ase incide nce of re flux oe sophagitis & he artburn,
de layed gastric e mptying.
·
Live r: physical finding such as te langie ctasia & palme r
e rythe ma, othe rwise sugge stive of live r dise ase in non-
pre gnant wome n, appe ar in up to 60e r ce nt of normal
pre gnancie s be cause of the hype roe strogenic state of
pre gnancy. Absolute he patic blood flow re main large ly
unalte red & he patic function remain normal.
The kidney & urinary tract
·
Incre ased kidne y size (1cm)
· D ilatation of re nal pe lvis & urete rs
· I ncre ase blood flow(60-75per ce nt)
· I ncre ase glome rular filtration (50pe r cent)
· I ncre ase renal plasma flow(50-80pe r cent)
· I ncre ase cle arance of most substance
· D e crease d plasma cre atinine , ure a& urate
·
Glycosuria is normal
11
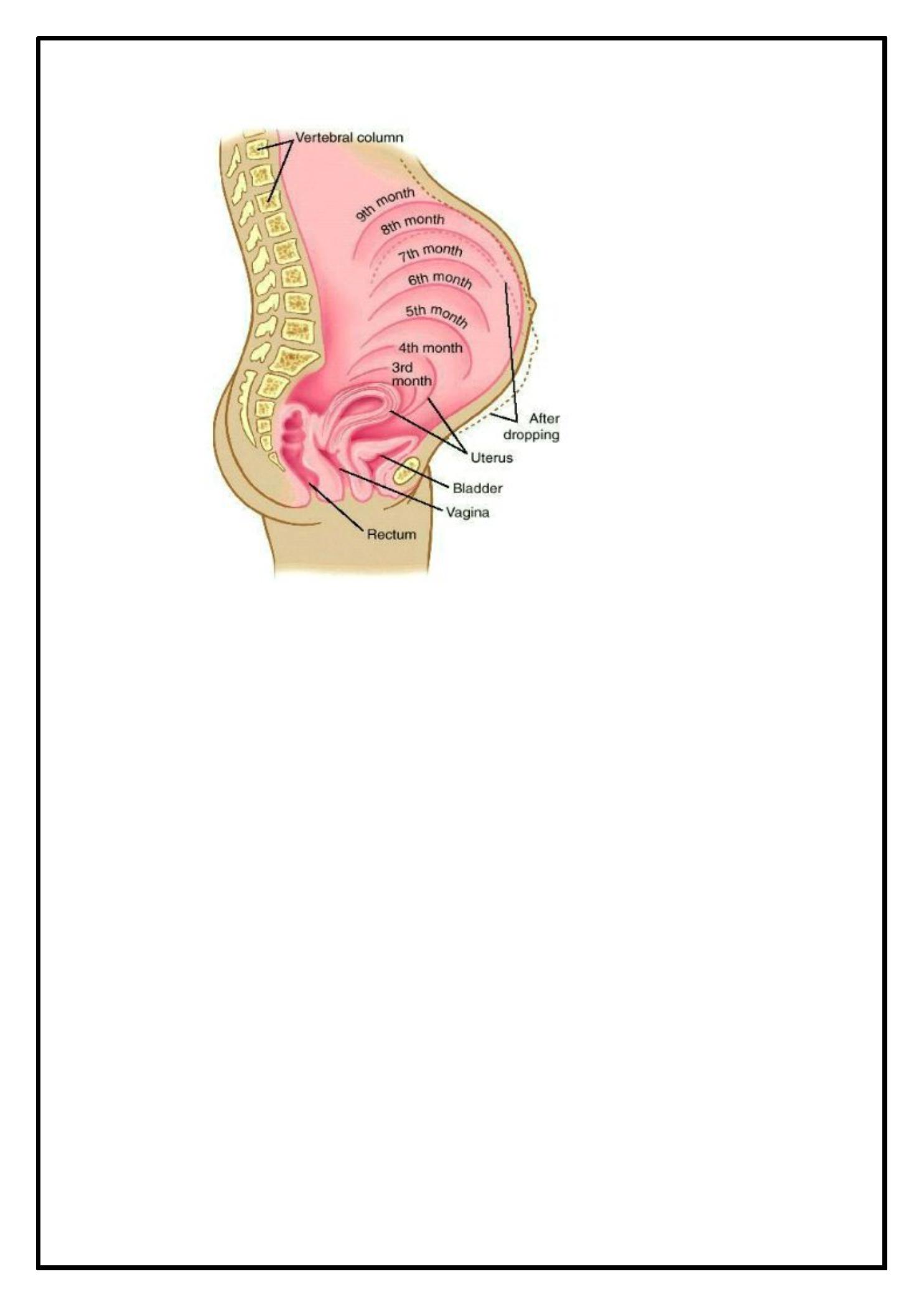
Reproductive organ
·
Ute rus:
uterine
blood
flow
increase s
40-
folds(700ml/ minute at te rm)
· H igh le vels of mate rnal oe stradiol & proge sterone induce
hype rplasia &hype rtrophy of the myome trium incre asing
the we ight of the ute rus from 50-60gm prior to pre gnancy
to 1000gm by te rm.
·
By the third trime ste r, the uterus is de scribe d in lowe r &
upper segme nts. In addition to changes in the size
&numbe r of myome trial ce lls, interce llular gab junction
facilitating the spre ad of me mbrane de polarization &
subse quent myome trial contraction. The se are appare nt
initially as Braxton Hicks, painle ss contractions that are
notice in the 2
nd
half of pre gnancy.
12
·
cervix: looks blue r during pre gnancy, swolle n &softer unde r
the influence of progeste rone & oe stradiol.
· V aginal e pithe lium be come s more vascular during
pre gnancy , & there is incre ased de squamation re sulting in
incre ase d vaginal discharge . This discharge has a more acid
pH& may prote ct against asce nding infe ction
·
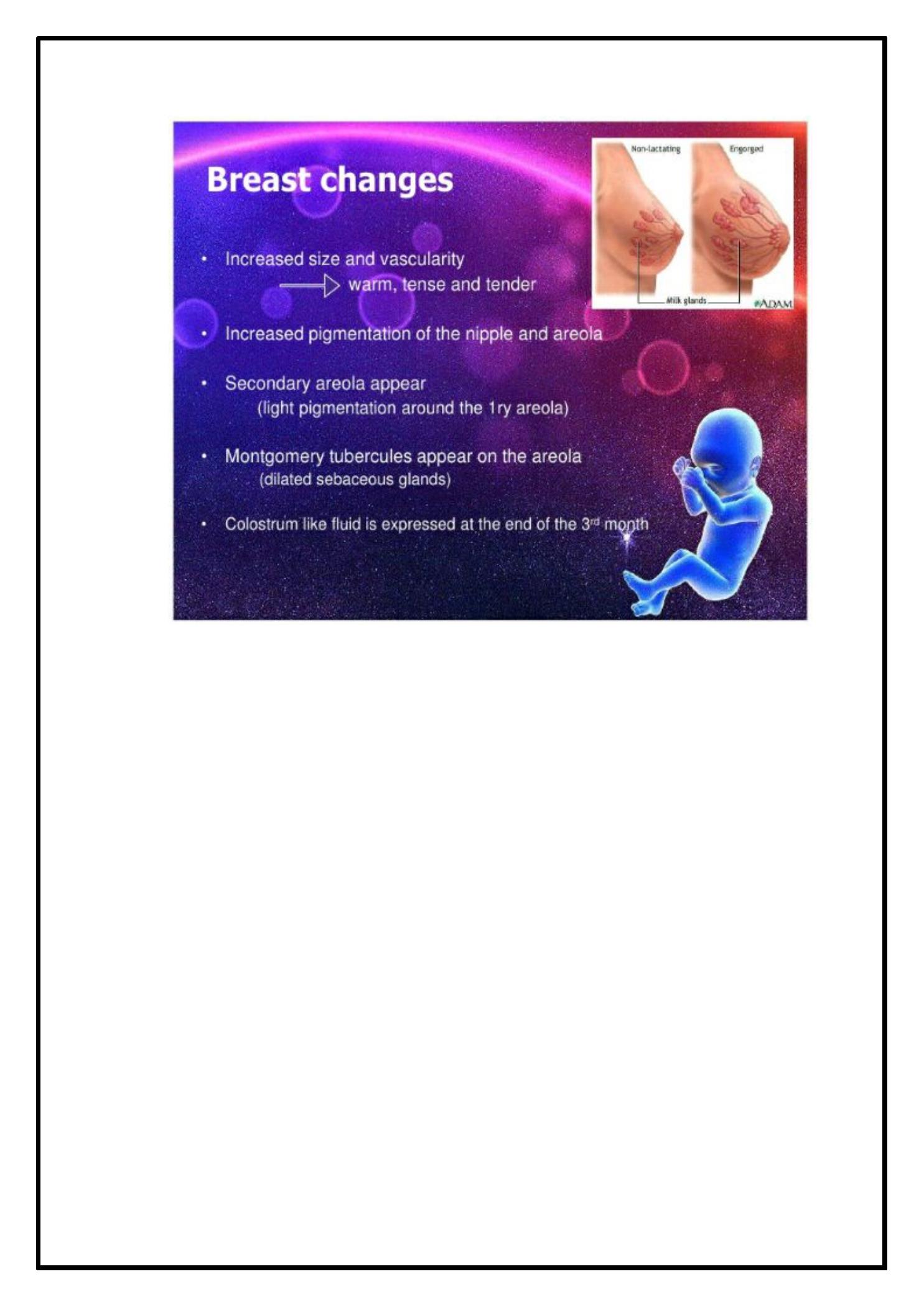
Bre ast & lactation: the number of glandular duct is
incre ase d by oe srtoge n, while proge ste rone & human
place ntal lactoge n incre ase the numbe r of gland alve oli.
13
Endocrinology
·
Hormones produce d within pre gnant ute rus
1.P re gnancy spe cific: hCG& hPL
2.H ypothalamus: GnRH& CRH
3.P ituitary: prolactin, hGH, ACTH
4.S te roids: oe stradiol, progeste rone
5. Othe r pe ptide s: insuline like growth factor, parathyroid
hormone re late d pe ptide , re nin & angiote nsin 2
14
Pituitary gland
·
Enlarge d, conce ntration of prolactin 15 fold incre ase which is
ne ce ssary for initiation of lactation , it also may play a role in
the regulation of insulin secre tion.
· H uman growth hormone production by the ante rior pituitary
gland is suppre sse d during pre gnancy & human place ntal
lactoge n is involve d in suppressing its re lease .
·
Thyroid function
: mate rnal TSH production
is
suppresse d during the first trime ster but return to normal
afte r this. Thyroid binding globulin incre ase s in the first 2
we eks of pre gnancy & re ache s a plate au by 20 wee ks.
Incre ase re nal loss of iodide which result in e nlarge me nt of
the thyroid gland during pregnancy.
Uterus & placenta
·
HCG produced by the trophoblast ce lls, the B-subunit is
pre gnancy spe cific & used as a se nsitive pregnancy te st ,
this hormone has a major role during early pregnancy in
maintaining the function of corpus lute um, which produce s
proge ste rone .
16
·
Sex ste roid hormones are produce d in large quantitie s by
the
place nta
& fe tus. Oestroge n encourage s
ce llular
hype rtrophy of the
myome trium
while
progeste rone
discourage s contraction &, togethe r with prolactin, on the
tissue s of breast.
Corticosteroids
·
A
progre ssive
incre ase
in
mate rnal
circulating
concentrations of cortisol throughout normal pre gnancy has
be en notice as e arly as 11we eks & re aches 2-3fold highe r
concentration than in the non-pre gnant. Much of cortisol is
bound
to
cortisol-binding
globulin,
which
doubles
in
concentration during pre gnancy, but the re is also a slight
incre ase in unbound cortisol.
· A ldoste rone incre ase ten-fold in pregnancy.
·
The incre ased production of angiote nsins is the re sult of
incre ase production of the e nzyme re nin & its substrate
angiotensinogen
·
Corticotrophin-rele asing hormone (CRH) is produced by the
place nta in the se cond half of pre gnancy, which stimulate
the fe tal adrenal to synthe size & re lease
18
dihydroepiandroste rone , which the placenta the n converts to
oe stroge n. It also stimulate the fe tal adrenal gland to
synthe size & re le ase cortisol.
·
CRH pe ak leve l 48hours be fore de live ry . The placental
re gulation of its own me tabolism through e ffe ct on the fe tus,
with subseque nt e ffe cts on mate rnal ute rine physiology, &
possibly the onse t of labor, has be e n calle d the place ntal
clock the ory.
Metabolism
·
Energy re quire me nts & we ight gain
· C arbohydrate metabolism
· L ipid me tabolism
· C alcium meabolism
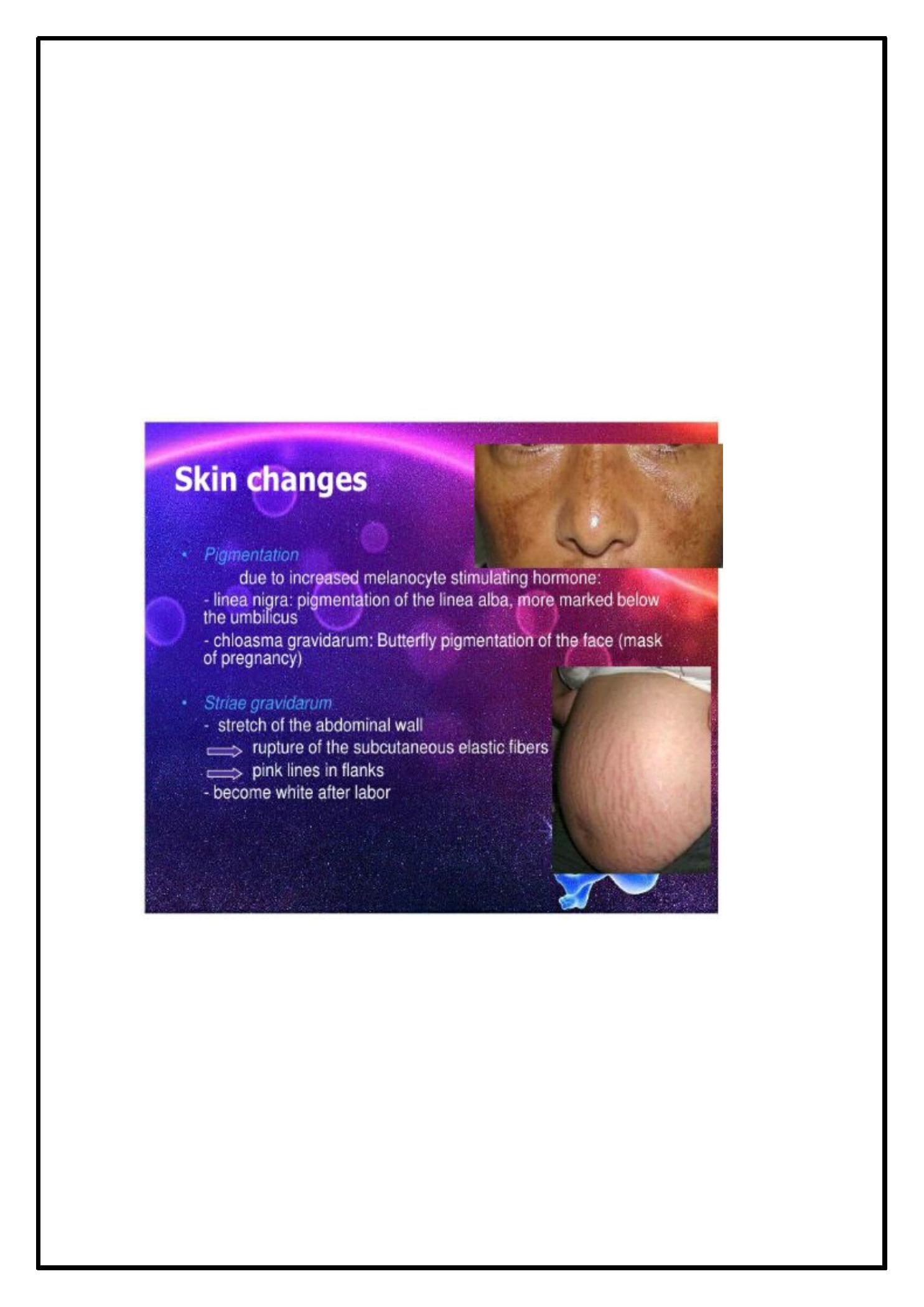
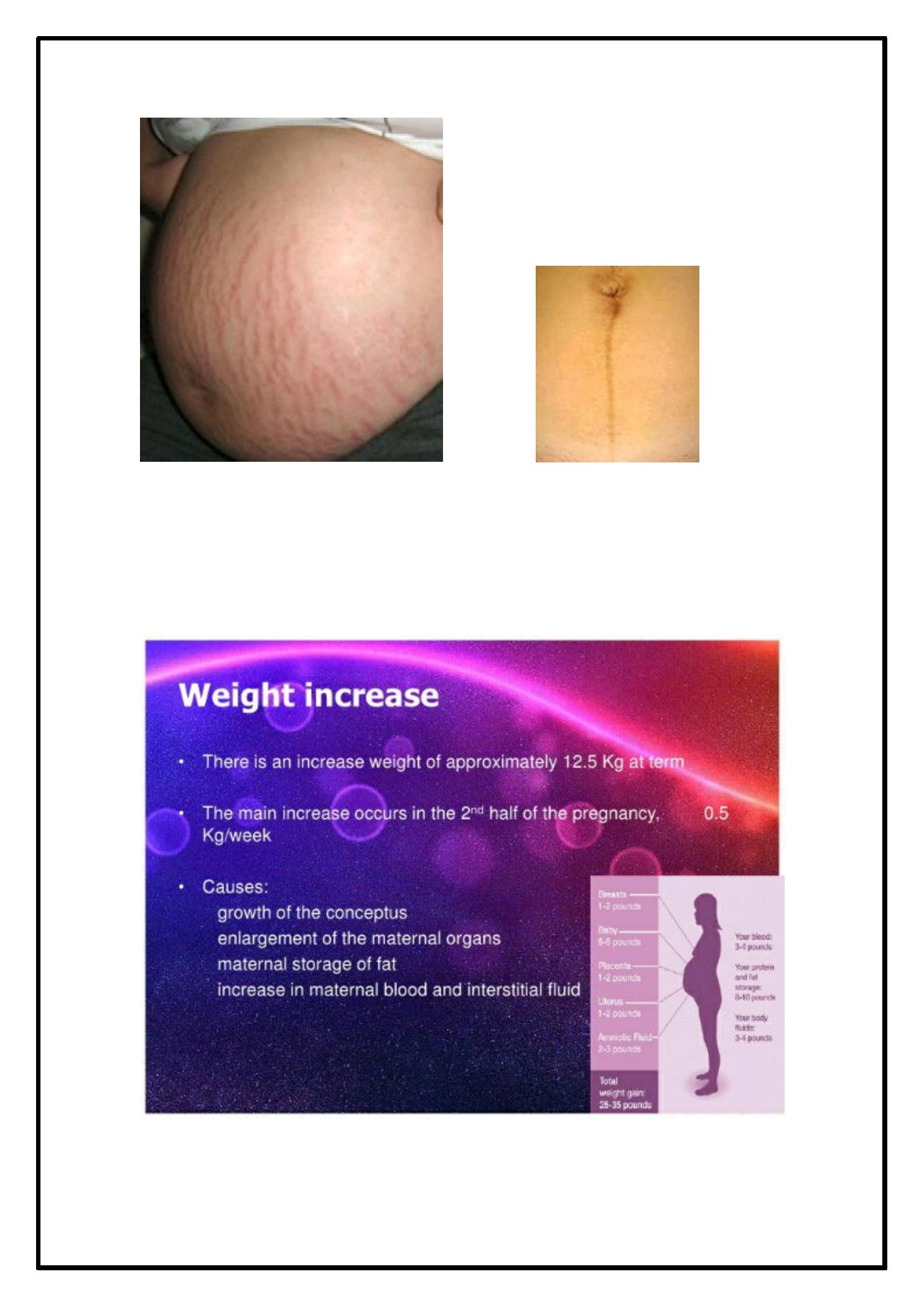
· S kin changes:
· H ype rpigme ntation
· S triae gravidarum
· H irsuitism
·
Incre ase se bace ous gland activity.
19
20

21
…

22

23

24

25

26
Done By:Ansam Rahumi
