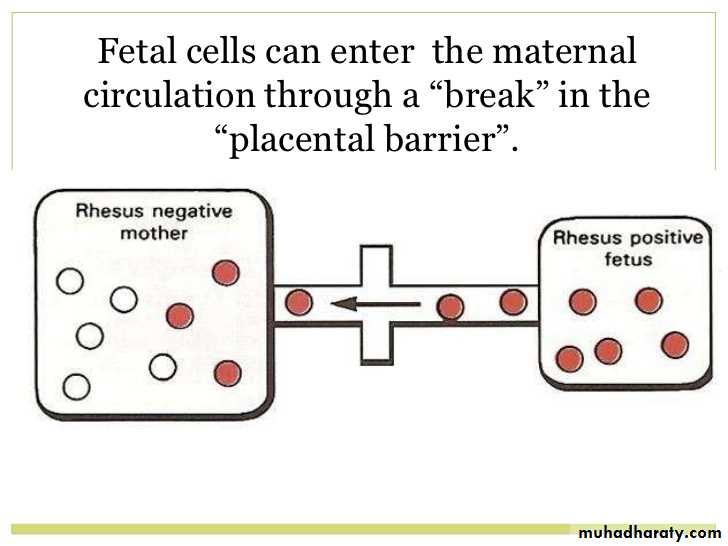
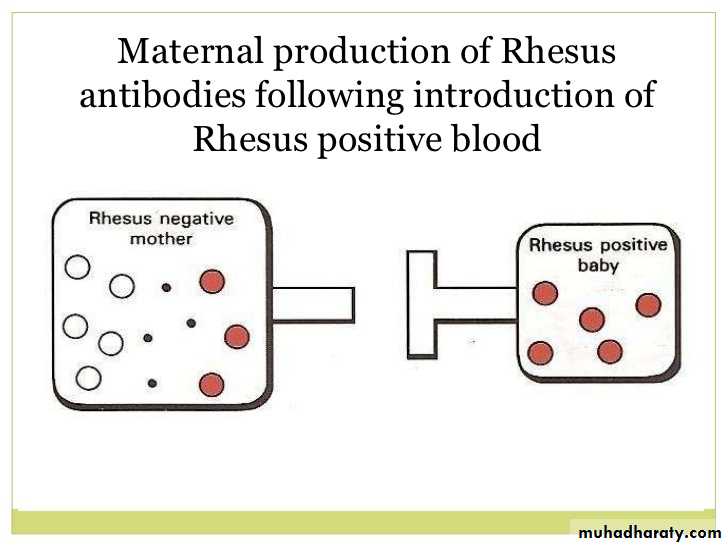
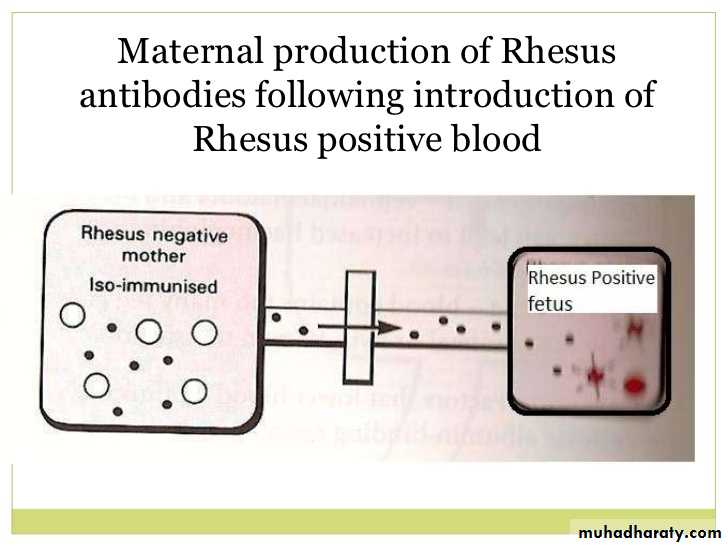
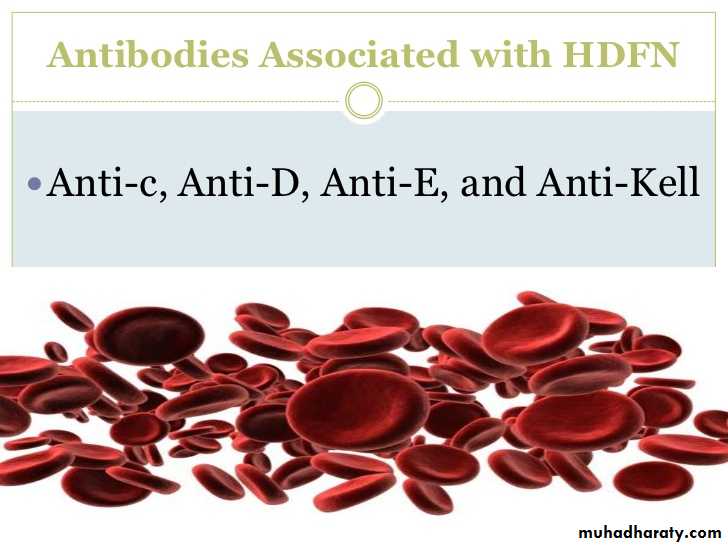
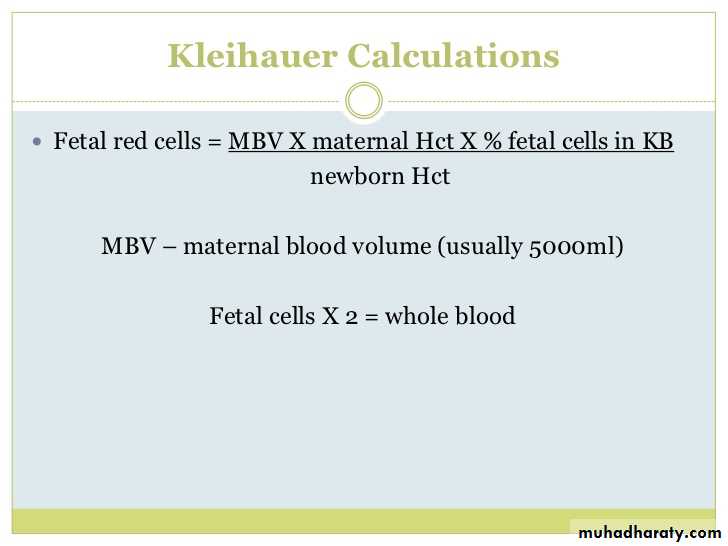
Rhesus isoimmunization
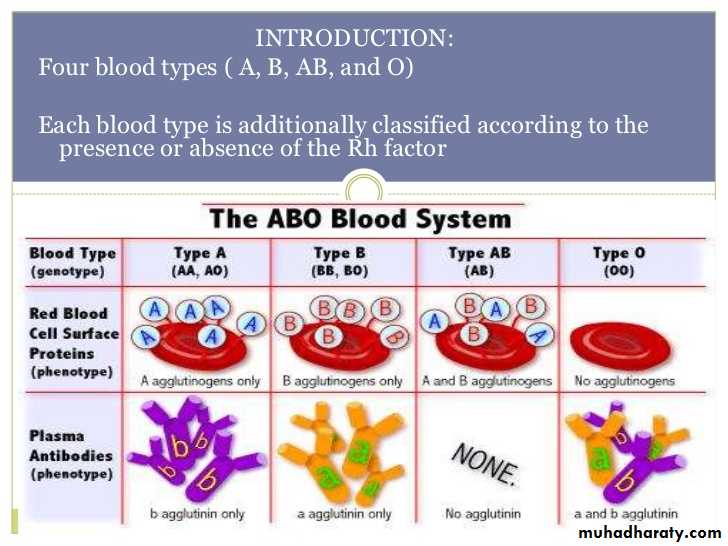
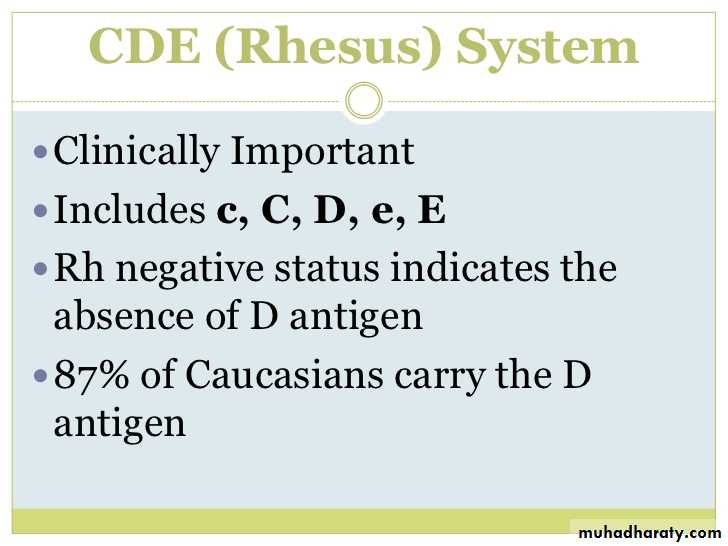
The Rh antigens on red cells result from the action of two genes (RHD and RHCE)leading to two haplotypes (combining c or C ,D or no D , e or E ).oF these Rh D is the most important in obistatrics.
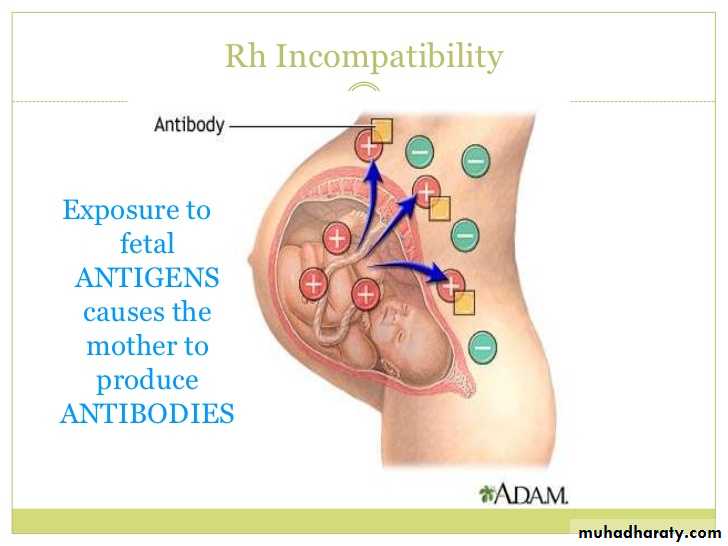
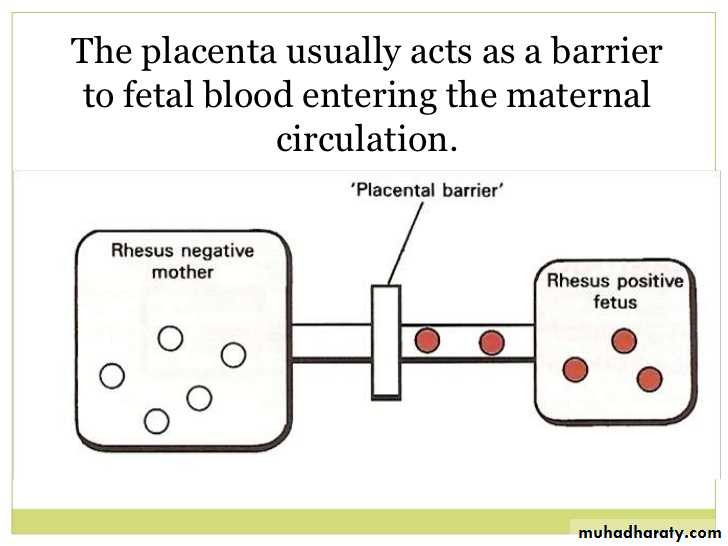
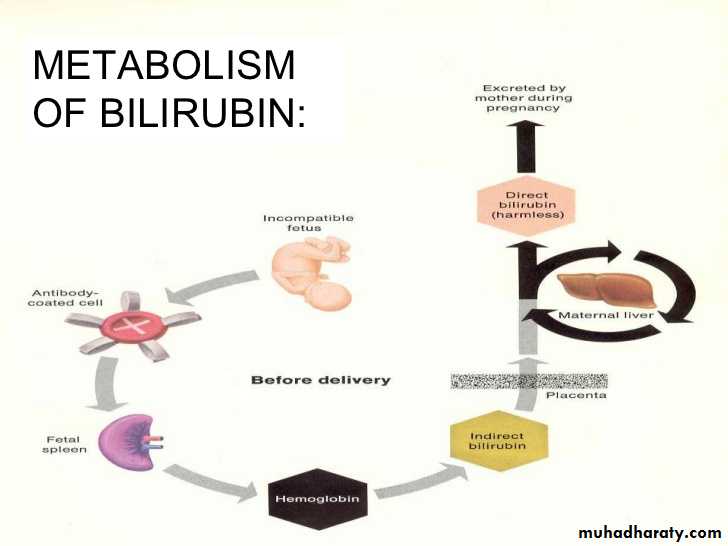
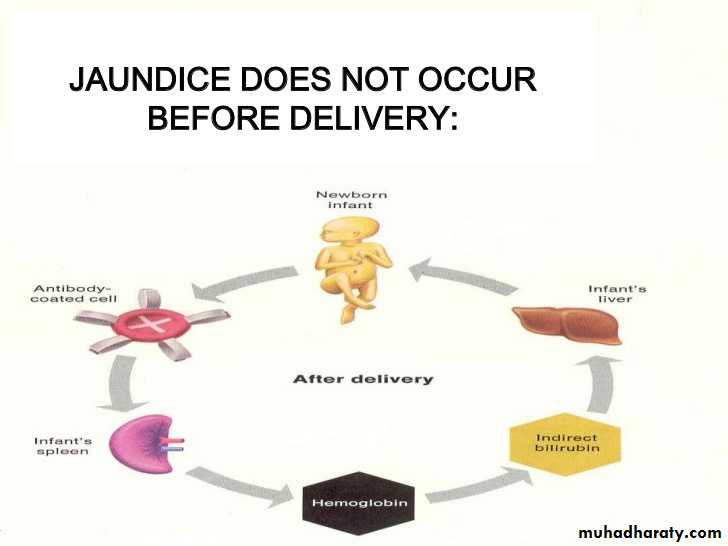
Haemolytic disease occur if an RhD-negative –mother carries an RhD-positive child.
-There is a one in six chance of maternal ant-RhD formation in the absence of prophylaxis.
-whether the mother develops such antibodies depends on the amount of fetomaternal haemorrhage and any feto-maternal ABO mismatch may clear fetal cells before immunization occurs.-RhD haemolytic disease of newborn most often occurs in the second or subsequent pregnancies,
but occasionally significant fetal haemolysis occurs in the first.
-All women should have their blood group determined at pregnancy presentation and again at 28-32 wks.
-A further estimation between 34 and 36 wks is also recommended .
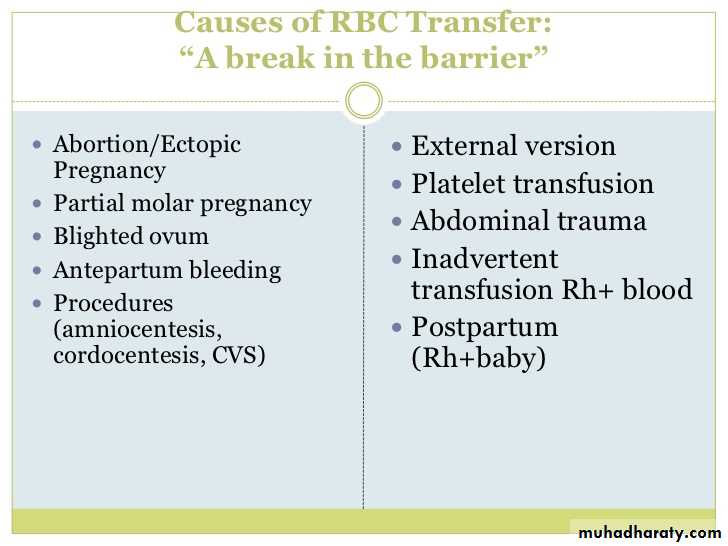
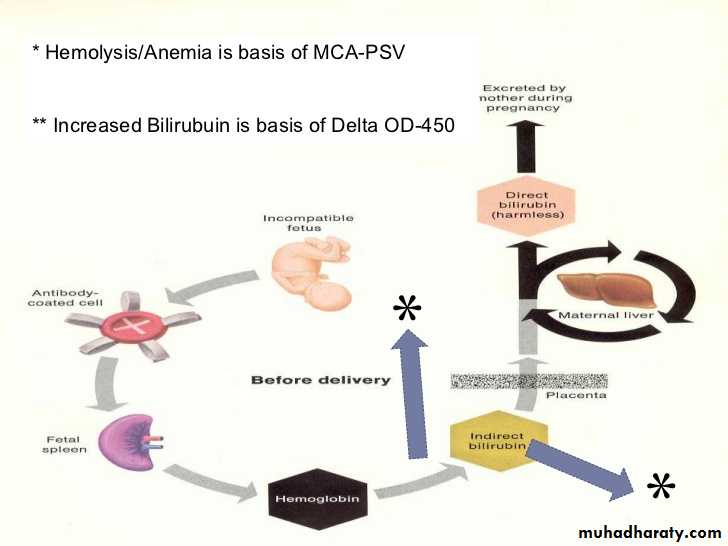
-when a potential sensitizing event occurs in an RhD negative woman , whether she has circulating anti-RhD should be determined and an FMH estimation carried out.