
/2/2016
28
Dr.Wasan
in pregnancy
Diabetes
1
Diabetes in pregnancy
General Consideration
Definition :
abnormalities of carbohydrate metabolism
Incidence :
4% ( 10%overt, 90%gestational)
•
Pregnancy itself is diabetogenic through :
- insulin resistance
o
Increased production of cortisol, estriol,
progesterone
o
Increased insulin destruction by kidney&
placenta
o
Production of placental somato- mmotropin
- Increased lipolysis: mother use fat for calories &
saves glucose for fetus
- Changes in gluconeogensis: fetus use alanine &
other a.a & depraves mother
•
Detection ( screening) of GD :
High risk patients ( risk factors) :
1-positive family history of DM
2-Poor obstetric hx (neonatal death)
3-Polyhydromnia in recent preg.
4-Previous delivery of a large baby.
5-Obese woman
6-Advanced maternal age ( more than 25 years)
/2/2016
28
Dr.Wasan
in pregnancy
Diabetes
2
Screening :
•
Random blood sugar test: 50 gm. Oral glucose, all
preg woman between ( 24-28) wk. without diet
prepartion
- 1 hour plasma glucose = 140 mg/dl ( cutoff value) = or
less than 7 mmol/l.
- 2 hour plasma glucose = 120 mg/dl= (4-6 mmol/l)
•
General urine examination for sugar :
if it more than 1+
•
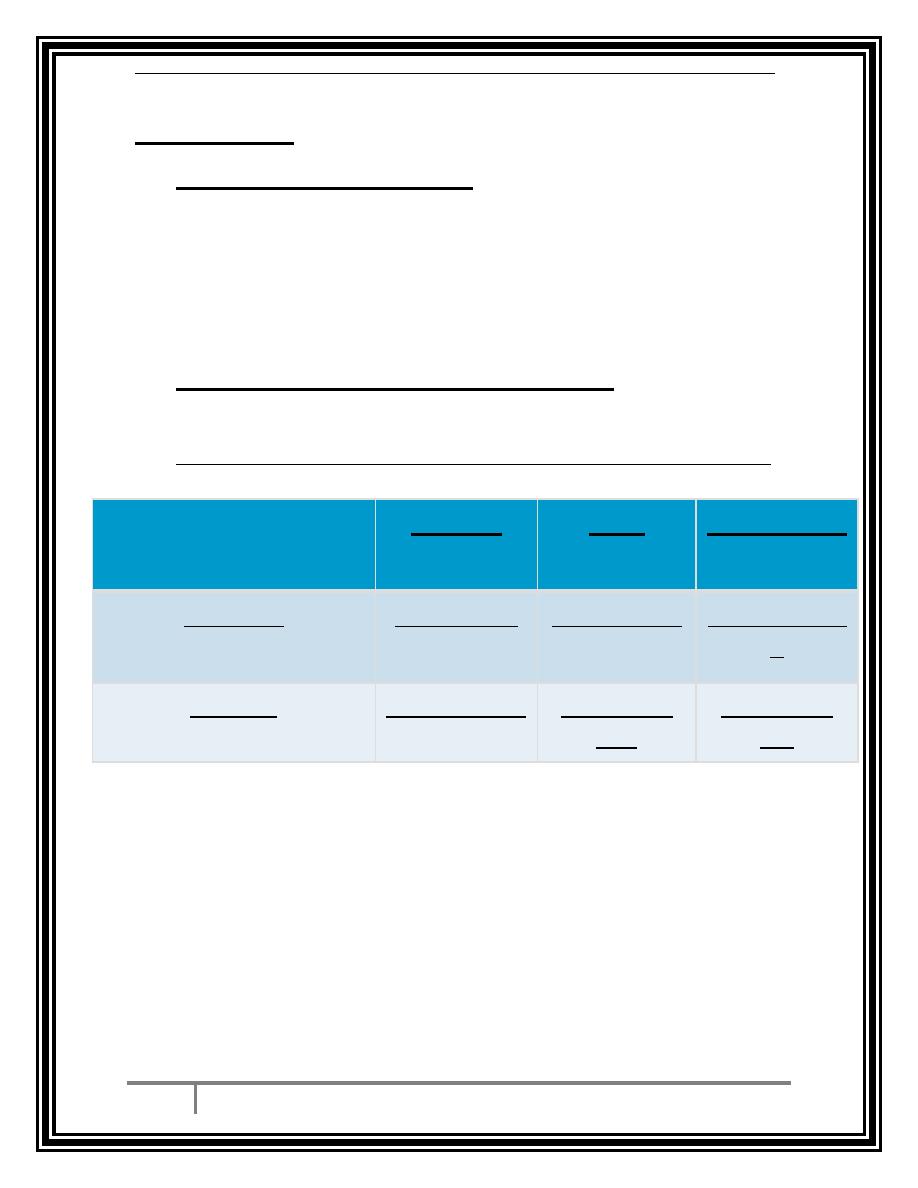
OGTT (75 g) ( prepared patient) modified WHO used
DIABETIC
IGT
normal
More than 7
Less than 7
Less than 7
fasting
More than
11
More than
7.8
Less than7.8
2 hours
/2/2016
28
Dr.Wasan
in pregnancy
Diabetes
3
Effect of diabetes on pregnancy
1. on the mother :
•
Increase incidence of PE & eclampsia espicially in pre-
existing DM.
•
Increase incidence of infection
•
Increase incidence of traumatic delivery & C/S.
•
Increase incidence of poly hydromna( fetal osmotic
diuresis) induced by materno- fetal hyper glycemia
•
Increase PPH
2. ON the fetus :
•
Intrauterine death ( sudden death of fetus in late
pregnancy) due to hypoxia & metabolic acidosis
•
Neonatal death
•
Neonatal morbidity ( birth injury esp. brachial plexuses
in shoulder dystocia)
•
Neonatal hypo-glycemia, hypo-calcemia
•
Congenital anomalies( sacral agenesis , CNS
anomalies)
•
RDS ( respiratory distress syndrome): due to
inhibition effect of cotisol on enz. System responsible
for production of surfactant in fetal lung

/2/2016
28
Dr.Wasan
in pregnancy
Diabetes
4
Management
Antenatal measurement :
•
Early U/S ( for dating, viable)
•
Folic acid supplement ( 3 months before& 1
st
trimester)
•
Advice on hyperglycemic prevention
•
HbA1C ( less than 6.5)
•
Screening for diabetic complication
2
nd
trimester :
•
Detailed U/S to exclude any congenital
abnormalities
•
Assessment fetal growth & amniotic fluid from 28
wks of preg / 2 weeks
•
Surveillance for medical obstetric complications :
increased risk for PIH
•
Optimization of glycaemic control :
- By diet ( 3 meals& 3 snacks)
- 1800 cal /day
- Diet ( CHO 40- 60%),(PROT 20-30% )& remaining
fat.
/2/2016
28
Dr.Wasan
in pregnancy
Diabetes
5
•
If 2 weeks no response . Start insulin :
- Regular 3 short acting & intermediate acting at
bed time.
- Aim FBS 4-6 mmol/l , 2 hour post prandial 7
mmol/l.
- Or dose : insulin ( unit) = BWT * 0.6 ( 1
st
trimester)
- Total dose divided 2/3 before breakfast ( 2
intermediate : 1 soluble)
- 1/3 dinner 1 ( intermediate) :1( soluble)
Third trimester :
1) Optimization of glycaemic control
2) Assessment of fetal growth ( at the end of the second
trimester & every 4 weeks)
3) Timing & mode of delivery
Protocol for insulin during labour & delivery
Intrapartum ( day of induction) :
•
½ dose of insulin at the morning & light breakfast
•
labour establish 500cc of 10% dextrose ( 100cc/hr)
& in other 6 unit of insulin in 60 cc of normal saline
( 1 unit / 10 cc/ hr)
•
Aim is blood sample = 4-6 mmol/l after ½ hr. if Bs
less than 4 mmol/l then 5cc/hr ( ½ unit). If Bs more
than 6 mmol/l then 20 cc/hr (2 unit/hr). Then should
mointer Bs every hour.
/2/2016
28
Dr.Wasan
in pregnancy
Diabetes
6
After delivery ( post partum) :
•
adjustment of insulin dosage :Halve infusion rate until
eating then stop.
•
Return to pre-pregnancy dose ( moniter blood sugar 2
hours & then post pranidal for 48 hours .
•
Discussing contraception
•
OGGT 6 weeks after delivery
THE END
BY:
TAHER ALI TAHER
