
Dr. Rabah
Lec. 6
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASES
–
PART 2
Tues. 5 / 4/ 2016
Done By: Ibraheem Kais
2015 – 2016
ﻣﻜﺘﺐ ﺁ
ﺷﻮﺭ ﻟﻼﺳﺘﻨﺴﺎﺥ
Inflammatory bowel diseases – Part 2 Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
1
Inflammatory bowel diseases – Part 2
Investigations
Used to:
Confirm the diagnosis.
Define disease distribution.
Define activity.
Identify complications.
Blood tests
Full blood count may show anaemia.
Serum albumin.
The ESR and CRP.
- Elevated in exacerbations and in response to abscess formation.
Bacteriology
Stool microscopy.
Culture and examination:
- Ova.
- Cysts.
- Clostridium difficile toxin.
Blood cultures.
Endoscopy with biopsies
Confirm the DX.
Define disease extent.
Detect dysplasia in long-standing colitis.
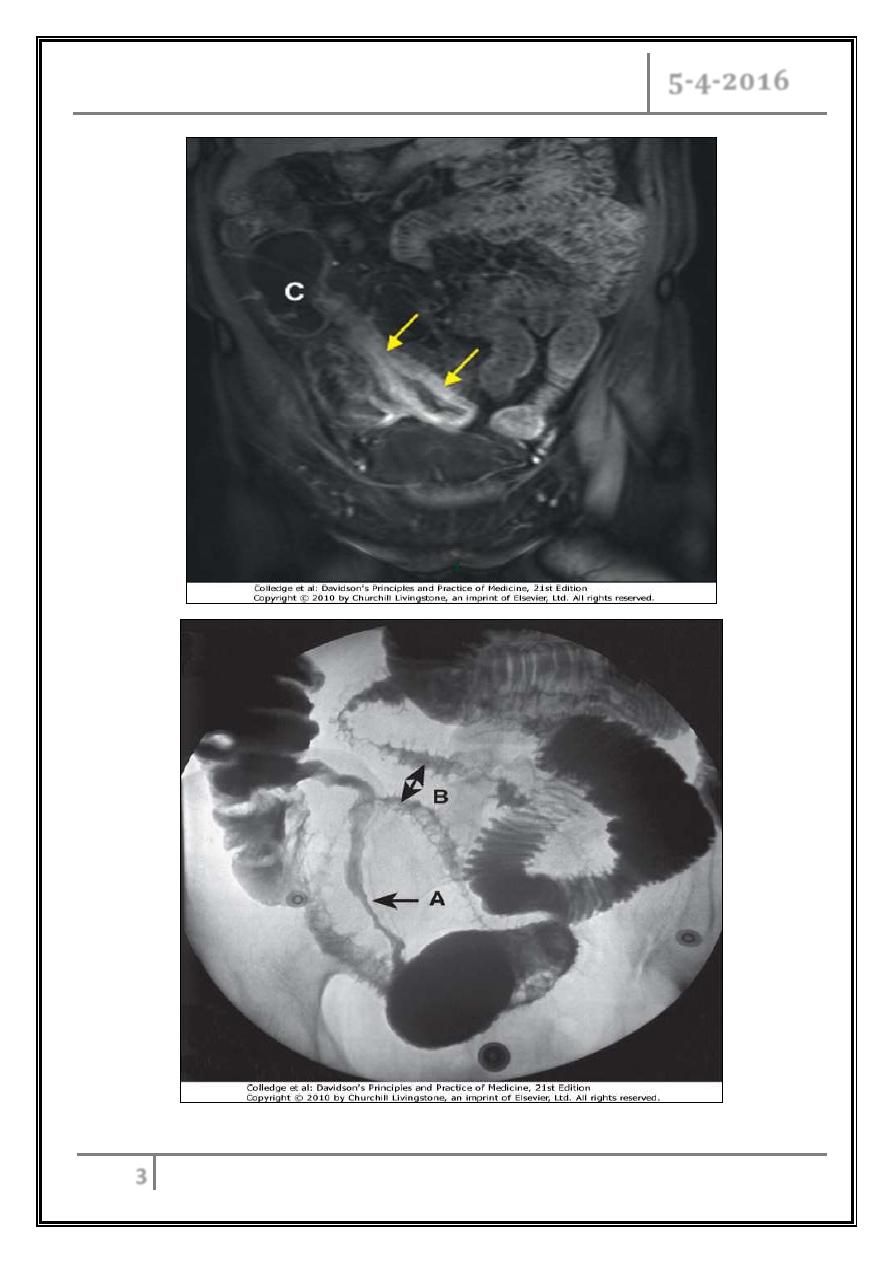
Capsule endoscopy
- The identification of small bowel inflammation.
Inflammatory bowel diseases – Part 2 Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
2
Radiology
Barium enema
- Less sensitive investigation than colonoscopy.
- Crohn's disease; affected areas are narrowed and ulcerated, and multiple
strictures are common.
Abdominal CT and MRI scans
- Provide bowel thickening.
- Pelvic or perineal involvement.
A plain abdominal X-ray
- Dilatation of the colon.
- In small bowel Crohn's disease there may be evidence of intestinal
obstruction.
Ultrasound
- Thickened small bowel loops.
- Abscess development in Crohn's disease.
Inflammatory bowel diseases – Part 2 Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
3
Inflammatory bowel diseases – Part 2 Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
4
Management
Treat acute attacks.
Prevent relapses.
Select patients for surgery.
Detect carcinoma at an early stage.
Treat acute attacks
Aminosalicylates
Mode of action: modulate cytokine release.
Oral or topical (enema/suppository).
Mesalamine
- Pentasa (time dependent release).
- Ascol (PH dependent release).
- With a carrier: sulfasalazine, balsalazide, olsalazine.
- Side-effects: 10-45%
Headache.
Nausea.
Diarrhoea.
Blood dyscrasia.
Corticosteroids
Anti-inflammatory.
Topical and oral and I.V.
- Prednisolone.
- Hydrocortisone.
- Budesonide.
Cyclosporine
Suppresses T-cell expansion.
Rescue' therapy to prevent surgery in severe ulcerative colitis responding
poorly to corticosteroids.
No value in Crohn's disease.
Major side-effects in.
Nephrotoxicity, infections, neurotoxicity.
Minor complications: tremor, paraesthesiae, abnormal liver function tests,
hirsutism.
Inflammatory bowel diseases – Part 2 Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
5
Anti-TNF antibodies (infliximab and adalimumab)
Suppress inflammation and induce apoptosis of inflammatory cells.
Used:
- Fistulating Crohn's disease.
- Severe active ulcerative colitis with no response to steroids or
cyclosporine.
Side effects:
- Anaphylactic reactions.
- Contraindicated in the presence of infections; reactivation of
tuberculosis.
Antibiotics
Useful in perianal Crohn's disease.
Antidiarrhoeal agents (codeine phosphate, loperamide,
lomotil)
Reduce gut motility and small bowel secretion.
Avoided in acute flare-ups of disease.
May precipitate colonic dilatation.
Prevent relapses
Thiopurines (azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine)
o Immunomodulation by inducing T-cell cytotoxic effect.
o Effective after 12 weeks of starting therapy.
o Complications :
- Flu-like syndrome with myalgia.
- Leucopenia in 3%.
Inflammatory bowel diseases – Part 2 Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
6
Methotrexate
o Anti-inflammatory (folic acid antagonist).
o Nausea, stomatitis, diarrhoea, hepatotoxicity and pneumonitis.
o Used in Crohn’s disease.
Anti-TNF antibodies (inflaximmab)
Ulcerative colitis
Treatment of acute attacks
Active proctitis and proctosigmoiditis
- Mesalamine enemas or suppositories combined with oral mesalazine are
effective first-line therapy.
- Topical corticosteroids for intolerant of topical mesalazine.
Active left-sided or extensive colitis
- High-dose aminosalicylates.
- Oral prednisolone 40 mg daily is indicated for more active disease or
when initial aminosalicylate therapy is ineffective.
Severe ulcerative colitis
- Hospital admission.
- Monitored clinically: for the presence of abdominal pain, temperature,
pulse rate, stool blood and frequency.
- Radiologically: for colonic dilatation on plain abdominal X-rays.
- Intravenous fluids.
- Transfusion blood if Hb < 10 g/ L.
- Nutritional support.
- I.V. corticosteroids.
- Oral aminosalicylates.
- Patients who do not promptly respond to corticosteroids are considered
for intravenous ciclosporin or infliximab.
Inflammatory bowel diseases – Part 2 Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
7
- Those who do not respond after “maximal” medical treatment usually
require urgent colectomy.
Maintenance of remission
Life-long therapy, recommended for:
- Extensive disease.
- Distal disease who relapse more than once a year.
Drugs:
- Oral aminosalicylates first line.
- Patients who frequently relapse despite aminosalicylate drugs are treated
with thiopurines.
Crohn's disease
Treatment of acute attacks
Active colitis or ileocolitis
- Aminosalicylates.
- Corticosteroids.
- In severe disease intravenous steroids.
Isolated ileal disease
- Corticosteroids.
- Aminosalicylates have little added value.
- Biological treatment.
Fistulas and perianal disease.
- Surgical intervention required for abscess.
- For simple perianal disease metronidazole and/or ciprofloxacin are first-
line therapies.
- Treatment of underlying active disease with corticosteroids.
- Infliximab heal enterocutaneous fistulas and perianal disease in many
patients.
Inflammatory bowel diseases – Part 2 Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
8
Maintenance of remission
Aminosalicylates have minimal efficacy.
thiopurines for relapse more than once a year or severe disease.
Patients who are intolerant of or resistant to thiopurines should be treated
with once-weekly methotrexate combined with folic acid.
Patients with aggressive disease are managed using a combination of
immunosuppressives and anti-TNF therapy.
Indications for surgery in ulcerative colitis
Failure of medical therapy:
- Failure of remission induction (severe colitis).
- Toxic megacolon no response to Rx.
- Failure of remission.
- Complications of drug therapy.
Disease complications unresponsive to medical therapy:
- Arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum.
Colon cancer or severe dysplasia.
Impaired quality of life:
- Loss of occupation or education.
- Disruption of family life.
Indications for surgery in Crohn's disease
The indications for surgery are similar to those for ulcerative colitis.
Unresponsive fulminant disease.
Operations are often necessary to deal with abscesses.
Relieve small or large bowel stricture.
Chronic fistulating small bowel disease may require resection if no response.
… End …
