
Dr. Rabah
Lec. 7
IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME
Tues. 5 / 4/ 2016
Done By: Ibraheem Kais
2015 – 2016
ﻣﻜﺘﺐ ﺁ
ﺷﻮﺭ ﻟﻼﺳﺘﻨﺴﺎﺥ
Irritable bowel syndrome Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
1
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional bowel disorder characterized by
abdominal pain or discomfort and altered bowel habits in the absence of
detectable structural abnormalities.
Approximately 20% of the general population fulfils diagnostic criteria for IBS
but only 10% of these consult their doctors because of gastrointestinal
symptoms.
Female predominant.
Etiology
The pathogenesis of IBS is poorly understood.
Psychosocial factors
- Anxiety.
- Depression.
- Somatisation and neurosis.
Altered gastrointestinal motility
- No consistent evidence of abnormal motility.
Altered visceral sensation
- A consequence of altered central nervous system processing of visceral
sensation.
Luminal factors
- Following an episode of gastroenteritis.
- Intolerant of specific dietary components, particularly lactose and wheat.
- Gut microflora.
Irritable bowel syndrome Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
2
Clinical features
Colicky abdominal pain.
Altered bowel habit.
Abdominal distension.
Rectal mucus.
Feeling of incomplete defecation.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain episodic and crampy (lower).
May be mild enough to be ignored or it may interfere with daily activities.
Pain is often exacerbated by eating or emotional stress and improved by
passage of flatus or stools.
Sleep deprivation is also unusual.
Altered bowel habits
o The most common pattern is constipation alternating with diarrhea, usually
with one of these symptoms predominating.
o Stools are usually hard with narrowed caliber.
o Diarrhea resulting from IBS usually consists of small volumes of loose stools.
o Nocturnal diarrhea does not occur.
o Diarrhea may be aggravated by emotional stress or eating.
o Stool may be accompanied by passage of large amounts of mucus.
Gas and Flatulence
Abdominal distention.
Increased belching.
Flatulence.
Most IBS patients have impaired transit and tolerance of intestinal gas loads.
Irritable bowel syndrome Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
3
Diagnosis
Is clinical with excluding secondary disease if needed.
Features supporting a diagnosis of IBS
Symptoms > 6 months without progressive deterioration.
Absence of other systemic symptoms such as fever and weight loss.
Small-volume stool without any evidence of blood.
Frequent consultations for non-GI problems.
Previous medically unexplained symptoms.
Stress worsens symptoms.
Diagnostic criteria (Rome)
Recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort at least 3 days per month in the last 3
months associated with two or more of the following:
1. Improvement with defecation.
2. Onset associated with a change in frequency of stool.
3. Onset associated with a change in form (appearance) of stool.
Investigation
Minimal for typical symptom. If we need:
Full blood count.
GSE.
Lower GI endoscopy (sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy).
- Alarm features.
- Diarrhoea-predominant.
Irritable bowel syndrome Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
4
Alarm features
Age > 50 years; male gender.
Weight loss.
Nocturnal symptoms.
Family history of colon cancer.
Anaemia.
Rectal bleeding.
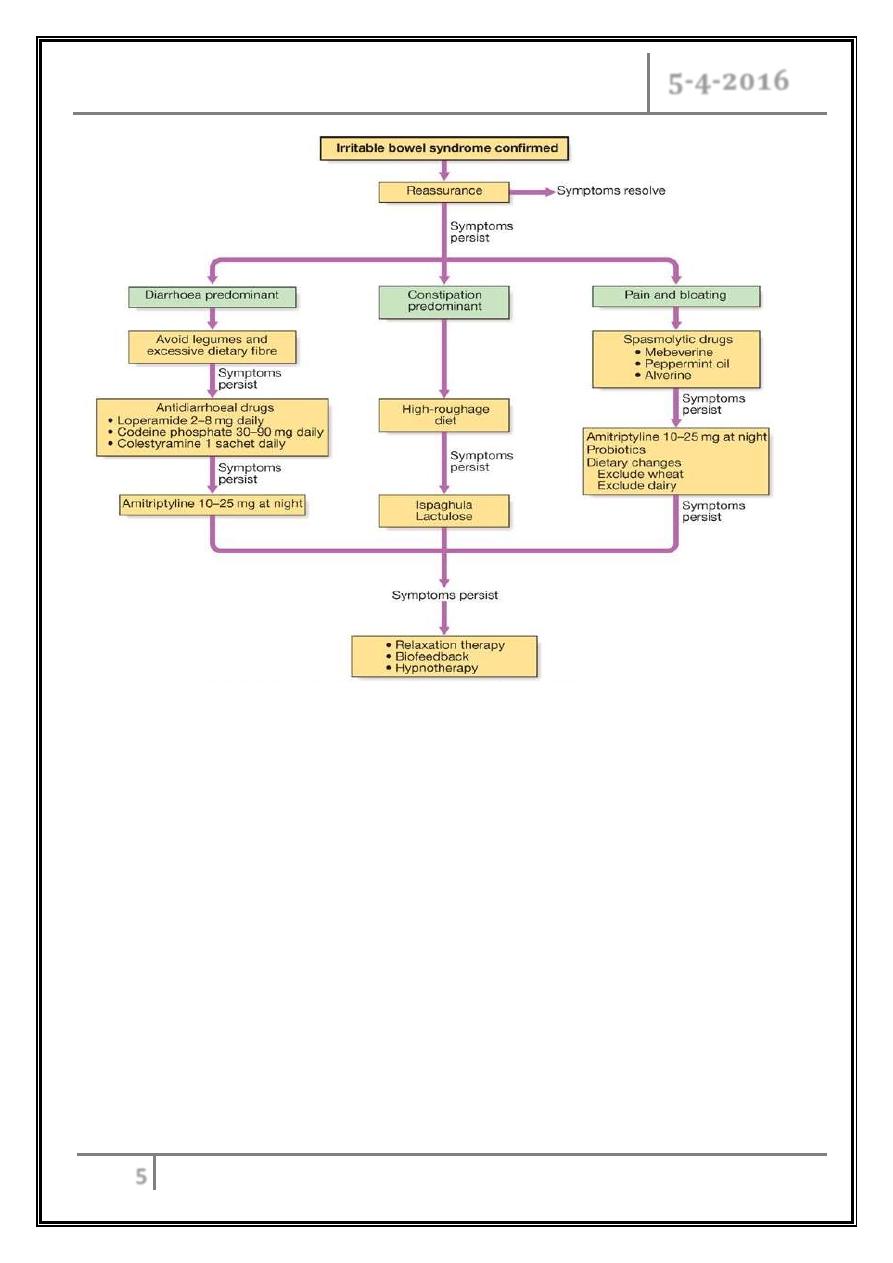
Management
Diagnosis.
Reassure the patient.
Dietary alteration:
- Wheat-free diet.
- Lactose exclusion.
Treatment of the predominant symptoms.
Therapy with tricyclic antidepressant.
5-HT4 agonists.
Psychological interventions.
Irritable bowel syndrome Dr. Rabah
5-4-2016
5
Prognosis
Most patients have a relapsing and remitting course. Exacerbations often follow
stressful life events, occupational dissatisfaction and difficulties with interpersonal
relationships.
… End …
