
Baghdad College of Medicine / 4
th
grade
Student’s Name :
Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
Lec. 4
DISEASES OF BREAST
Tues. 22 / 12 / 2015
DONE BY : Ali Kareem
مكتب
اشور لالستنساخ
2015 – 2016
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
22-12-2015
2
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
Diseases of Breast
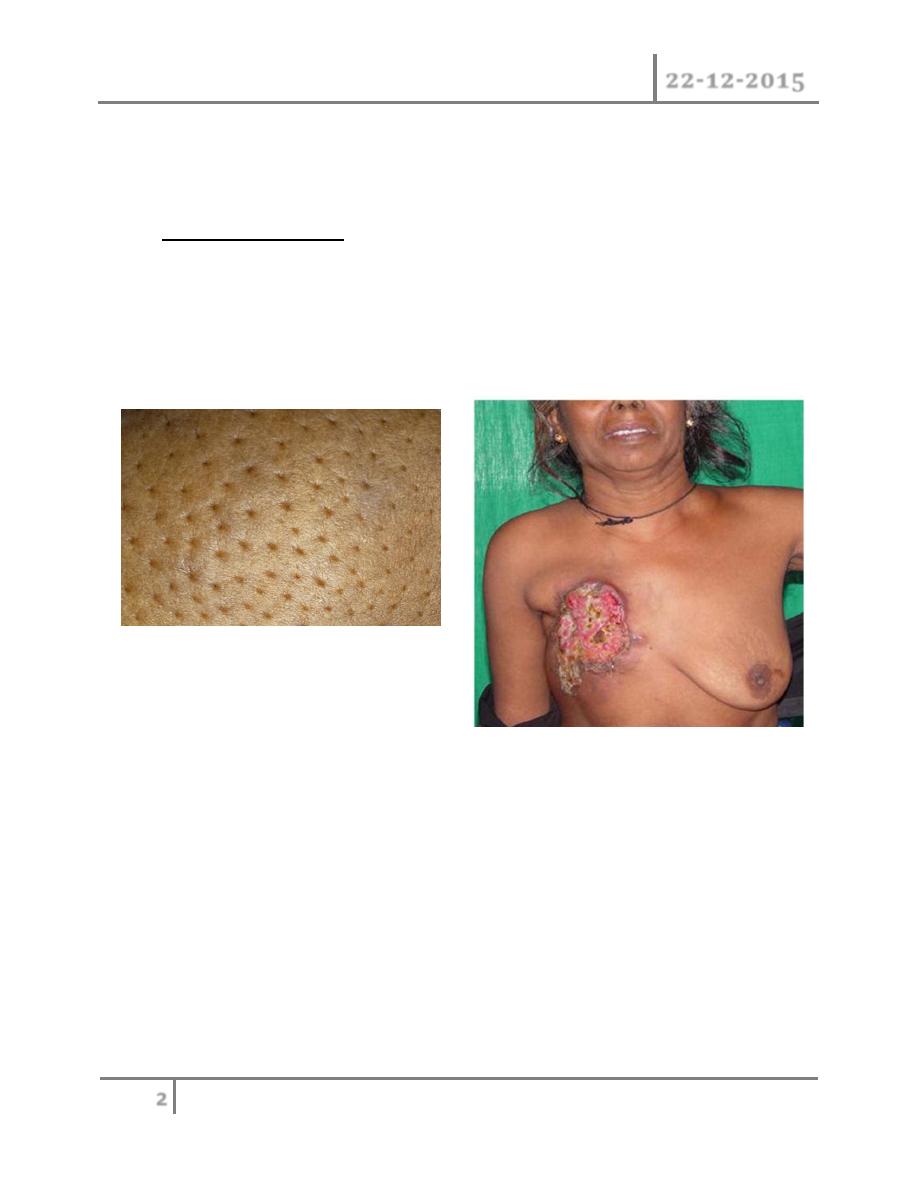
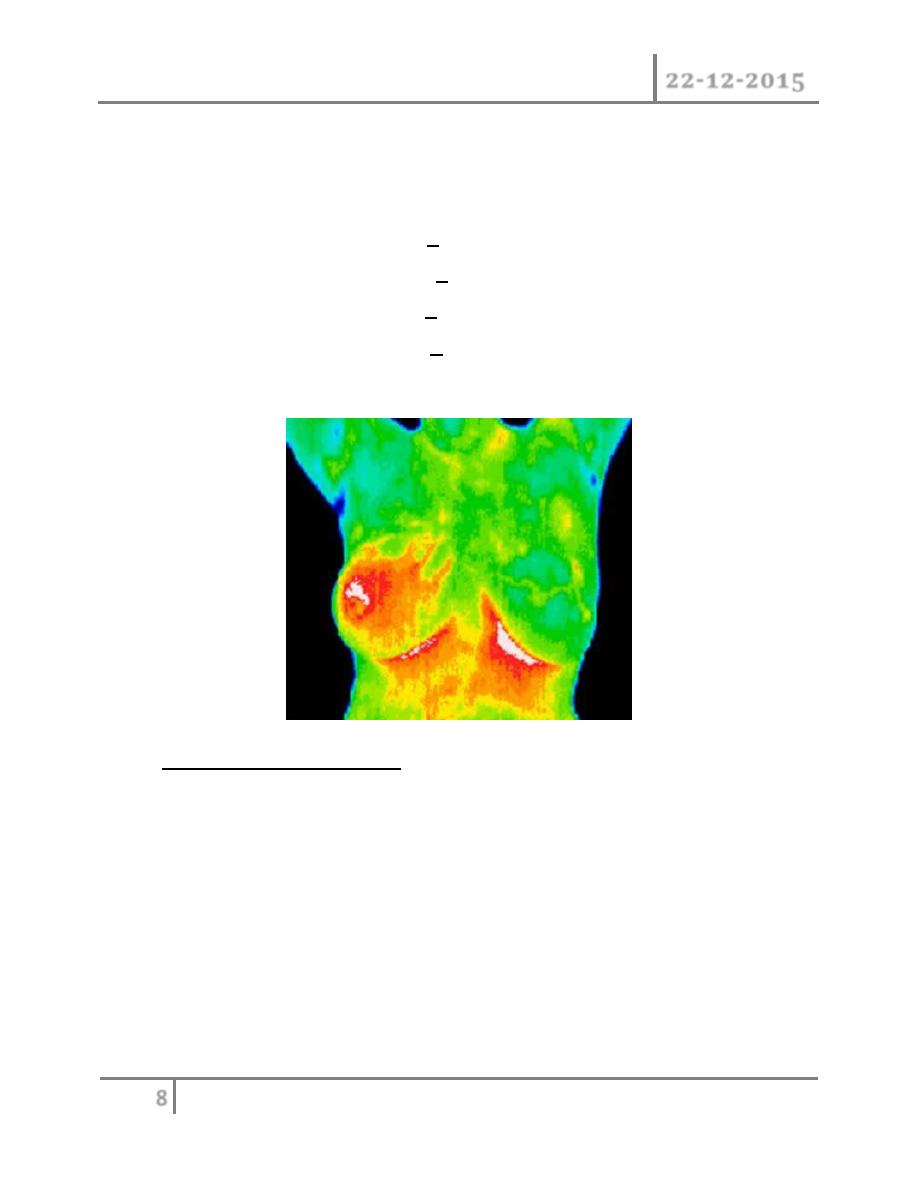
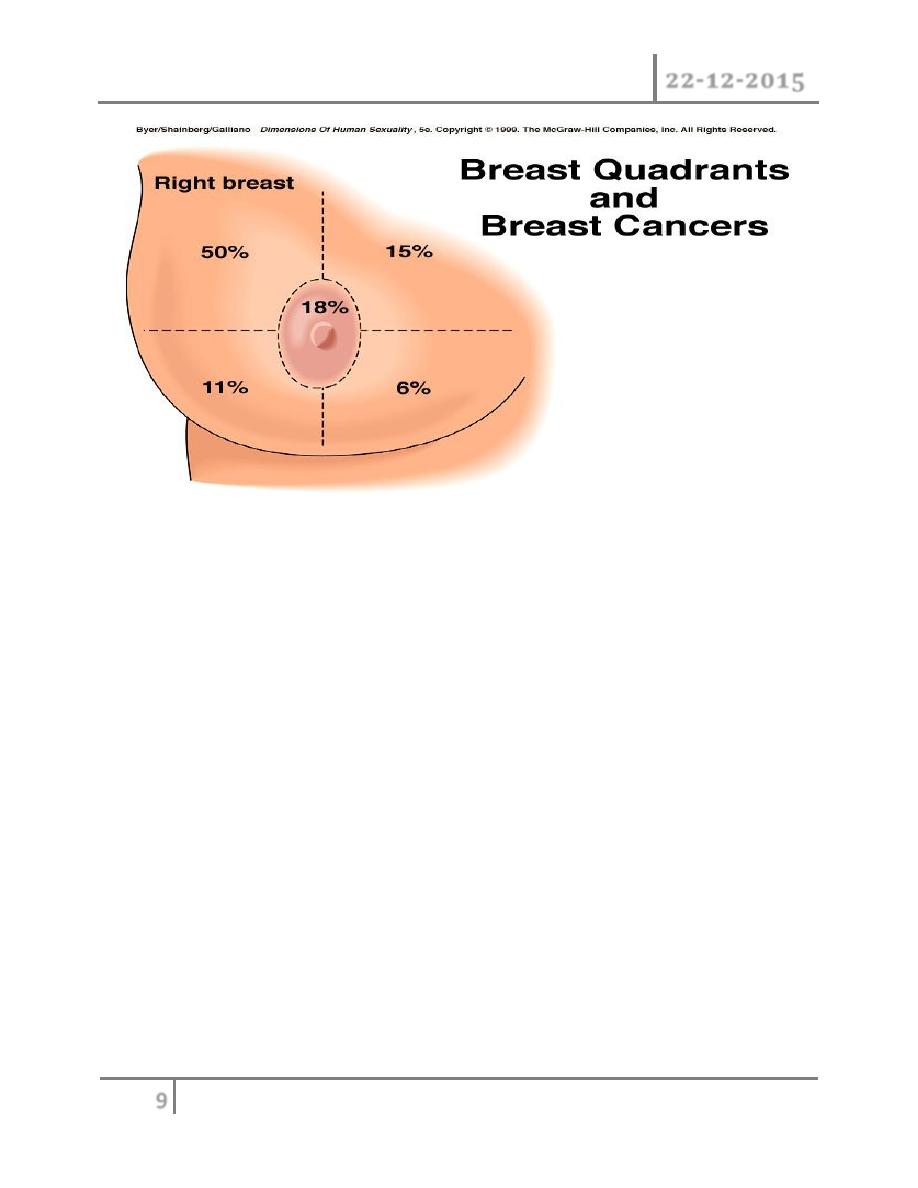
Clinical presentation : although any portion of the breast including axillary
tail may be involved breast cancer is found most frequently in the upper
outer quadrant most carcinoma will present as a hard lump which may be
associated with indrawing of the nipple, as the disease advances locally
there may be skin involvement with peau d orange or frank ulceration and
fixation to the chest wall.
This is described as cancer en-cuirasses when disease progress around
chest wall. About 5% carcinoma in UK presented as locally advanced or
symptoms of metastatic disease this figure is much higher in developing
countries. These patients under goes staging evaluation so this will include a
careful clinical examination, chest x-ray, CT scan chest and abdomen and
isotope scan, bone scan.
This will be important for both prognosis and treatment. A patient with wide
spread visceral metastases may obtain an increased length and quality of
survival from systemic hormone therapy or chemotherapy but is unlikely to
benefit from surgery as she will die from her metastases before local disease
becomes a problem.
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
22-12-2015
3
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
Investigations :
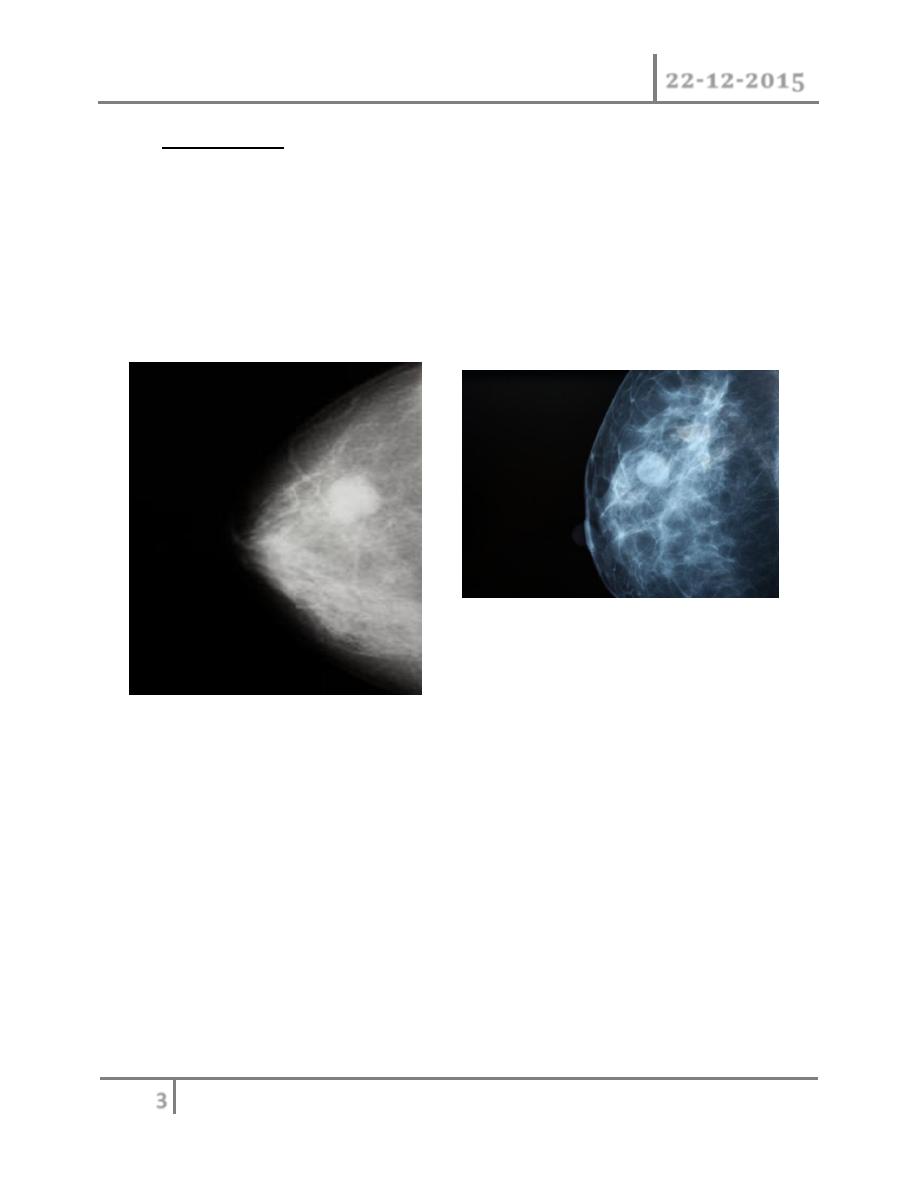
1) Mammaography : soft tissue radiographs are taken by placing the
breast in direct contact with ultrasensitive film and exposing it to low-
voltage, high amperage x-rays. The dose of radiation is very low so it
is a safe investigation. The sensitivity of this investigation increases
with age as the breast becomes less dense. In total, 5% of breast
cancers are missed by population –based mammographic screening
programme , even in retrospect , such carcinoma are not apparent.
Thus, a normal mammogram does not exclude the presence of
carcinoma. Digital mammography is being introduced, which allow
manipulation of the images and computer aided diagnosis. Tomo-
mammography is also being assessed as a more sensitive diagnostic
modality.
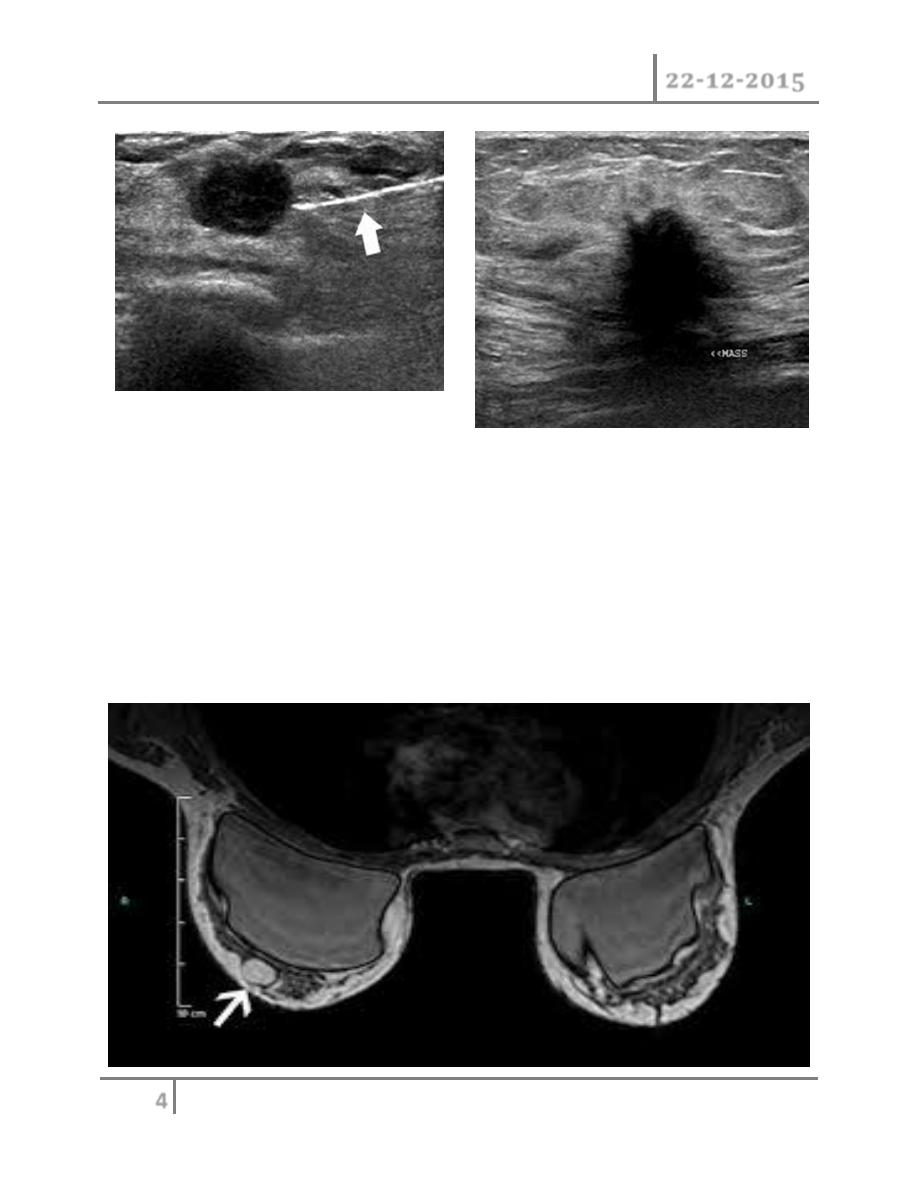
2) Ultrasound : ultrasound is particularly useful in young women with
dense breasts in whom mammograms are difficult to interprets, and in
distinguishing cysts from solid lesions. It also can be used to localize
impalpable areas of breast pathology. It is useful as screening tool
and remains operator dependent. Increasingly, ultrasound of the
axillary tissue is performed when cancer is diagnosed and guided
percutaneous biopsy of any suspicious glands may be performed.
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
22-12-2015
4
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
3) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); MRI is of increasing interest to
breast surgeons in a number of setting: it can distinguish scar from
recurrence in women who have had previous breast conservation
therapy for cancer. It is the best imaging modality for the breast of
women with implants. It has proven to be a useful as screening tool in
a high risk women because of a family history. It is less useful than
ultrasound in the management of the axilla in both primary breast
cancer and recurrent diseases.
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
22-12-2015
5
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
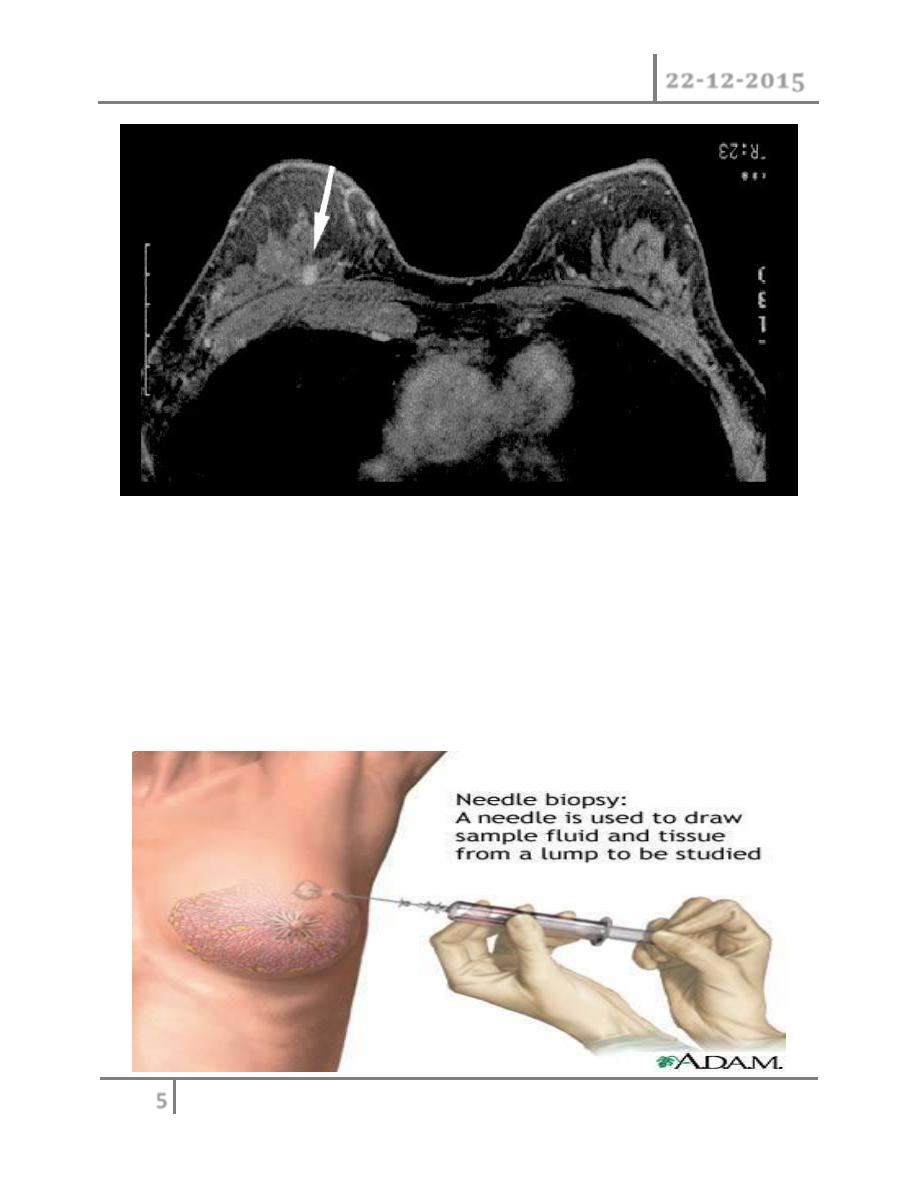
4) Needle biopsy/ cytology: histology can be obtained under local
anesthesia using a spring loaded core needle biopsy device. Cytology
is obtained using a 21 G or 23G needle and 10 ml syringe with
multiple passes through the lump with negative pressure in the
syringe. The aspirate is then smeared on to a slide which is air dried
or fixed. Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is the least invasive
technique of obtaining a cell diagnosis and is a rapid and very
accurate if both operator and cytologist are experienced.
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
22-12-2015
6
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
o However, false negative do occurs, mainly through sampling error, and
invasive cancer cannot distinguished from in situ disease. A histological
specimen taken by a core biopsy allows a definitive preoperative diagnosis,
differentiates between duct carcinoma in situ and invasive disease and also
allows the tumor to be stained for receptor status.
o This is important before commencing neoadjuvant therapy. (5)large needle
biopsy with vacuum systems: the sampling error decreases as the biopsy
volume increases and using 8G or 11G needles allows more extensive
biopsies to be taken this is useful in management of micro calcifications or
in complete excision of benign lesions such as fibroadenomas.
o Triple assessment: the diagnosis should be made by a combination of
clinical assessment, radiological imaging and a tissue sample taken for
either cytological or histological analysis, the so called triple assessment.
The positive predictive value of this combination should exceed 99.9%.
Staging of breast cancer : classical staging of breast cancer by means of
TNM ( tumor, nodes, metastasis) criteria is used less often as we gain more
knowledge of the biological variable that affect prognosis. It is becoming
increasingly clear that it is these factors rather than anatomical mapping
that influence the outcome of the disease and treatment. As shown below.
group
Approximate 5
year survival
example
treatment
Very low risk
90%
Screen detected
DCIS
Local
Low risk prim
tumor
70-90%
Node negative with
favorite histology
Locoregional with
or without systemic
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
22-12-2015
7
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
High risk prim
tumor
<70%
Node positive or
unfavorite
histology
Locoregional with
systemic
Locally
advanced
<30%
Large prim or
inflammatory type
Primary systemic
metastatic
------------
-------------------
Primary systemic
Prognosis of breast cancer : the best indicator of likely prognosis in breast
cancer remains tumor size and lymph node status. It is realized that some
large tumors remain confined to the breast for decades whereas some very
small tumors are incurable at time of diagnosis. Hence the prognosis of a
cancer depends not on chronological age of tumor but on its invasive and
metastatic potential.
In attempt to define which tumor will behave aggressively and thus require
early systemic treatment, a host of prognostic factors have been described.
These include histological grade of tumor, hormone receptors status,
measure of tumor proliferation such as S-phase fraction, growth factor
analysis and oncogene or oncogene product measurement.
Prognostic indices as Nottingham prognostic index have combined these
factors to allow subdivision of patients in to discrete prognostic group.
Others put gene profile with other group indicator to give recurrence score
but still unproven at moment. Others develop gene signatures said able to
detect cancers of good or poor prognosis but still again unproven
Nottingham prognostic index: it depends on pathological size of the tumor in
cms and node status as score 1 if no node is involved, score 2 if 1-3 nodes
are involved score 3 if four or more nodes are involved. And also depend on
grade of the tumor as score 1 if grade 1 and score 2 if grade 2 and score3 if
grade 3.
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
22-12-2015
8
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
Nottingham prognostic index= (0.2
×
size cm)+score node+ score grade
o Prognostic group value 10 year
survival %
o Excellent <2.4 94
o Good 2.4- <3.4 83
o Moderate 1 3.4-<4.4 70
o Moderate2 4.4-< 5.4 51
o Poor >5.4 19
Treatment of breast cancer : the two basic principles of treatment are to
reduce the chance of local recurrence and the risk of metastatic spread. The
treatment of early breast cancer will usually involve surgery with or without
radiotherapy. Systemic therapy such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy is
added if there are adverse prognostic factors such as lymph nodes
involvement, indicating a high likelihood of metastases relapse.
At other end of spectrum locally advanced or metastatic disease is usually
treated by systemic therapy to palliate symptoms with surgery playing a
much smaller role. Algorithm for management of breast cancer is shown in
summary as
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
22-12-2015
9
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
1) Achieve local control
2) Appropriate surgery include (a) wide local excision (clear
margin)+radiotherapy (b) mastectomy+\- radiotherapy immediate or
delayed. Combined with axillary procedure.
3) Treat risk of systemic disease by chemotherapy if prognostic factors are
poor and hormone therapy if estrogen and progesterone receptor are
positive.
Details of local treatment or early breast cancer: local control is achieved
through surgery and or radiotherapy. The aim of treatment is to
(1) cure: likely in some cases but late recurrence is possible.
(2) Control local disease in breast and axilla.
(3) Conservation of local form and function.
(4)Prevention or delay of occurrence of distant metastases.
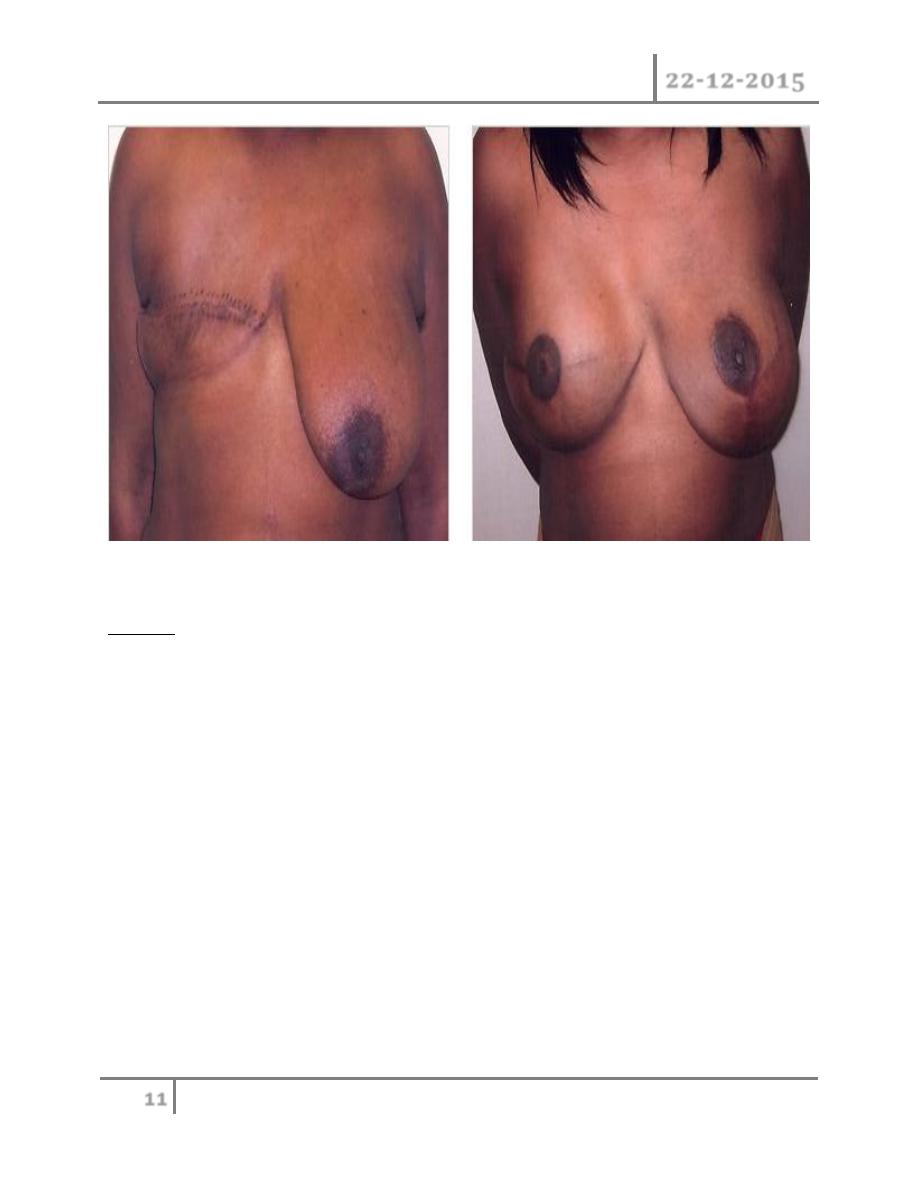
Surgery: still has central role to play in the management of breast cancer
but have been gradual shifts toward more conservative techniques, that
might show equal efficacy between mastectomy and local excision followed
by radiotherapy. It was initially hoped that avoiding mastectomy would help
to alleviate the considerable psychological morbidity associated with breast
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
22-12-2015
10
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
cancer but recent studies as has shown that over 30% of women develop
significant anxiety and depression following both radical and conservative
surgery .
After mastectomy women tend to worry the effect of operation on their
appearance and their relationship whereas after conservative surgery they
may remain fearful of recurrence. Mastectomy indicated for
(1) a large tumor in relation to size of the breast
(2) central tumor beneath or involving the nipple
(3) multifocal disease
(4) local recurrence
(5) patient preference.
Types of operation: the radical Halsted mastectomy including excision of
breast axillary lymph nodes + pectorals major and minor, this operation is
no longer preformed it cause excessive morbidity with no survival benefits.
The modified radical (Patey) mastectomy is more commonly performed by
preservation of pectorals major and division of pectorals minor. Simple
mastectomy, wide local excision.
Conservative breast surgery is aimed at removing the tumor plus a rim of at
least 1 cm of normal breast tissue this called wide local excision.
Lumpectomy is removal of benign lump. Quadrantectony involve removing f
entire segment of the breast that contains the tumor.
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
22-12-2015
11
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
END …
