
Baghdad College of Medicine / 4
th
grade
Student’s Name :
Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
Lec. 5
DISEASES OF BREAST
Thurs. 24 / 12 / 2015
DONE BY : Ali Kareem
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
2015 – 2016

Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
2
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
Diseases of Breast
Radiotherapy : it performs to the chest wall after mastectomy in selected
patient in whom the risk of local recurrence is high. This includes patient
with large tumor and those with large numbers of nodes or extensive lymph
vascular invasion. it improve survival in women with node positive breast
cancer. It is conventional to combine conservative surgery with
radiotherapy to remaining breast tissue. Recently radiotherapy can be given
intraoperatively at one sitting or as accelerated postoperative course.
Adjuvant systemic therapy : it was targeted at these putative
micrometastases that might expect to delay relapse and prolong survival for
about 30% relapse free. So women with hormone receptors positive tumors
will obtain worthwhile benefit from about 5 years of endocrine therapy,
either 20mg daily of tamoxifin if she premenopausal or newer aromatase
inhibitors as anastrazole (femara) or letrozole and exemstane if she is
postmenopausal. No need to give these drugs in hormone negative receptors
tumors.
Hormone therapy : tamoxifin (antiestrogen) is most widely used treatment
in breast cancer. It reduces the annual rate of recurrence by 25% with 17%
reduction in annual rate of death. It is also useful in reduce the tumor in
contralateral breast. Other hormone includes LHRH agonist (zoladex)
which induces reversible ovarian suppression and has beneficial effect as
surgical or radiation induced ovarian ablation in premenopausal receptor
positive tumor. It also used in recurrent tumor as it is superior on tamoxifin.
The third drug is aromatase inhibitor has benefit on relapse free and less
side effect.
Chemotherapy : first generation regime such as a six monthly cycle as
cyclophosamide, methotraxate and 5flurouracil all is called (CMF) it
reduces relapse by 25% over 10-15 years period. Modern regime include
anthrocycline (doxorubicin) and newer agent such as taxanes suitable for
premenopausal with poor prognosis. Recently it also given to
postmenopausal patients.

Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
3
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
Primary chemotherapy (neoadjuvant) : it is being used in many centers for
a large tumor but operable that requires mastectomy. The idea is to shrink
the tumor before surgery to enable breast conserving surgery to be
performed. Newer biological agent used frequently as molecular targets as
trastuzumab (herciptin) it is active against tumor containing growth
receptor c-erb2. Others as bevacizumab a vascular growth receptor
inhibitor, still is not widely used.
Follow up of breast cancer : she is followed for life to detect recurrence and
dissemination, so yearly or 2 yearly mammography of treated and contra
lateral breast. Ultrasound of breast and abdomen can also be used; tumor
marker is not routine checking for the patients.
Multidisciplinary team approach (MDT) : this team including surgeon,
medical oncologist , radiotherapist, and histopathologist also
physiotherapist and psychologist working together for treatment decisions in
breast cancer. This has been shown good for the patient to achieve good
treatment
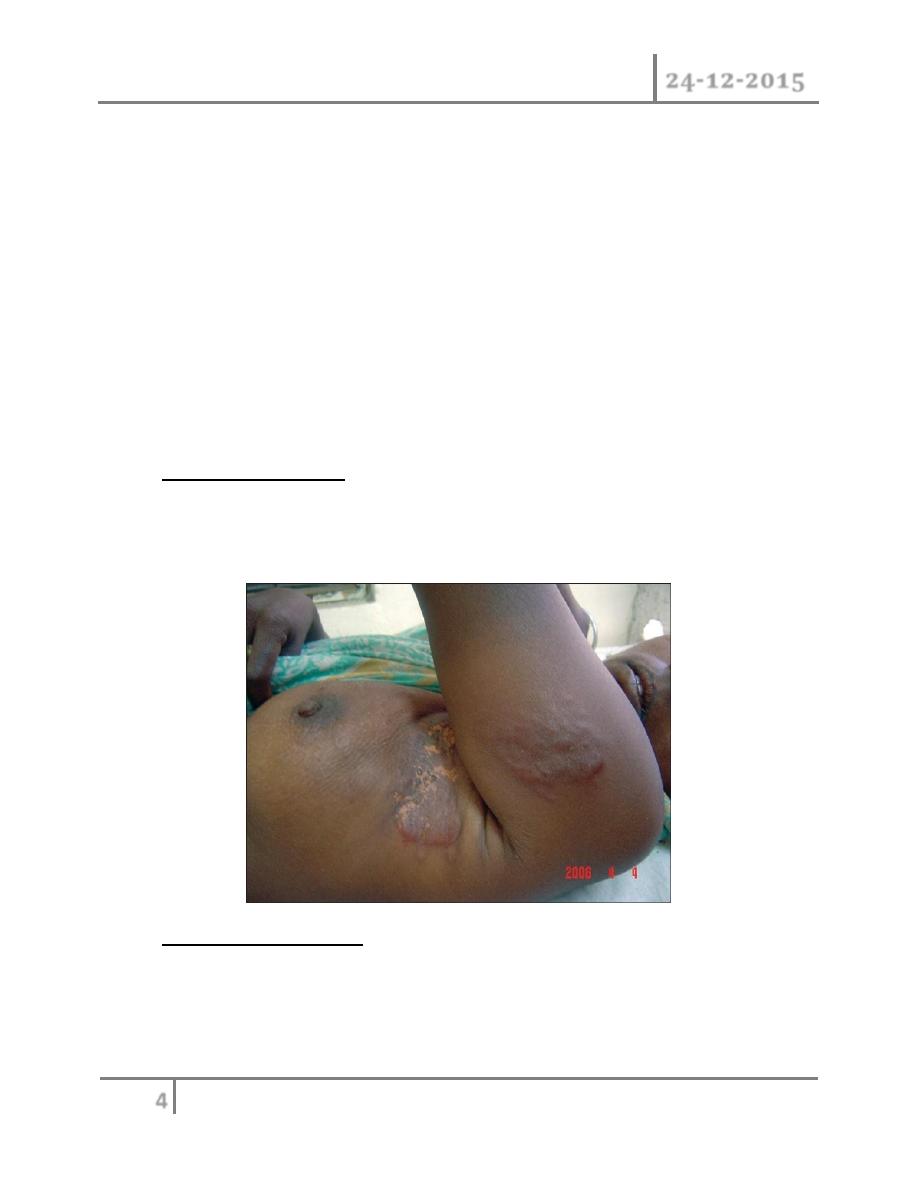
Phenomena resulting from lymphatic obstruction in advanced and breast
cancer:
peau d'orange : caused by coetaneous lymphatic edema when the infiltrated
skin is tethered by the sweat ducts .it cannot swell leading to appearance
like orange skin. it also seen in chronic abscess . late edema of the arm in
troublesome complication of breast cancer threats .fortunately seen less
often now that radical axillary dissection and radio therapy are rarely
combined .
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
4
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
it might appears at any time from months to years after treatment .there is
usually no precipitating cause but recurrent tumors should be excluded
because infiltration block both lymphatic and venous .edematous limb is
susceptible for bacterial infection following quite minor trauma and this
requite vigorous antibiotics .treatment of limb edema is difficult but limb
elevation, elastic arm stocking and pneumatic compressive devices can be
useful.
cancer-en-cuirasses:- the skin of the chest is infiltrated with carcinoma and
has been likened to coat ,it may be associated with grossly swollen arm .it
usually occurred with local recurrence of the mastectomy and following
irradiation to the chest wall .it has poor prognosis.
Lymphangiosarcoma : is rare complication of lymphadema with an onset
many years after the original treatment it take form of multiple
subcutaneous nodule in the upper limb and must be distinguish from
recurrent tumor .it has poor prognosis.
o Familial breast cancer : recent development in molecular genetics and the
identification of number of breast cancer predisposition gene (BRCA,
BRCA2, P53) have done much to stimulation interest in this area .yet women
whose breast cancer is due to inherited genetic change actually account for
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
5
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
less than 5% of all cases of breast cancer . These women have a risk of
developing breast cancer that in 2-10 times above baseline .
o Pregnancy and breast cancers : breast cancer presenting during pregnancy
or lactation tends to be at late stage ,presumably because the symptoms are
masked by the pregnancy ,however in other respect it behaves in similar
way to the breast cancer in non pregnancy women .treatment is similar with
some modification ,radiotherapy should be avoided ,chemotherapy is not
used in first trimester but appears safe subsequently ,most tumors are
hormone receptor negative and so hormonal treatment which is potentially
teratogenic is not required . For women they have breast cancer, they
should wait for 2 years before be pregnant as it is within this time that
recurrence most often occurs.
Benign breast disorder
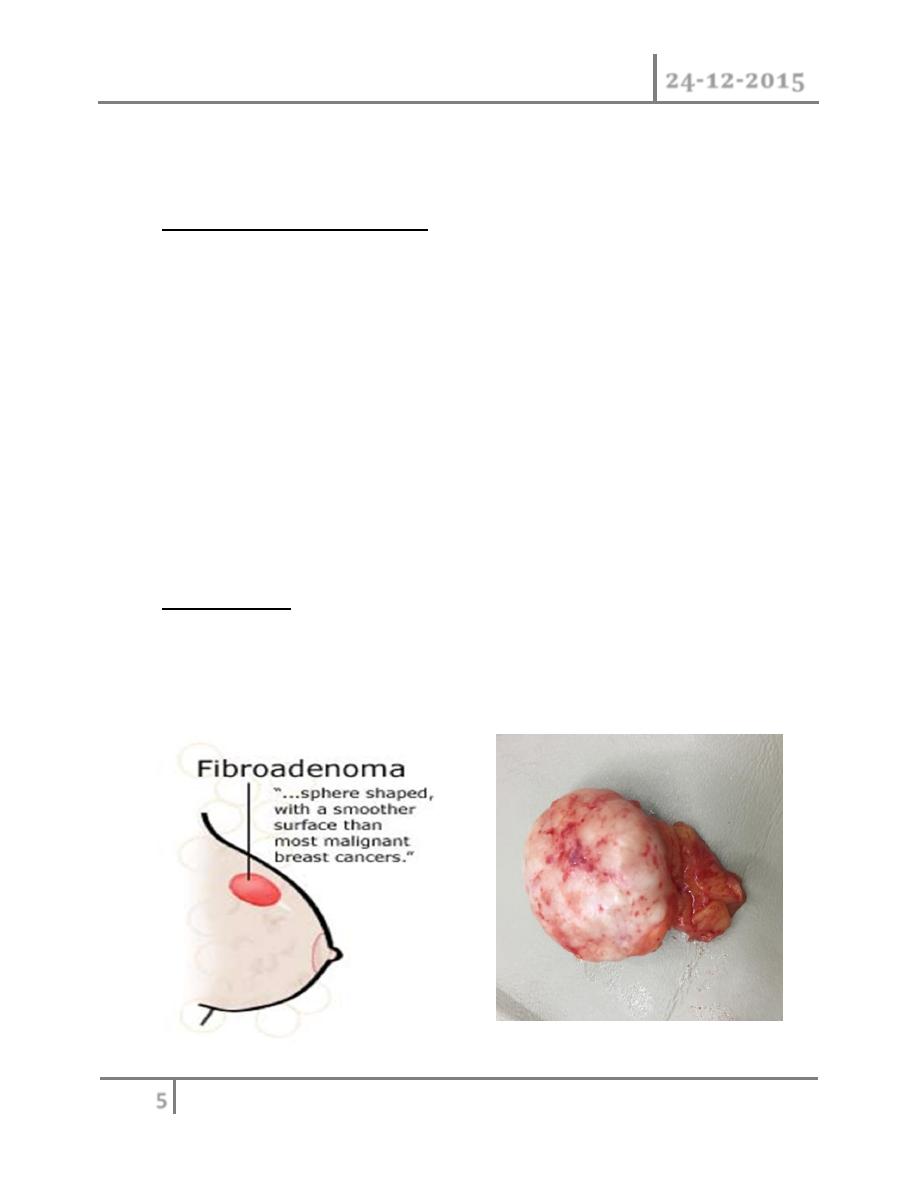
Fibroadenoma : this is usually arise in the fully developed breast between
the age of 15-25 years although occasionally they occur in much older
women .they arise from hyperplasia of single lobule and usually grow up to
2-3 cm in this case ,they surrounded by well marked capsule and can thus be
enucleated through cosmetically appropriate incision
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
6
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
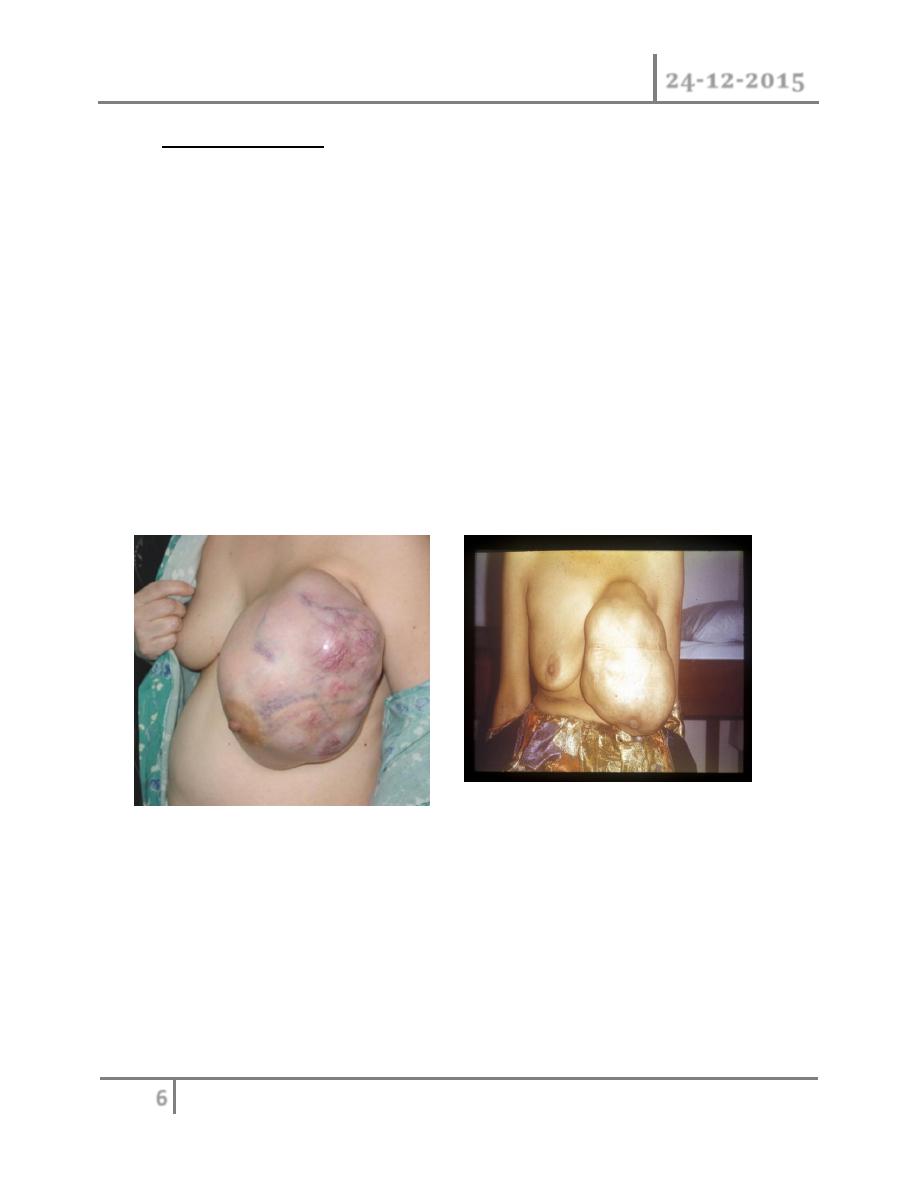
Phyllodes Tumors : these benign Tumors previously sometimes known as
serocystic disease of Brodie or cystosacroma phyllodes, usually occur in
women over the age of 40 years ,but can appear in younger women. They
present as large, sometimes massive, tumor with unevenly bosselated
surface, occasionally ulceration of over lying skin occurs because of
pressure necrosis, despite their size they remain mobile on the chest wall.
fibroadenoma does not require excision unless associated with suspicious
cytology ,it becomes very large or the patient expressly desire the lump to be
removed .Giant fibroadenoma occasionally occur during puberty they are
over 5cm in diameters and are often rapidly growing but in other respects
are similar to smaller fibroadenoma and can be enucleated through
submammary incision .
Histologically there is a wide variation in their appearance with some of
low malignant potential resembling a fibroadenoma and others having
mitotic index which histologically worrying, the latter may recur locally but
despite the name of cystosaroma phyllodes, they are rarely cystic and only
very rarely develop features of sarcomatous Tumor . These may metastases
via blood stream. Treatment for benign type is enucleation in young women
or wide local excision. Massive Tumor, recurrent tumors and those of the
malignant type will require mastectomy.
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
7
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
Galactocele : is rare, usually present as a solitary, subareolar cyst and
always dates from lactation , it contain milk and in longstanding cases its
wall tend to calcify .
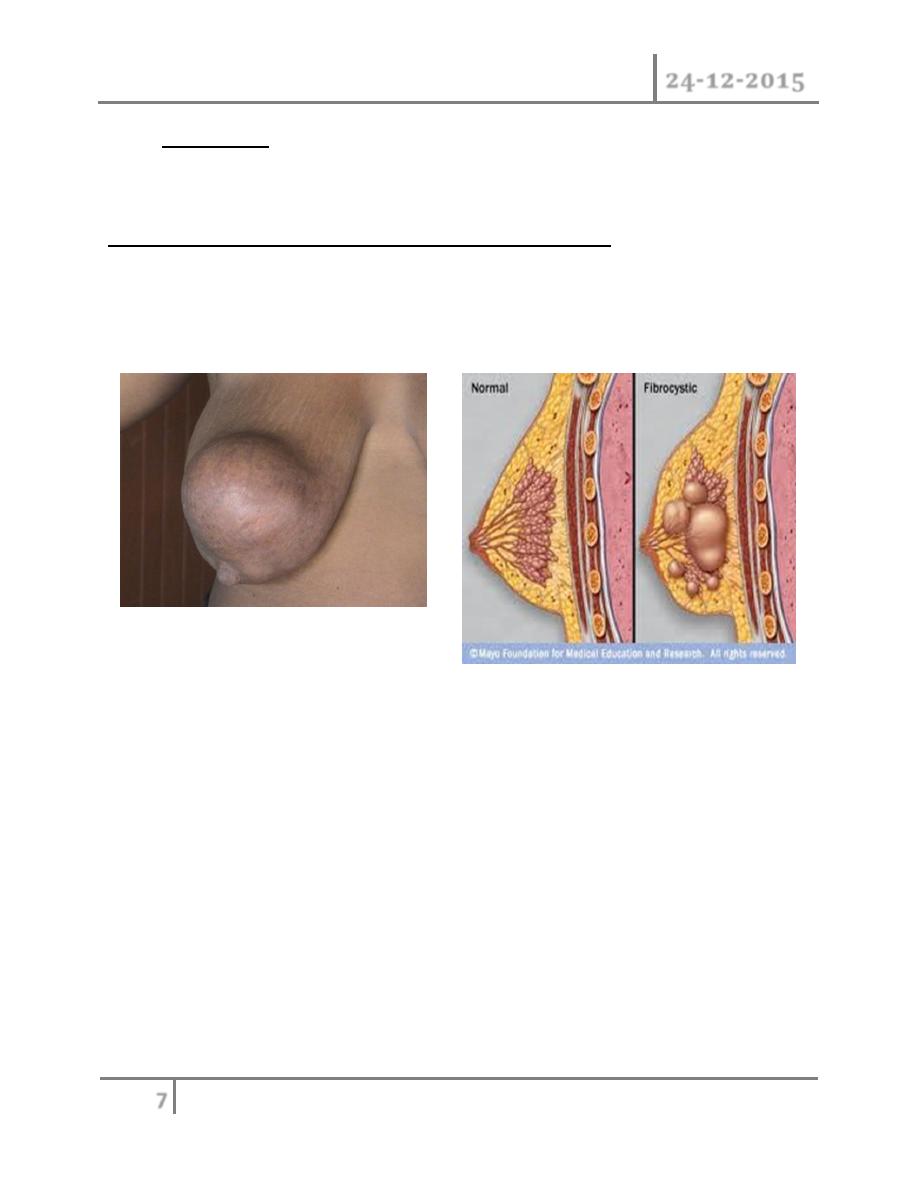
Aberration of normal development and involution (ANDI)
Nomenclature: the names are confusing. The name (ANDI) has been
applied to this condition including fibrocystic disease, fibroadenosis,
chronic mastitis and mastopathy.
Etiology: the breast is a dynamic structure that undergoes changes
throughout a women's reproductive life and superimposed up on this ,
cyclical changes throughout the menstrual cycle, the pathogenesis of ANDI
involve the disturbance in the breast physiology extending from perturbation
of normality to well defined disease process. There is little correlation
between the histological appearance of the breast and symptoms. Pathology
of the breast consists essentially of four features that may vary in extent and
degree in any one breast.
(1) Cyst formation (variable in size),
(2) fibrosis: fat and elastic tissue disappear and replaced with dense white
fibrous trabeculae, the interstitial tissue is infiltrated with chronic
inflammatory cell
(3) Hyperplasia of epithelium in the lining of the ducts and acini may

Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
8
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
occur with or without atypia.
(4) Papillomatosis: the epithelium hyperplasia may be so extensive that it
results in papillomatous overgrowth within the ducts.
Clinical features: the symptoms of ANDI are may as the term is used to
encompass a wide range of benign conditions, but often include an area of
lumpiness (seldom of discrete) and/or breast pain ( mastalgia )A benign
discrete lump in the breast is commonly a cyst or fibroadenoma . The true
lipoma occurs rarely. Lumpiness may be bilateral commonly in the upper
outer quadrant or less commonly confined to one quadrant of the breast.
The changes may be cyclical with an increase in both lumpiness and often
tenderness before menstrual period. Non cyclical mastalgia is more common
in peri menopausal than post menopausal women. it should be distinguish
from referred pain due to musculoskeletal disorder . Breast pain in post
menopausal women not taking hormone replacement therapy is usually
derived from the chest wall. About 5% of breast cancers exhibit pain at
presentation.
Treatment of lumpy breast: if the clinician is confident that she is not
dealing with discrete abnormality and clinical confidence is supported by
mammography and or ultrasound scanning if appropriate, then initially the
women can be offered firm reassurance. It is worth while reviewing the
patient at a different point in menstrual cycle for example 6 weeks after
initial visit and often the clinical signs will have resolved by that time.
There is tendency for women with lumpy breasts to be rendered un
necessarily anxious and to be submitted to multiple biopsies because the
clinician lacks courage of lies or conviction. treatment of mastalgia :- Rx
recommended of the pain interfere with women's life ,disturb her sleep and
impair sexual activity ,initially firm reassurance that the symptoms are not
associated with cancer will help the majority of the women .
acknowledgement that this is a real symptom , non dismissive attitude and
an explain of etiology are all helpful in managing the conditions .in first
instance , an appropriately fitting and supportive bra should be worn
throughout the day and a soft bra ( such as sports bra ) worn at night .
Avoiding caffeine drinks is said to be help. A patient symptoms diary helps
her to chart the pattern of pain throughout the month and determine whether
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
9
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
this is cyclical mastalgia. If these measures are not enough in treatment with
evening primrose oil (it is Gammalinolenic acid metabolized to anti
inflammatory prostaglandin) adequate dose given over 3 months will help
more than half of these women, it appears to achieve higher response rates
in those over 40 years of age rather than younger age. For those of
intractable pain, antigonadotrophin drug such as danazol cap 200mg, or
prolactin inhibitor (parlodel tab promocriptin) may be tried. Very rarely it is
necessary to prescribe anti estrogen for example tamoxifin or LHRH agonist
to deprive the breast epithelium of estrogenic derives.
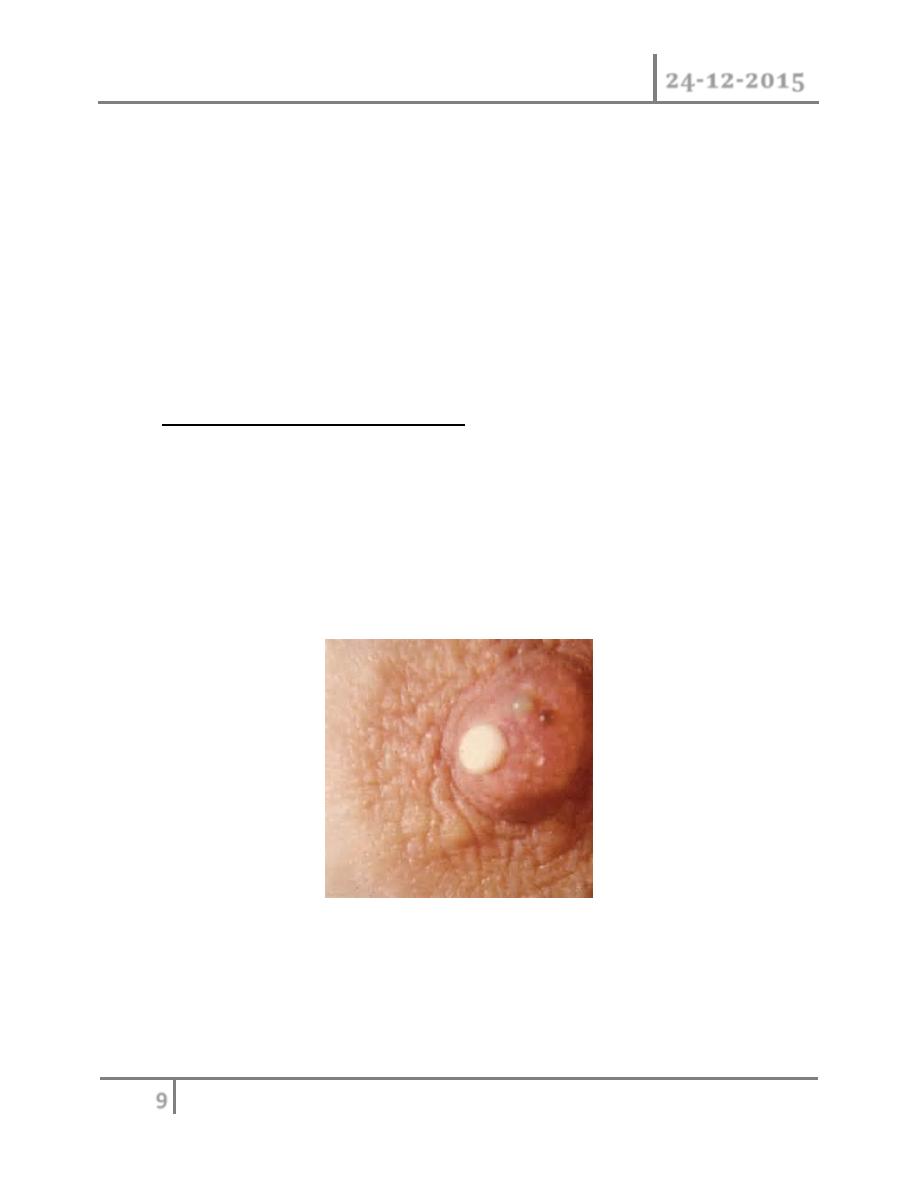
Duct ectasia : ( periductal mastitis) : pathology. this is dilatation of the
breast ducts which is often associate with periductal inflammation . the
pathogenesis is obscure and almost certainly not uniform in all cases.
Although the disease in much more common in smokers. it is dilatation in
one or more of the larger lactiferous ducts which fill with a stagnant brown
or greenish secretion , this may discharge .these fluids then set up an
irritant reaction in surrounding tissue leading to periductal mastitis or even
abscess and fistula formation.
In some cases a chronic indurations has forms .beneath the areola, which is
mimes as carcinoma .fibrosis eventually develops which cause may slit like
nipple retraction. Some believes it is anaerobic bacterial infection and
smoking causing arteriopathy. Clinical features: nipple discharge of any
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
10
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
color, subareolar mass, abscess, mammary duct fistula and nipple retraction
are most common symptoms.
Treatment : in case of a mass or nipple retraction carcinoma must be
excluded by obtaining mammography and negative cytology or histology.
Any suspicion should be excised. Antibiotics should be tried co-amoxiclav or
flucloxacillin and metronidazole. Surgery is often the only option likely to
bring about cure of this condition; this consists of excision of all major ducts
(Hadfield's operation). It is particularly important to shave the back of the
nipple to ensure that all terminal ducts are removed, failure to do so will
lead to recurrence.
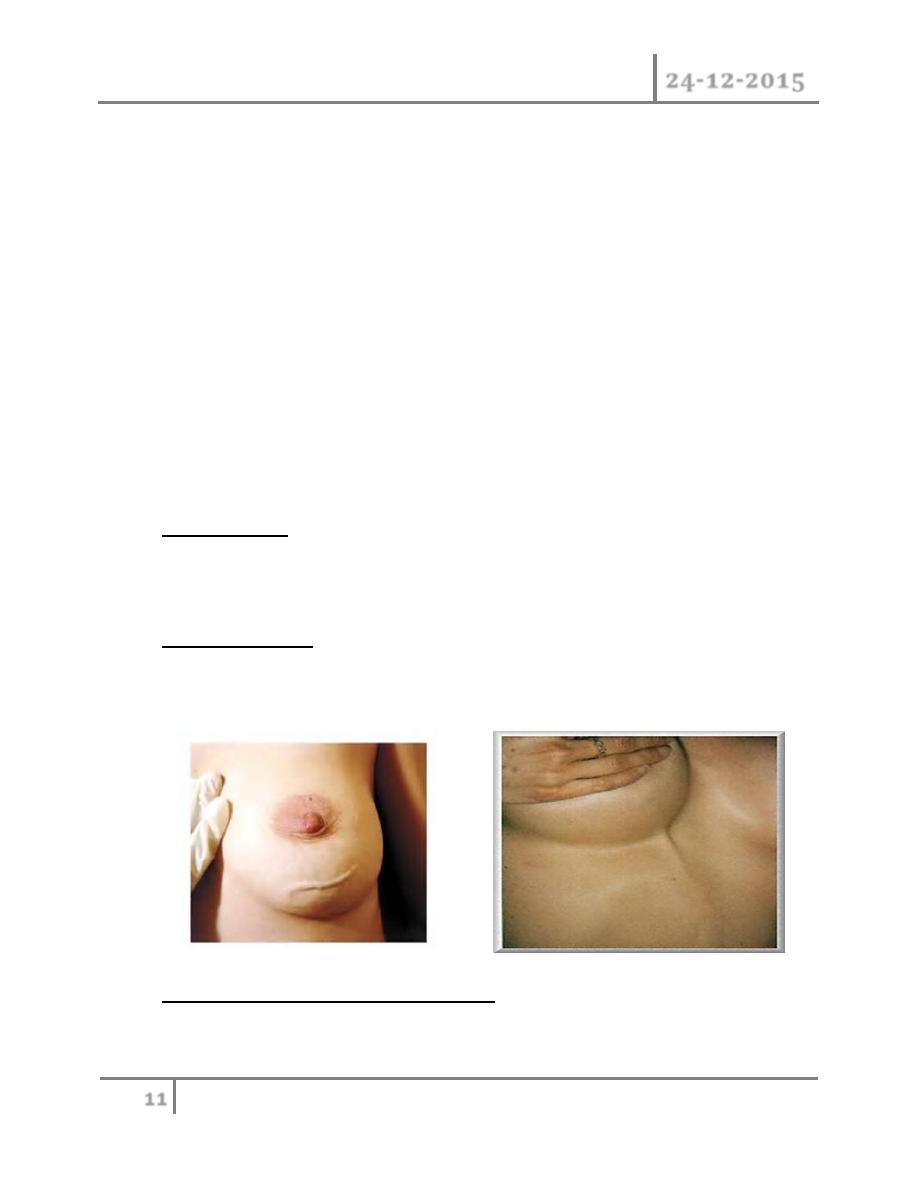
Bacterial mastitis : it is the most common variety of mastitis and is
associated with lactation in majority of the cases. Etiology: lactational
mastitis is seen less frequently than previously. Most of the cases caused by
staph, infective from the hospital or from infants who 50% of them harbor
staph in their nasopharynx. Although ascending infection from a sore and
cracked nipple may initiate mastitis, in many cases the lactiferous ducts will
first become blocked by epithelial debris leading to stasis, this theory is
supported by relatively high incidence of mastitis in women with a retracted
nipple.
Once within ampulla of the duct, staph. cause clotting of the milk and with
clot bacteria multiply. Clinical features: classical signs of acute
inflammation (pain, fever, rigor, edema, erythema, tender swelling) and
start as general cellulitis end by abscess formation. Treatment: during
Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
11
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
cellulitis stage patient should be treated by appropriate antibiotics as
flucloxacillin or amoxiclav.
Feeding from the affected breast side may continue if the patient can do,
local heat and analgesia will help to relieve pain. If an antibiotic is used in
presence of undrained pus an antibioma may form. This is large, sterile,
brawny edematous swelling that take many weeks to resolve.
It is used to recommended that the breast should be incised and drained if
the infection did not resolve within 48 hours or if after being emptied of milk
there was an area of tense indurations or other evidence of underlying
abscess, this advice has been replaced with recommendation that repeated
aspiration under antibiotics cover and ultrasound guide be performed. This
often allows resolution without need foe incision scar and also allows
carrying on breast feeding.pus should be sending for culture and sensitivity.
Breast abscess : if there is lactational abscess and marked skin thinning
drainage can be done under local or general anesthesia. Drainage is done
by opening all loculi by removing septi between loculi to make one room or
loculi, with this procedure we ensure we draining the entire abscess.
Mondor's disease : it is superficial thrombophlibitis of superficial veins of
the breast and anterior chest wall, it appears as subcutaneous cord. It
should be distinguish from cancer permeation.
Congenital abnormalities of the breast : amazia: congenital absence of the
breast on one or both sides, it might be associated with absence of pectorals

Diseases of Breast Dr. Tariq Al-Obaidi
24-12-2015
12
©Ali Kareem 2015-2016
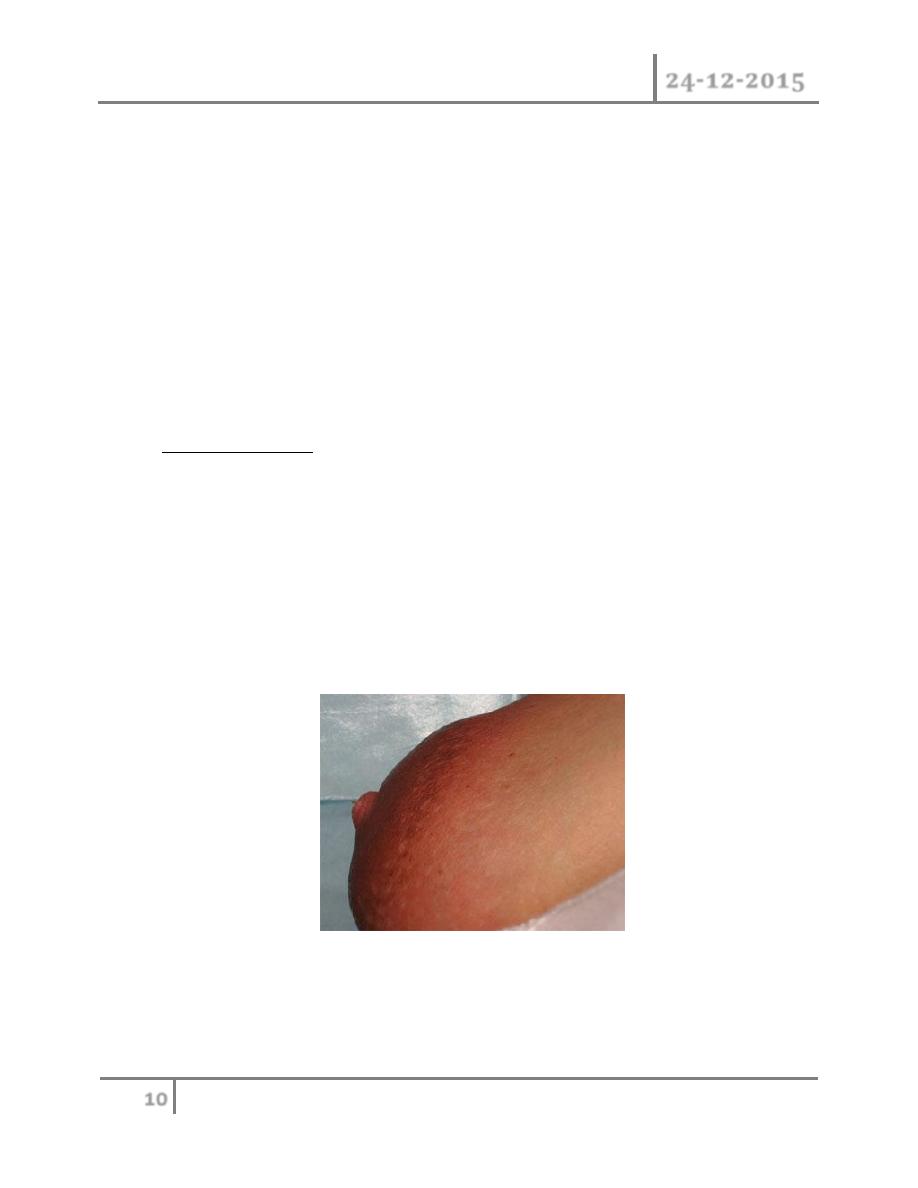
major or absence of the nipple. Polymazia: accessory breast has been
recorded in axilla most often, buttock and thigh.
Mastitis in infant : equal in boys and girls and usually in 3
rd
or 4
th
day of
life, if pressed lightly a drop of colorless fluid can be expressed or milky
secretion and usually disappear at 3
rd
week , this called witch's milk. It
caused by stimulation of the fetal breast by prolactin in response to drop in
maternal estrogen and it essentially physiological, mastitis usually due to
staph. aurous.
END …
