
by
Dr. Ammar Tlib Al-yassiri

objectives
definition
Epidemiology
Pathophysiology
Classification
Prevention
management

Definition
The complications of longstanding diabetes mellitus
which often appear in the foot and, causing chronic
disability.

Epidemiology
More than
30%
of patient attending diabetic
clinics have evidence of peripheral neuropathy or
vascular disease
about
40%
of non-trauma related amputations are
for complications of diabetes
.
nearly
one in six
patients
die
within
one year
of
their infection

Pathophysiology
Factors predisposing diabetic patients to developing
:
diabetic foot are
1.Peripheral vascular disease
2.damage to the peripheral nerves
3.Reduced resistance to infection,
4. Osteoporosis

Peripheral vascular disease
atheroseclerosis
affects mainly the
medium sized
vessels
below the knee
The pt. may complain of claudication or ischemic
changes and ulceration in the foot.
The skin feels smooth and cold the nails show trophic
changes .
pulses are weak or absent
Superficial ulceration occurs on the toes
deep ulceration typically under the heel these ulcers
are painful and tender

Digital vessels occlusion may cause dry gangrene of
one or more toes.
proximal vascular occlusion resulting in extensive wet
gangrene.

:
Peripheral neuropathy
early on the pt usually unaware of the abnormality but
clinical tests will discover
loss of vibration and position sense and
diminish of temperature
Diminish of discrimination in the feet

Symptoms : mainly due to
sensory impairment:
symmetrical numbness and parasthesia,
dryness and blistering of the skin,
superficial burns and skin ulcers due to shoe scuffing or
localized pressure
Motor loss:
muscle weakness and intrinsic muscle imbalance
usually manifests as claw toes with high arches and
this may in turn predispose to plantar ulceration.

Neuropathic joint disease (Charcot joints)
it is chronic, progressive, destructive process affecting
bone architecture and joint alignment in people
lacking protective sensation.
the mid tarsal joints are most commonly affected
followed by the MTP and ankle joints
There is usually provocative incident such as a twisting
injury or a fracture following which joint collapses
relatively painlessly
In late cases there may be severe deformity and loss of
function. A rocker-bottom deformity from collapse of
mid foot is diagnostic.

Osteoporosis
there is generalized loss of bone density in diabetes.
In the foot the changes may be severe enough to result in
insufficiency fractures
around the ankles and or in the
metatarsals.

Infections
diabetes, if not controlled is known to have
adverse effect on the white cell function.
This combined with the
local ischemia,
insensitivity to skin injury and
localized pressure due to deformity,
makes sepsis an ever recurring hazard.

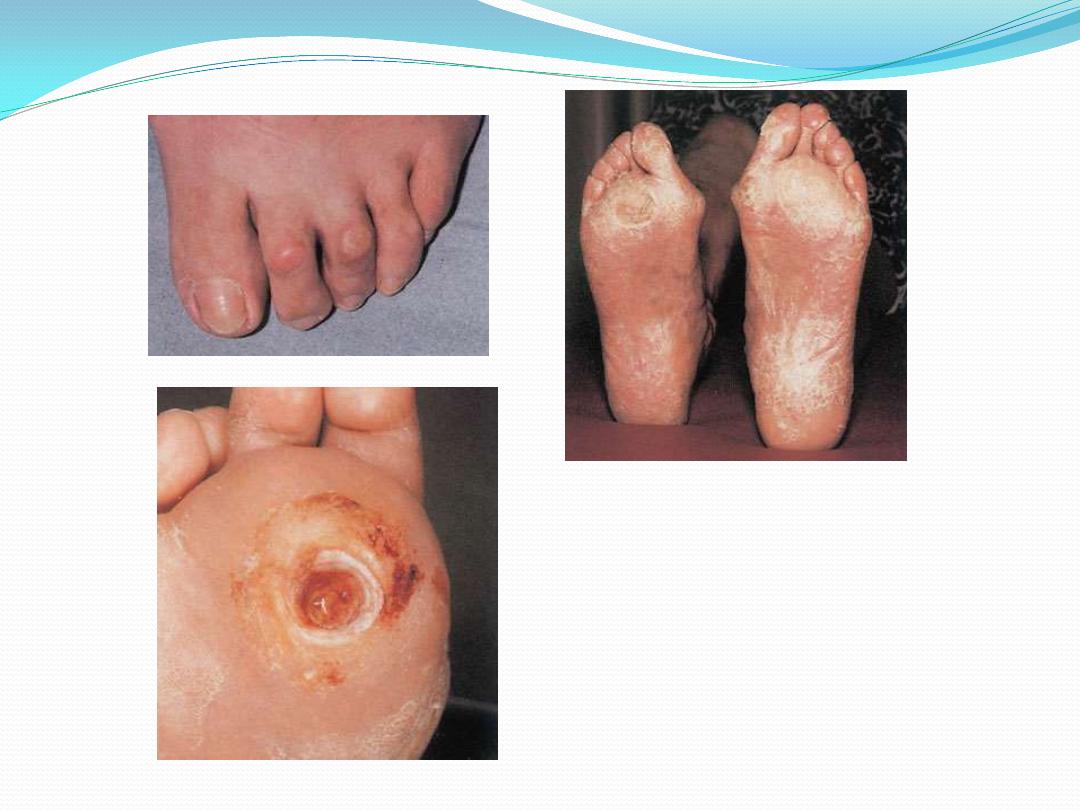
Classification
Diabetic foot
infection
may be classified as:
superficial: often associated with ulceration.
Deep infection: may involve
soft tissues only with abscess formation or
can involve bones (osteitis or osteomylitis). This type of
infection can also involve local joints (pyogenic
arithritis).

Wagner classification system
most widely used and universally accepted grading
systems for DFU
used to assess ulcer depth
0 Pre-ulcerative area without open lesion
1 Superficial ulcer (partial/full thickness)
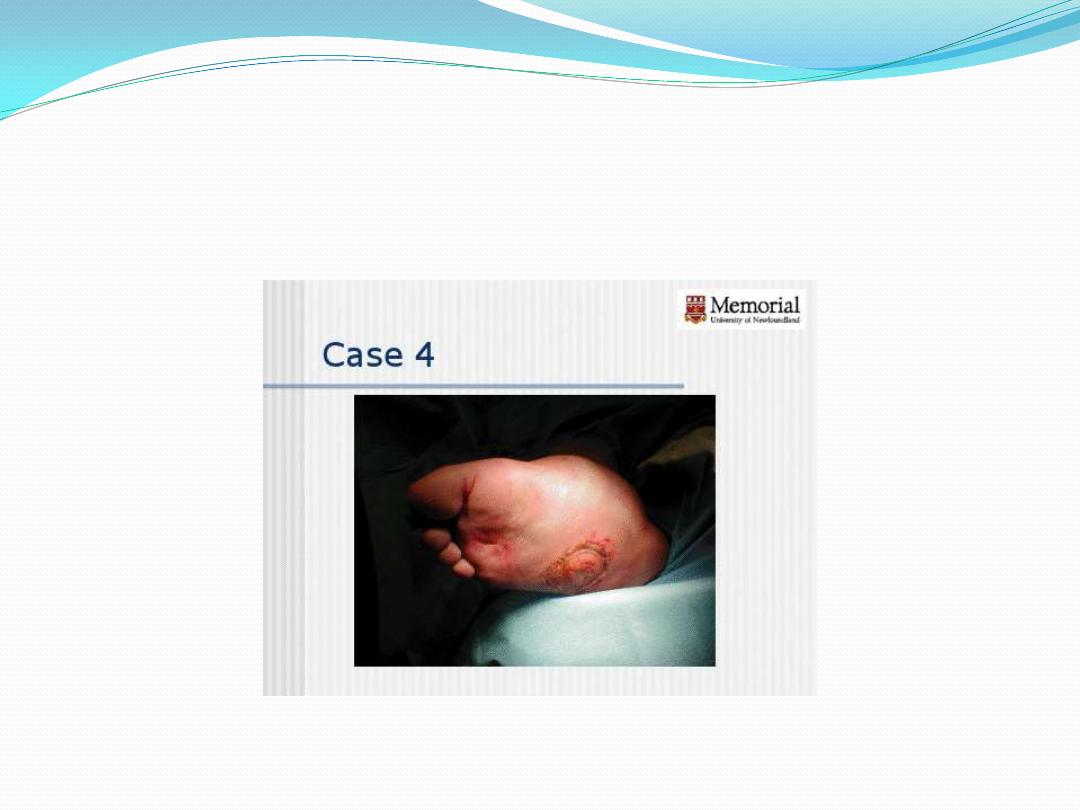
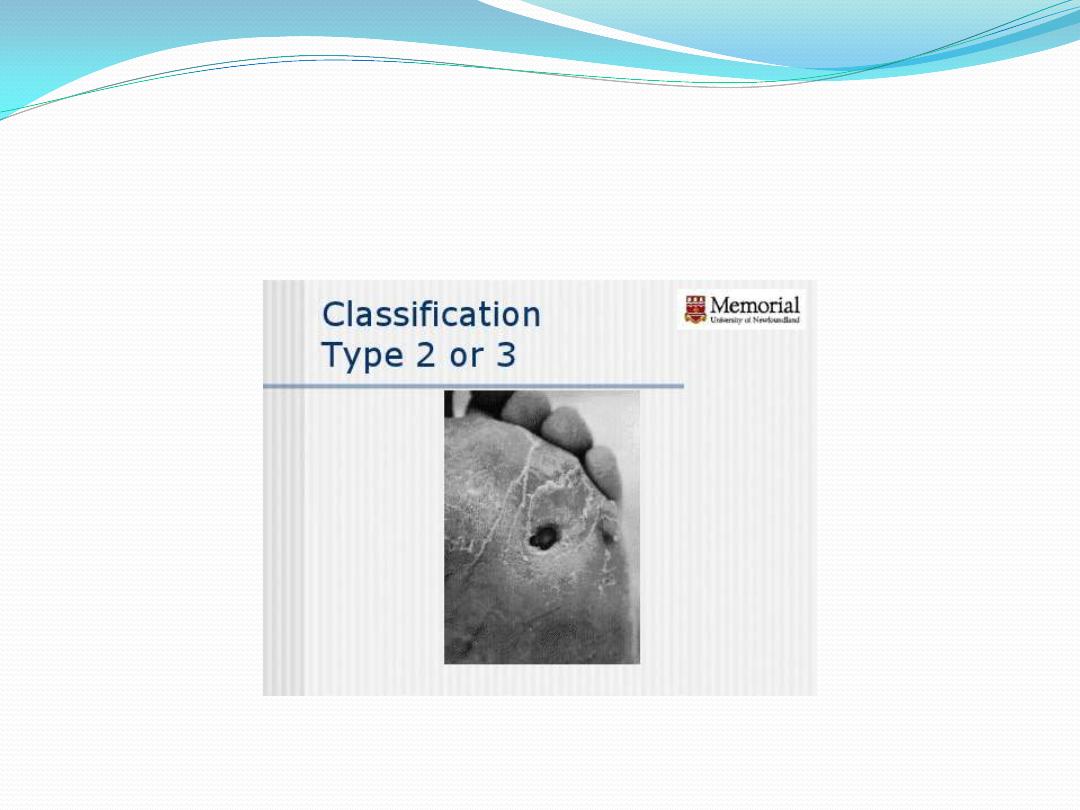
2 Ulcer deep to tendon, capsule, bone
3 Stage 2 with abscess, osteomyelitis or joint sepsis
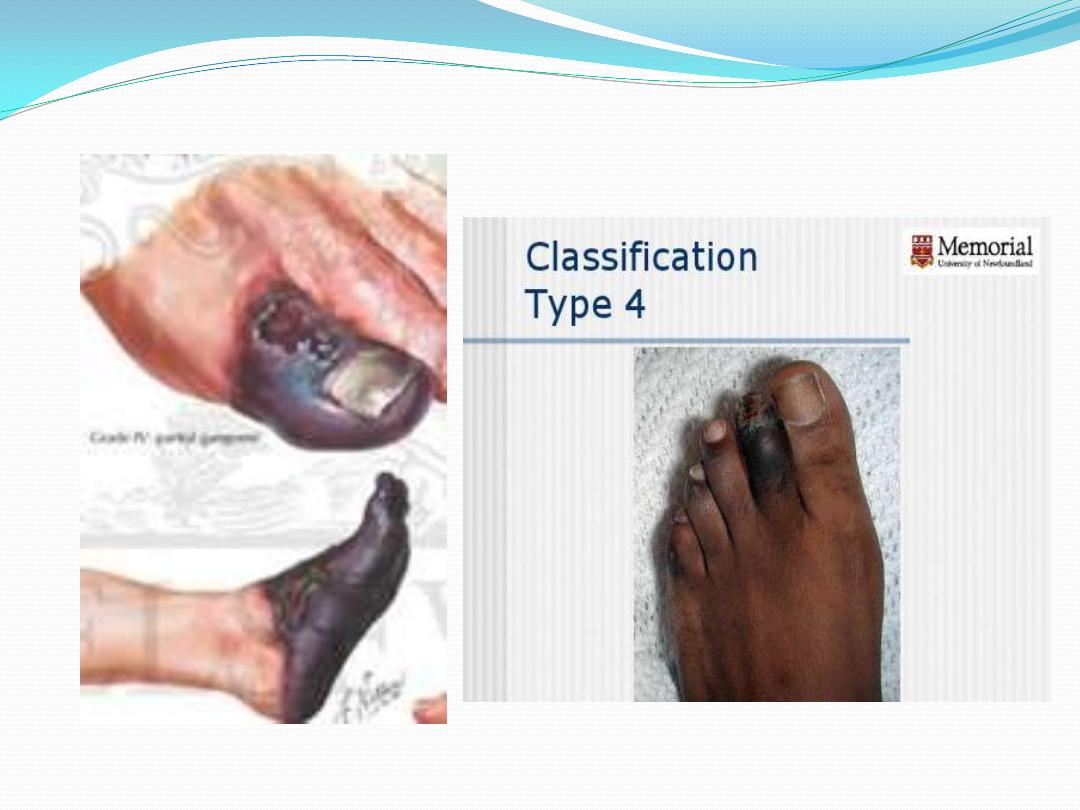
4 Localized gangrene
5 Global foot gangrene.

Prevention:
insist on regular attendance at a diabetic clinic.
full compliance with medication
examination for early signs of vascular or neurological
abnormality.
advice on foot care and footwear and a high level of
skin hygiene.

Foot care for the at risk patients
:
To do list
*Inspect the foot daily using a mirror to see the sole and
don’t forget between the fingers.
*Wash feet daily
*Apply lotion to avoid skin cracks and if present skin
cracks should be kept clean and covered
*Use a comfortable shoe wear and change it often
*Inspect shoes before wearing it from inside and outside.
*Great care is needed with nail trimming

:
Not to do list
* Smoking
*Step into bath tub without checking the temperature of
the water.
*use hot water bottles or heating pad.
*use keratolytic agent to treat the calluses or corn.
*Wearing a tight shoes or stocking.
*walking with barefeet

Management of diabetic foot
For the management of diabetic foot there should be a
multidisciplinary team
comprising
a physician (or endocrinologist) ,
orthopaedic surgeon,
General surgeon,
chiropodist and orthotist

Evaluation of diabetic foot patient
:
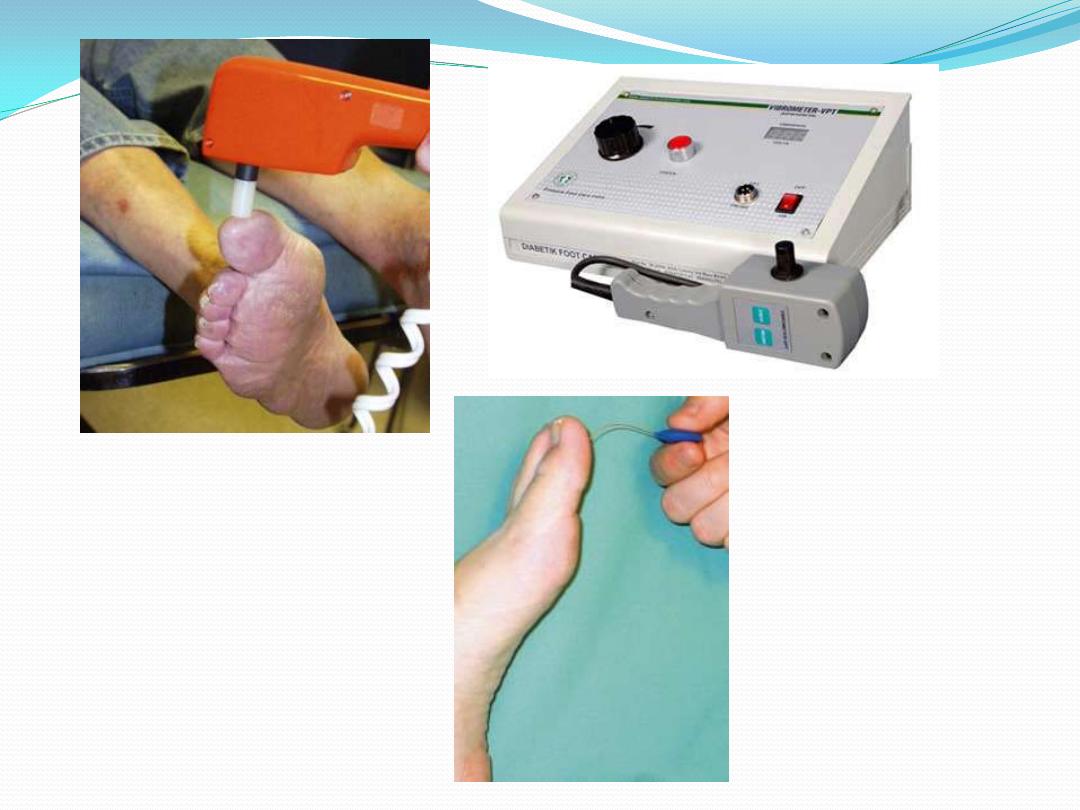
Peripheral neuropathy
Sensory: Examination for early signs of neuropathy
should include the use of
Semmes-Weinstein hairs (for testing skin sensibility)
Biothesiometer (for testing vibration sense),
Thermal discrimination test,
And joint position sense.
Motor: examine for wasting, weakness, absent or
diminished tendon reflex, and deformities (claw toes,
hammer toes, pes cavus). This can be enhanced by the
EMG & N/C study.

: examine for
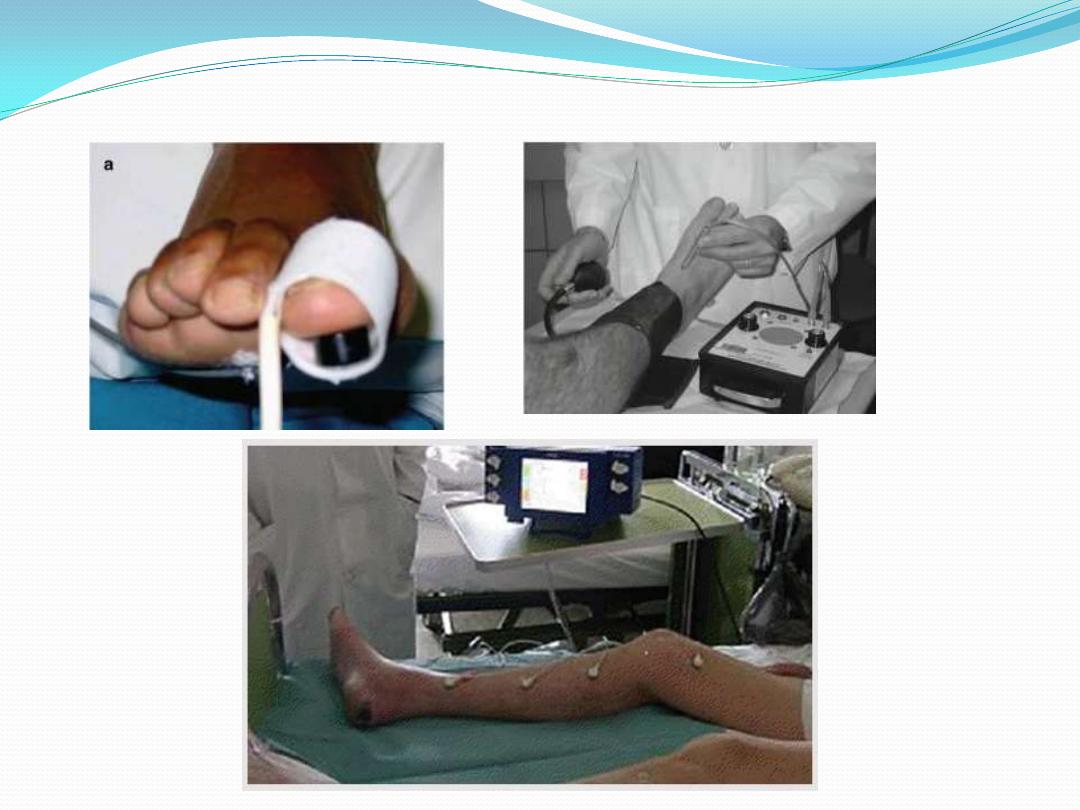
Peripheral vascular damage
the pulses,
skin temperature,
trophic changes in the skin and nails
Peripheral vascular examination is enhanced by using
Doppler ultrasound probe,
ankle brachial index measurement,
Absolute toe pressure,
transcutaneous oxygen measurement,
angiography.
:
Infection
the local and systemic signs of infection.
Ulcers must be swabbed for infecting organisms.
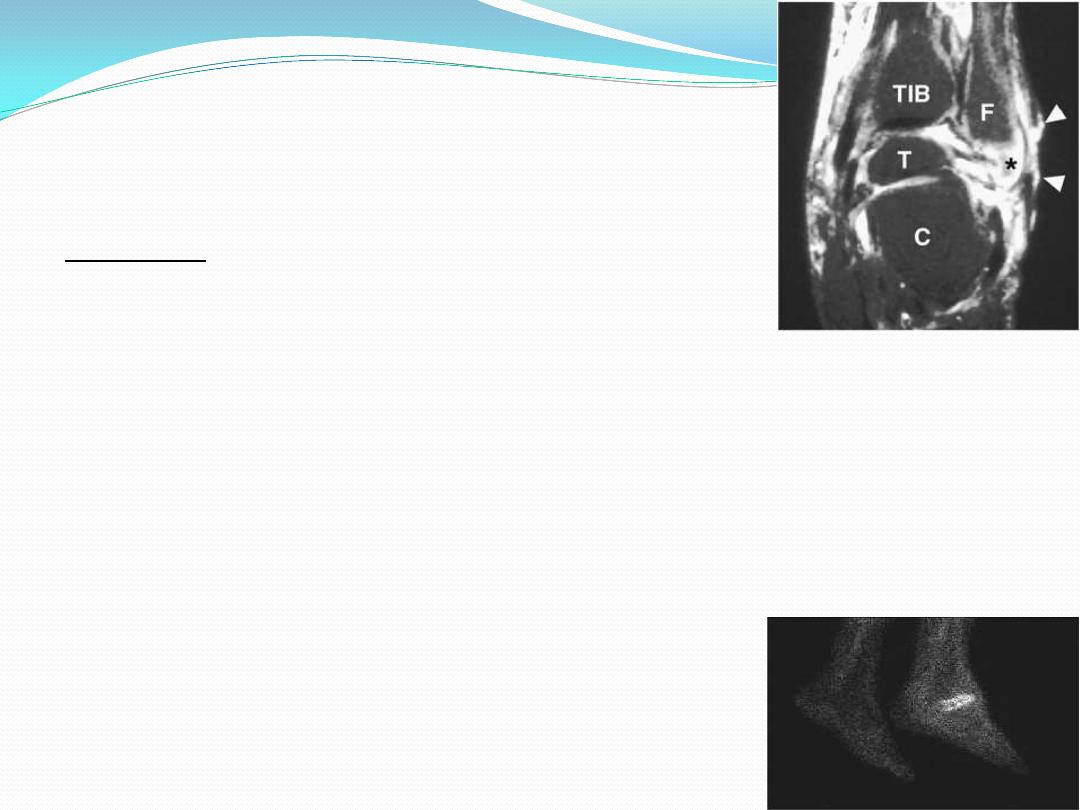
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most specific
and sensitive non-invasive test to evaluate
Osteomyelitis
probable abscess
sinus tract formation.
Bone scans, such as the white blood cell labeled Indium-111,
Technetium-99m HMPAO and Sulfur Colloid Marrow Scan,
distinguishing acute and chronic infections,
identifying OM from Charcot neuroarthropathy

Osteopathy:
Examine for Charcot deformities
flatening of the foot arches,
rocker-bottom deformity,
prominent metatarsl heads.
X-ray examination may reveal
periosteal reactions,
osteoporosis,
cortical defects near the articular margins and
osteolysis - often collectively described as 'diabetic osteopathy

Laboratory investigations :
WBC elevated in 50% of patients.
renal function,
electrolytes,
acidosis,
blood glucose level.
Hemoglobin A1C levels provide a barometer of glycemic
control averaged over the previous 2-3 months.
Acute phase reactants ESR &CRP (baseline and post-
treatment CRP, ESR and WBC were significantly elevated
in patients who ultimately required amputation).
Total serum protein and albumin→nutritional status.

treatment
According to wagner classification:
Grade 0 (skin intact): calluses should be trimmed so as not
mask active ulcer, advise the patient how to do daily foot
care and apply the preventive measures.(extra depth shoes
and pressure relieving insole)
Grade 1&2(superficial & deep ulcer but without infection ):
the aim here is to heal the skin, after desloughing the ulcer
and removing the hyper keratotic skin the ulcer can be
dressed locally, the application of a skin - tight POP(total
contact cast) changed weekly will allow most of the ulcers
to heal. It also allows the patient to be mobile

Grad 3 (grade2 with infection):
deep infection without abscess formation can be treated
by strict rest, elevation, soft tissue support and AB.
Occasionally, septicemia calls for admission to
hospital and treatment with intravenous antibiotics.
Any form of abscess formation needs to be drained
urgently and the deeper tissues thoroughly debrided.
Deep ulcers in certain sites are more problematic than
elsewhere . Once an ulcer is healed the use of
appropriate insoles and shoes can prevent further
ulceration.

Grade 4(localized gangrene):
Ischaemic changes need the attention of a vascular surgeon
who can advise on ways of improving the local blood supply.
Arteriography may show that bypass surgery is feasible.
Dry gangrene of the toe can be allowed to demarcate before
local amputation.
With diabetic gangrene septic arithritis is not uncommon ,
the entire ray(toe+metatarsal bone ) should be amputated.
In More extensive gangrene partial foot amputation done e.g.
through the midtarsal joints(Chopart),thruogh
tarsometatarsal joints(lisfranc), thruogh metatarsal bone,
syme’s amputation

Grade 5(Global foot gangrene) :
severe occlusive disease with wet gangrene may call for
immediate amputation.
This should be undertaken at a level where there is a
realistic chance of the wound healing.

Treatment of special problems
Ischaemic changes : need the attention of a vascular
surgeon who can advise on ways of improving the local
blood supply. Arteriography may show that bypass
surgery is feasible.
Insufficiency fractures: should be treated, if
possible, without immobilizing the limb; or, if a cast is
essential, it should be retained for the shortest
possible period.
Fixed foot deformities : corrective surgery should be
considered.

Neuropathic joint disease : is a major challenge.
Arthrodesis is fraught with difficulty,
very poor union rate,
sometimes is simply not feasible.
'Containment'
of the problem in a weight-relieving
orthosis may be the best option.

Home message
Diabetic foot is the complications of longstanding
diabetes mellitus.
common problem and can lead to serious
consequences.
Four major predisposing factors: ischemia,
neuropathy, immunopathy and osteopathy.
insist on regular attendance at a diabetic clinic and
apply preventive measures.
multidisciplinary team is required
for the
management of diabetic foot.
