
Intestinal
Obstruction
Dr Aqeel Shakir Mahmood
Assistant Professor
Consultant General and Laparoscopic Surgeon
FRCS
–( London)

Today we will be talking about intestinal obstruction
Definition
Review of Basics
History and Examination
Differential Diagnosis
Investigation
Fluid prescription
Clinical algorithm

Definition
Clinical condition
,
Due to; failure of the intestine small or large to pass
gas, liquid and solid material
.

Review of the Basics
Pathophysiology
The 3 pains / The 3 guts
Causes

Intestinal Obstruction; Pathophysiology
Blocked Lumen
Distension (solid, liquid, gas); Pain, vomit,
constipation
Increased Wall tension; Perforation
Ischaemia
Closed and Open loops
Closed and Open loops

Review of the Basics
Pathophysiology
The 3 pains / The 3 guts
Causes

The 3
Pains
Visceral
Referred
Somatic

Visceral Pain
Is a pain that results from the activation of
nociceptors of the thoracic pelvic or abdominal
viscera (organs)

Referred Pain
It’s when the pain is located away from or adjacent to the
organ involved

Somatic Pain
When the parietal peritoneum is inflammed
;
Pain is severe
Breathing shallow
Movement
impaired
Tenderness
marked

The 3 guts
There are 3 main guts to be aware of when it comes to pain
Fore gut

The 3 guts
There are 3 main guts to be aware of when it comes to pain
Fore gut
Mid gut

The 3 guts
There are 3 main guts to be aware of when it comes to pain
Fore gut
Mid gut
Hind gut
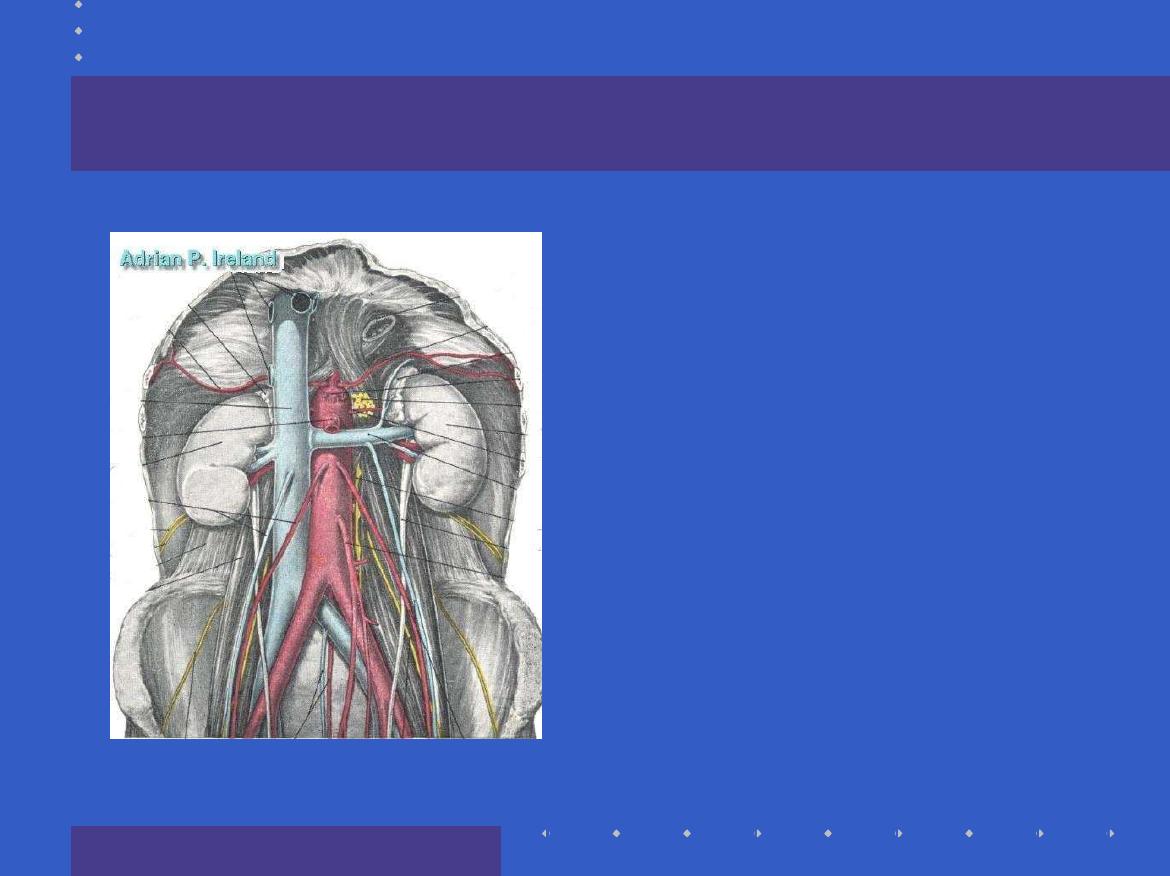
The 3 guts; Based upon arterial supply
Fore-gut
Mid-gut
Hind-gut
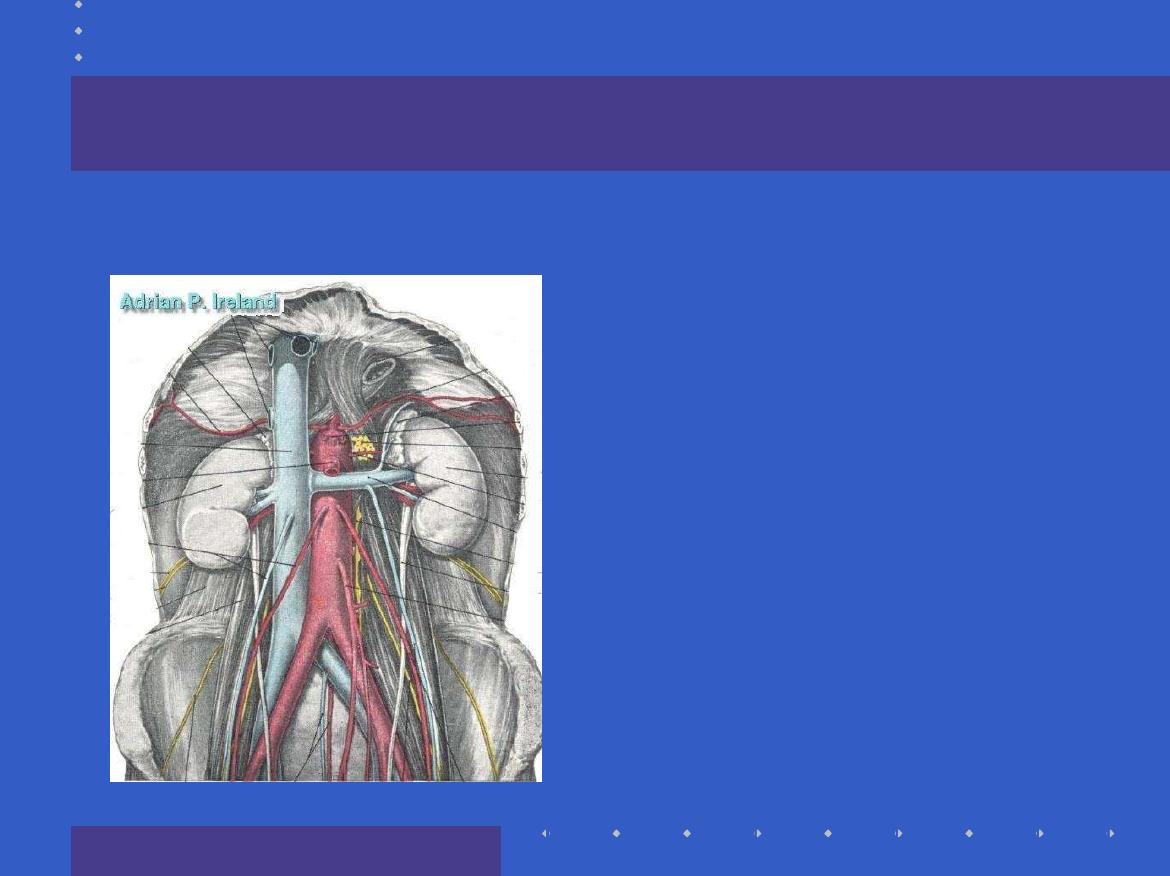
The Fore-gut
In the distribution
of the Coeliac
artery
Extends from the
lower esophagus
to
half way down
D2
Pain is referred to
the epigastrium
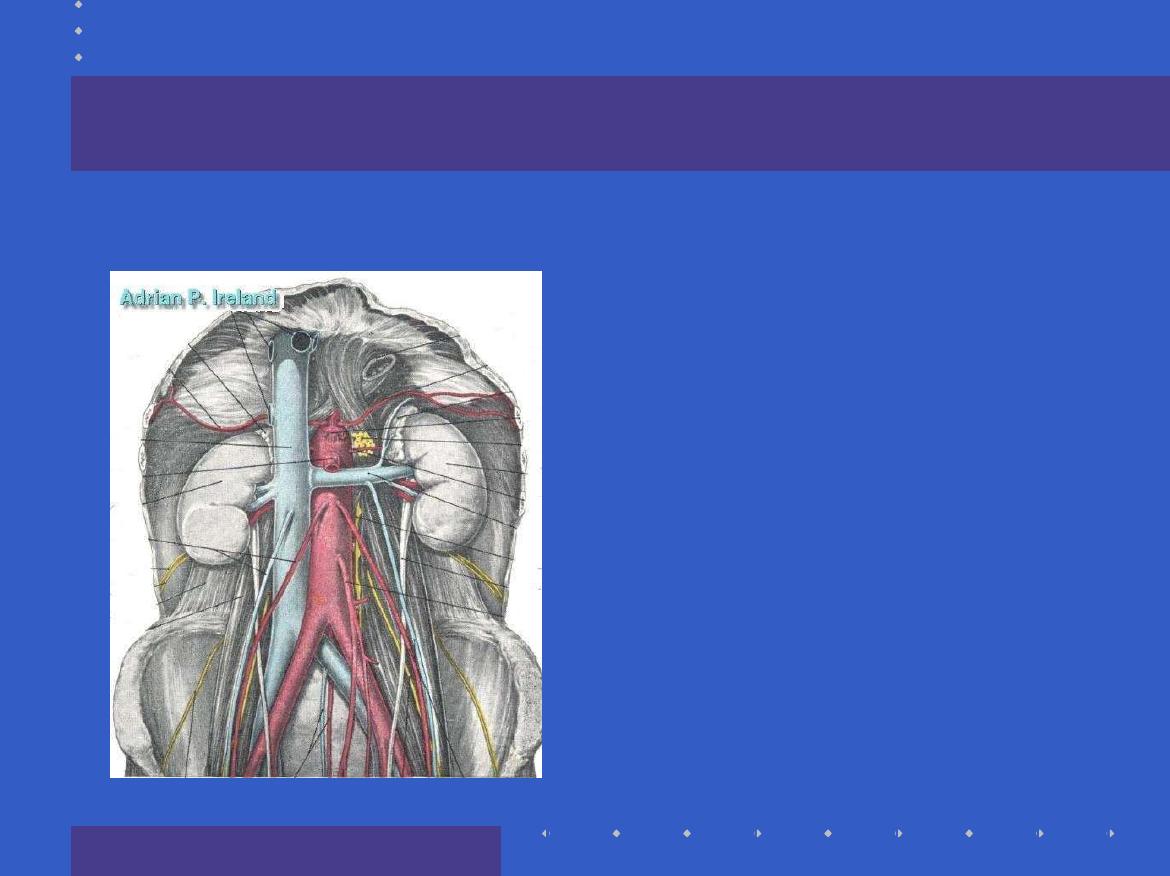
The Mid-gut
In the distribution
of the Superior
Mesenteric artery
Extends from
half
way down D2
to
the
distal
transverse colon
Pain is referred to
the umbilicus
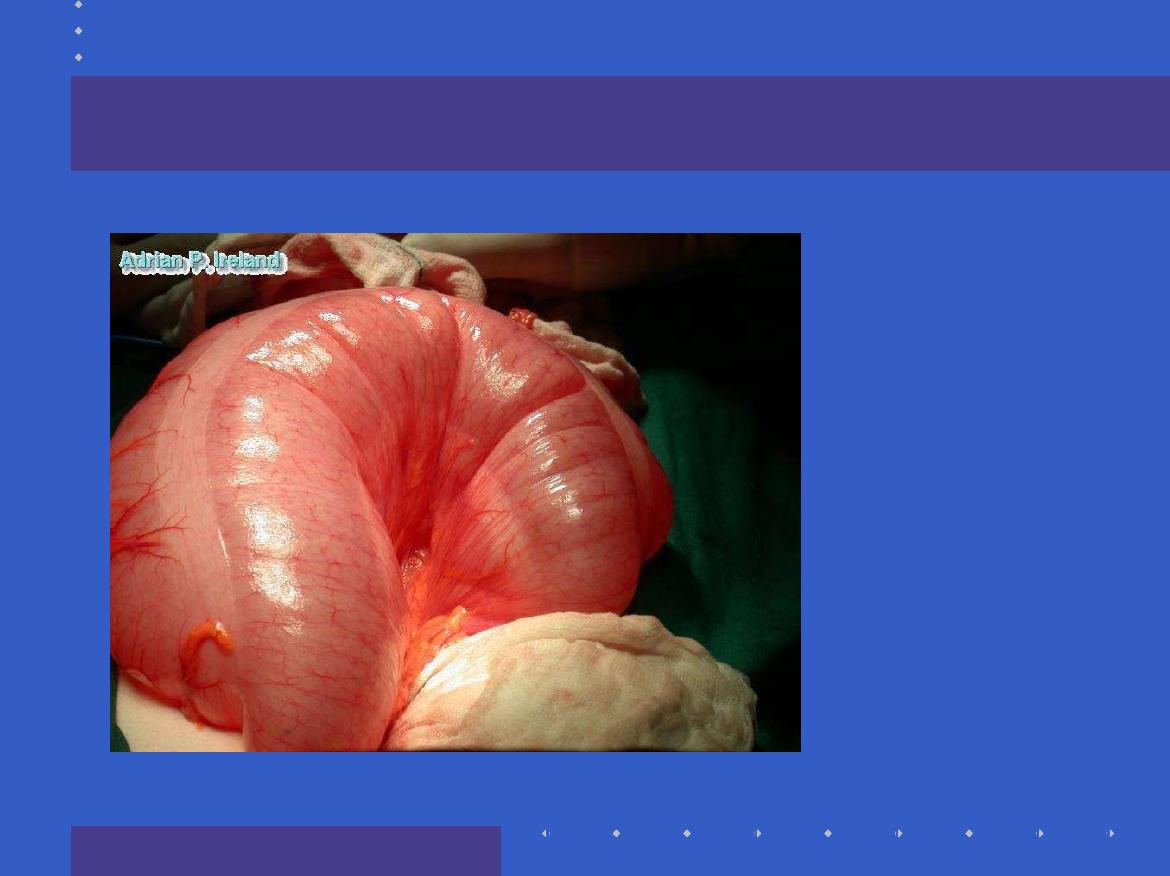
What is this
?
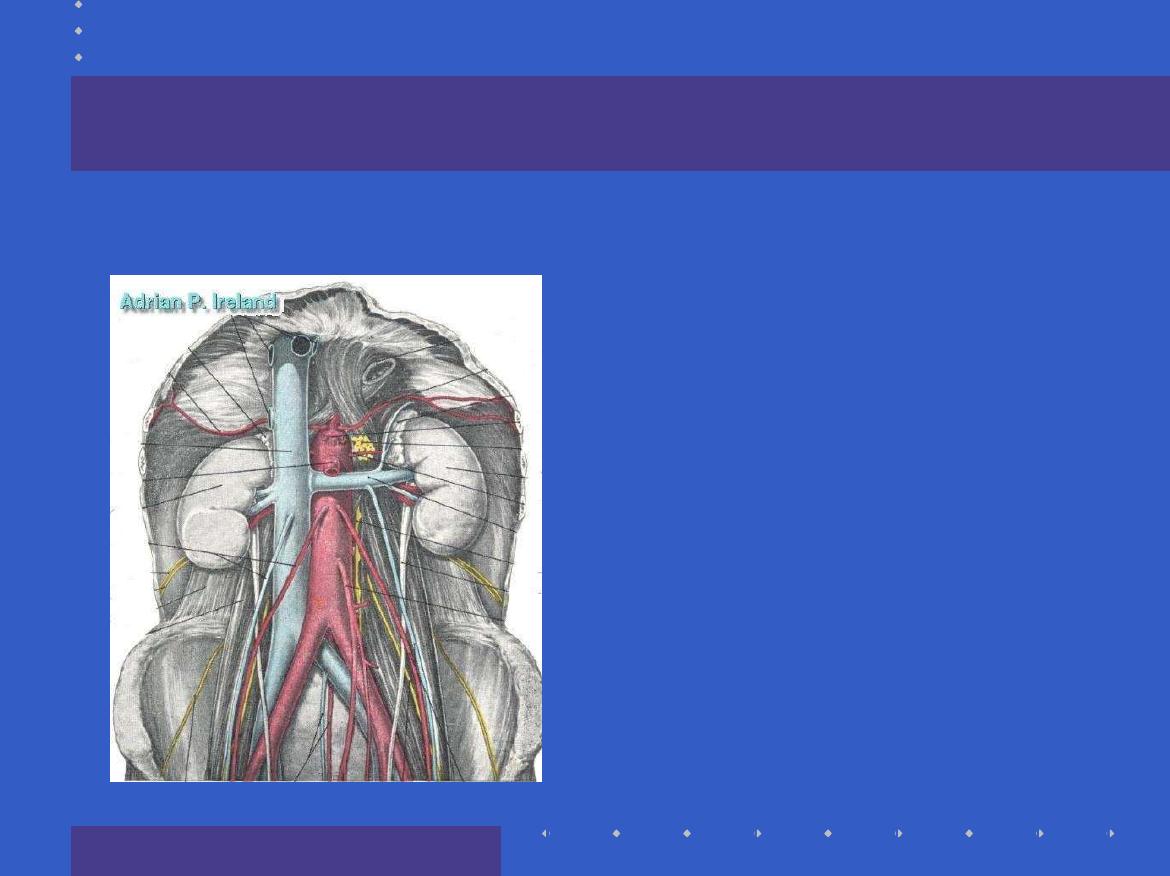
The Hind-gut
In the distribution
of the Inferior
Mesenteric artery
Extends from the
distal transverse
colon
to the
rectum
Pain is referred to
the hypogastrium

Review of the Basics
Pathophysiology
The 3 pains / The 3 guts
Causes

Causes of Intestinal obstruction
Classification based upon;
lumen, wall, outside and combinations
open and closed loop Identify dangerous types
simple and complex Clinically useful
small intestine, large intestine Clinical and
Radiological
common and rare (Clinical)

Lumen, Wall, Outside and Combinations
Lumen
; Gallstone, Beezoar, Foreign Body
Wall
; Stricture
Outside
; Volvulus, Hernia, Adhesions,
Metastases
Combinations
; Intussusception
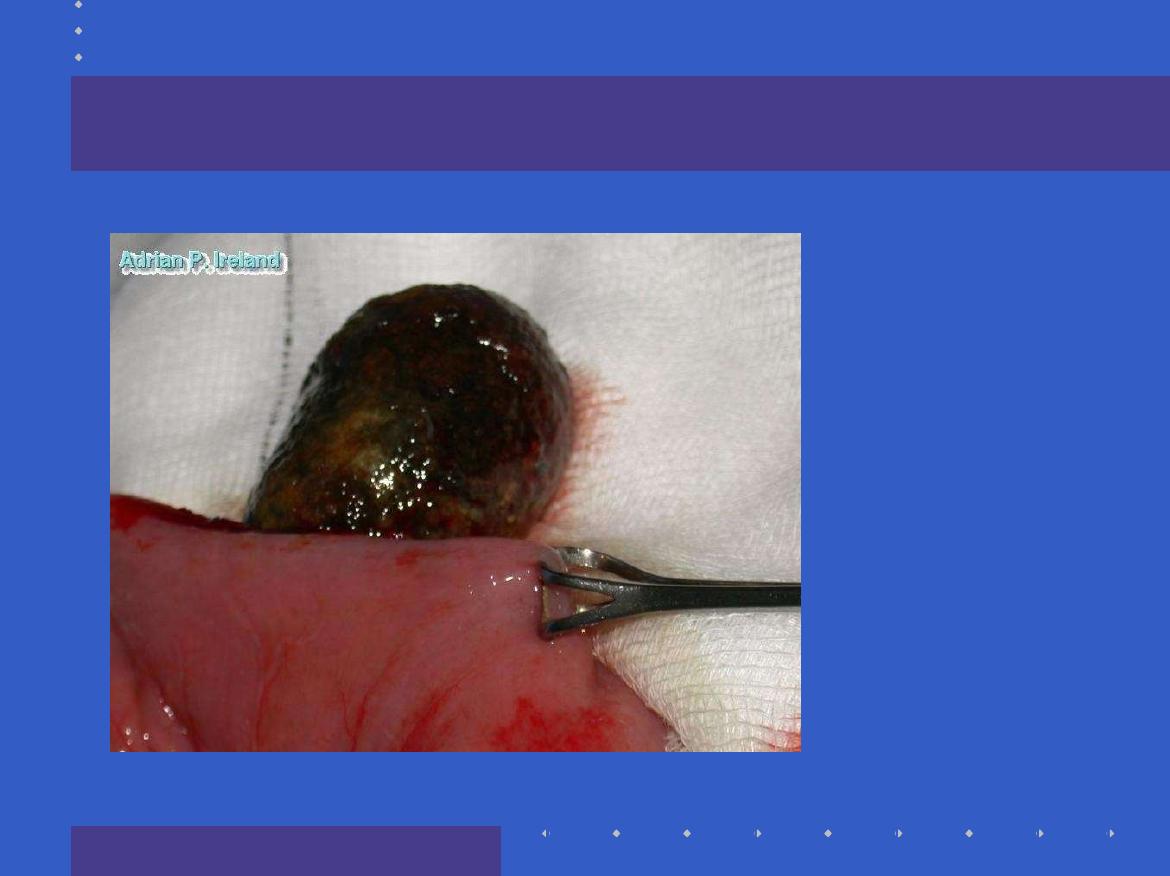
Lumen
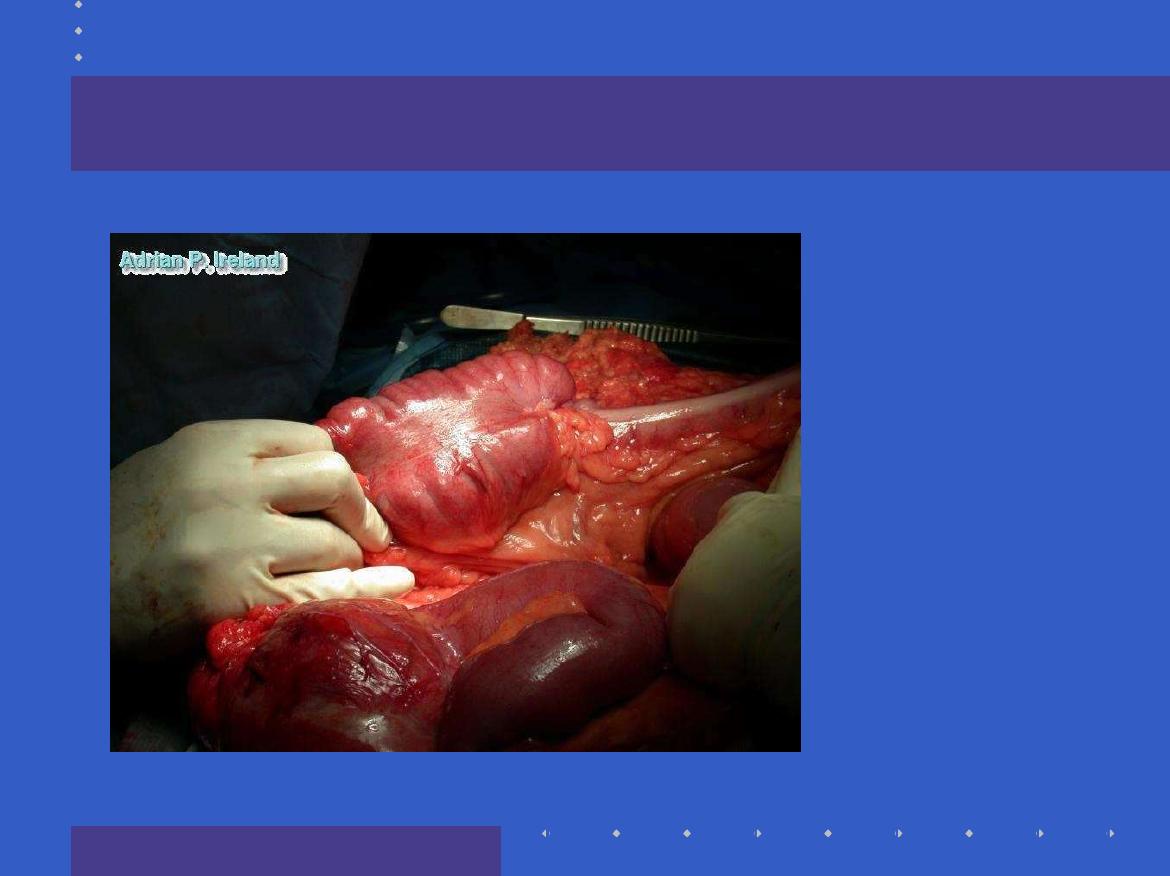
Wall
Outside

Causes of Intestinal obstruction
Classification based upon
;
lumen, wall and outside
Small Intestine, Large Intestine
common and rare

Small Intestine
Post operative adhesions
Stuck onto tumor or inflammatory mass somewhere
Hernia; External, Internal
Volvulus
Intussusception
Crohn’s stricture
Ischaemic stricture
Tumors of the small intestine
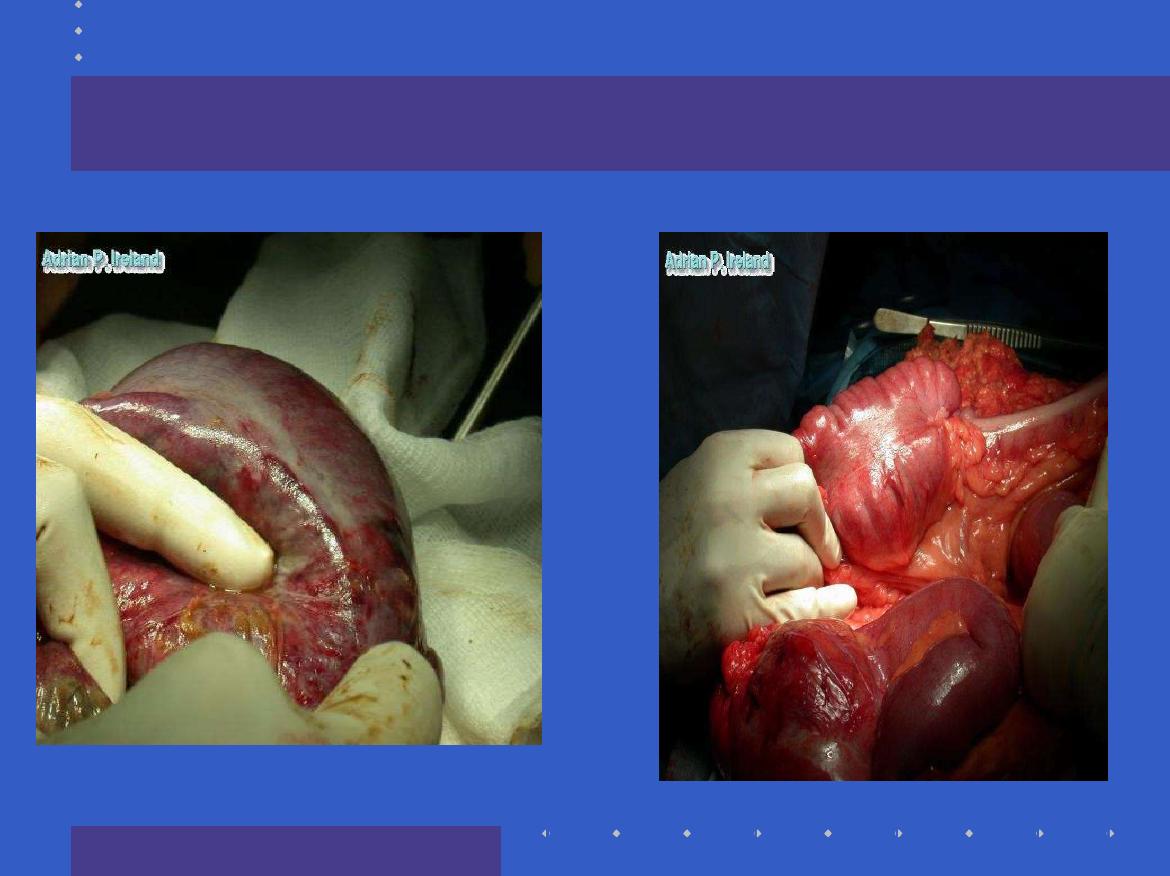
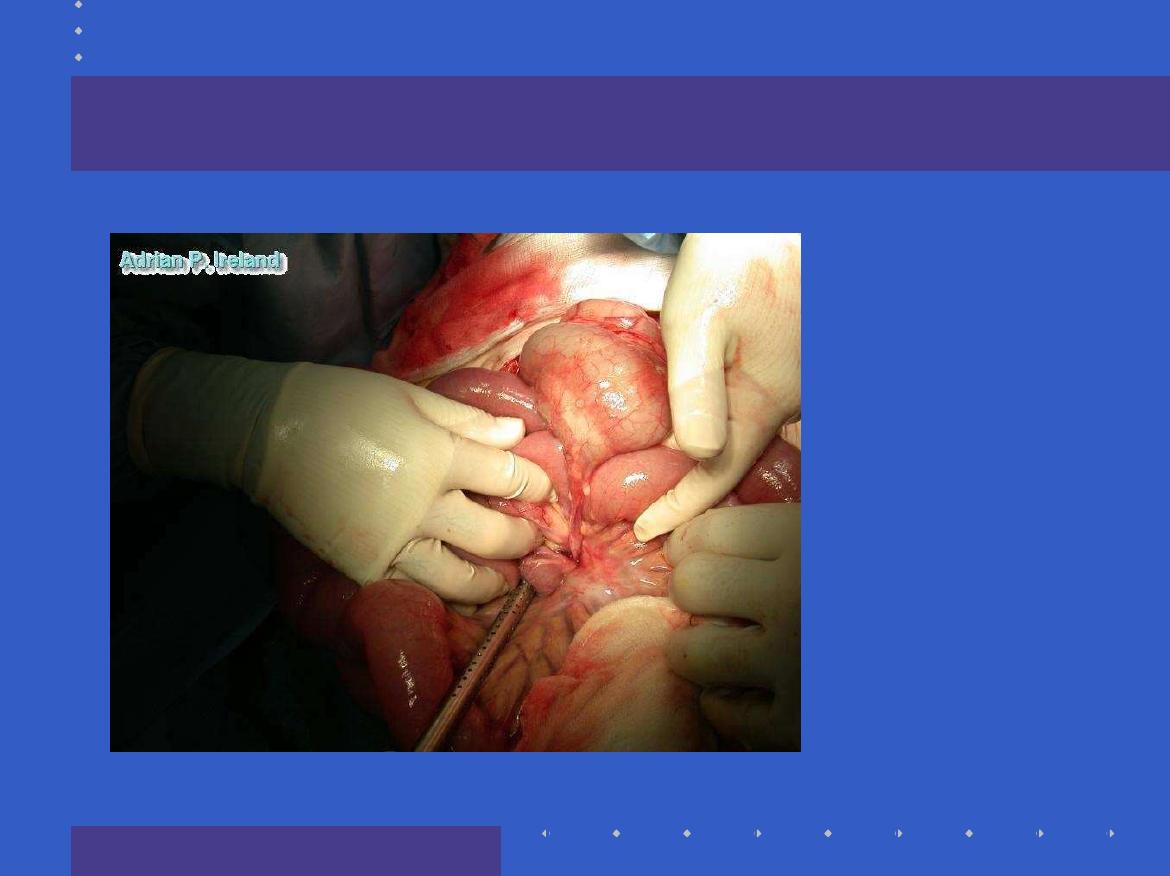
Operative Findings; Small bowel volvulus

Large Intestine
Colo-rectal cancer
Volvulus; Sigmoid, Caecal
Inflammatory Stricture

Causes of Intestinal obstruction
Classification based upon
;
lumen, wall and outside
small intestine, large intestine
Common and Rare

Common and Rare
Common
;
Post operative adhesions
Herniae; Groin, Femoral and Inguinal, Incisional
Colorectal Cancer
Rare
; Internal hernia

Presenting Complaint
Abdominal Pain
Vomiting
Distension
Constipation,
Complete, obstipation

Pain
Site
Radiation
Type
Severity
Onset and Duration
Aggravating and Relieving factors
Associated symptoms
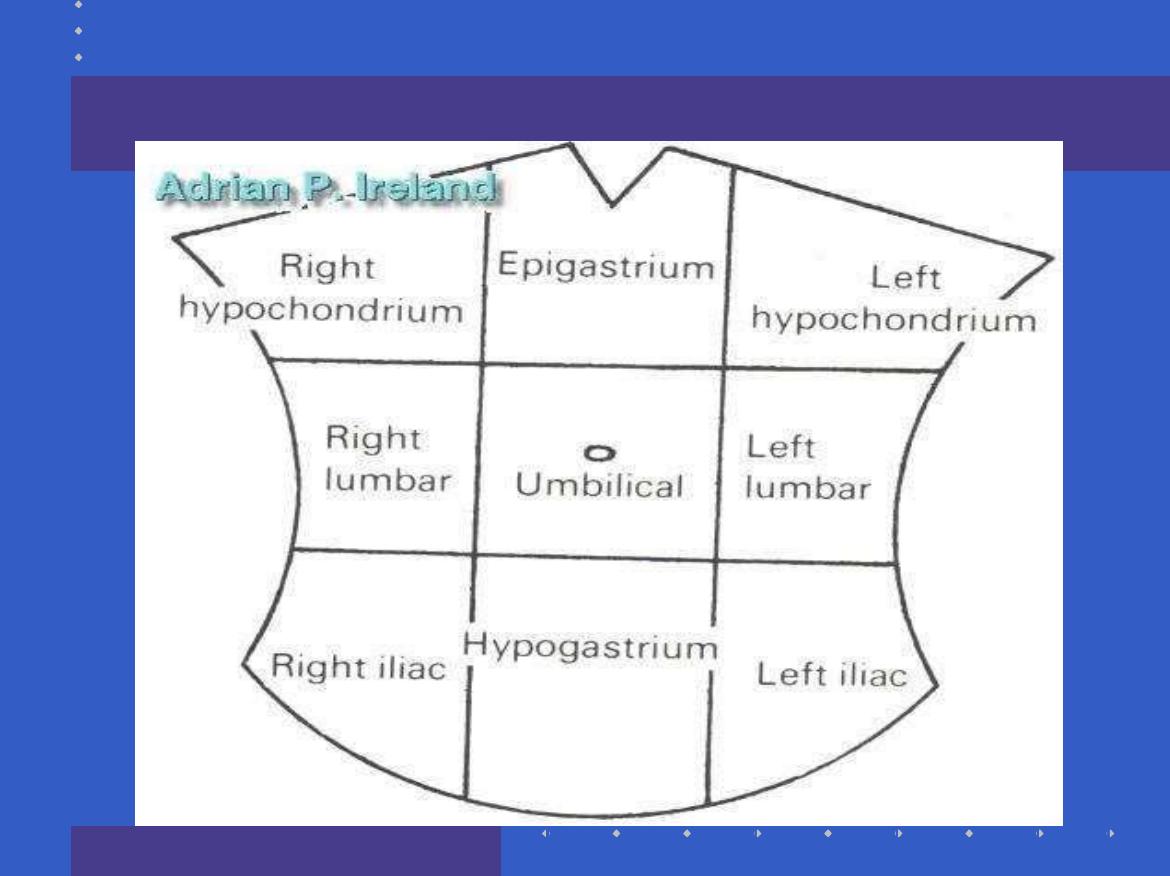
Site
Whats this
?
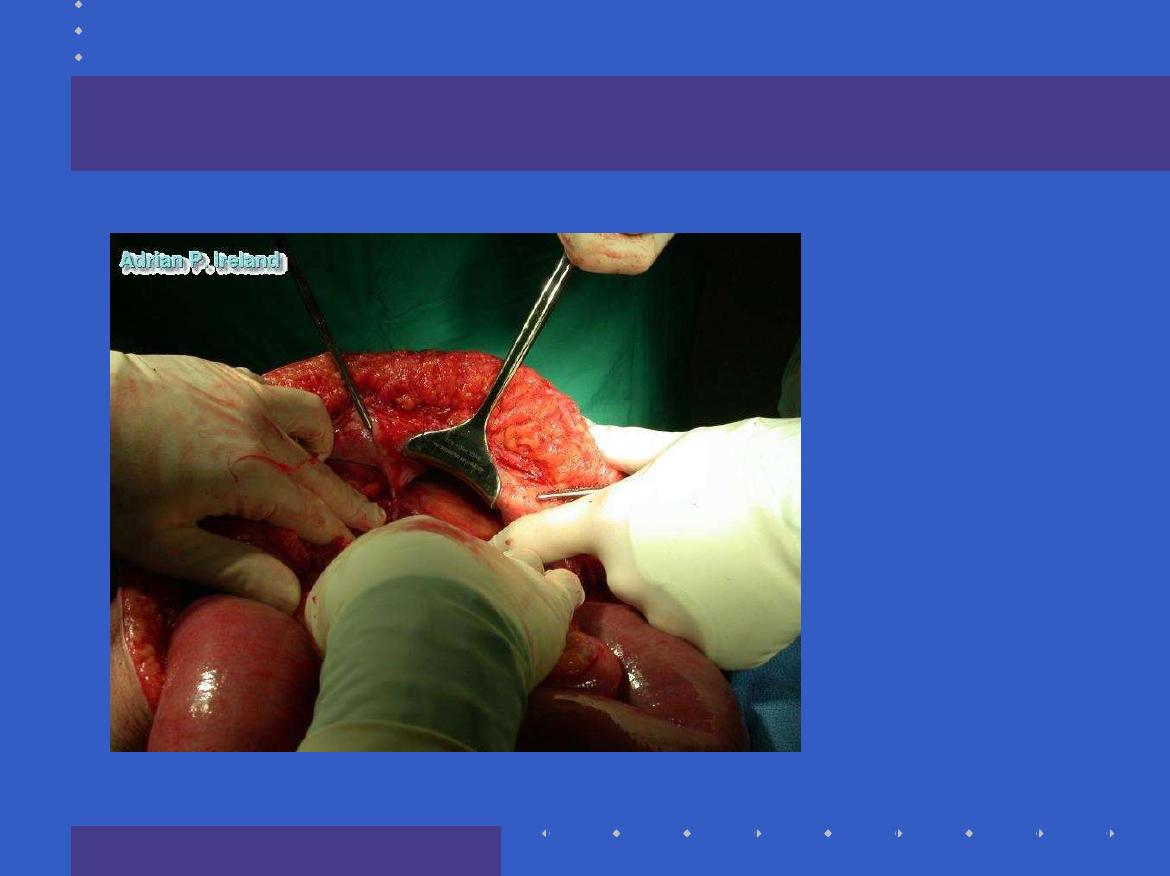
Whats this
?
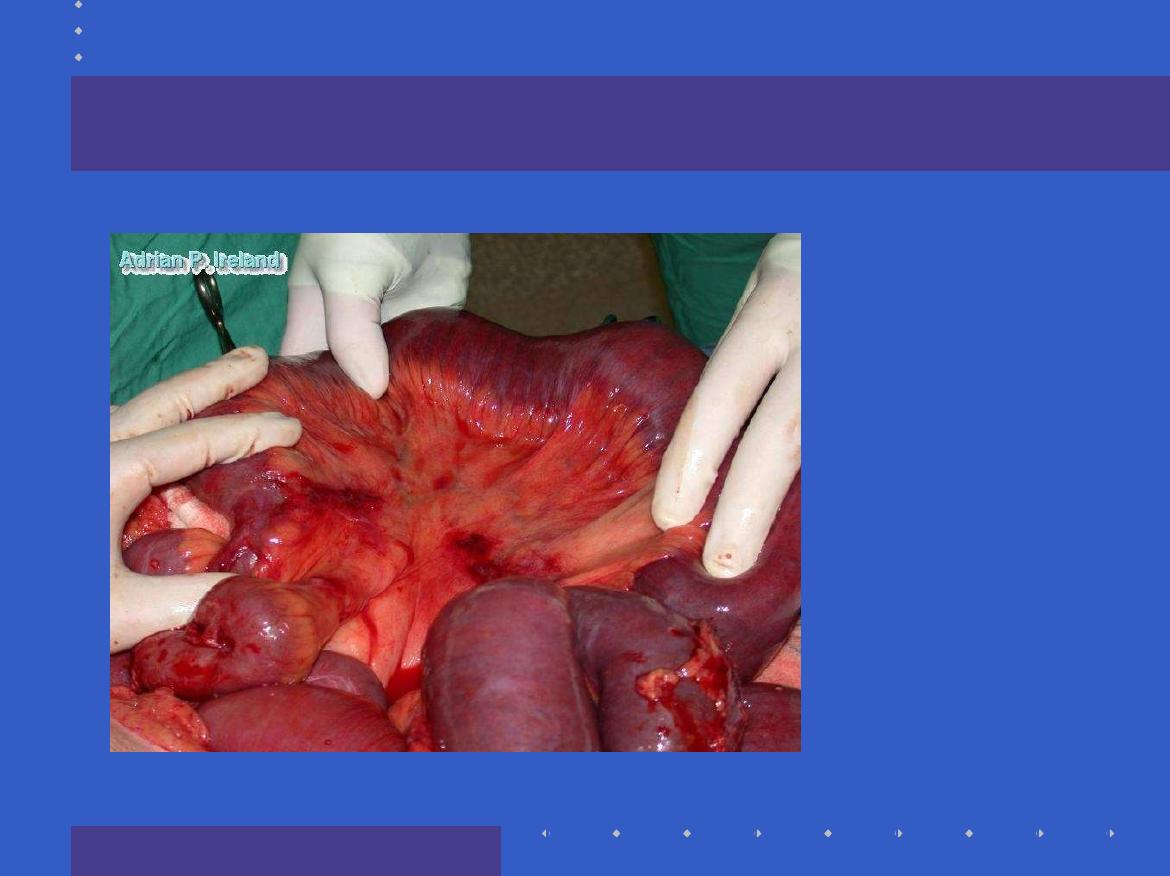
Whats this
?

Past history
Had this before
?
Previous surgery
Other illness (drugs)

Examination
Overall state; distressed, comfortable, cachexia
Vital signs
State of Hydration
Abdominal Examination; distension, peristalsis,
tenderness, mass
Hernial orifices, Perineum, Rectal, Genitalia, Femoral
Pulses
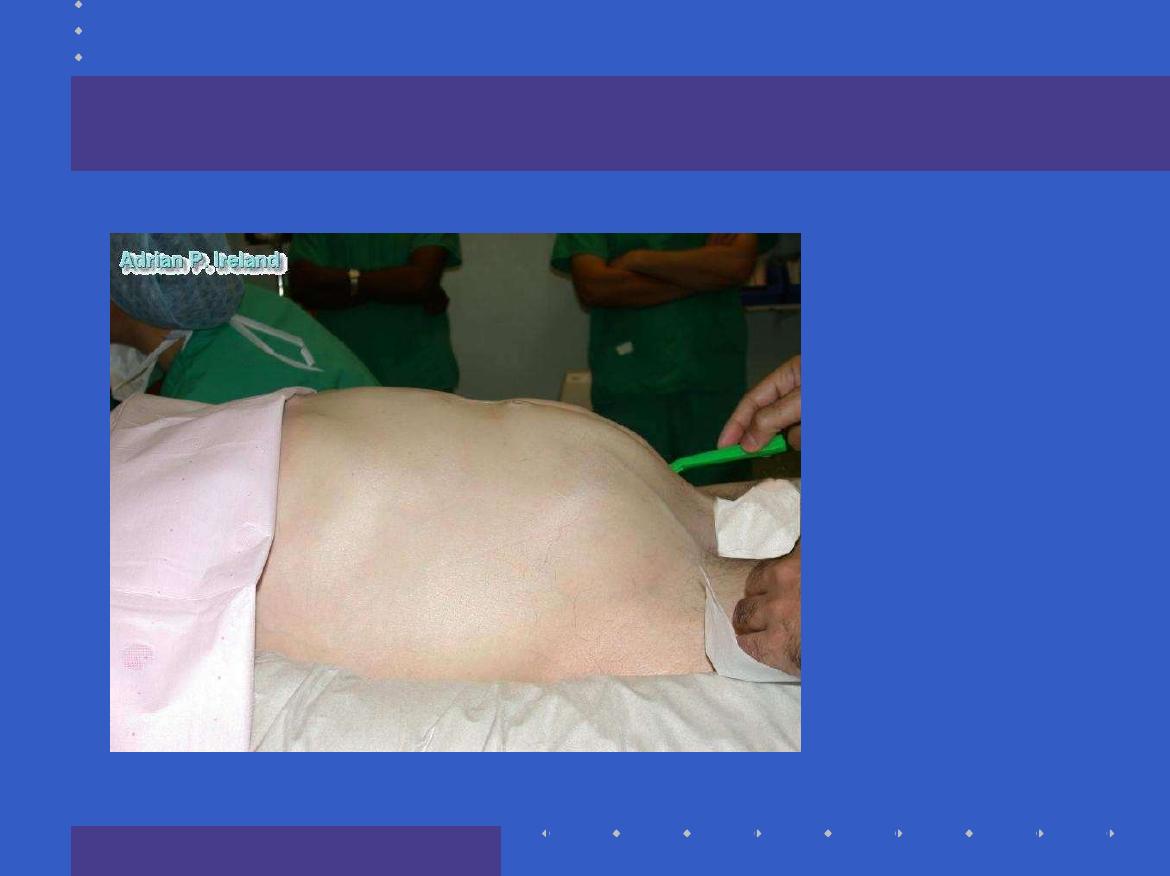
Inspection
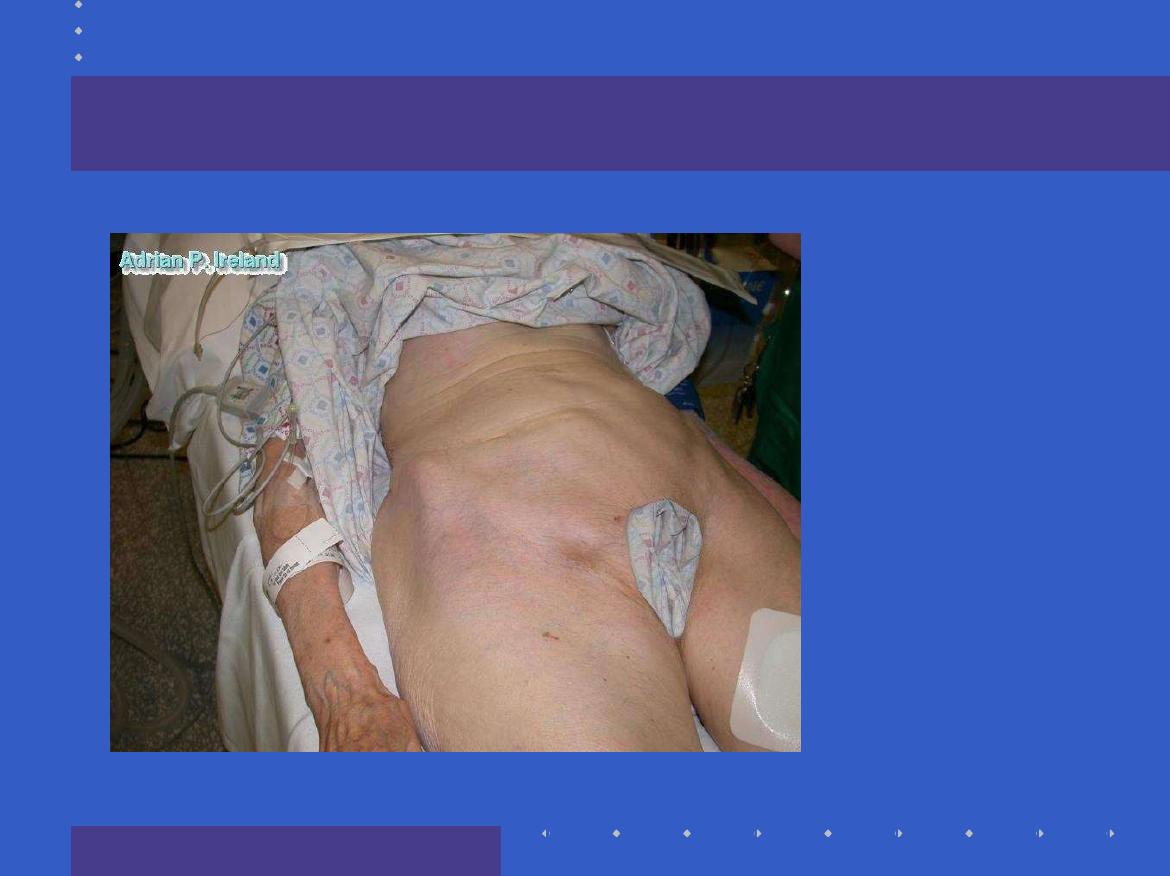
Inspection

Clinical approach
Has the patient got intestinal obstruction
?
Is it simple or complicated?
What is the fluid deficit
?
What is the level of the obstruction?
What is the cause of the obstruction
?

Differential Diagnosis
Obstuction or Pseudo-obstruction
Of the pain; Abdominal, Non Abdominal
Of the distension; Fluid, Flatus, Fat, Faeces, Fetus
,

Investigation
Blood; U & E, FBC, Amylase, Muscle Enzymes
,
Radiological; PFA, Erect CXR, CT scan, Enemas
.

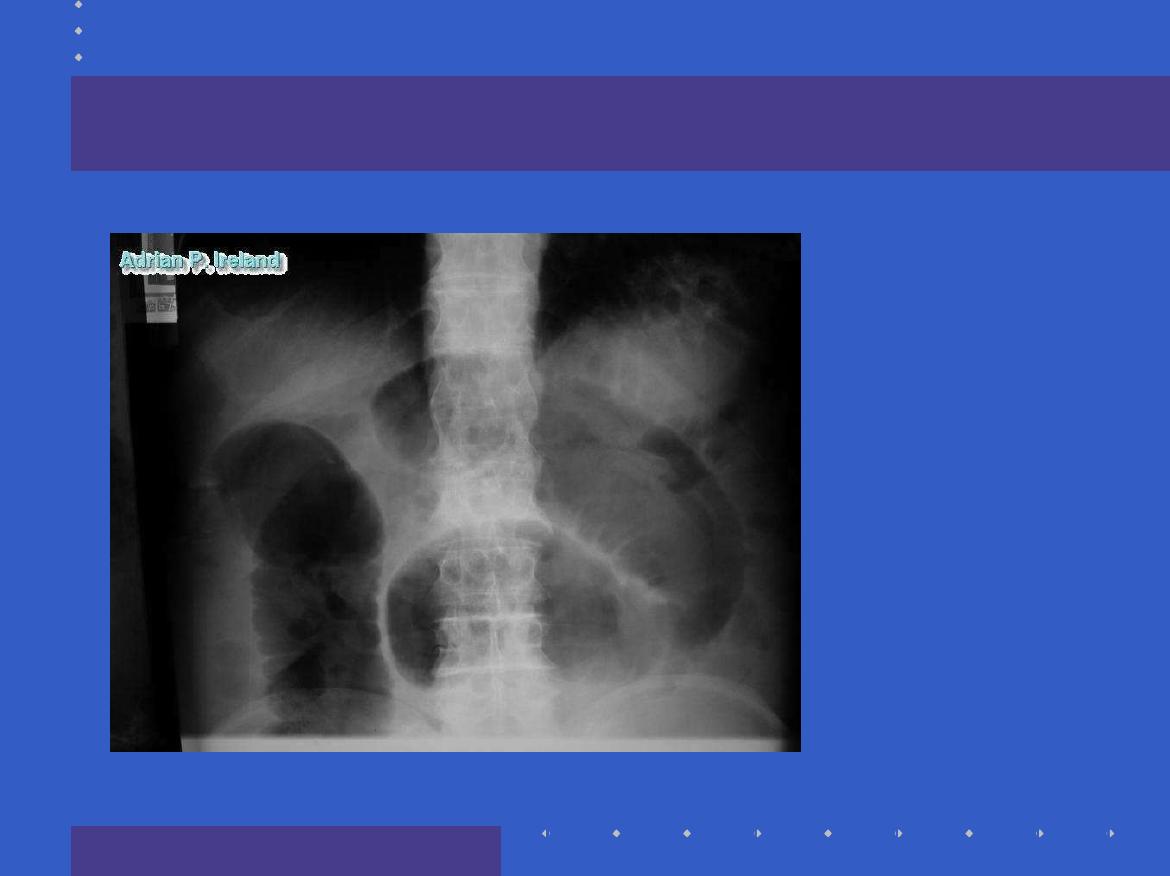
Radiology
Quite simple
,
Gaseous distension, what is distended?
Fluid levels, fluid distension
Transition zone, any gas distally?
Contrast wont pass, show mass
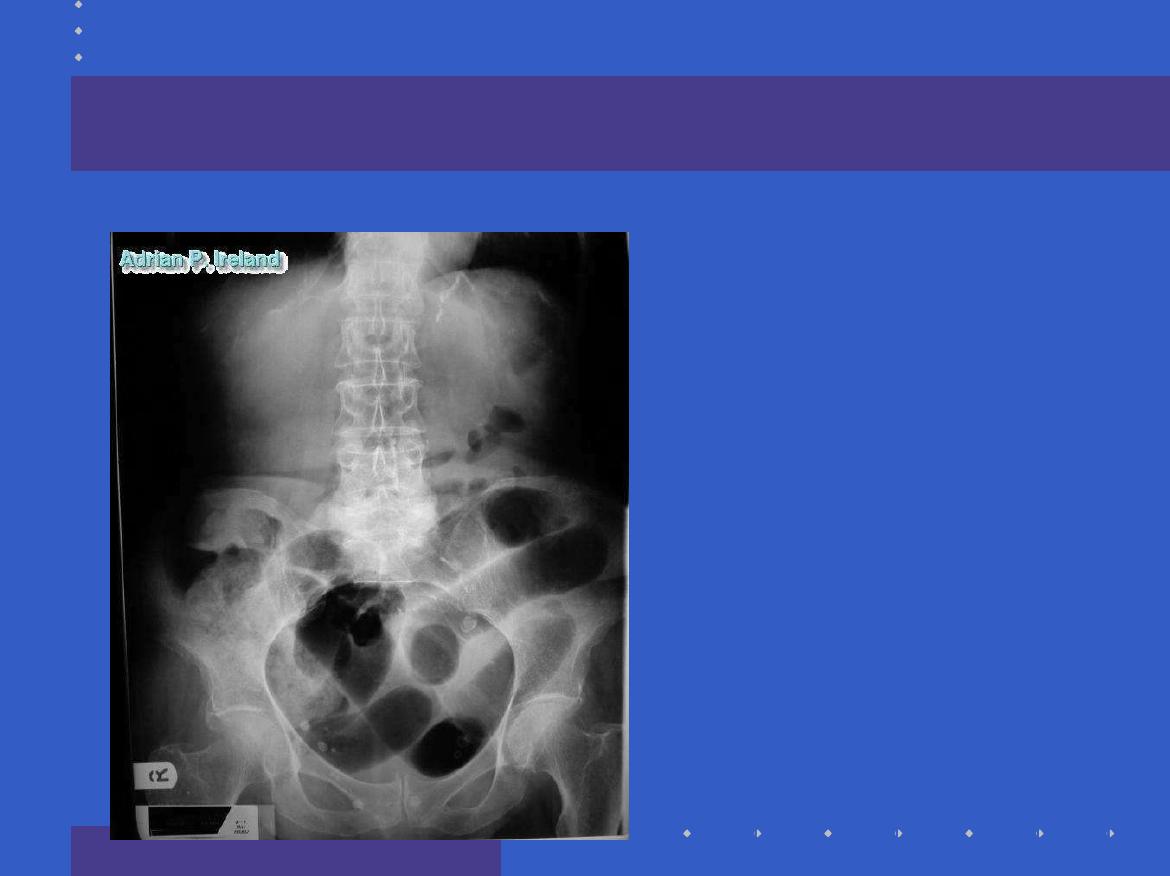
Radiology, Small bowel obstruction
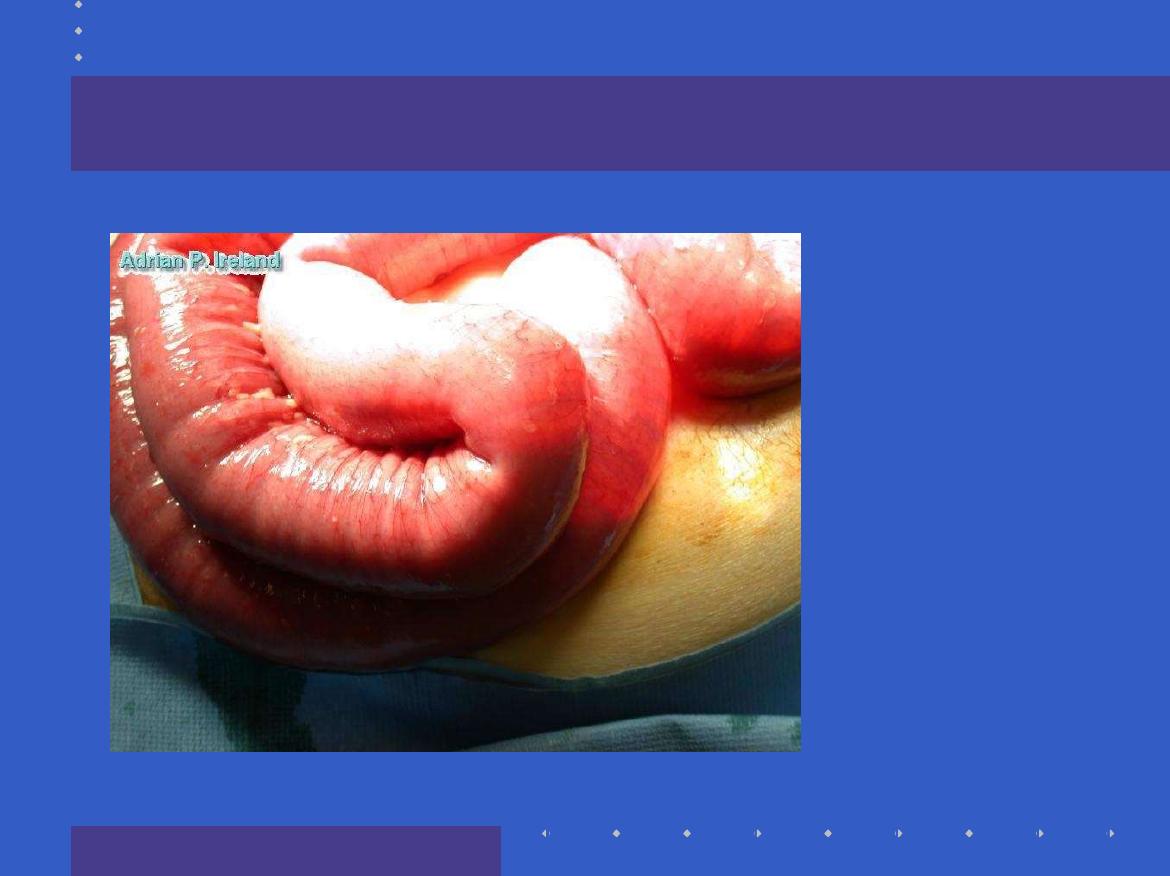
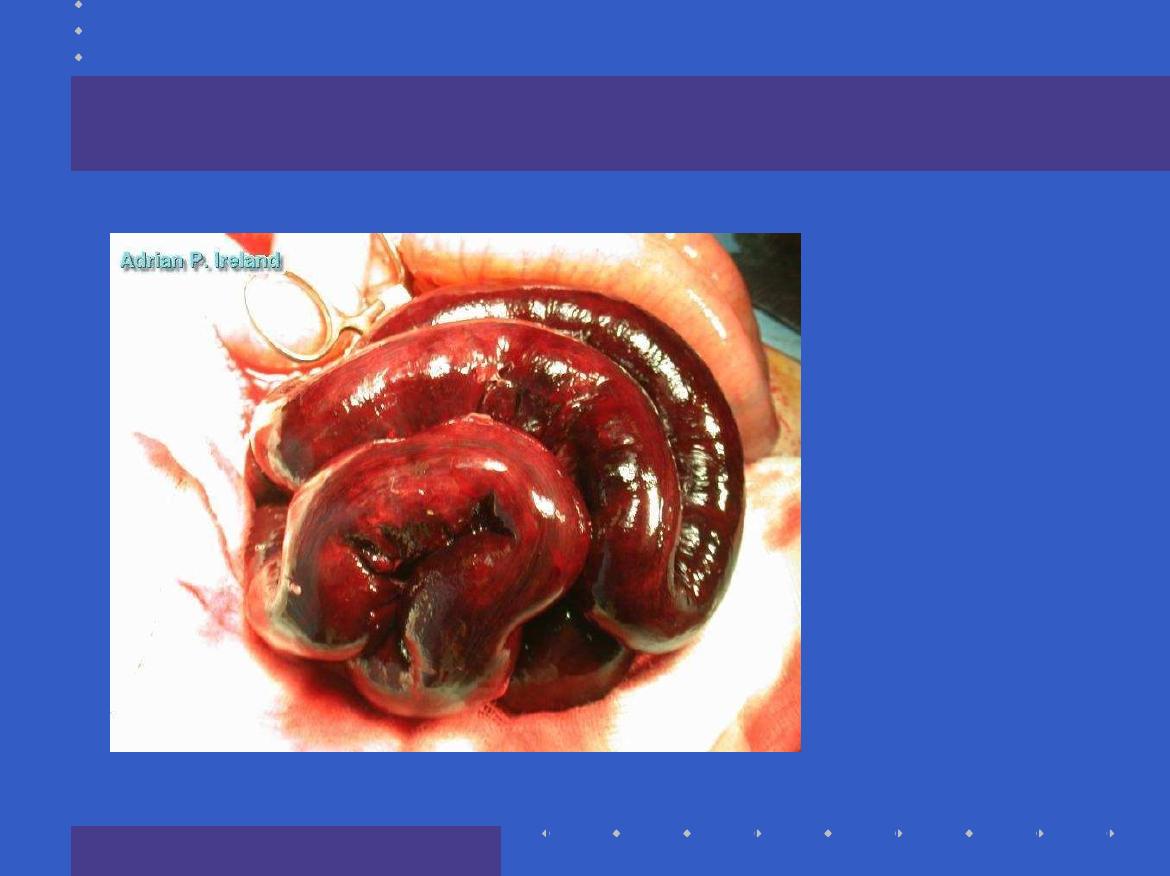
Operative Findings; Small bowel obstruction
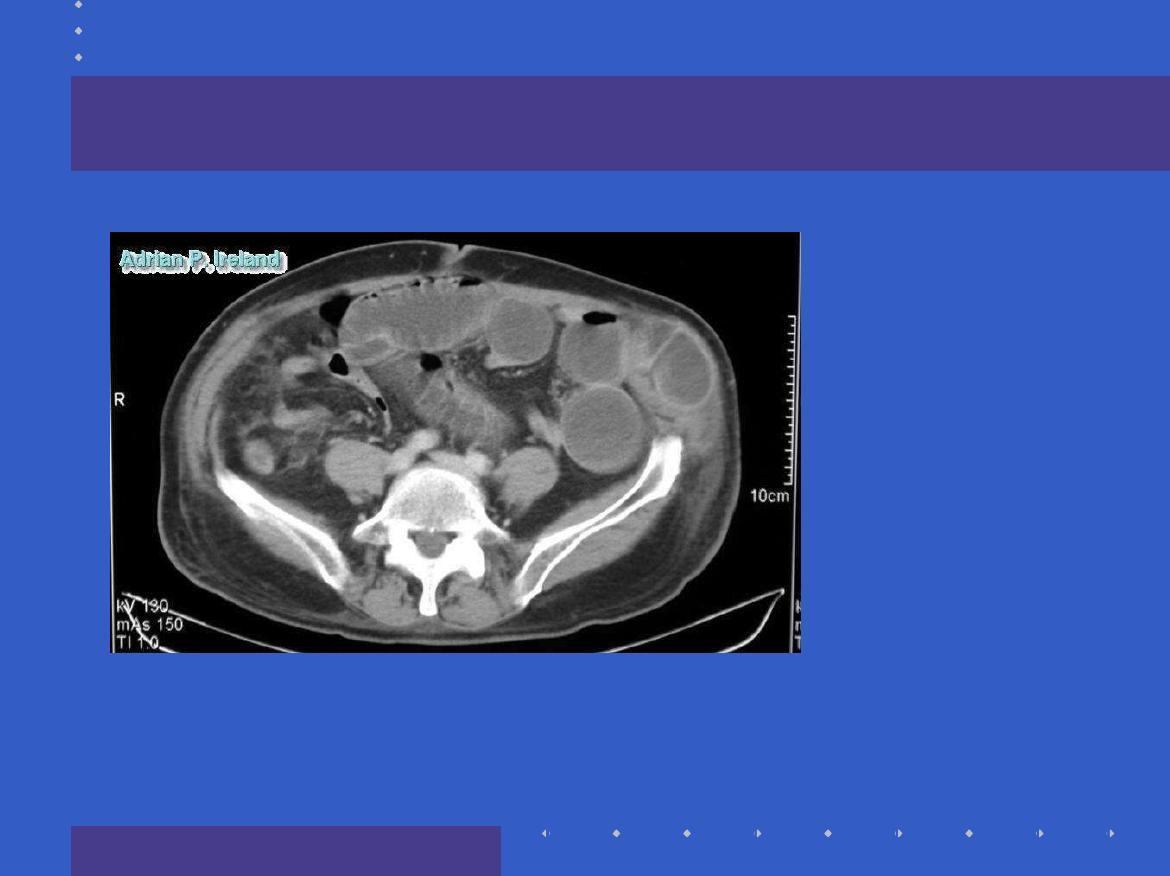
Radiology; CT, Small bowel obstruction
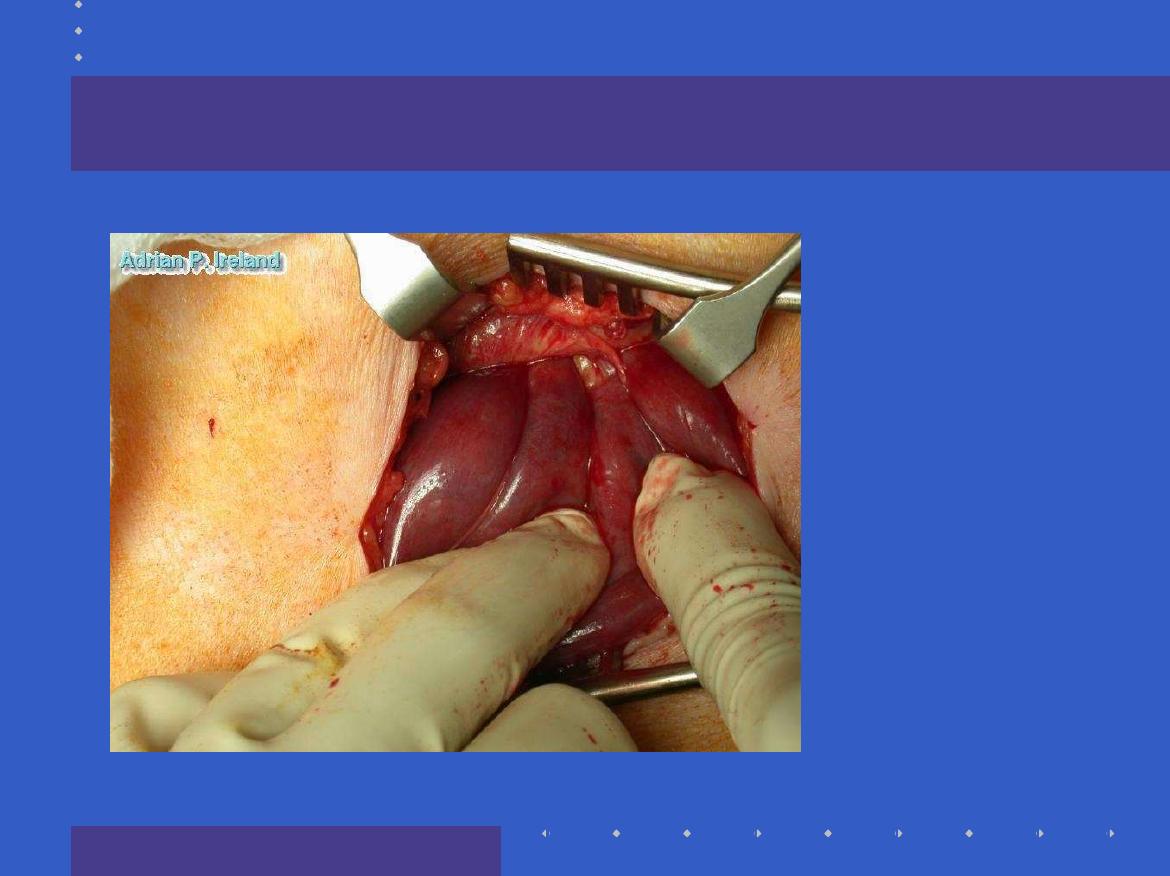
Operative Findings; Small bowel obstruction
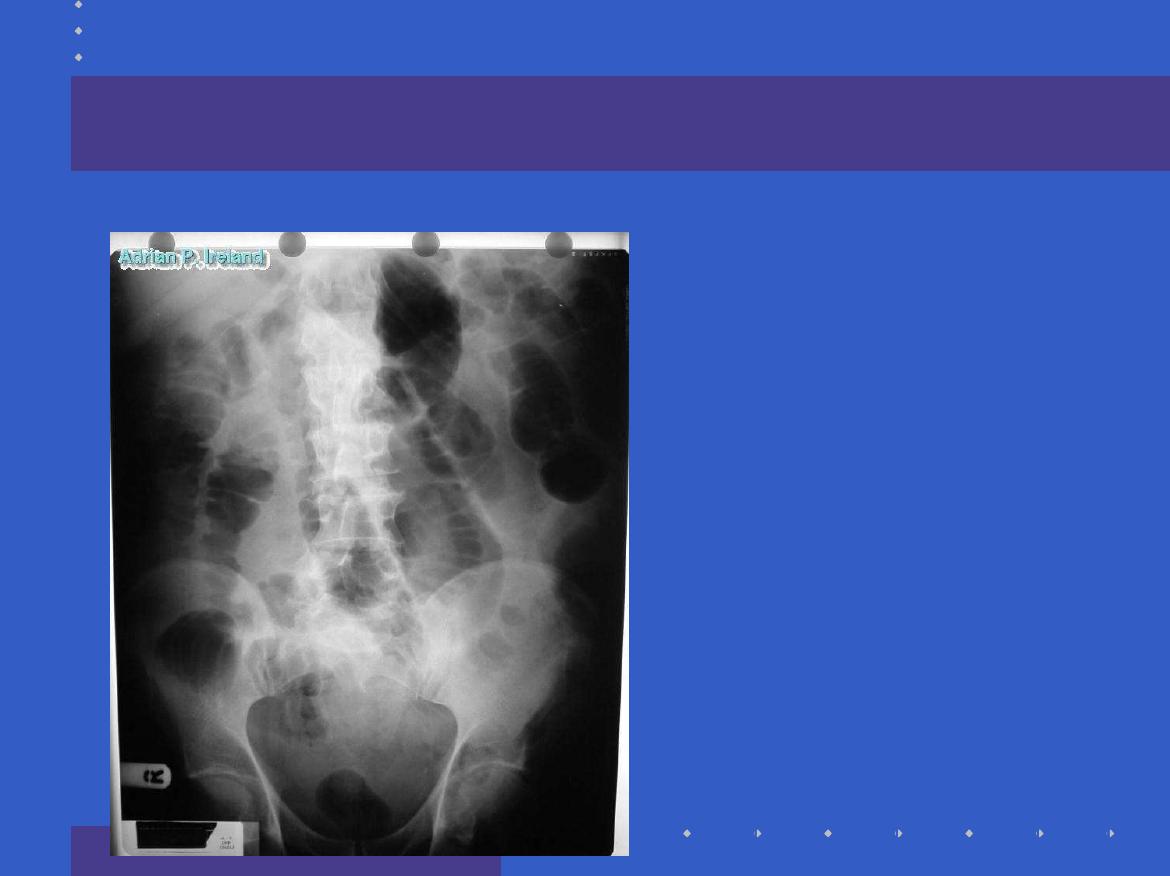
Radiology; PFA, Large bowel obstruction
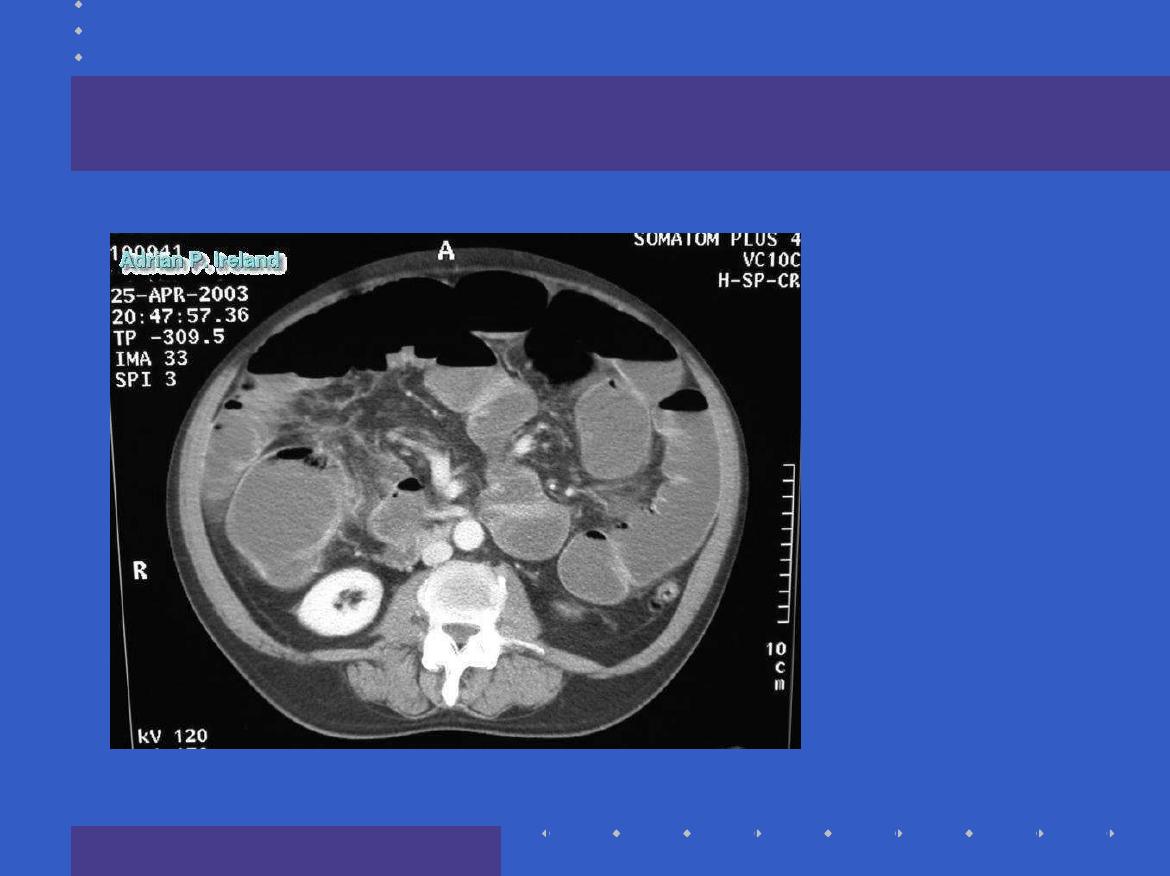
Radiology; CT, Large bowel obstruction
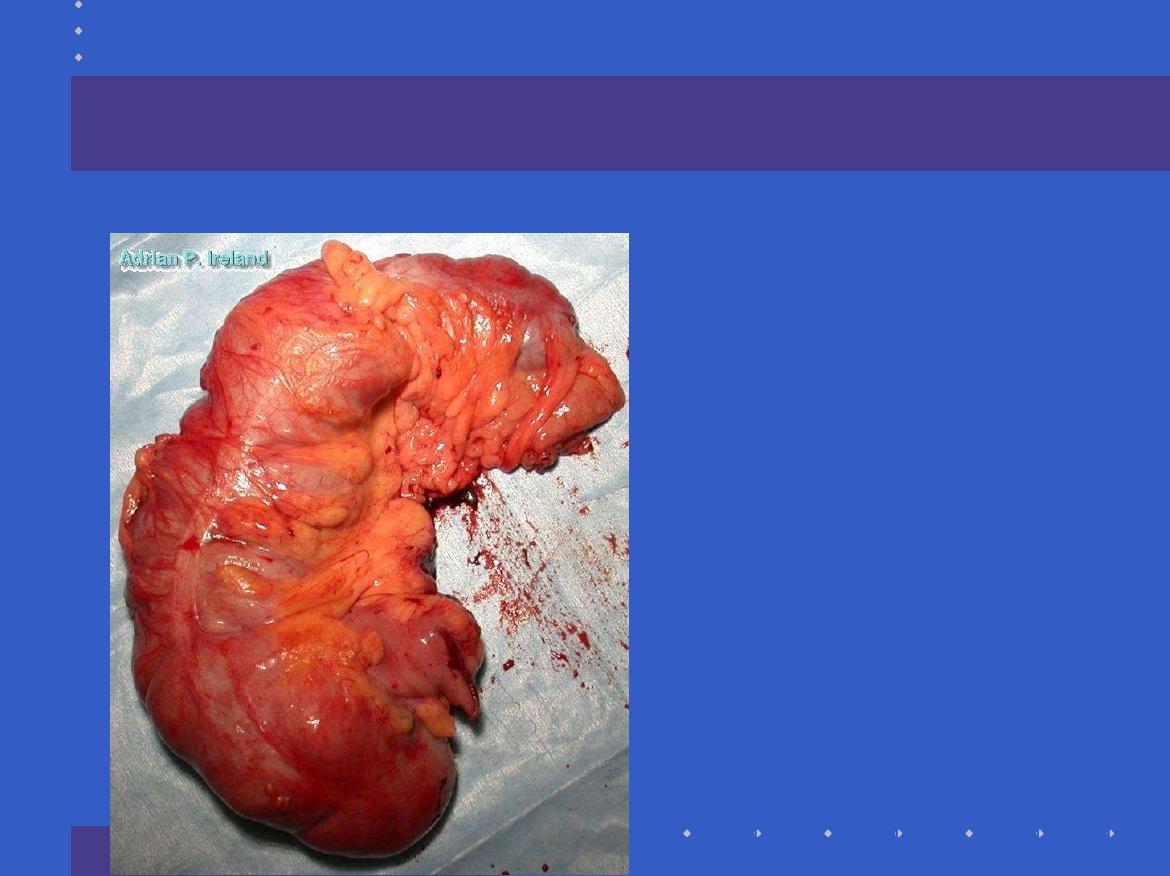
Operative Findings; Large bowel obstruction

Thanks
