Intestinal Obstruction
Dr Aqeel Shakir MahmoodAssistant Professor
Consultant General and Laparoscopic Surgeon
FRCS –( London)
• Today we will be talking about intestinal obstruction• Definition
• Review of Basics History and Examination Differential Diagnosis Investigation
• Fluid prescription Clinical algorithm
• Definition
• Clinical condition,• Due to; failure of the intestine small or large to pass
• gas, liquid and solid material.
• Review of the Basics
• Pathophysiology• The 3 pains / The 3 guts Causes
• Intestinal Obstruction; Pathophysiology
• Blocked Lumen
• Distension (solid, liquid, gas); Pain, vomit, constipation
• Increased Wall tension; Perforation Ischaemia
• Closed and Open loops
• Closed and Open loops
• Review of the Basics
• Pathophysiology• The 3 pains / The 3 guts Causes
• The 3 Pains
• Visceral• Referred Somatic
• Visceral Pain
• Is a pain that results from the activation of nociceptors of the thoracic pelvic or abdominal viscera (organs)
• Referred Pain
• It’s when the pain is located away from or adjacent to the organ involved• Somatic Pain
• When the parietal peritoneum is inflammed;• Pain is severe Breathing shallow Movement impaired Tenderness marked
• The 3 guts
• There are 3 main guts to be aware of when it comes to pain• Fore gut
• The 3 guts• There are 3 main guts to be aware of when it comes to pain
• Fore gut Mid gut
• The 3 guts
• There are 3 main guts to be aware of when it comes to pain• Fore gut Mid gut Hind gut
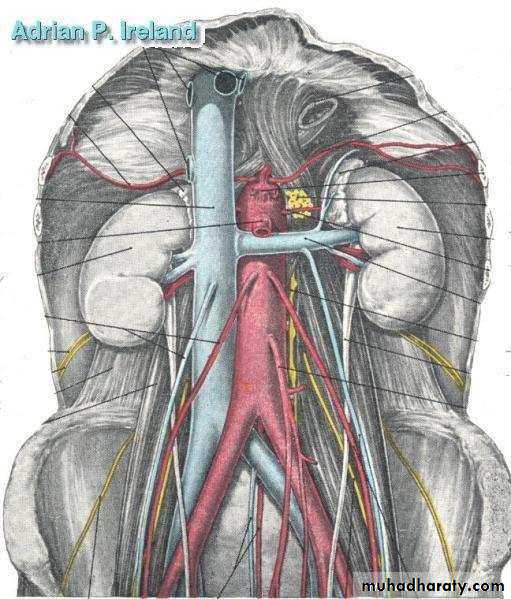
• The 3 guts; Based upon arterial supply
• Fore-gut
• Mid-gut Hind-gut• The Fore-gut
• In the distribution of the Coeliac artery
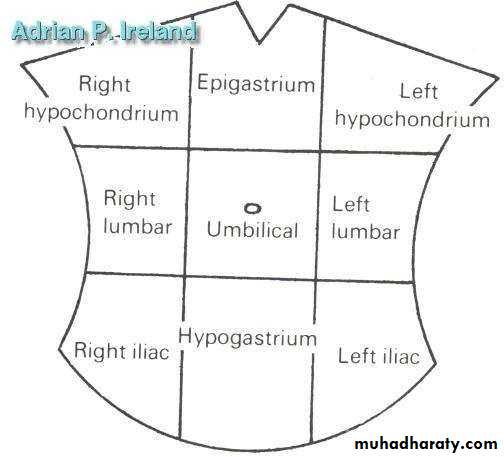
• Extends from the lower esophagus to half way down D2• Pain is referred to the epigastrium
• The Mid-gut
• In the distribution of the Superior Mesenteric artery
• Extends from half way down D2 to the distal transverse colon• Pain is referred to the umbilicus
• What is this?
• The Hind-gut
• In the distribution of the Inferior Mesenteric artery
• Extends from the distal transverse colon to the rectum• Pain is referred to the hypogastrium
• Review of the Basics
• Pathophysiology• The 3 pains / The 3 guts Causes
• Causes of Intestinal obstruction
• Classification based upon;• lumen, wall, outside and combinations
• open and closed loop Identify dangerous types simple and complex Clinically useful
• small intestine, large intestine Clinical and Radiological
• common and rare (Clinical)
• Lumen, Wall, Outside and Combinations
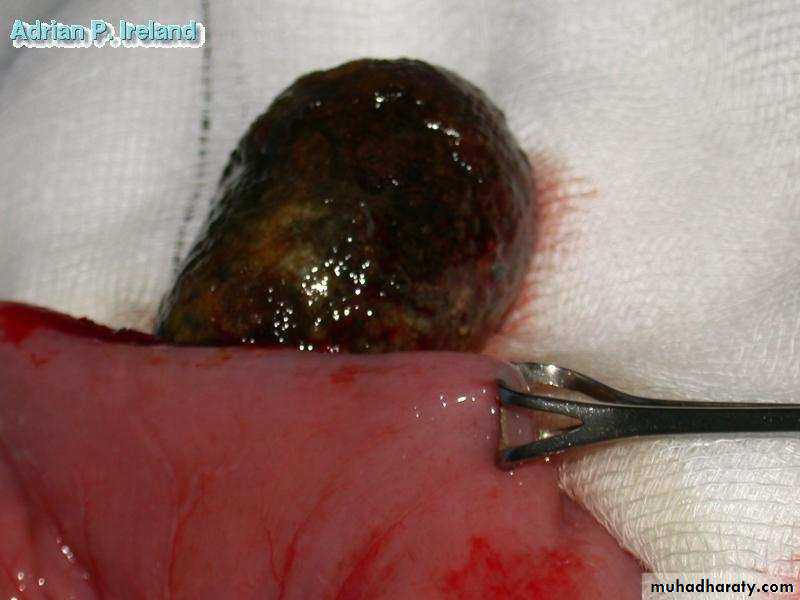
• Lumen; Gallstone, Beezoar, Foreign Body• Wall; Stricture
• Outside; Volvulus, Hernia, Adhesions, Metastases• Combinations; Intussusception
• Lumen
• Wall
• Outside
• Causes of Intestinal obstruction
• Classification based upon;
• lumen, wall and outside
• Small Intestine, Large Intestine common and rare• Small Intestine
• Post operative adhesions• Stuck onto tumor or inflammatory mass somewhere Hernia; External, Internal
• Volvulus Intussusception Crohn’s stricture Ischaemic stricture
• Tumors of the small intestine
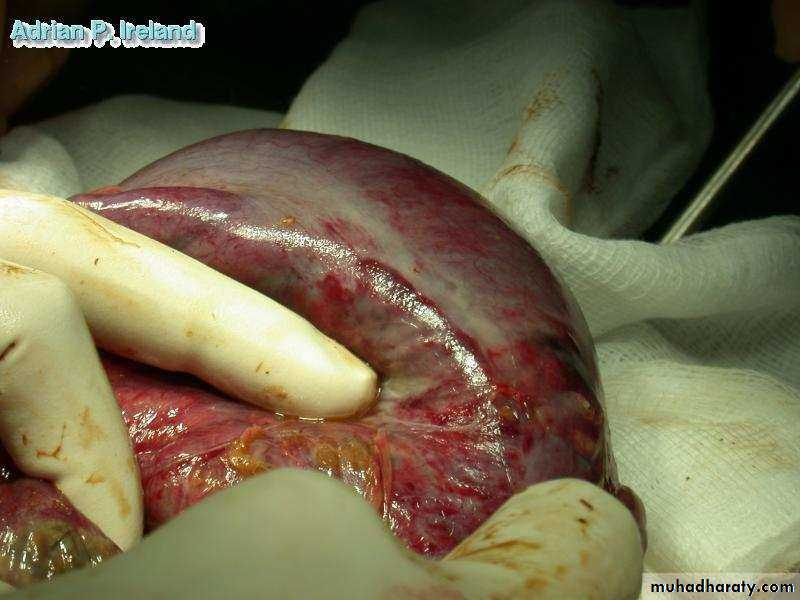
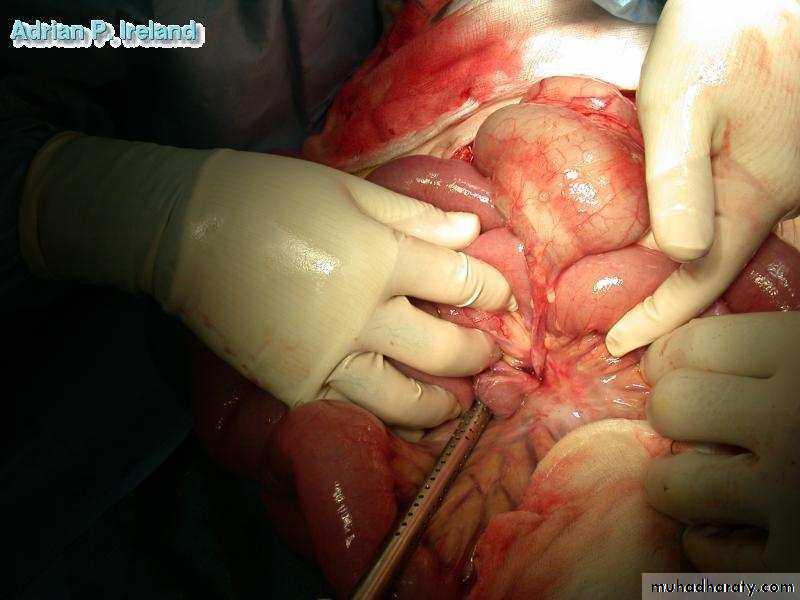
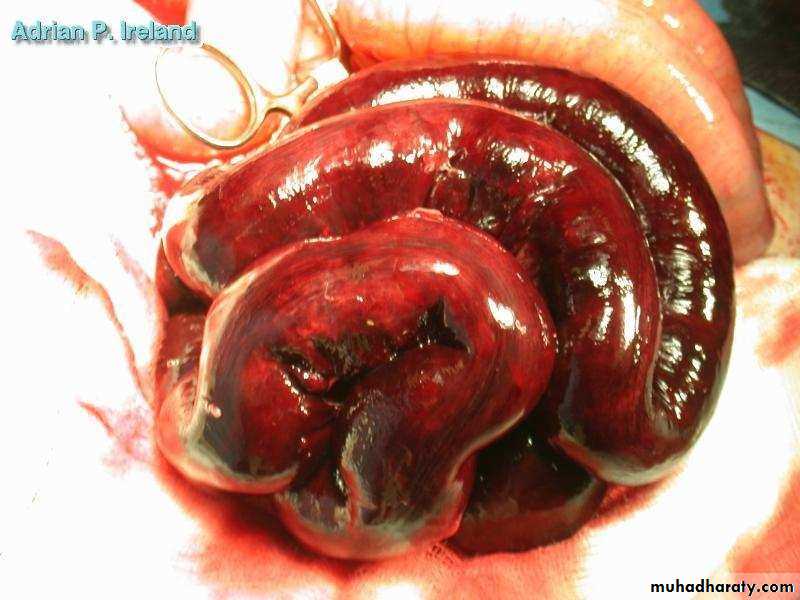
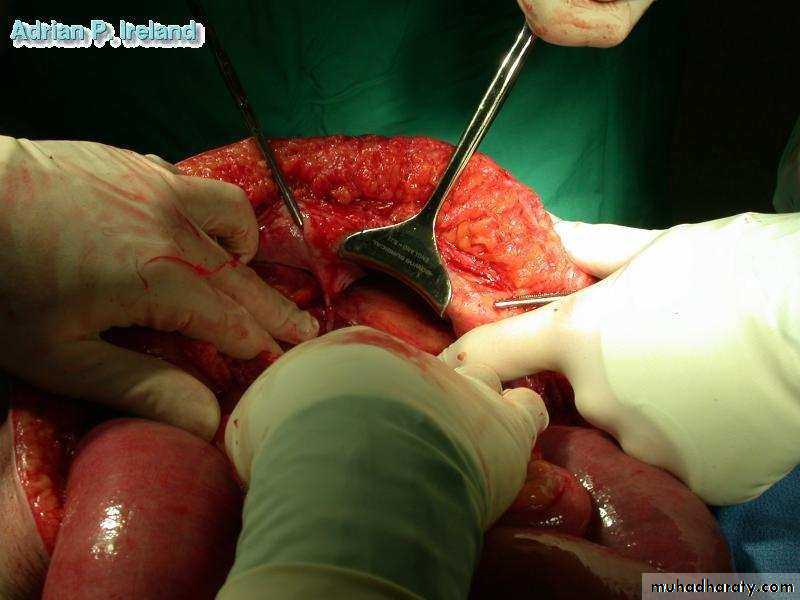
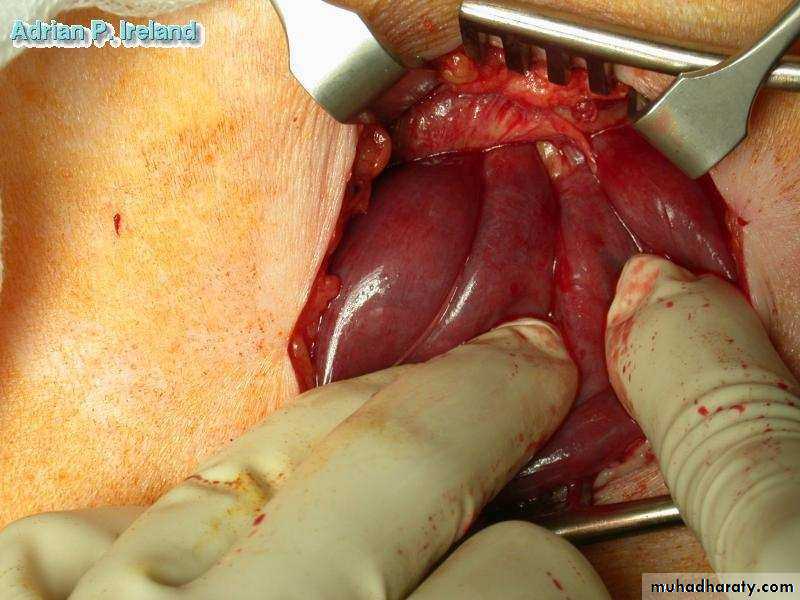
• Operative Findings; Small bowel volvulus• Large Intestine
• Colo-rectal cancer• Volvulus; Sigmoid, Caecal Inflammatory Stricture
• Causes of Intestinal obstruction
• Classification based upon;
• lumen, wall and outside
• small intestine, large intestine Common and Rare• Common and Rare
• Common;• Post operative adhesions
• Herniae; Groin, Femoral and Inguinal, Incisional Colorectal Cancer
• Rare; Internal hernia
• Presenting Complaint• Abdominal Pain
• Vomiting Distension
• Constipation, Complete, obstipation
• Pain
• Site• Radiation Type Severity
• Onset and Duration
• Aggravating and Relieving factors Associated symptoms
• Site
• Whats this?
• Whats this?
• Whats this?
• Past history
• Had this before?• Previous surgery Other illness (drugs)
• Examination
• Overall state; distressed, comfortable, cachexia• Vital signs
• State of Hydration
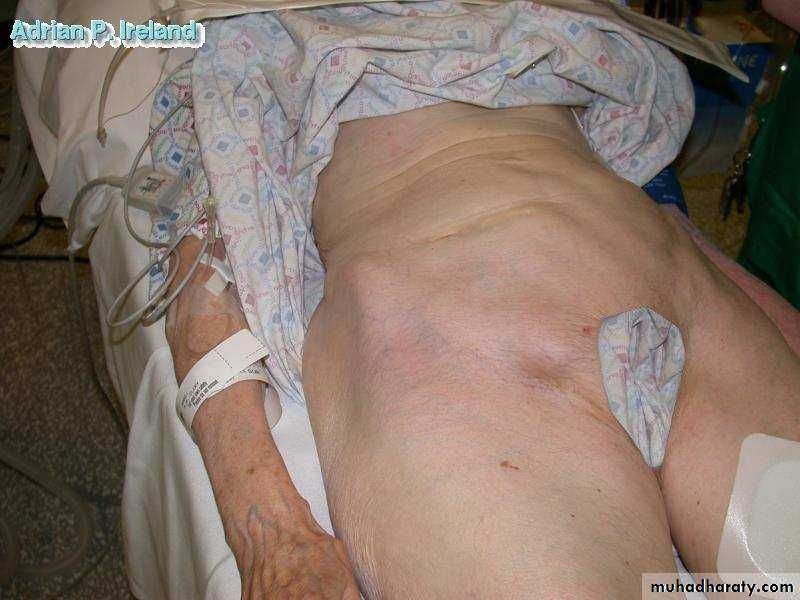
• Abdominal Examination; distension, peristalsis, tenderness, mass• Hernial orifices, Perineum, Rectal, Genitalia, Femoral Pulses
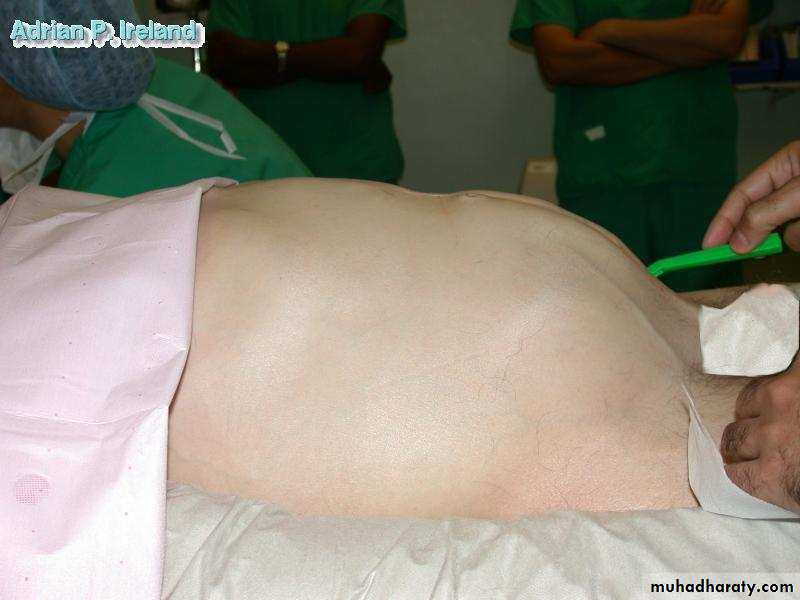
• Inspection
• Inspection
• Clinical approach
• Has the patient got intestinal obstruction?• Is it simple or complicated? What is the fluid deficit?
• What is the level of the obstruction? What is the cause of the obstruction?
• Differential Diagnosis
• Obstuction or Pseudo-obstruction• Of the pain; Abdominal, Non Abdominal
• Of the distension; Fluid, Flatus, Fat, Faeces, Fetus,
• Investigation
• Blood; U & E, FBC, Amylase, Muscle Enzymes,• Radiological; PFA, Erect CXR, CT scan, Enemas.
• Radiology• Quite simple,
• Gaseous distension, what is distended? Fluid levels, fluid distension
• Transition zone, any gas distally? Contrast wont pass, show mass
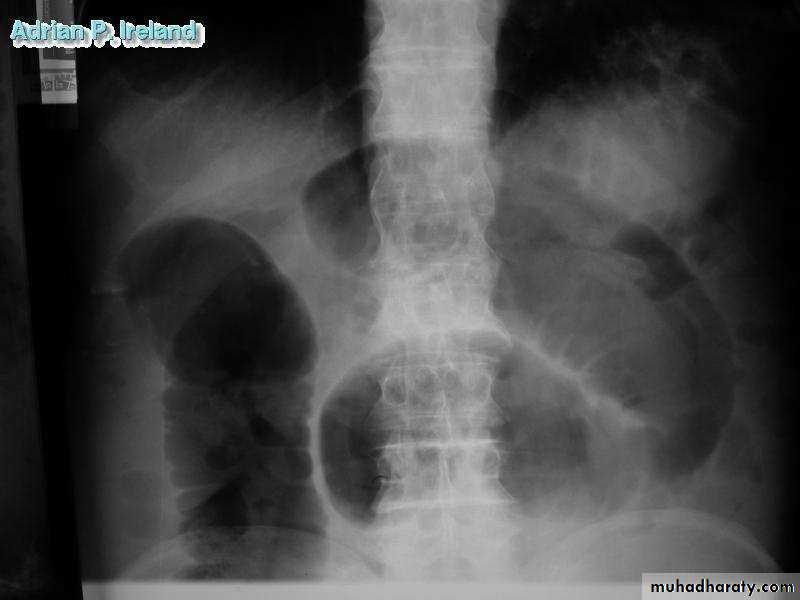
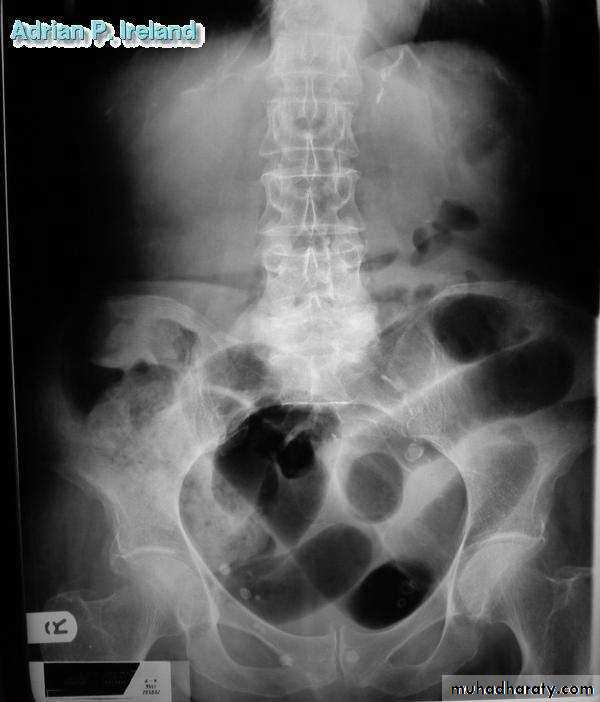
• Radiology, Small bowel obstruction
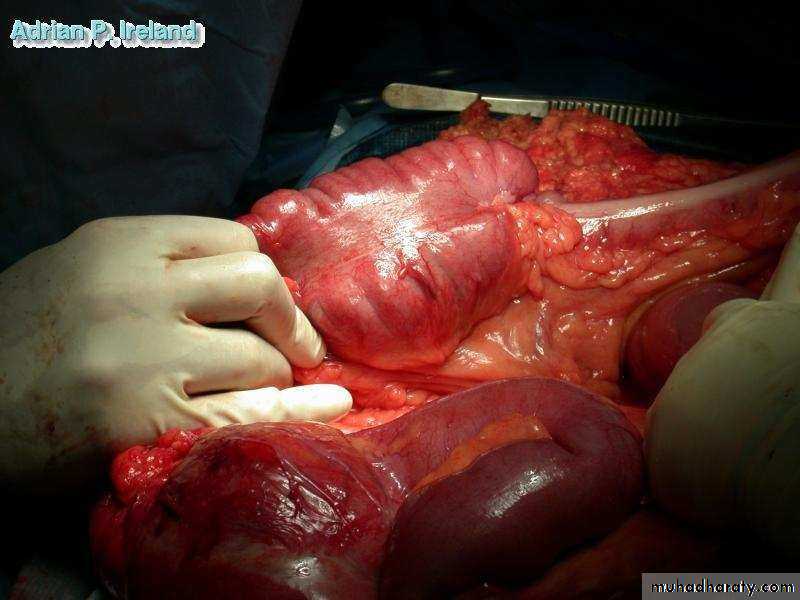
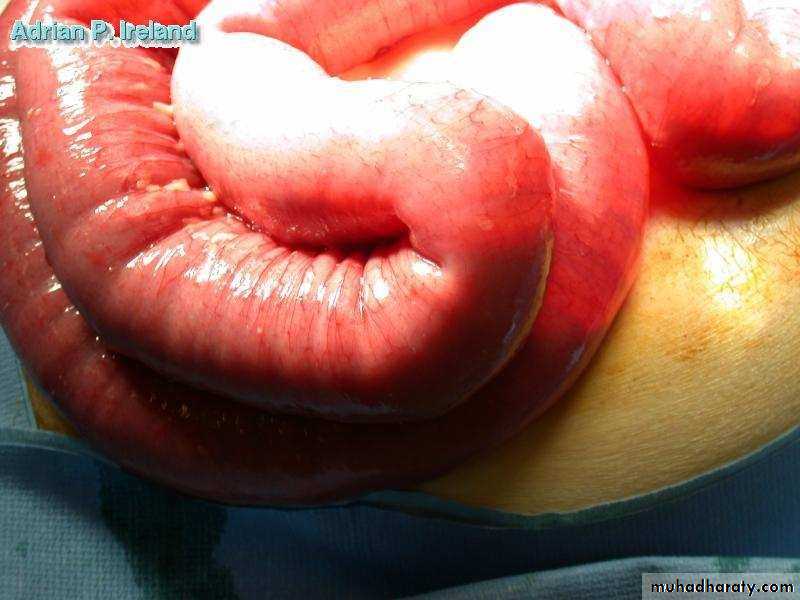
• Operative Findings; Small bowel obstruction
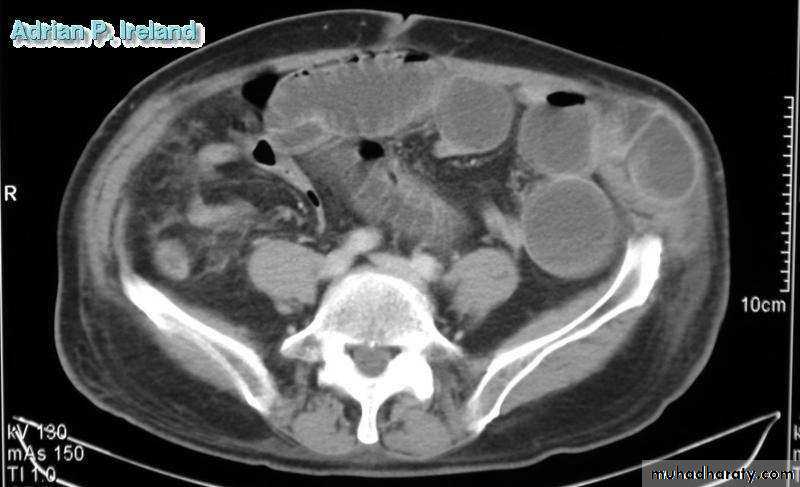
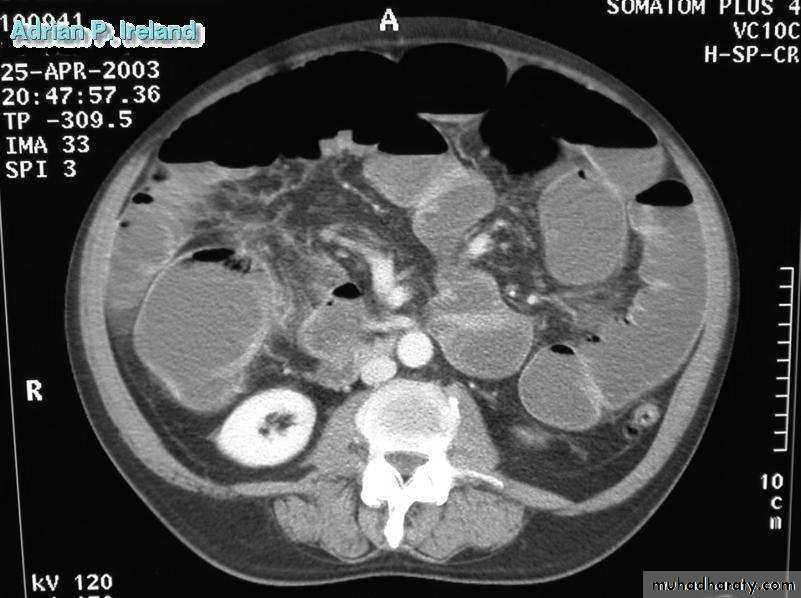
• Radiology; CT, Small bowel obstruction
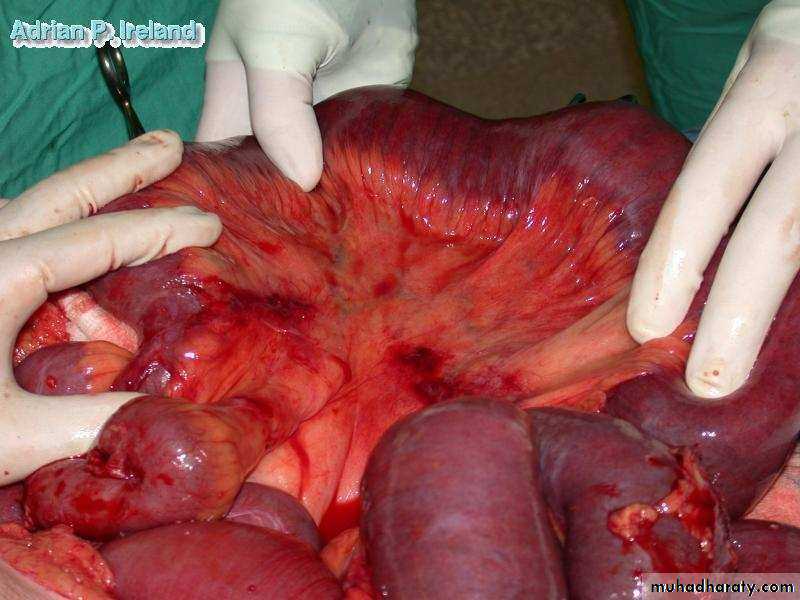
• Operative Findings; Small bowel obstruction
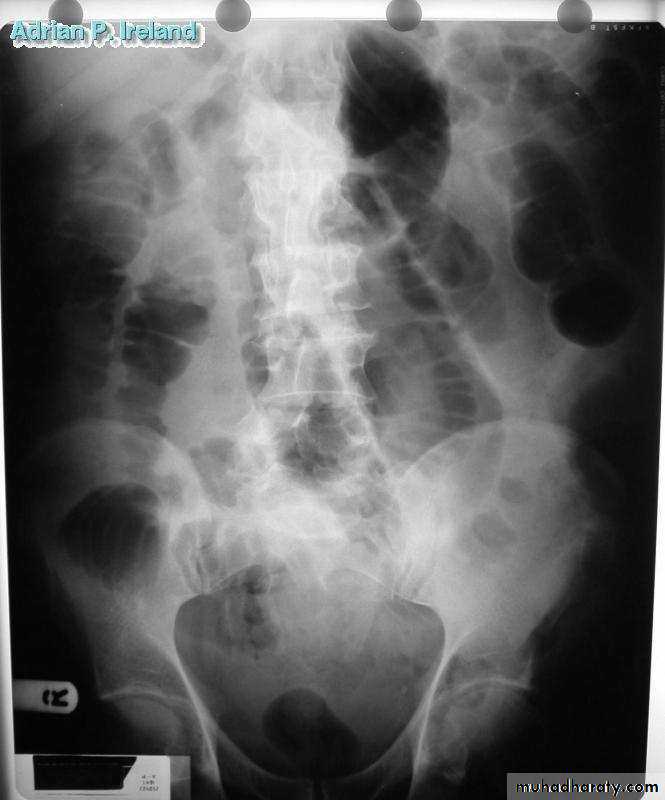
• Radiology; PFA, Large bowel obstruction
• Radiology; CT, Large bowel obstruction
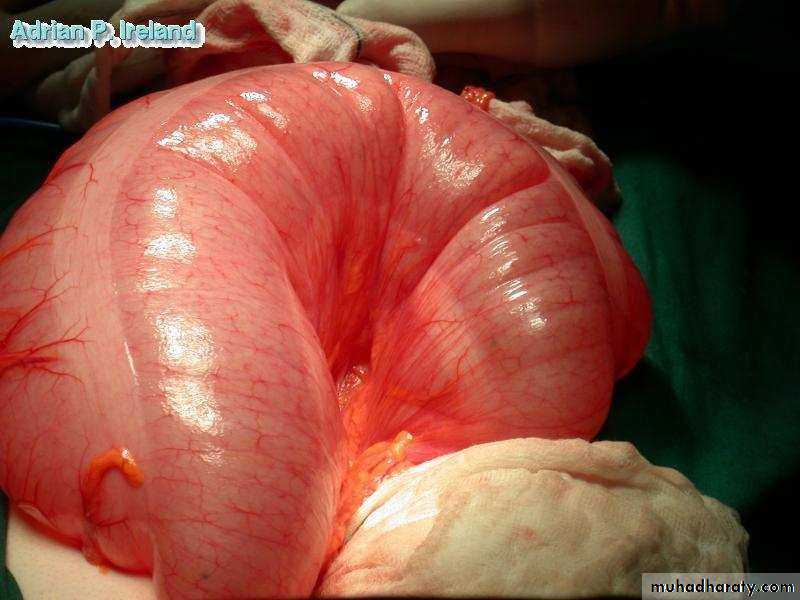
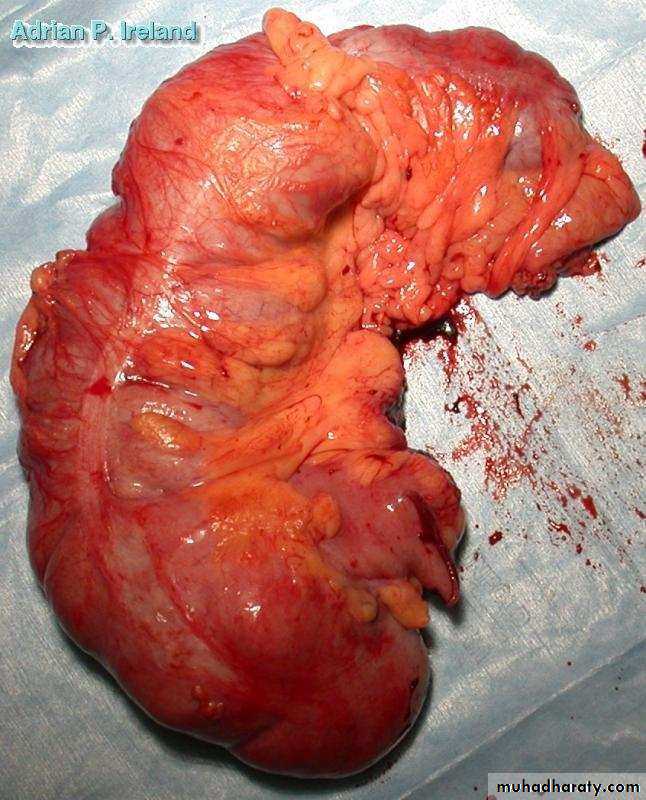
• Operative Findings; Large bowel obstruction
• Thanks