CASE 1
A 50 year old diabetic female presented with burning micturition associated with urinary frequency & suprapubic pain.WHAT IS THE FIRST STEP IN THE EVALUATION OF THIS PATIENT ?
URINANALYSISColor : Yellow
Appearance : Cloudy
Sp. Gravity : 1.033
pH : 6.5
Protein : Negative
Glucose : Negative
Ketone : Negative
Bilirubin : Negative
WBCs : 40 – 50 / HPF
RBCs : 7-10 / HPF
Casts : None
Crystals : None
Squamous epithelia : 2 -3 / HPF
WHAT IS THE MOST LIKELY DIAGNOSIS & THE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISMS ?
Dx. : Cystitis
Causative microorganism : Most likely E.coliHOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT ?
Oral antibiotics for 3 – 5 days.If this patient presented to you with recurrent infection associated with left loin pain, nausea & hematuria; how would you evaluate her ?
Urinanalysis
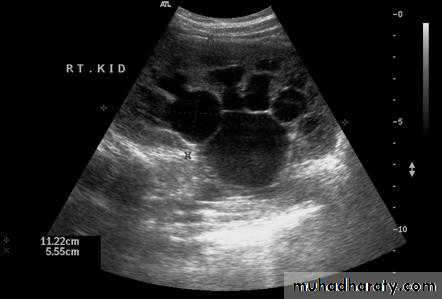
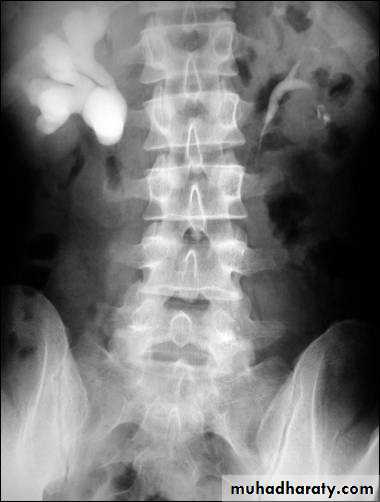
Urine cultueU / S
KUBURINANALYSIS
Color : YellowAppearance : Cloudy
Sp. Gravity : 1.033
pH : 8
Protein : Negative
Glucose : Negative
Ketone : Negative
Bilirubin : Negative
WBCs : 40 – 50 / HPF
RBCs : 12 - 15 / HPF
Squamous epithelia : 2 -3 / HPF
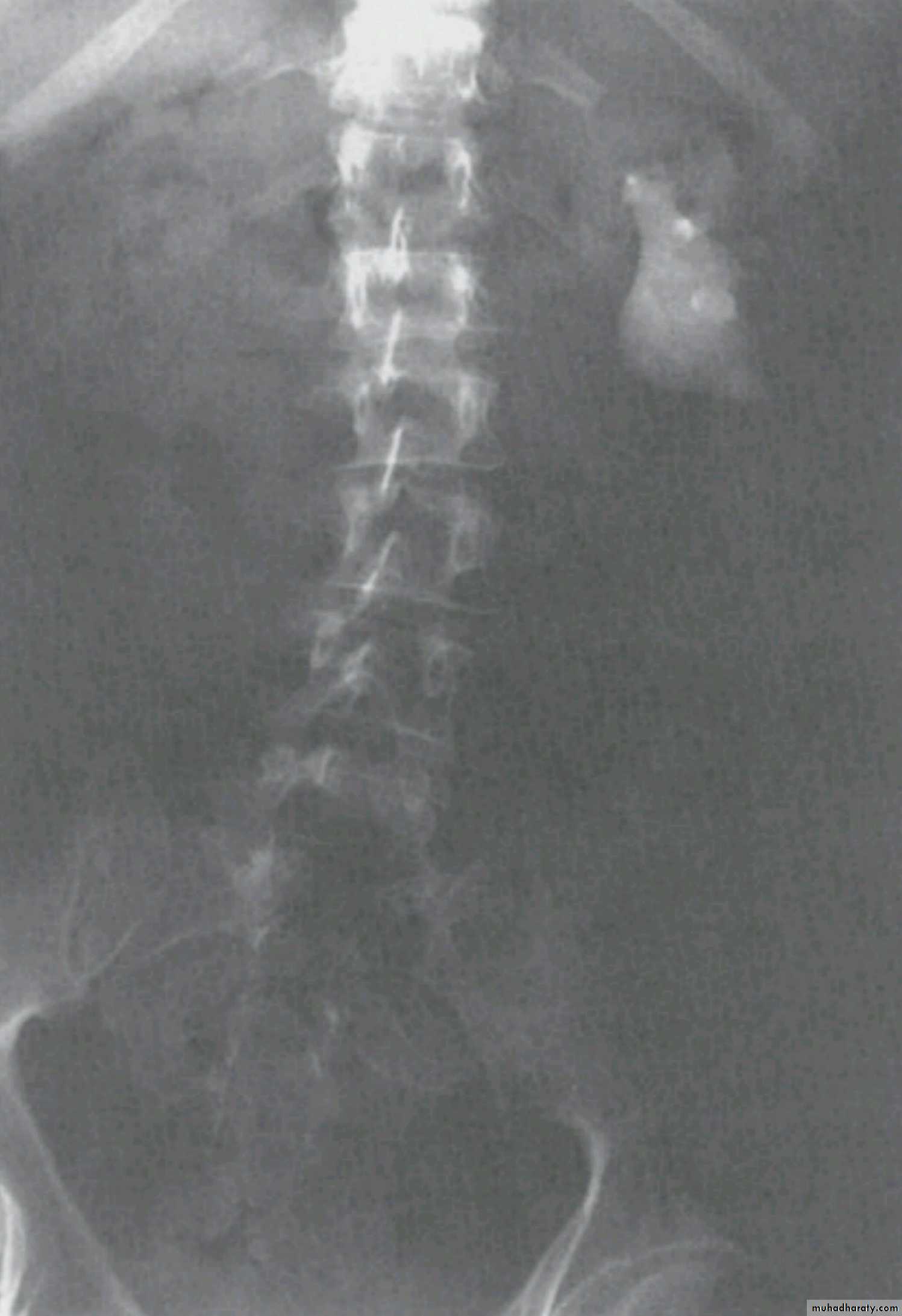
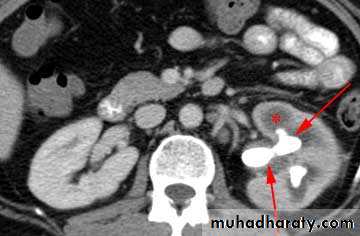
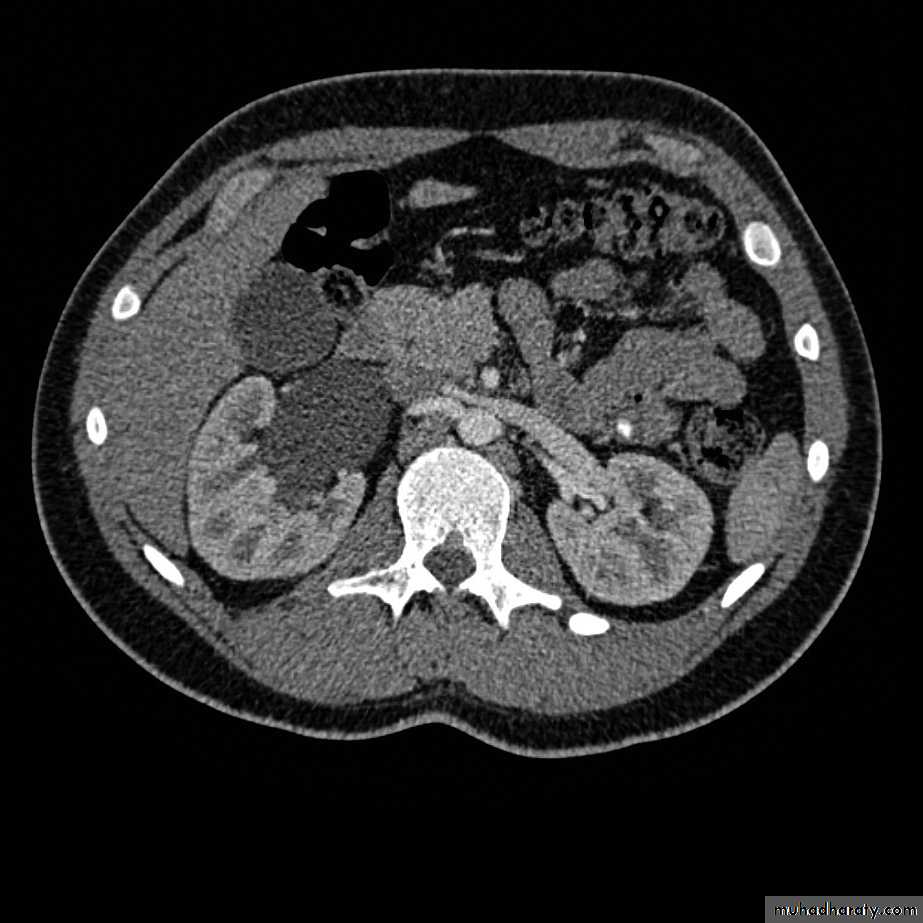
WHAT IS THE MOST APPROPRIATE RADIOLOGICAL MODALITY ?
CT scanWHAT IS THE DIAGNOSIS & THE CAUSATIVE ORGANISM ?
Struvite stone ( MAP stone ).Urea splitting microorganisms.
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT HER ?PCNL
Controlling the infection (pre, peri, postoperatively)Good hydration
Good glycemic control
If this patient neglects herself & develops fever & chills associated with costovertebral angle tenderness; what is the most likely diagnosis & how would you treat her ?
Dx. : Acute pyelonephritis
Management :- Hospitalization
- Parenteral antibiotics ( 7 – 10 days )
CASE 2
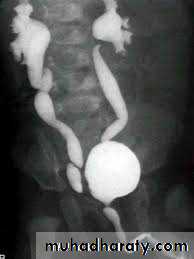
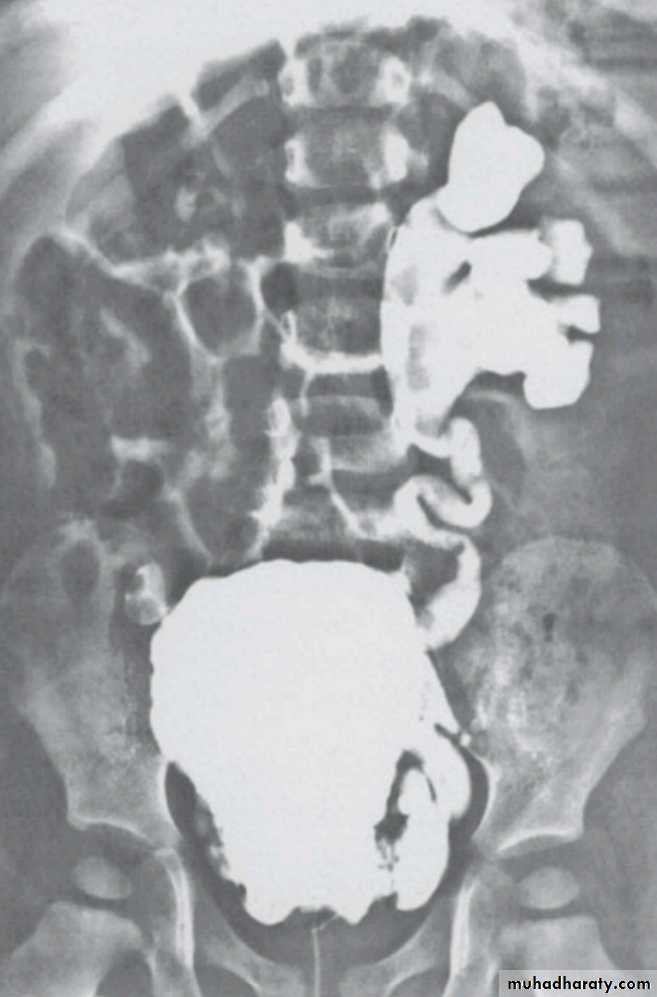
A 27 year old pregnant lady discovered during prenatal U/S to have antenatal hydronephrosis. How would you interfere ?Watchful surveillance
HOW WOULD YOU EVALUATE HER POSTNATALLY ?U/S in the first week of life
WHAT ARE THE POSSIBLE UNDERLYING CAUSES ?PUJ obstruction
VURPosterior urethral valve ( males only )
HOW CAN YOU DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN THESE THREE CONDITIONS ?
PUJ obstruction
U/S : AP diameter of the renal pelvis, kidney size.IVP
CT scanRadionuclide renography : the best radiographic study.
U/SIVP
CT scan
VUR
Voiding cystourethrogram
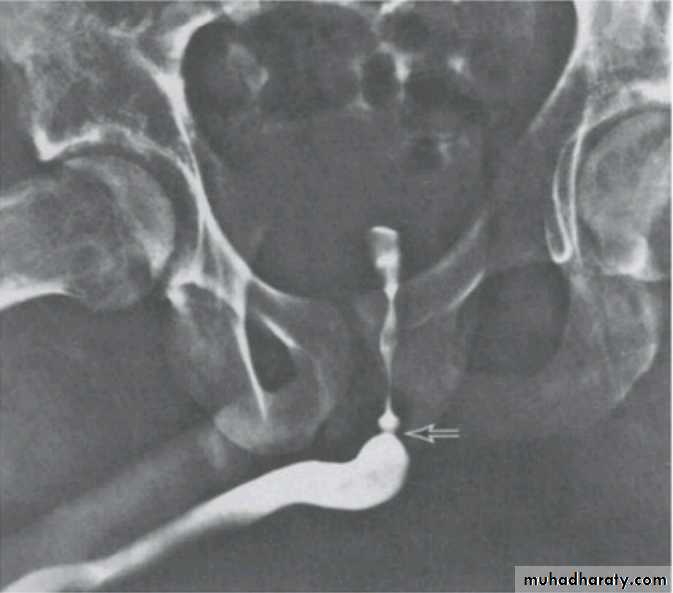
POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVE
Voiding cystourethrogram.Excretory urogram.
CASE 3
A 70 year old male presented with hesitancy, decreased force & caliber of stream, sensation of incomplete bladder emptying, excessive straining, urgency, frequency & nocturia.
What we call these symptoms collectively? And how we classify them?
Lower urinary tract symptoms :1- Obstructive symptoms
2- Irritative symptomsWhat are the differential diagnosis of these symptoms?
UTIBPH
Urethral stricture
Bladder neck contracture
Vesical stone
Ca prostate
Neurogenic bladder disorders
How would you evaluate this patient ?
History
Previous urethral instrumentation, urethritis, or trauma
Hematuria & pain
Hx of neurologic diseases, stroke, DM, back injury
Physical examination
DRE : smooth, firm, elastic enlargement of the prostate.Focused neurologic examination.
Lab findingsUrinanalysis : to exclude infection or hematuria
RFT
Serum PSA (optional)
Additional tests
Upper tract imaging (optional)Cystometrograms & urodynamic profiles (optional)
How can you assess the severity of these symptoms?
AUA self-administered questionnaire
What are the therapeutic options for BPH?
A-Watchful waitingFor mild symptom scores (0-7)
B-Medical therapy
Alpha blockers5 alpha reductase inhibitors
Combination therapy
C-Surgical treatment
Indications :Refractory urinary retention
Recurrent UTI
Recurrent gross hematuria
Bladder stones
Renal insufficiency
Bladder diverticulum
What is the gold standard surgical technique?
TURP
What are the indications of open prostatectomy?
IndicationsToo large prostate
Associated bladder pathology
Dorsal lithotomy position is not possible
If following prostatic resection, patient is discovered to have >5% cancerous prostatic tissue; how would you stage this condition?
T1b
What is your further management ?
DRE (nodular surface, induration)PSA
TRUS
Prostatic biopsy
Additional tests
RFT
CBC
Alkaline phosphatase
Bone scan
Axial imaging (CT & MRI)
What is the most common histological subtype of prostatic carcinoma ?
AdenocarcinomaHow would you treat this patient ?
Radical prostatectomyCASE 4
A 65 year old smoker male presented with painless, intermittent hematuria for the last 6 months associated with urinary frequency, poor appetite & weight loss. He is a worker in a rubber industry.How would you evaluate this patient ?
Investigations
Urinanalysis
CBC
Renal function test
Urine cytology
Tumor markers
Imaging modalities
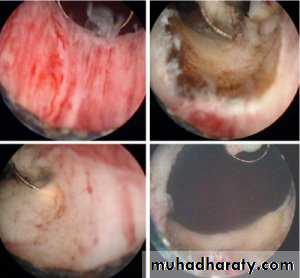
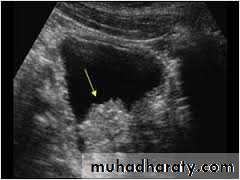
U/S : fixed massEXU : filling defect
CT & MRI : looking for LN
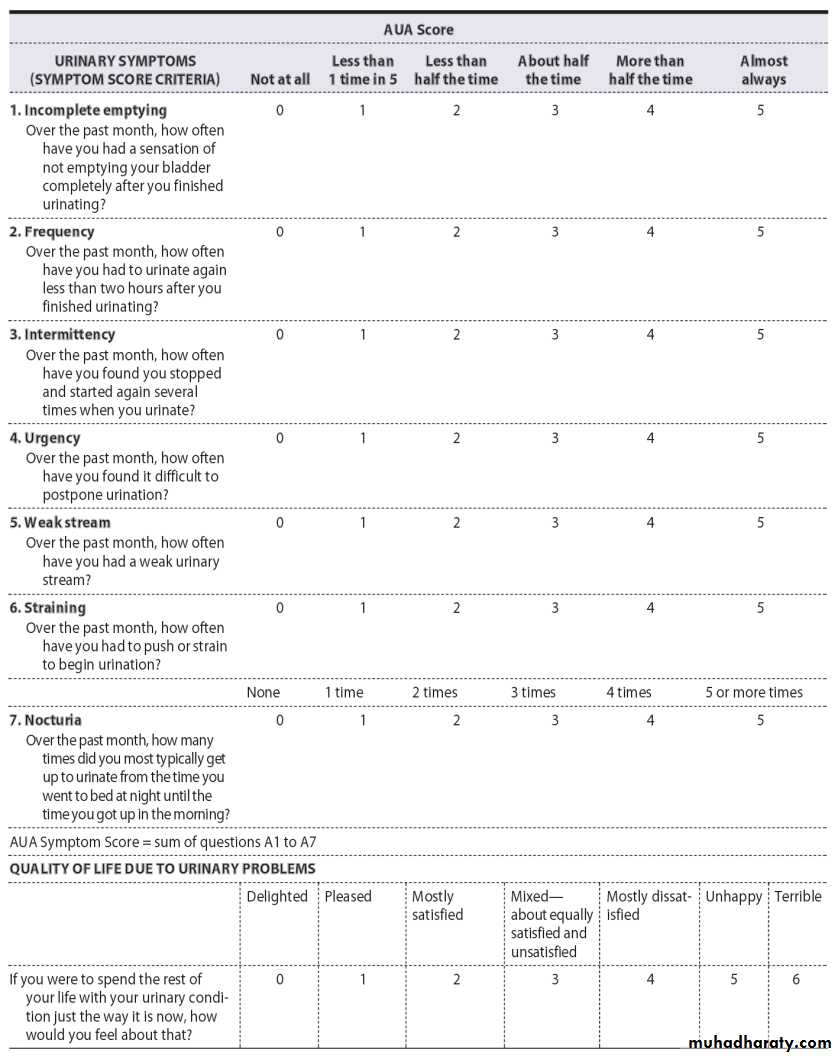
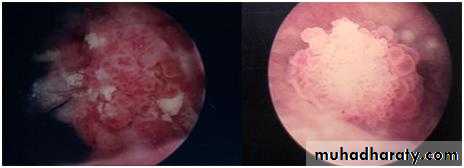
Cystoscopy : is the definitive method
Molecular markers : done on the tissue
U/S
IVP
CYSTOSCOPY
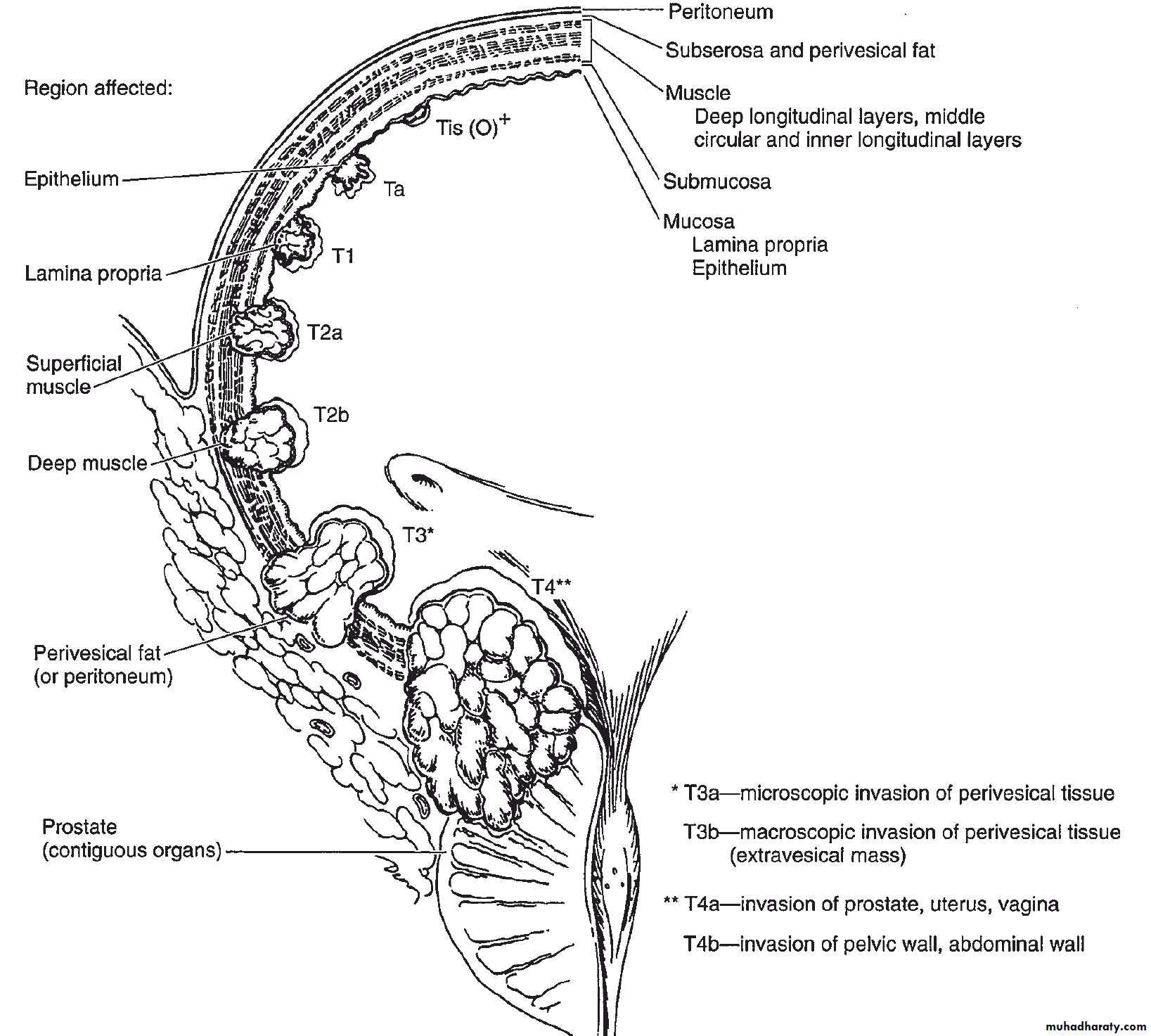
How would you stage this disease?
By :CT scan
TUR
What is the stage of this lesion if it is reaching the deep muscular layer ?
T2bWhat is the most common histological subtype of this tumor?
TCC
If you know that this is an Egyptian patient, What is the possible histological subtype? Why?