University of IshikFaculty of Dentistry2nd stage Lec. Physiology
Abdulqadir Kh. HamadAbdulqadir.bio@raparinuni.org
The Cardiovascular System: The Blood
Blood• Transportation
• Gases, nutrients, hormones, waste products
• Regulation
• Regulation of pH and osmosis osmotic pressure
• Maintain of the body
• Protection
• Protection against foreign substances
• By white blood cells, immune proteins (Antibodies & Compete Protein )
• Clot formation prevent bleeding
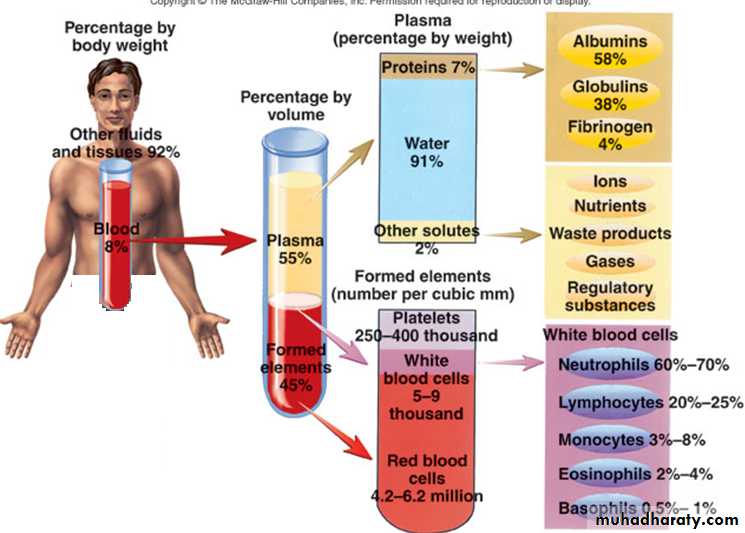
Components of Blood
Blood plasma – water liquid extracellular matrix
90.5 % -91.5% water, 8.5% solutes (primarily proteins)
Hepatocytes synthesize most plasma proteins
Albumins, fibrinogen, antibodies
Other solutes include electrolytes, nutrients, enzymes, hormones, gases and waste products
Formed elements – cells and cell fragments
Erythrocytes: Red blood cells (RBCs) :
Leukocytes : White blood cells (WBCs)
Thrombocyte : Platelets
Components of Blood 1- Plasma
Liquid part of bloodBlood plasma – water liquid extracellular matrix
91.5% water, 8.5% solutes (primarily proteins)
Hepatocytes synthesize most plasma proteins
Albumins, fibrinogen, antibodies Colloid: Liquid containing suspended substances that don’t settle out
Albumin: Important in regulation of water movement between tissues and blood
Globulins: Immune system or transport molecules
Fibrinogen: Responsible for formation of blood clots
Other solutes include electrolytes, nutrients, enzymes, hormones, gases and waste products
II. Plasma
C. ~2% organic solutes
1. amino acids
2. vitamins
3. hormones
4. lipoproteins
D. ~1% inorganic salts
E. dissolved gases
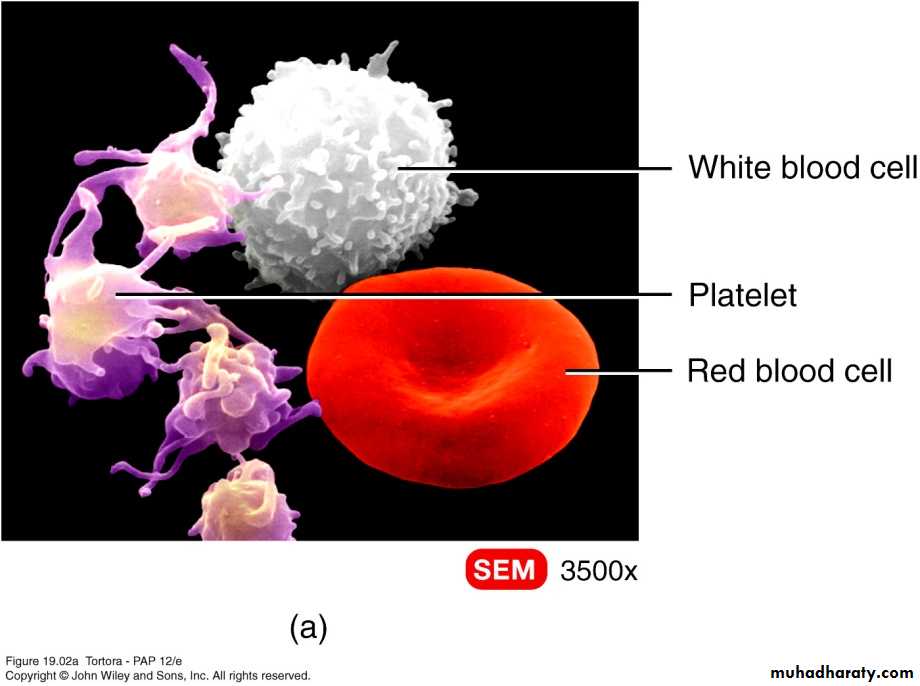
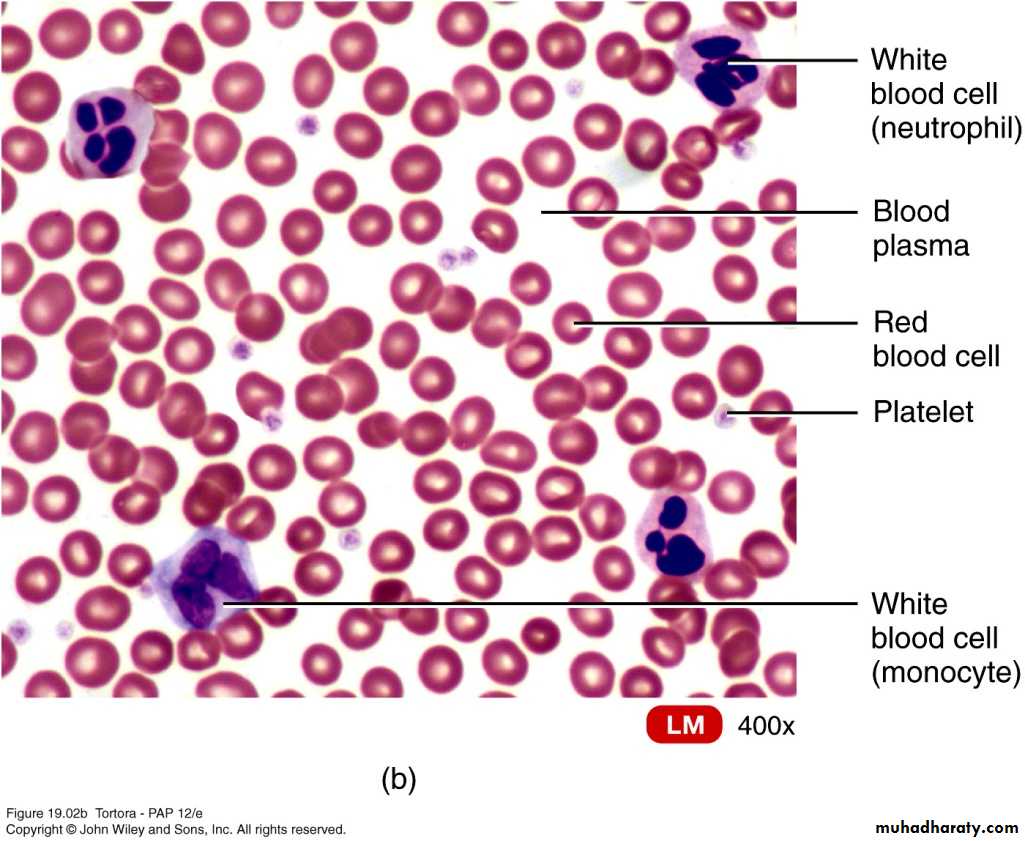
Formed Elements of Blood
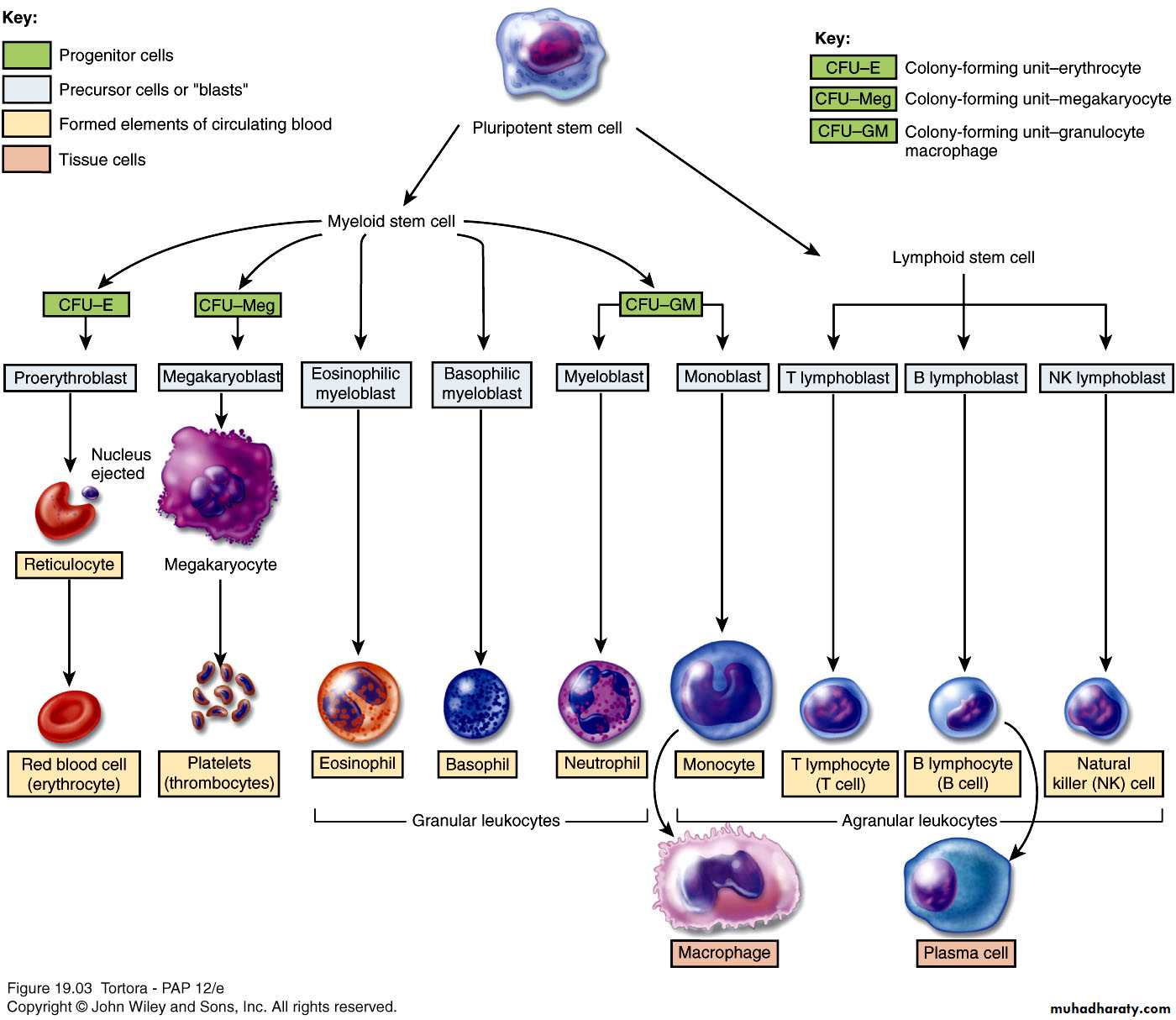
Formation of Blood Cells
Negative feedback systems regulate the total number of RBCs and platelets in circulationAbundance of WBC types based of response to invading pathogens or foreign antigens
Red bone marrow primary site
Pluripotent stem cells have the ability to develop into many different types of cells
Formation of Blood Cells
Stem cells in bone marrowReproduce themselves
Proliferate and differentiate
Cells enter blood stream through sinusoids
Formed elements do not divide once they leave red bone marrow
Exception is lymphocytes
Formation of Blood Cells
Pluripotent stem cells produceMyeloid stem cells
Give rise to red blood cells, platelets, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils
Lymphoid stem cells give rise to
Lymphocytes
Hemopoietic growth factors regulate differentiation and proliferation
Erythropoietin – RBCs
Thrombopoietin – platelets
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) and interleukins – WBCs
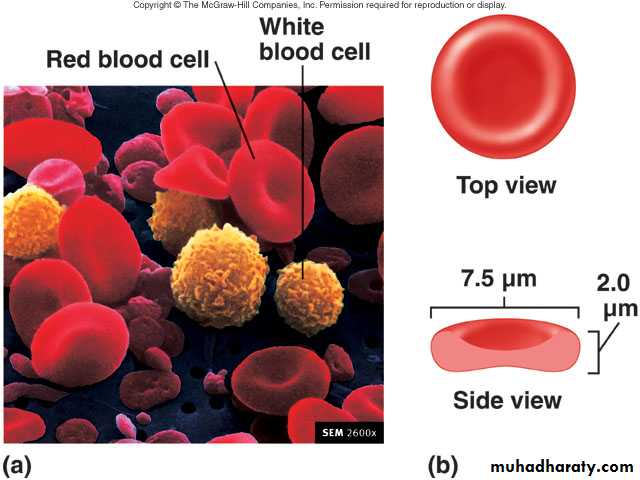
Red Blood Cells/ Erythrocytes
Contain oxygen-carrying protein hemoglobin
Production = destruction with at least 2 million new RBCs per second
Biconcave disc – increases surface area
Strong, flexible plasma membrane
Glycolipids in plasma membrane responsible for ABO and Rh blood groups
Lack nucleus and other organelles
No mitochondria
19-13
ErythrocytesStructure
Biconcave, anucleate
Components
Hemoglobin
Lipids, ATP, carbonic anhydrase
Function
Transport oxygen from lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs
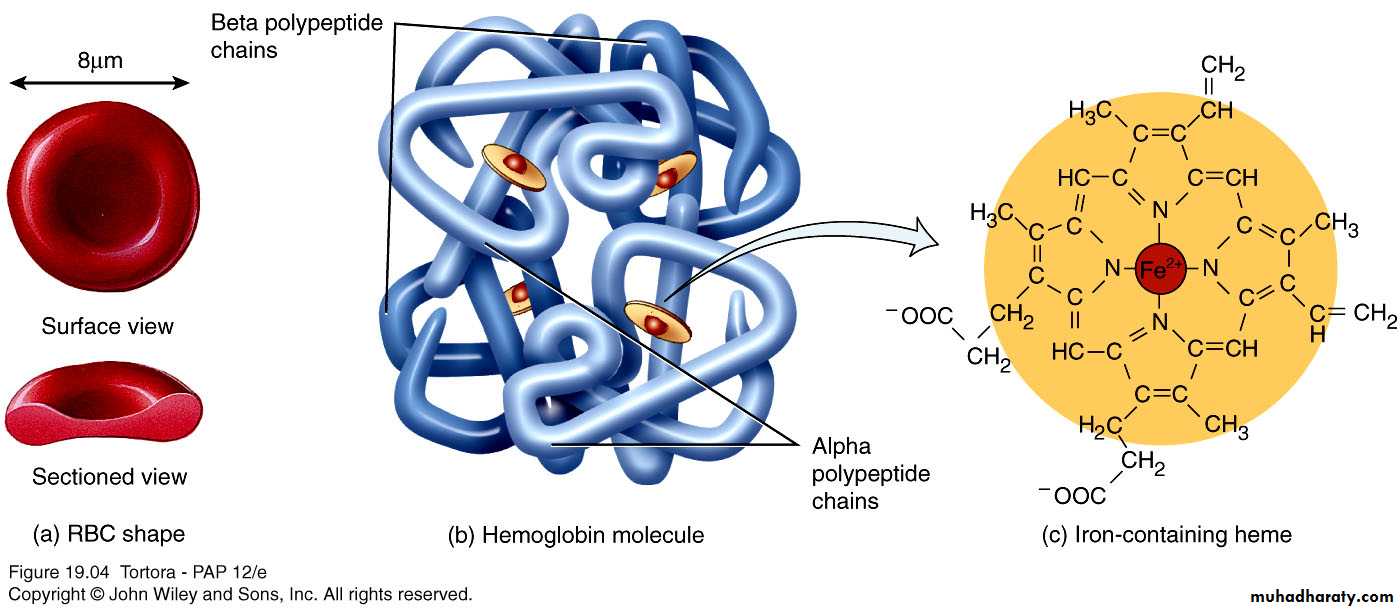
Hemoglobin
Globin – 4 polypeptide chains
Heme in each of 4 chainsIron ion can combine reversibly with one oxygen molecule
Also transports 23% of total carbon dioxide
Combines with amino acids of globin
Nitric oxide (NO) binds to hemoglobin
Releases NO causing vasodilation to improve blood flow and oxygen delivery
Shapes of RBC and Hemoglobin
Red Blood Cells
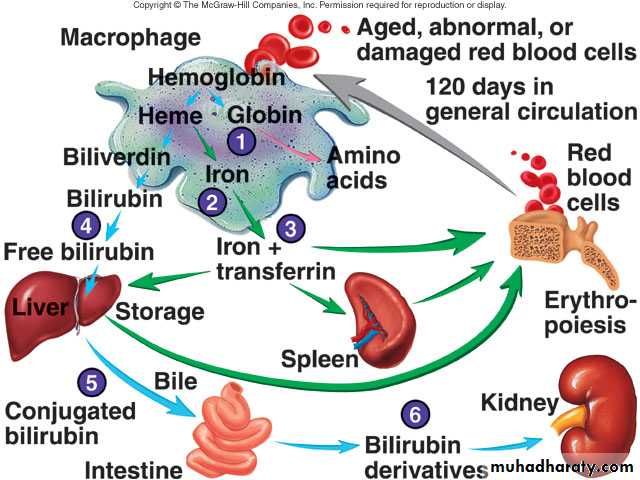
RBC life cycleLive only about 120 days
Cannot synthesize new components – no nucleus
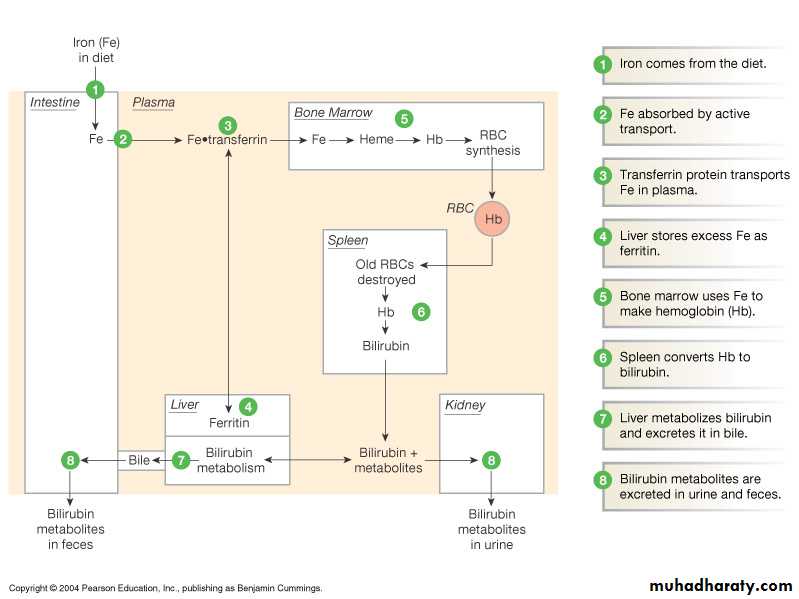
Ruptured red blood cells removed from circulation and destroyed by fixed phagocytic macrophages in spleen and liver
Breakdown products recycled
Globin’s amino acids reused
Iron reused
Non-iron heme ends as yellow pigment urobilin in urine or brown pigment stercobilin in feces
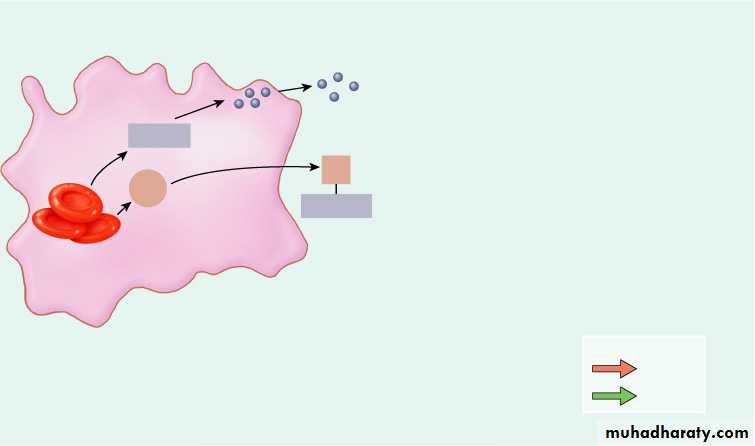
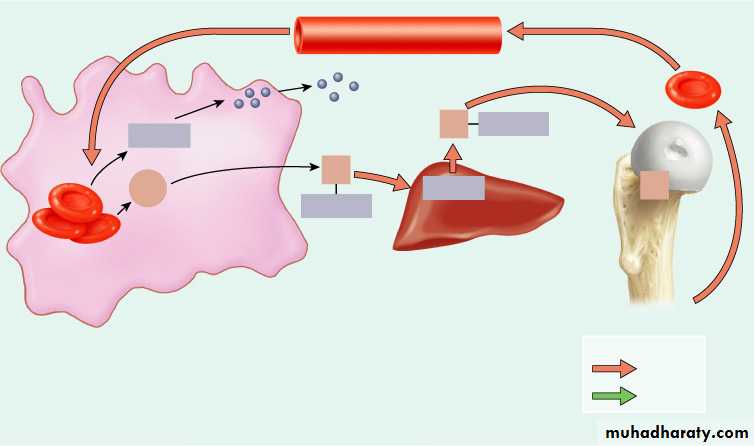
Formation and Destruction of RBC’s
Red blood cell
death andphagocytosis
Key:
in blood
in bile
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
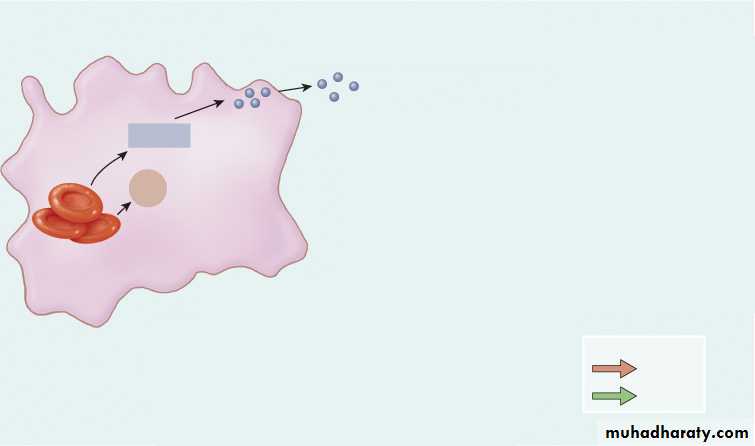
1
Globin
Red blood celldeath and
phagocytosis
Key:
in blood
in bile
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
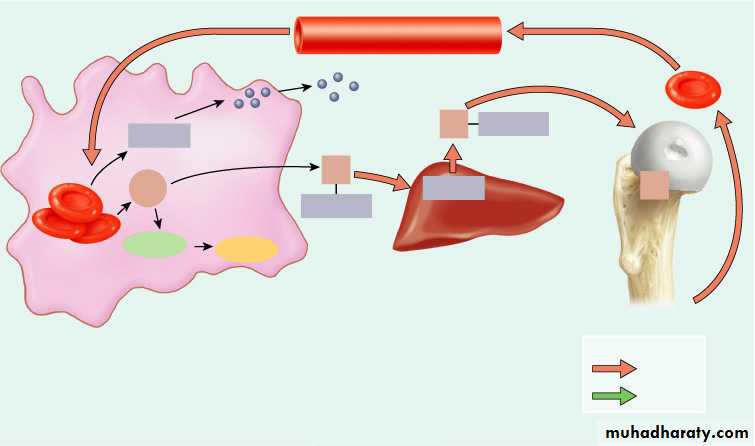
Heme
2
1
Amino
acids
Reused for
protein synthesis
Globin
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
Key:
in blood
in bile
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Heme
3
2
1
Amino
acidsReused for
protein synthesis
Globin
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
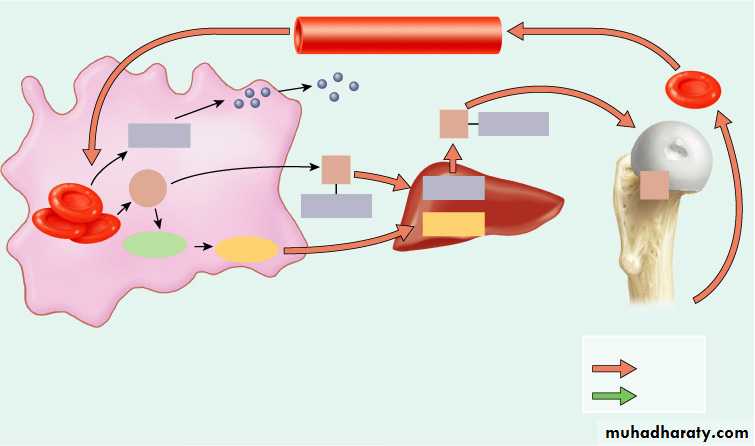
Transferrin
Fe3+
Key:
in blood
in bile
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Heme
4
3
2
1
Amino
acids
Reused for
protein synthesis
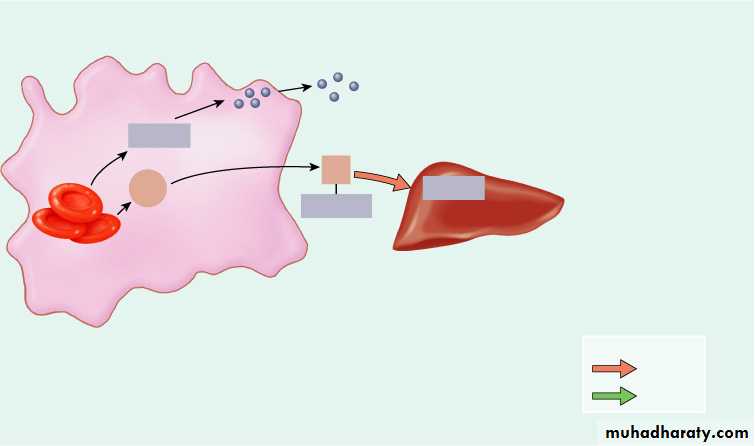
Globin
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
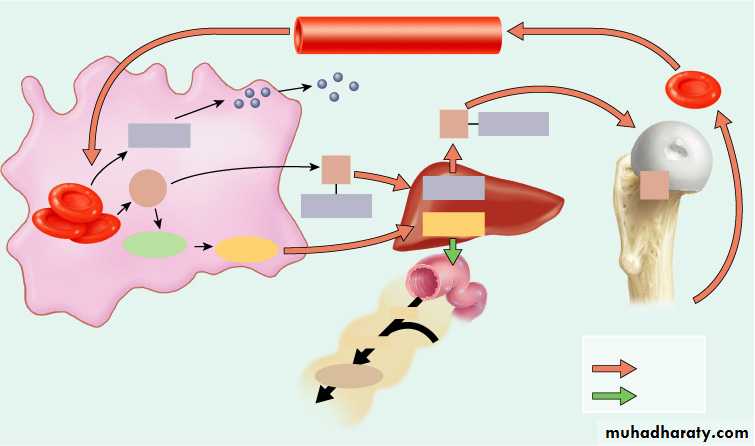
Transferrin
Fe3+
Liver
Key:
in blood
in bile
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Ferritin
Heme
5
4
3
2
1
Amino
acids
Reused for
protein synthesis
Globin
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
Transferrin
Fe3+
Fe3+
Transferrin
Liver
Key:
in blood
in bile
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Ferritin
Heme
6
5
4
3
2
1
Amino
acids
Reused for
protein synthesis
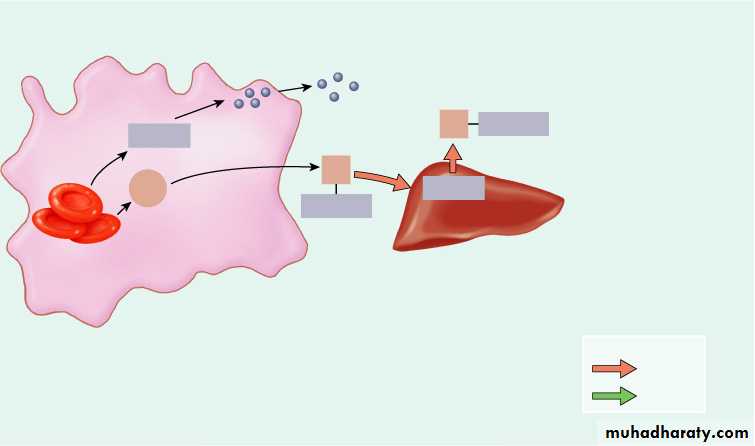
Globin
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
Transferrin
Fe3+
Fe3+
Transferrin
Liver
+
Globin
+
Vitamin B12
+
Erythopoietin
Key:
in blood
in bile
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Ferritin
Heme
Fe3+
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Amino
acids
Reused for
protein synthesis
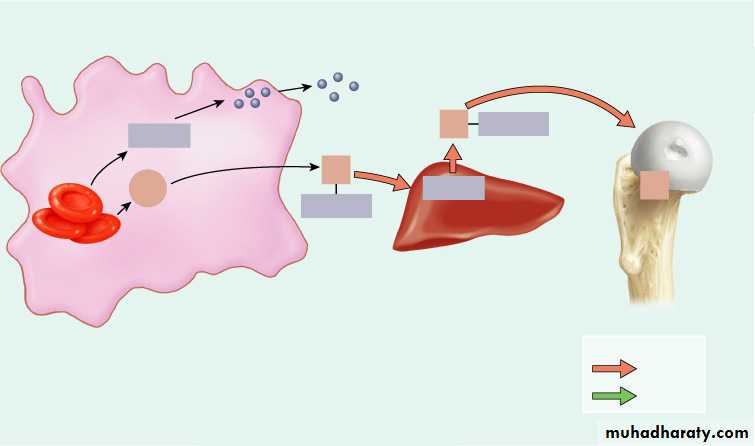
Globin
Circulation for about
120 days
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
Transferrin
Fe3+
Fe3+
Transferrin
Liver
+
Globin
+
Vitamin B12
+
Erythopoietin
Key:
in blood
in bile
Erythropoiesis in
red bone marrow
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Ferritin
Heme
Fe3+
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Amino
acids
Reused for
protein synthesis
Globin
Circulation for about
120 days
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
Transferrin
Fe3+
Fe3+
Transferrin
Liver
+
Globin
+
Vitamin B12
+
Erythopoietin
Key:
in blood
in bile
Erythropoiesis in
red bone marrow
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Ferritin
Heme
Biliverdin
Bilirubin
Fe3+
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Amino
acids
Reused for
protein synthesis
Globin
Circulation for about
120 days
Bilirubin
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
Transferrin
Fe3+
Fe3+
Transferrin
Liver
+
Globin
+
Vitamin B12
+
Erythopoietin
Key:
in blood
in bile
Erythropoiesis in
red bone marrow
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Ferritin
Heme
Biliverdin
Bilirubin
Fe3+
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Amino
acids
Reused for
protein synthesis
Globin
Stercobilin
Bilirubin
Urobilinogen
Feces
Small
intestine
Circulation for about
120 days
Bacteria
Bilirubin
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
Transferrin
Fe3+
Fe3+
Transferrin
Liver
+
Globin
+
Vitamin B12
+
Erythopoietin
Key:
in blood
in bile
Erythropoiesis in
red bone marrow
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Ferritin
Heme
Biliverdin
Bilirubin
Fe3+
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Amino
acids
Reused for
protein synthesis
Globin
Urine
Stercobilin
Bilirubin
Urobilinogen
Feces
Small
intestine
Circulation for about
120 days
Bacteria
Bilirubin
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
Transferrin
Fe3+
Fe3+
Transferrin
Liver
+
Globin
+
Vitamin B12
+
Erythopoietin
Key:
in blood
in bile
Erythropoiesis in
red bone marrow
Kidney
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Ferritin
Urobilin
Heme
Biliverdin
Bilirubin
Fe3+
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Amino
acids
Reused for
protein synthesis
Globin
Urine
Stercobilin
Bilirubin
Urobilinogen
Feces
Large
intestine
Small
intestine
Circulation for about
120 days
Bacteria
Bilirubin
Red blood cell
death and
phagocytosis
Transferrin
Fe3+
Fe3+
Transferrin
Liver
+
Globin
+
Vitamin B12
+
Erythopoietin
Key:
in blood
in bile
Erythropoiesis in
red bone marrow
Kidney
Macrophage in
spleen, liver, or
red bone marrow
Ferritin
Urobilin
Heme
Biliverdin
Bilirubin
Fe3+
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
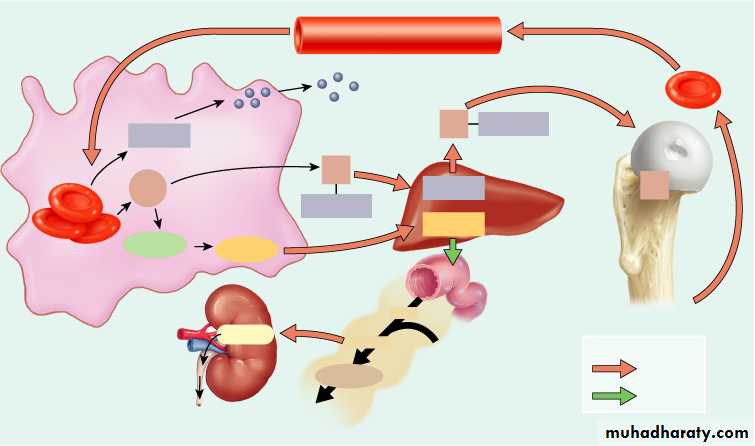
Erythropoiesis
Starts in red bone marrow with proerythroblast
Cell near the end of development ejects nucleus and becomes a reticulocyte
Develop into mature RBC within 1-2 days
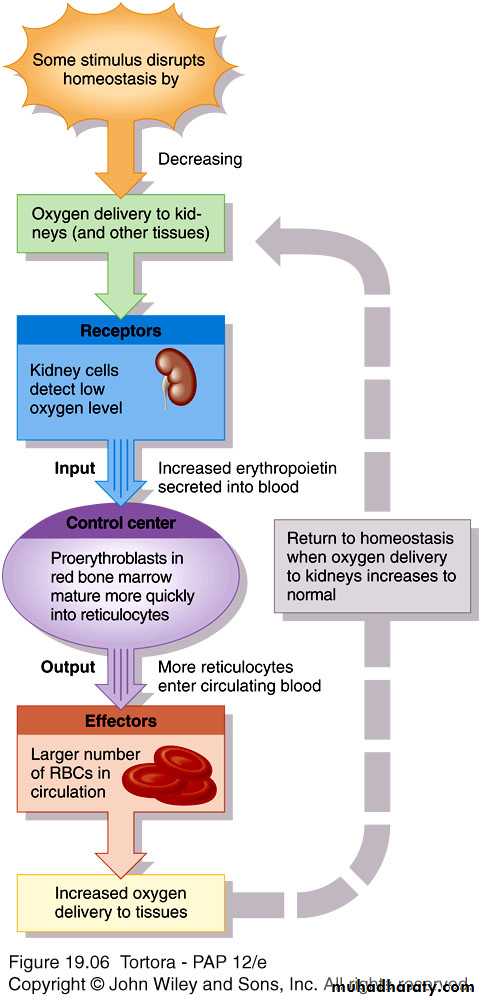
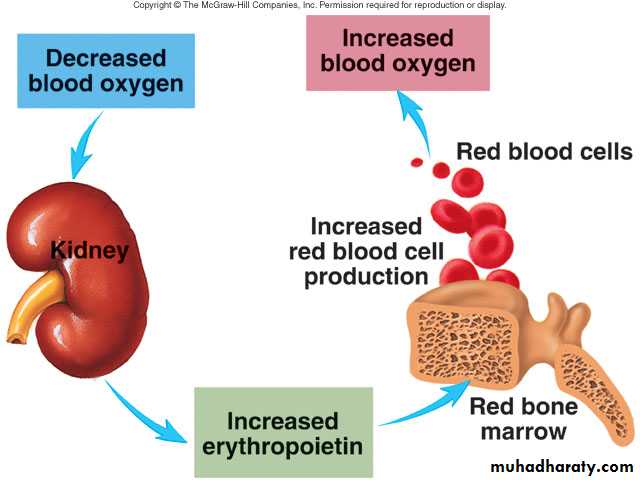
Negative feedback balances production with destruction
Controlled condition is amount of oxygen delivery to tissues
Hypoxia stimulates release of erythropoietin
Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
19-21
ErythropoiesisProduction of red blood cells
Stem cells proerythroblasts early erythroblasts intermediate late reticulocytes
Erythropoietin: Hormone to stimulate RBC production