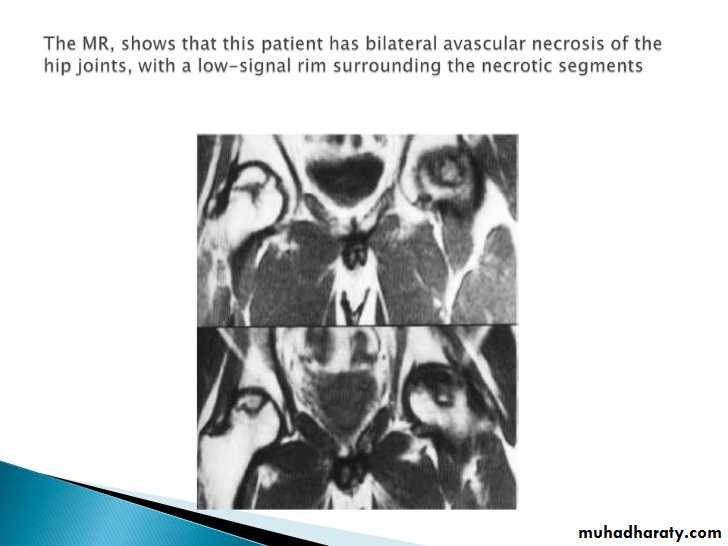
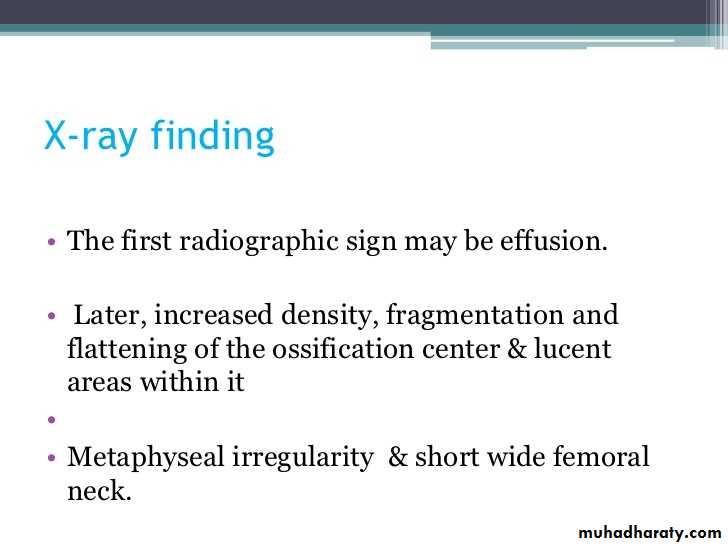
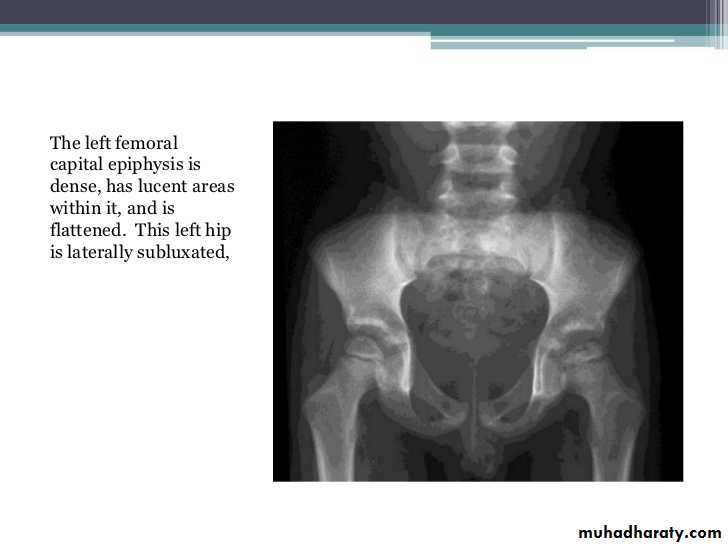
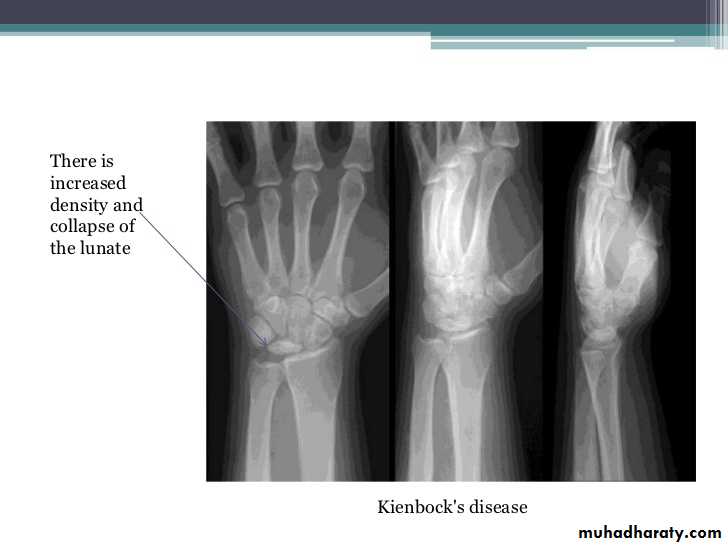
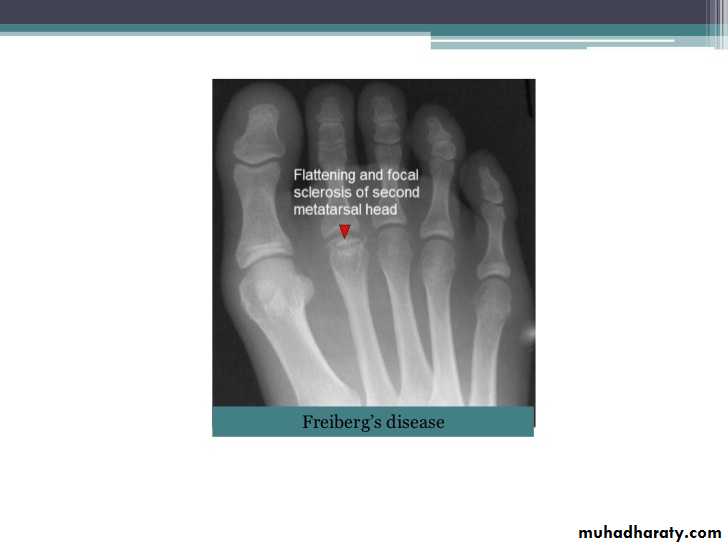
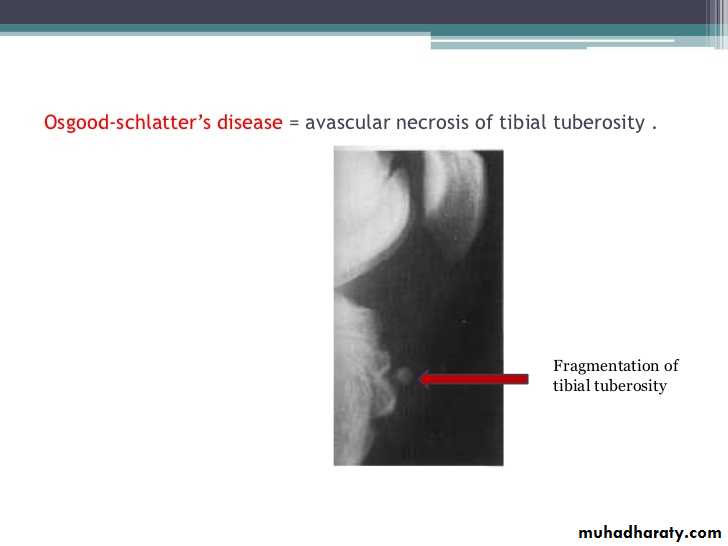
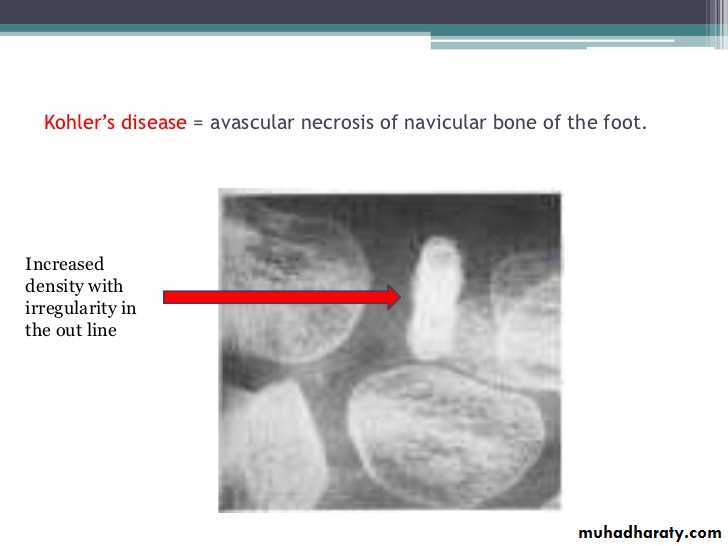
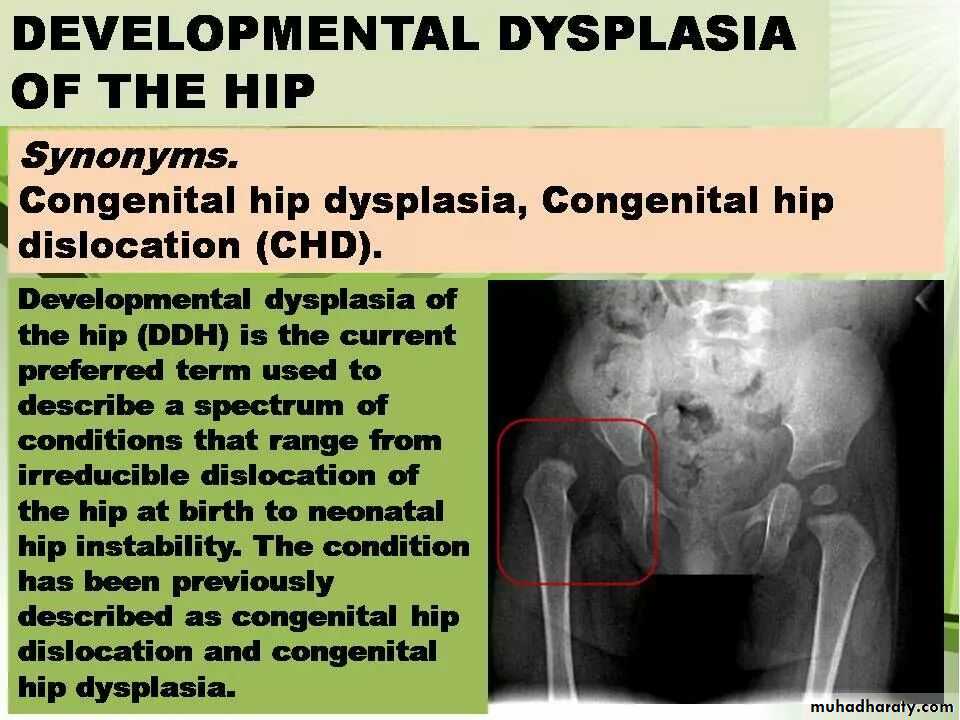
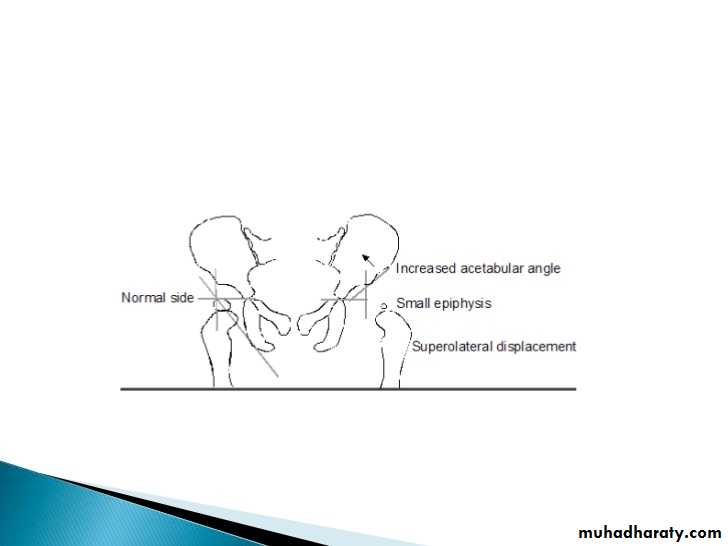
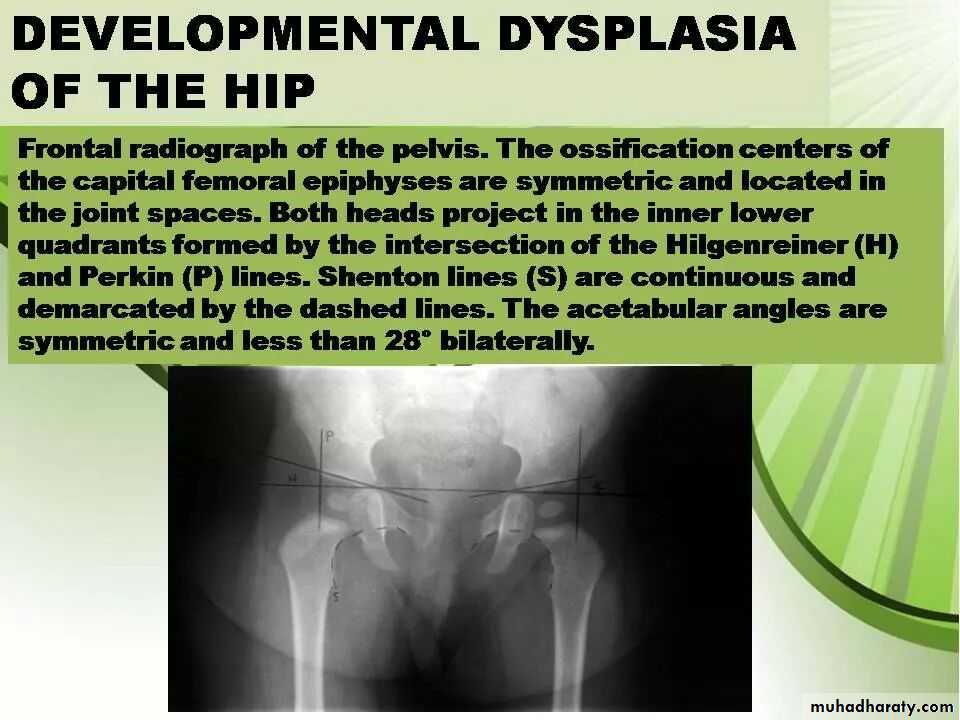
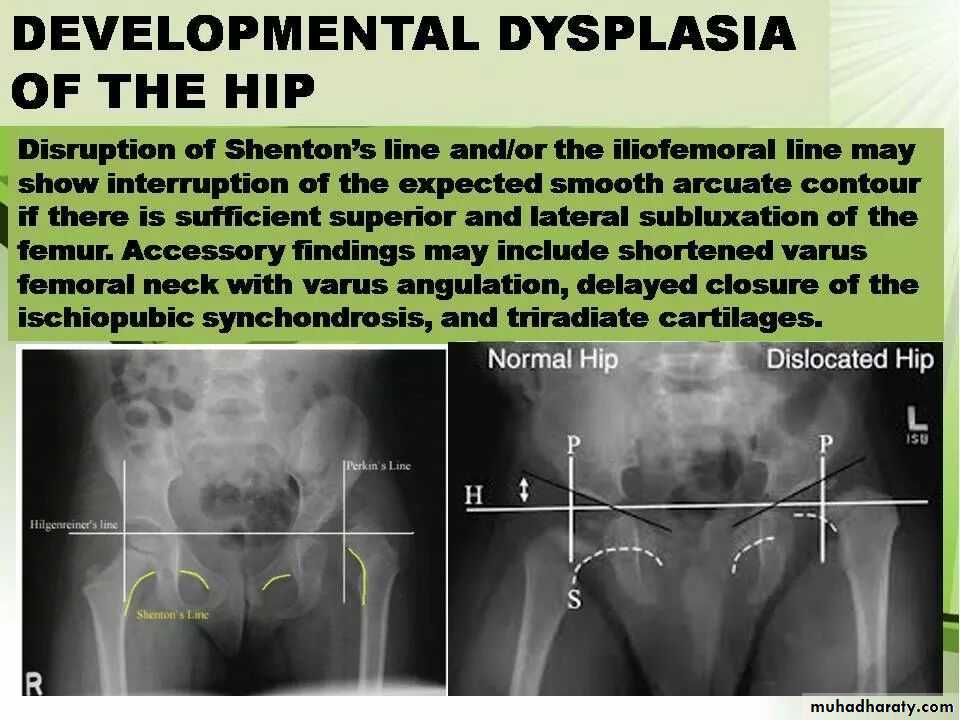
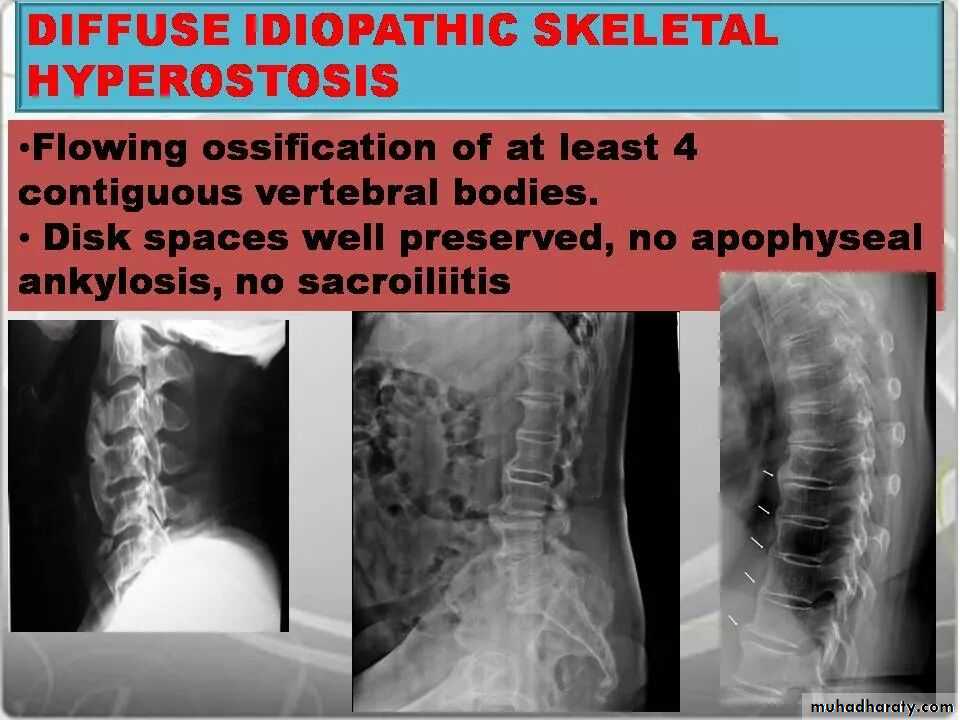
Imaging of joint diseases
Qais A. Altimimy, DMRD, CABMS-RAD.Lecturer, Radiology
Alkindy college of medicine, university of Baghdad
2014
There are three types of arthritis which ca be distinguished radiologically :
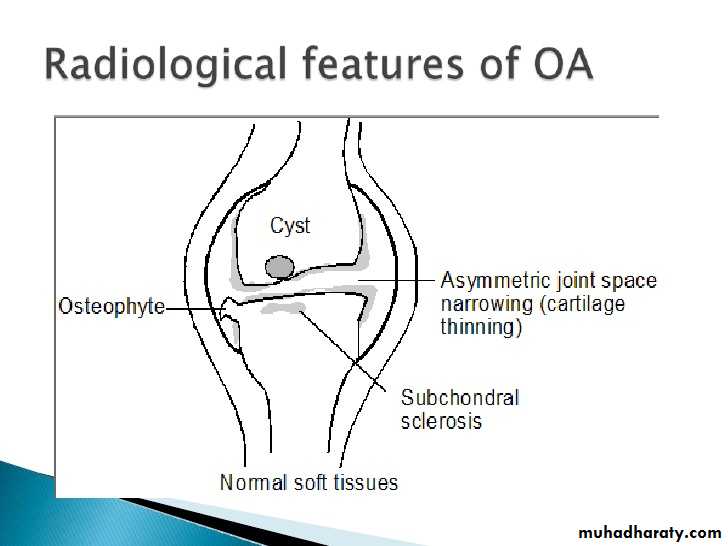
1. Degenerative arthritis:Osteophytes
Subcondral sclerosis
Uneven loss of articular space
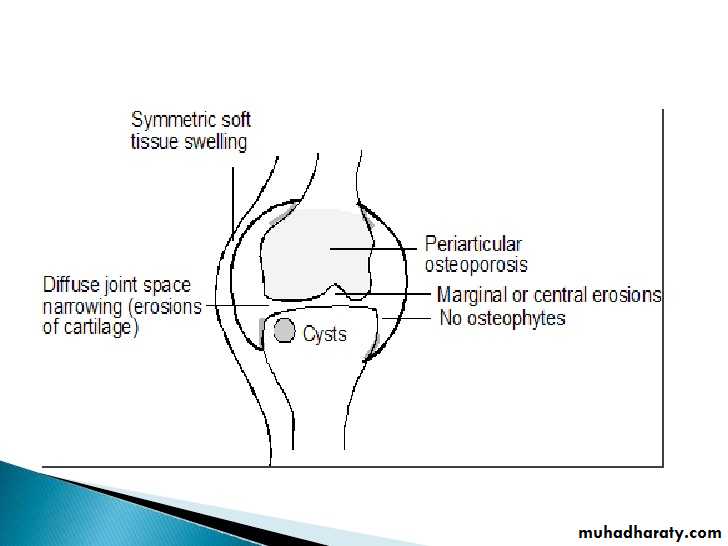
2. Inflammatory arthritis:
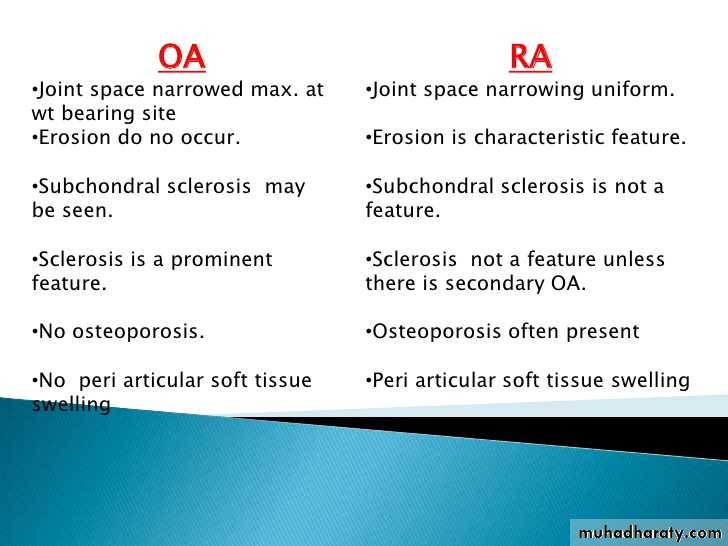
Unmarginated erosions
Periarticular osteoporosis
Soft tissue swelling
Uniform loss of articular space
3. Metabolic arthritis lumpy soft tissue swelling
Marginated bony erosions with overhanging edges
The joints commonly involved are DIP, 1st carpal-metacarpal, knee, hip and spine
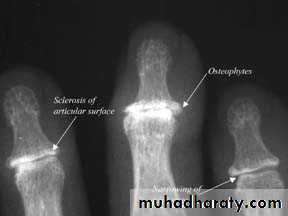
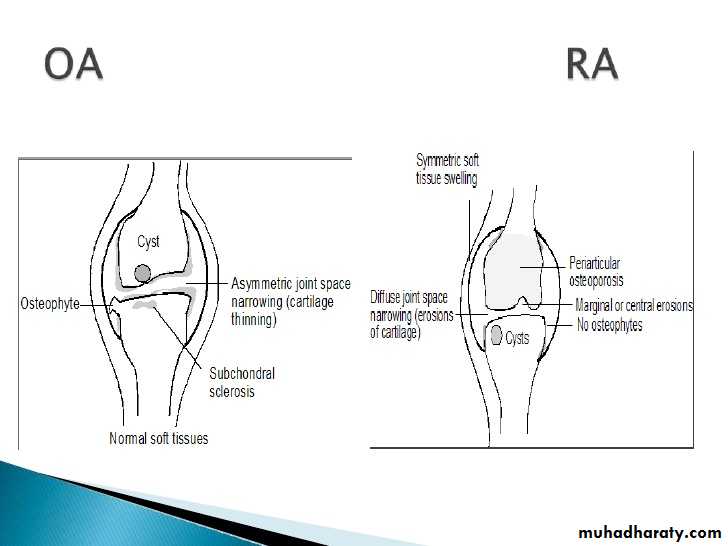
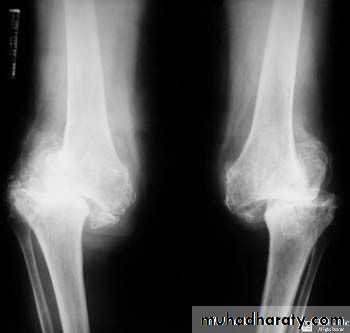
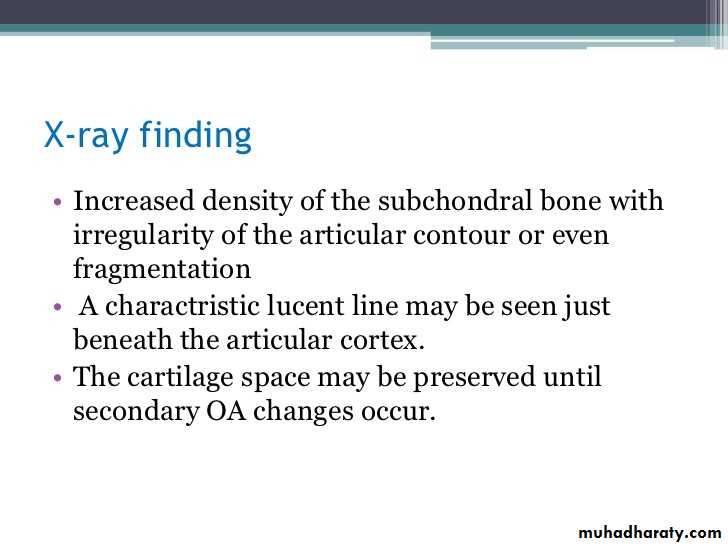
OA – Radiographic findings1. Joint space narrowing
2. Osteophyte formation (white arrow)3. Subchondral sclerosis (black arrows)
Another example of OA
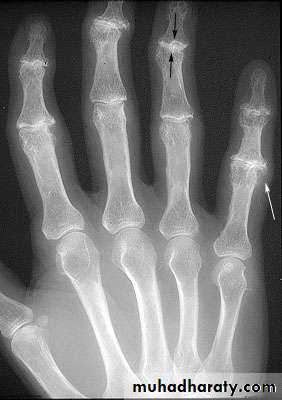
Oblique and AP views
1st carpal metacarpal shows decreased joint space and subchondral sclerosis
2nd and 3rd DIP shows osteophytes and subchondral sclerosis (Heberden’s nodes)
Inflammatory arthritisThere are three types
1. Auto immune arthritis: RA, Scleroderma, SLE and dermatomyositis2. Seronegative spondyloarthropathies: AKS, Reiter and psoriasis
3. Erosive OA
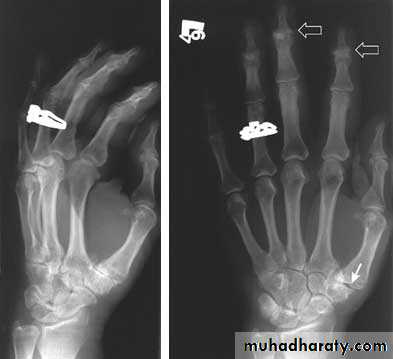
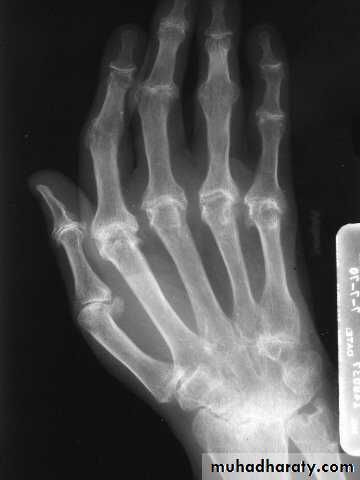
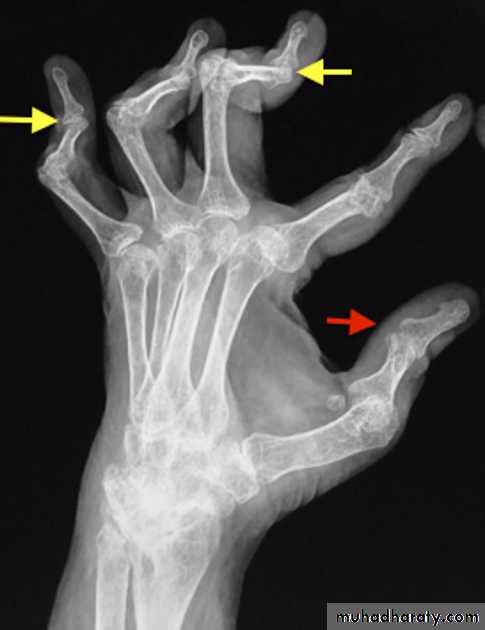
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
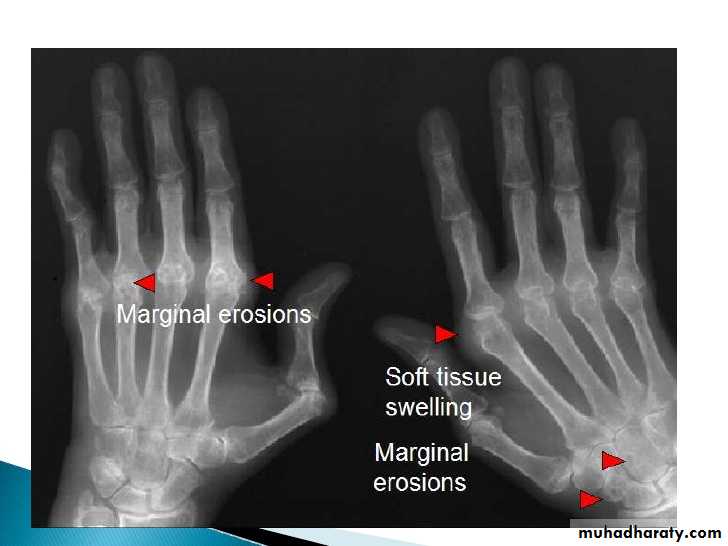
Earliest signs include
1.soft tissue swelling due to effusion, tenosynovitis, and edema2.Symmetric Periarticular osteopenia
3.Marginal erosions often first seen at 2nd and 3rd MCPs and 3rd PIP articulations
Preferred sites of early involvement:
Hand: 2nd & 3rd MCP jointsFoot: 4th & 5th MTP joints
Late signs include:
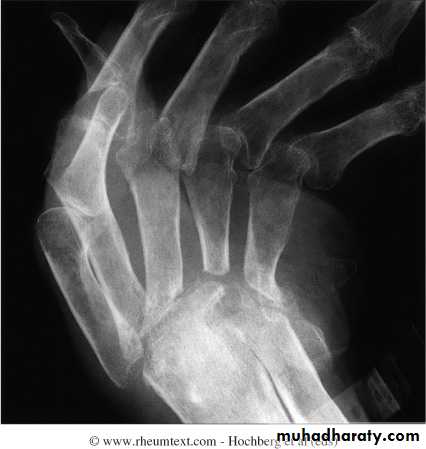
1.Large marginal erosions have nearly destroyed the joints
2.Erosion of ulnar styloid
3.Subcondral cyst
4.Subluxation
5.Carpal instability and fusion
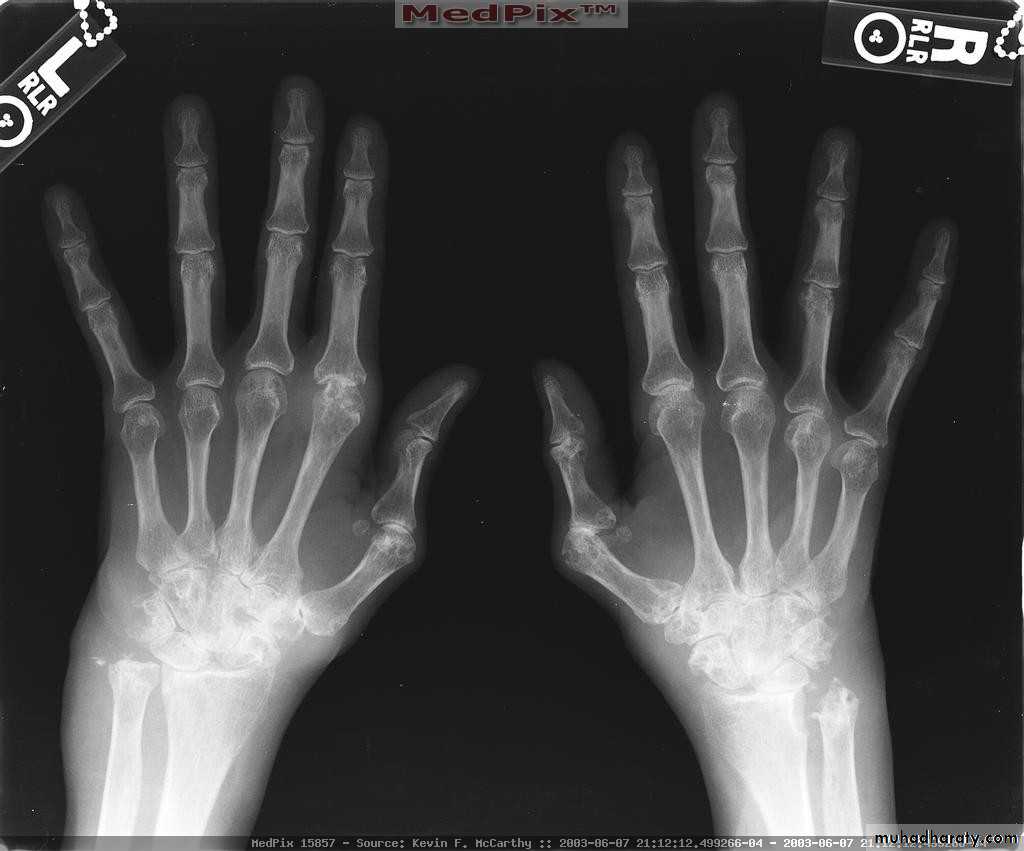
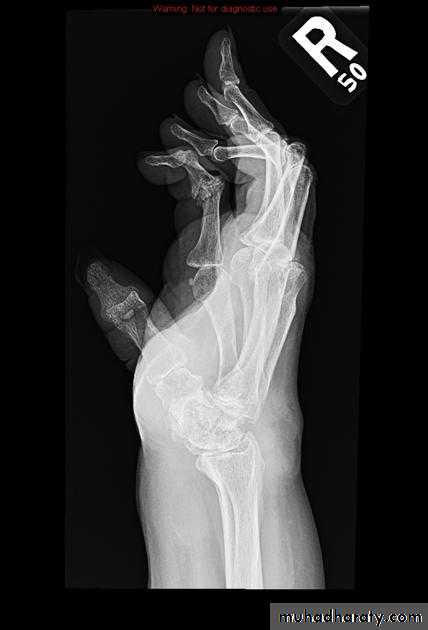
Severe erosive changes at radio-ulnar joints carpal bones at the metacarpal heads
Bilaterally symmetricSevere ulnar deviation
Severe erosions of MCPsComplete destruction of the wrist
Resorption of the carpals and the heads of the metacarpals
Radial deviation of the wrist
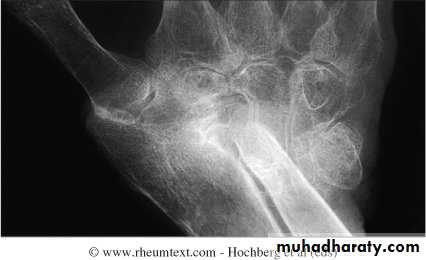
Rheumatoid wrist: articular destruction, carpal fusion and carpal collapse.
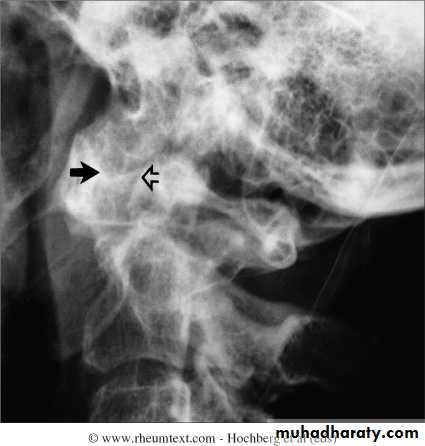
Severe destruction of the distal radius and ulna.Atlanto-axial subluxation in RA
Always a concern in patient with longstanding RA and neck pain or cervical neurological symptomsBoutonniere deformity
is one of the musculoskeletal manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis in hand with:flexion contracture of the PIP joints
extension of the DIP joints
Swan neck deformity is a deformity of the digits that consists of:
hyperextension of the PIP jointscompensatory flexion of the DIP joints
Swan neck deformity is seen in :
1.rheumatoid arthritis (classical association)
2.post-traumatic:Mallet finger
3.scleroderma
4.psoriatic arthritis
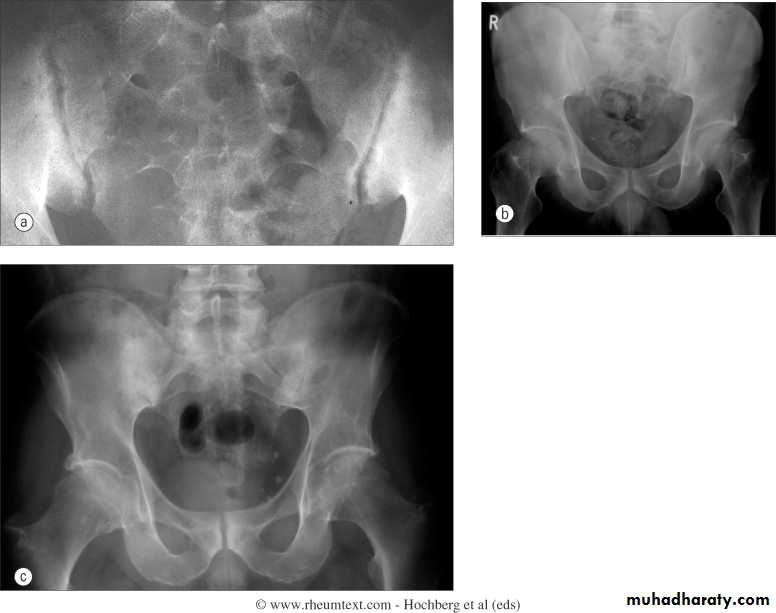
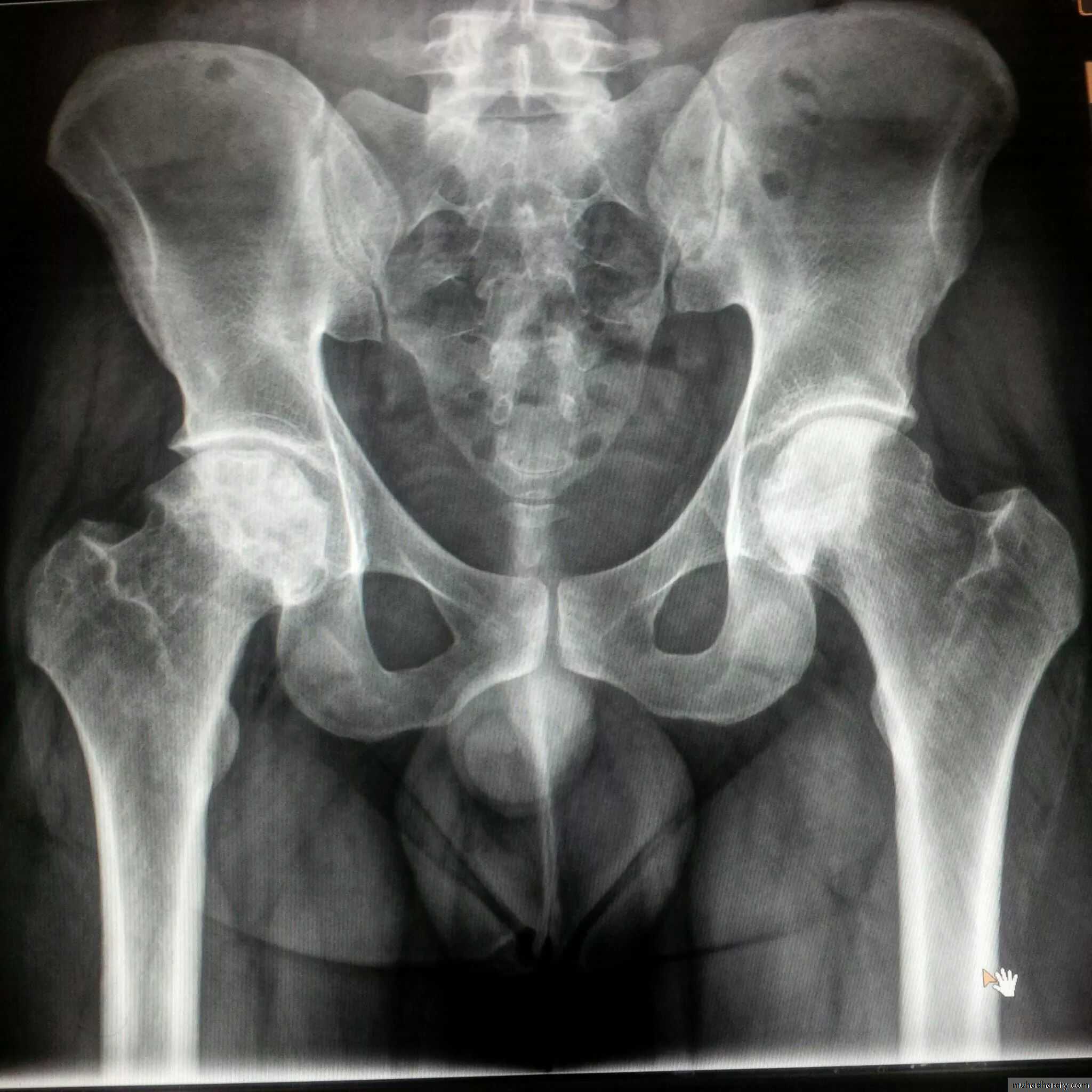
Sacriliac joints
Are the initial site of involvement(bilateral symmeterical)Erosions early
Sclerosis intermediate
Ankylosis late
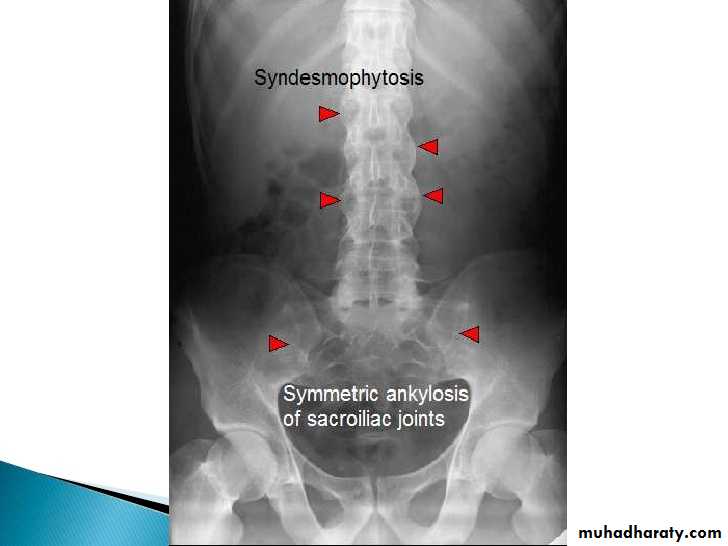
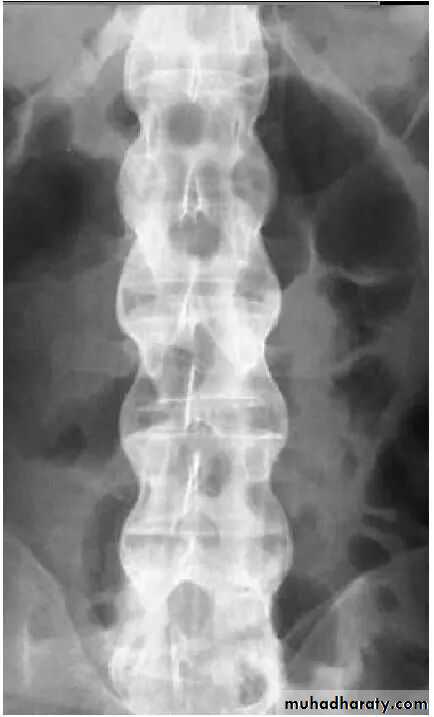
Spine
• Early changes include squaring of the anterior vertebral body
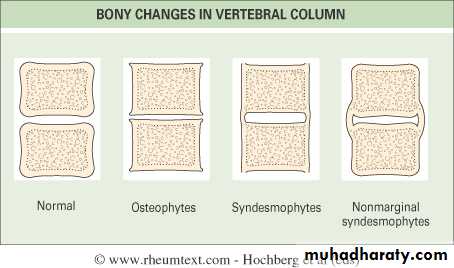
• Progressive mineralization of Sharpey’s fibres to form osseous bridging syndesmophytes
• Bamboo spine
• Dagger sign apperance
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Erosions and sclerosis on iliac side
Bamboo spine
Gout
Recurrent attacks of arthritis secondary to deposition of sodium urate crystals in and around jointsHyperuricemia not always present
90% of patients are male
Radiological features are:
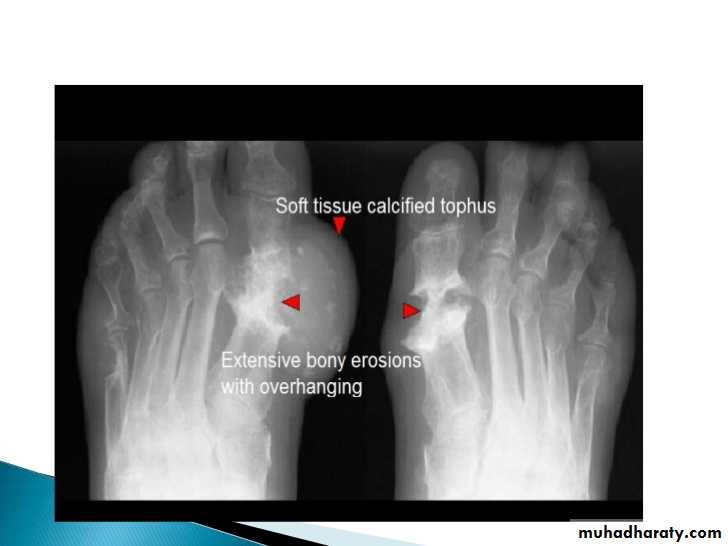
1.Affect lower>upper extremity, small>large joints2.First MTP is the most common site
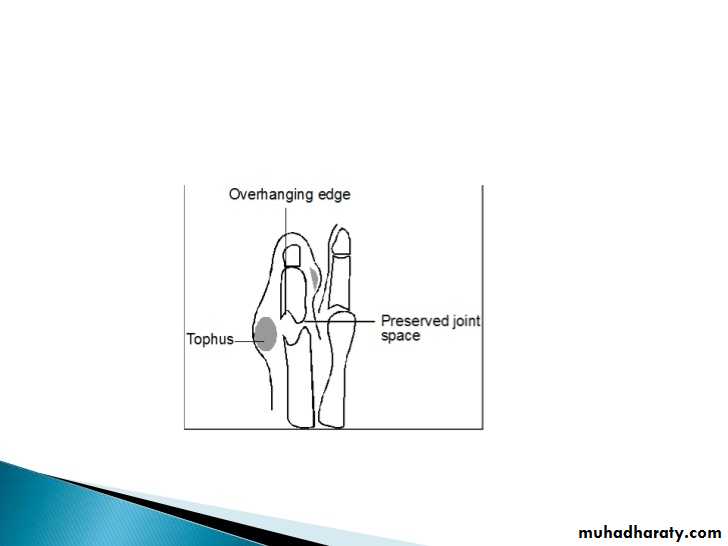
3.Marginal paraarticular erosions; overhanging edges
4.Erosions may have sclerotic borders
5.joint space is preserved