Introduction to thoracic Surgery
Dr. Muthanna Alassal
Consultant Thoracic & Vascular SurgeonAnatomy
The respiratory system consists of the :Nose , Nasal passage , Nasopharynx , larynx ,Trachea ,Bronchi & lungs . The chest wall is covered by Pectoralis muscle anteriorly while posteriorly both (Latissmus dorsi and serratus muscle) are encountered .
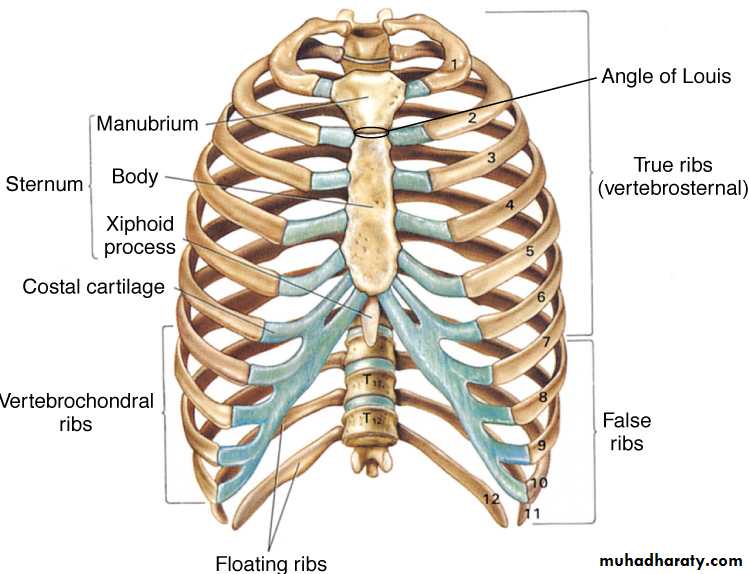
There are (12) pairs of ribs ,
Seven of which are termed (True Ribs) as the cartilages articulate with the sternum.
The lower 3 ribs are termed (False Ribs) which are not connected directly to the sternum.
The eleventh and the twelfth ribs are termed (Floating Ribs )
Because they are not attached anteriorly .
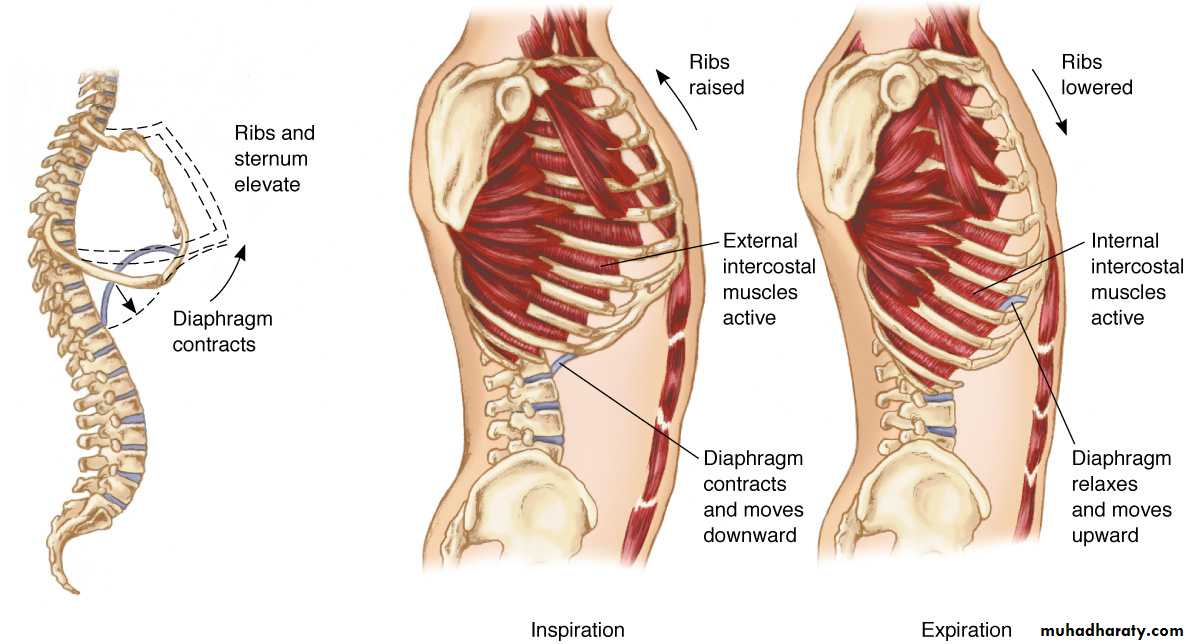
The sternum is divided into the Manubrium .Body and xiphoid . The clavicle articulates with the sternum and Ist.costal cartilage .Muscles associated with the intercostals space are , The external intercostals ,internal intercostals and transversus thoracic muscles .There are (11) intercostals spaces containing a vein ,an artery and a nerve which course along the lower edge of each rib .
• Pleura is a fibro elastic membrane lines by squamous epithelial cells .It consists of two portions:-1-Parietal pleura which lines the thoracic cavity and it is divided into four parts a- Costal pleura which lies against the ribs &intercostal muscles b-Diaphragmatic pleura which covers the upper surface of the diaphragm.C-Mediastinal pleura which lies against the mediastinum .D-Cervical pleura which covers the dome of the thoracic space 2-Visceral pleura which intimately invests the lung .
• Costo –phrenic angle is the angle between the costal &diaphragmatic pleura.
• Cardio –phrenic angle is the angle between the heart &diaphragmatic pleura• Inferior pulmonary ligament is the anterior & posterior reflection of the pleura between the root of the lung & the diaphragmatic surface
The function of the pleura is to maintain the environment of the pleural space in which the lung is function.
The bronchial arteries originate from the aorta or the intercostals arteries . Pulmonary veins drain into the left atrium .No bronchial veins. The Lymph nodes found along the lobar branches are termed(hilar LN).There are also Tracheal and tracheo-bronchial LN.Phrenic nerve located anteriorly while the vagus nerve located posteriorly in the thoracic cavity .
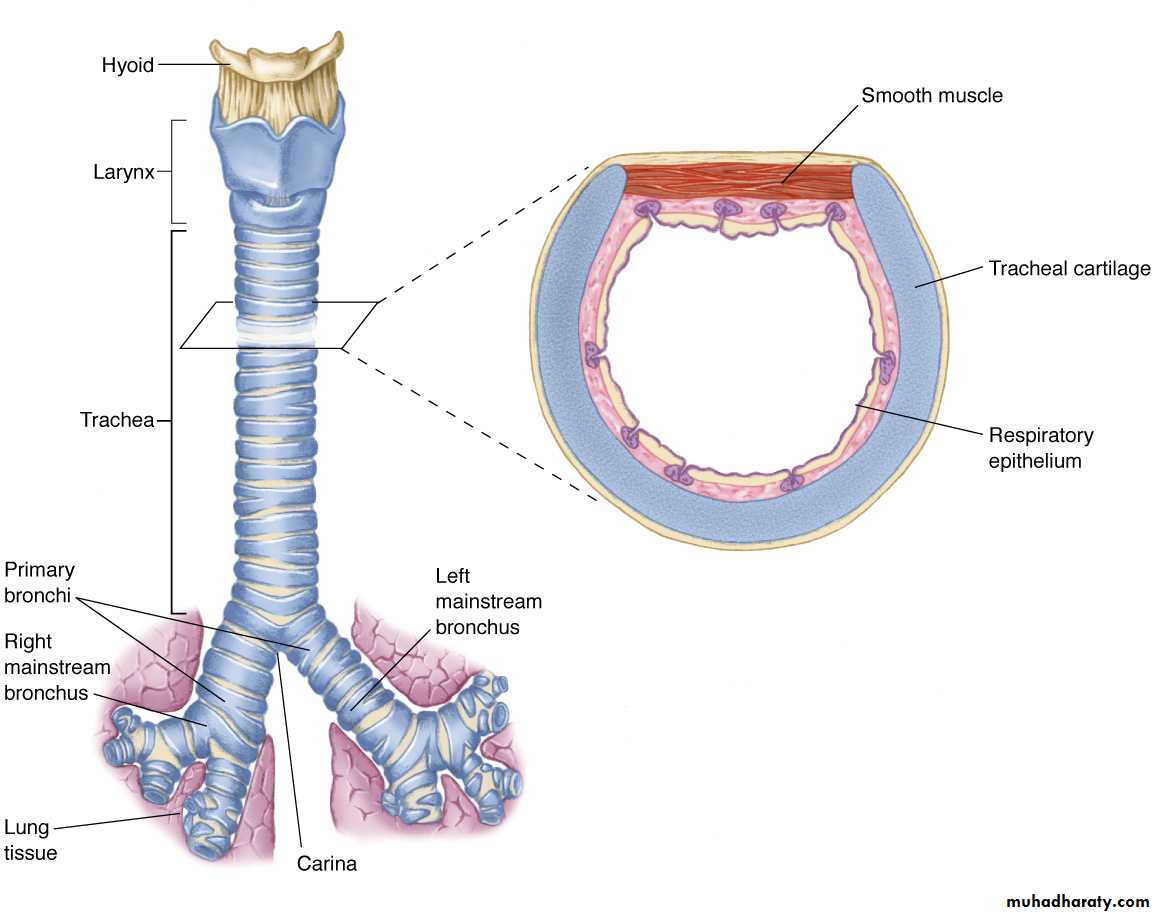
The Trachea is a fibro muscular tube (10-12 cm) in length and (13-22 mm) in width. Supported laterally and ventrally by (16-22) U-shaped hyaline cartilages . The trachea originates at the level of the cricoid cartilage down to its bifurcation at the level of the sternal angle where it divided into right and left main bronchi .The spur at the bifurcation is termed the (Carina) . The right main bronchus is (12-16 mm) in diameter ,the left is ( 10-16 mm) in diameter .The right main bronchus deviates less from the axis of trachea than the left ,this explains why foreign body is more common in the right main bronchus .The main bronchi are divided into the segmental bronchi which end into the terminal bronchiole which divided into the respiratory bronchiole which terminate into the alveoli .
Clinical manifestations of respiratory dieases
1-Cough2-Dyspnea or breathlessness , it is an unpleasant subjective awareness of the sensation of breathing .
3-Chest pain in diseases with pleural or chest wall involvement .
4-Haemoptysis .
Investigations :-
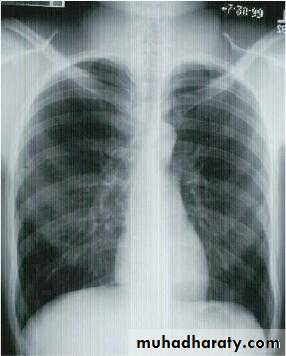
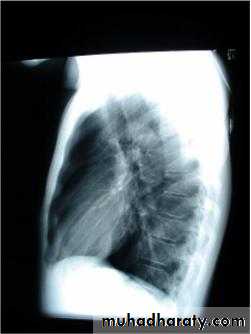
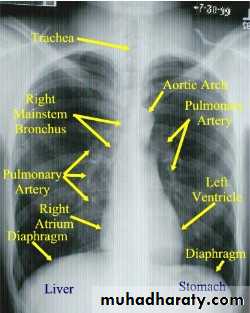
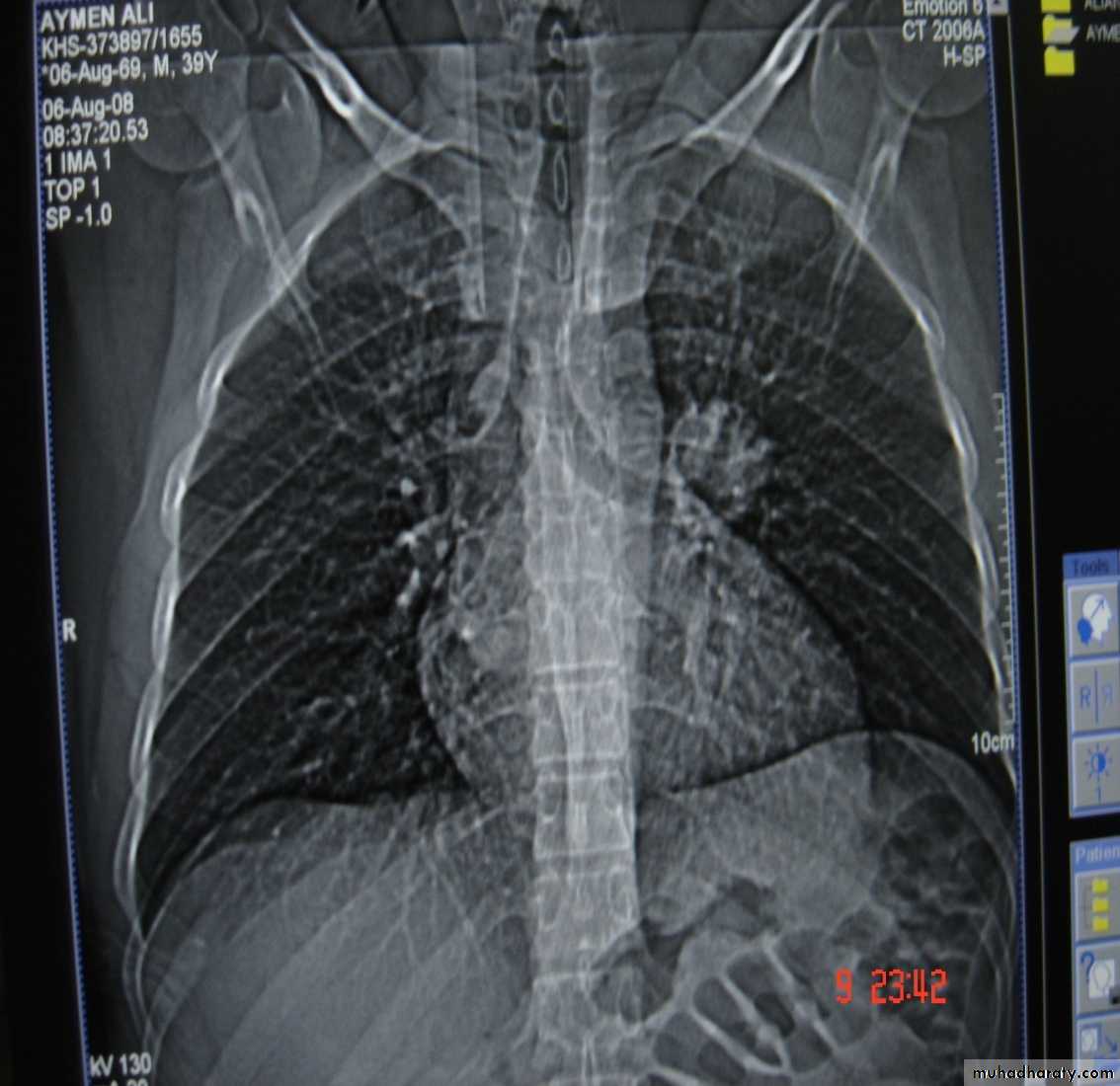
1-Chest X-Ray2-CT chest
3-MRI mediastinum
4-US chest to detect any effusion .
5-Pleural aspiration .
6-Bronchoscopy flexible or rigid .
Pulmonary Function Tests
1-Tidal Volume (TV)
Is the amount of air inspired or expired per single breath .
2-Functional residual Capacity (FRC)
The amount of gas contained in the lung at the end of quiet expiration .
3-Inspiratory reserve volume;-
Is reached when the patient makes a maximum inspiration and increased the lung volume ,compared with that contained at the peak tidal volume.
4-Vital capacity :-
The volume expired from maximal inspiration to maximal expiration.
5-residual volume :-
Is the amount of air remaining in the lung after maximal expiration.
6-FEV1
Is the volume of air expired in one second .