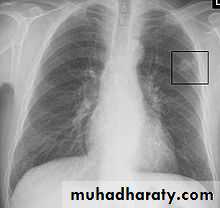
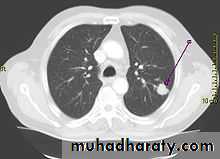
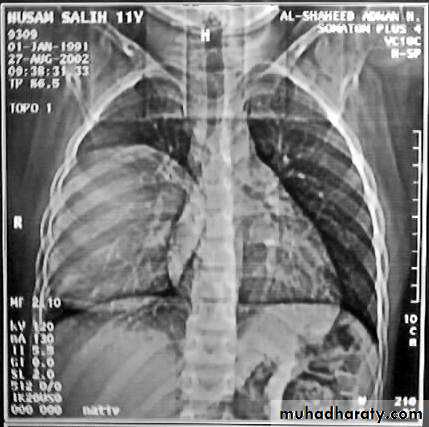
• Differential diagnosis of a solitary lung lesion (COIN LESION)
• 1-Hydatid cyst 4- Primary benign lesion• 2-Tuberculoma 5-primary malignancy of the lung
• 3-Angiomatous malformation (AV fistula) 6-metastatic tumors
• Pulmonary Echinococcosis (Hydatid Cyst)
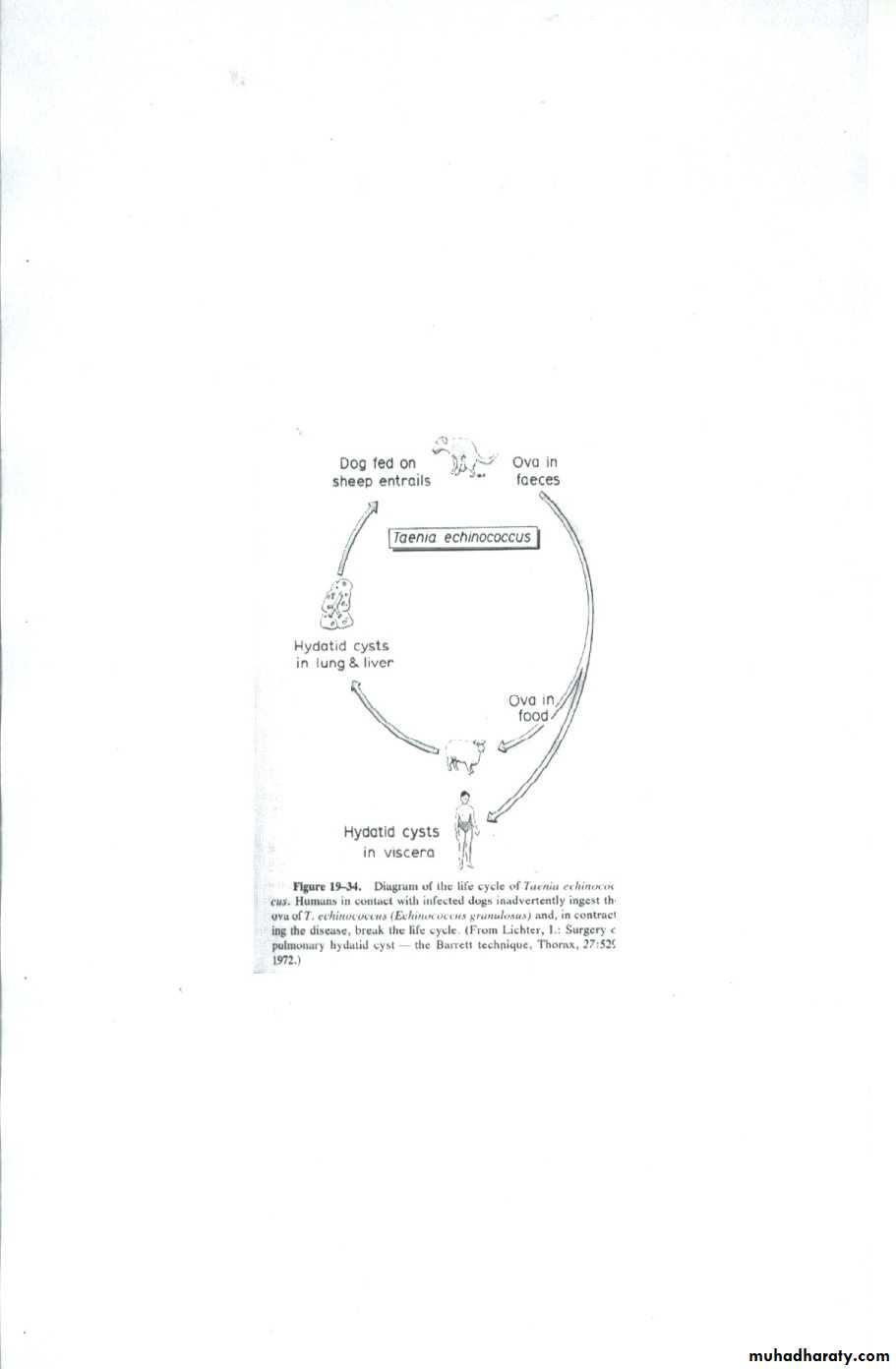
Hydatid disease of the lung is caused by the .small. tape worm (Echinococcus Granulosus) Hydatid cyst means cyst full of water .It has a life cycle between dogs & sheep .Parasites in the elementary tract of the dog shed ova that excreted in the dog faeces , contaminated the food of the sheep in which hydatid cyst will develops in the viscera . Including the lung .Infected sheep when slaughtered and its entrails are eaten by dogs , the life cycle is completed .When a human being hands or food become contaminated with canine fecal material containing ova which will be ingested .The parasitic larva burrow through the gastric mucosa and are carried to the liver in the portal venous circulation where most of them filtered out to form hydatid cyst of the liver , some escape the liver & lodge in the lung to form one or more hydatid cyst which grows slowly or rapidly over years .
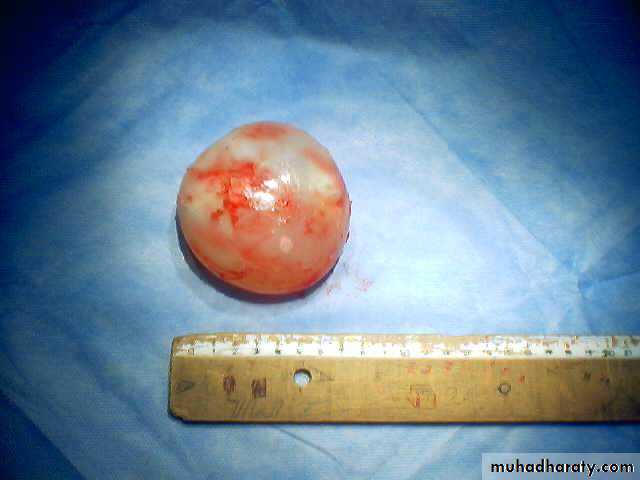
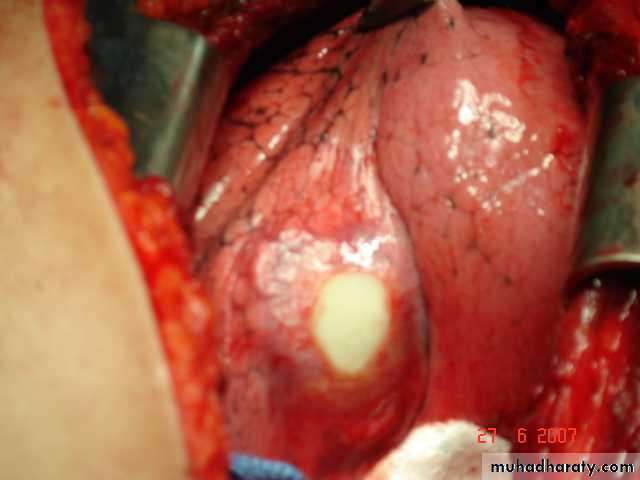
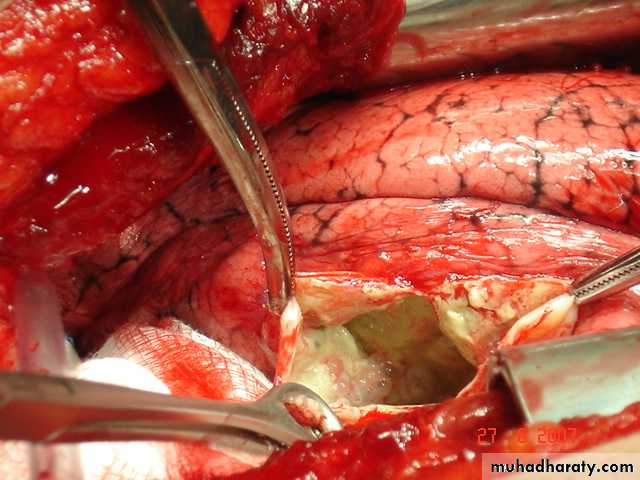
• The cyst consists of a germinal layer & cyst fluid containing broad capsule & scoleses . A cellular white hyaline layers are laid down outside the cyst so that the cyst is enclosed by a laminated cyst membrane .As the cyst enlarged , it usually reaches the pleural surface . Compression of the lung tissues produces a thin fibrous layer of atelectatic lung tissue around the cyst (capsule , pericyst or adventia)
• Clinical Manifestation
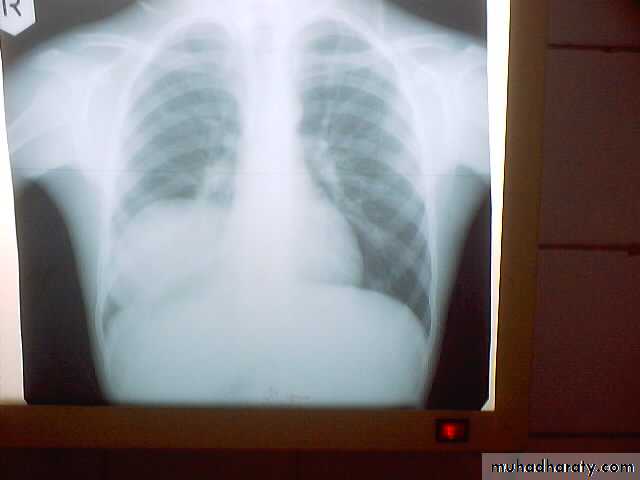
• A-Asymptomatic• Any smooth homogenous opacity of uniform density with clear cut border and little or no reaction around it on a chest X-Ray is a hydatid cyst unless proved the other wise .
• B-Cough & haemoptysis due to rupture of the cyst , or it can lead to severe dyspnea , or asphyxia ,or a hyper sensitivity reaction ,
• If the cyst get infected ,it will lead to formation of lung abscess or bronchiectatic changes .
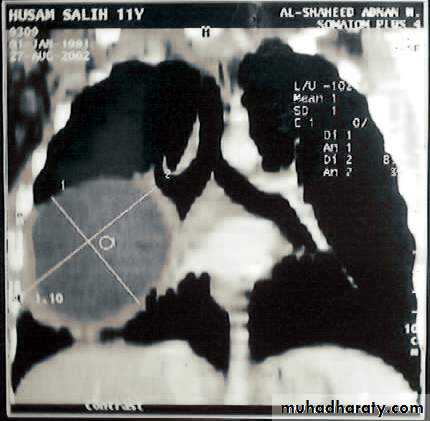
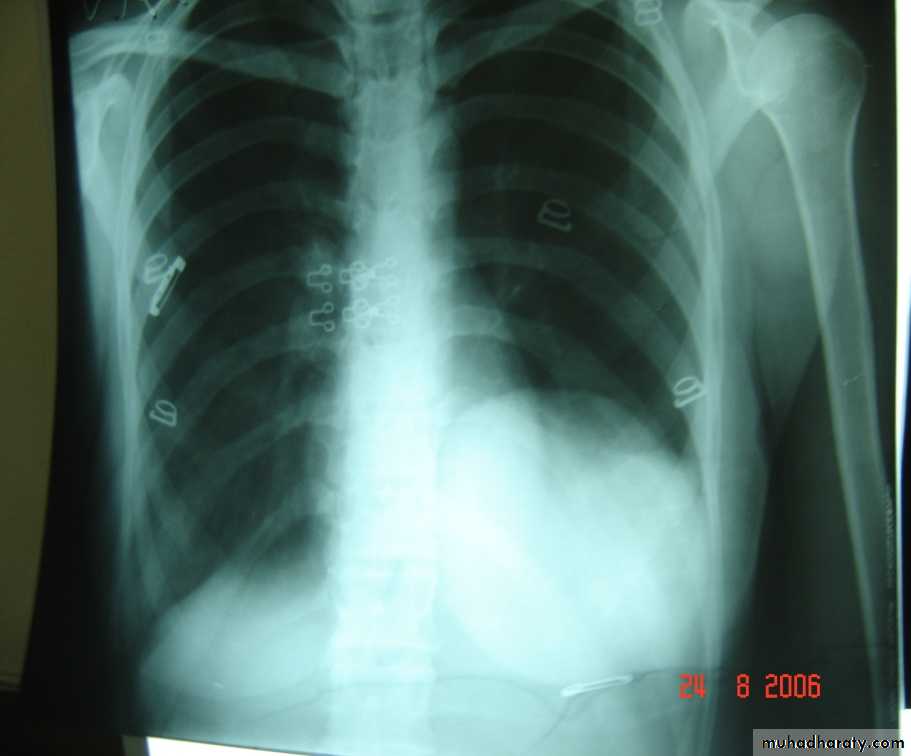
• Radiological Findings
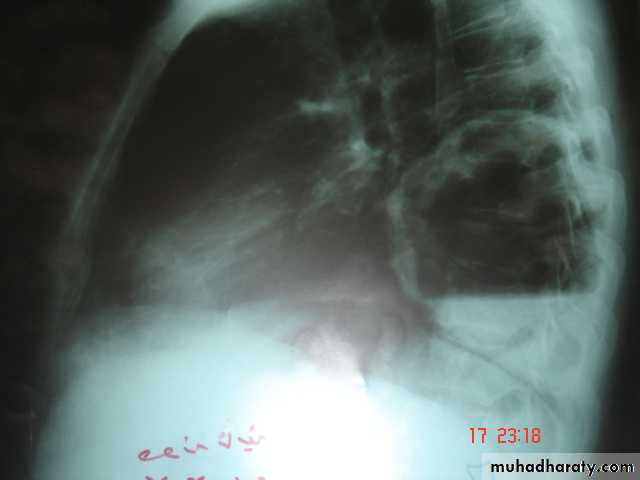
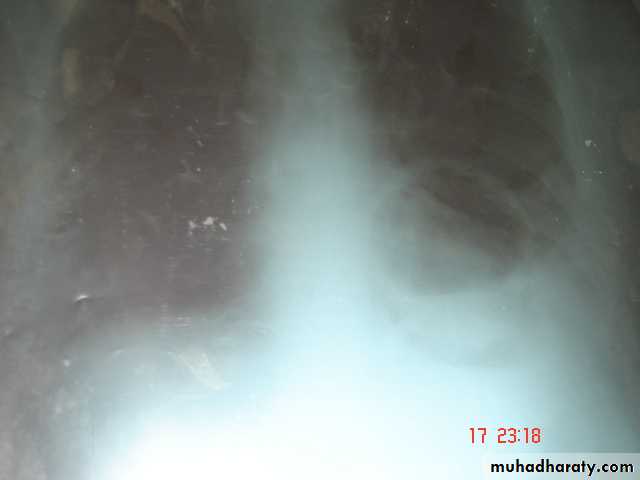
• 1-Smooth homogenous opacity (Intact H.C).• 2-Partial rupture (peri-vesicular pneumocyst).
• 3-Complete rupture (Water –lilly sign) .
• 4-Formation of lung abscess(Air –fluid level) .
• 5-Completely coughed out cyst(empty cavity )
• 6-Rupture into the pleura (hydropneumothorax)
• Treatment
• Surgical• A-Inoculation means to remove it intact.
• B-Aspiration &evacuation technique
• C-Wedge resection or excision of the cyst with adjacent lung tissue.
• D-Segmentectomy ,Lobectomy or Pneumonectomy (rare ).
• Lung Abscess It is a localized area of suppuration and cavitations in the lung.It includes TB , mycotic or parasitic cavitations ,bronchiectasis ,ruptured infected hydatid cyst , even pulmonary infarction with abscess formation & cavitating tumors
• Simple lung abscess (pyogenic) can occurs as a result of aspiration of a septic debris from the oropharynx into the lung or following dental or tonsillar operations .
• Esophageal diseases that lead to regurgitation &subsequent aspiration of esophageal content into the lung is another cause.
• Usually the aspiration is into the RMB leading to severe pnemonitis and liquefaction may occurs .As the liquefied necrotic material empties through the bronchus , a necrotic cavity containing pus and air is formed .The organism responsible may be streptococcus , staphylococus &eschrescia coli .
• Clinically cough & foul smelling sputum fever , pleuritic chest pain night sweat & weight loss in severe cases dyspnea & cyanosis
• Chest X-Ray
• Can shows the characteristic air fluid level ,may associated with pleural thickening , pneumothorax
• CT chest is helpful in demonstrating the abscess .
• Treatment
• 1- Primary treatment is Medical• Prolonged antibiotics treatment
• Bronchoscopy useful to remove a FB or drainage of abscess
• 2-Surgery indicated in
• Failure of medical treatment
• Massive haemoptysis
• persistent of a thick wall cavity
• when malignancy is suspected
• when empyaema develops
• Complications :-
• Empyaema , septicaemia ,metastatic brain abscess ,bronchogenic spread &development of chronicity
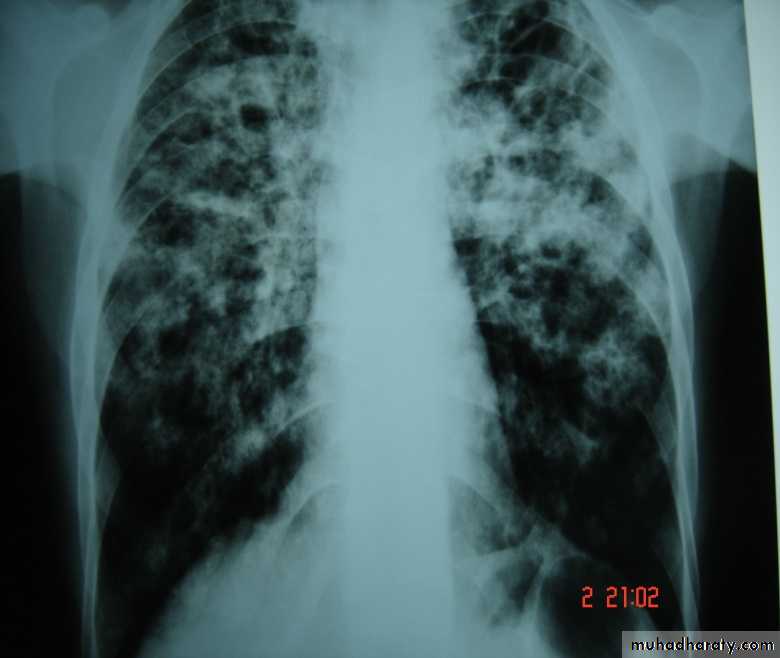
• Pulmonary Tuberculosis:
• Microbiology: Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacilli (acid fast bacilli). As few as 3 organisms can produce infection.
• Clinical Picture: cough (dry mostly), fever, night sweating, loss of weight, loss of appetite, & sometimes haemoptysis.
• X-ray appearance: T.B. could present with any X-ray appearance.(pneumothorax, pleural eff.,
• Collapse, Empyema, miliary shadows, tented diaphragm, thickened pleura, calcified fissures, etc).
• But an apical cavity is the classical & most common appearance.
• Diagnosis: C/F, CXR, Elevated ESR, anemia , Sputum for AFB( 3 morning samples)( Non sensitive), PCR for T.B.( theoretically 100% sensitive).
• Empirical Anti T.B.( important)
T.B. Cavity Asperigelloma
• Medical treatment:• 6 mo. & 9 mo. regimens
• 6mo. : Initiation phase(4 drugs) 1mo + continuation phase(2 drugs) 5 mo.
• 9 mo. : Initiation phase (4 drugs) 2mo + continuation phase(2 drugs) 7 mo. (recommended in our country)+ add streptomycin vial 750 mg /day, I.M. during initial phase.
• Drugs& Doses:
Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Indications :-
1-Massive or recurrent haemoptysis . Surgery is indicated to remove the source of bleeding .
2-Broncho pleural fistula
3-Open cavity with positive sputum resistant to 3-6 months of treatment .
4-TB bronchiectasis .
5-When malignancy is suspected as TB and malignancy can co exist.Carcinoma can arise in TB scar (Scar carcinoma ).
6-Patients with (Trapped lung syndrome ) after chronic empyaema .
It includes segmetectomy ., lobectomy ., or pneumonectomy ., or to remove thickened adherent parietal and visceral pleura( decortication ) alone or in combination with pulmonary resection .