Aneurysms
What is an aneurysm??An aneurysm is a localized, permanent dilatation of an artery greater than 1.5 times its normal diameter.
Aneurysms occur all over the body and in any vessels, including the aorta, and the iliac, femoral, popliteal, subclavian, axillary and carotid arteries.
Aneurysms:
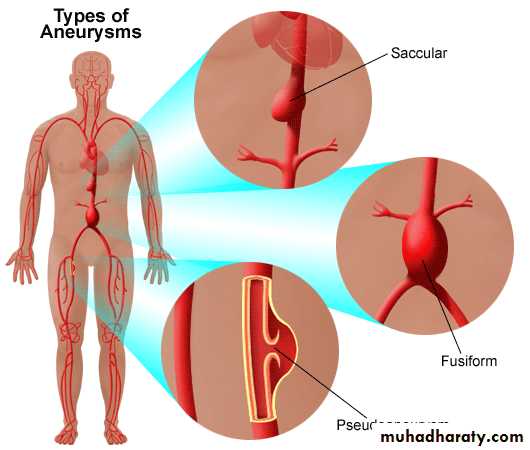
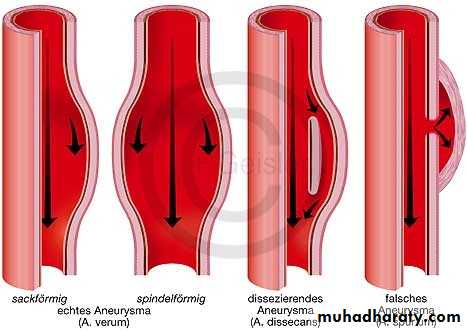
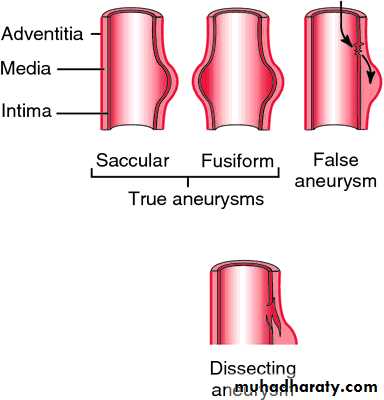
Classification:Wall
True aneurysms
False aneurysms
Morphology
Fusiform
Saccular
Dissecting
Etiology
Atherosclerosis
Mycotic
traumatic
Clinical presentation:
AsymtomaticSymptomatic
Pressure on nearby structures
Aneurysm thrombosis leading to ischemia
Aneurysm embolization
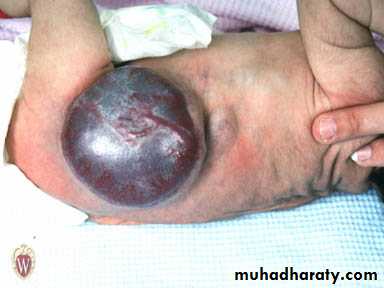
Aneurysm rupture.
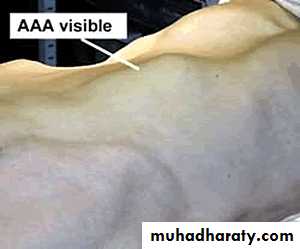
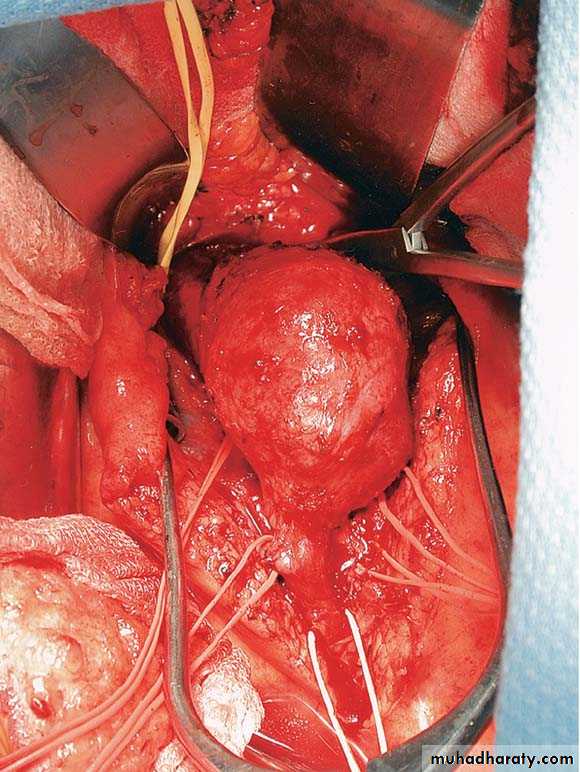
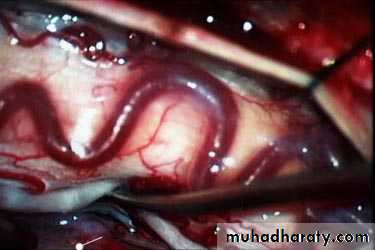
O/E: palpable, expansile mass, with or without thrill
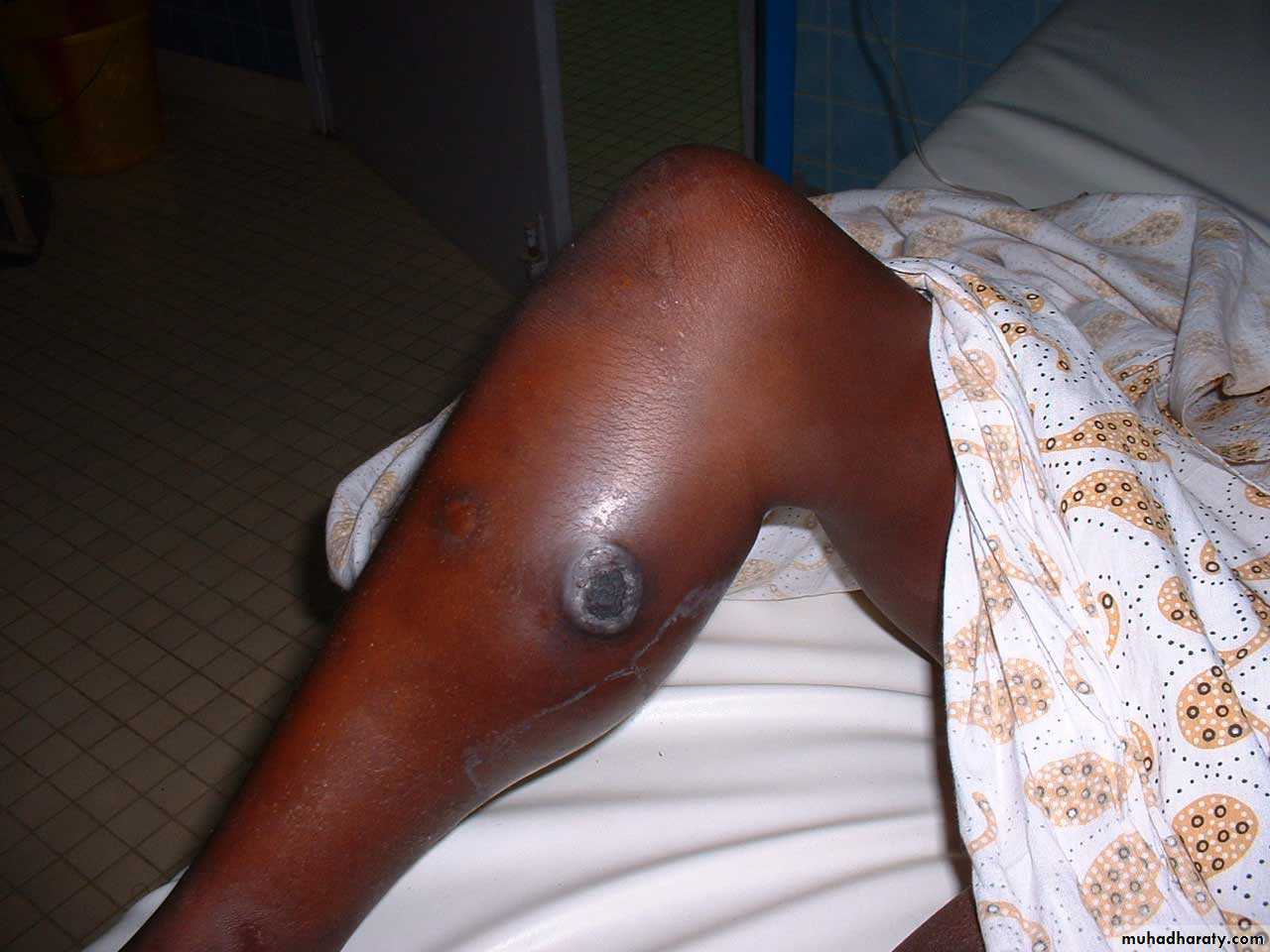
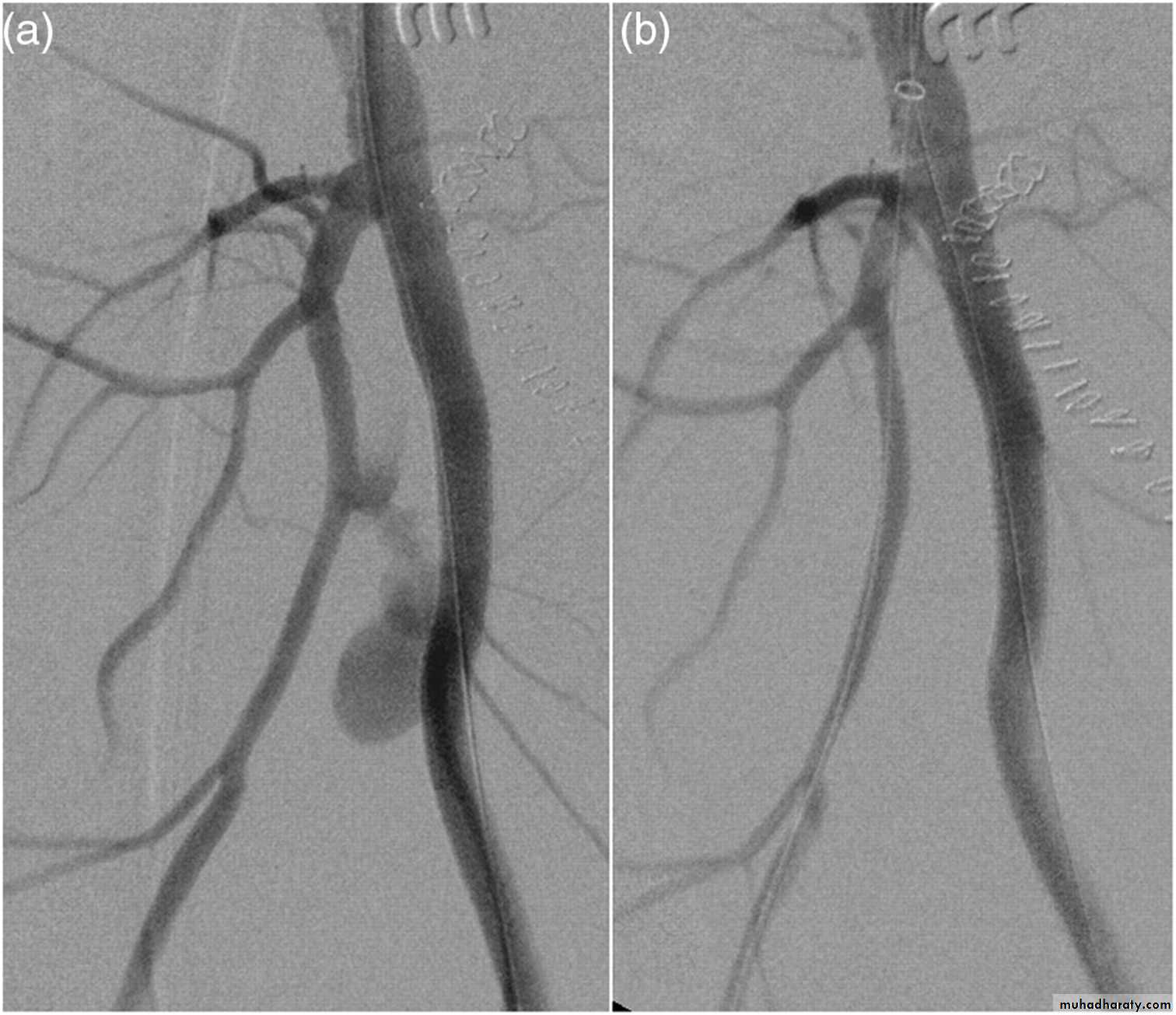
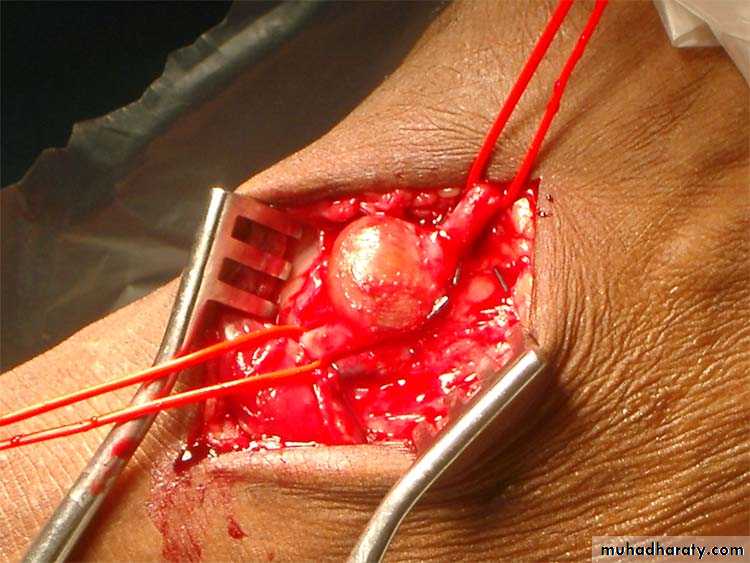
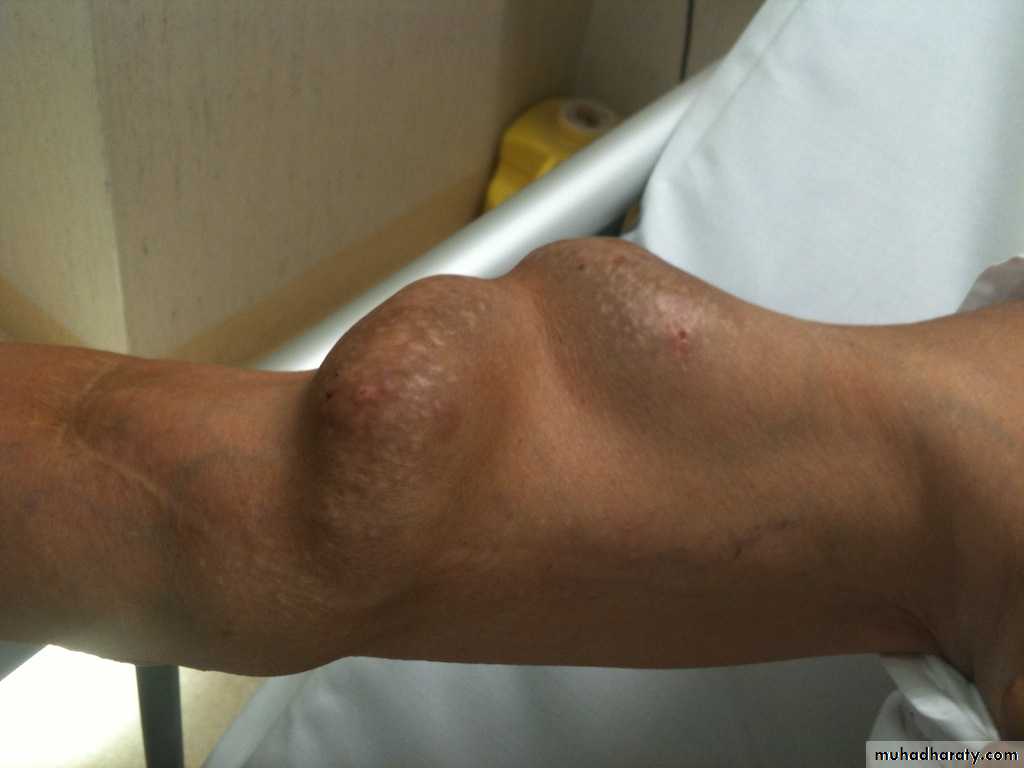
Pseudoaneurysm of popletial artery
Differential diagnosis:
• Cyst or abscess overlying an artery• Mass overlying an artery
• Tortuous artery
Investigatons:
• Ultrasonography• Duplex ultrasound
• Angiography
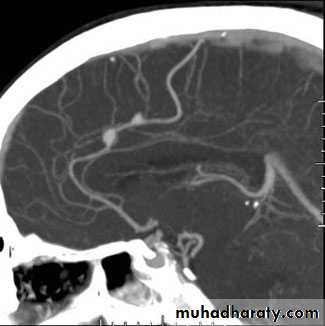
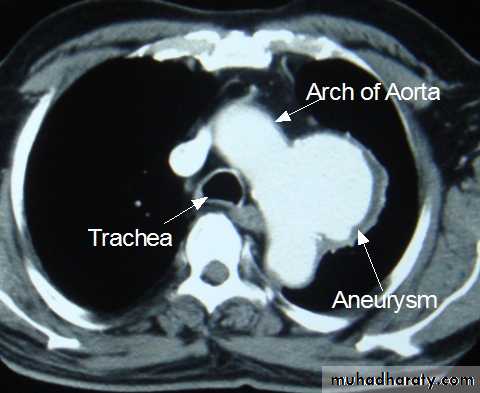
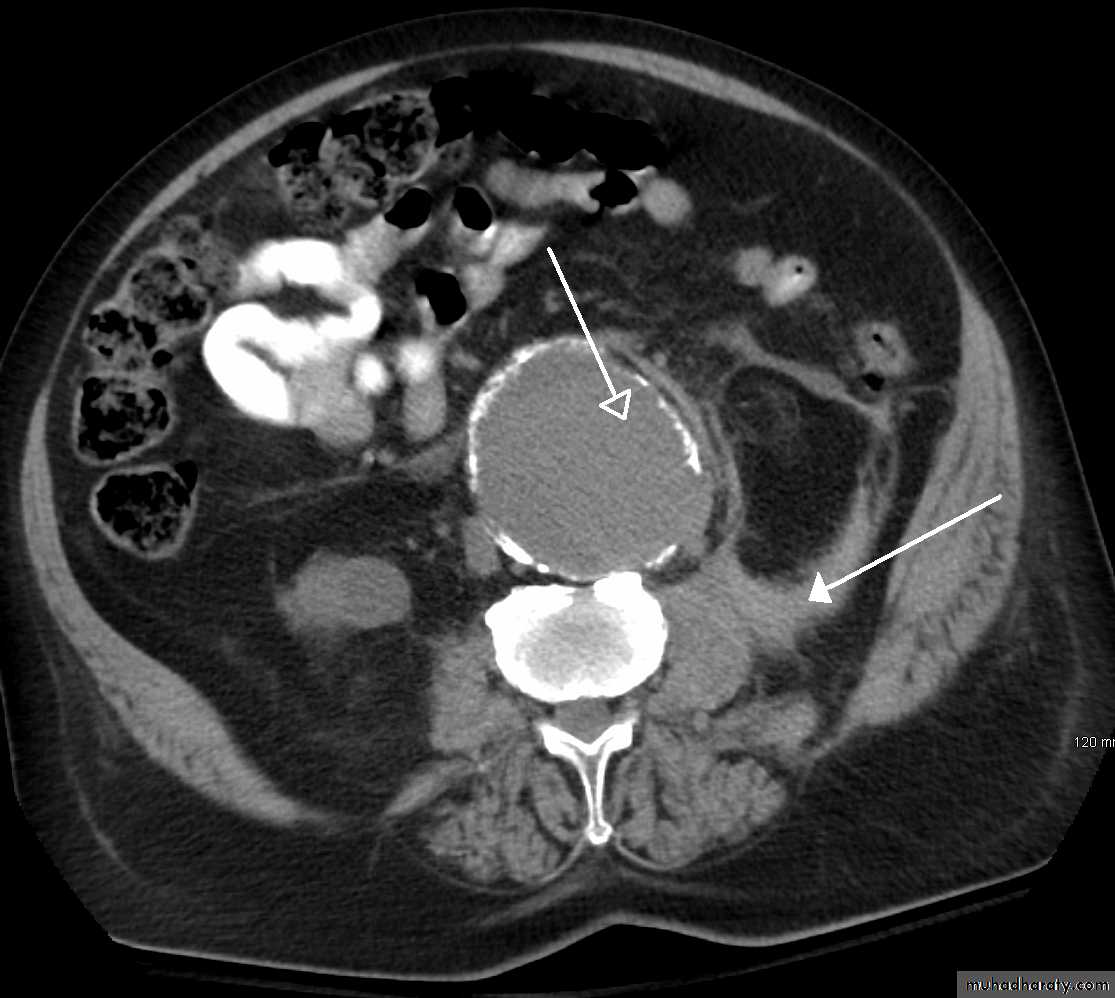
• CT and CT angiography
• MRA
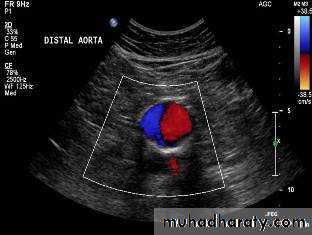
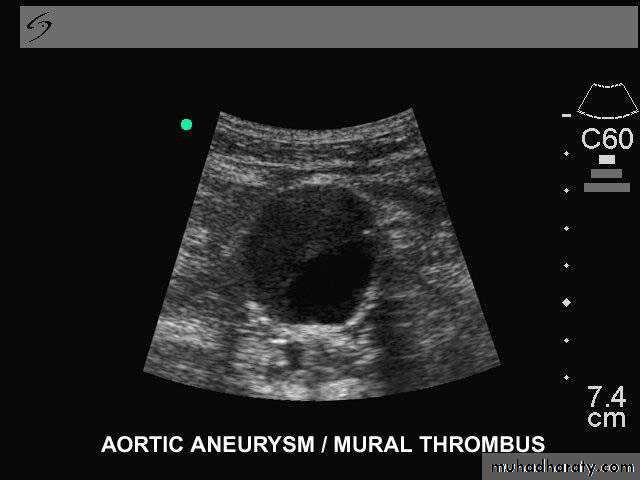
Ultrasound & Duplex Ultrasound:
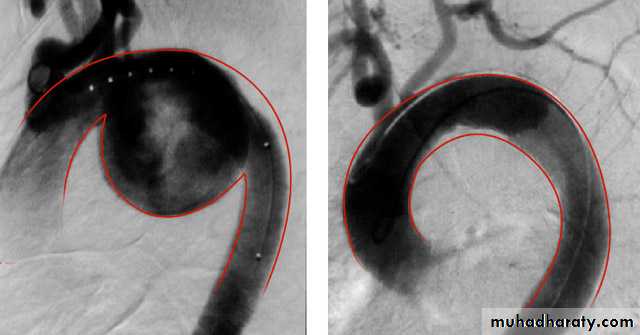
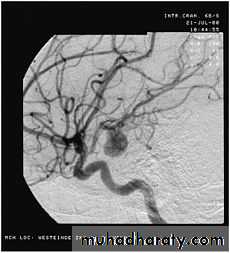
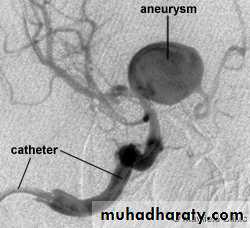
Angiography:
CT angiography:
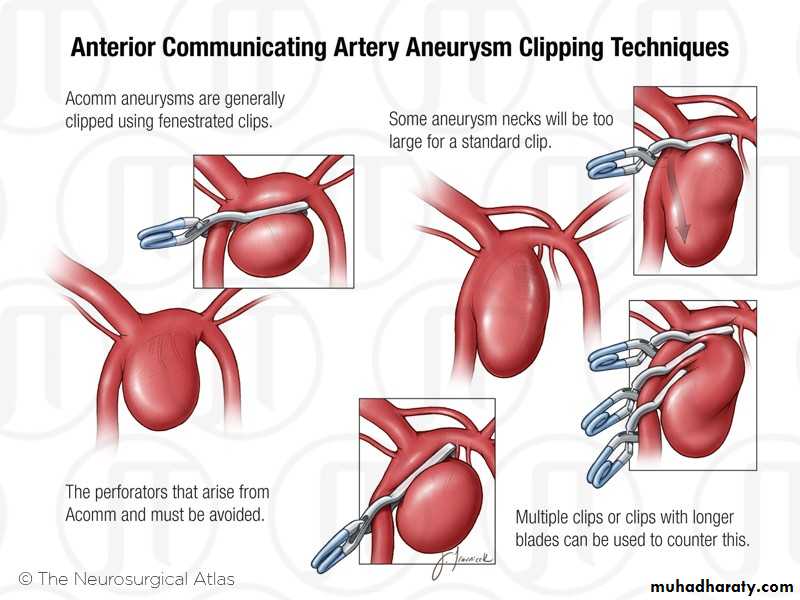
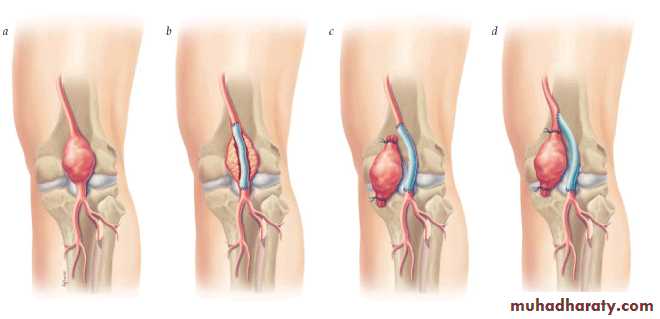
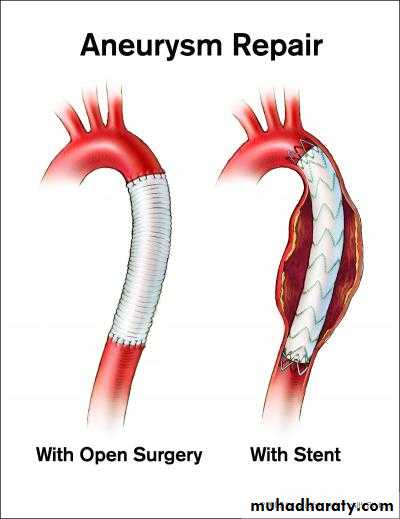
Treatment:
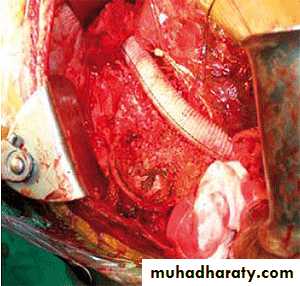
• Aneurysm excision with graft interposition• Aneurysm repair
• Aneurysm excision with resection of supplying tissue
• Aneurysm excision without arterial reconstruction
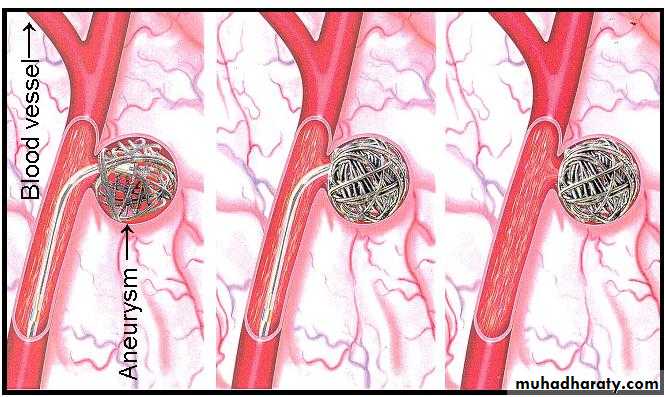
• Endovascular aneurysm repair
Arterio-Venous Fistula
What is an AV fistula??
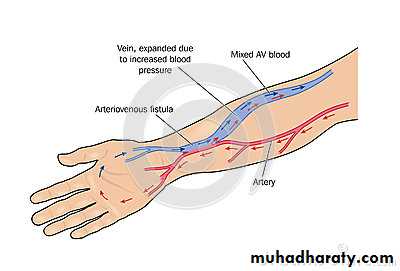
Abnormal direct communication between the arterial and venous system that bypasses the capillary bed.Etiology:
Causes of AV fistulas:• Congenital (arteriovenous malformations or hemangiomas
• Acquired which may be
• Traumatic
• Iatragenic.
• Neoplastic.
• Spontaneous
• Surgically created
Clinical Presentation:
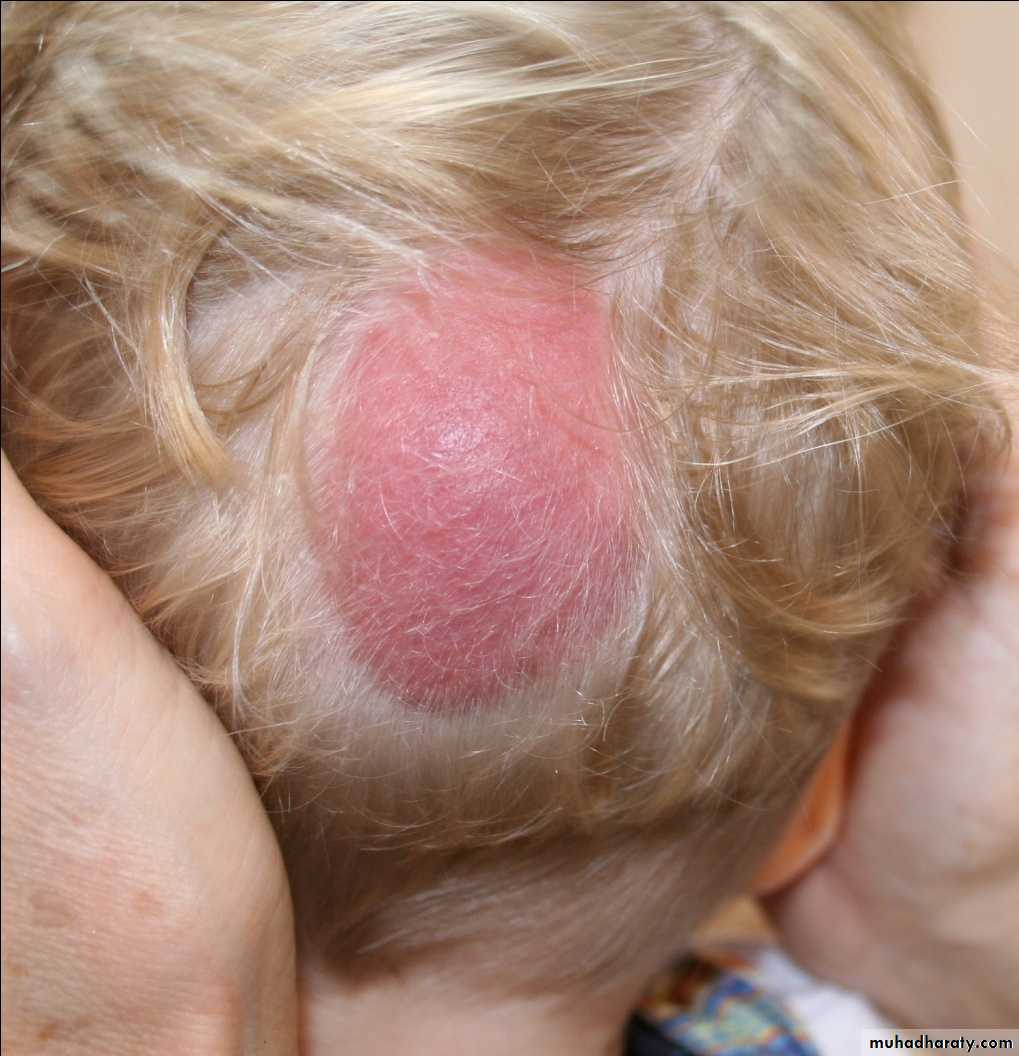
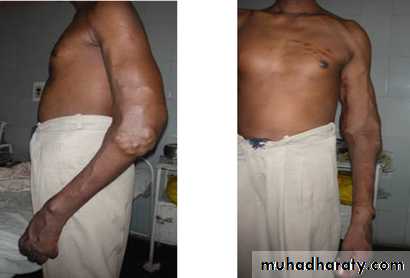
Congenital AV malformation:
• Cosmetic effect
• Pressure effect on nearby structures
• Bleeding and ulceration
• Thrombosis or thrombophlebitis
Benign AV malformations
Complex AV malformations
Acquired AV fistulas
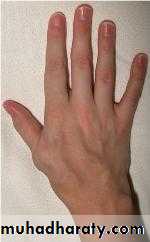
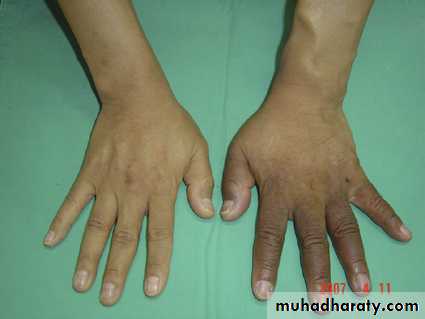
• Distal limb ischemia leading to ischemic ulcers and gangrene.• Dilated tortuous veins in the area (varicose veins)
• Limb edema with pain and discomfort due to the chronic venous hypertension
• Increased venous return to the heart leading to increase work load on the heart and eventually heart failure
• Aneurismal dilatation leading to what is called an "aneurismal fistula"
• A chronic fistula in a limb of a growing child may affect the growth of that limb.
Treatment:
AV malformationsStaged operations
Percutaneous embolization,
Multidisciplinary teams
Acquired AV fistulas:
Percutaneous embolization of the fistula,Excision with or without vascular reconstruction, or
4 limb ligation of the fistula
Thank You