
1
Third stage
Surgery
Lec-1
.د
سعدالله الزكو
1/1/2014
Introduction to Surgery
Surgical diagnosis is based on sound knowledge of anatomy, physiology & pathology, a
specific history & exam with confirmation by imaging & operative surgery.
No matter how good the operation, if it is performed for wrong diagnosis, the benefit for
the patient will be limited.
In other patient presented with severe illness & present as a surgical emergency, a skilled
preop. resuscitation & management can turn a high risk procedure into a routine operation.
Similarly, the very ill patient can be saved by expert post-op. management.
The skill of op. surgery is primarily taught in the op. theatre &
by supervised practice aided by specific texts of op. surgery.
Too little attention has been paid by the surgeon to the ancillary process of investigation.
Just as the stethoscope is helpful in diagnosis, so the U/S, endoscopy & other forms of
imaging will confirm the clinical finding the clinical findings:
U/S-gall stone, sigmoidoscopy-rectal carcinoma, X-Ray-fracture (#) bones.
We have to consider the benefit of the patient from the op. for the disease & the mortality
& morbidity if left untreated.
Surgical history
History of the complaint is the key in surgical diagnosis.
History of 2 types:
1-outpatient ( emergency) history: where specific complaint of the patient is pinpointed.
The object is to obtain diagnosis & assess treatment planned.
2-history for elective surgery.
Clinical exam.
1- general
2-local
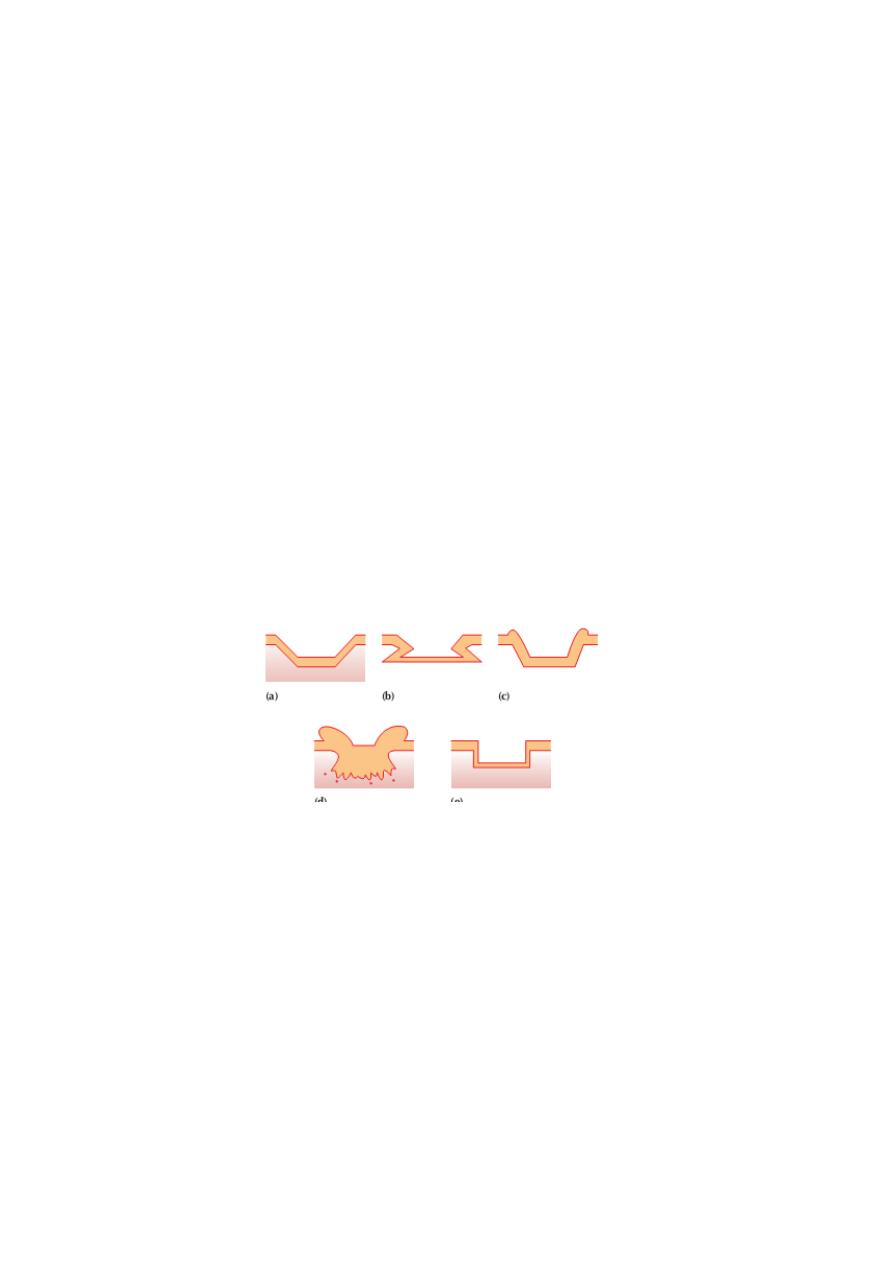
2
Diagnosis of lump
1- anatomical plain: skin, muscle, tendon.
2- physical characteristic : tender, round, regular, consistency ( cystic, soft, firm , hard,
stony hard).
Importance of specific signs
Thrill: percussion of middle finger & feel by 2 fingers.
Compression sign: decrease size after compression means vascular lesion.
Indentation sign: can be molded, mean fecal impaction.
Pulsation: in aneurysm.
Ulcer
Size,shape, edge, floor, base, surrounding tissue, lymph node, vessels.
Terminology
1-Fistula: tunnel connecting 2 epithelial surfaces.
2-Sinus: blind tract open on skin or mucosa.
3-Lymphangitis: inflammation of lymph vessels shows red line leading to lymph node.
Phlebitis: inflamed vein.
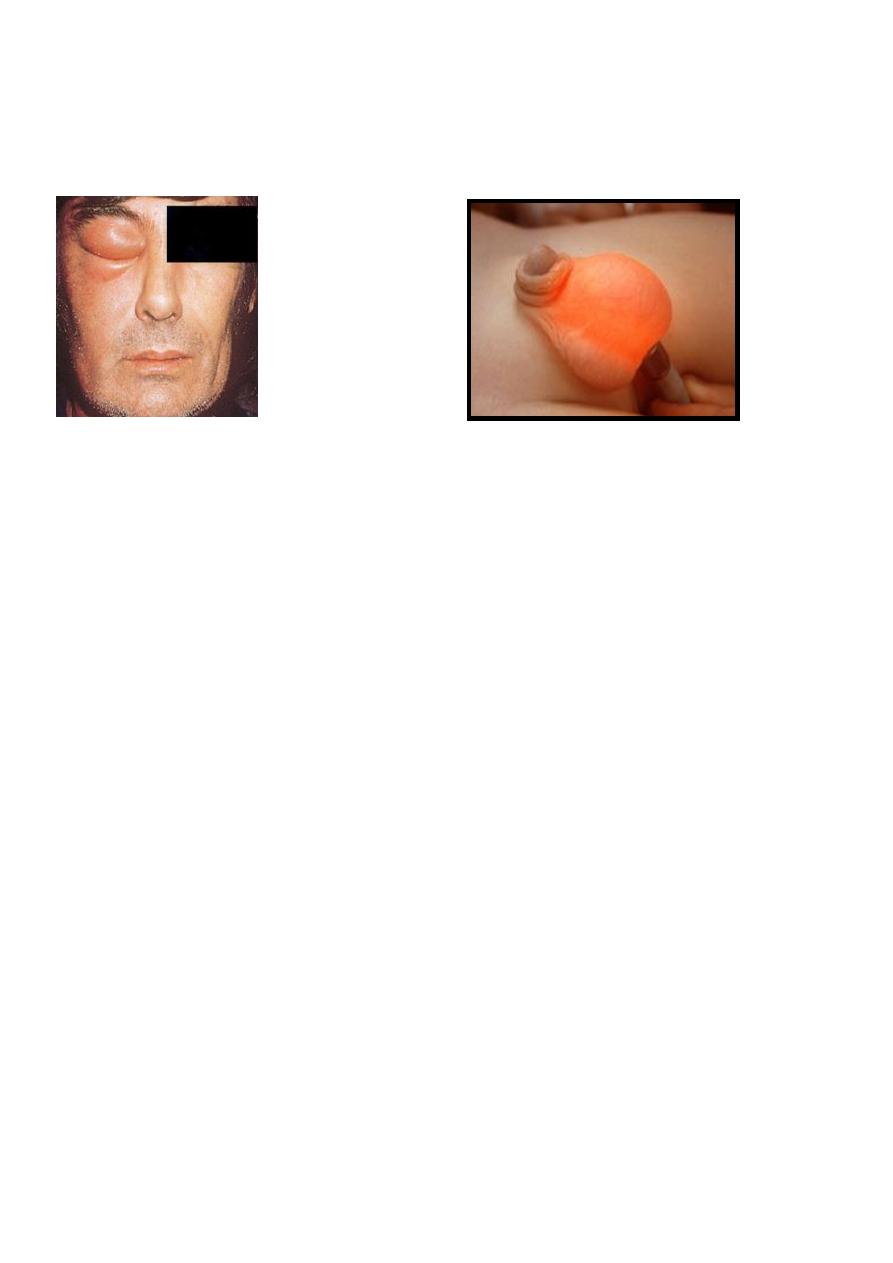
Cellulitis: inflammation of tissue ( skin & subcutaneous tissue).
Inflammation: redness, swelling, tender, hot, loss of function.
3
Crepitus: bone #, joint arthritis
Translucency: clear fluid collection.
Fluctuation: presence of fluid. (2directions)
Cellulitis Translucency
