1
Third stage
Medicine
Lec-6
د
.
عبدالحق
1/1/2014
Acid and Base Disturbance
PH Review
H
+
is a proton
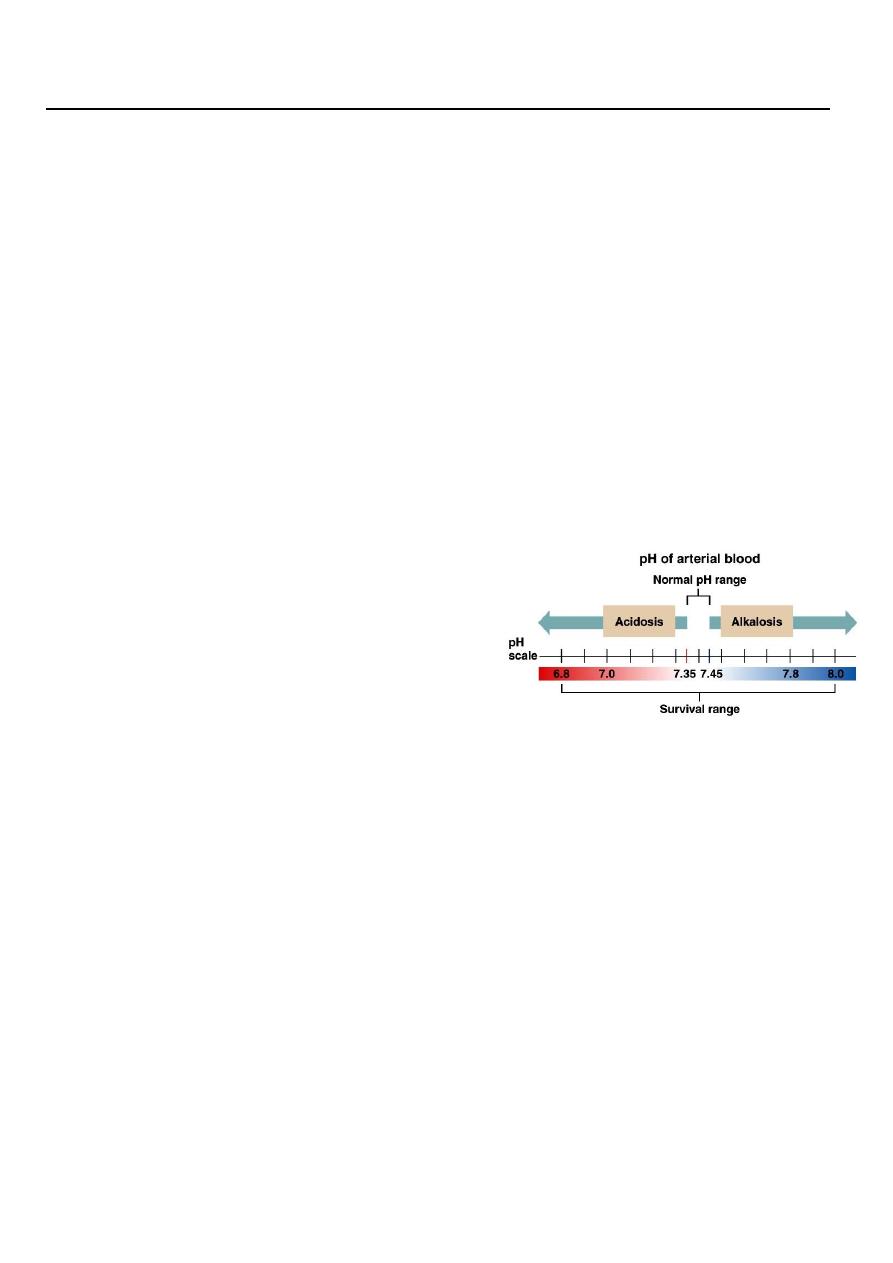
pH Range is from 0 - 14
If [H
+
] is high, the solution is acidic; pH < 7
If [H
+
] is low, the solution is basic or alkaline ; pH > 7
The Body and pH
Homeostasis of pH is tightly controlled
Extracellular fluid = 7.4
Blood = 7.35 – 7.45 (7.40)
< 6.8 or > 8.0 death occurs
Acidosis (acidemia) below 7.35
Alkalosis (alkalemia) above 7.45
Normal Serum HCO3- is 21-29 mmol/L
Small changes in pH can produce major disturbances
Most enzymes function only with narrow pH ranges
Acid-base balance can also affect electrolytes (Na+, K+, Cl-)
The body produces more acids than bases
Acids take in with foods
Cellular metabolism produces CO2.
CO2 + H20 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3-
Slightly Alkaline plasma of 7.40(H+ : 40 nmol/L) is maintained by kidney
capacity to produce an Acidic Urine(PH typically 5-6)in which the excess of
metabolic acid can be excreted.
2
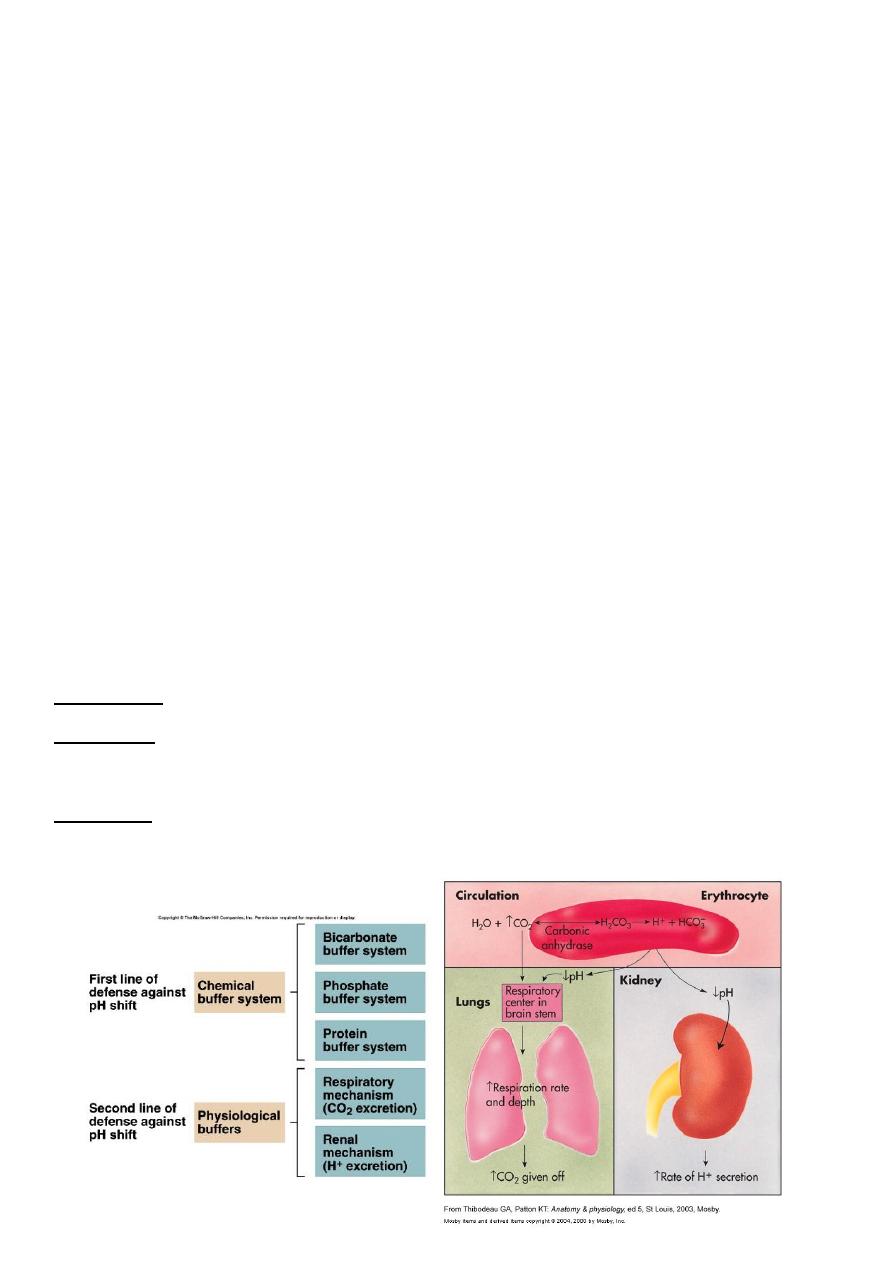
Renal Control of Acid-Base balance
Kidneys are Most effective regulator of pH
If kidneys fail, pH balance fails
Collecting ducts cells, Can eliminate large amounts of acid (Acid is secreted
into the lumen by H+_ATPas )
Can also excrete base
Can conserve and produce bicarb ions Renal compensatory mechanisms
may take hours to days OR EVEN WEEKS
Respiratory mechanisms
Exhalation of carbon dioxide CO2
CO2 + H20 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3-
Body pH can be adjusted by changing rate and depth of breathing
Respiratory mechanisms (hypo or hyperventilation) take several minutes to
hours
Urinary Buffers
Bicarbonate: some 85% of the filtered Bicarbonate reabsorbed in the Proximal tubule
phosphate: Maintain a 20:1 ratio
HCO
3
-
: H
2
CO
Ammonia : Major intracellular buffer
• H
+
+ HPO
4
2-
↔ H
2
PO4
-

3
Compensation to Acid-Base Imbalances
If underlying problem is metabolic, hyperventilation or hypoventilation can help :
respiratory compensation.
If problem is respiratory, renal mechanisms can bring about metabolic compensation.
Acidosis
Principal effect of acidosis is depression of the CNS through ↓ in synaptic
transmission.
Generalized weakness
Deranged CNS function the greatest threat
Severe acidosis causes
o Disorientation
o coma
o death
Alkalosis
Alkalosis causes over excitability of the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Numbness
Lightheadedness
It can cause :
o Nervousness
o muscle spasms or tetany
o Convulsions
o Loss of consciousness
o Death
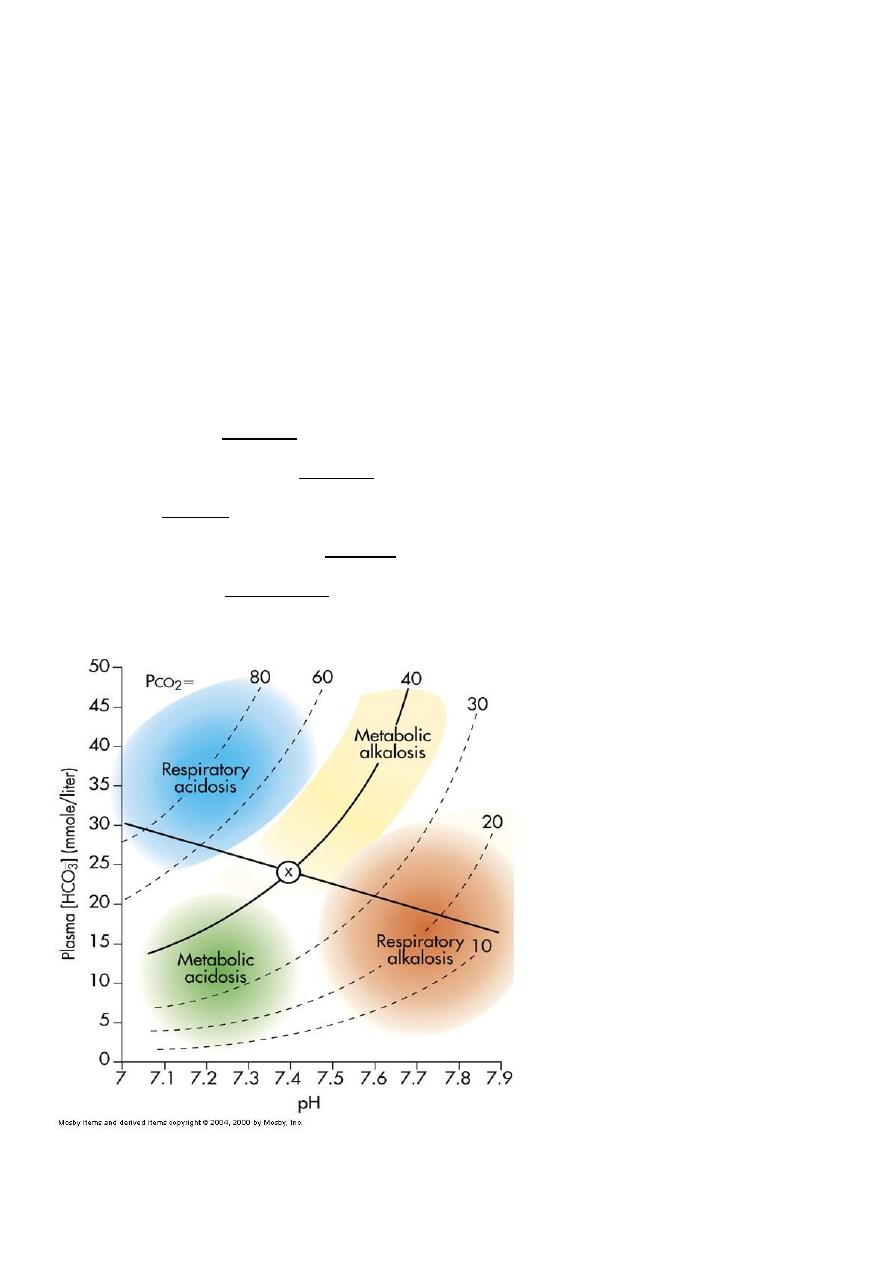
Simple Acid-Base Disorders
4
Respiratory Acidosis
• Carbonic acid excess caused by blood levels of CO
2
above 45 mm Hg(= PCO2 5.33
kpa). Hypercapnia – high levels of CO
2
in blood causes
• Chronic conditions:
– Depression of respiratory center in brain that controls breathing rateby drugs
or head trauma
– Paralysis of respiratory or chest muscles
_Emphysema
• Acute conditons:
– Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome
– Pulmonary edema
– Pneumothorax
* Compensation: Kidneys eliminate hydrogen ion and retain bicarbonate ion
Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Acidosis
Breathlessness
Restlessness
Lethargy and disorientation
Tremors, convulsions, coma
Respiratory rate rapid, then gradually depressed
Skin warm and flushed due to vasodilation caused by excess CO2
Treatment
Restore ventilation
Treat underlying dysfunction or disease
Respiratory Alkalosis
• cause is sustained hyperventilation
• Carbonic acid deficit..washing of CO
2
• pCO
2
less than 35 mm Hg (hypocapnea),Most common acid-base imbalance causes
5
high altitudes (Oxygen deficiency) Hyperventilation
Pul embolisim,Acute anxiety….HYS,Fever, anemia
Early salicylate intoxication..stim brain stem resp.center
&Cirrhosis chronic liver disease
Cl/p: perioaral & digital tingling ,Tetany (due to decrease ionised Ca++ caused by increase
binding of Ca++ to Albumen in Alkalosis
• Treatment :Treat underlying cause
• rebreathe into a paper bag
Metabolic Acidosis
characterized HCO3- less than 24,Caused by:
– Loss of bicarbonate through diarrhea or renal dysfunction
– Accumulation of acids (lactic acid or ketones)
– Failure of kidneys to excrete H+
Causes of Normal AG (Hyperchloremic) Metabolic Acidosis
AG = (Na
+
+ K+) - (Cl
-
+ HCO
3
-
) = 15
High K
+
Low K
+
Adrenal insufficiency
Diarrhea
Interstitial nephritis
RTA proximal,Distal
Ureteral diversion
Metabolic Acidosis:
Elevated Anion Gap
AG = (Na
+
+ K+) - (Cl
-
+ HCO
3
-
) = 15
[Note: Diagnostic utility is best when AG > 25]
Causes Ketoacidosis
Lactic acidosis
Intoxications(salicylate ,Methanol poisoning)
Renal failure
Rhabdomyolysis
6
Compensation for Metabolic Acidosis
Increased ventilation
Renal excretion of hydrogen ions if possible
K+ exchanges with excess H+ in ECF
( H+ into cells, K+ out of cells)
Metabolic Alkalosis
• Bicarbonate excess - concentration in blood is greater than 24 mmol/L
• compensation…hypoventilation..ie PCO2 will be more than 5.33 kpa
• Causes:
– Excess vomiting = loss of stomach acid
– Loop &Thiazide Diuretics (loss of H+ in urine)
– Cushing synd, ,primary hyperaldoteronism(corticosteroid excess)
– Heavy ingestion of antacids
– Severe dehydration
