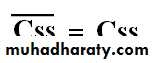Dr. Najlaa Saadi Ismael
Department of PharmacologyMosul college of Medicine
University of Mosul
Dose Modification in Renal Failure
• Objectives :
• To classify the drugs in terms of their dependence on renal elimination• To calculate the dose of drug in patient with renal impairment
Drug may be classified in terms of their dependence on renal elimination as the following example:
• Drug that are eliminated almost exclusively by the kidney:
• Benzylpenicillin
• Ampicillin
• Acyclovir
• Gentamicin
• Sotalol
• Atenolol
• Tetracycline
• Plasma t1/2(h)
• Drugs
• Severe renal• impairment
• Normal
8
0.5
Benzyl penicillin
14
1
Ampicillin
20
2.5
Acyclovir
50
2.5
Gentamicin
100
6
Atenolol
75
8
Tetracyclin
• Drugs that are almost entirely metabolized:
• Paracetamol
• Clindamycin
• Propranolol
• Rifampicine
• Lorazepam
• Doxycycline
• Nortriptiline
• Warfarine
• Plasma t1/2(h)
• Drugs• Severe renal impairment
• Normal
• 2
• 2• Paracetamol
2
2
Clindamycin
3
3
Propranolol
15
15
Lorazepam
40
40
Warfarin
• Drugs that are partly metabolized and partly eliminated by the kidney:
• Lincomycin
• Amphetamine
• Chlorpropamide
• Digoxin
• Digitoxin
• Plasma t1/2(h)
• Drugs• Severe renal impairment
• Normal
• 12
• 5• Lincomycin
• 120
• 36
• Digoxin
Dosing regimens for patient with renal impairment
Concentration of steady state (Css):• It is concentration of the drug which is reach after specific time of drug administration.
• 5 × half life time
Concentration of steady state (Css)
At steady state
• Drug input = drug output
• Maximum effect
• Neither toxicity nor decline of effect
• The amount of the drug in the body is constant
Example :what is the dose of carbencillin in patient with renal impairment?
• 20years old, 70kg male patient, serum creatinine conc. 5mg\100ml• 50years old, 85kg female patient, serum creatinine conc. 2mg\dl.
• CrCl = 0
• CrCl = 30 ml\mi
• Carbencillin Dose = 2g\day
• K = 0.55 hr-1
• KM = 0.055 hr-1