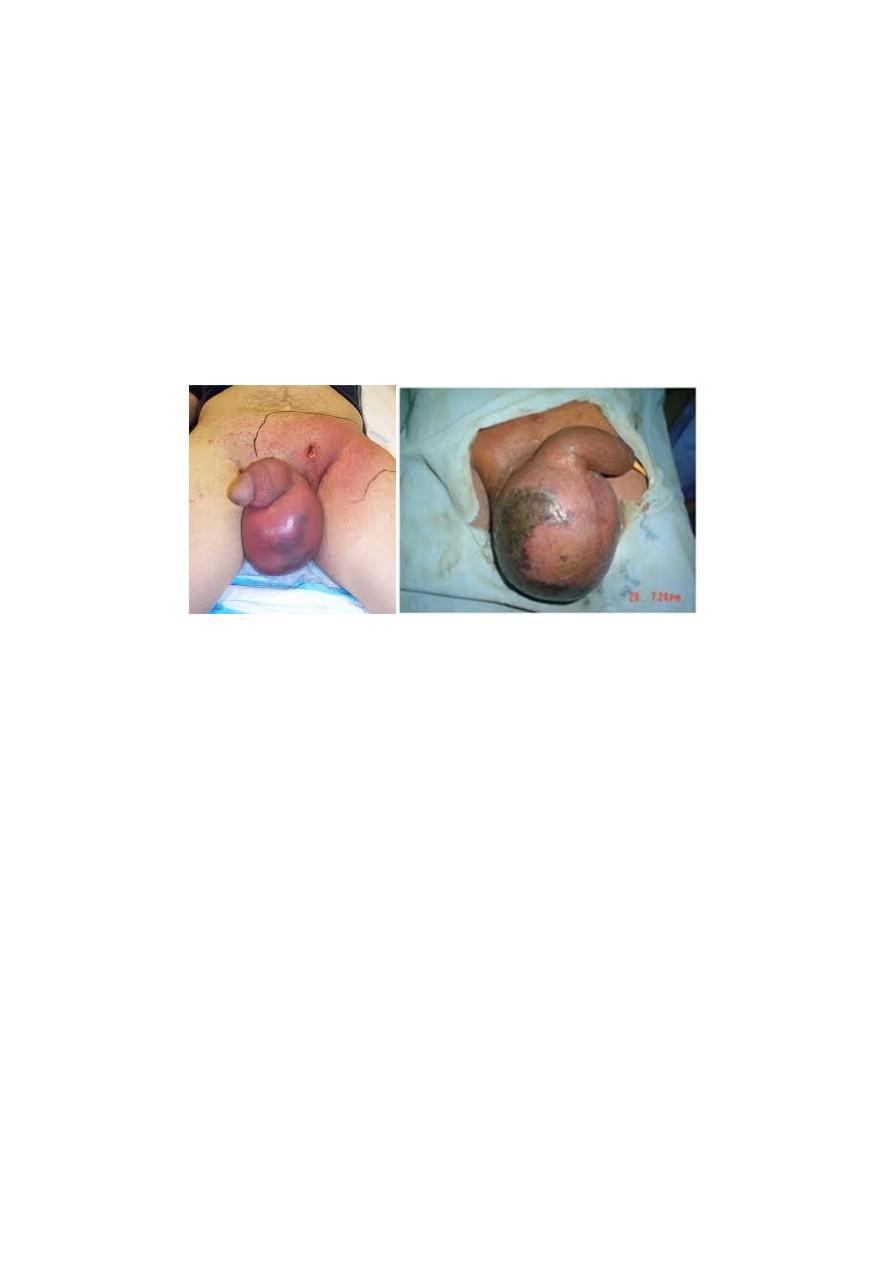
(Fournier’s gangrene)
• Causative organisms: mixed infection of Haemolytic
streptococci , Staphylococcus, E. coli, Clostridium welchii.
Tx :1-
gentamicin and cephalosporin
2-
Wide excision of the necrotic scrotal skin
•
3-
Many patients die despite active treatment
Vesicoureteral reflux:
Definition: abnormal retrograde flow of urine from the bladder
into the upper urinary tract(exam)
causes:1-congenital 2-iatrogenic 3-contracted bladder 4-
voiding dysfunction
complication:
1-
Hydroureteronephrosis 2-UTI 3-HT 4-progressive
renal failure
definitive examination:voiding cystourethrogram
Tx:1-long term antibiotic
2-anticholinergic drugs(treat bladder overactivity)
3-surgery:ureteral re-implantation in:
a-failure of medical Tx
b-grade 4 or 5
c-
low-pressure reflux and significant hydroureter
d-
persistant reflux in girls after puberty
Hydronephrosis:
aseptic dilatation of the renal pelvis
usually caused by obstruction to the outflow of
urine(exam)
Hydroureteronephrosis: dilatation of renal pelvis &
ureter.
Causes of hydronephrosis:
1-Extramural obstruction:tumor +retrocaval
2-Intramural obstruction:puj obstruction+ureterocele
3-Intraluminal obstruction:stone
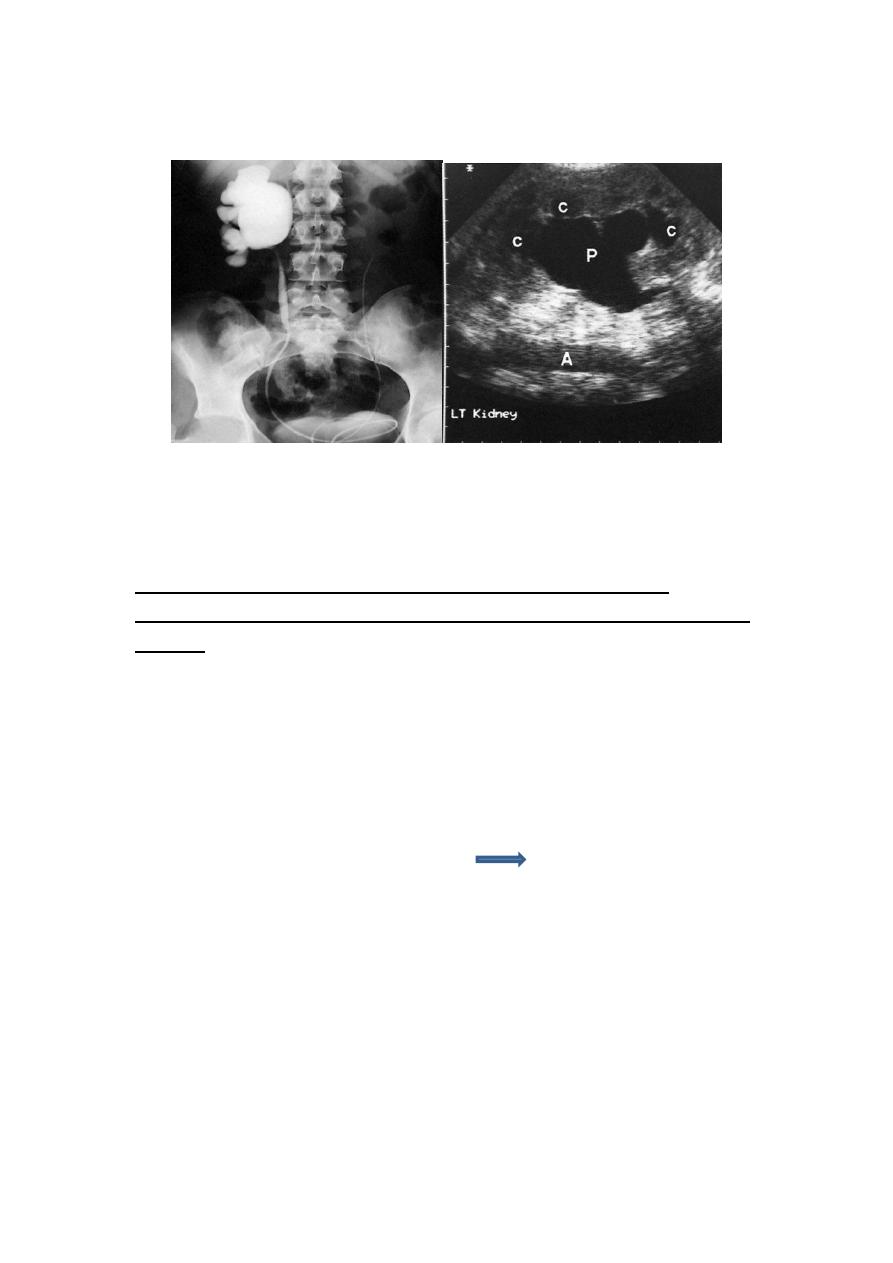
Most common diagnostic test?U/S then IVU
Renal colic: sudden severe agonizing pain.(exam)
radiats from costovertebral angle, toward the lower anterior
rotum
rse of the urether into the sc
u
abdominal quadrant, along the co
or vulva
Evaluation of patient:
Hx: Socrates+MAY BE VOMITING, NAUSEA
Ex:renal angle tenderness +soft abdomen + PR exam(VERY RARELY WE
DO IT).
IX:lab.:GUE+CULTURE+RFT. RADIOLOGY:U/S +KUB+IVU+NON
CONTRAST CT
TX(EXAM):
1-DICLOFENAC(VOLTARINE)(IM)(NOT MORE THAN 150
ML\DAY)(C.I.:HT+ASTHMA+PU+RENAL IMPAIRMENT)(IF VOLTARINE IS
CONTRAINDICATED USE NARCOTICS)
2-ANTIBIOTICS
3-ANTI-EMETICS

4-IV FLUID
5-INDICATION OF ADMISSION(10%)(*90% NOT NEED ADMISSION):
Child , elderly, pregnant
PAIN NOT RESPONDING(UNCERTAIN DX)
persistent vomiting
RENAL IMPAIRMENT
single kidney with ureteral obstruction
bilateral ureteral stones
Differential Diagnosis of Renal Colic
❏pyelonephritis
❏ acute ureteral obstruction
stone
UPJ obstruction
sloughed papillae
blood clot
❏radiculitis (L1 nerve root irritation)
• herpes zoster
• nerve root compression
❏acute abdominal crisis (biliary, bowel)
❏leaking abdominal aortic aneurysm

Hematuria :
More than three red blood cells are found in
centrifuged urine per high-power field microscopy.(exam)
*normally:1-3intact RBC ,but presence of 1 abnormal RBC is not normal
DDx of red urine(exam): 1-hematuria 2-hemoglobineuria 3-
myoglobinuria 4-metabolic:porphyria and alkaptonuria 5-drugs like
rifampicine 6-polluted urine(menstruation) 7-food dyes.
DDX of hematuria(causes of hematuria) كلش مهم التفريق بينهم االثنين:
1-GN 2-interstial nephritis 3-uroepithelium malignancy 4-AV
malformation 5-sickle cell trait 6-stones -6-drugs 8-SLE 9-TB 10-trauma
Ix :1- Three-glass test(collecting the three stages of urine of a patient
during micturition)
Result:
the initial specimen containing RBC—the urethra
the last specimen containing RBC—the bladder neck and trianglar area
all the specimens containing RBC—renal or ureter or bladder
2-
Phase-contrast microscopy:
to distinguish glomerular from post
glomerular bleeding
Result :
post glomerular bleeding: normal size and shape of RBC
glomerular bleeding: dysmorphic RBC (acanthocyte)
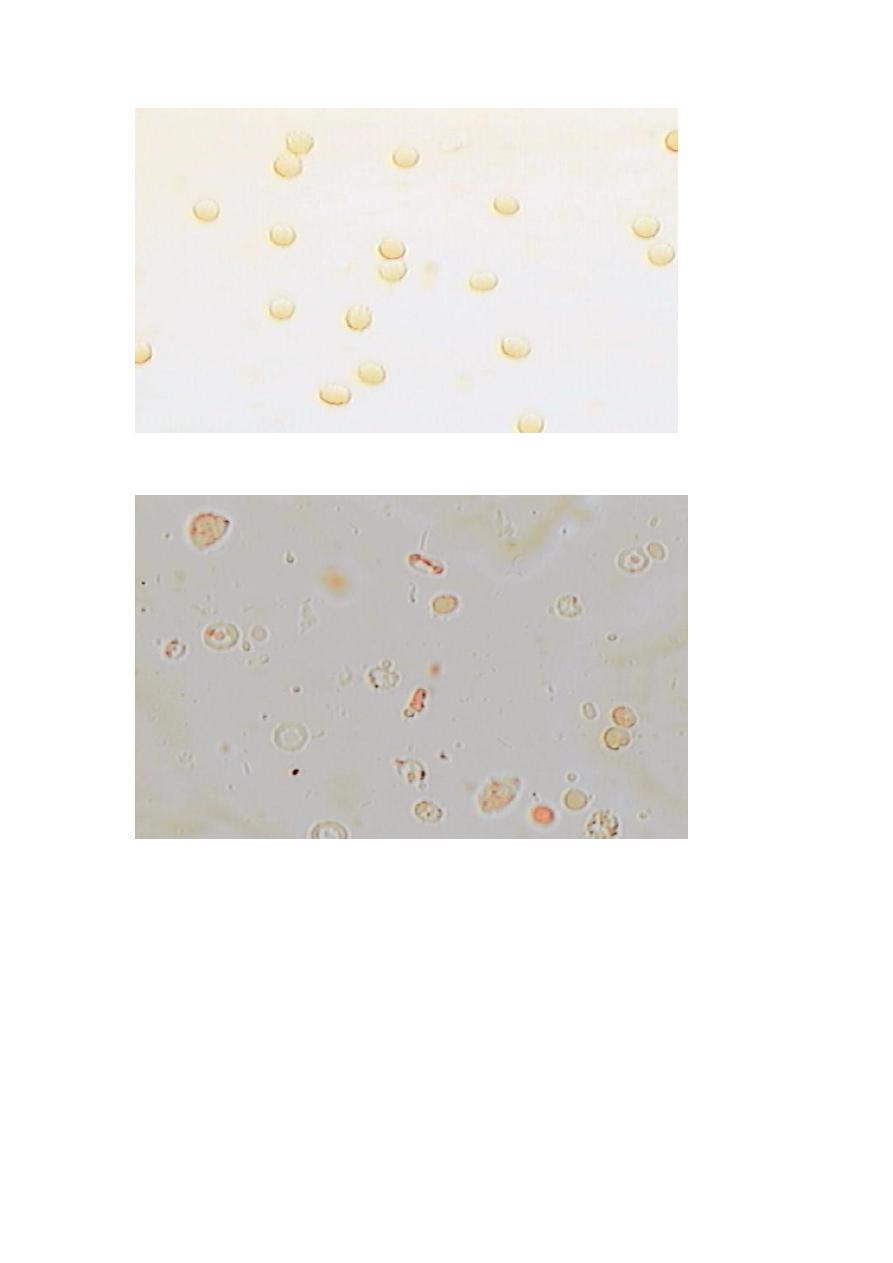
PHASE-CONTRAST MICROSCOPY TEST (non-glomerlar bleeding)
PHASE-CONTRAST MICROSCOPY TEST (glomerular bleeding)
Symptoms of urology
Associated symptoms : Fever, Chills, Weight loss, Nausea, Vomiting .
Irritative symptoms : Frequency, Nocturia, Dysuria, Urgency .
Obstructive Symptoms :poor stream , dribbling , Hesitancy,
incontinence, retention of urine.
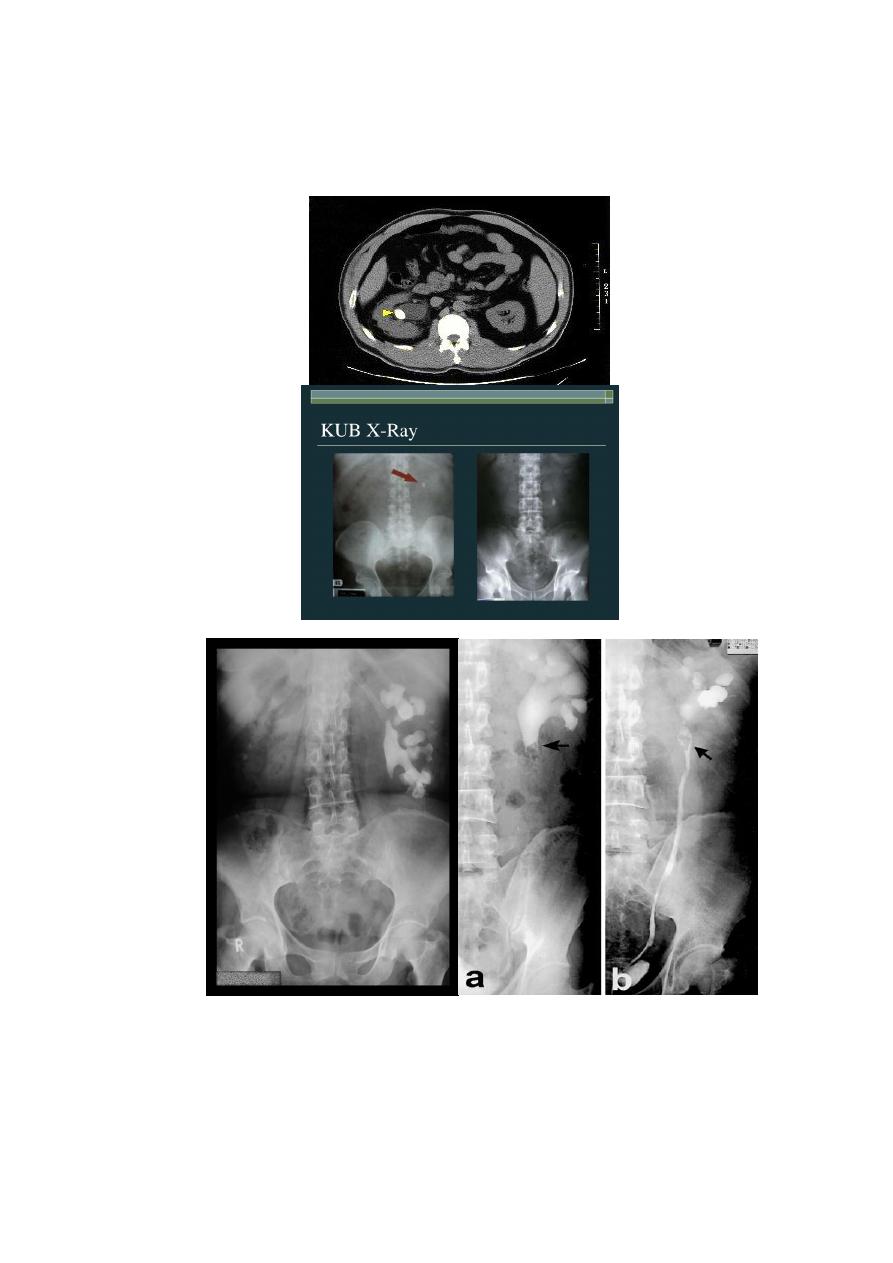
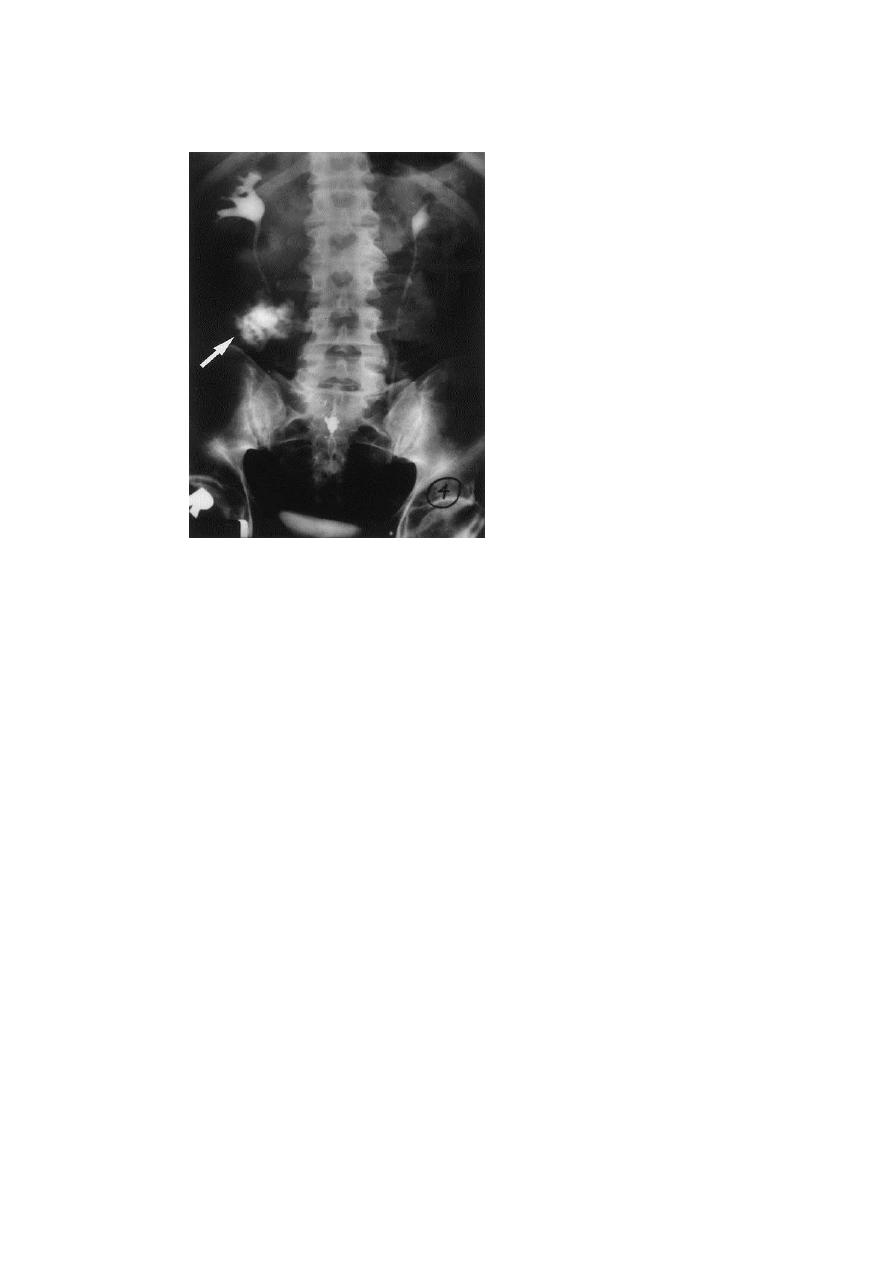
Stone :
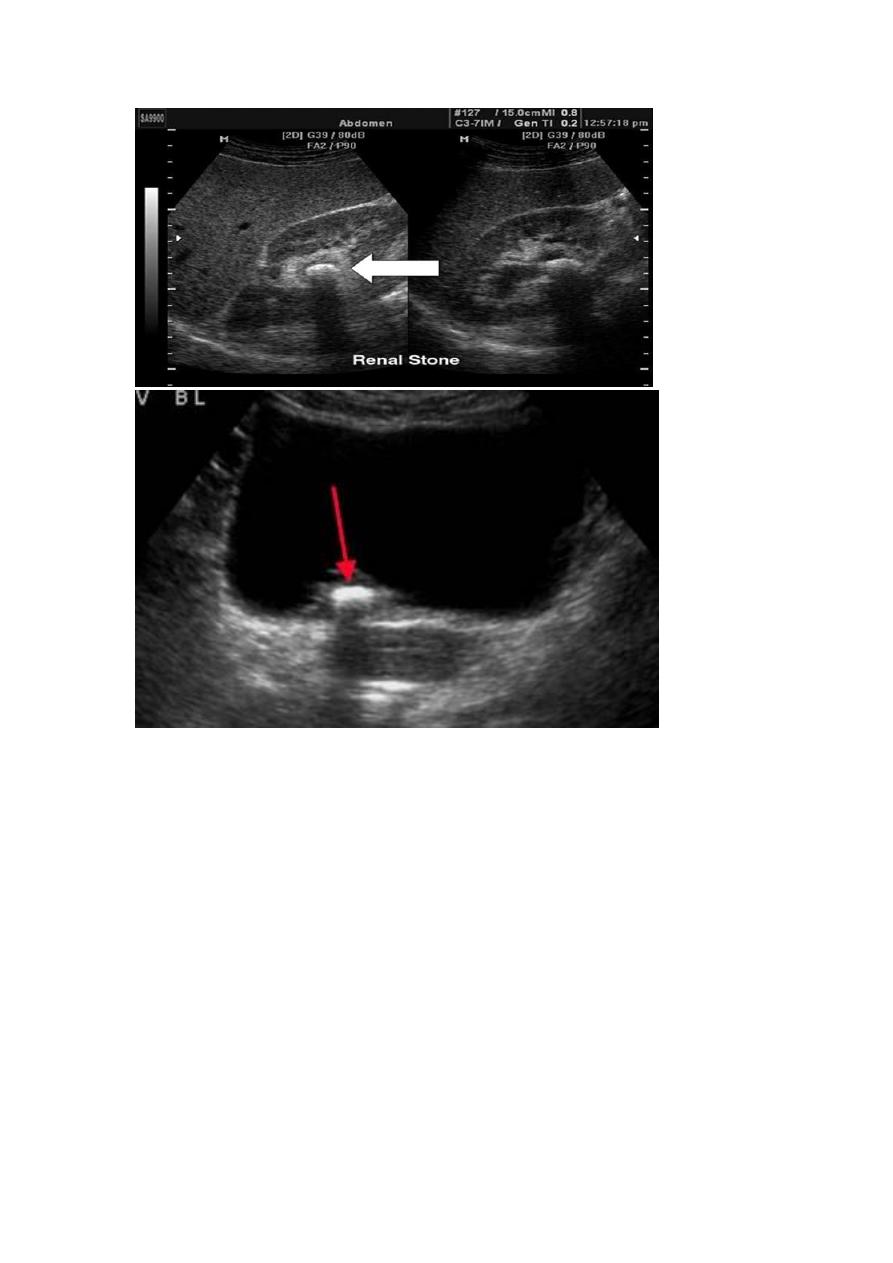
Types : calcium stones , struvite stones , uric acid stones, cysteine stones
,other rare types.
Ix :1-general:CBC,RFT,GUE
2-RADIOLOGY:
KUB:radiopaque mass(white)
u/s :hyperechoic mass(white) with acoustic shadow
CT: hyperdense mass(white)
IVU:filling defect(dark)

INDICATION OF KUB(EXAM):
1- Radio-opaque urinary calculi (90% of calculi)(all stone visble except
pure uric acid stone ans xanthine stone)
2- Soft tissue masses in the renal areas and pelvis
3-Gallstones (10%)
4- Pelvic phleboliths
5-Calcified lymph nodes
-6 Sclerotic deposits in prostate cancer
7-other tumours
Tx :
medical
a-blocker
NSAIDs help lower intra-ureteral pressure
Surgical(exam):5 options in general
1-
extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy(C.I. in pregnancy(the only
absolute one),too hard stone , uncontrolled HT, bleeding tendency ,
over weight)
2-endoscopy ,cystoscopy,uretroscopy
3-
percutaneous nephrolithotomy
4-laproscopy
5-open surgery
options in selected cases:
#case of renal stone :
extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy
percutaneous nephrolithotomy
open nephrolithotomy
#case of uretric stone:
extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy
ureteroscopy
open ureterolithotomy
#case of bladder stone :
Lithotrities
Cystolithotomy
Remove outflow obstruction
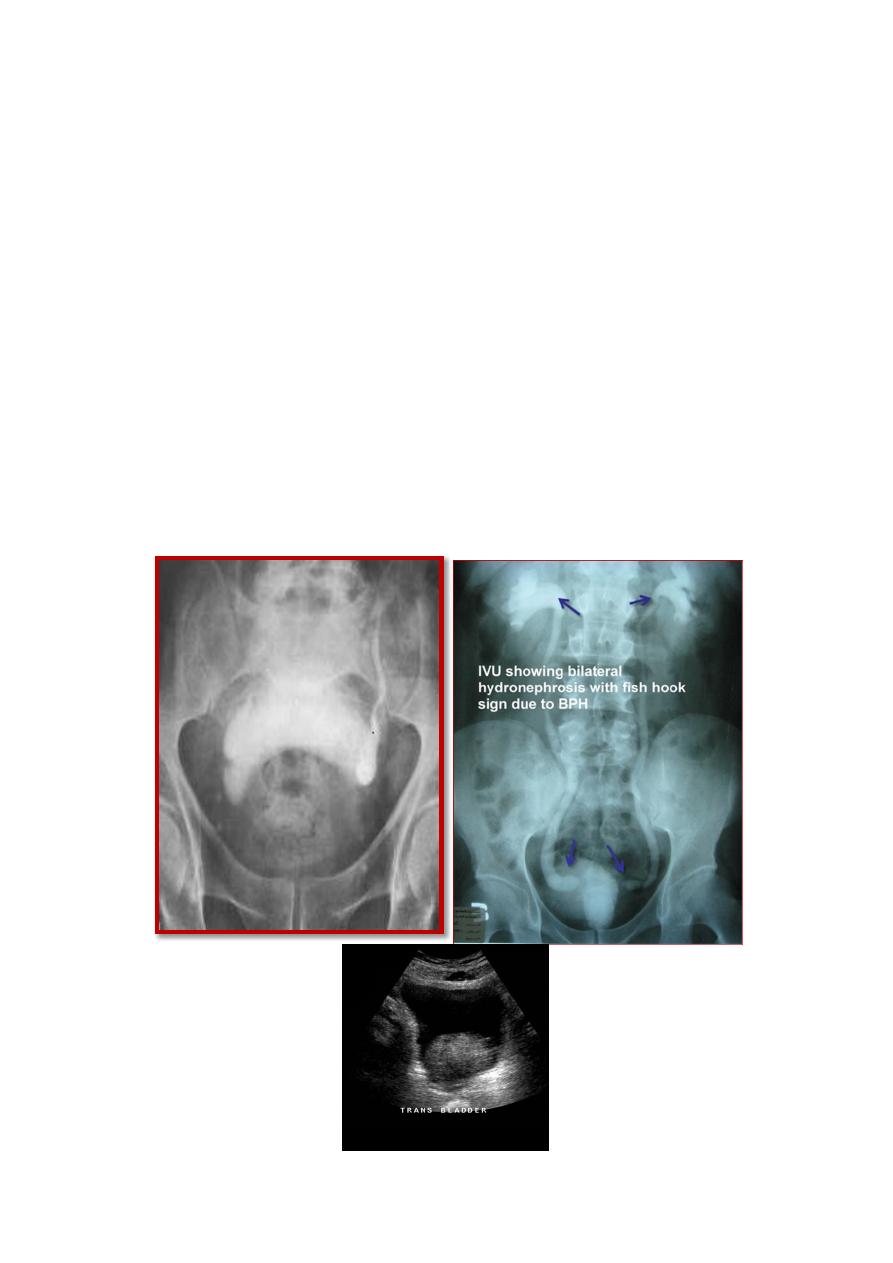
BPH:

DDX: Bladder Neck Contracture.
ž
Bladder Stone.
ž
Bladder tumor
ž
Neuropathic bladder
ž
Ca. Prostate.
Urethral Stricture
Indication of surgery:
1-bladder diverticulum
2-bladder wall hypertrophy and trabeculation
3-bladder stone
4-hydroureter
5-hydronephrosis
TX:
ž
A. WATCHFUL WAITING.
ž
B. MEDICAL THERAPY.(A-BLOCKER +5-alpha reductase inhibitor)
ž
C. MINIMALLY INVASIVE THERAPY.(thermal based
therapies,laser,others)
ž
D. SURGICAL THERAPY
ž
1-endoscopic:transurethral resection of prostate(risks:retrograde
ejaculation , impotence ,incontinence)+transurethral incision of
prostate.
ž
2-open surgery:retropubic prostatectomy+transvesical
prostatectomy
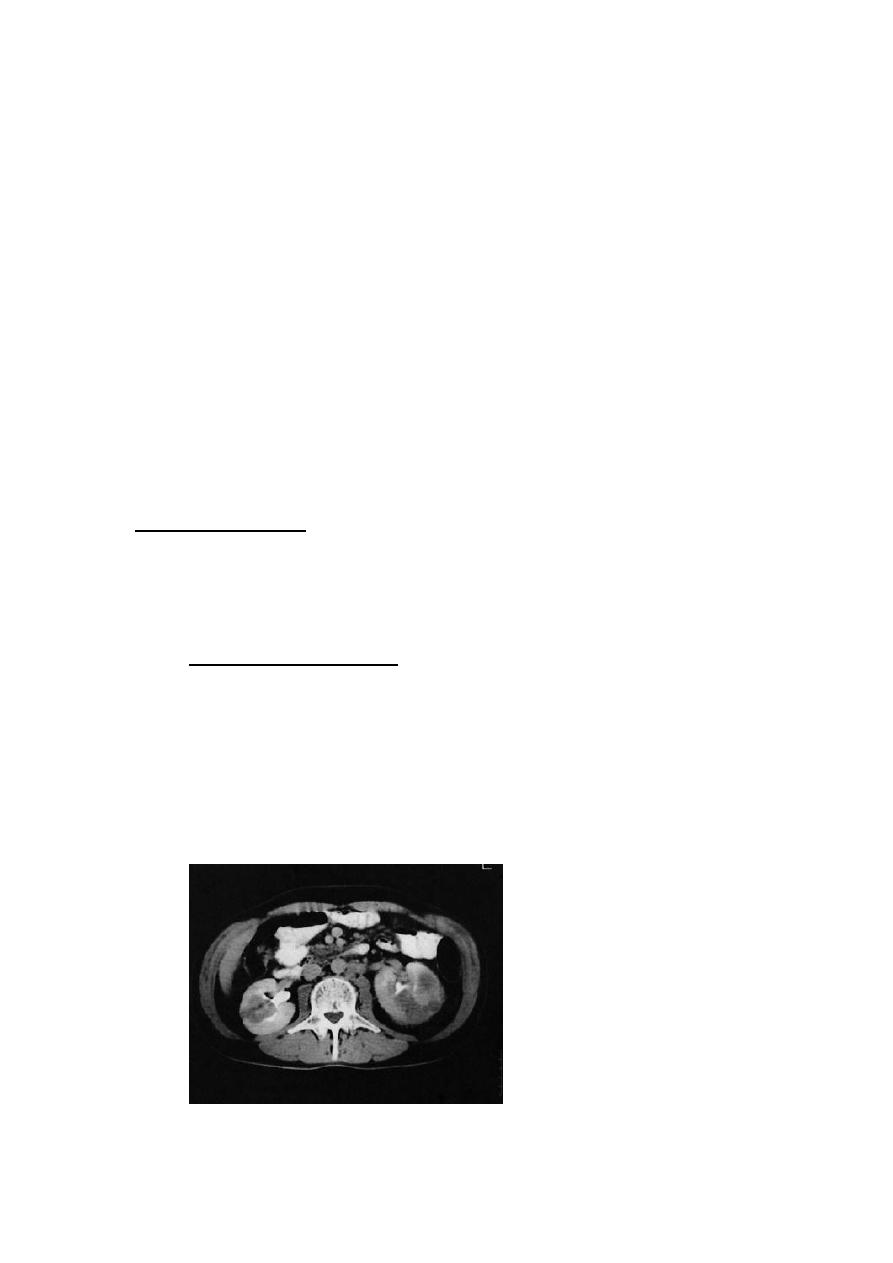
RCC:
DDX:
Carcinoma of renal pelvis
Renal lymphoma
Adrenal cancer
Benign renal tumor
Renal cysts
Renal abscess
TX:
LOCALISED DISEASE
partial nepherctomy
radical nephrectomy
DISSEMINATED DISEASE
radical nephrectomy withremoval of solitary metastasis
Immunotherapy
Radiotherapy (RCC is a radioresistant)
Chemotherapy (is also chemoresistant )

Renal trauma
(American Associaton for the Surgery of Trauma)AAST
classification:
1. Contusion, non-expanding subcapsular haematoma, no
laceration
2. Non-expanding perirenal haematoma, cortical laceration < 1 cm
deep, no urinary extravasation
3. cortical laceration > 1cm, no u.extravasation
4. Laceration: through corticomedullary junction into collecting
system OR vascular: segm. renal artery or vein injury with
contained haematoma
5. Shattered kidney OR major vascular injury (renal pedicle injury
or avulsion)
1,2 = minor injuries – 85-95% 3,4,5 = major injuries

Primary imaging -> ultrasonography
Tx
:
grade I-III in stable patients:
microscopic hematuria + isolated minor injuries do not need
hospitalization
gross hematuria + contusion/minor lacerations: hospitalize, bedrest,
repeat CT if bleeding persists
Surgery(exam):
absolute indications: hemorrhage and hemodynamic instability
relative indications:
1-nonviable tissue and major laceration
2-urinary extravasation
3-vascular injury
4-incomplete staging
5-laparotomy for associated injury
Complication:
Early: Haemorrhage, retroperitoneal urinoma, haematoma,
abscess
Late: Hypertension 5%, AV fistula, calculi, late bleeding
Urethral injery:
Causes:
Pelvic surgery
RTA
Penetrating injury
Severe blunt trauma
TX :
First-line: urinary diversion (nephrostomy, ureteral stenting)
Second line: Reconstructive surgery
Urethral stenosis:
Causes:congenital ,instrumentation , external trauma , infection
Tx : 1-dilatation 2- internal urethrotomy 3-open surgical reconstruction
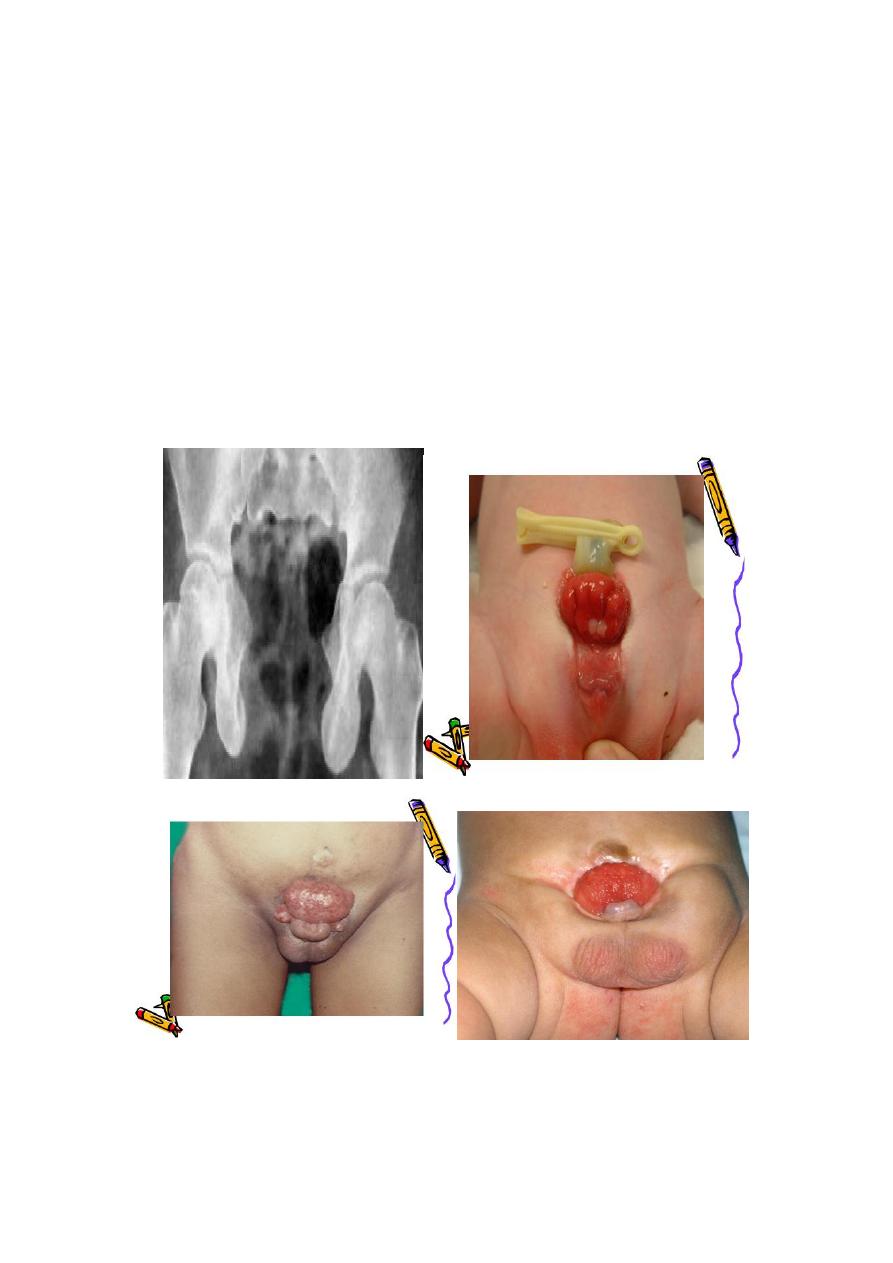
ECTOPIA VESICA: incomplete development of the infra-umbilical
part of the anterior abdominal wall+absent umbilicus+ incomplete
development of the anterior wall of the bladder+low located
bladder+separation of pubic bones.
Most common urethral abnormality?
epispadiac penis
Tx : 1-Staged reconstruction in first year of life(Iliac osteotomy,
closure of the bladder and closure of abdominal wall)
2-Urinary diversion
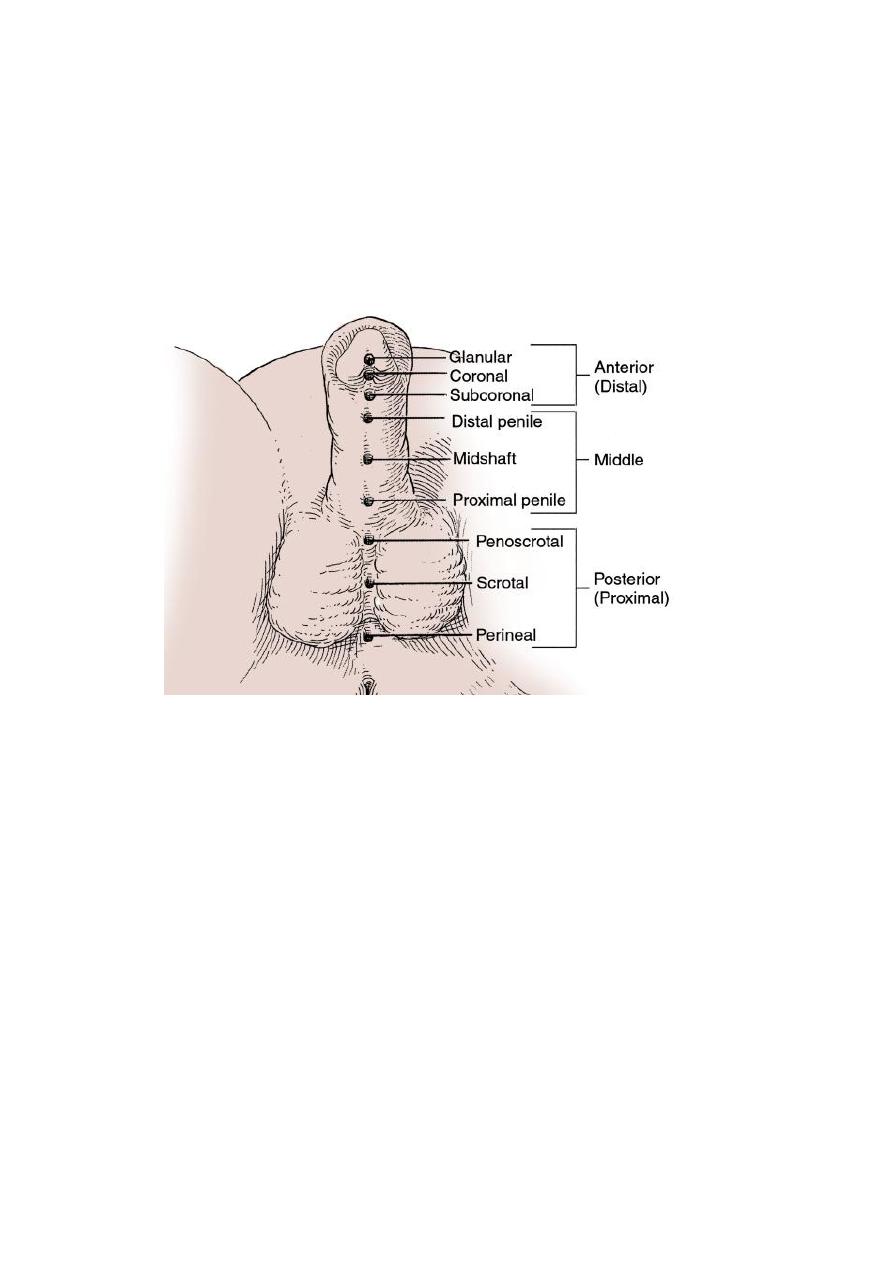
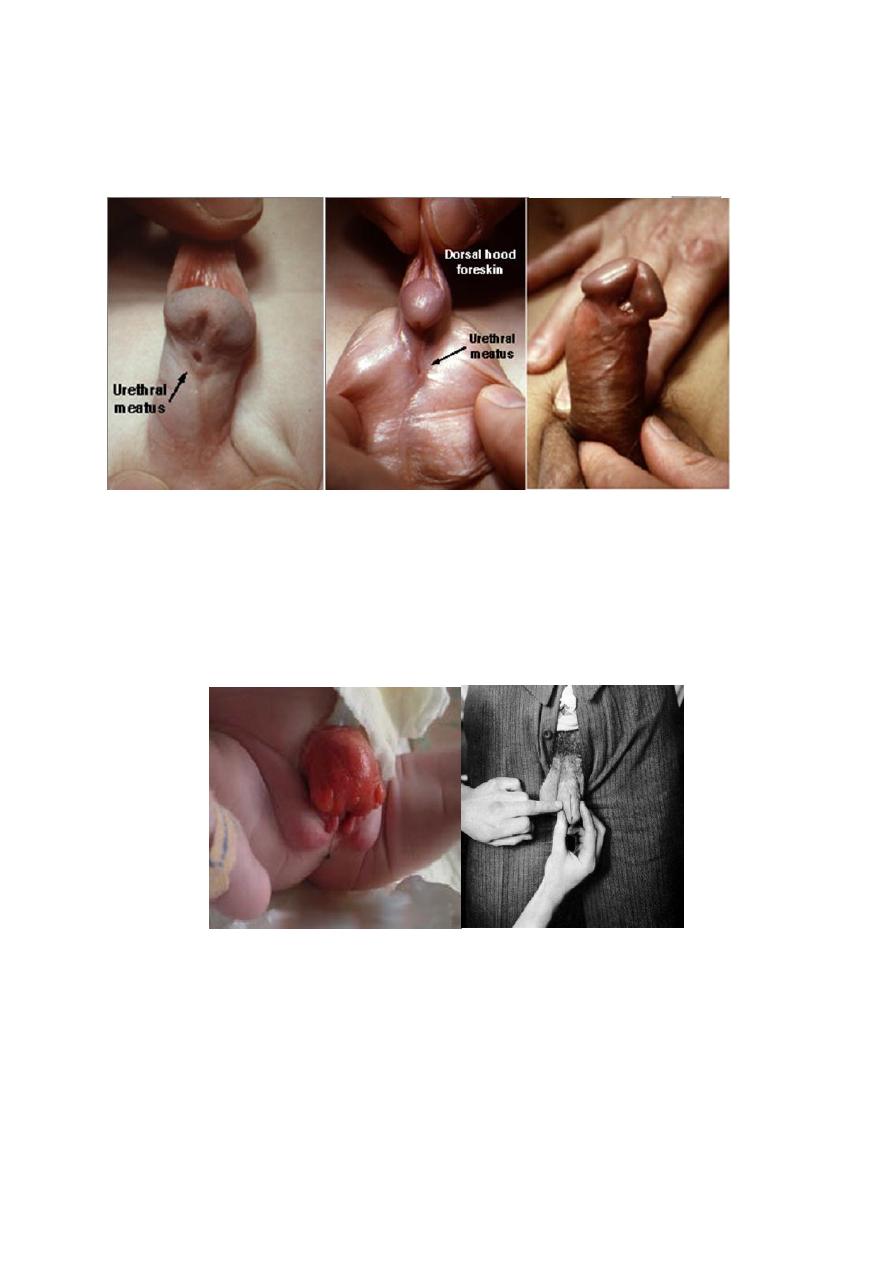
Hypospadias :the external urethral meatus(EUM)opens on the
ventral side of the penis prximal to the tip of the glans penis or on the
scrotum or perineum+ There may be poorly developed ventral part
of the prepuce( hooded prepuce)+There may be ventral penile
curvature(chordee).
Glanular hypospadias isthe commonest type.
Causes:Congenital(Esrogens & progestins given in prgnancy increase
its incidence)
Time of surgery: 6-18 montha of age
Indication of surgery:
improve sexual function
-
1
2- Improve urine stream.
3-Cosmotic reasons.
Steps of surgery
1. Orthoplasty
2. Urethroplasty
3. Glanuloplasty
circumcision should be delayed till hypospadias repair succeeded.
Epispadias:
ERM OPEN ON THE DORSUM OF THE PENIS(VERY RARE)
Most common associated abnormality?ectopia vesica
Phimosis(scaring prepuce which becomes tight & cant be retracted
over the glans):
DDX: physiologic adhesions between the the foreskin & glans.
Rx. : circumcision.
Indications of circumcision:
1. Religious or cultural habits.
2. Phimosis & paraphimosis.
3. Recurrent UTI or balanoposthitis
4. Obstruction of urine flow.
Paraphimosis(tight retracted foreskin that act as a ring):
Tx : 1-Gentle manual squeezing of the glans+ icebags.
2-Circumcision(if the first step fails).
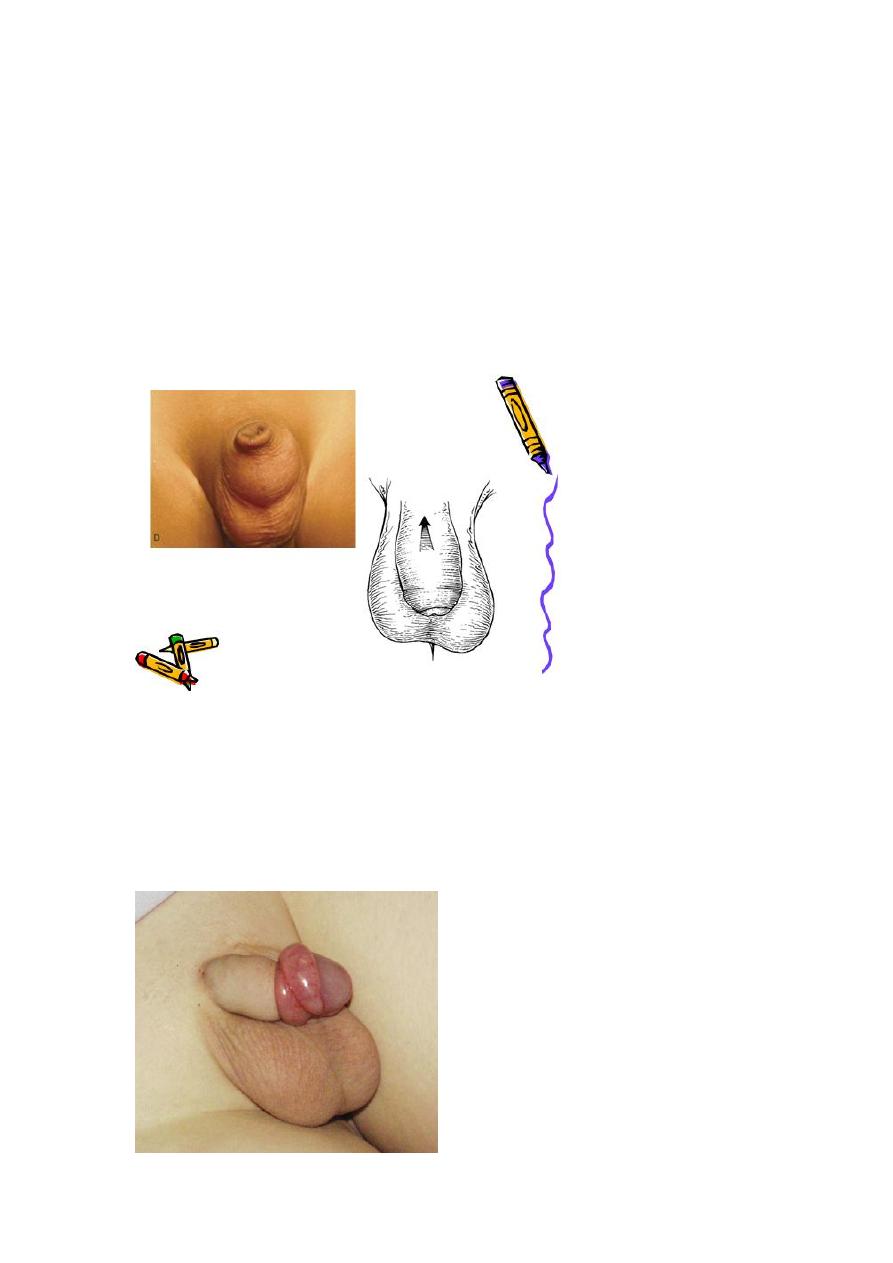
PUJ Obstruction:
Bilateral PUJO
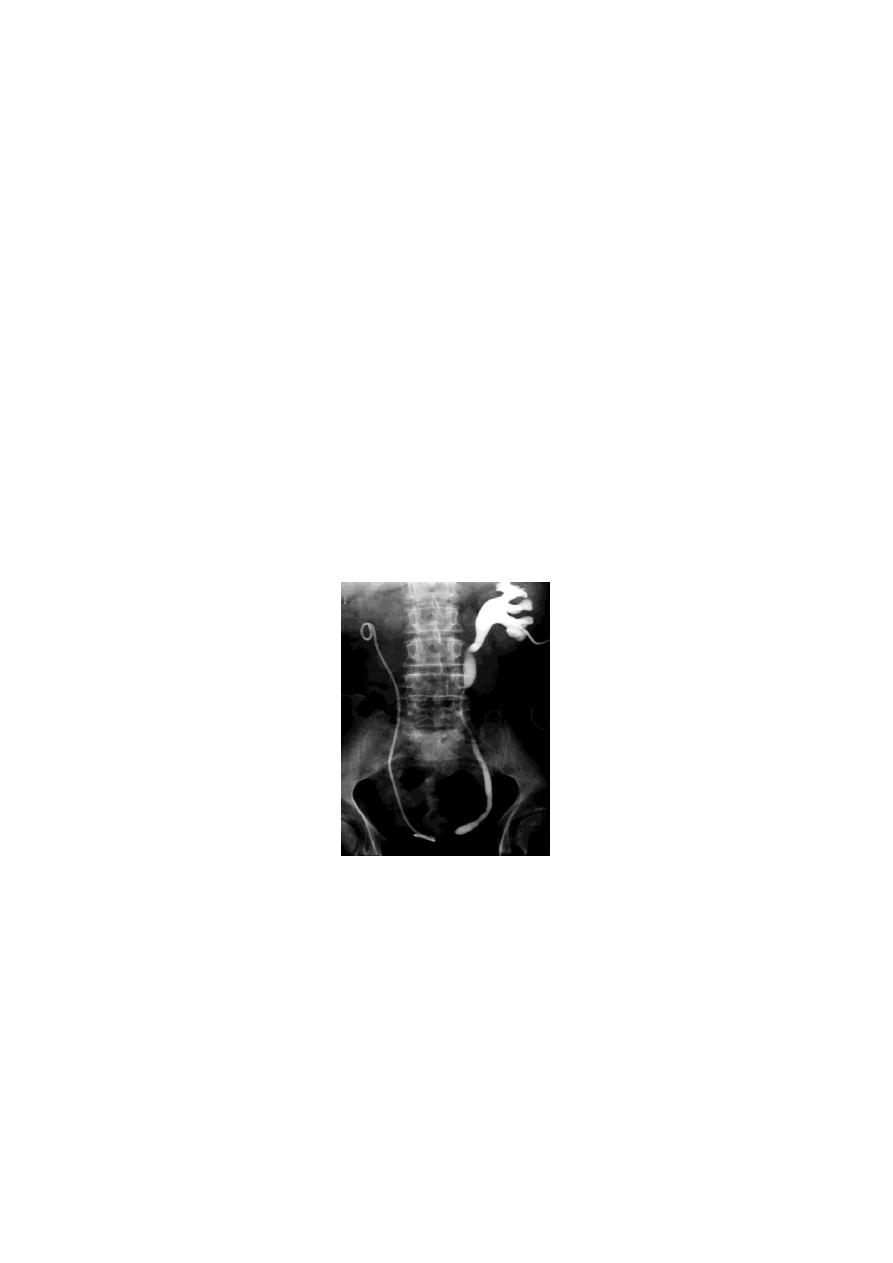
Medical: control infection and pain.
Surgical:
Indications for surgery:
1-progressive hydronephrosis.
2- UTI, and symptomatic patients.
3- Severe hydronephrotic non functioning kidney.
SURGICAL REPAIR including open surgical techniques, laparoscopic, &
endoscopic approaches
Uretrocele:
Treatment
Asymptomatic : no treatment
Cystoscopy with diathermy cauterization of the hole
Nephrectomy in non functioning kidney
In complicated cases, ureteral reimplantation and vesical
reconstruction
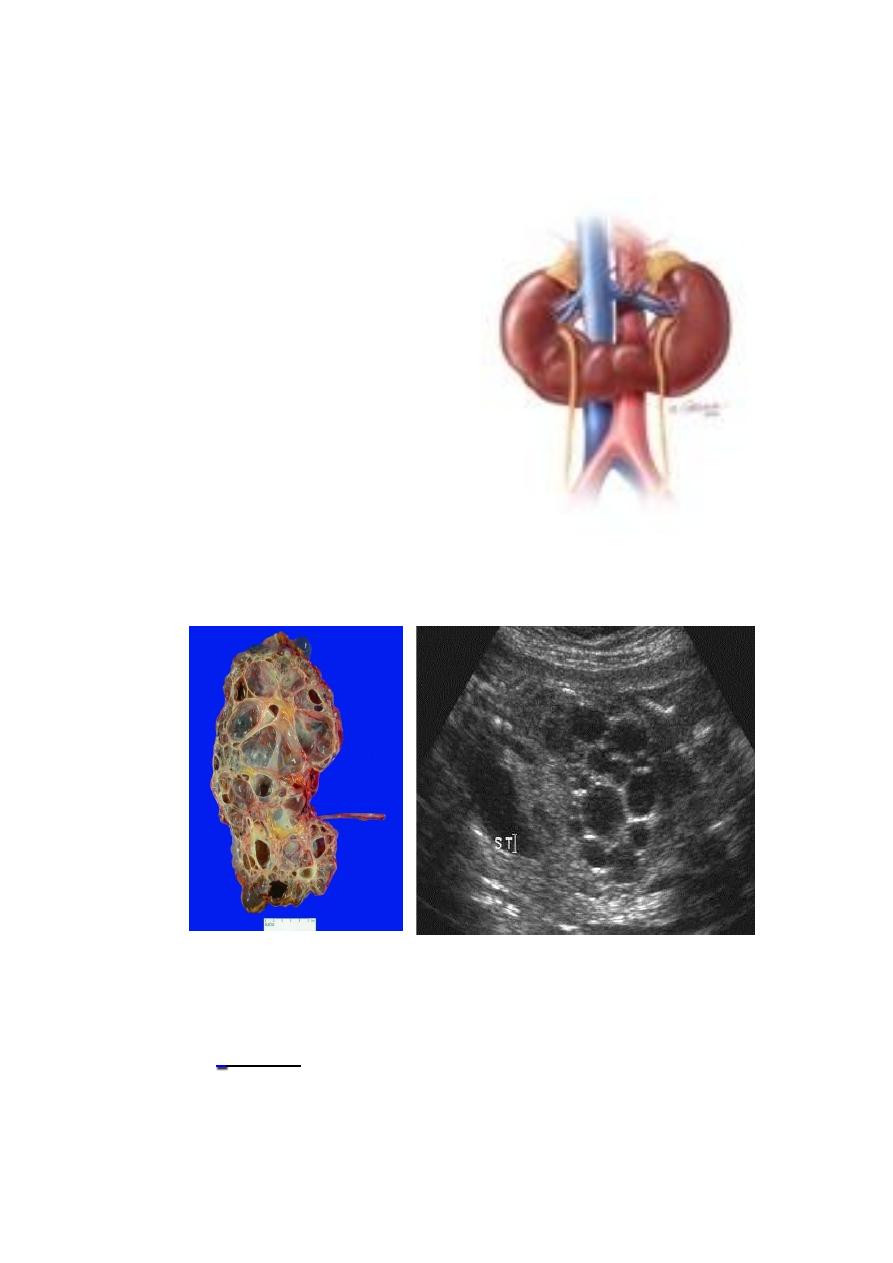
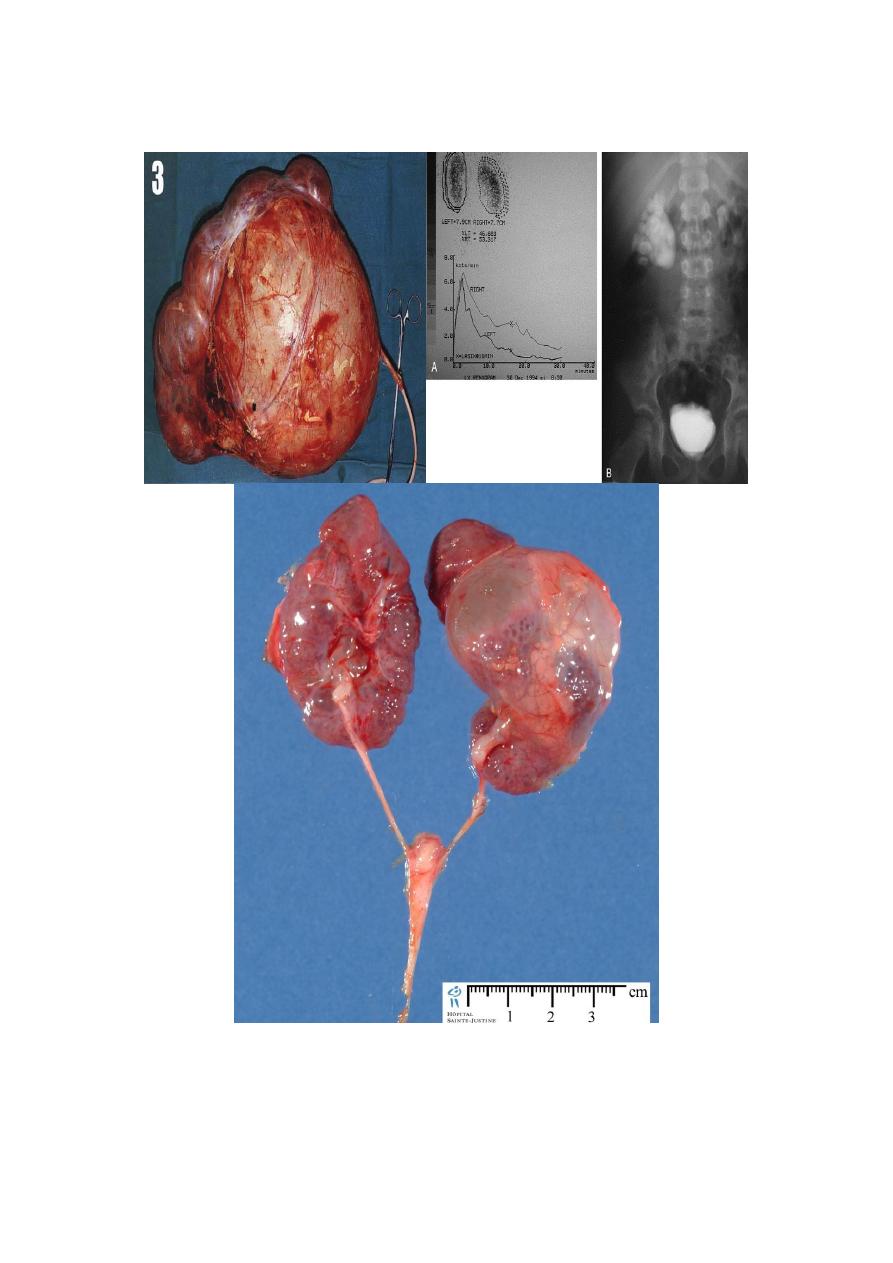
Horseshoe Kidney:
fused lower ploes
low located kidney
malrotated
pelvis lies anteriorly
compllications:
1-HN
2-Infection
3-stone
Adult cystic renal disease:
Other organs involved: liver, lung, pancreas or spleen.
Tx :
Medical: (Expectant)
control infection, hypertension, pain and anemia.
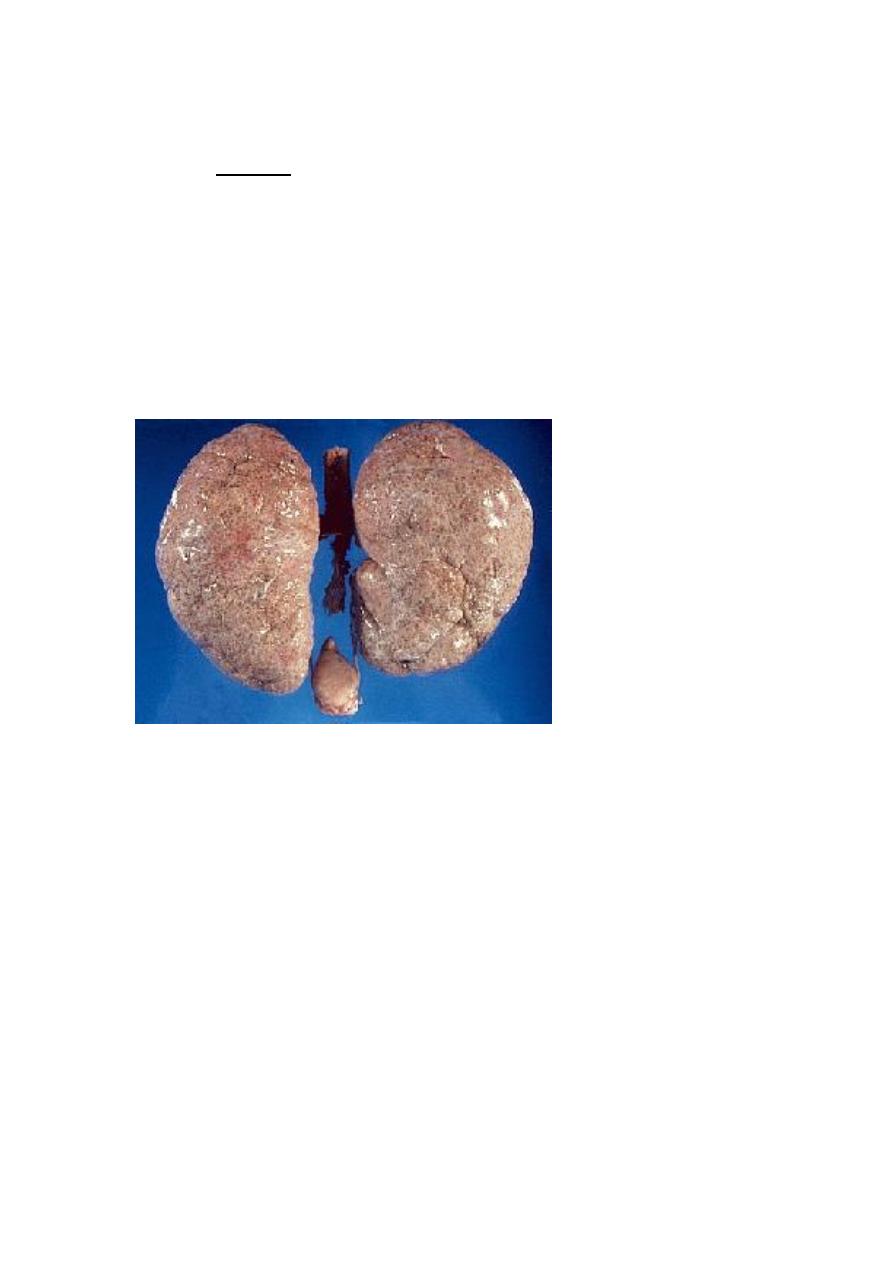
Renal impairment: by low protein diet and dialysis.
Surgical:
Rovsing’s operation
Stone removal.
Renal failure: Renal transplantation.
Infantile polycystic disease of the kidney(incompatible with life).:
