Pediatric surgeryClinical practice
DR. Bassam Al-Abbasiالصور من الدكتورالشرح من كتابة الطلاب
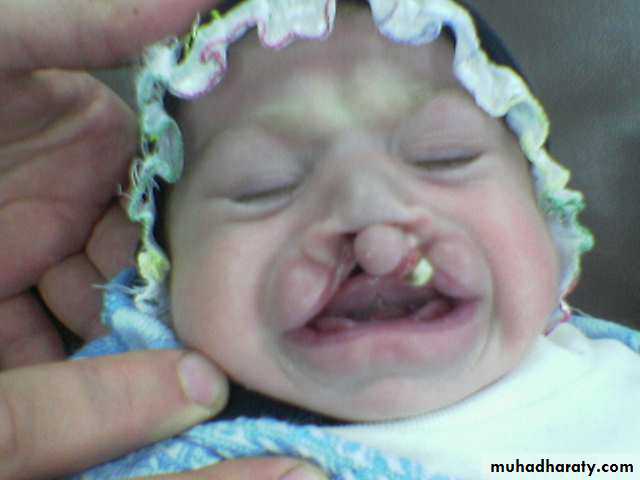
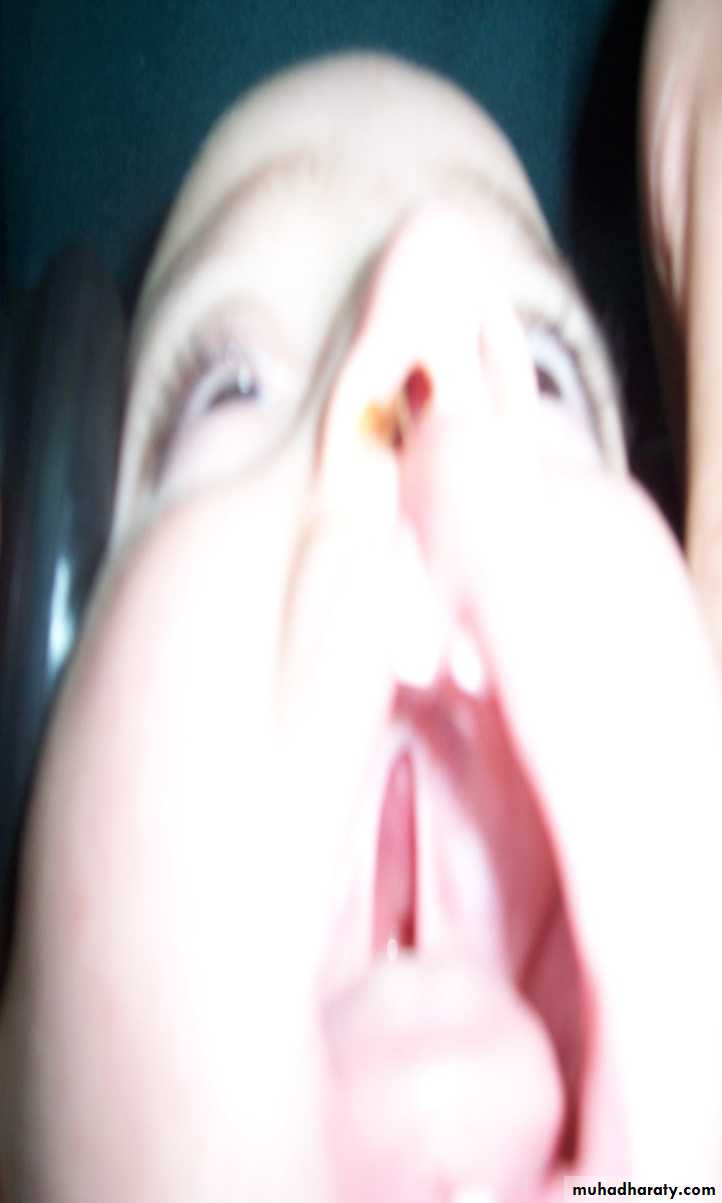
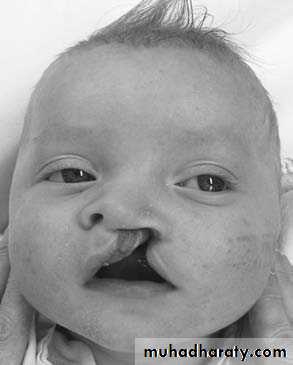
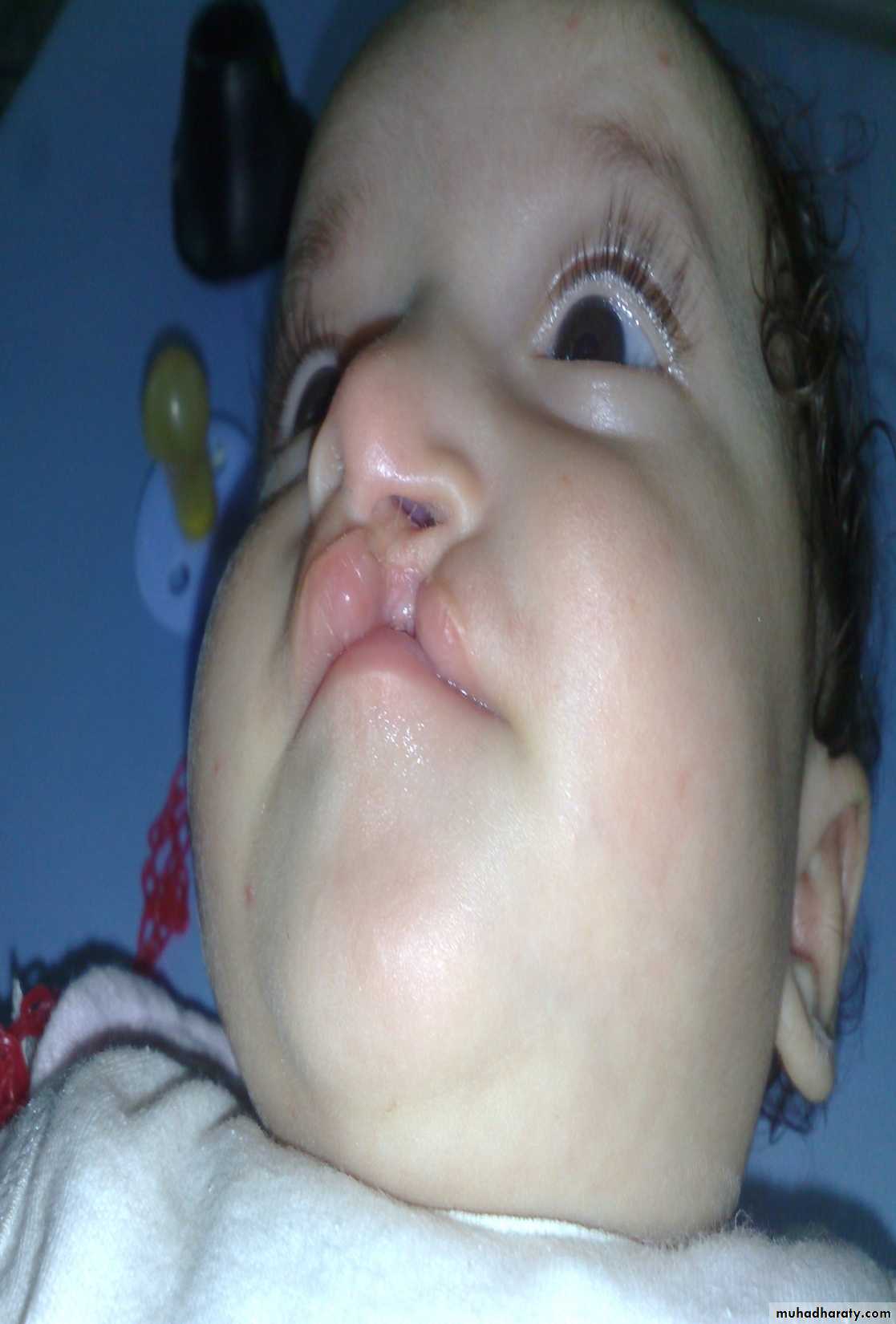
Head and NeckCleft lip and palate
Problems:• Aspiration during feeding
• Nasal speech
• Cosmetic problems
• Affect the hearing (glue ear)
• Lead to recurrent chest infection
Surgery:
• In 6 months to 1 year for cleft palate
• In 3 months for cleft lip
Feeding:
• Use special bottle tit
• In setting position
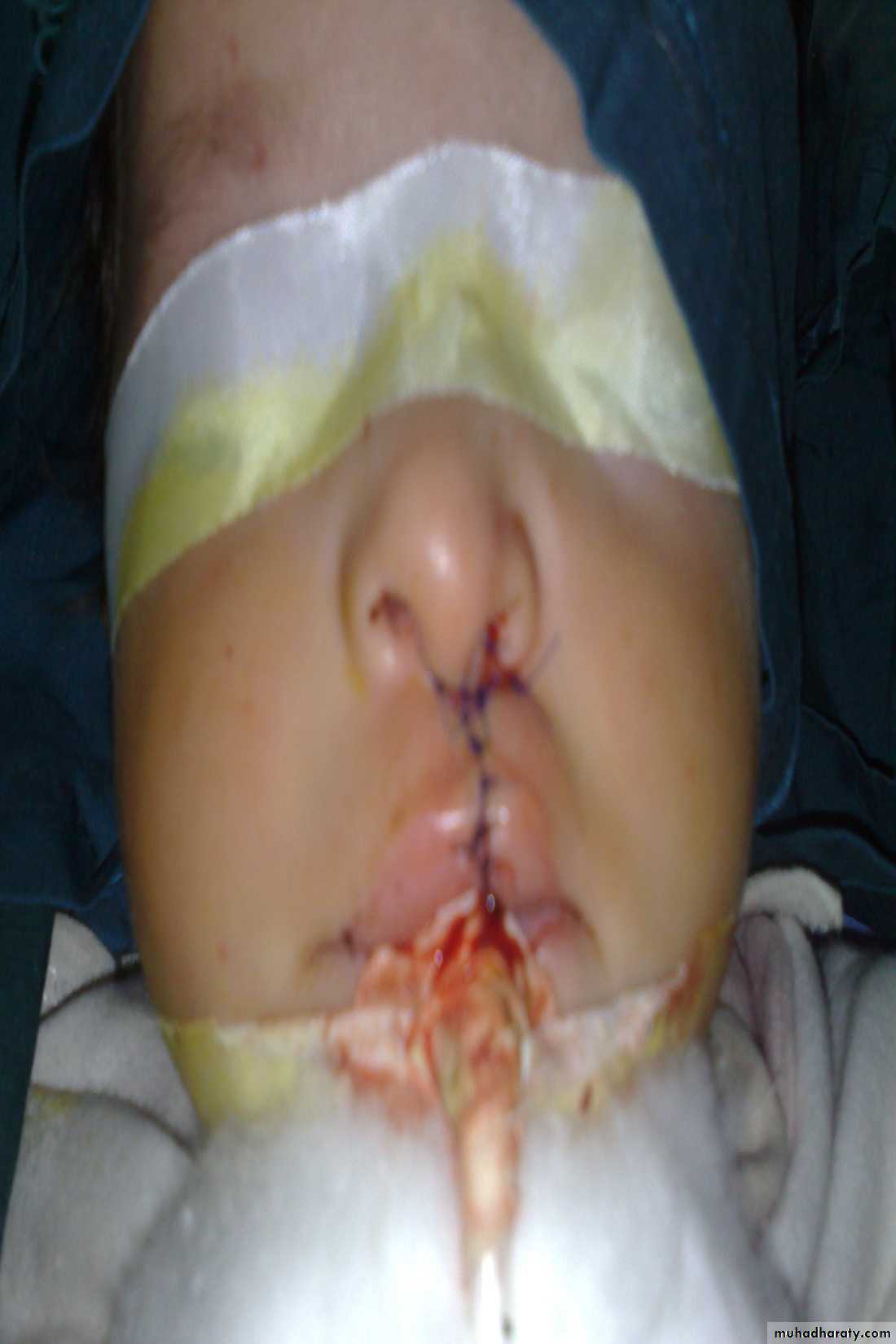
Cleft lip repair (cheiloplasty)
First photo:
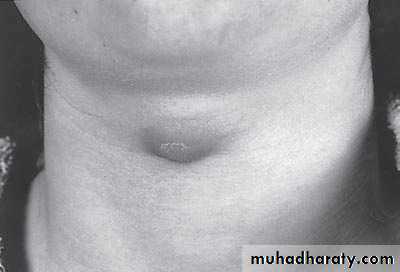
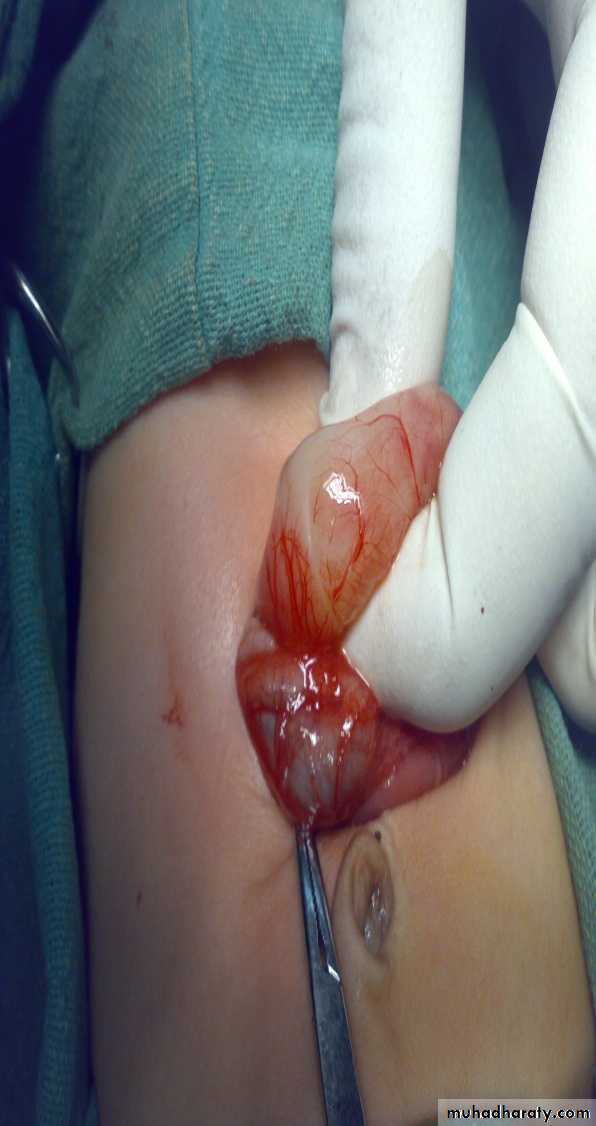
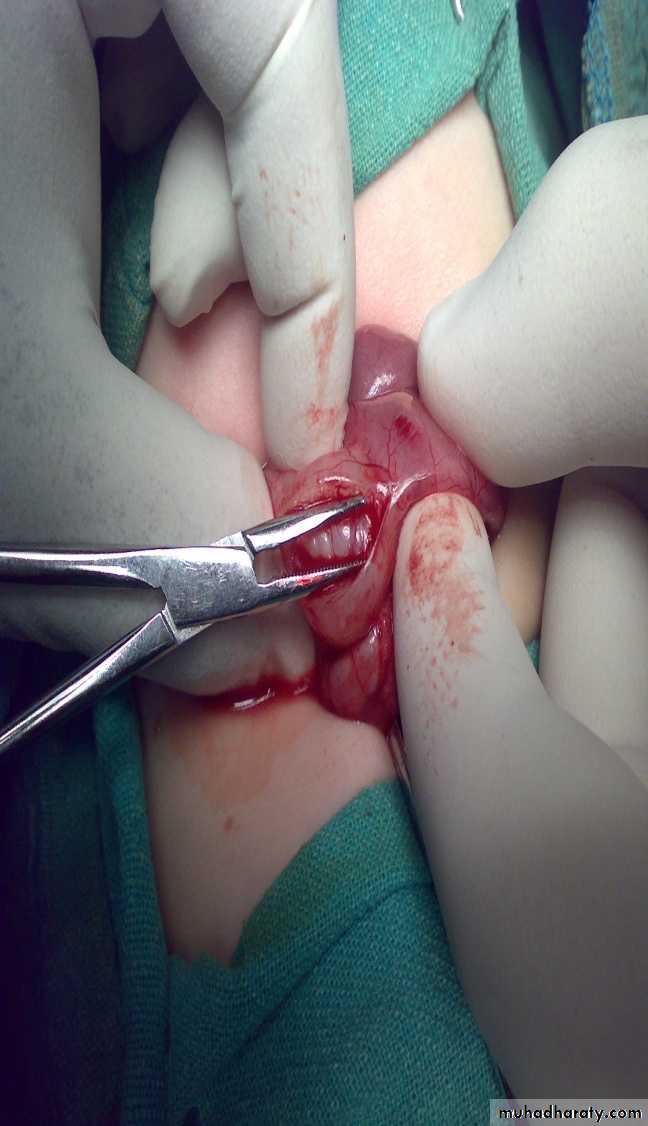
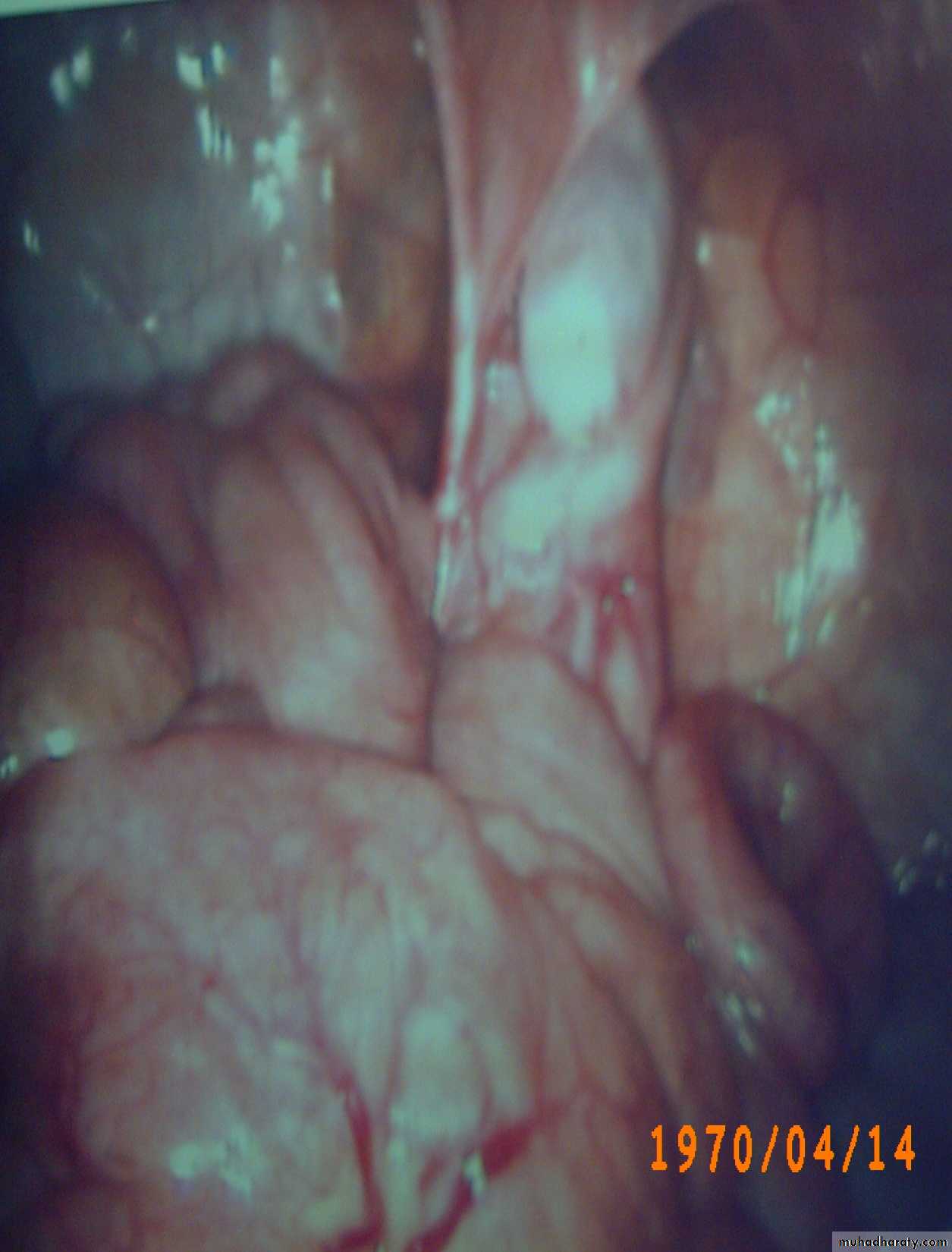
Diagnosis: thyroglossal cystProblems:
• Lead to infection
• Lead to fistula
• Could convert to malignancy
Need surgery remove the fistula tract + remove the hyoid bone to
prevent recurrence
Second photo:
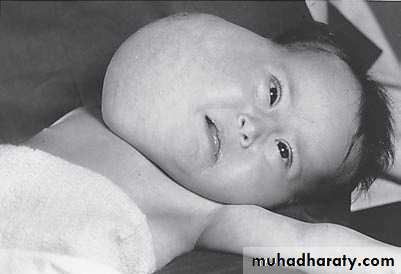
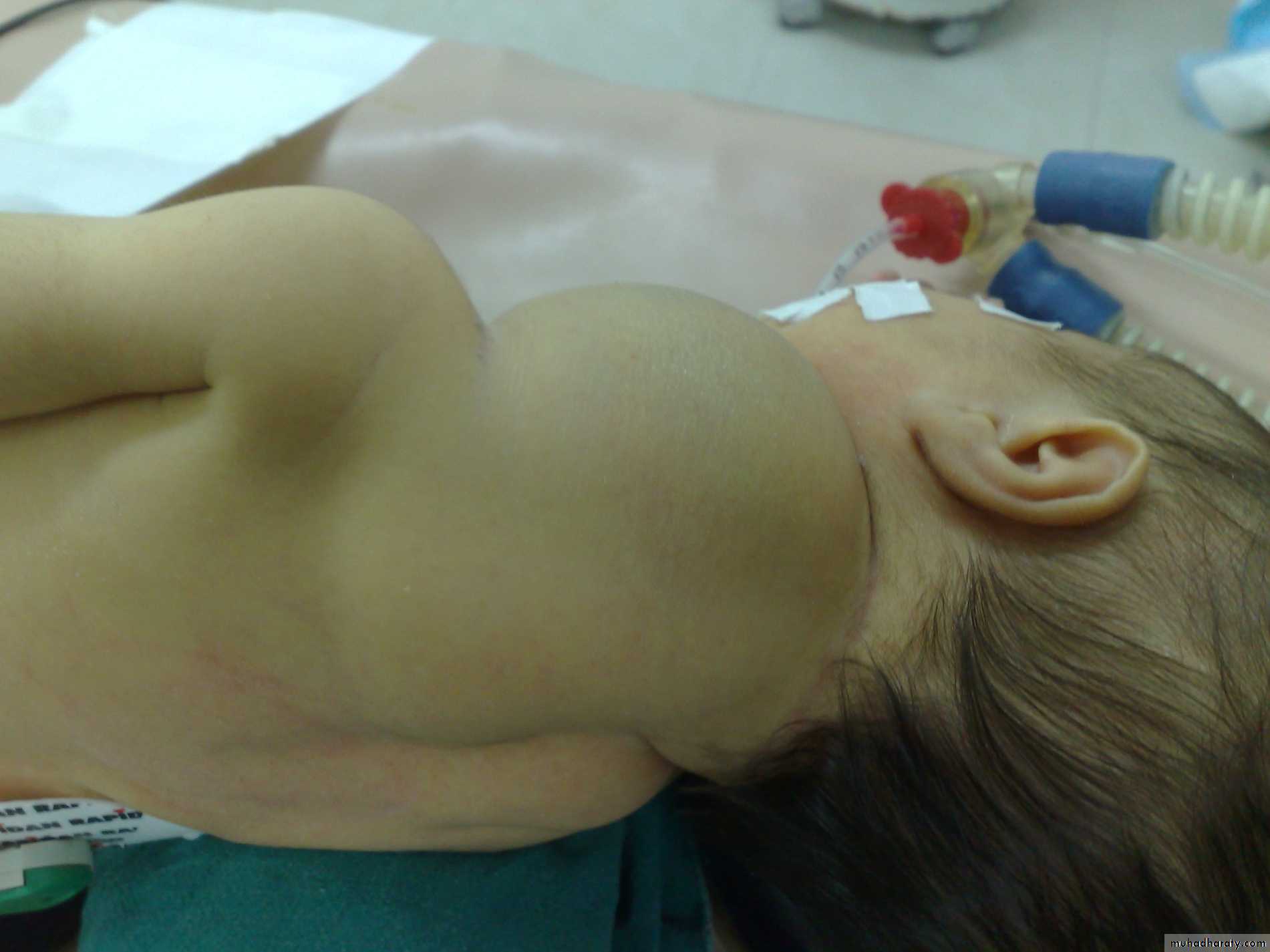
Diagnosis: cystic hygromaNotes:
• It is due to lymphatic obstruction
• Common at the sites of communication between the trunk and the extremities
like cervical region, axilla, groin.
Treatment:
• By surgery: it depends on presence of complications like compression, infection
bleeding (rapid increase in size and become pale and shock)
• During surgery be careful to some nerves like hypoglossal never, spinal
accessory nerve, mandibular branch of facial nerve
Diagnosis:
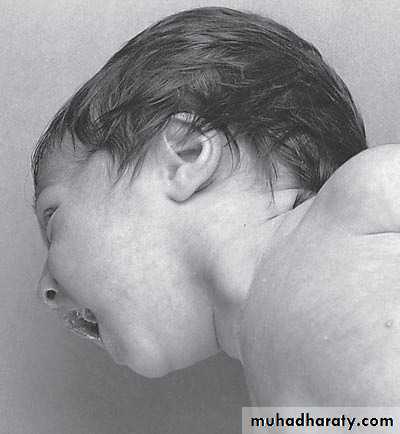
sternocleidomastoid torticollis (first photo)sternocleidomastoid mass (second photo)
Notes:
• Ask about breech presentation and obstructed labor• If not treat the mass it could be converted to torticollis
• Treatment of mass is by physiotherapy by twisting the chin and movement of
ear and massage 90% will disappear if not treated do surgery by
cutting the mass and muscle.
• Treatment of torticollis is by surgery.
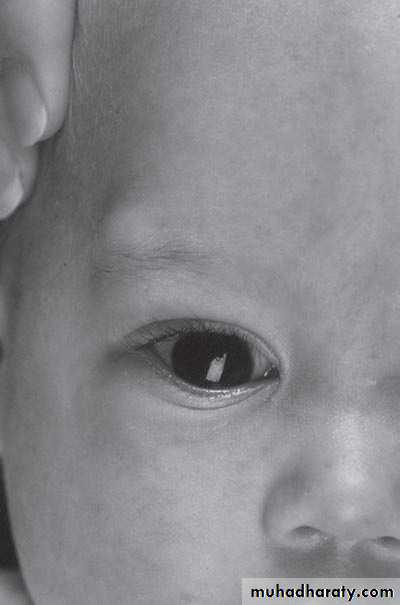
First photo:
Diagnosis: External angular dermoid
Notes:
• Treated by surgery excision and complete remove• Problems infection, trauma, cosmetic
Second photo:
Diagnosis: remnant of second branchial arch branchial cyst or fistula
Site: anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle between tonsil
and lower two third of sternocleidomastoid muscleProblems: infection – malignancy
Treatment: surgery (excision)The Umbilicus
First photo:
Diagnosis: umbilical herniaTreatment: could resolve spontaneously or by surgery
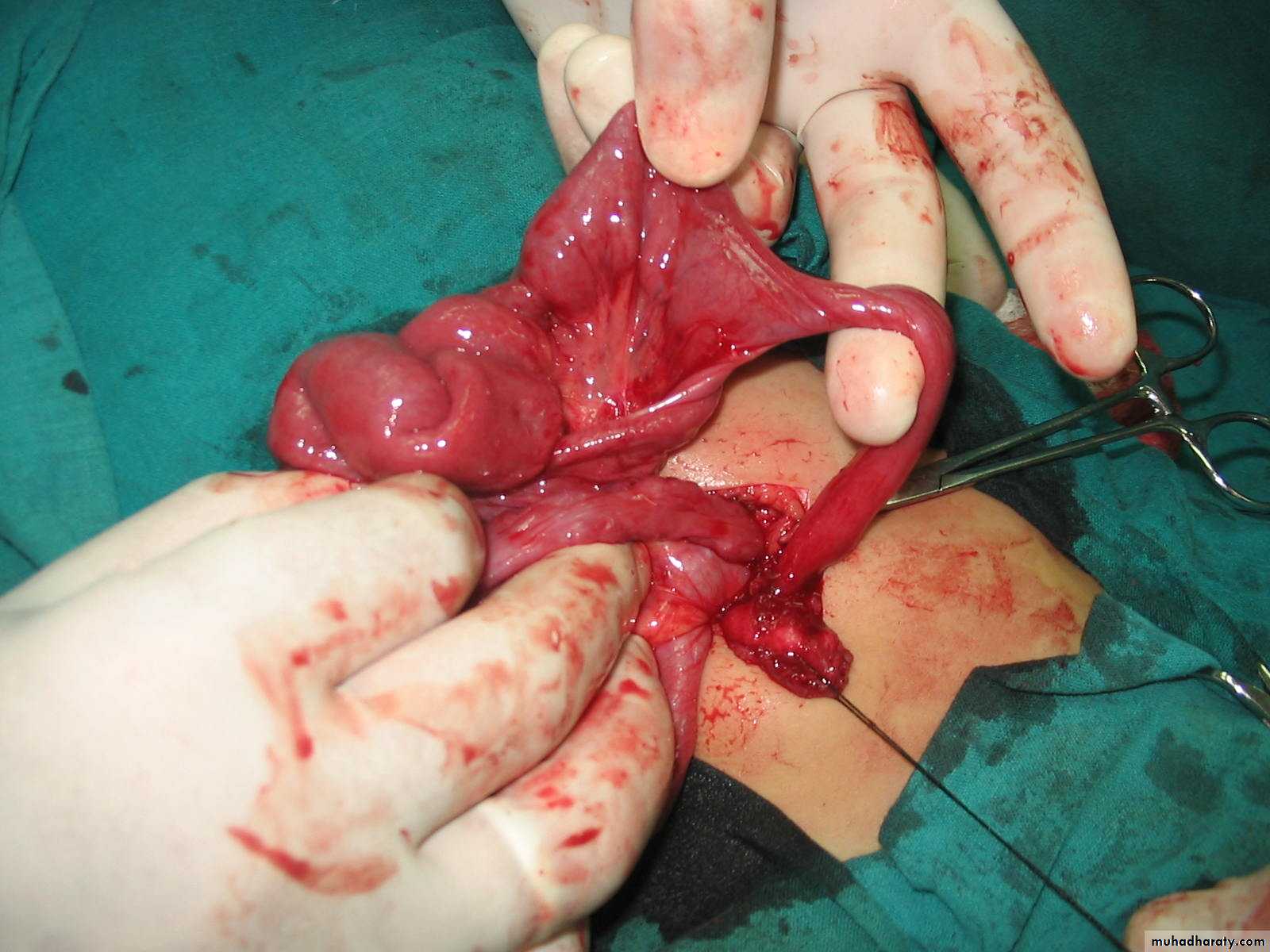
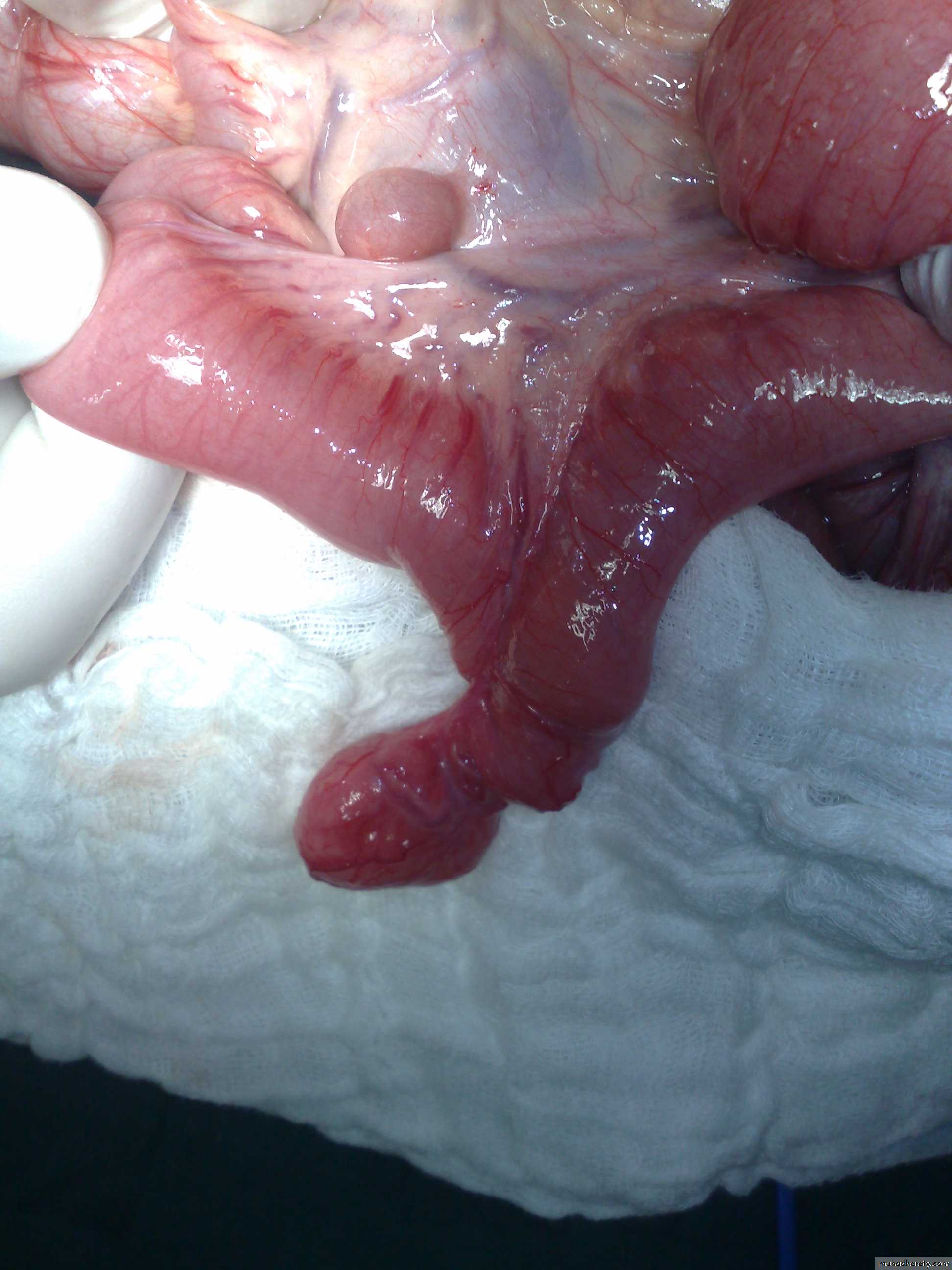
Second photo:Omphalo-mesenteric duct connection between umbilicus and bowel
Diagnosis: Michaels diverticulum
Role of 2:• 2% of population.
• 2 type of mucosa(ectopic gastric mucosa).
• 2 feet from iliocecal valve.
• 2 inches in length.
Presentation:
• Bleeding per rectum (painless – bright red – profuse)
• Infection (lead to abdominal pain)
• Complication intestinal obstruction, volvulus, intussusception
• Incidental finding
Diagnosis:
• Use isotope (bind to gastric tissue (parietal cell) within the Michaels)• Laparoscope (diagnostic and therapeutic)
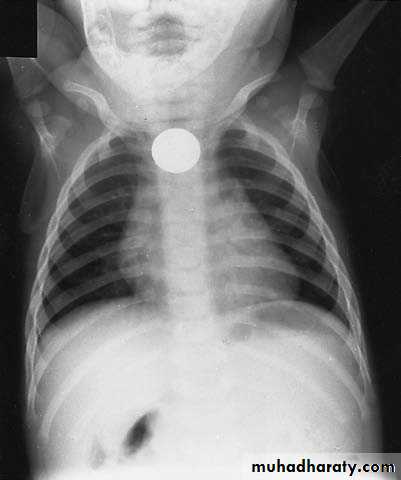
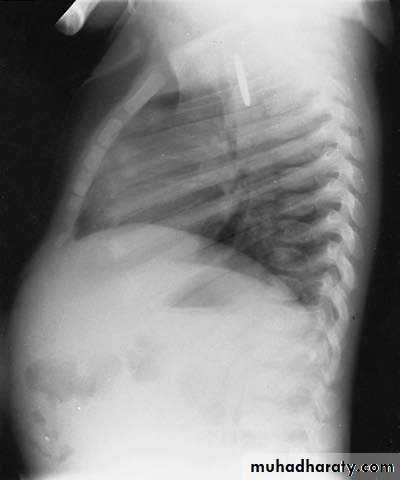
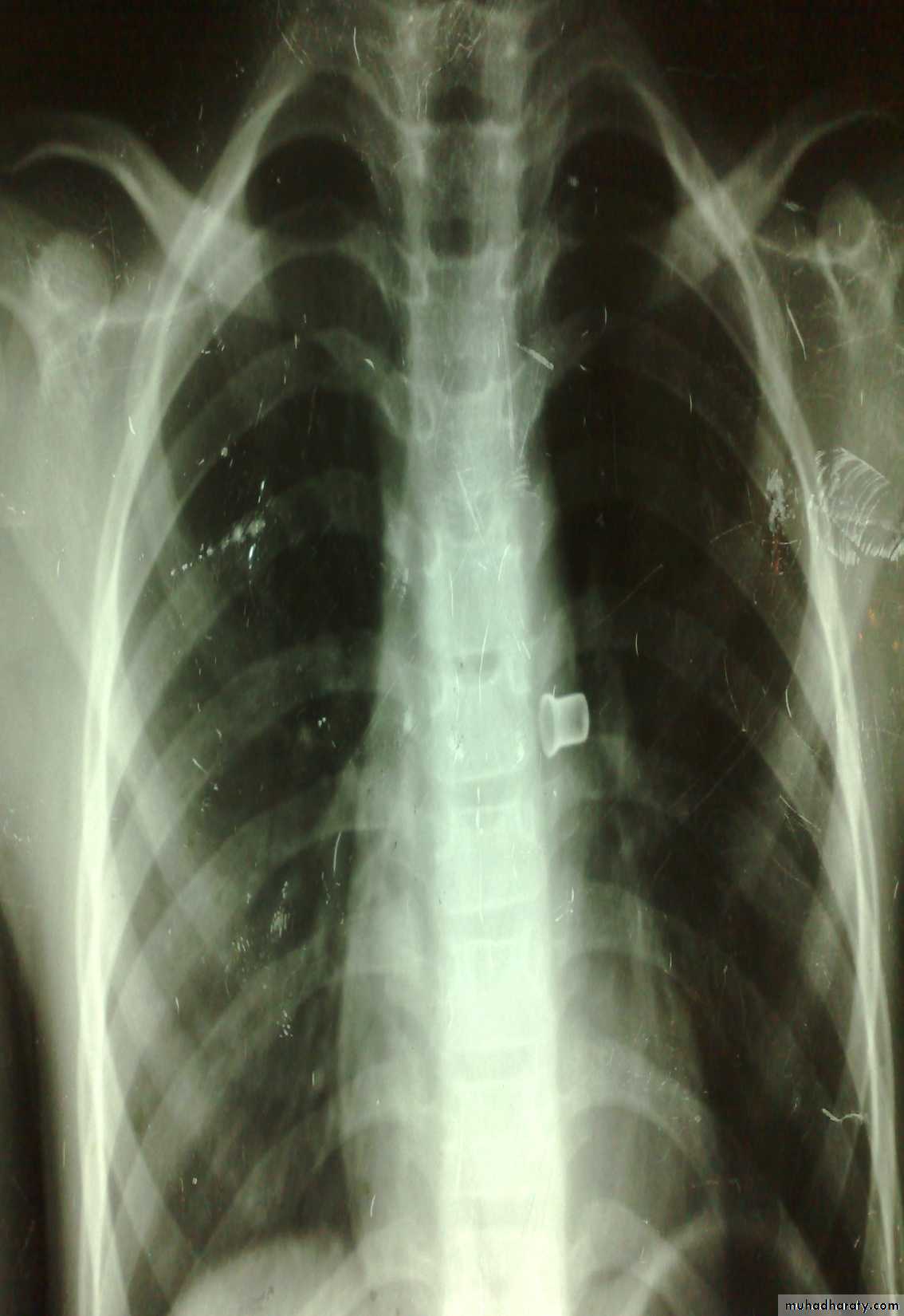
Vomiting in the First Months of Life
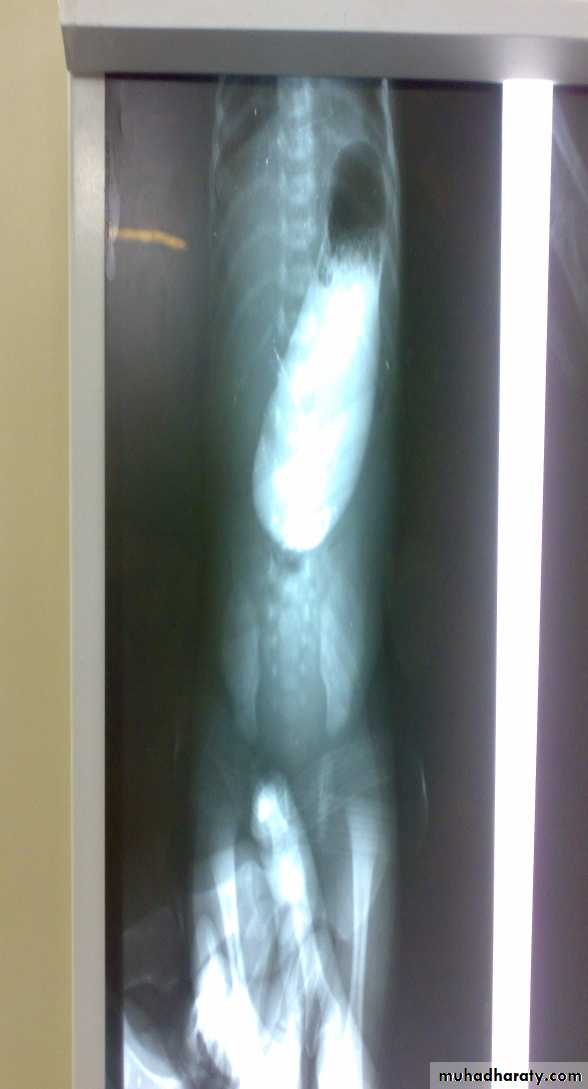
Diagnosis: pyloric stenosis
Presentation:• Projectile vomiting (not present in first two weeks)
• Olive mass in the abdomen
• Positive prestalsis
• FTT
Diagnosis:
• Clinically
• Ultrasound
• Ba-meal dilated stomach – failure to pass to intestine – string sign
Treatment: surgery pyloromyotomy (rami stick surgery)
Diagnosis: achalasia cardia
Presentation:• Hailtosis
• Vomiting (not projectile)
• Wheezing
• Chest infection
Ba-swallow dilatation of esophagus with narrowing of lower part.
Treatment cardiomyotomy
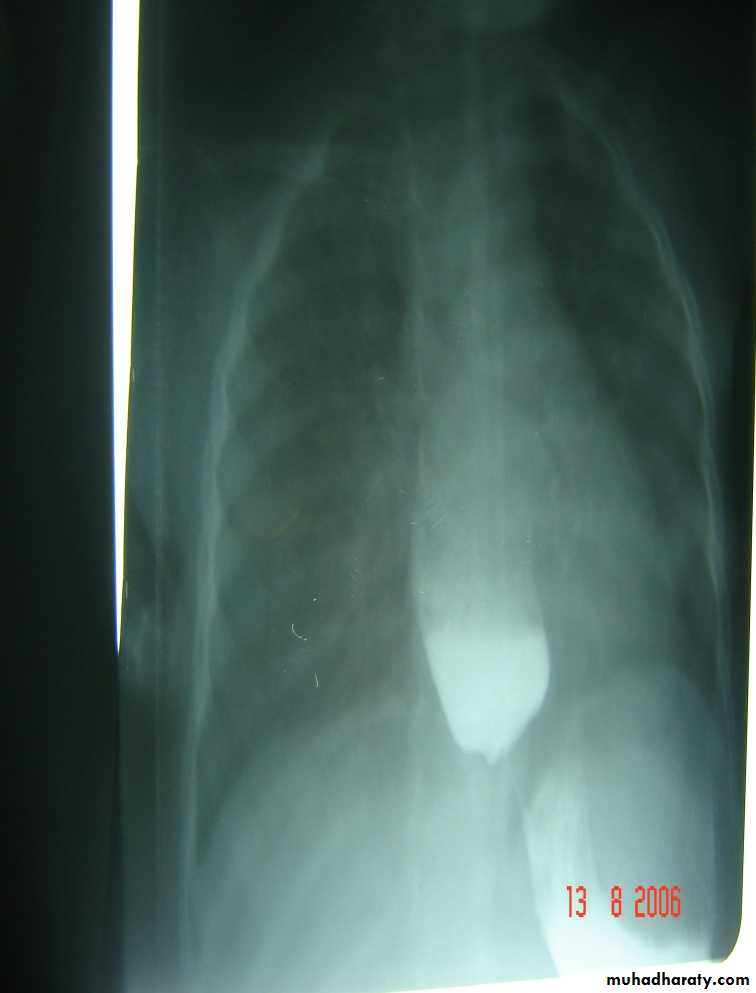
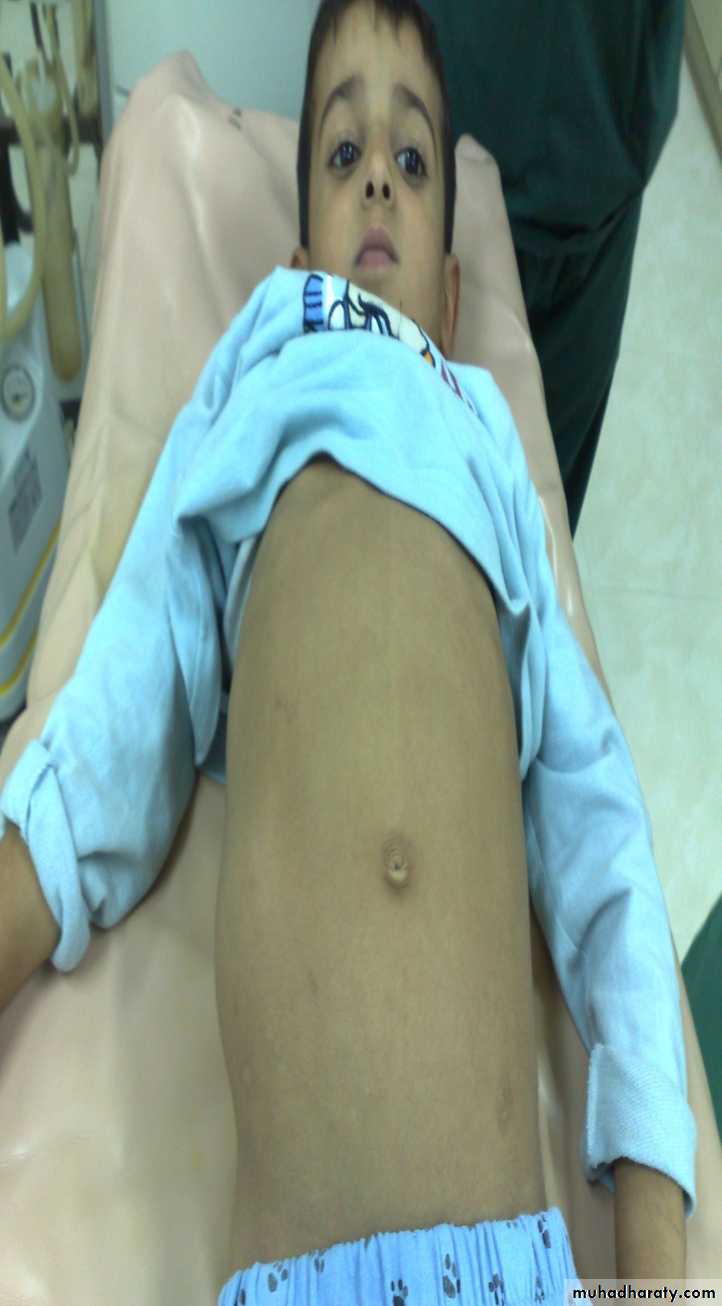
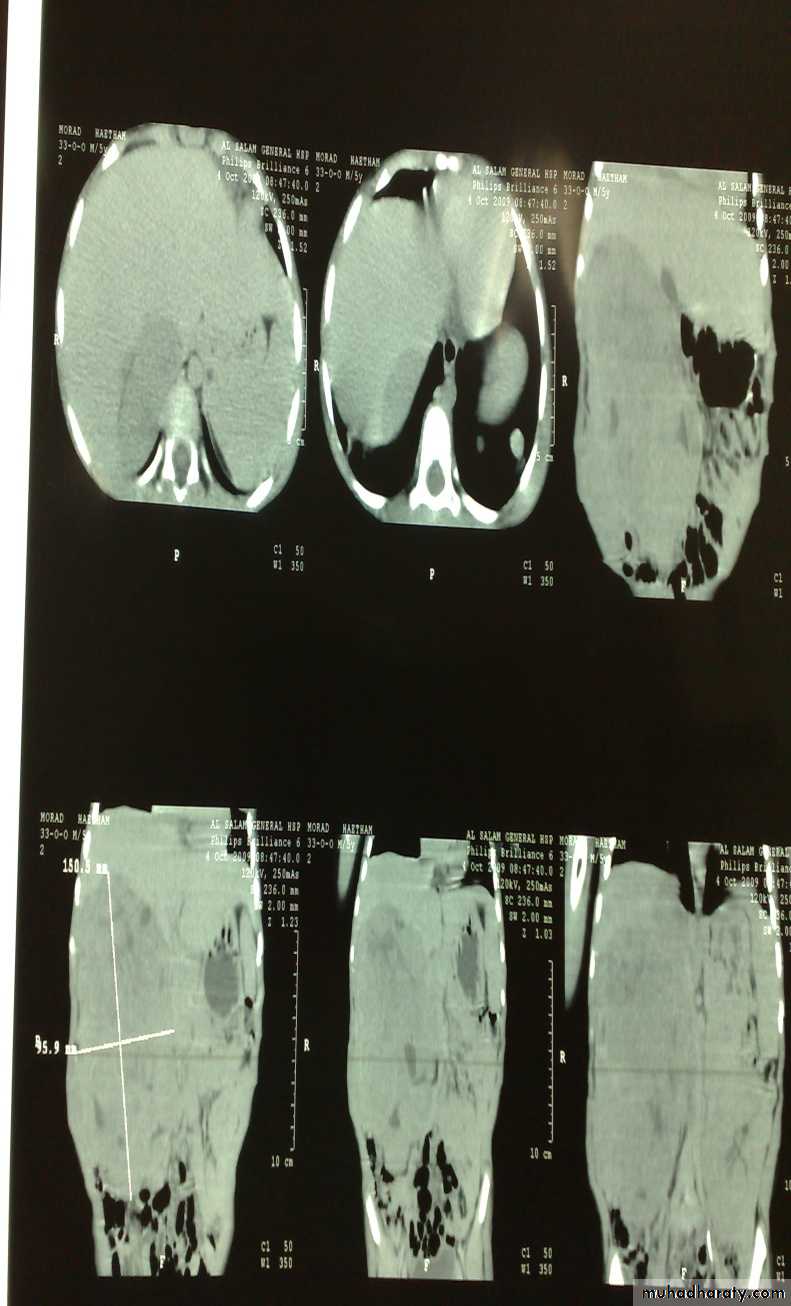
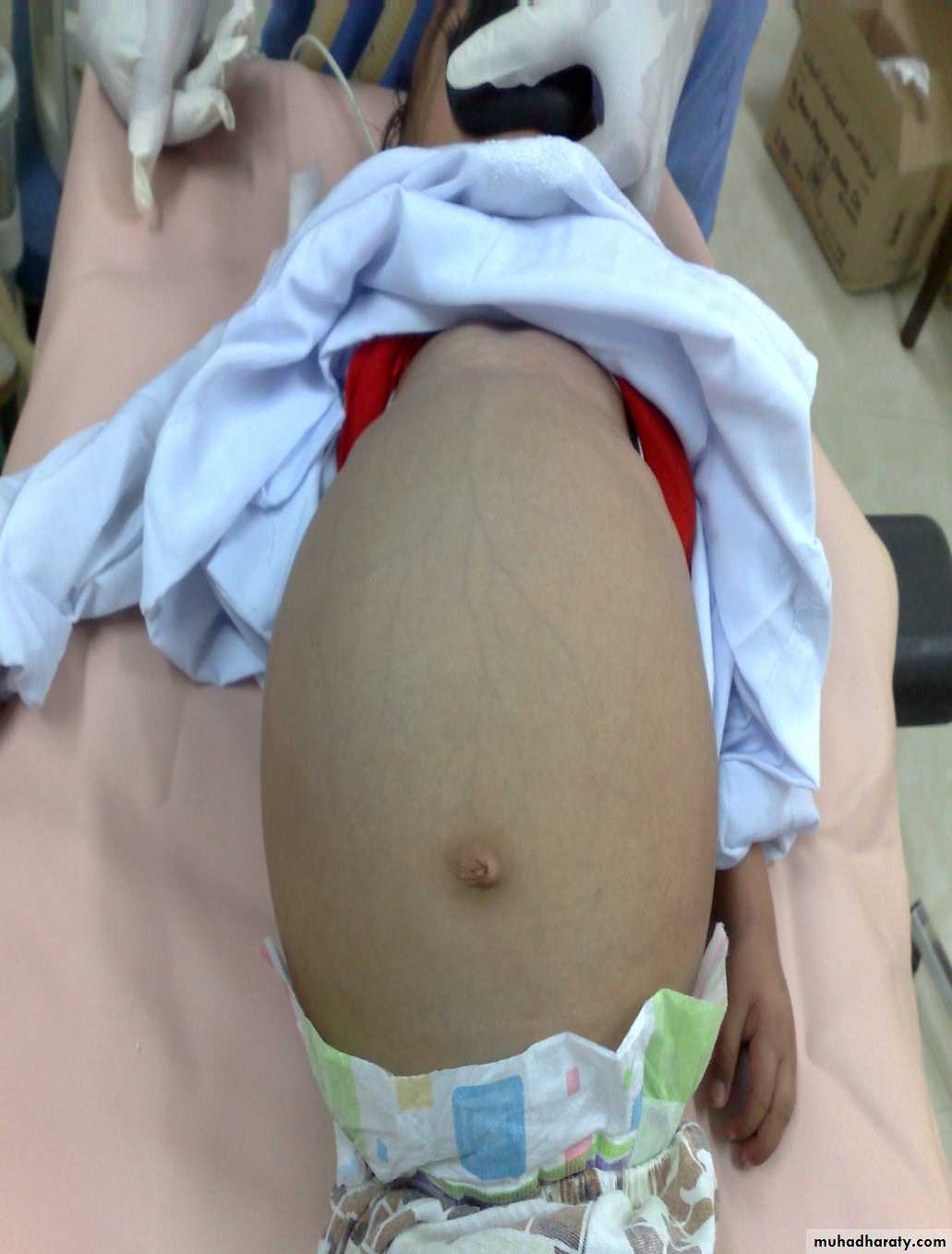
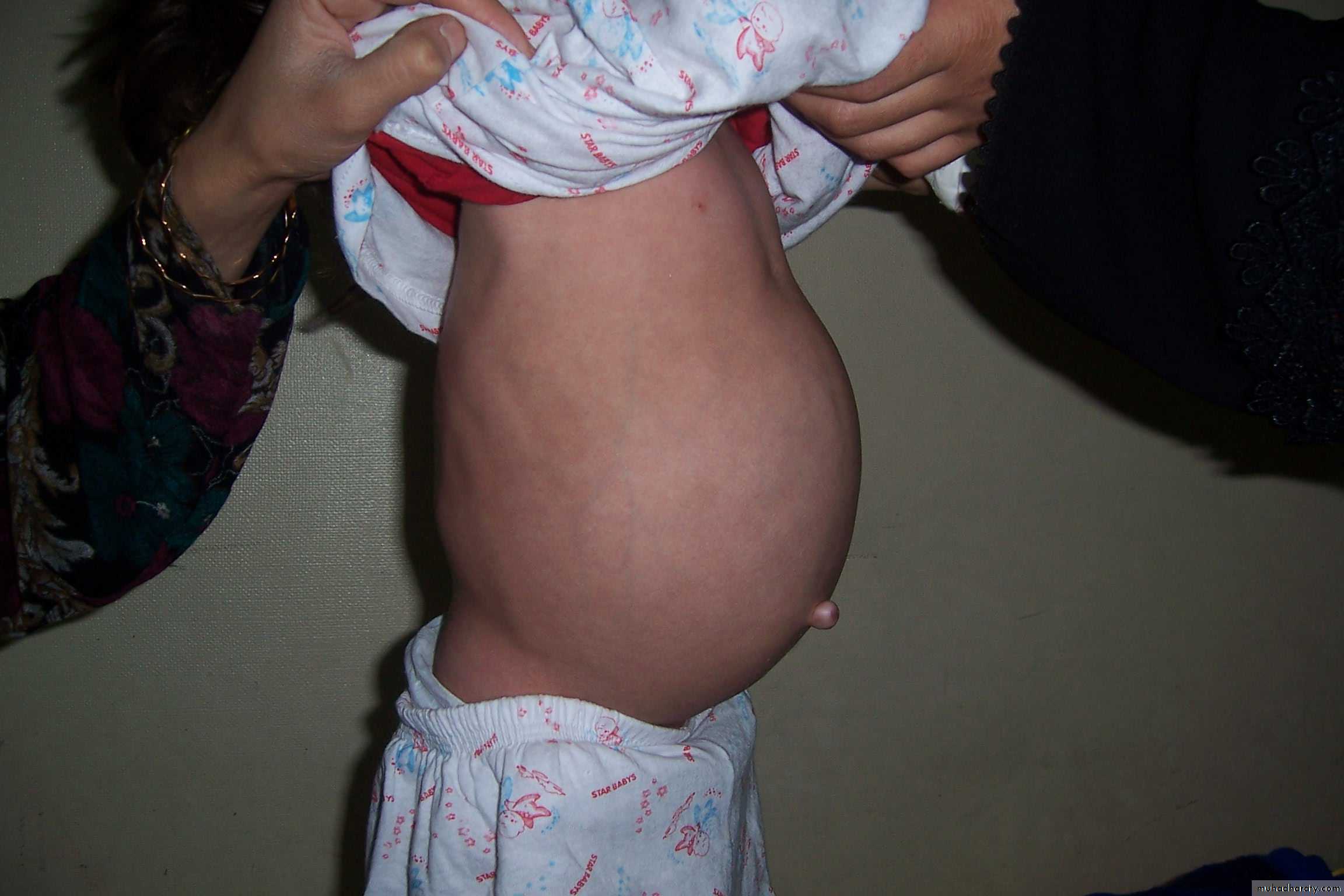
The Child with an Abdominal Mass5 years child, presented with mass in the flank.
DDx of mass in the flank:1- Wilms tumor
2- Neuroblastoma
3- Neglected PUJ obstruction
Presentation:
1- Mass2- hematuria
3- hypertension
Treatment by surgery remove the kidney + chemotherapy
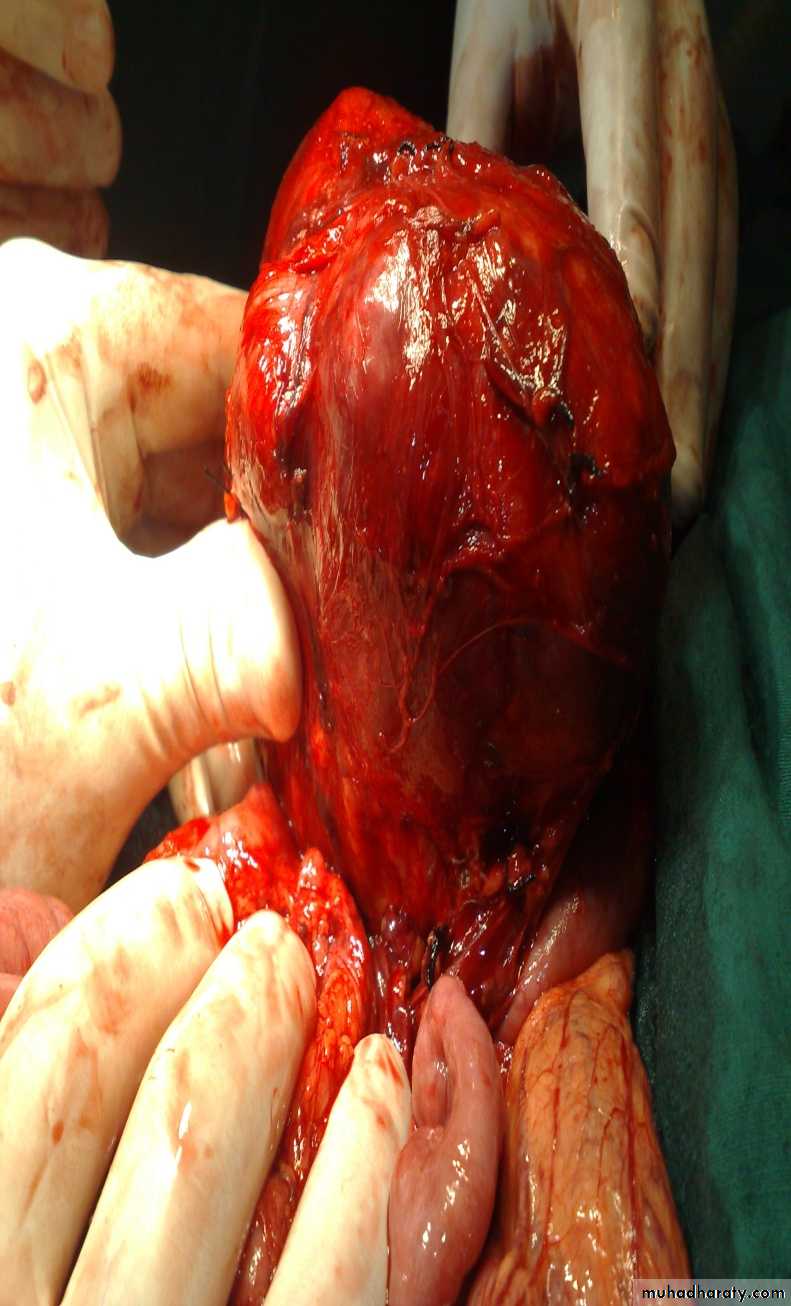
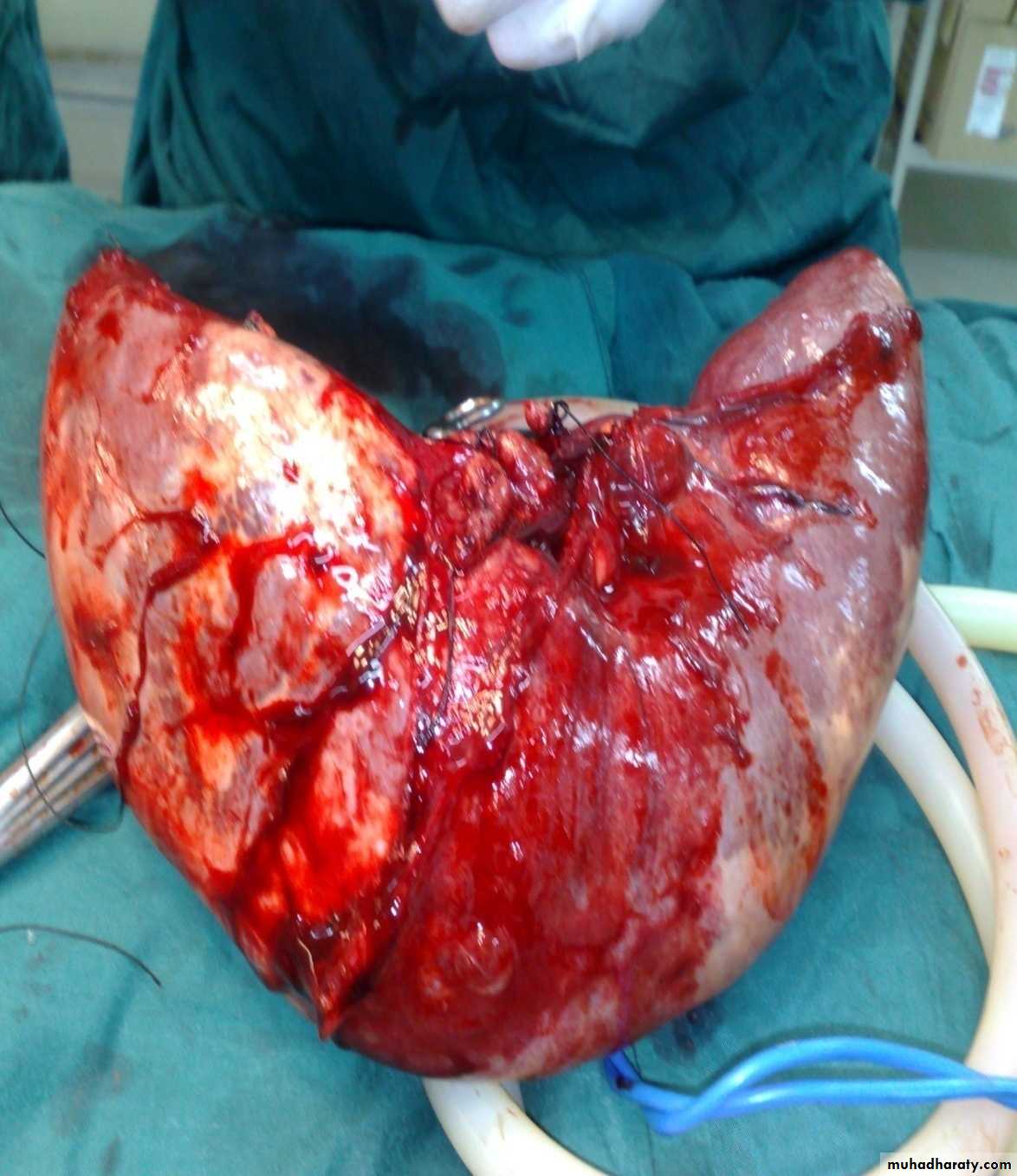
Neuroblastoma in the adrenal gland
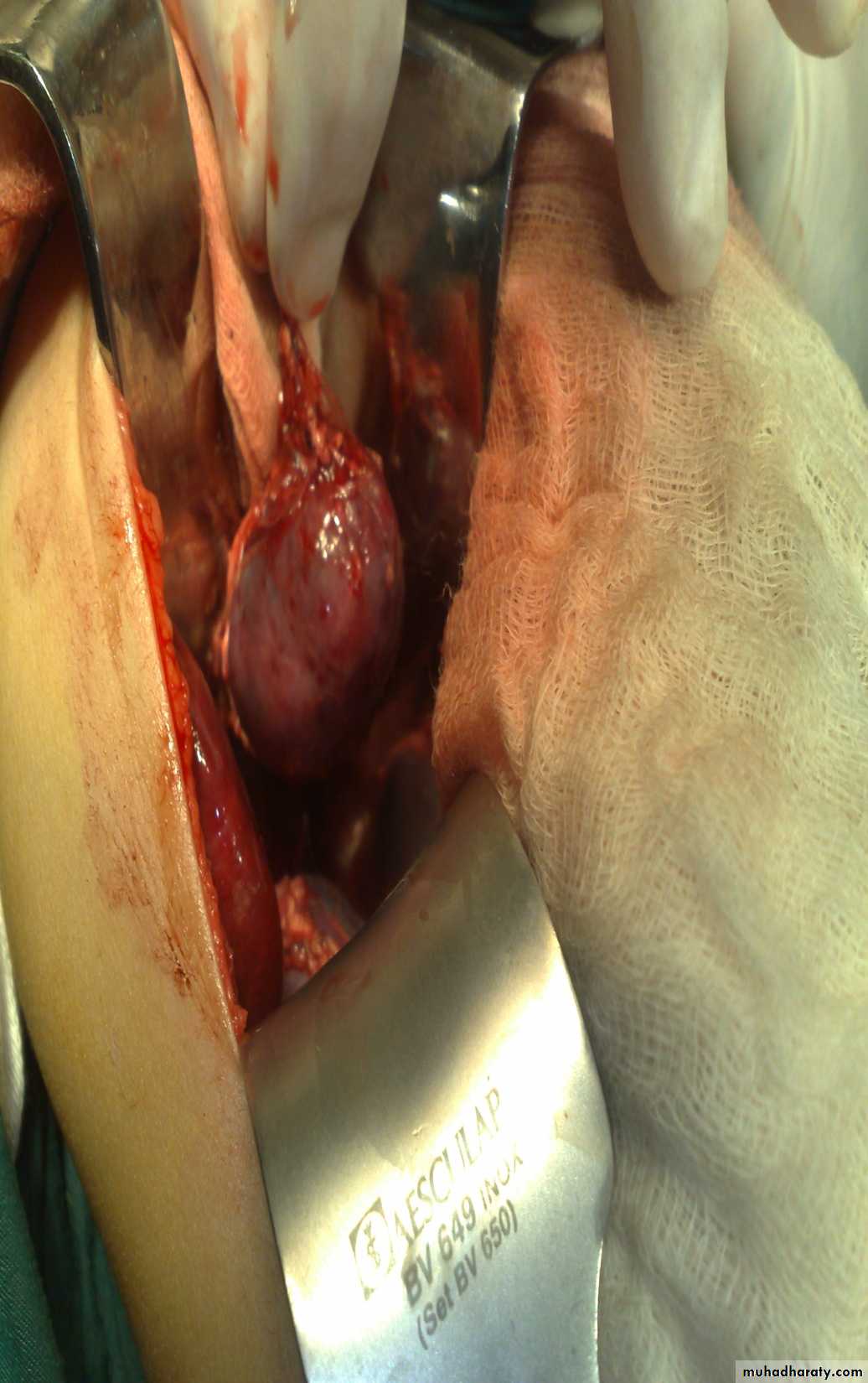
Diagnosis: non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Presentation:1- Mass
2- Intussusception
Investigation: FNA
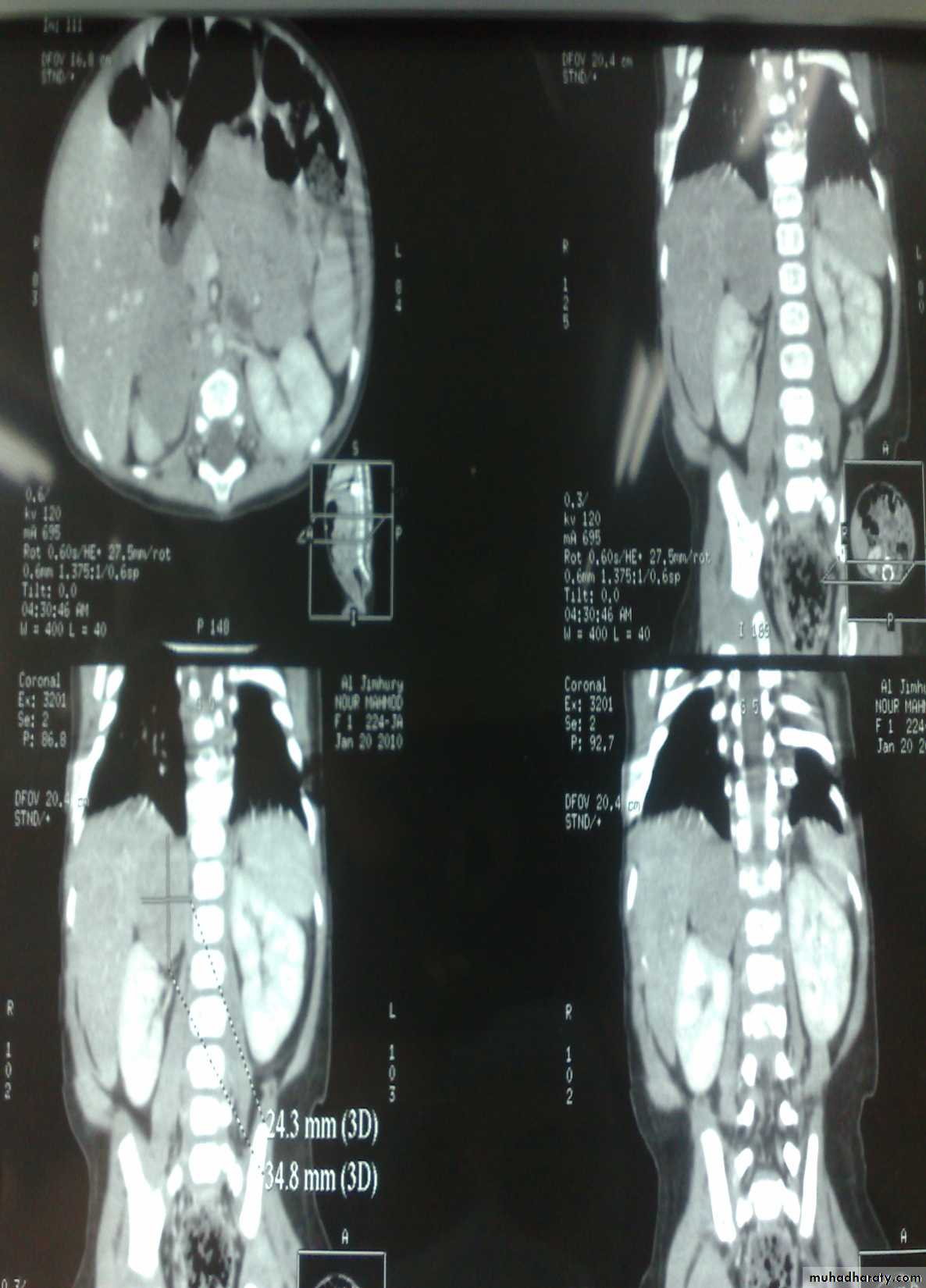
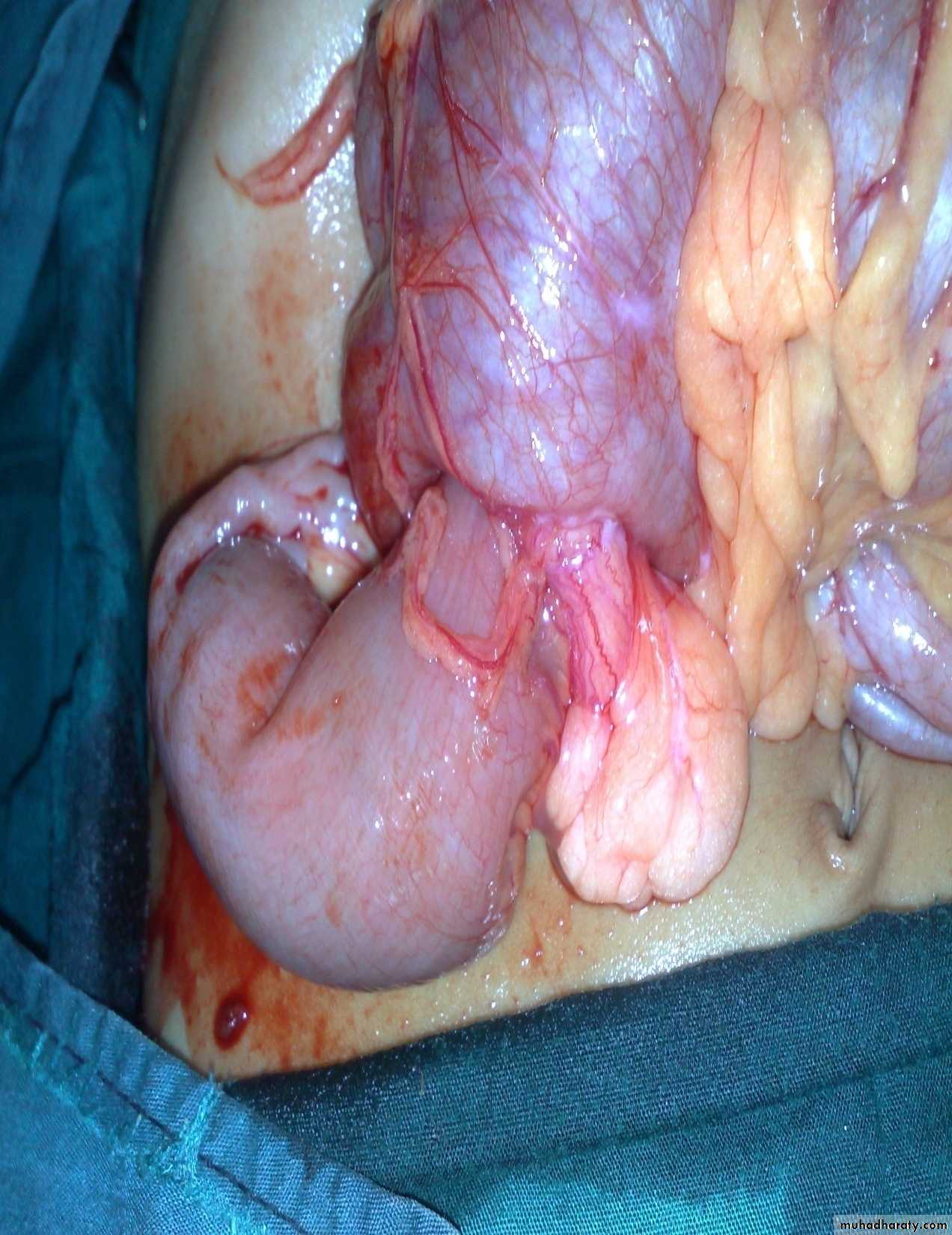
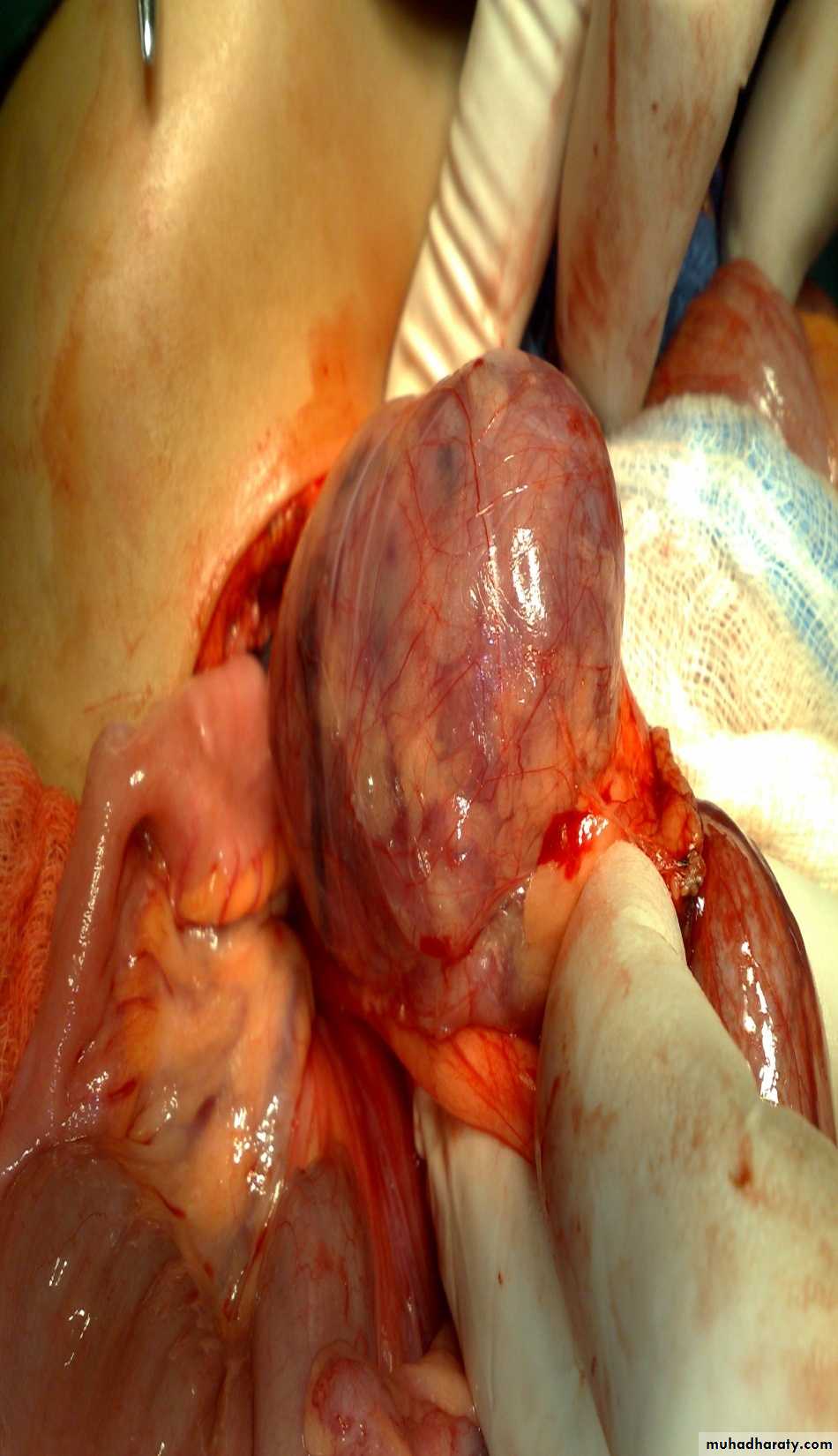
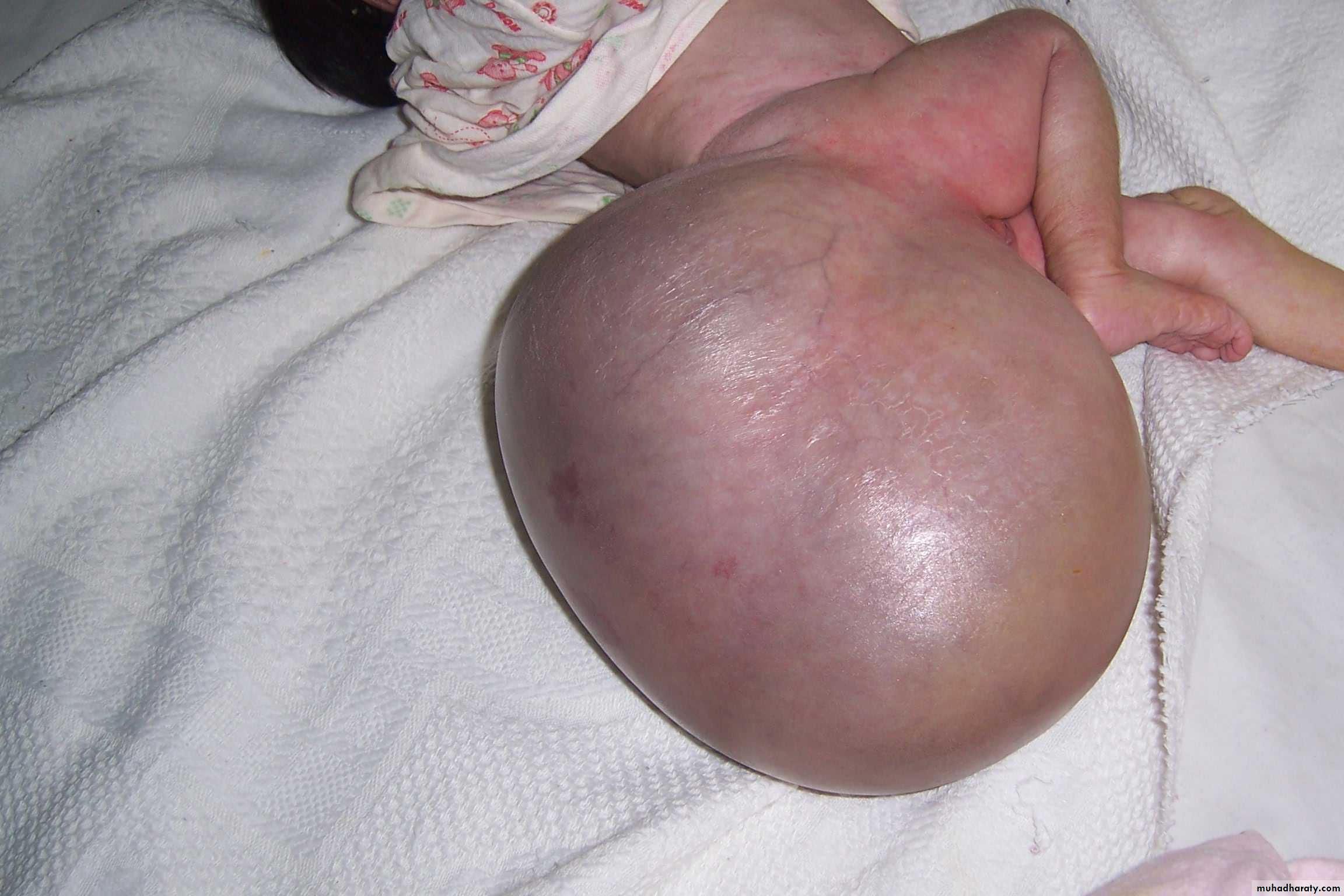
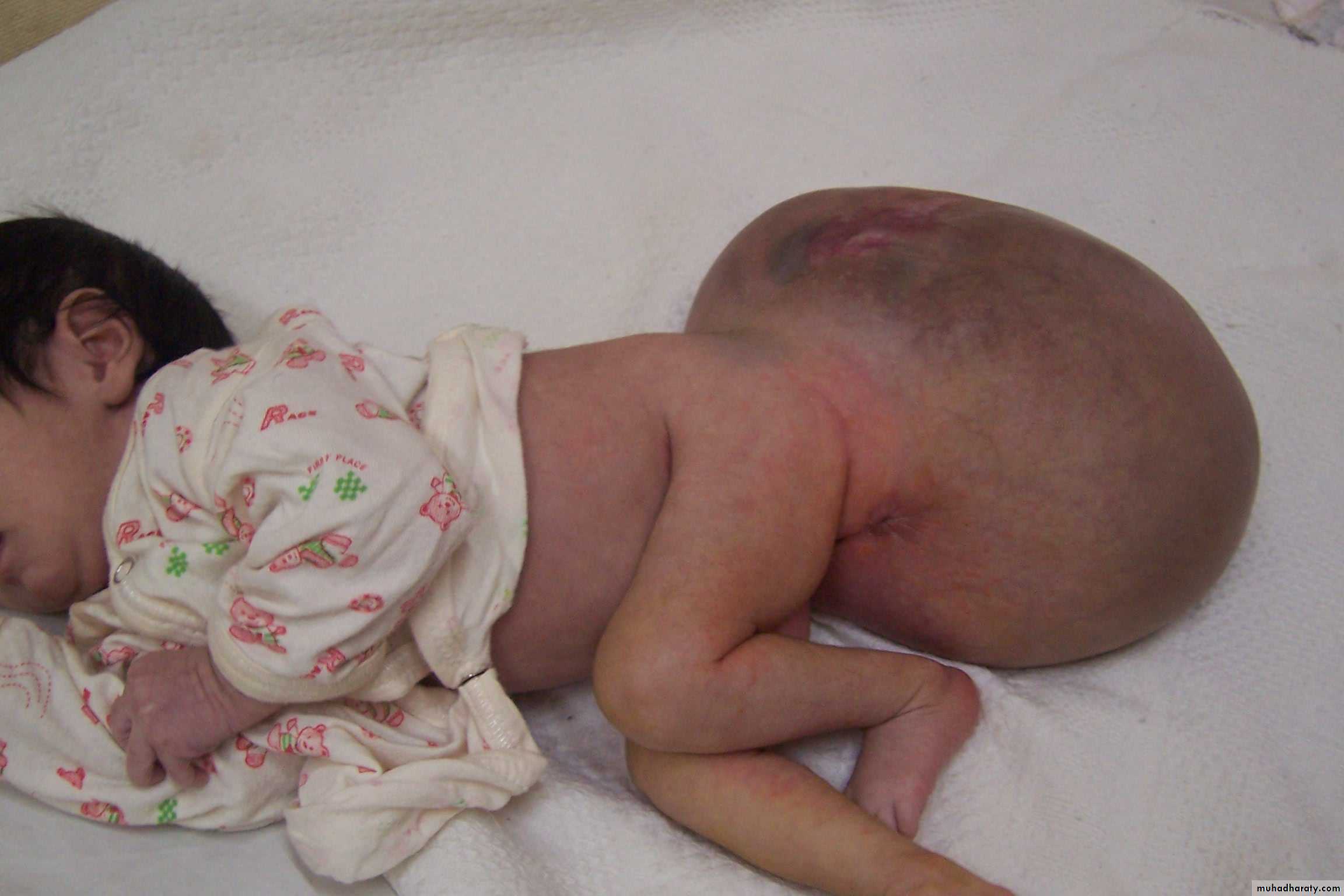
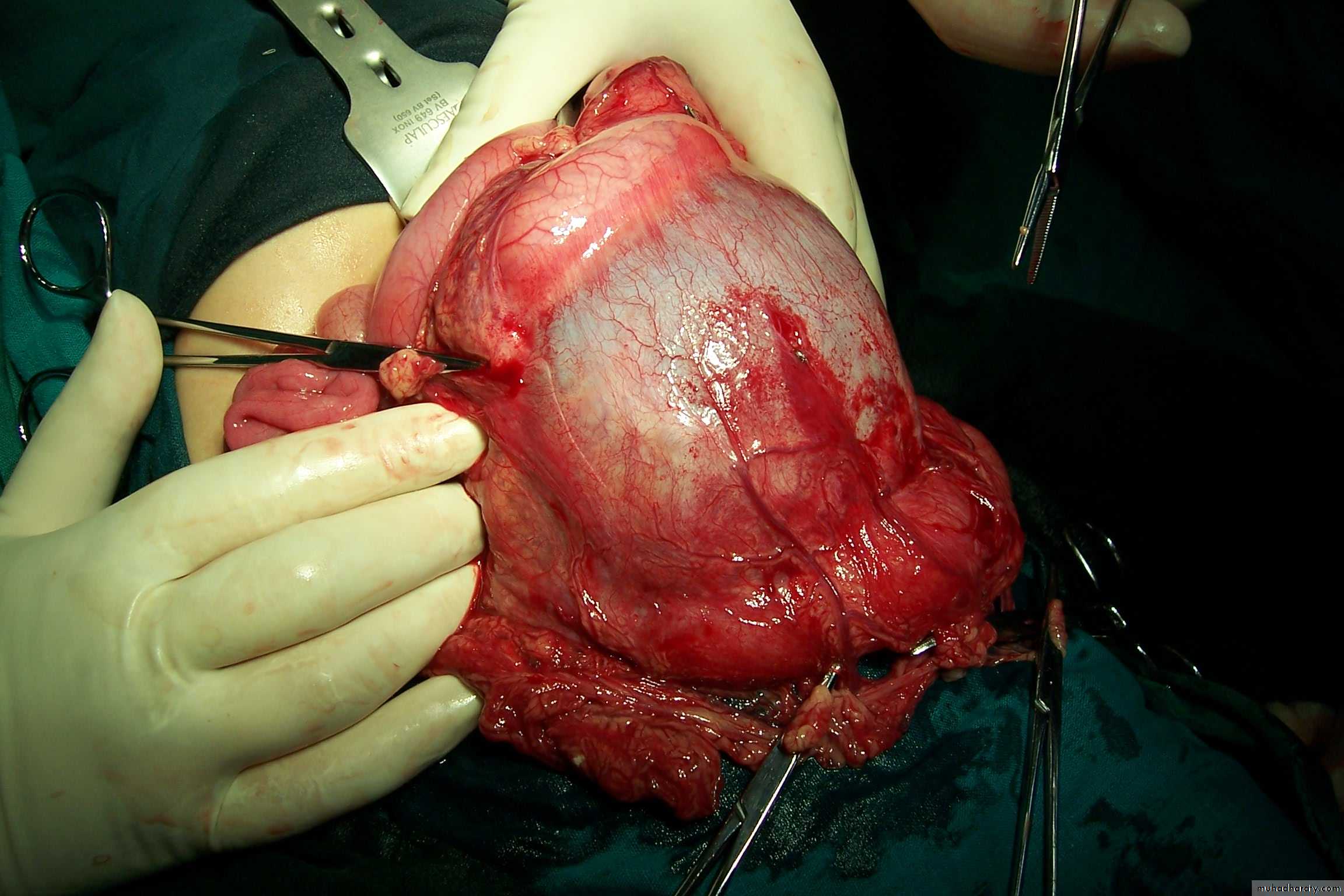
Treatment: surgery + chemotherapy (for one year)Diagnosis: Sacro-coccygeal teratoma
Problems:1-obstructed labor
2- Malignancy (if neglected for 2-3 months)
Treatment: surgery + remove the coccyx to prevent recurrence
Spleen, Pancreas and Biliary Tractغير مطلوب
غير مطلوب
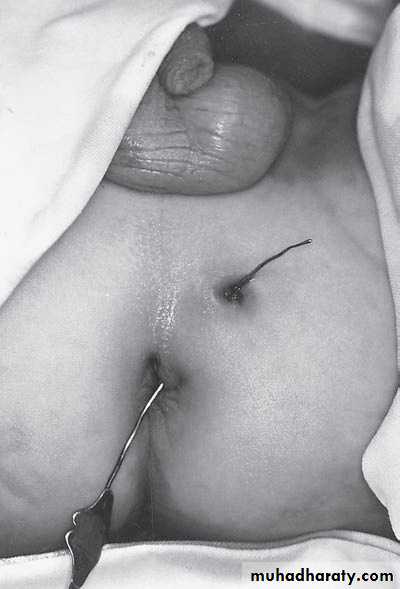
First photo:
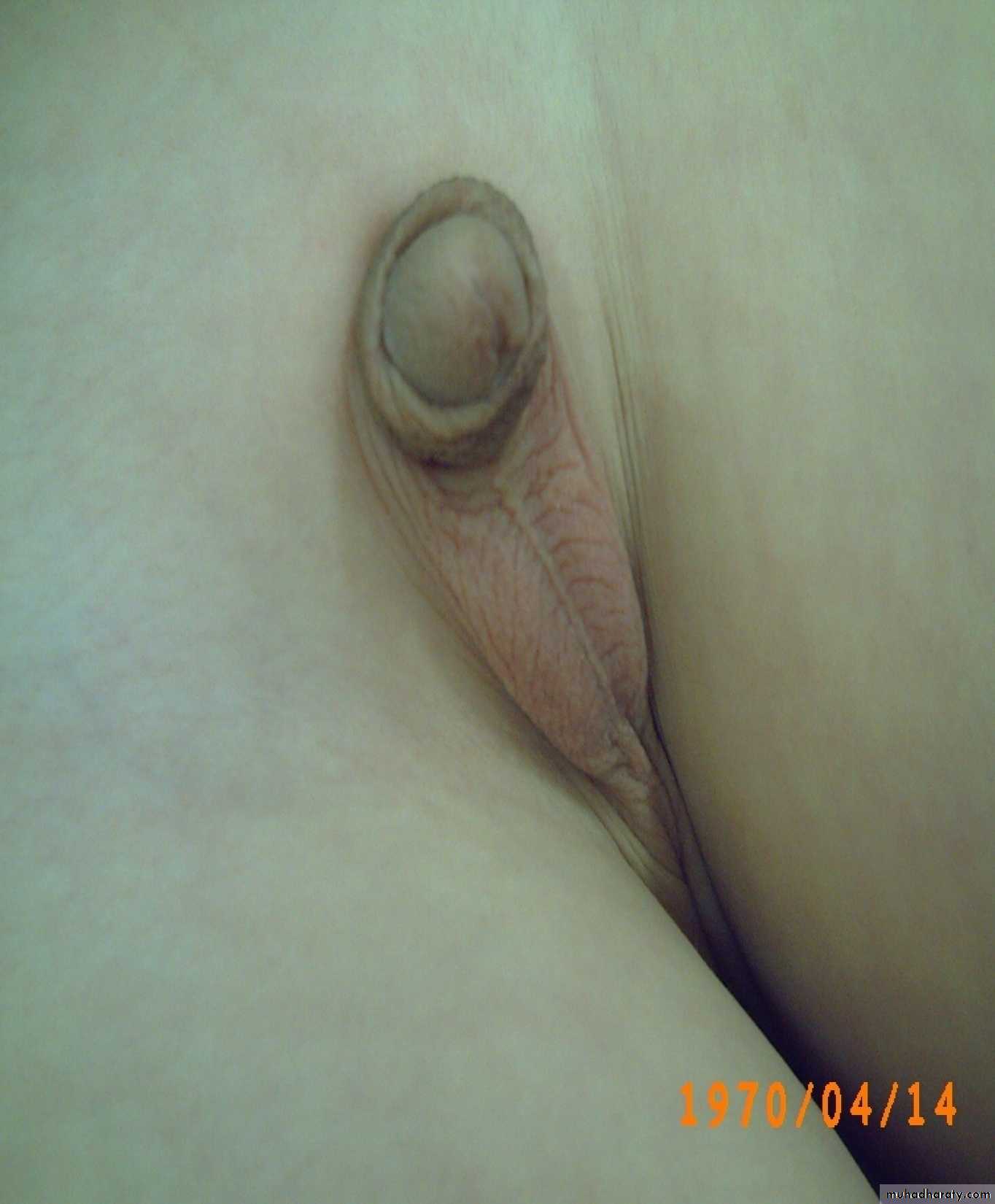
Diagnosis: rectal prolapseCauses:
• Constipation or diarrhea
• Weak pelvic muscles
• Worm (trichuris trichiura)
Grades:
• Grade1 يطلع ويرجع conservative treatment by taping
• Grade2 يطلع ويحتاج الى دفع للدخول surgery (Therach operation)
• Grade3 يطلع وما يرجع ابد surgery (Therach operation)
Second photo:
Diagnosis: Perianal fistula
Treatment: surgery (fistulectomy or fistulotomy)
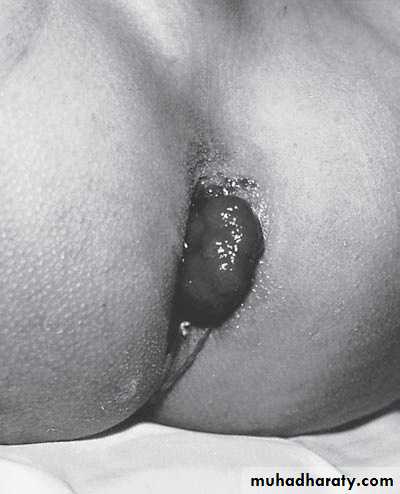
Third photo:
Diagnosis: rectal polyp
Cause in infection
Red-bleed mass + bleeding per rectum
Treatment: excision (use sigmoidoscope)
Hernia
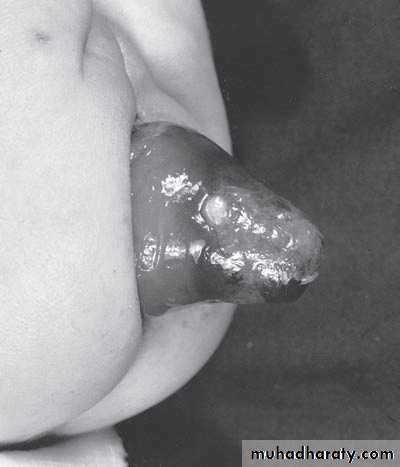
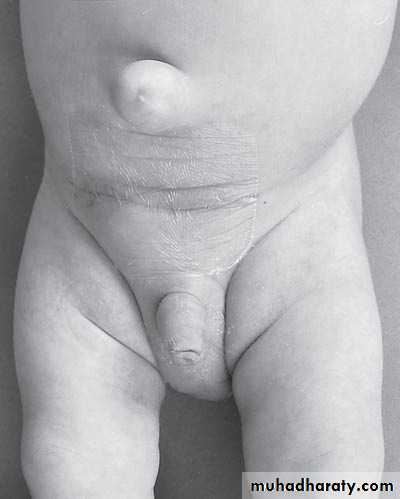
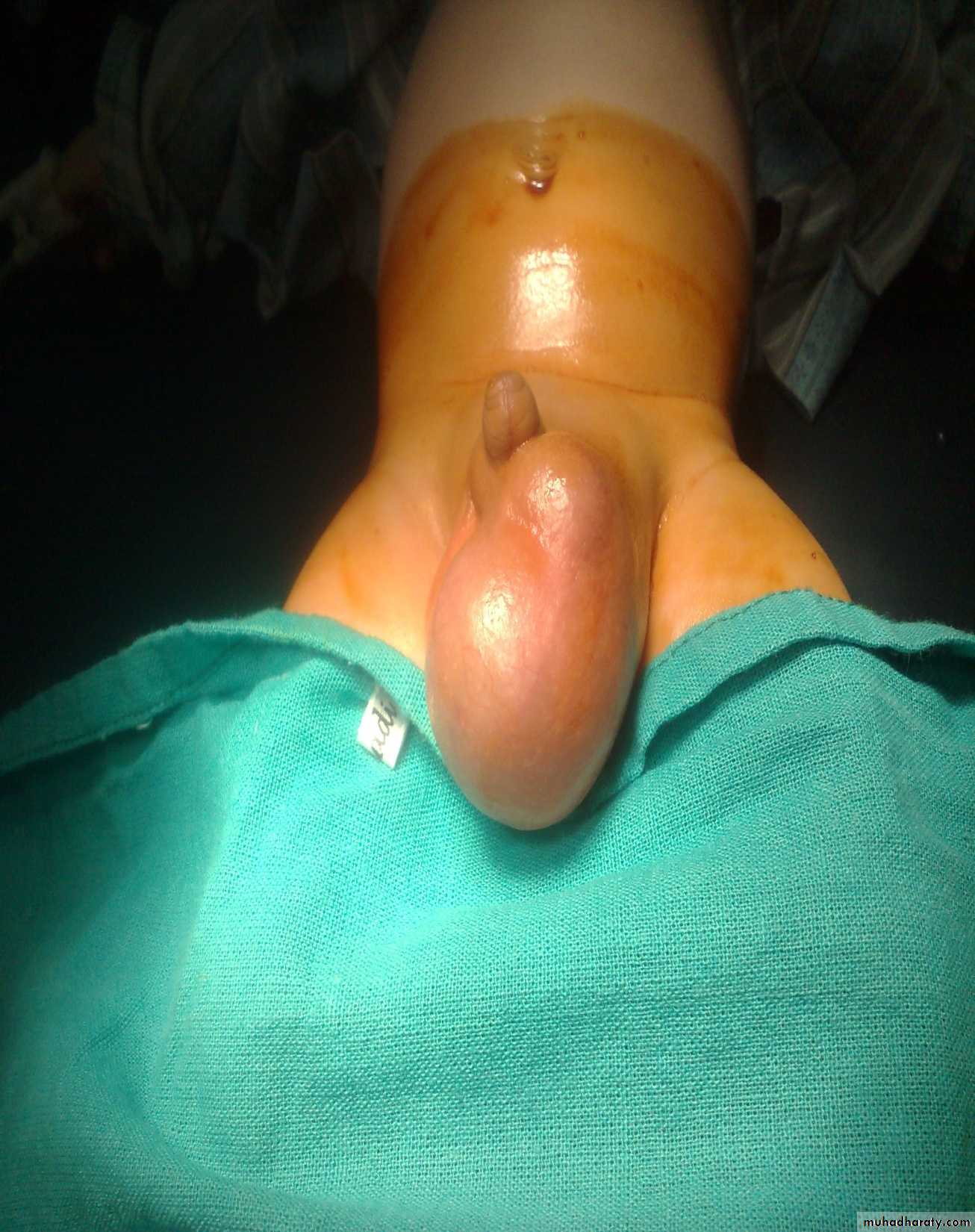
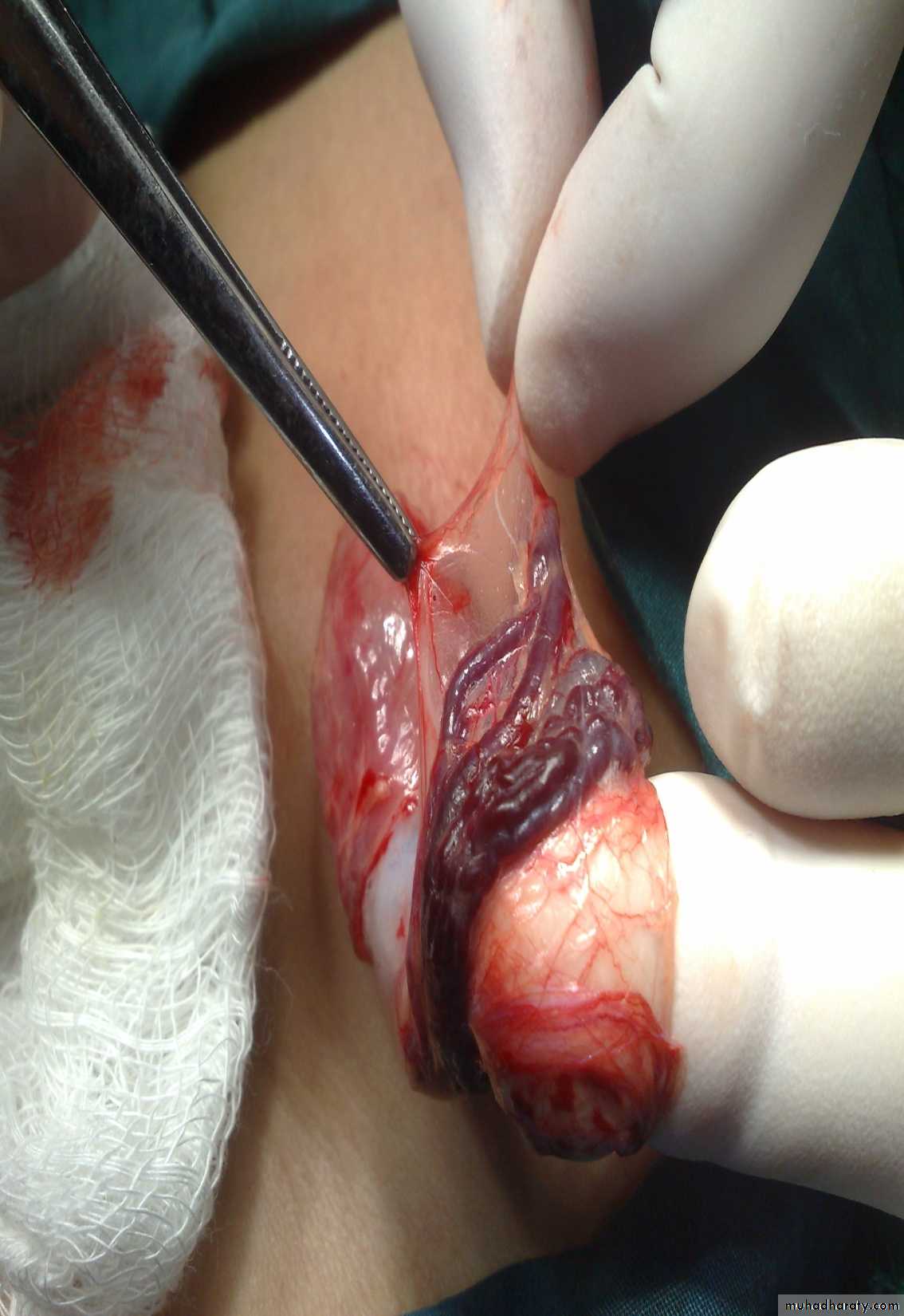
VaricoceleDiagnosis: undescended testes
Problems:• Tumor
• Sterility
• Infection
• Orchitis (like appendicitis)
Treatment:
• If palpable do fixation
• If not palpable do laparoscopy
• If not present do nothing