
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
Notes on practical orthopedics
06 صورة ص
Function of meniscus :-
1-deepen the joint space
2-add stability
3-more mobilization of the joint is allowed
4-as cushion absorb shock.
*this condition mostly affect the athlets as twisting injury mostly in the posterior
part of the meniscus.
*menisci has poor vascularity.
Dx :-partial meniscal tear.
Mx :-
If mildconservative.
If severe (complete)arthroscopy&suturing.
06صورة ص
Test:-apley compression destruction test(Mc murry test).
*If we did external rotation means we're examining the medial meniscus.
06 صورة ص
--Dx:-patellar fracture.
--Describe ?
Plane x ray ,no name,no date,no label,lateral view adult pt ,showing 3 segmented
fracture of the patella.
The influence of this fracture the pt can't extend the knee.

*patella functions:-
1-attachment of muscles
2-protection of knee joint
--Type of patellar fracture? Comminuted fracture.
--History or mechanism of fracture:-
1. Fall from Ht
2. Car accident.
**some people normally they have bipartite patella ,so always take two views to
exclude this .
--Signs :-
1-pain
2-swelling (hemarthrosis)
3-crepitus
4-bruising
5- examine the neurovascular bundle.
--How you can confirm clinically that this patient had such a problem?
Ask the pt to extend the knee , can he extend it?
--Complications:-
1-non union
2-malunion.
06صورة ص
--Metaphyseal site of long bone is the common site for osteiomylites
development?why?
Because :-
1-most common site of trauma

2-tortousity of blood vessels stasis of bloodgrowth of M.O
3-paucity of WBCs.
*abscess will follow the infection as bone is NOT extensible.
Signs & symptoms?
Fever ,,dehydration,,fatigue ,, if child (relctant to feeding) ,if chronic infection
FTT.
Local RUBOR/DOLOR/FUNCTIONLESSIA/swelling/pain.
Investigations ?
**he explained about the pathogenesis.
Rx:-
1-supportive
2-ABS according to culture &sensitivity.
3-splintage
4-if abscessdrain .
Complications:-
1—chronic osteomyelitis
2-septic arthritis
3-septicemia.
4-deformity(FTT)
06 صورة ص
Dx:-ganglion :-most commonly dorsal wrist ganglion in the RT hand
Out pouching of the synovial space.
RX:-asymptomatic :-leave it
Symptomatic /cosmetic:-
1. blow it with something (like book).
2. Steroid
3. Surgical aspiration.
06 صورة ص
--wrongly applied immobilizing tool by inlay people.طب عرب
Others methods:-
1-traction(skin or skeletal)
2-cast splintage.
3-functional brace.
Dx:-left femoral fracture.
Mx:-take x-ray(according to role of 2).
Complications:-
1-compartment syndrome
2-neuropraxia
3-vessels compression.
00 صورة ص
Dx :-hand infection.

Describe :-
Swelling edema in the dorsum of the left hand
Why the edema not develops iin the palm?
As the skin of palm is not extensible, so the edema takes the least Resistance
way(the dorsum)
**
--
اسم الحالة>flexor tenosynovitis
DDx:-
1-trauma
2-hand infection
3-RA
4-tumour.
Rx:-
1-elevation
2-warming
3-ABs
4-surgical drainage.
06 صورة ص
Dx:-Ring infection(fractured ring with compressing the ring finger)
Describe:-swelling of ring finger with bleeding on both sides of the ring in the lt
hand.
Bruising & discoloration
Rx:-removal.

***the sinus in any infection can be easily diagnosed by sinogram(
(
صبغة
06 صورة ص
Dx:-chronic osteomyelitis.
Swelling & edema with redness & sinus is opened & discharging pus.
Dx:-
Sinogram.
DDx:-
1-T.B
2-brucella.
3-acute suppurative arthritis.
4-osteomyelitis of Gary
06صورة ص
X ray of the knee joint AP view showing foreign body at the level of the epiphyseal
plate.
**bullet(it has high density).
Cut off in the velocity of bullet(1500-2000)m/sec.
--we should take lateral view before treating him
--indications of F.B removal ?
1-benefit outweigh the problem
2-infection
3-open wound.

4-in dangering Bvs or nerve.
**endogenous foreign bodies?
1-cornea
2-synovium.
3-thyroglobulin.
صورةص70
Name of the test:-adam forward bending test.
lateral flexion of the back bone=scoliosis
This is performed to(purpose of this test) :-
Differentiate between structural kyphosis(abnormality in the tissues itself) &
postural scoliosis(like pain induced kyphosis).
--Describe what you see clinically and in x-ray?
1-lateral tilting.
2-rotation.
3-rib deformity
66 صورة ص
1-ortolani test & Barlow test for DDH examination.
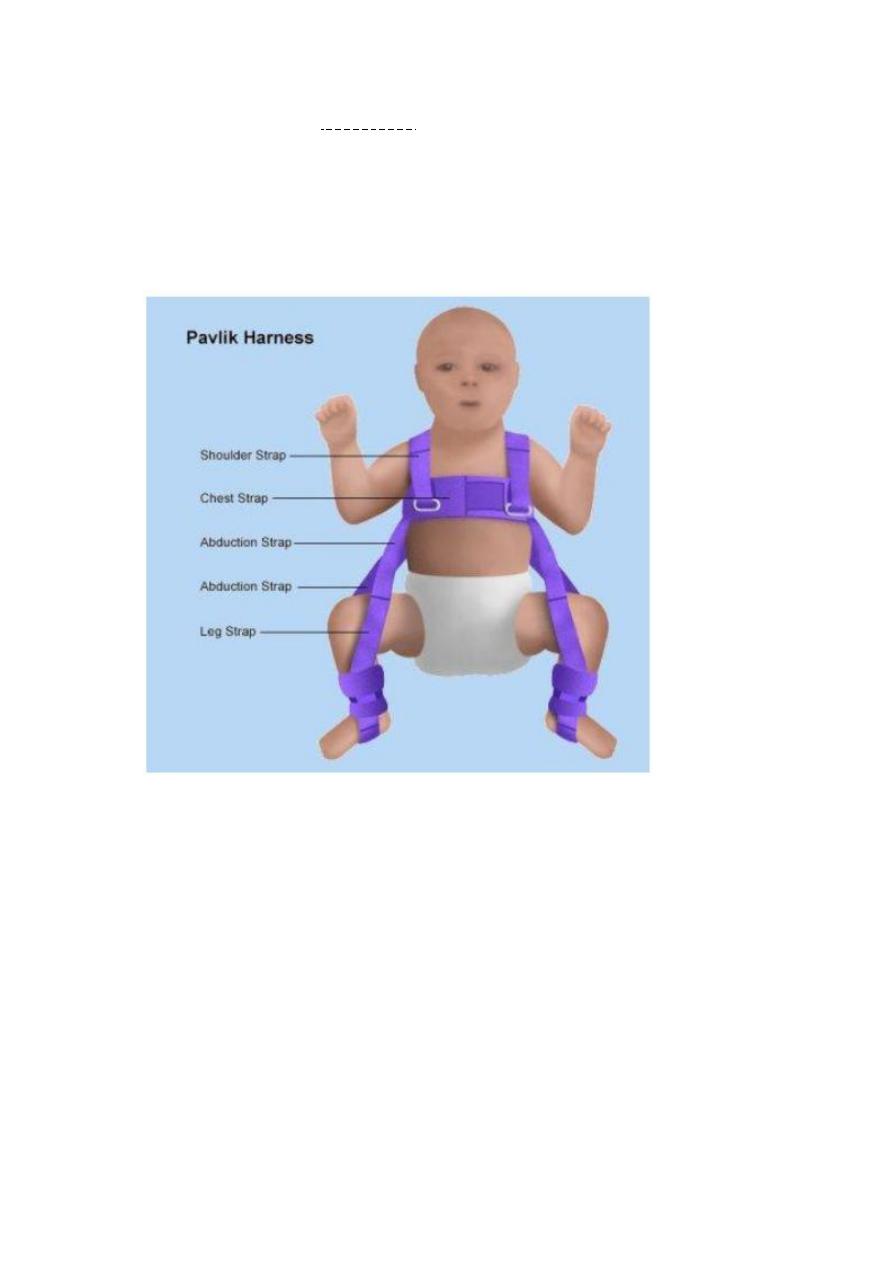
--Describe one of themOrtolani test:- baby's thigh is held with the thumb medially
& others fingers on greater trochanter of femur then flex hip90degree ,then gently
abduct normally smooth abduction about 90degree.
Rx:-Pavlik harness ;used in the first 6months to treat DDH.

Tourniquet indications:-
1-to stop bleeding
2-in surgery
3-following snake bite.
Complications:-nerve injury//ischemia.
-:66 صورة ص
Refracture as the bone with the plate bends forward.
Complications:-
1-failure of implant
2-infection
3-non union.
صورة ص
66
--he try to do forward flexion of spine.
Schober's test.

Straight leg rising test:to detect lumbar spine diseases such as prolapse
صورة ص
66
Swelling of the MPJ(small joints of the rt hand)+PIP+muscles
With wasting & ulnar deviation ,slight swan neck deformity.
DX:-rheumatoid hand arthritis.
صورة ص
66
DDH=Dx.
Proximal displacement of femur
Dysplastic acetabulum
How we Dx all this ?by shenton+perkine+Helignieriere lines
Rx :-
<6monthsPavlik Harness
>6months _18monthsclosed reduction & spica.
>18monthsopen reduction.
How you make an approach to DDH?
1-ortolani test
2- barlow test.
3-US

صورةص
60
Blister + bruising of leg
If blister filled with blooddon't open
If filled with serousopen &drainage.
Important slide
صورة ص
66
Dx:- osteomyelitis
نفس الشرح في الساليد السابق
صورة ص
66
Onion peel appearance
DDX:-
1-ewing's sarcoma
2-osteosarcoma
3-osteomyelitis.
صورة ص
67
Involcrum sequestrum &sclerosis &cloaca
Dx:-chronic osteomyelitis.
صورة ص
66
Dx:-Unilateral genovarum

DDX:-Infection –trauma -tumour
صورةص
66
Dx :-Fracture pelvis with chest injury
How you manage a pt with major trauma?
ABCD
Investigations :Xray----abdominal ultrasound,,etc
صورة ص
66
--Spiral fracture of the shaft of femur with soft tissue swelling
--3wks for spiral fracture healing in the upper limb(more contact between bones
ends).
Complications :-
Early :-
Late :-
***avascular necrosis :- scaphoid fracture, talus.
***fracture around joint osteoarthritis
RIP Reduction ,, immobilization,, physiotherapy.
صورة ص
66
--xray of distal leg showing transverse Frcature of tibia & fibula with sindesmosis
injury
--

صورة ص
66
Bimalleollar fracture=Dx.
Rx :-reduction & fixation
صورة ص
66
Fractured fibula with sindesmosis injury (which connects tibia &
fibula)subluxation of the joint.
صورة ص
60
Huge swelling of lt leg(proximal part of leg) in old man pt ,irregular,
Dx :- bone tumour.
Ddx :-
Ewing
Osteosarcoma
ص
66
--single metaphyseal bony outgrowth directed away from the joint with its
cartilage cap.
Dx:-osteochondroma.
Complications:-
1-malignancy
2-compression on nerves & BVs
*types of exostosis:-
1-single
2-multiple

ص
66
--well defined osteolytic lesion,fall fragment sign in the metaphyses of proximal
humerus
Dx:-simple bone cyst.
ص
67
--diffuse echymoses ,bruising,patch of gangrene,loss of big toe in the rt foot of this
pt.
Ischemic limb
Causes:-injury,fracture,severe burn,D.M,Raynaud disease.
ص
76
--Multiple myeloma or secondary metastases
Finding:-rain drop appearance.
ص
76
--eccenteric osteolytic lesion in the end of femur&proximal tibia subchondrical in
site.
Dx:-Giant cell tumour.
ص
76
--well defined osteolytic lesion with overlying periosteal reaction in form of onion
peel appearance.
Dx:-Ewing's sarcoma.

ص
76
--osteoarthritis
Fusiform swelling
In proximal phalanx & middle fingers.
(
وقل
ربي
زدني
علما
)
