بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
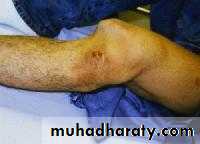
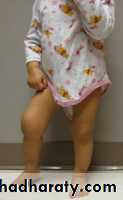
SYMPTOMS
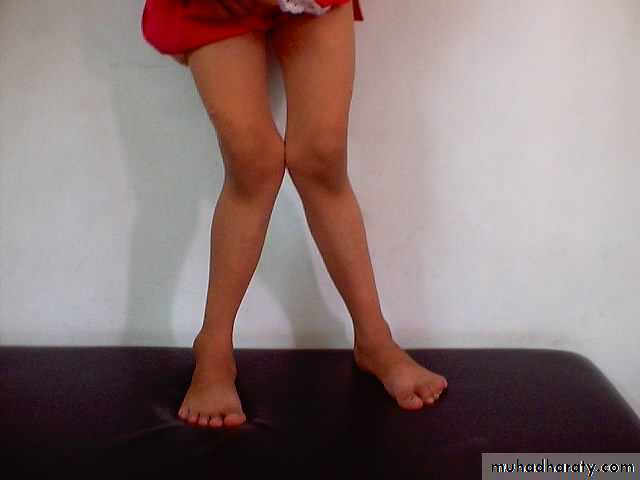
PAINSTIFFNESS
DEFORMITY
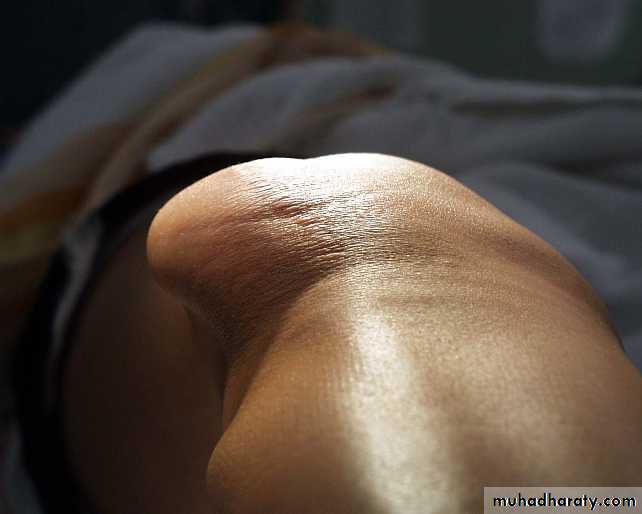
SWELLING
LIMPING
8
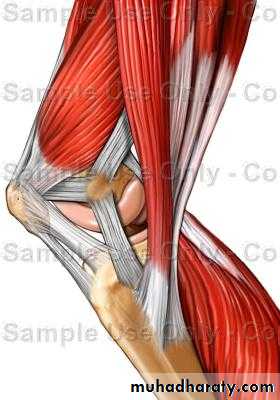
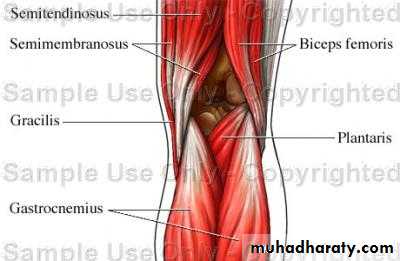
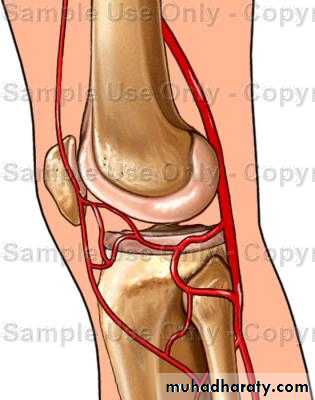
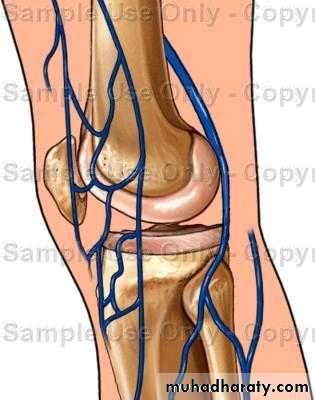
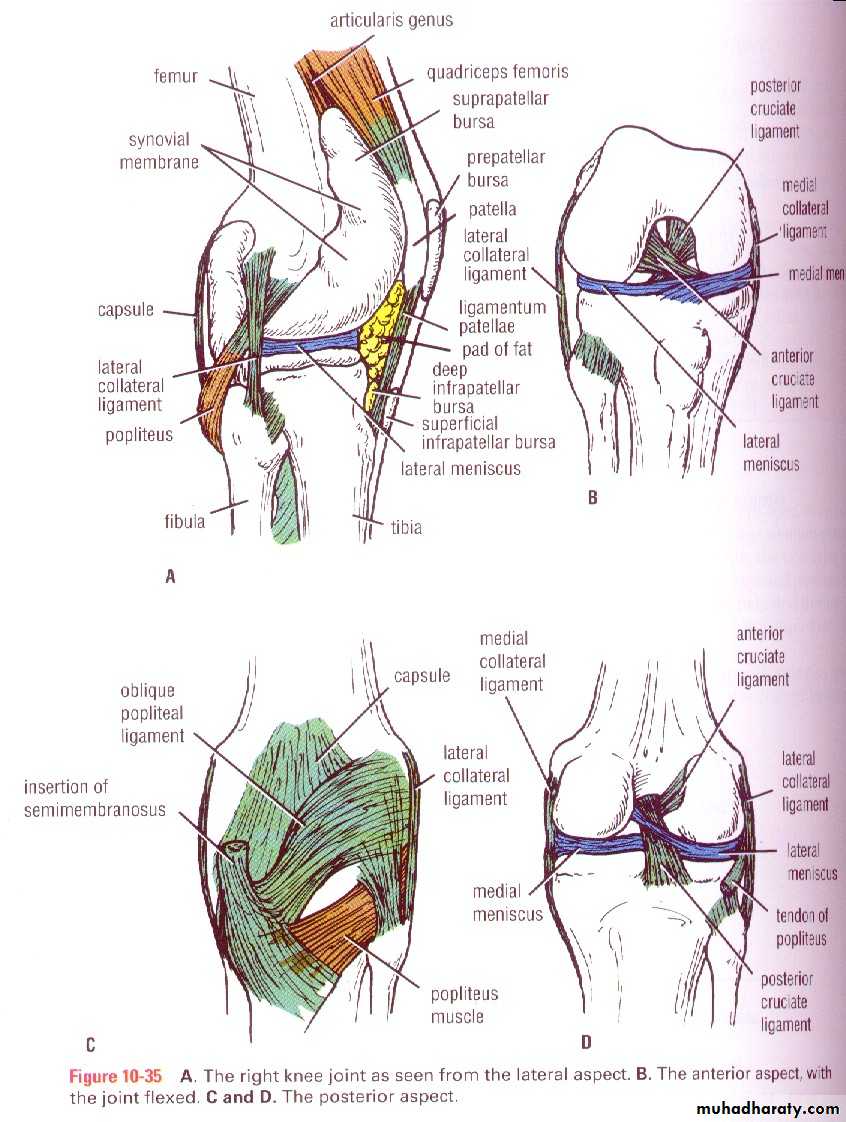
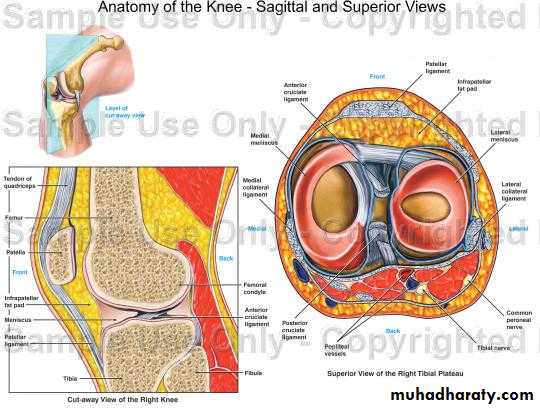
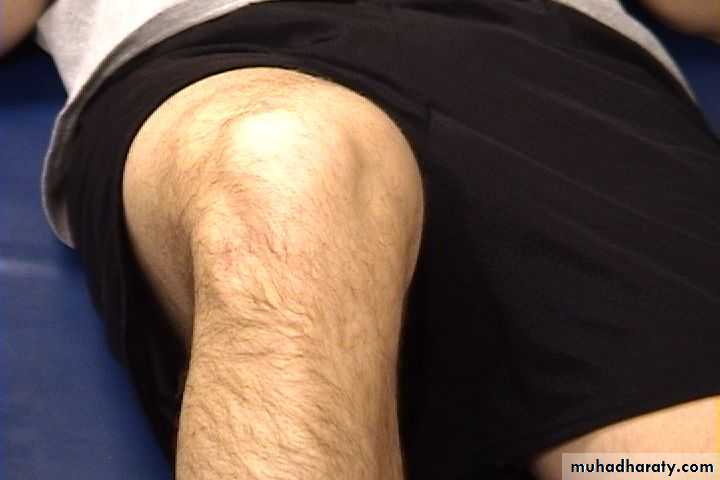
Normal Knee – Anterior, Extended
9Surface Anatomy - Anterior, Extended*
10
Patella
Hollow
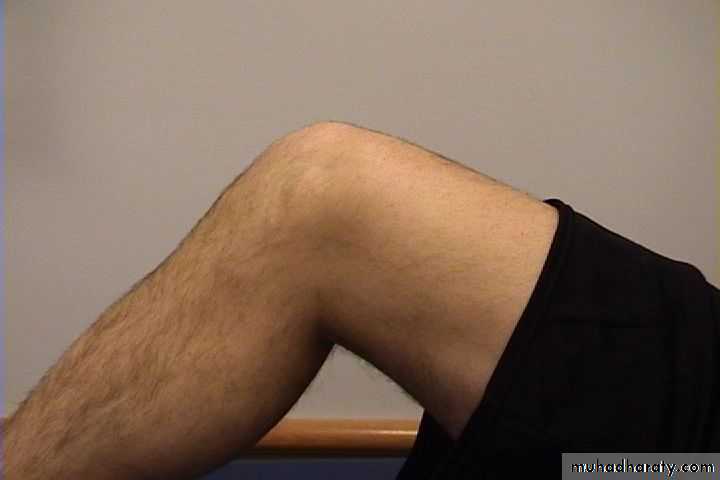
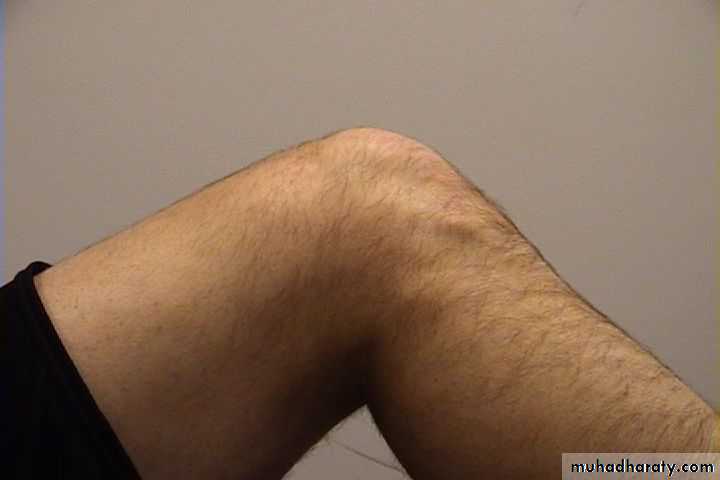
IndentedNormal Knee – Anterior, Flexed
11Surface Anatomy - Anterior, Flexed
12
Head
Of
Fibula
Patella
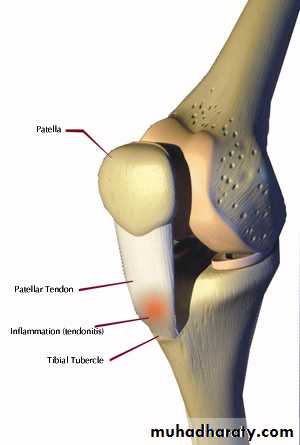
TibialTuberosity
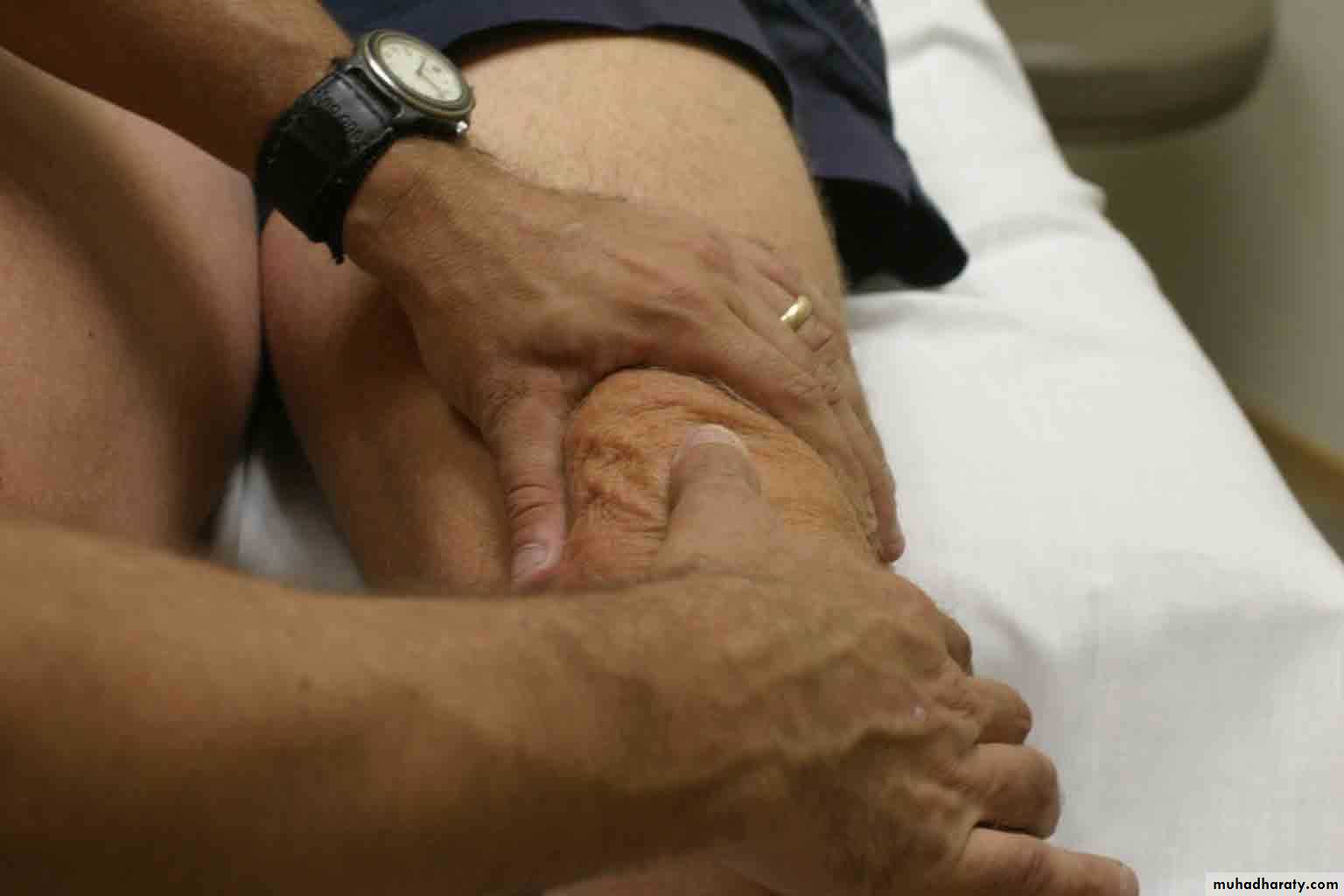
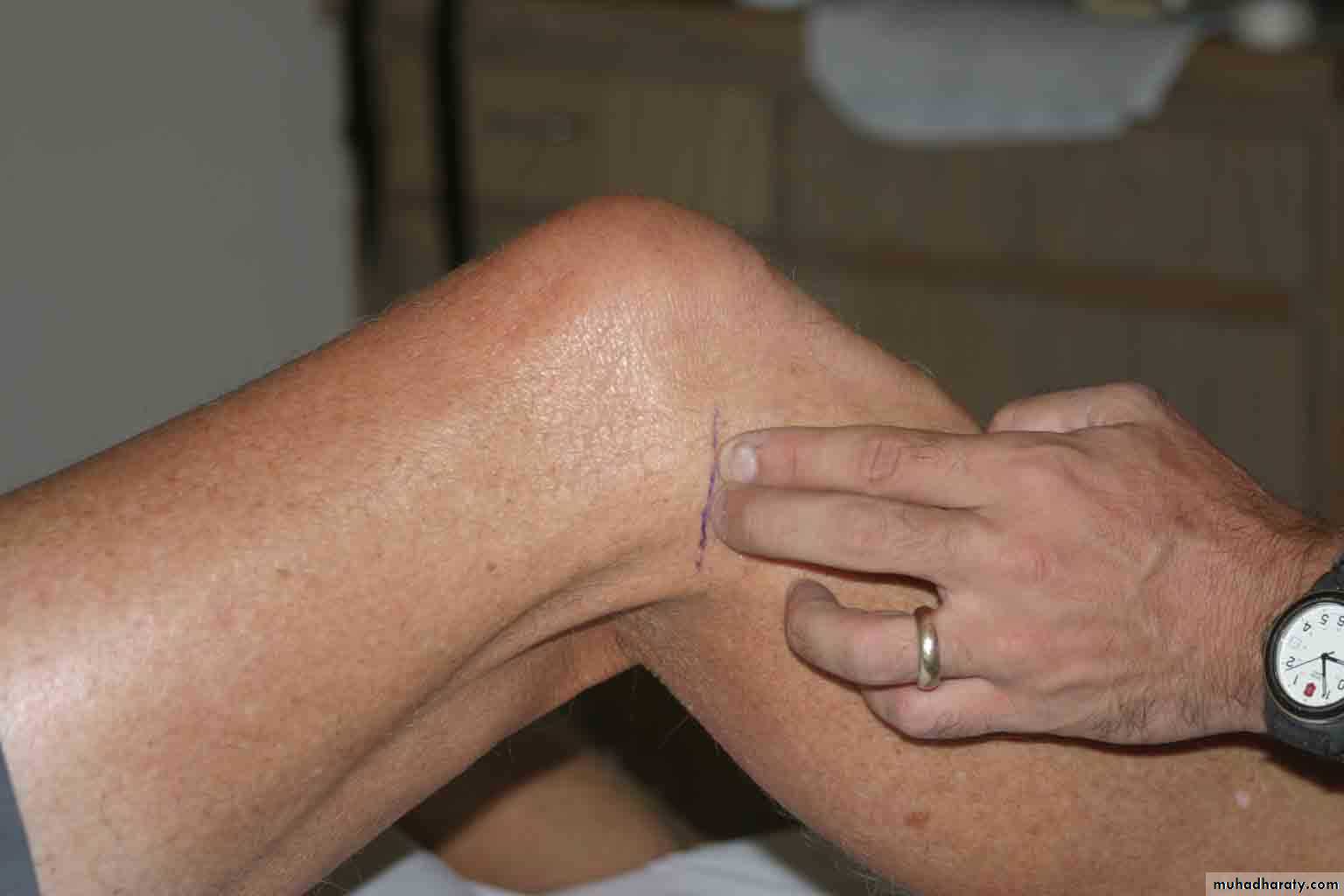
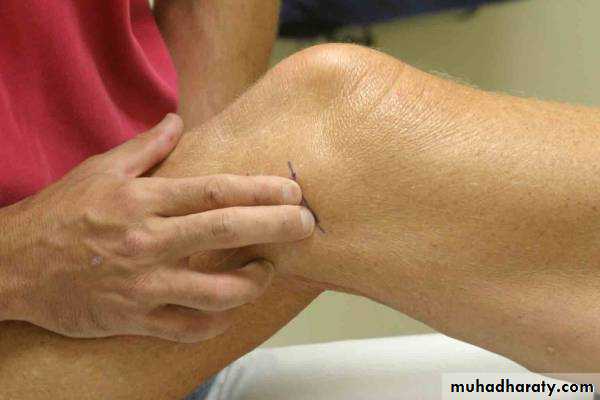
Palpation – Anterior*
13Patella:
Lateral and Medial Patellar FacetsSuperior
And
Inferior
Patellar Facets
Patellar Tendon**
Lateral Fat PadMedial Fat
Pat
Surface Anatomy - Medial
14
Medial
Femoral
Condyle
Patella
JointLine
Medial
Tibial
Condyle
Tibial
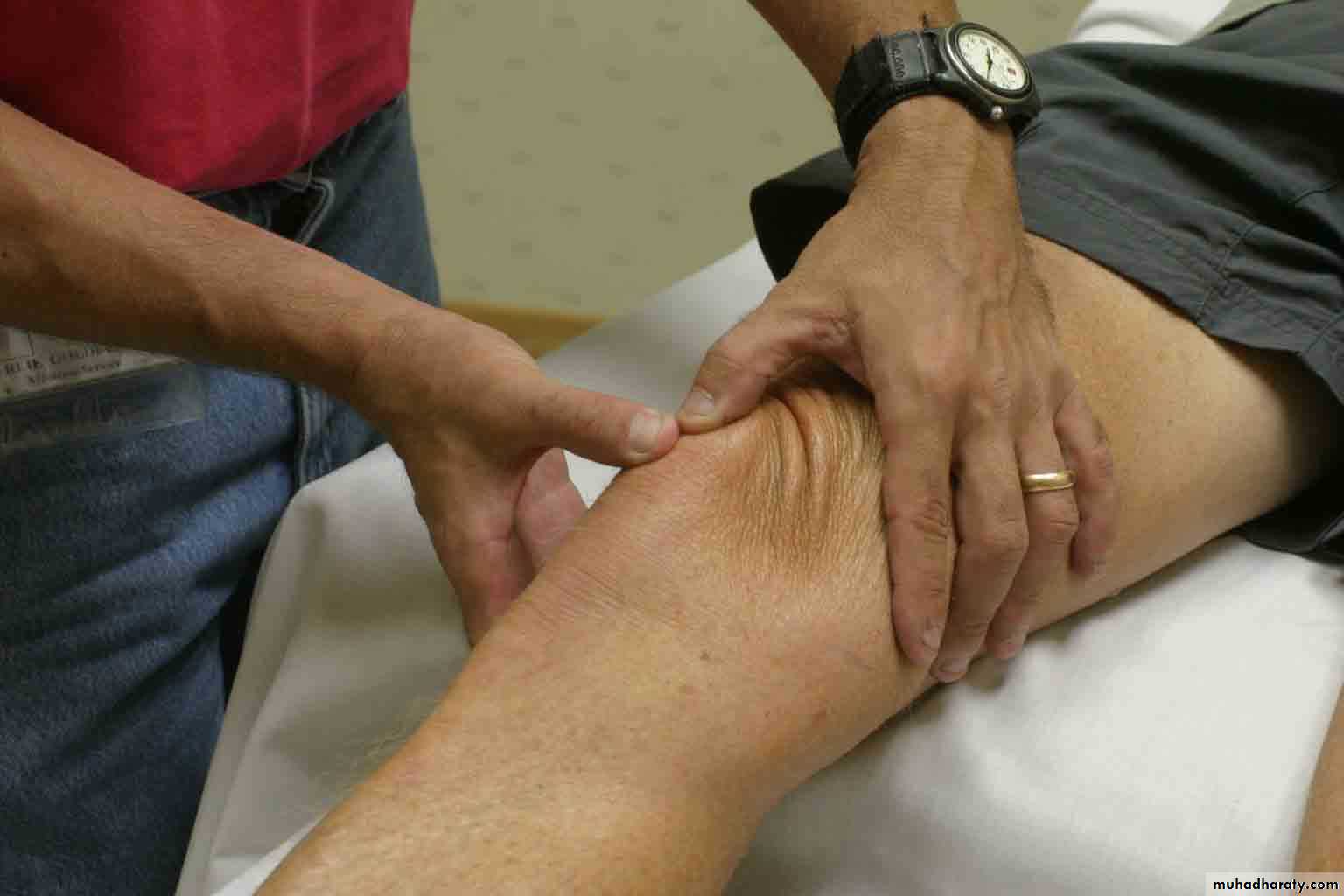
TuberosityPalpation - Medial
15Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)*
Pes anserinebursa**
Medial joint
lineSurface Anatomy – Lateral
16
Patella
Head
OfFibula
Tibial
TuberosityQuadriceps
Palpation – Lateral*17
Lateral joint
lineLateral Collateral
Ligament (LCL)**How to Start
• IPEEP
• INTRODUCE.
• PERMISSION.
• EXPLANTION.
• EXPOSURE.
• POSITION.
18
The Apley System
All joint examinations follow this system:Look
Feel
Move : Active then Passive
Special Tests
Radiograpgy.
19
LOCAL EXAMINATION OF THE THIGH AND KNEE
20Inspection (LOOK)
Bone contours and alignment
Soft-tissue contours
Colour and texture of skin
Scars or sinuses
21
22
23
24
Instability - Example
25
http://www.carletonsportsmed.com/Libraria_medicus/PF_patella_dislocation.JPG
Patellar dislocation
26
27
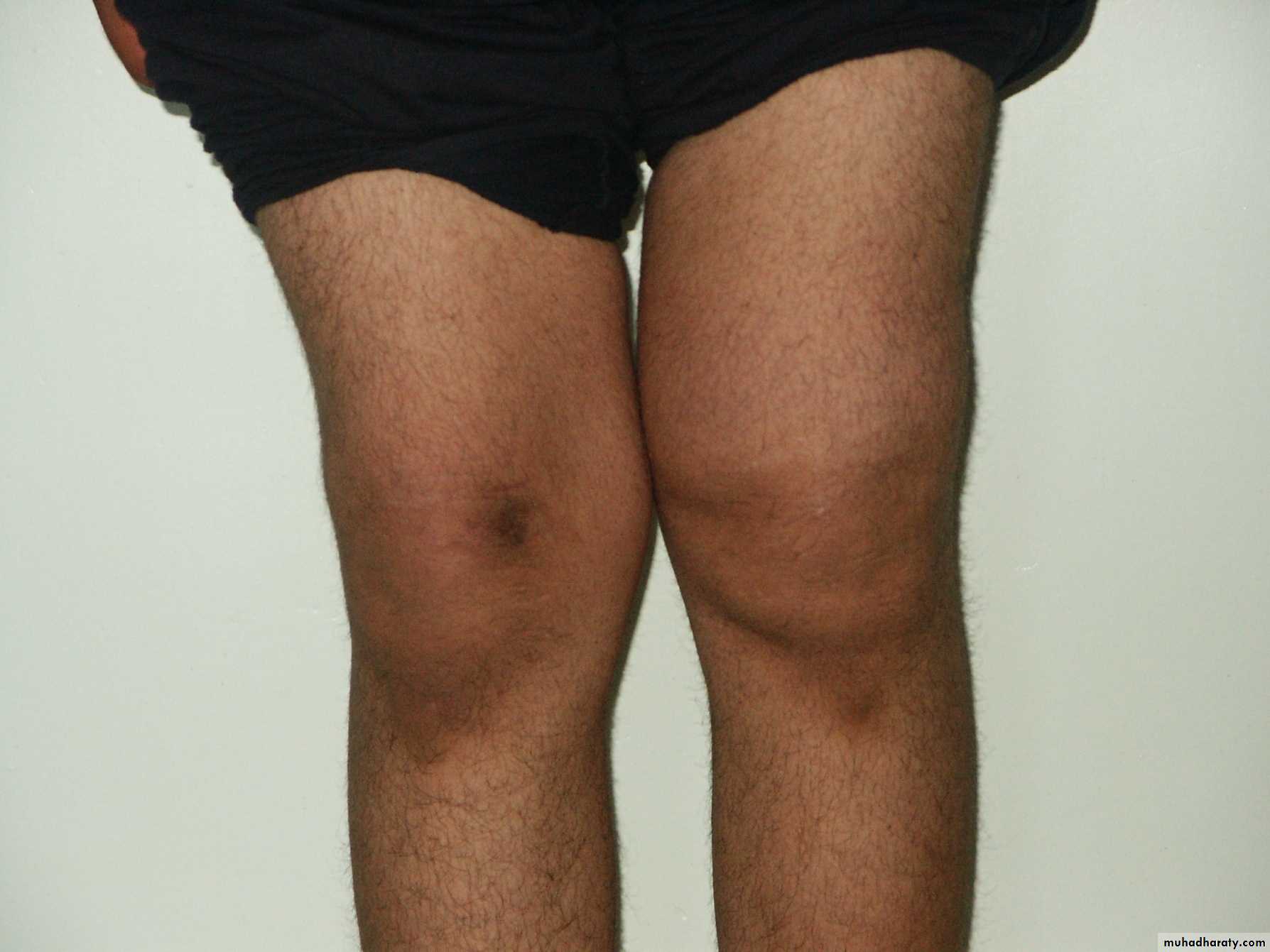
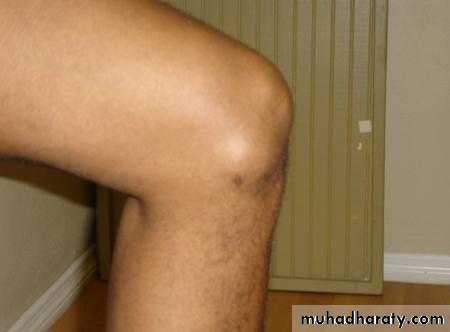
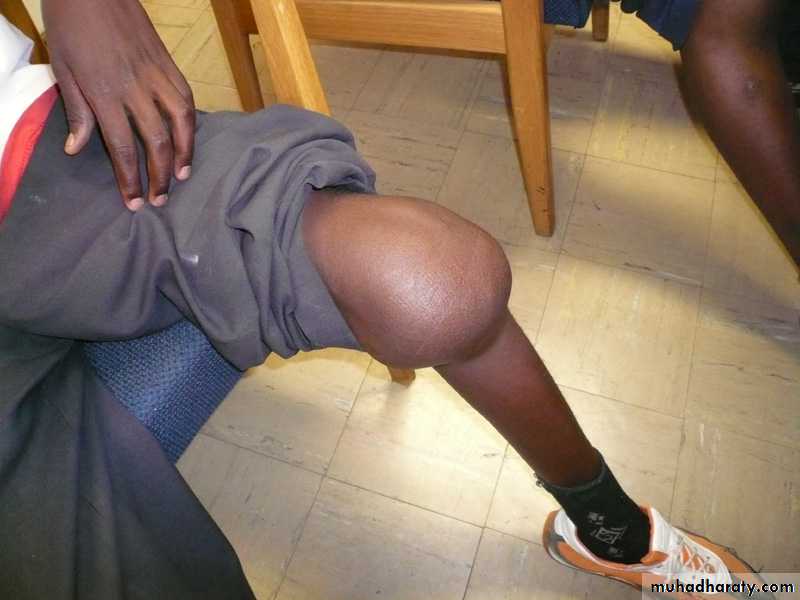
diffuse swelling of the knee can
arise only from three fundamentalcauses:
I) thickening of bone;
2) fluid within the joint;
and
3) thickening of the synovial membrane
28
Distinction between effusions of blood, serous fluid, and pus is
madepartly from the history,
partly from the clinical examination.
29
(haemarthrosis)
Aneffusion of blood appears within an hour or two of an
injury and rapidly becomes tense.
30
clear fluid
An effusion developsslowly (twelve to twenty-four hours) and is never so tense as a blood.
An effusion of pus is associated with general illness and
31
Palpation (FEEL)
Skin temperatureBone contours
Soft-tissue contours
Local tenderness
32
33
34
35
36
Measurement of thigh girth
Comparative measurements at preciselythe same level In each limb.
(Note particularly the bulk of the quadriceps muscle)
37
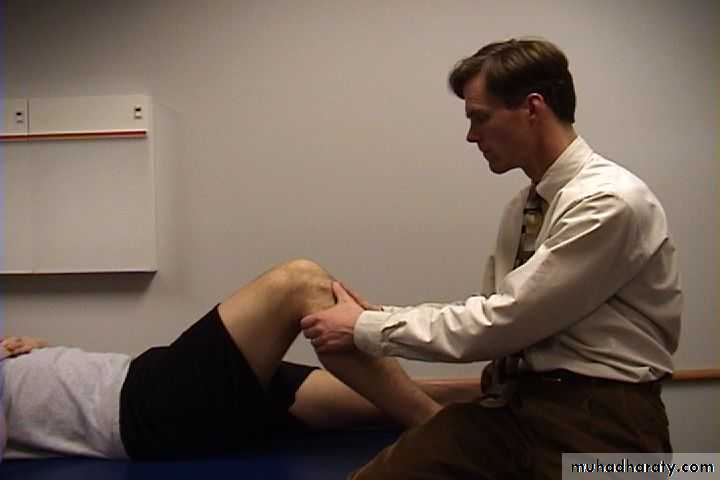
Movements (active and passive)
against normal knee for comparison)38
? Pain on movement
? Crepitation on movement
39
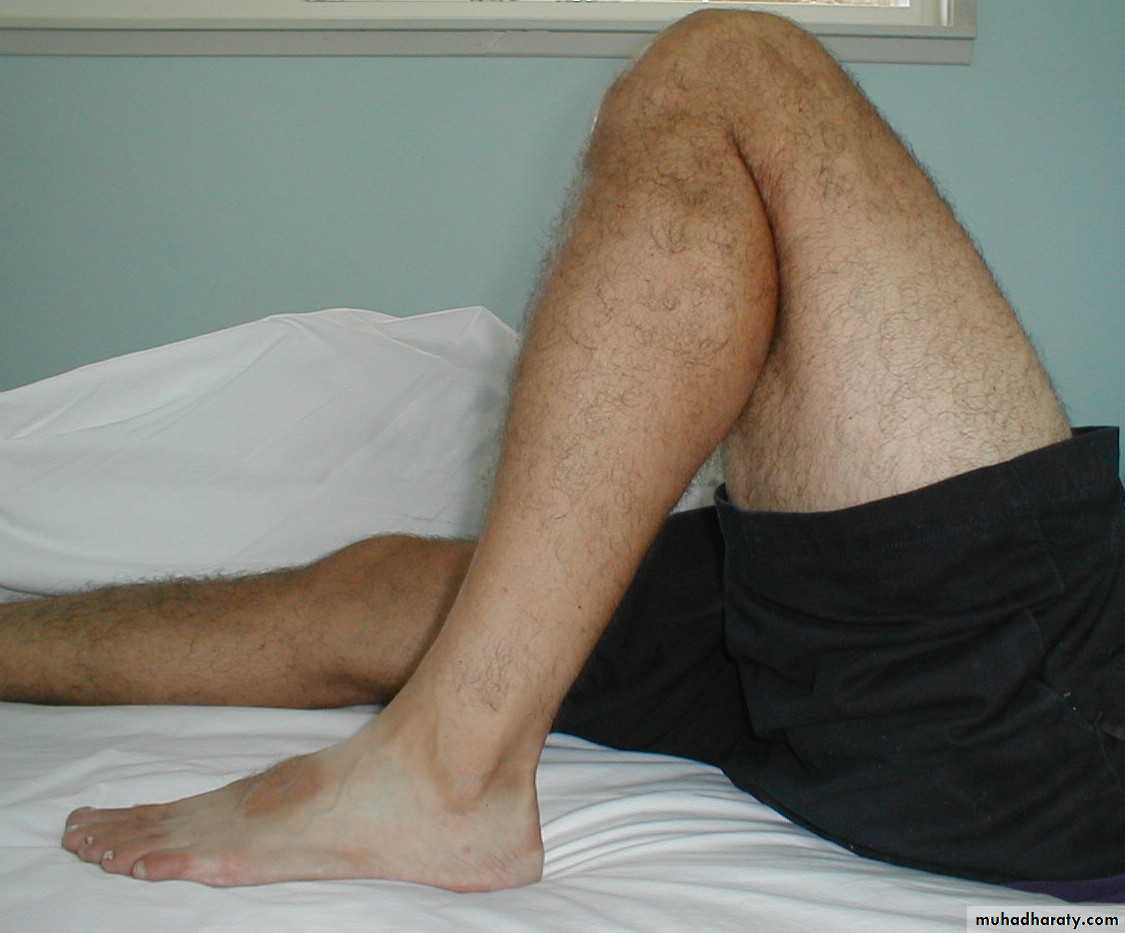
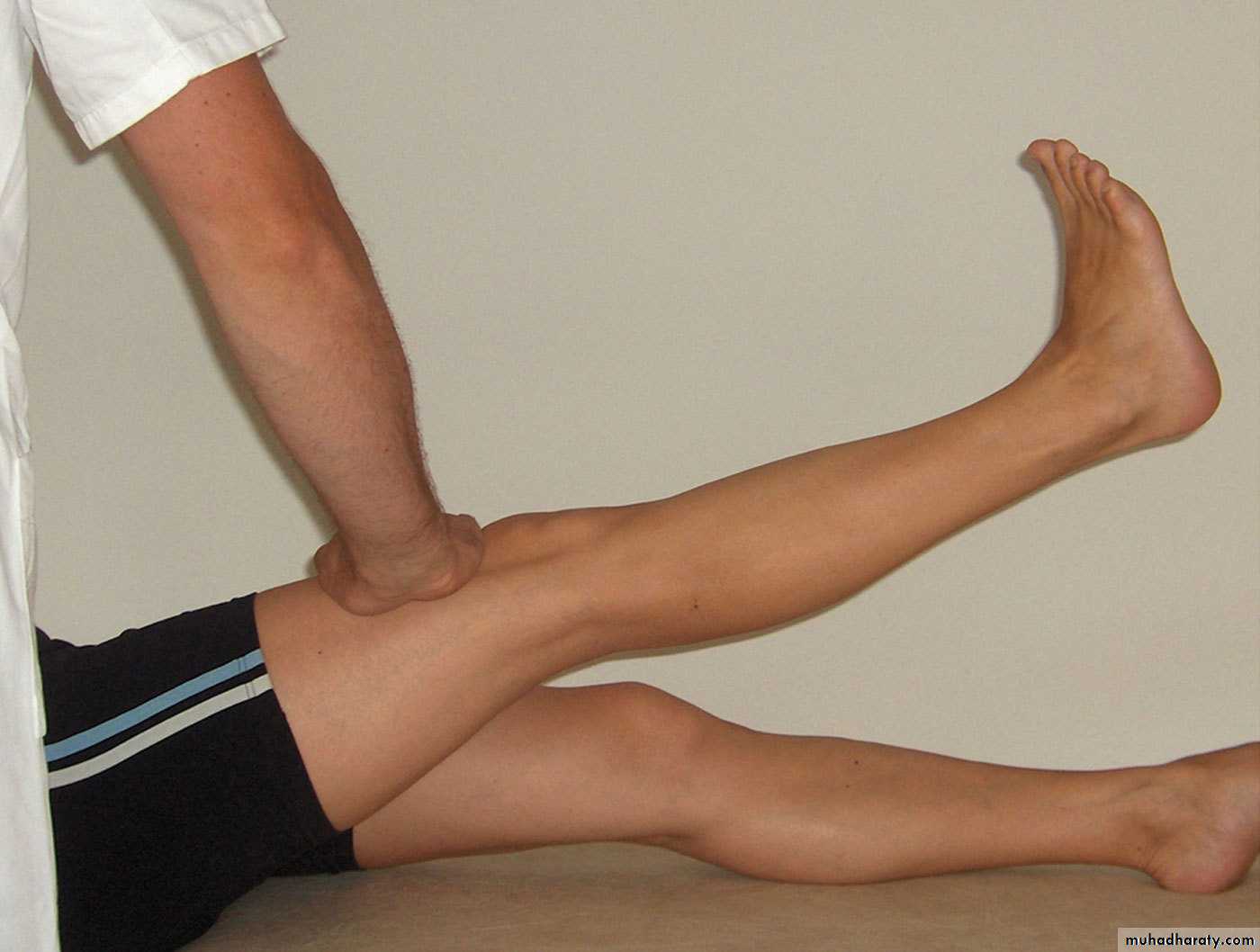
Flexion.
patients can flex enough to bring the heel in contact with the buttock.The range of the sound knee must be taken as the normal for the individual.
4041
42
43
Extension
It is wrong to accept 0 degrees as the start in point of movement:therefore the range on the sound side must be taken as the yardstick of
44
Power
(tested against resistance of examiner)Flexion
Extension45
Stability
Medial ligamentLateral ligament
Anterior cruciate ligament
Posterior cruciate ligament
46
Tests for stability
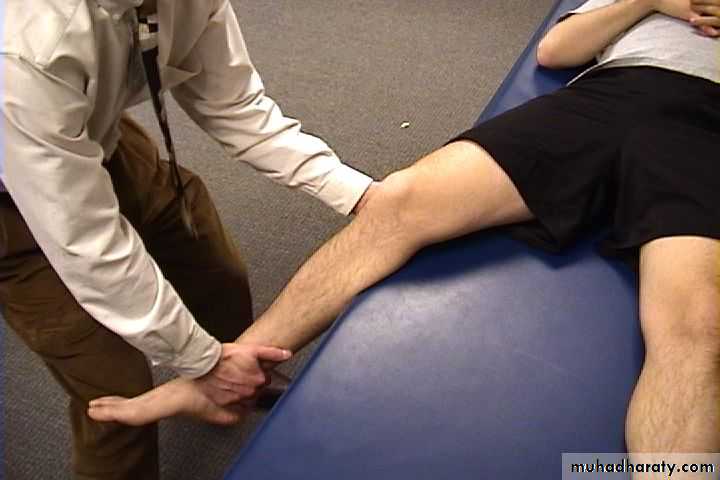
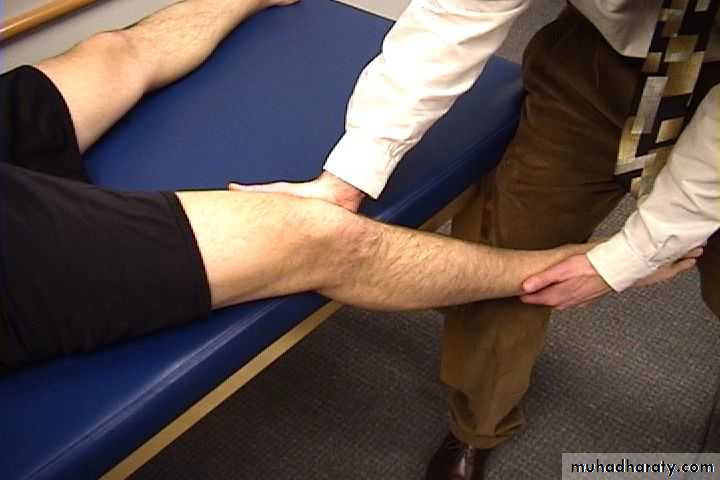
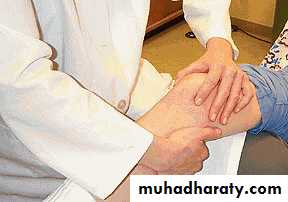
47Testing the medial and lateral ligaments.
48
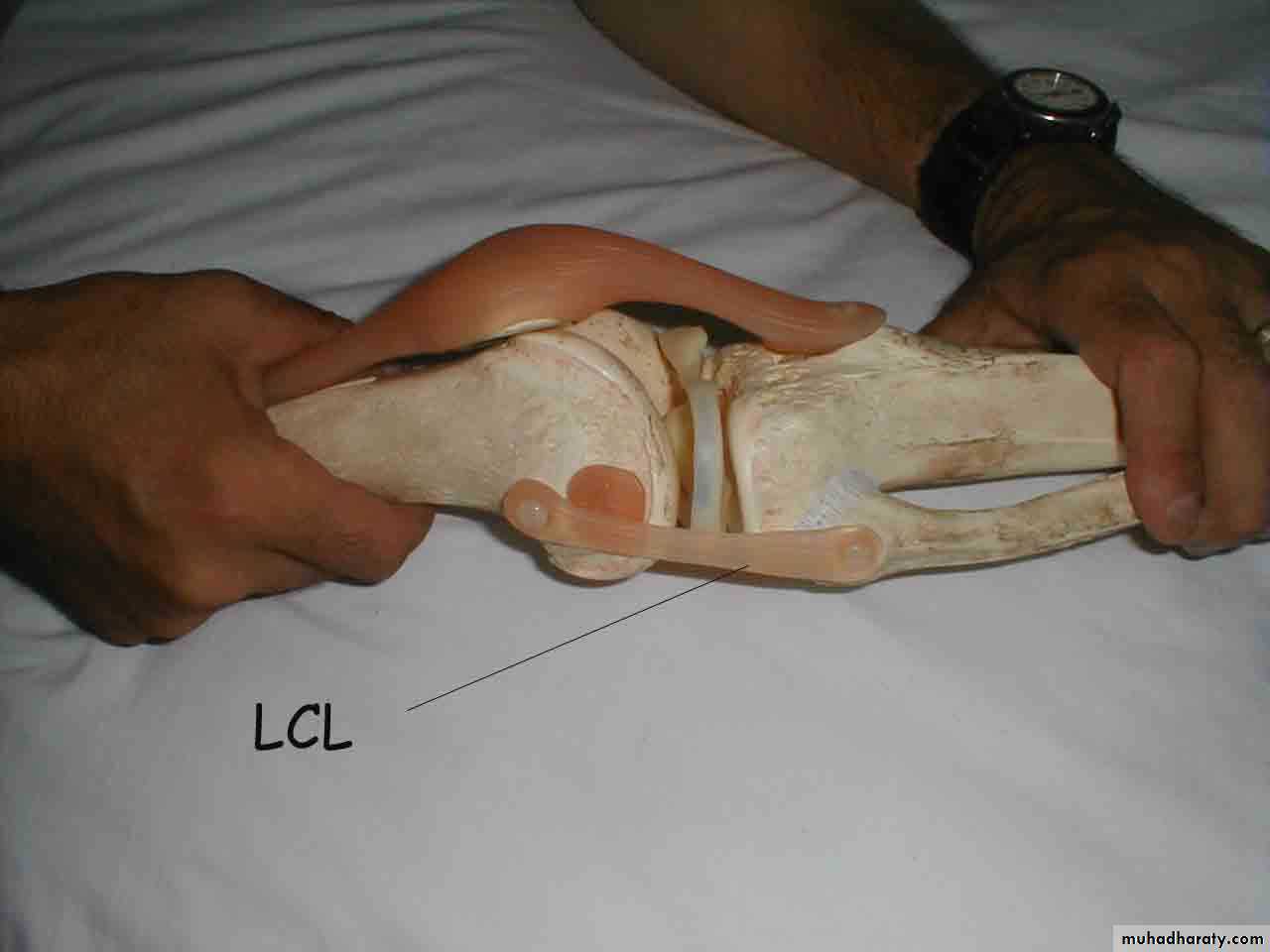
Collateral Ligament Assessment
49Patient and Examiner
Position*
Valgus Stress Test for MCL*
50Note Direction Of Forces
Varus Stress Test for LCL*51
• Note direction of forces
Rotation tests (McMurray)(Of value mainly when a torn
meniscus is suspected)
52
53
54
The maneuver is carried
out by repeatedlyI) flexing the knee, first fully but in succeeding tests progressively less fully
then
2) rotating the tibia upon the femur, first laterally but in further tests medially;
and finally
3) extending the knee while the rotation of the tibia is still
maintained.
55
A loud click,
distinct from the normal patellar click and usually associated with pain,suggests a tag tear (not a 'bucket-handle‘ tear) of a meniscus.
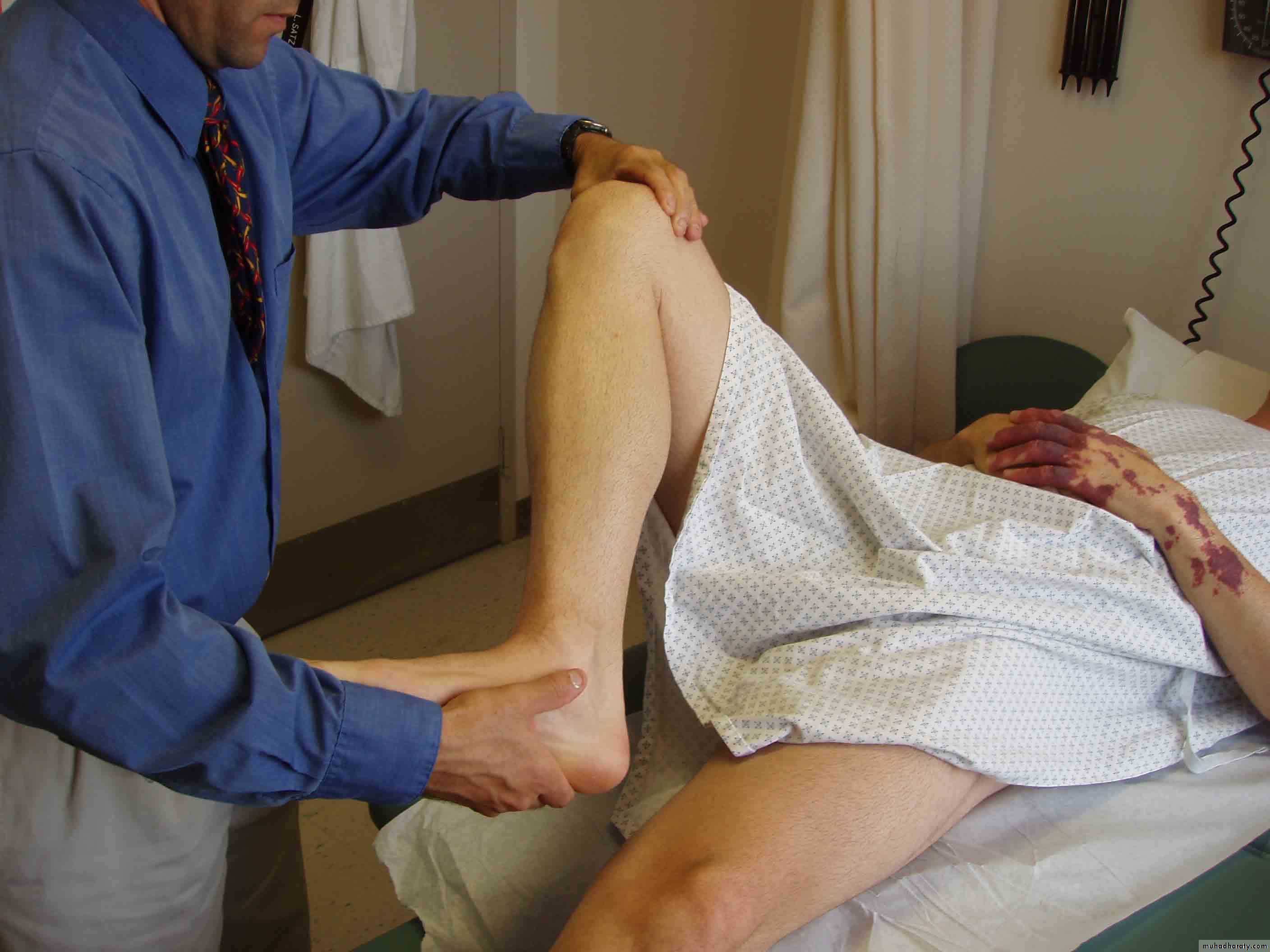
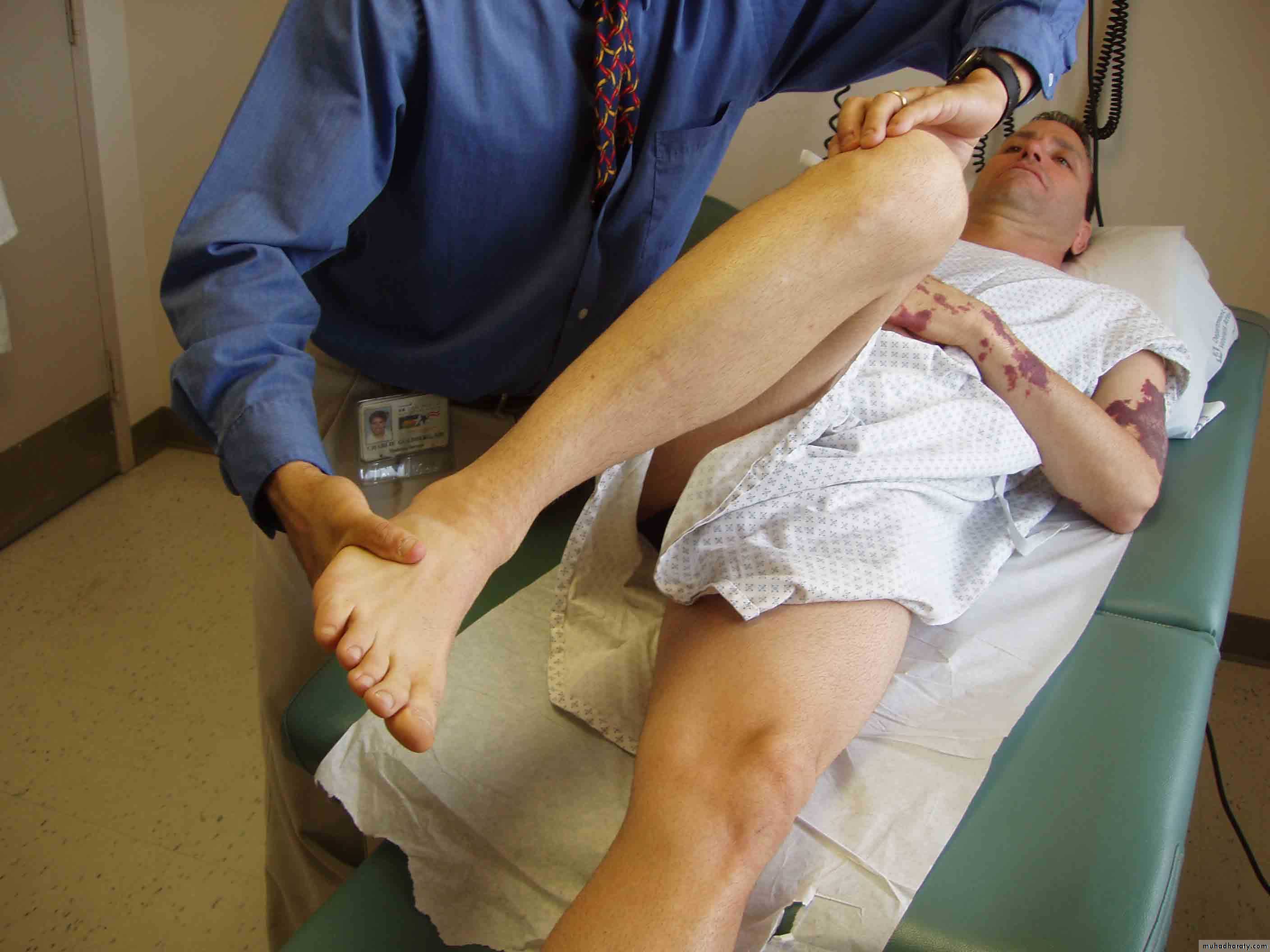
56Testing the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments.
57Anterior Drawer Test for ACL
Physician Position & Movements*Patient Position
58
• Note direction of forces
Posterior Drawer Testing- PCL*
59• Note direction of forces
60
Stance and gait
61EXAMINATION OF POTENTIAL EXTRINSIC SOURCES OFTHIGH OR KNEE SYMPTOMS
This is important if a satisfactory explanation for the symptoms is not found on local examination.The investigation should include:
I) the spine.
2) the hip.
62
GENERAL EXAMINATION
General survey of other parts of the body.The local symptoms may be only one manifestation of a widespread disease.
63
CLASSIFICATION OF DISORDERS OF THE THIGHAND KNEEDISORDERS OF THE THIGH
64INFECTIONS
Acute osteomyelitisChronic osteomyelitis
Syphilitic infection
65
66
TUMOURS
Benign bone tumorsMalignant bone tumors
67
68
ARTICULAR DISORDERS OF THE KNEE
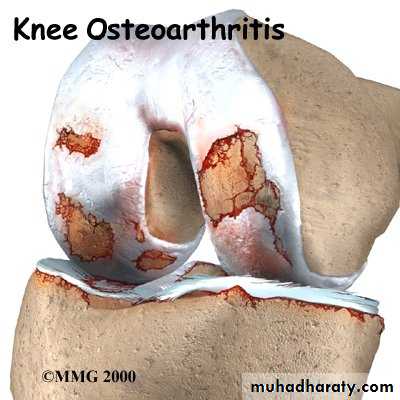
ARTHRITISPyogenic arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Tuberculous arthritis
Osteoarthritis
Haemophilic arthritis
Neuropathic arthritis
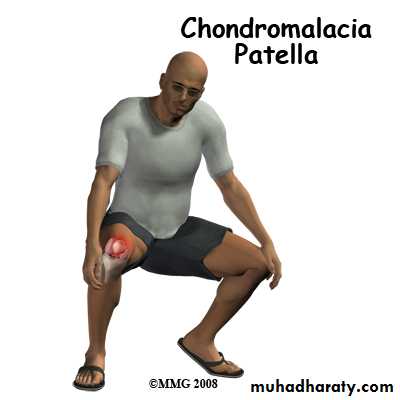
Chondromalacia of the patella
69
70
71
72
MECHANICAL DISORDERS
Tears of the menisciCysts of the menisci
Discoid lateral meniscus
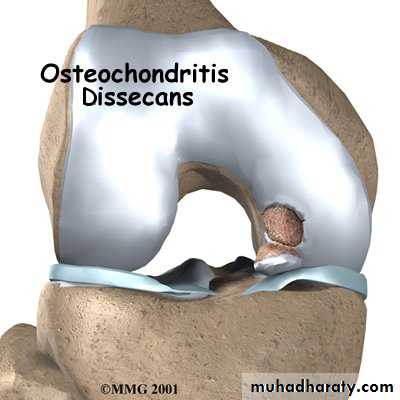
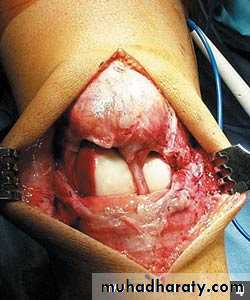
Osteochondritis dissecans
Intra-articular loose bodies
Recurrent dislocation of the patella
Habitual dislocation of the patella
73
74
http://www.carletonsportsmed.com/Libraria_medicus/PF_patella_dislocation.JPG
Patellar dislocation
75
EXTRA-ARTICULAR DISORDERS IN THE REGIONOF THE KNEE
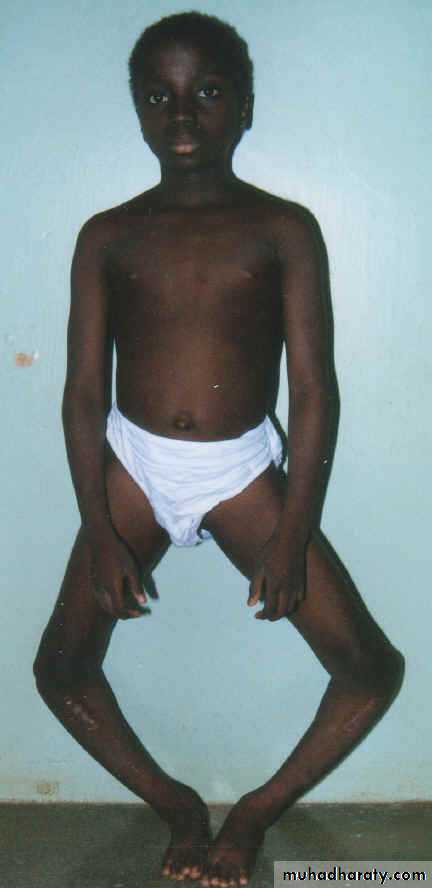
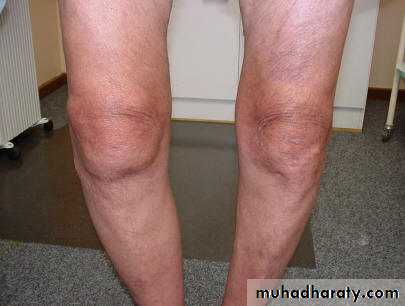
DEFORMITIESGenu varum
Genu valgum
76
77
INJURIES
Rupture of the quadriceps apparatusOsgoodSchlatter's disease
7879
80
81
82
83
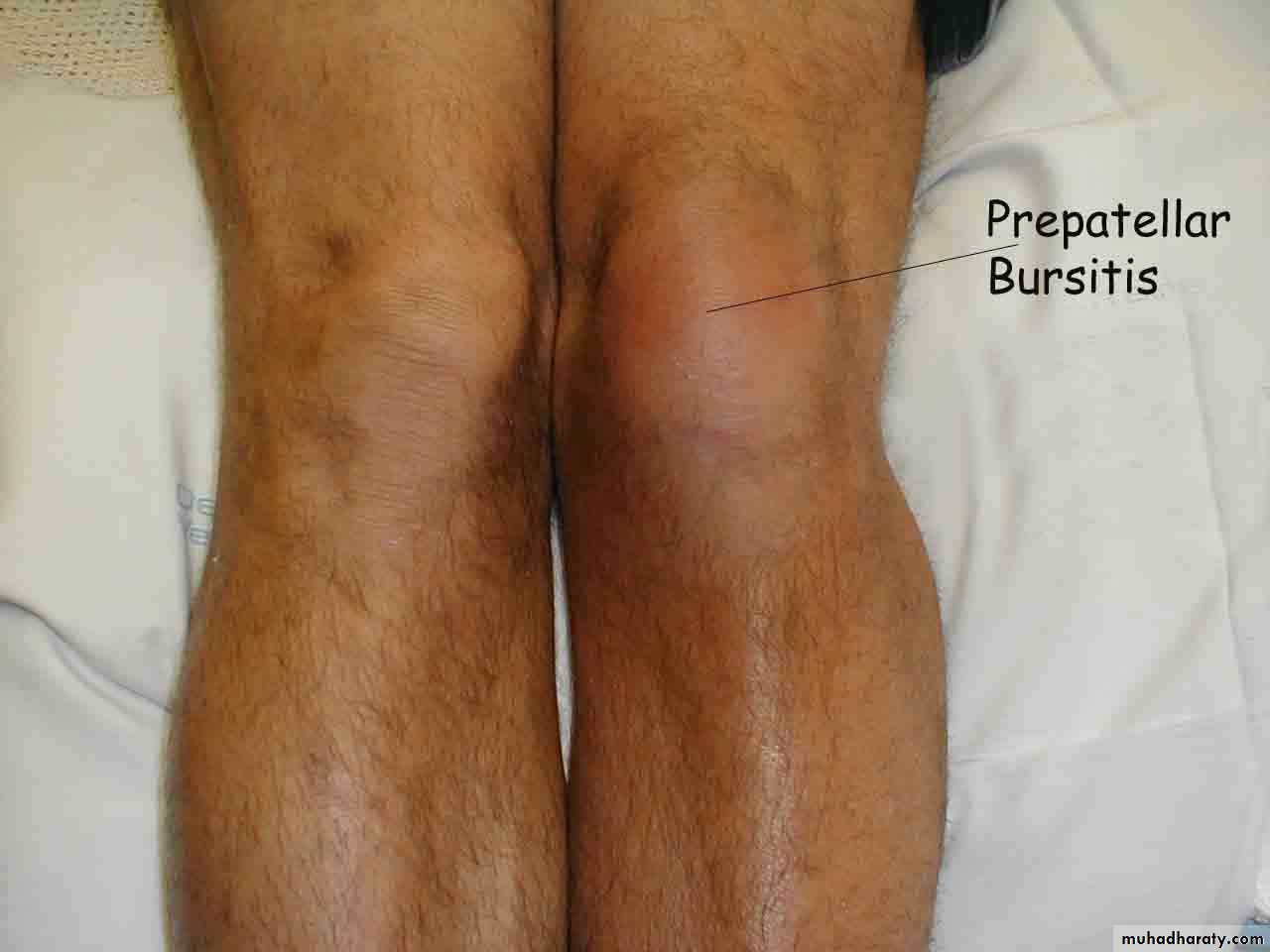
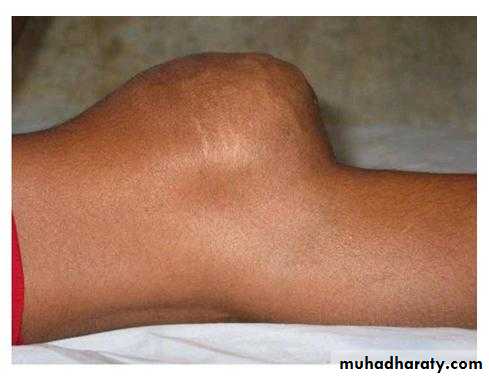
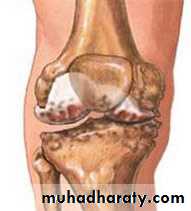
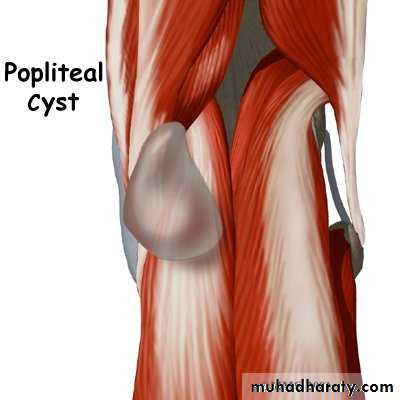
CYSTIC SWELLINGS
Prepatellar bursitisPopliteal cysts
84
85
POST-TRA UMA TIC OSSIFICATION
Pellegrini-Stieda's disease of the medial femoralcondyle
86