بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
1The shoulder 'joint' in fact comprises three components-
the gleno-humeral joint orshoulder joint proper,
acromio-clavicular joint,and
the sterno-clavicular
2
SYMPTOMS
PainStiffness
Deformity
Swelling
3
How to Start
• IPEEP• INTRODUCE.
• PERMISSION.
• EXPLANTION.
• EXPOSURE.
• POSITION.
4
The Apley System
All joint examinations follow this system:Look
Feel
Move : Active then Passive
Special Tests
Radiograpgy.
5
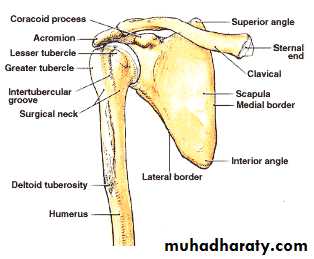
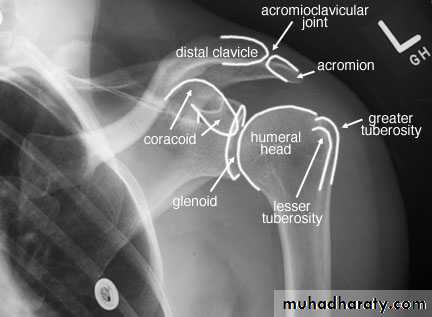
Radiographic Anatomy
6
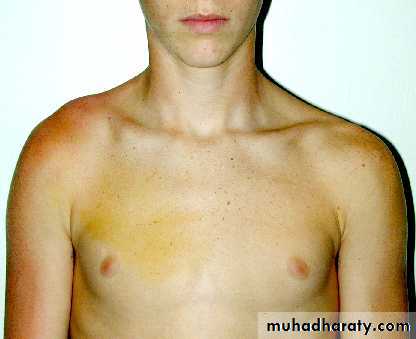
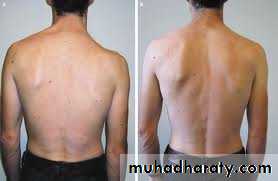
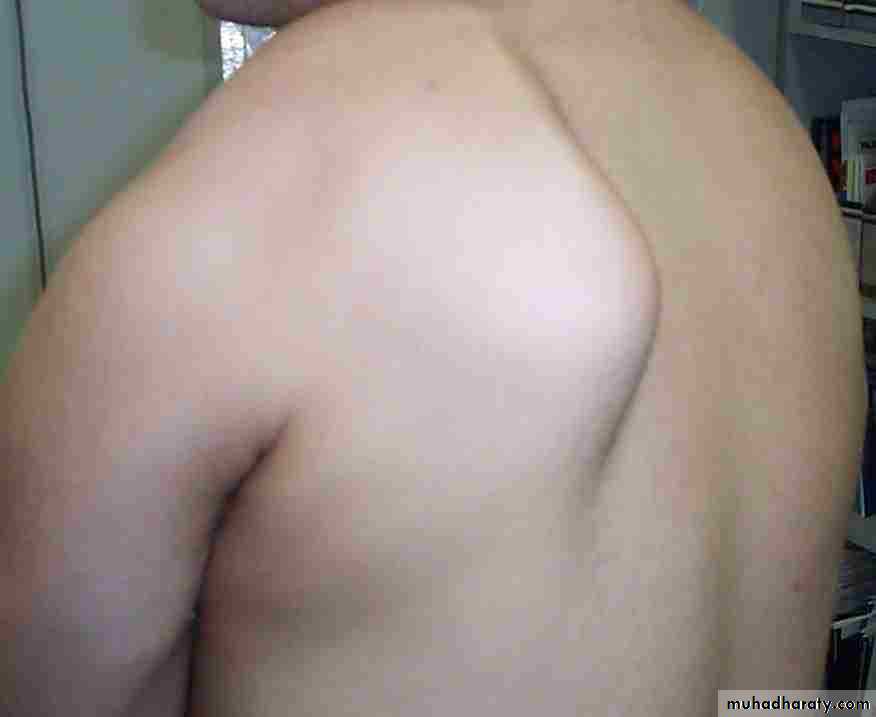
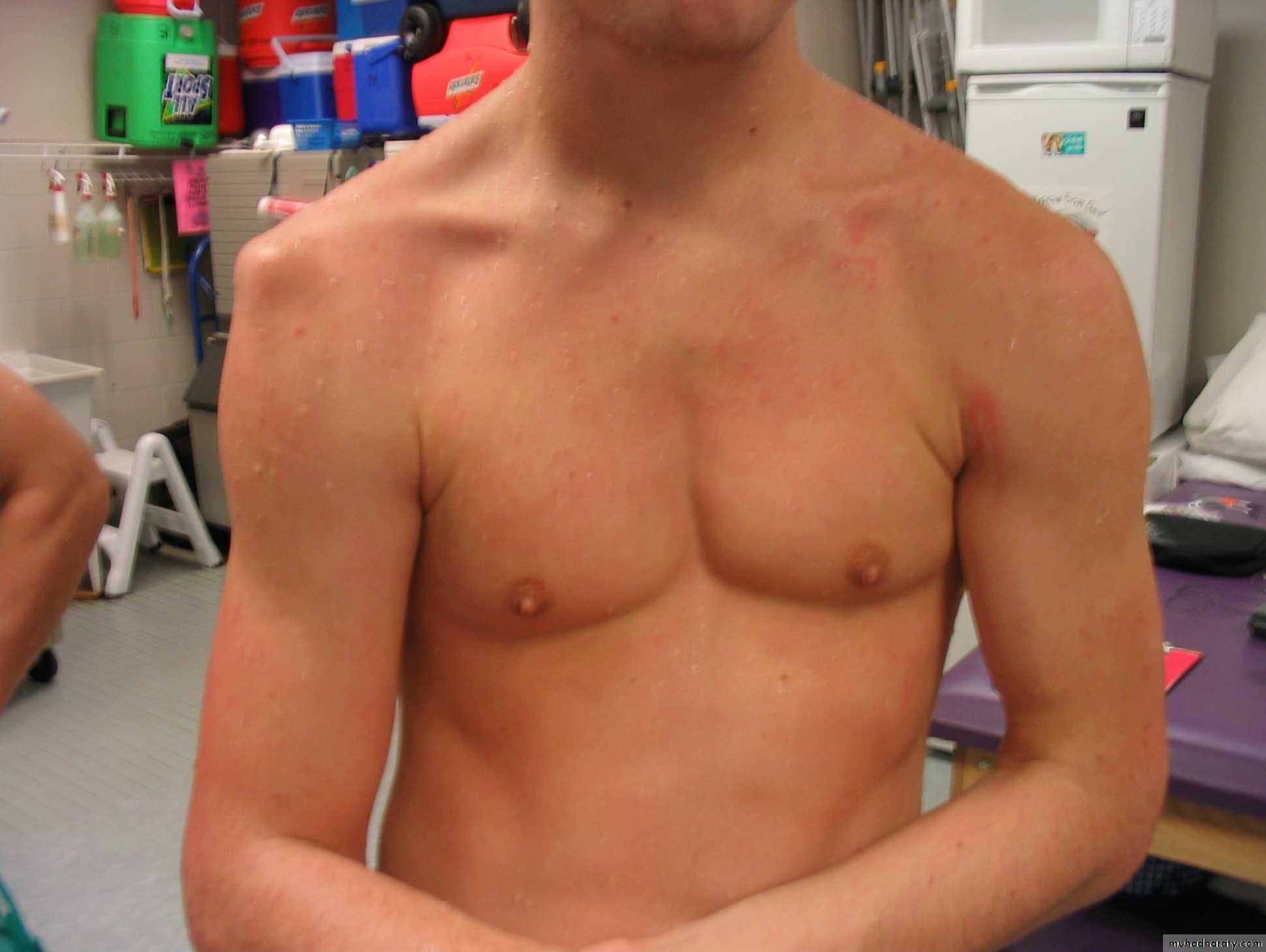
Inspection
Bone contours and alignmentSoft-tissue contours
Colour and texture of skinScars or sin uses
7
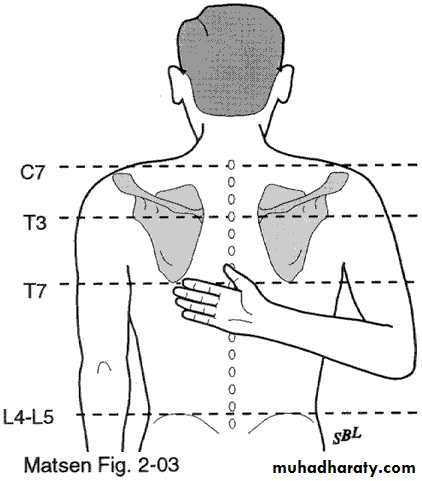
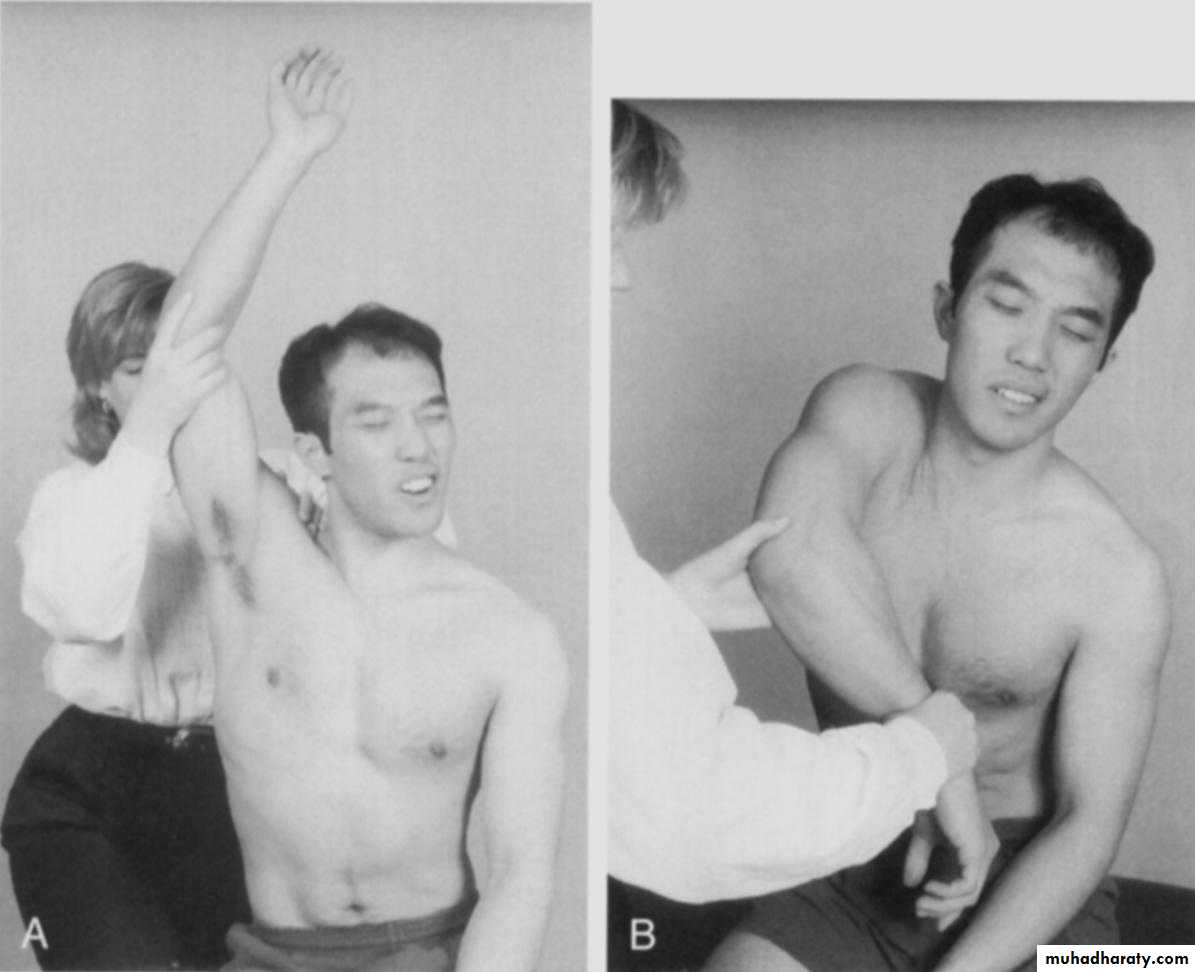
Inspection(look)
Front & back
Height of shoulder and scapulae
Muscle atrophy,asymmetry
8
9
10
11
12
Palpation
Skin temperatureBone contours
Soft-tissue contours
Local tenderness
13
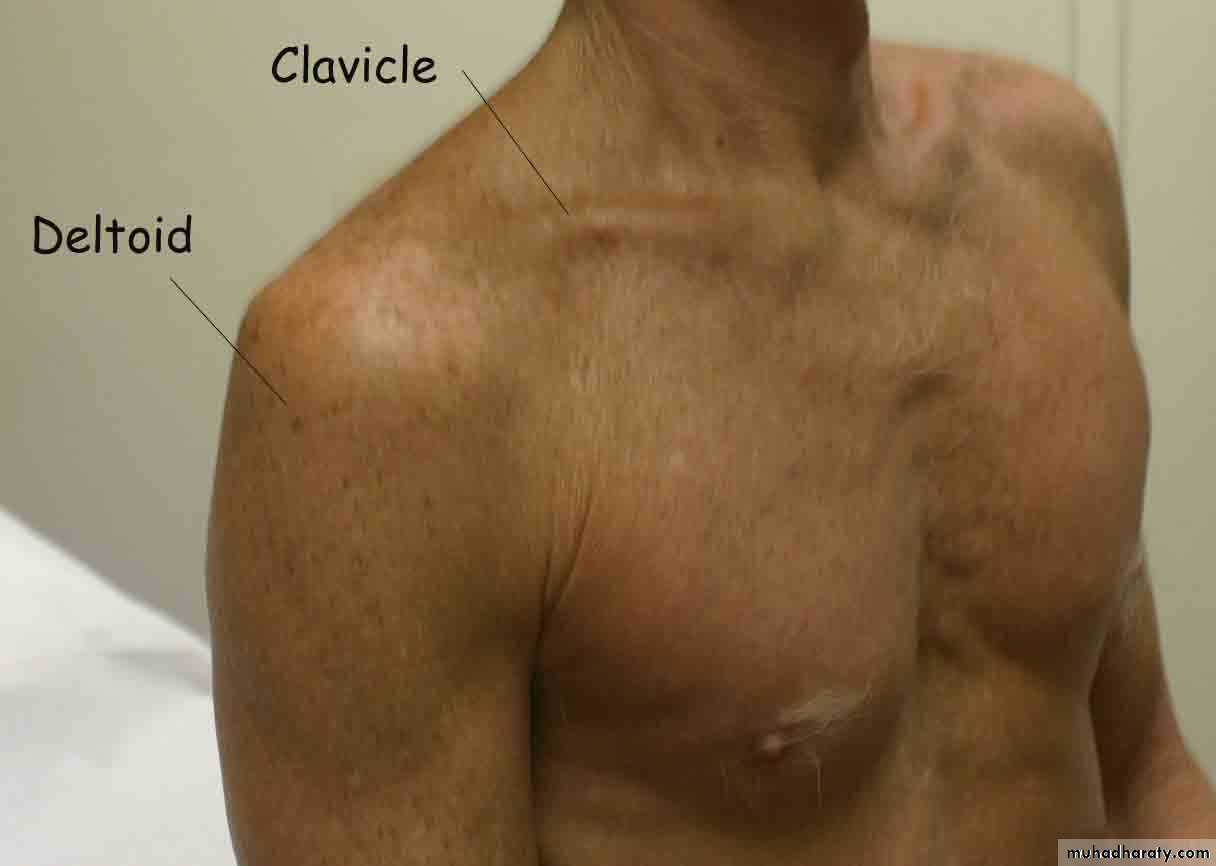
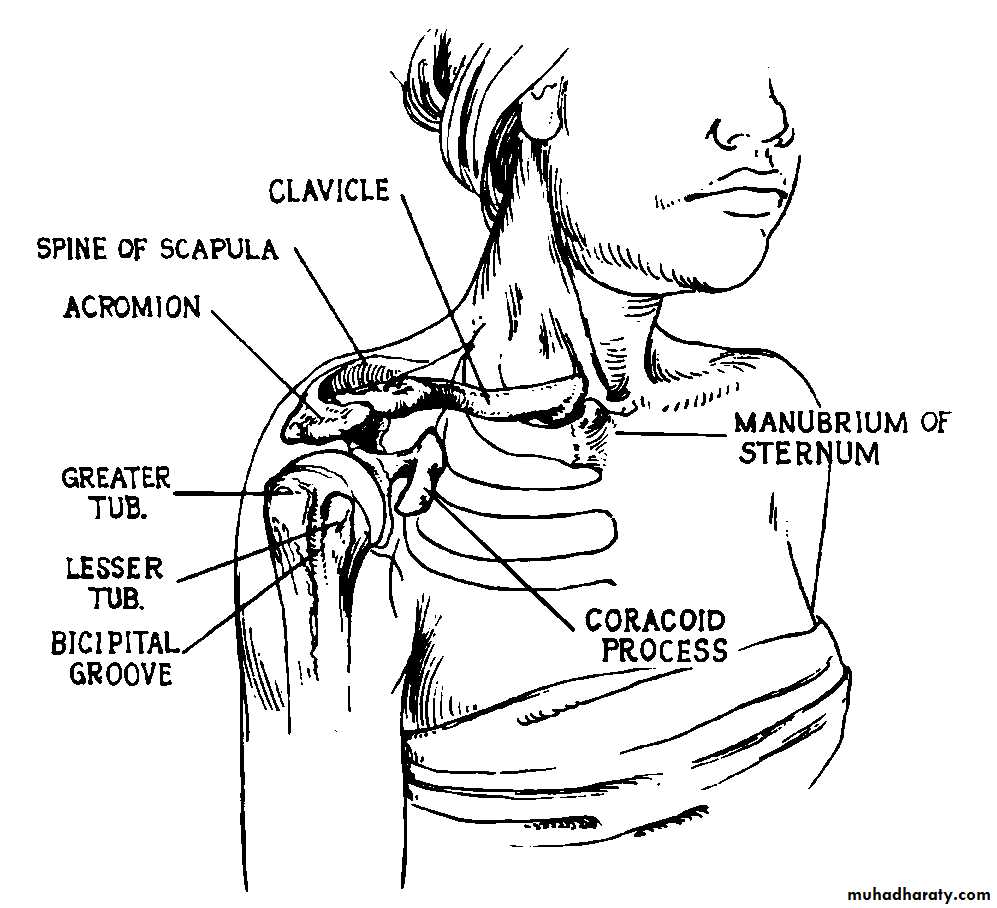
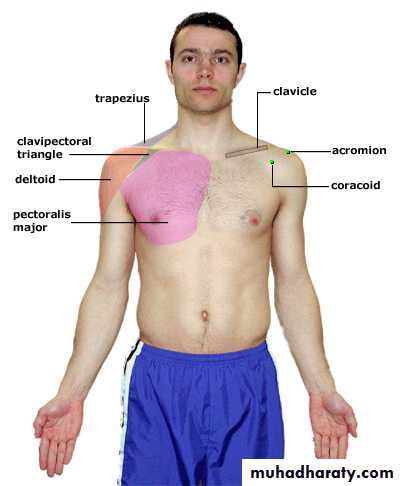
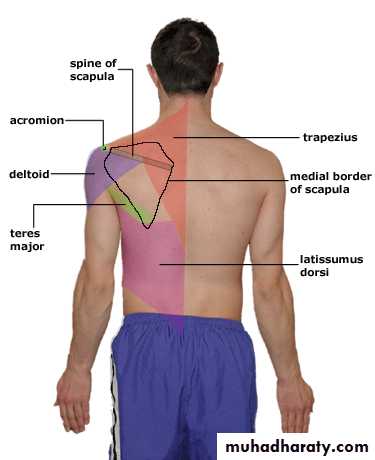
Palpation
Surface Anatomy (Anterior)
Clavicle
SC JointAcromion process
AC Joint
Deltoid
Coracoid process
Pectoralis major
Trapezius
Biceps (long head)
AC joint
SC jointbiceps
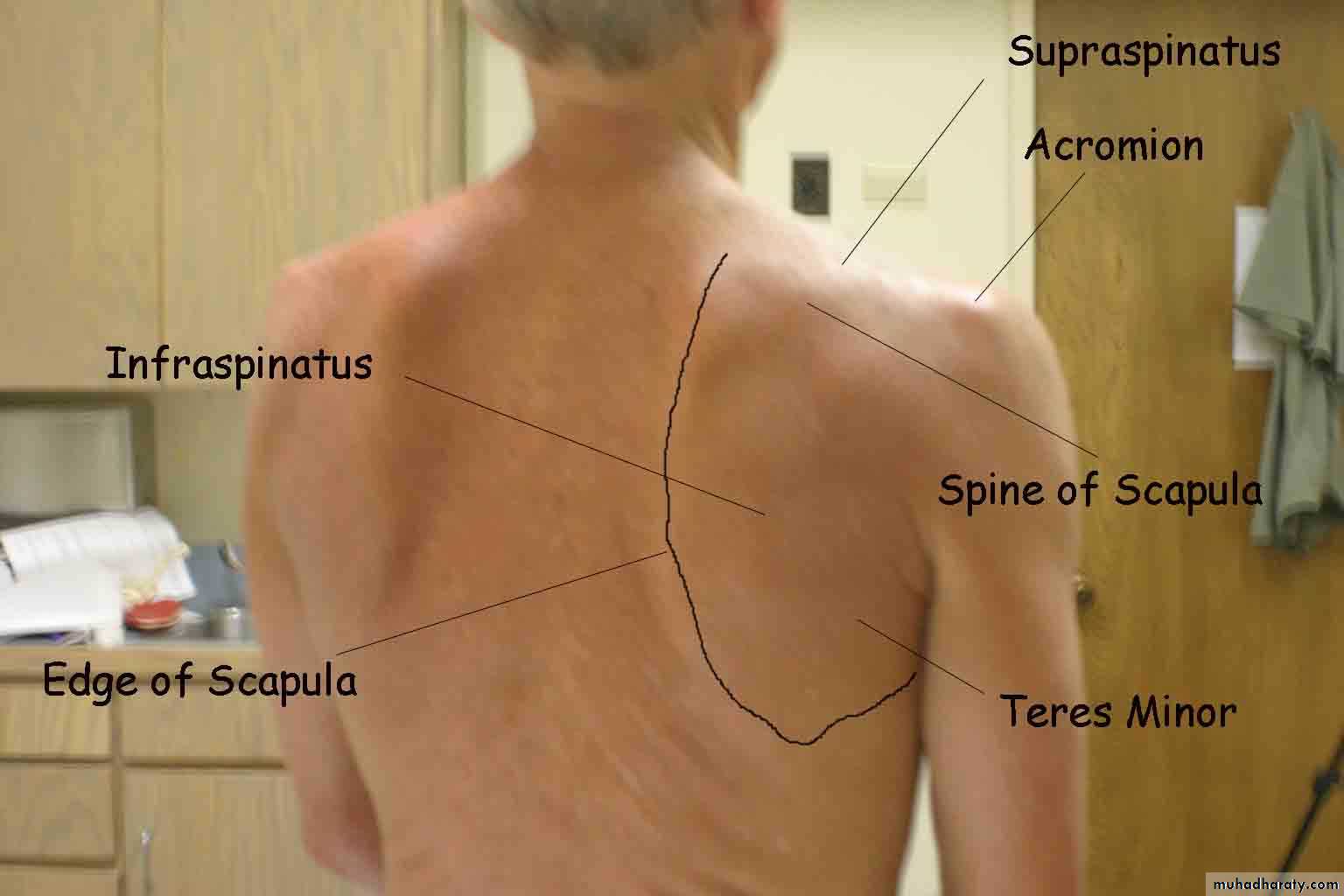
14Palpation
Surface Anatomy (Posterior)
Scapular spine
Acromion processSupraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Deltoid
Trapezius
Latissumus dorsi
Scapula
Inferior angle
Medial border
Supraspinatus
InfraspinatusInferior angle of scapula
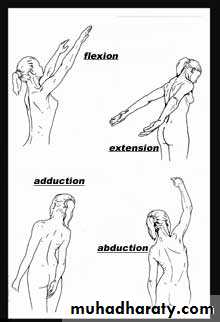
15Movements
Distinguish between gleno-humeral Movement
and
Scapular movement during
16
abduction,
flexion,extension,
lateral rotation,
and medial rotation
17
Pain on movement
? Muscle spasm? Crepitation on movement
18
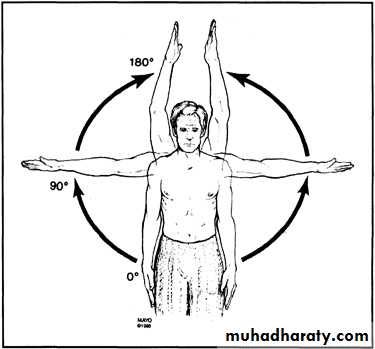
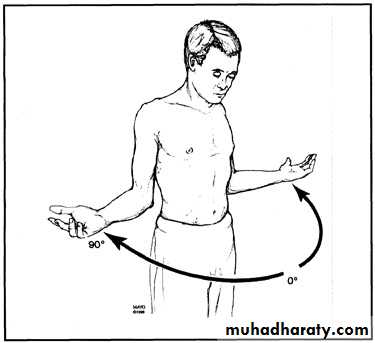
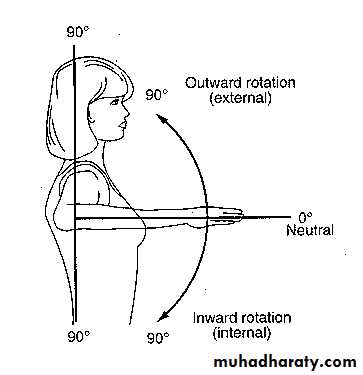
Range of Motion
Forward flexion:160 - 180°
Extension: 40 - 60°
Abduction: 180◦
Adduction: 45 °Internal rotation:
60 - 90 °External rotation:
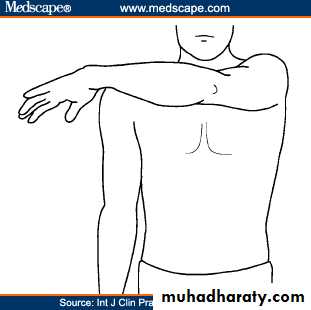
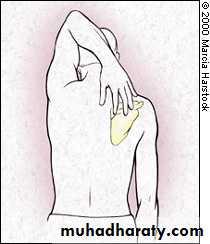
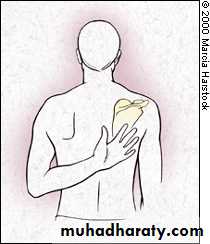
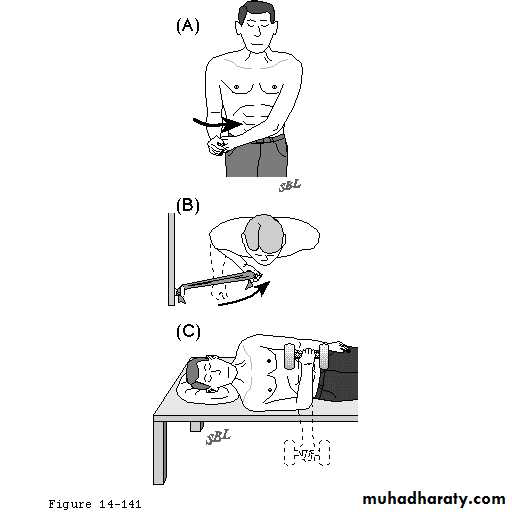
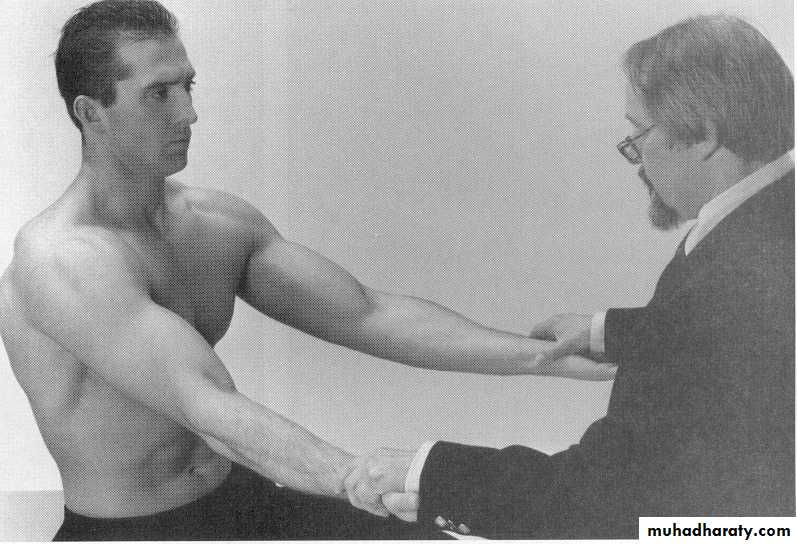
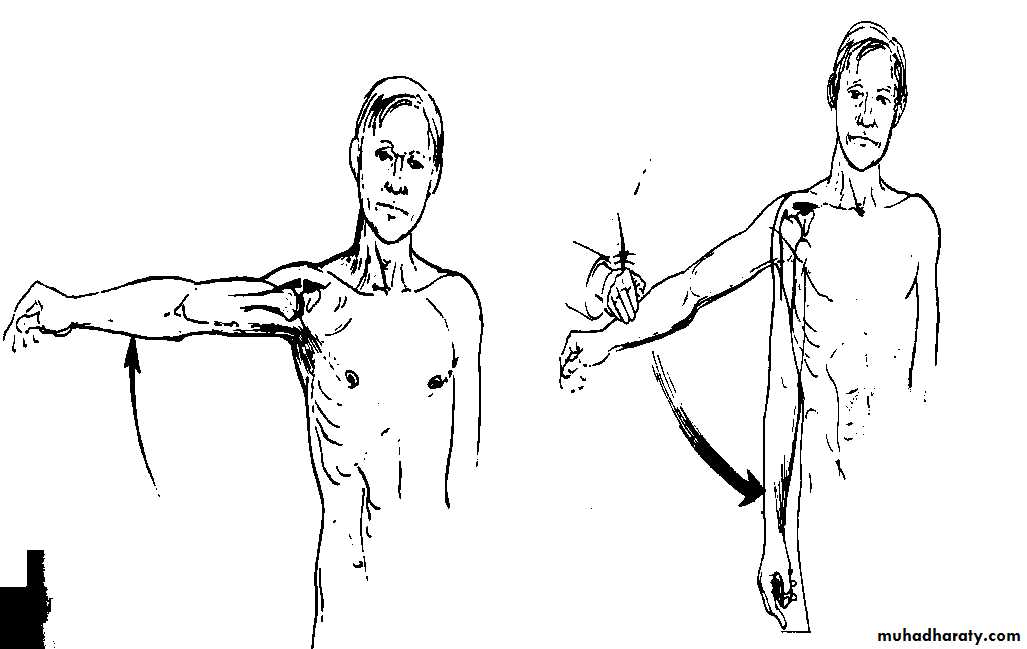
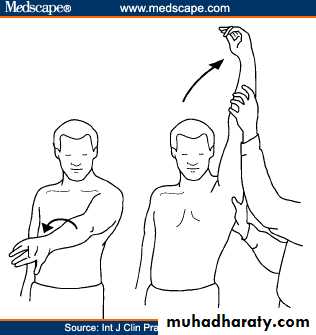
80 - 90 °Apley Scratch Test
1920
21
Power
Cervico-scapular and thoraco-scapular
muscles
(controlling scapular movement)-
Elevation of scapula,
retraction of scapula,
abduction-
rotation of scapula.
22
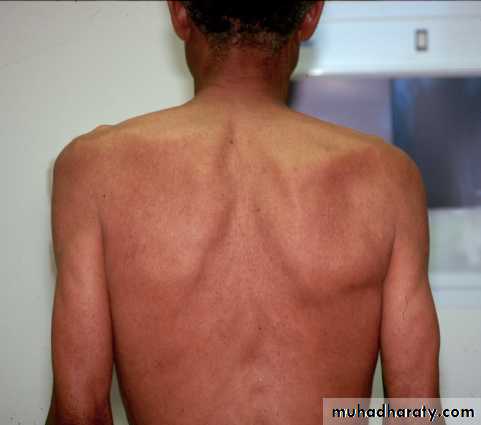
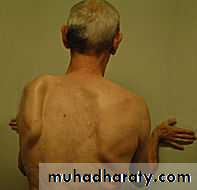
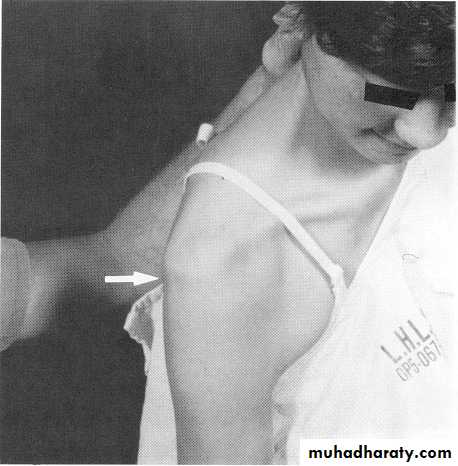
Scapular dyskinesis (Scapulothoracic dysfuntion)
Compare scapular motion through ROM on both sidesWall push-ups
SymmetricalSmooth
No or minimal winging
23
S capulo-humeral muscles (controlling
movement at gleno-humeral joint)-Abduction, adduction,
flexion, extension,
lateral rotation,
medial rotation
24
Acromio-clavicular joint
Examine for swelling,increased
warmth, tenderness,
movement, and stability
25
Sterno-clavicular joint
Examine for swelling,increased warmth, tenderness,
Movement.
and stability
26Grade strength on 0 → 5 scale
0: no contraction1: muscle flicker; no movement
2: motion, but not against gravity
3: motion against gravity, but not resistance
4: motion against resistance
5: normal strength
27
Strength Testing
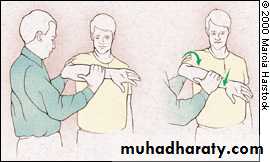
External rotationTests RTC muscles that ER the shoulder
InfraspinatusTeres minor
Arms at the sides
Elbows flexed to 90 degrees
Externally rotates arms against resistance28
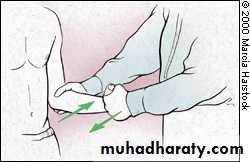
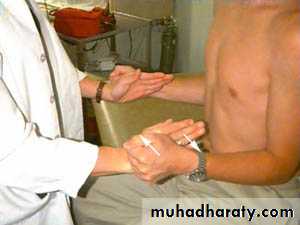
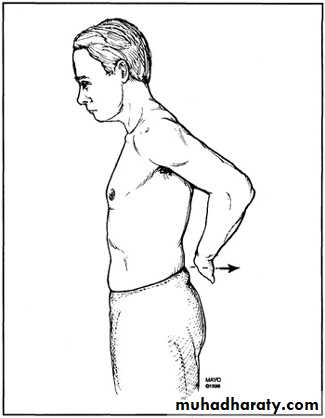
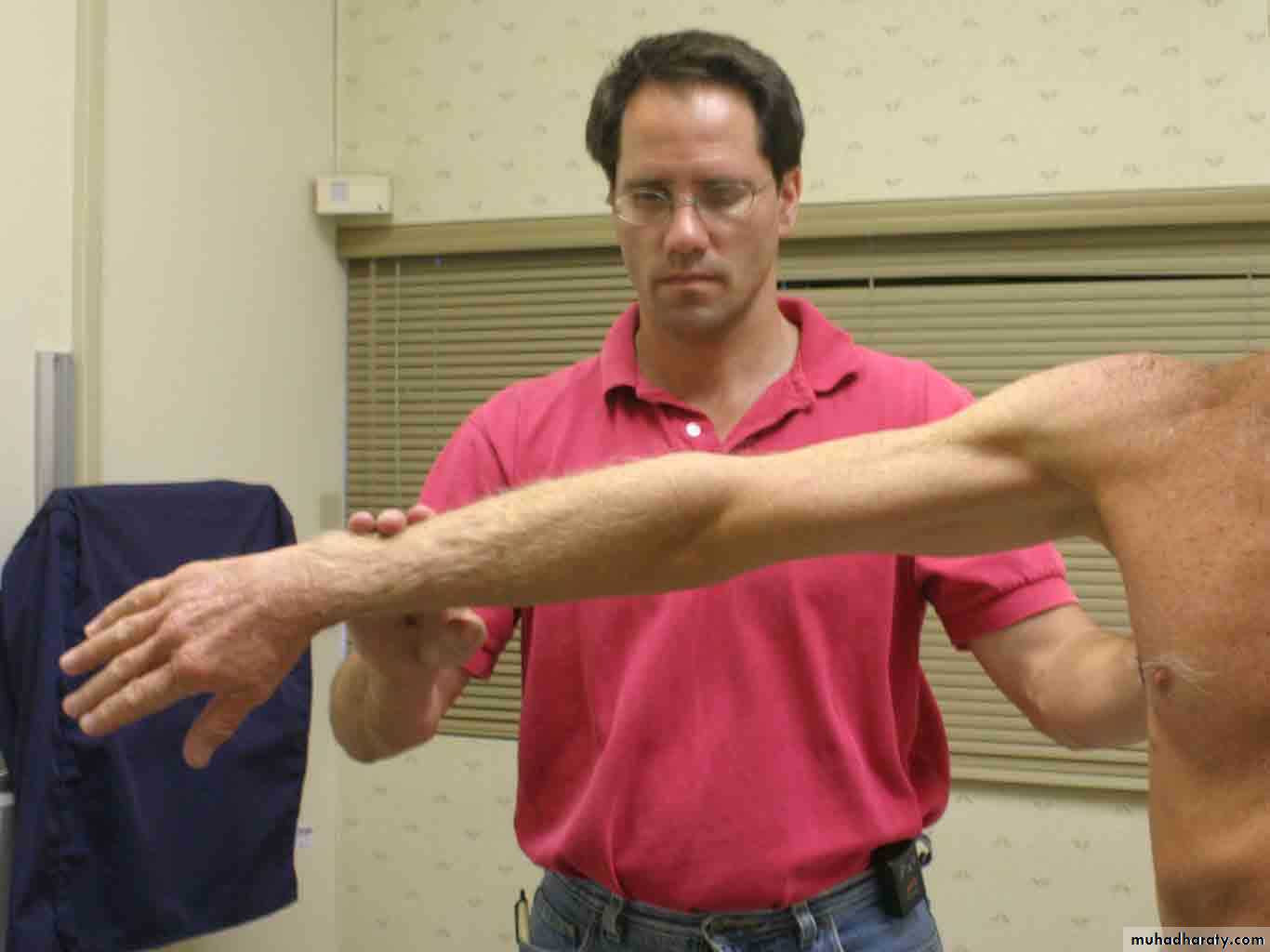
Strength Testing
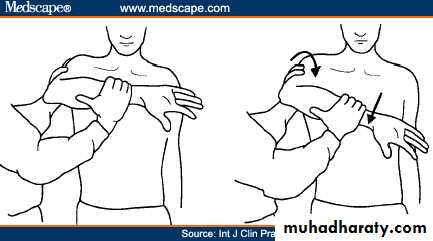
Internal rotationTests RTC muscle that IR the shoulder
SubscapularisArms at the sides
Elbows flexed to 90 degreesInternally rotates arms against resistance
Subscapularis Lift-Off Test
Other techniques
29
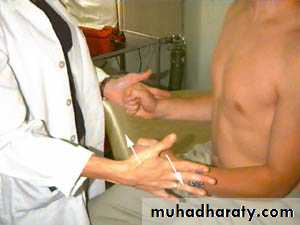
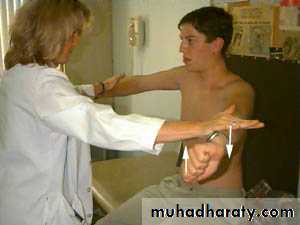
Strength Testing
Supraspinatus“Empty can" test
Jobe’s TestTests Supraspinatus
Attempt to isolate from deltoidPositioned sitting
Arms straight outElbows locked straight
Thumbs down
Arm at 30 degrees
(in scapular plane)
Attempts to elevate arms against resistance
30
SENSORY EXAMINATION
3132
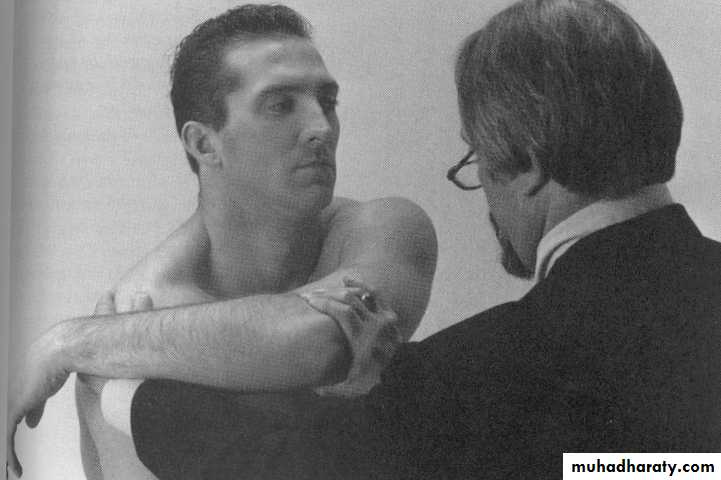
Impingement Signs
Hawkins
Neer33
Speed’s TestBiceps Tendinopathy
Long head of biceps tendonitis
Fwd flex to 90°, abd 10°, full supination
Apply downward force to distal arm
Pain = (+) test
weakness w/o pain = muscle weakness or rupture
34
Sulcus Sign
Inferior instabilityArm relaxed in neutral position, pull downward at elbow
(+) test = sulcus at infra-acromial area
compare to unaffected side
35
Instability: Apprehension Test
Anterior instabilityShoulder abducted to 90°
Slight stress to humeral head directed in anterior direction
While externally rotating shoulder
Positive test is apprehension due to feeling of instability or impending dislocation
Beware if false positives36
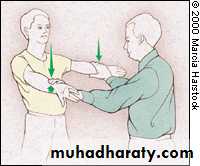
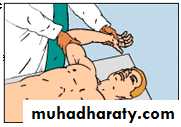
Drop Arm TestSuggestive of Rotator Cuff Tear
Passive abduction to 90°Instruct patient to slowly lower arm
At 90° abducted arm will suddenly drop, may need to add slight pressure
(+) drop = (+) test
37
Cross-Arm Adduction Test
AC joint pathology
Arm flexed to 90°
Hyperadduct arm across body as far as possible
Pain in AC = (+) test
38
EXAMINATION OF POTENTIAL EXTRINSIC SOURCESOF SHOULDER SYMPTOMS
The investigation should include:I) the neck,with the brachial plexus;
2) the thorax, with special reference to the heart and pleura; and
3) the abdomen, for subdiaphragmatic lesions.
39
GENERAL EXAMINATION
3.General survey of other parts of the body.
Referred pain in the shoulder region. The pain referred from an irritative lesion of the brachial plexus often extends from the base of the neck,
over the top of the shoulder,
and thence into the arm.
40
CLASSIFICATION OF DISORDERS OF THE SHOULDER REGIONDISORDERS OF THE SHOULDER (GLENO-HUMERAL) JOINT
41
ARTHRITIS
Pyogenic arthritisRheumatoid arthritis
Tuberculous arthritis
Osteoarthritis
42
MECHANICAL DERANGEMENTS
Recurrent dislocationComplete tear of the tendinous cuff
Painful arc syndrome
(including calcified deposit in tendon)
Rupture of the long tendon of biceps
43
MISCELLANEOUS
Tenosynovitis of the long tendon of biceps.'Frozen' shoulder
44
DISORDERS OF THE ACROMIO-CLAVICULAR j01NT
OsteoarthritisPersistent dislocation or subluxation
45
DISORDERS OF THE STERNO-CLAVICULAR JOINT
ArthritisPersistent or recurrent dislocation
46
Examples for shoulder joint problems
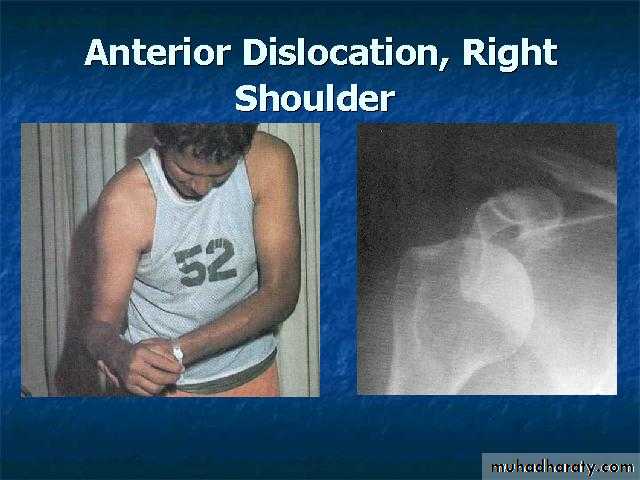
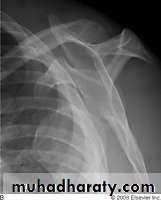
47Shoulder Dislocation/Anterior Instability
Humeral head dislocates from glenoid fossaAlmost always anterior (95%)
Usually traumatic with injury to capsule-labrum complex
48
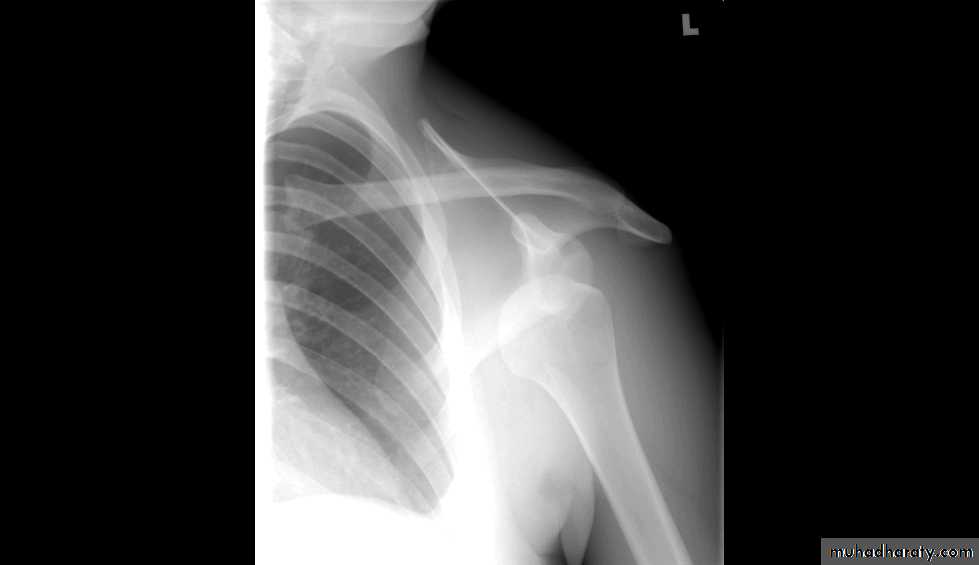
X RAYS
DIAGNOSIS???
49
Impingement Signs
• Neer’s Sign• Arm fully pronated and placed in forced flexion
• Trying to impinge subacromial structures with humeral head
• Pain is positive test
•
50
Impingement Signs
• Hawkin’s Sign• Arm is forward elevated to 90 degrees, then forcibly internally rotated
• Trying to impinge subacromial structures with humeral head
• Pain is positive test
51
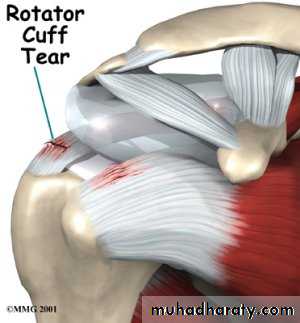
Rotator Cuff Tear
Partial thickness tearFull (Complete) thickness tear
May be due to:
ImpingementDegeneration
Overuse
Trauma
Partial tears
Conservative
Complete tears
Surgery52