مادة سنية / د . هالة (م 11)
ثاني اسنان موصل10 / 3 / 2016
مادة سنية / د . هالة (م 11)
ثاني اسنان موصل10 / 3 / 2016
MAXILLOFACIAL MATERIALS
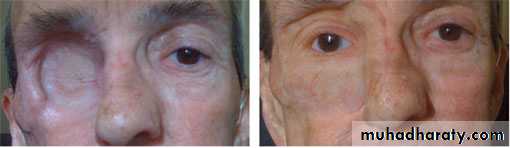
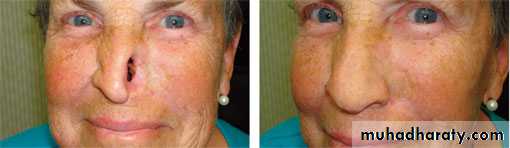
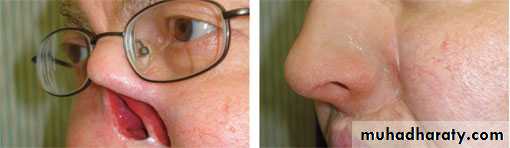
Maxillofacial materials (mfm)are used to correct facial defects resulting from cancer, surgery, accident or even congenital deformities. Nose, eye, orbit, or any other missed part of the head may be replaced by maxillofacial prostheses.Maxillofacial materials are difficult to fabricate and have relatively short life of six months to several years in service.
Requirements of Maxillofacial materials
1. retain softness throughout the temperature change.
2. easy to clean.
3. Capable of adhering to human tissue.
4. Physically and mechanically similar to the replaced tissue.
5. Compatible with human tissue
6. Coloring can be done both intrinsically and extrinsically to match the skin tone .
7. have color stability
8. resist staining.
9. resist tearing .
10. Polymerizing process of the maxillofacial material should be simple, sensitivity to polymerizing processing should be nonexistent or negligible, and materials required for fabrication and processing techniques should be used in a common basis in the dental settings.
11. The material should be capable of serving the patient at least one year while maintaining those properties.
Note:
There is no a recent material that fills full all these requirements. However, the silicone rubber materials may have the best overall mfm requirements.
TYPES OF MAXILLOFACIAL MATERIALS
Poly methylmethacrylate (PMMA)
Plasticized poly vinyl chloride
Poly urethane
Heat vulcanized silicone
Room-temperature vulcanized silicone
TYPES OF MAXILLOFACIAL MATERIALS
Poly methylmethacrylate (PMMA) :PMMA acrylic resin was commonly used for maxillofacial prostheses, and it is still used occasionally to make artificial facial parts like orbits. When properly pigmented, these prostheses can look quite realistic.
The main disadvantages are that the acrylic is hard and heavy, does not flex when the face moves, and does not have the feel of skin.
Types of acrylic resin used for this purposes:
1. heat activated resin.
2. chemically activated resin.
3. light activated resin.
A stone mould is used.
Plasticized poly vinyl chloride:
It had been used widely for construction of maxillofacial prostheses, but it has been replaced by newer materials with superior properties. It is a rigid plastic but plasticizer is added to produce elastomer at room temperature.
A cross linking agent is added to strengthen the material, An ultraviolet stabilizer is added for color stability.
Ferrous pigment can be incorporated to give longest life and best esthetic result, Cream conditioner is recommended to be applied nightly to prostheses made from this material to prolong its life.
This material is supplied as a finely divided plasticized poly vinyl chloride particles suspended in a solvent. When the fluid material is heated, the plasticized poly vinyl chloride will dissolve in the solvent. When it is cooled, an elastic solid is formed. The processing temperature is 150 ͦ C.
A metal mould is used.
Poly urethane:
1, This material is prepared by a direct addition of di-isocyanate to polyol in the presence of an initiator.
2.The processing temperature is 100 ͦ C.
3.This reaction must be carried in a dry atmosphere, otherwise carbon dioxide is formed and a porous elastomer is produced.
The di-isocyanate is very toxic and must be handled with care. 4.
A stone mould is used. 5.
Heat vulcanized silicone:
It is a poly dimethyl vinyl seloxane copolymer with an initiator and fillers.
The pigments are incorporated into the copolymer.
The copolymer is supplied as a rubbery solid with a high viscosity.
The processing temperature is 220 ͦ C.
Excellent results can be obtained with this material.
Room-temperature vulcanized silicone:
It has become popular and more often used than any other mfm because of:
1. Its good physical properties.
2. easy to be colored and processed.
3. allow the use of stone mould.