The try-in appointment
صناعةثاني اسنان موصل
4 / 4 / 2016
1
THE TRY – IN APPOINMENT :
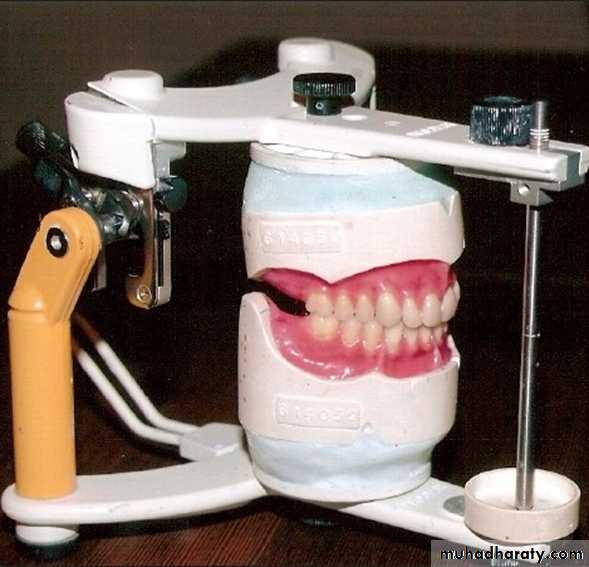
Trial fitting: the process of fitting the traildenture in patient mouth for evaluation
. A trial denture defined as preliminary arrangement of denture teeth that has been prepared for placement into the patient’s mouth to evaluate aesthetics and maxillo – mandibular relationship.
Various aspects of try in:
Extraoral examination of the trial dentures.
Intraoral examination of the trial dentures.
2(Objectives (What to look at in the Try-In stage
1. Accuracy of the casts and dentures on articulator.2. Checking the Jaw relation records: - at
A.Occlusion.
b.Vertical dimension.
c.Centric relation.
D.Eccentric occlusion
3. Checking the Esthetic
4 Checking the Speech.
5.Registering the protrusive record.
3
CHECKING THE TRIAL CASTS ON THE ARTICULATOR Extra oral examination
1.The incisal pin of the articulator .2.The trial denture bases lie properly on
their cast
3.The teeth meet evenly in centric.
4.The casts should be in a good shape
and neat(free from wax)
5.Trial base should be:
A. stable on their casts .
B. No sharp edges .
C. No touch between the upper and lower bases and between the bases and the opposite casts
6.Checking the teeth setting.
4
Intraoral Examination Of The Trial Dentures
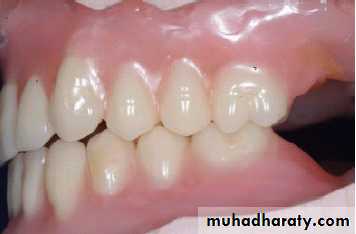
Checking denture base extension:The labial and buccal extension marked overextension of the flanges, will stretch the sulcus tissues and when denture is inserted, leads to immediate denture displacement after its seating.
Checking the upper and lower dentures together
It is usually advisable to insert the lower trial denture first and then the upper because there is less chance of having the upper denture drop down.
Labial frenum checked to see that it is absolutely free, so relation of the lip to the teeth can be observed
VDR & VDO must be evaluated by
Amount of inter occlusal distance when the mandible is in
rest position free way space (should be around 2- 4mm)
5
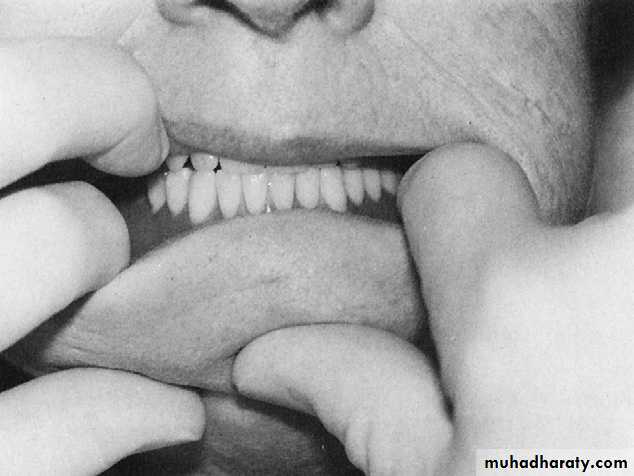
Occlusion
1.Direct the patient to make contact with his teeth lightly in centric occlusion. This should coincide with the centric relation.2. Look for any tilting movement or rocking of either dentures due to premature contact. If there is movement, its cause must be isolated with the aid of arrticulating paper. In most cases it is possible to remove one or two interfering teeth or readjust teeth.
3. If the interference is of a great magnitude, such as Incorrect Centric, the check bite must be registered and the lower cast remounted. The teeth should then be re-set and the dentures tried in again. Repeat these trials until the intraoral occlusion exactly duplicated the articulator set-up.
4. Direct the patient to move into protrusive and lateral positions and serve for proper articulation in these positions.
6
Working side
Balancing side
Occlusion at centric
7
Aesthetic
Aesthetic With both dentures inserted,1.observe the effects of the denture form on the contours of the lips and cheeks.
2.Study the lip for relaxed closure or for excessive bulging of the area under the nose due to over-contour of the denture flanges. Corrections should be made by adding or reducing wax to the desired amount.
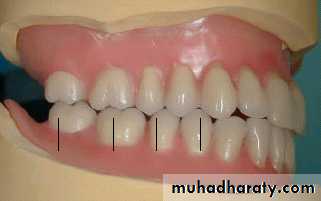
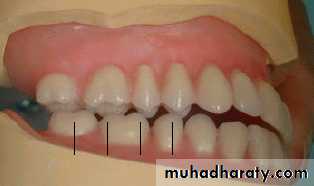
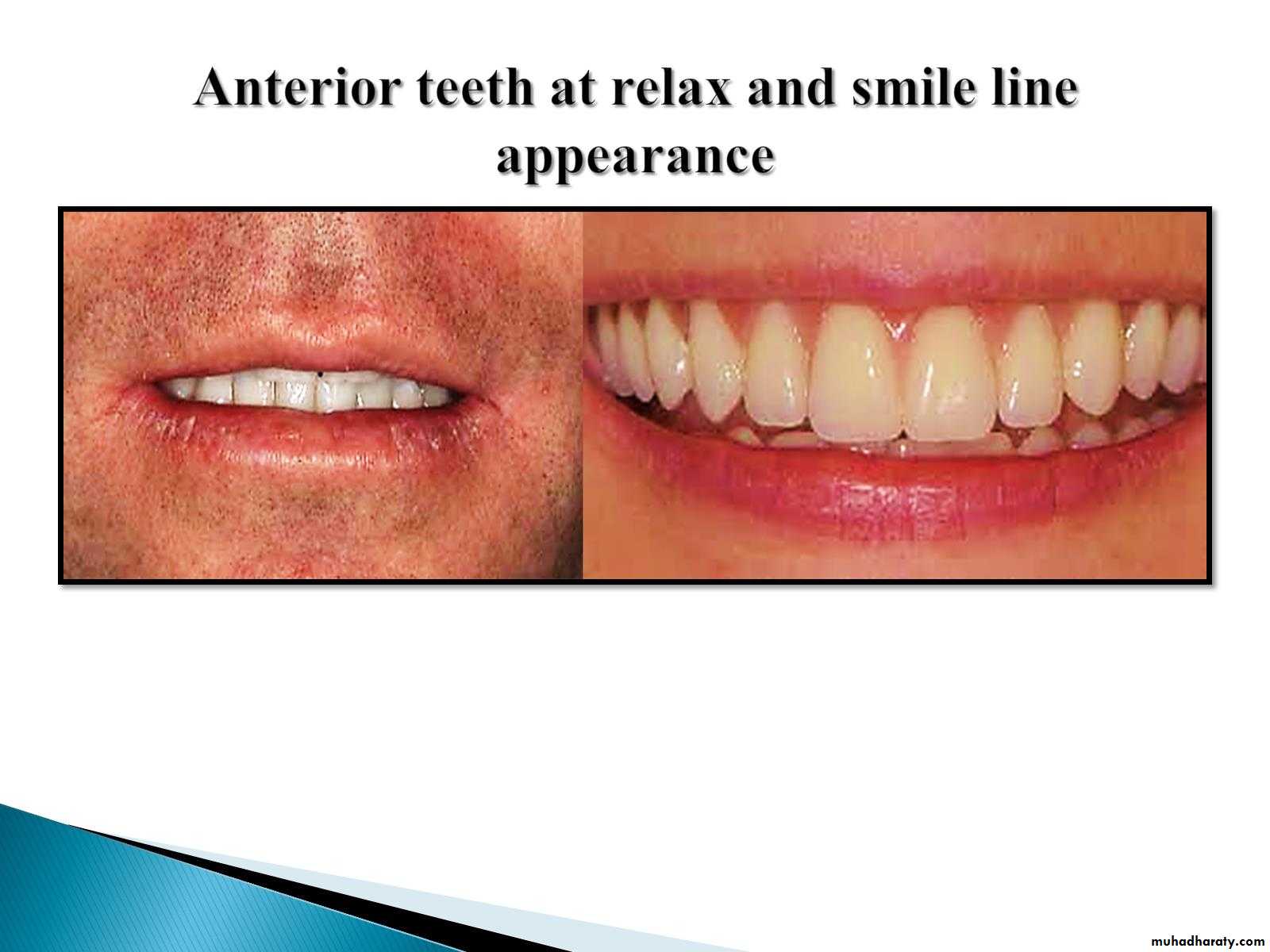
3.Direct the patient to slightly open the mouth and study the relation of the maxillary incisors to the lip. In the average patient, 1- 2 mm of tooth should be visible beyond the lower border of the relaxed lip.
4.Direct the patient to smile and study the high lip line. A minimum of denture base material should be Visible.
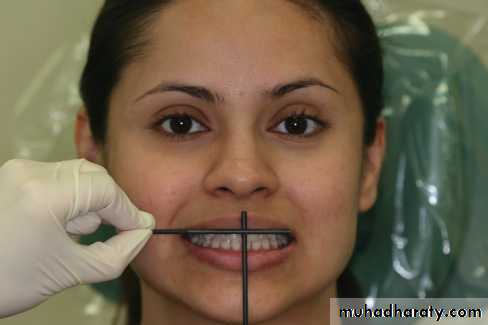
5.Check the midline with a strip of dental floss. Make any necessary changes in position of the anterior teeth.
8
9
SPEECH
Test for phonetics. especially for "S". "F" and "Th" sounds. .1.Bilabial sounds B, P, M are the sounds where the two lips contacts.
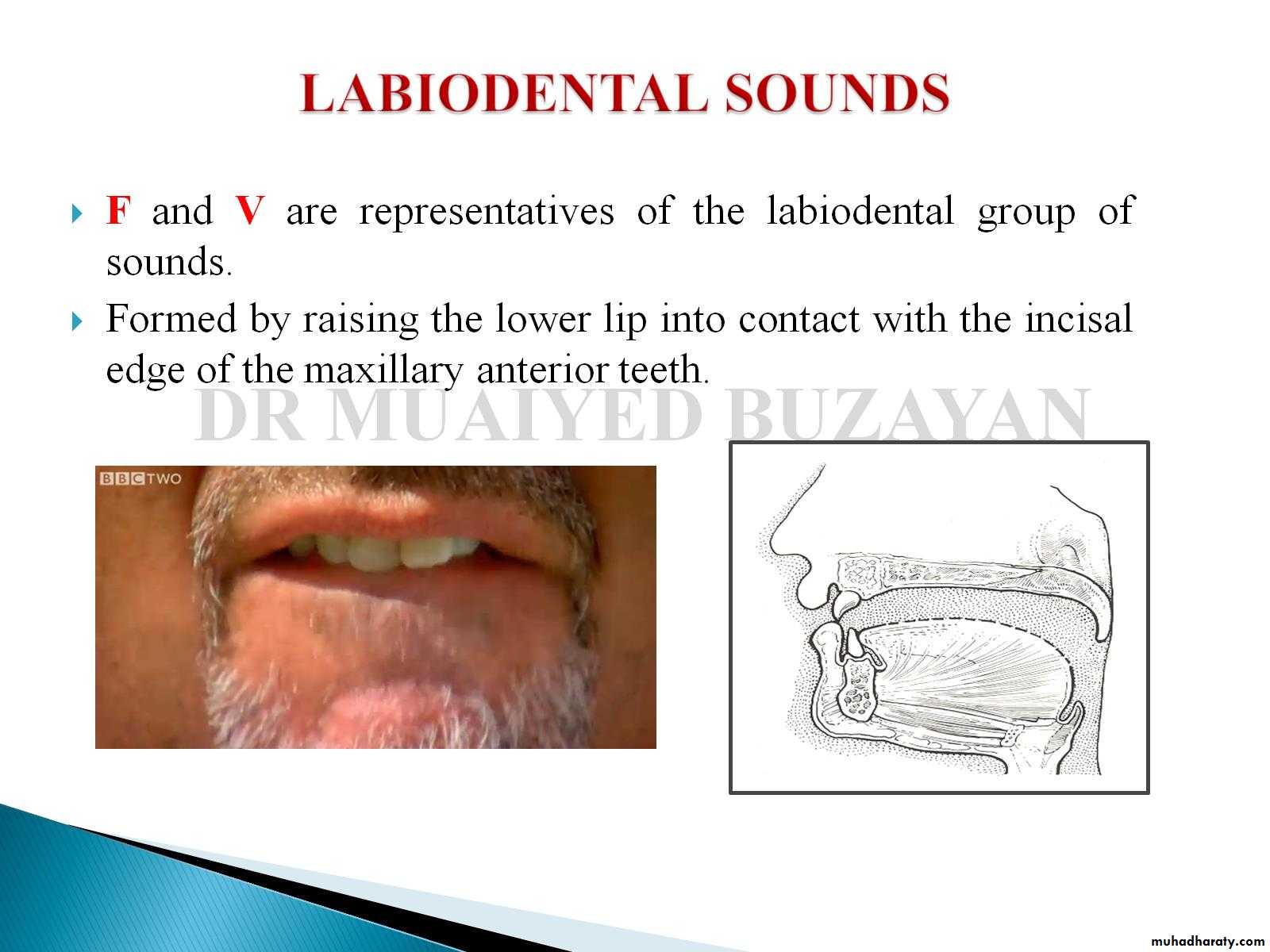
2.Labiodental sounds . F, V are the sounds shows the relationship of the incisal edges of the maxillary incisors to the lower lip.
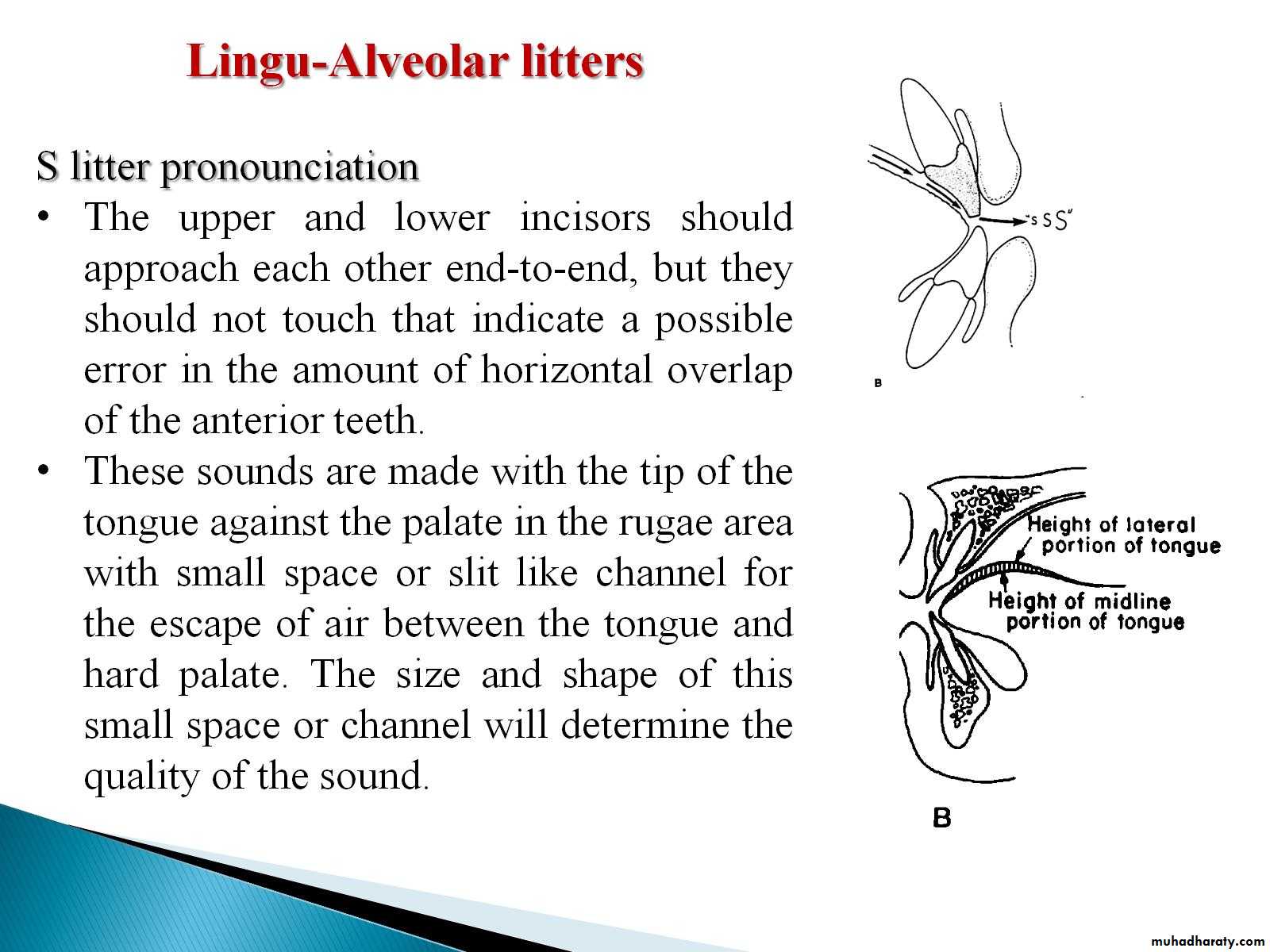
3.Alveolar and Linguoalveolar sounds T , D, S, Z, L are the sounds which makes the contact of the tip of the tongue with the most anterior part of the palate.
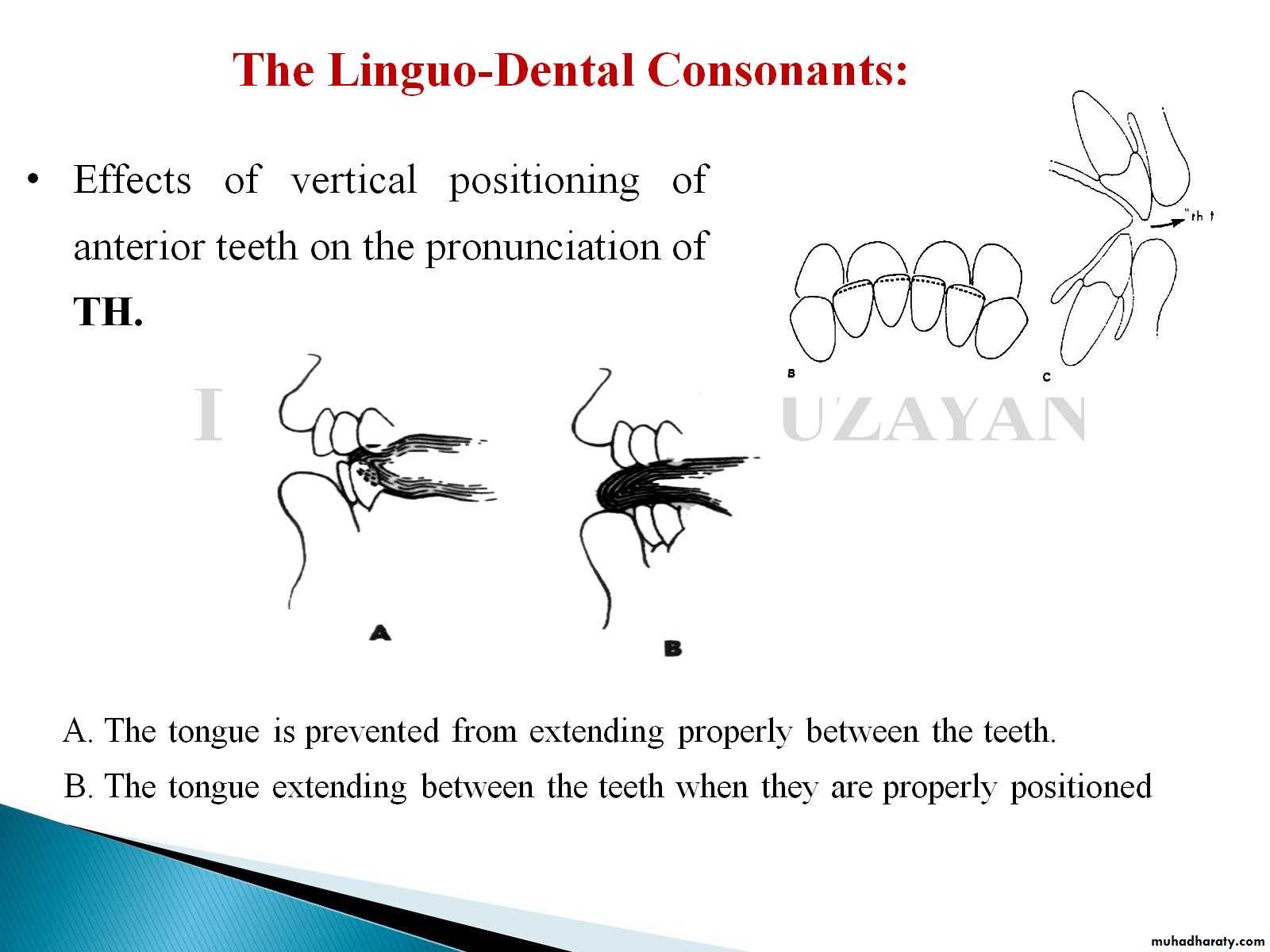
4.Linguodentalsounds Th are made with the tip of the tongue extending slightly between the upper and lower anterior teeth.
10
F and V’ are representatives of the labiodental group of sounds. Formed by raising the lower lip into contact with the incisal edge of the maxillary anterior teeth.
11
12
13
Establishing the posterior palatal seal
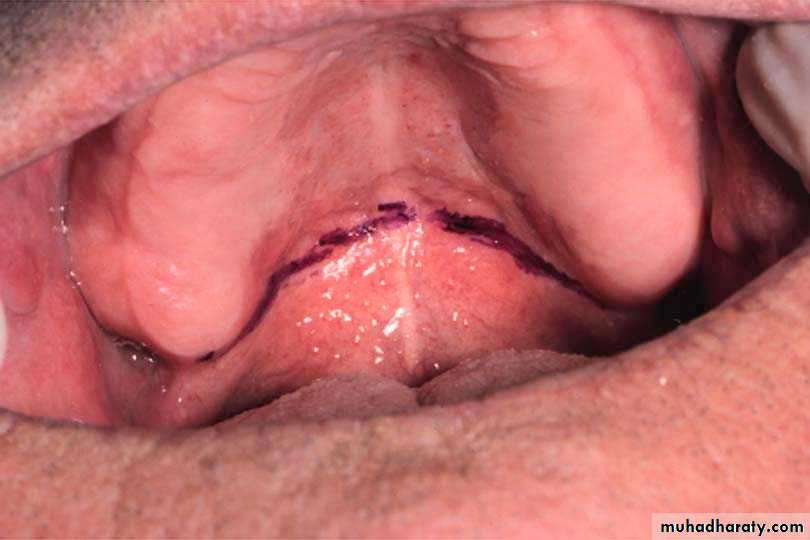
The posterior palatal seal is developed to maintain contact between the denture base and the movable soft palate during speech and swallowing.Determination of posterior palatal seal created by locating the vibrating line.
Vibrating line:its an imaginary line located at the junction of hard and soft palate. Extends from one hamular notch to the other.It passes about 2mm in front of the fovea palatina.
It is determined in patient mouth when the patient said “AH” with a color transfer applicator. The trial denture base is inserted so the indilible pencil line will be transferred from the soft palate to trial denture base, & the excess base plate is reduced to this line
The width of posterior palatal seal 1.5 mm, & 1-1.5 mm high.
14
Post dam:
butterfly depression carved in the cast to enhance posterior palatal seal(retention) of upper denture15
festooning
16Surfaces of the denture
• Occlusal surface.• Tissue surface.
• Polished surface.
•
17
The polished surface is defined by :
• The width of border of the denture according with the width of sulcus.• The buccolingual position of artificial teeth.
• The fullness that given to the wax to obtain convexity and concavity in the facial and lingual aspects.
18
• The polished surfaces, which are in contact with oral tissues ( lips, cheeks and tongue), must be smooth and have the natural details. This smoothing will be developed by waxing or festooning.Q- why we do festooning?The polished surface has an effect on:- retention.- esthetic.- feeling of patient and phonetics (because there is a relation between the tongue and the palatal part of the teeth).
19
Festooning : is process of carving the denture base to simulate the contour of the natural tissues which are being replaced by the denture.
The form of the denture bases between the teeth and the border should be shaped in such a manner as to aid retention by the mechanical directional forces of the muscles and tissues.
20
requirements
• They should duplicate the covered soft tissues as accurately as possible.• Labial and buccal fullness of the maxillary and mandibular dentures should be present.
• Notches should be provided to accommodate the mucous membrane attachment both in size and direction.
• The contour of the denture flanges should be compatible with the shape of the cheeks and lips.
• The contour of the lingual flange of the mandibular dentures should have the least possible amount of the bulk, except the border.
21
They have a scalloped appearance. The gingival margins are carved at an angle 45° to the tooth surface.
The level of the exposure depends on the age of the patient.
Older patients have more receded gums.
It is convex in shape both mesio-distally and occluso-gingivally.
It extends up to the contact point of the two adjacent.It is given a uniform thickness of 2.5 mm. excess bulk here can
interfere with the tongue function and speech.
Gingival margins:
Interdental papilla
Palatal surface
22
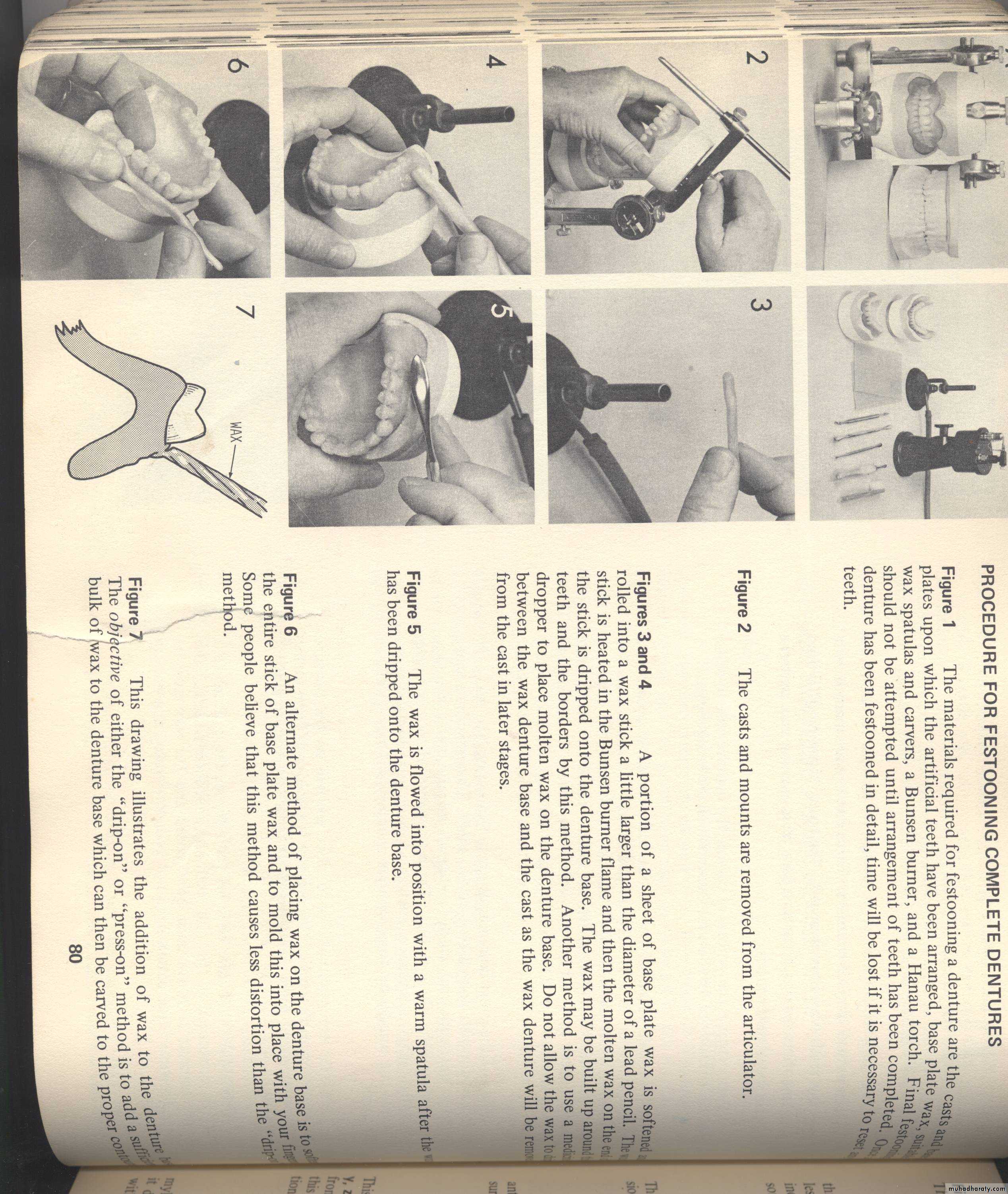
In general , we have two methods for festooning:
1.Press on method:This method can be achieved by softening sheet of wax, then it will be adapted on the flanges of record base, and by using a hot spatula or wax knife we give the natural appearance of this outer surface as present in patient’s mouth, followed by using lacron carver to carve the forms of the roots and maintain the border of the denture. And finally we use a piece of cotton to smoothen this surface to be ready for flasking.
23
2.Drop on method:
In this method, we use stick of wax. The stick is heated on Bunsen burner flame and then the molten wax on the end of stick is dripped onto record base.we give the shape and contour of the outer surface by drop of wax followed by another drop until we finished all outer surface and sealed the record base with cast, then we start the carving and smoothing as mentioned in press method.
24
Stippling: it is a procedure of giving the outer surface of denture from premolar –to – premolar region the shape of orange shell.
Advantages of stippling:
Scattered of the light to maintain the natural esthetic of the denture.
Give natural appearance and enhance the comfort of the patient.
Improve the stability of the denture.
Disadvantages of stippling:
Is the accumulation of food. For this reason, stippling would made in the anterior region only.
25
26
The procedure of stippling:
It is done by warming the outer surface of record base on burner; from premolar-to-premolar region, and by using of toothbrush, apply rubber motion on the warmed outer surface.If we forget make stippling during the step of festooning, then we can do it during the finishing of the denture by using small round bur to give irregularities (like orange shell) to the outer surface of record base.
27
One of the most common error in festooning is to make the interdental papilla non existent, or too small. This provides a space between the teeth into which food tends to pack, and also makes the denture difficult to polish.
28
Polishing
Carving of the work is followed by polishing.Prior to polishing, excess wax on the tooth surface should be removed. Wax is smoothened by gentle flaming using an alcohol followed by immediate cooling in chilled water.
29
BORDER SEAL
After finish the festooning of all polished surfaces and carving of the cast in the post dam area. Now the next step is to do border seal. In this step, we firstly seat the record base correctly on the cast, then drop melted wax on the interface between border of record base and the cast.
Then smooth the wax. Care must be taken in that to ensure not to leave any space between base and cast. Like this mistake will failed the denture.
30