1
Fifth stage
Surgery
Lec-3
.د
أركان
29/3/2016
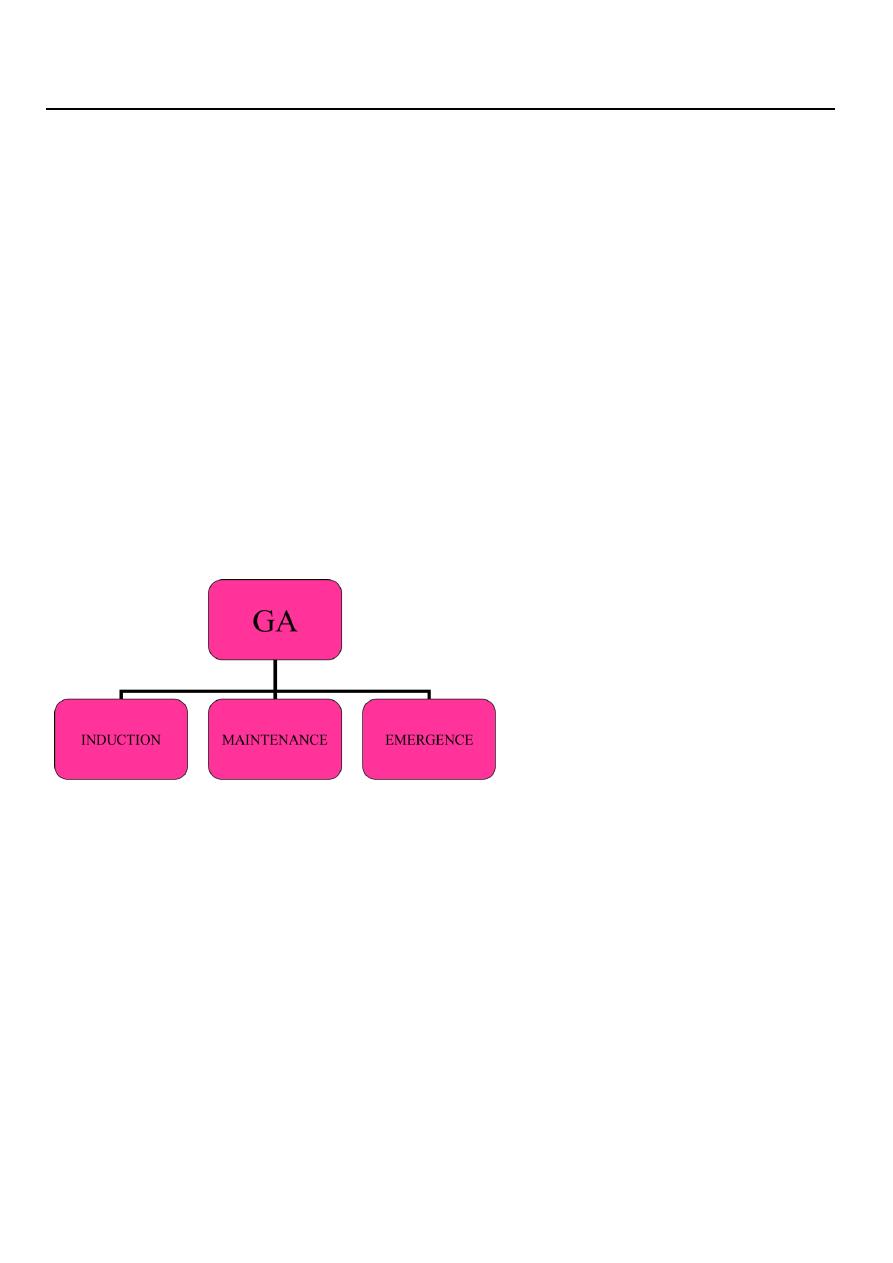
GENERAL ANESTHESIA
Definition of General anesthesia GA
Delivery of anesthetic drugs (inhaled or infused) to produce a level of CNS depression with
the following goals :
• Anesthesia :Hypnosis , loss of consciousness (reversible)
• Analgesia : pain control
• Amnesia : loss of recall
• Areflexia : muscle relaxation ( this is not always required)
• Autonomic Areflexia : decrease sympathetic nervous system (SNS) function
• Anxiolysis : Intra-operative & Post-operative
INTRAVENOUS ANESTHETICS IV
Thiopental (sodium thiopentone)
• Ultrashort acting thiobarbiturate
• Most commonly used as an induction agent
• Short duration of action 6-8 min
• After IV bolus , rapidly distributes to vessel rich organs (brain,liver,heart,kidney) thus
achieves unconsciousness in approximately 30 sec
• Metabolism & elimination occur at a slower rate resulting in residual effects (usually
sedation) during post-anesthesia recovery which may last hours

2
Propofol (Diprivan)
• Used for induction and/or maintenance of anesthesia
• Thick white soybean-based solution
• Metabolism & elimination much more rapid due to increase rate of liver metabolism
compared to thiopental
• Less residual sedative effect, patients recover sooner, thus popular for outpatient
surgery
• More suited for continuous infusion than thiopental due to rapid elimination
• More expensive
Ketamine: -
• Cause dissociative anesthesia; - that the patient appears conscious (e.g. eye opening,
swallowing, muscle contracture) but unable to process or respond to sensory input.
• Use as i.v. & i.m. anesthetic agent.
• Can cause hallucination, but it is less common in children & in patient premedicated
with benzodiazepines.
• Onset of anesthesia is slower than that with thiopental.
• Duration of action longer than thiopental, its (10-15 min).
• Cardiovascular stimulant (BP well maintained in poor risk patient e.g. shock state).
• Bronchodilator
Etomidate: -
• Onset is rapid.
• There is pain at injection site.
• It is least likely of commonly used agent to cause depression of the CVS or release of
histamine.
• It may depress the cortisol production especially if given by infusion
Benzodiazepines ( eg. Diazepam.midazolam,lorazepam)
• Used as a premedication prior to induction or as an induction agent in combination
with other drugs

3
• Oral & injectable formulations are available
• Act on a specific brain GABA receptors to produce selective anti-anxiety & sedative
effects
• Duration of action long but variable/somewhat unpredictable
• Benzodiazepine antagonist→→ Flumazenil
Opioids
Opioids used in anesthesia : morphine , codeine , meperidine , fentanyl, sufentanyl,
alfentanyl, remifentanil
Indications
• Opioids used for pre, intra, post-operative analgesia
• Also used as an induction agent alone or as adjuvant
• Can be administered IV , IM , PO
General effects of morphine (prototype opioid)
• CNS (depression) :analgesia , mood changes ,sedation , respiratory depression ,
decreased cough reflex
• CNS (excitation): miosis , nausea & vomiting ,hyperreflexia
• CVS : vasodilatation , orthostatic hypotension
• Respiratory :central depression , bronchial constriction
• GI : constipation , biliary colic
• GU : urinary retention
• Other : histamine release ,smooth muscle contraction (e.g. biliary & bladder
sphincters)
Opioid antagonists (e.g. naloxone , naltrexone)
Volatile inhalational agents :
• Halothane , Isoflurane , Enflurane , sevoflurane
• Characteristics : liquid , colorless, non-flammable ,non-explosive
• vaporizer delivers controlled concentration of anesthetic agent to respiratory system
of the patient via anesthetic machine
4
Nitrous oxide N2O
Characteristics : gas , colorless ,mild sweet odor at room temperature
Uses : Analgesia
Adverse effects :
• During emergence , N2O can diffuse rapidly from the blood to the alveoli , resulting
in a dilution of O2 in the alveoli (diffusion hypoxia) it is therefore necessary to
provide 100% O2 for several minutes until N2O is eliminated
• Bone marrow depression
• Chronic neuropathy
• Tends to diffuse into closed air spaces causing increased pressure & volume
(important if there is trapped air e.g. air embolus , pneumothorax)
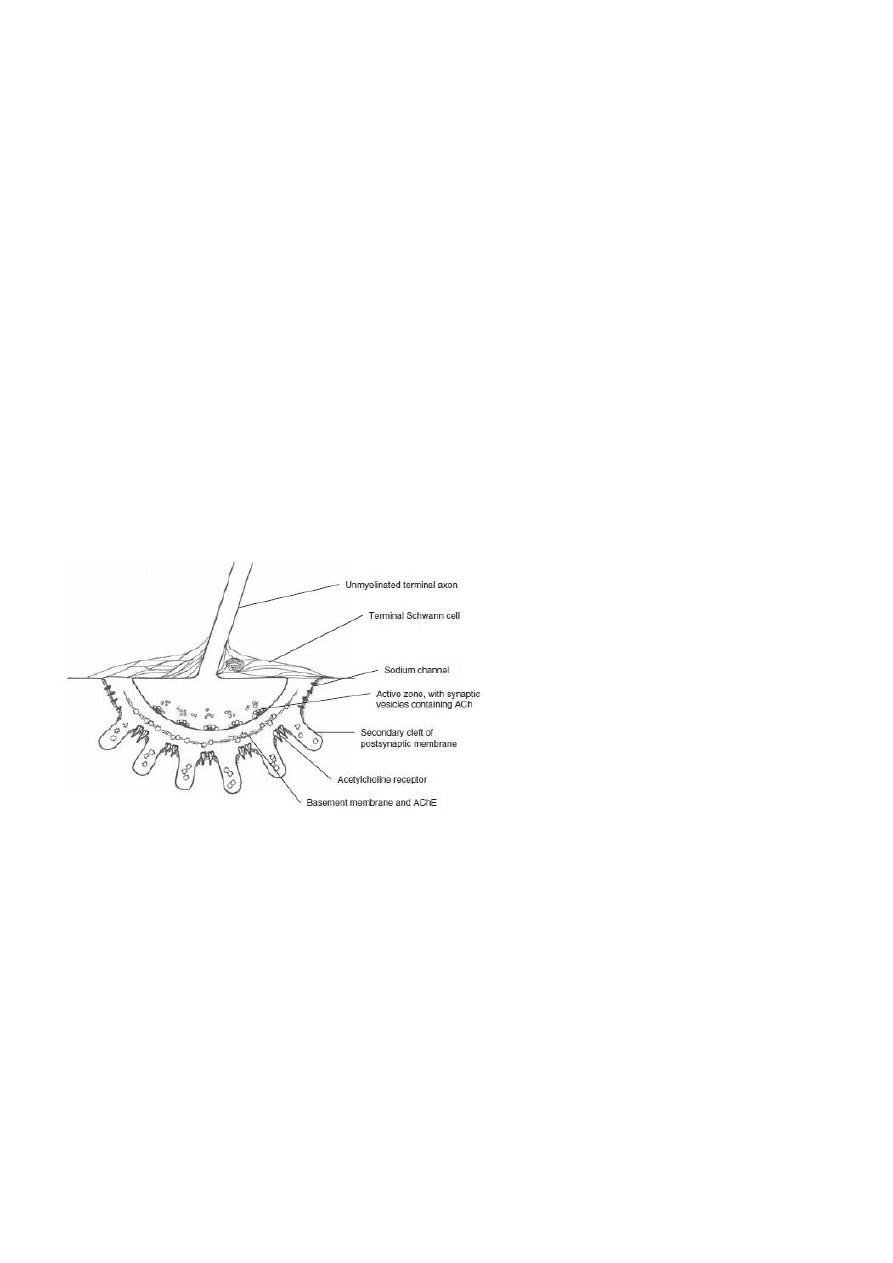
Muscle Relaxants
• Muscle relaxants often required during surgical procedures for various reasons :
1. Prevent muscle stretch reflex & suppresses muscle resting tone
2. Facilitate intubation
3. Facilitate controlled ventilation
4. Allow access to the surgical field
• Muscle relaxants classified on the basis of the neuromuscular blockade they provide :
1. Depolarizing
2. Non-depolarizing
• And according to their duration of action

5
1. Short
2. Intermediate
3. long
Depolarizing
Succinylcholine (suxamethonium)
• Onset :rapid (30-60 sec)
• Duration : short (5 min)
• Metabolism of sch by plasma cholinesterase
• Side effects :
1. Sch also binds to autonomic cholinergic receptors
• Muscarinic receptors in the heart can cause sinus bradycardia
• Muscarinic receptors in the salivary glands result in increase secetions
2. Hyperkalemia
3. Other side effects
• Increased intracranial ICP , intraocular IOP ,intragastric pressure
• Triggers malignant hyperthermia
• Sustained contraction in myotonia
• fasiculations
Non-depolarizing muscle relaxants
Mivacurium , atracurium ,cis-atracurium , rocuronium ,pancuronium , doxacurium
Reversing agents for non-depolarizing blockade (neostigmine , pyridostigmine)
• Reversible anticholinesterase
• Inhibit enzymatic degradation of Ach , increases the amount of Ach at nicotinic
receptors ,displacing the non-depolarizing muscle relaxants
• With reversal ,Ach concentration will increase at muscarinic ( before nicotinic) sites
causing bradycardia , salivation etc.
• Therefore simultaneous administration of atropine or glycopurrolate is necessary to
decrease cholinergic side effects
