May 13
1بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
Complication of dental extraction
د . برع سلطانمدرس / جراحة الفم والوجه والفكين
زميل الهيئة العراقية للاختصاصات الطبية
14- Excessive hemorrhage
During tooth removalOn completion of the extraction
Postoperatively.
Any patient with a history of a hemorrhagic diathesis should be referred to a hematologist for investigation before the extraction are undertaken.
More severe bleeding can be controlled by pressure on a hot normal saline pack held in position for a few minutes.
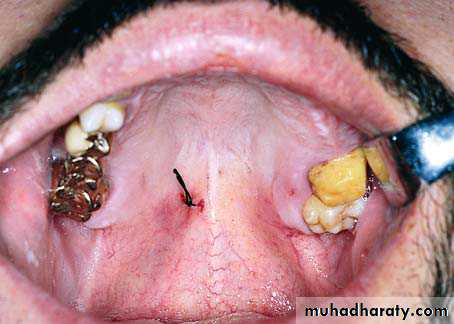
In most circumstances it will be advisable to suture the mucoperiosteum to control the bleeding.
The object of suturing is not to close the socket by approximating the soft tissue over it, but to tense the mucoperiosteum over the underlying bone so that it becomes ischemic.
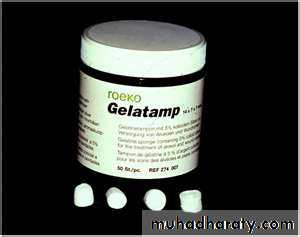
Gel foam or fibrin foam may be tucked into the socket .
Tannic acid powder is beneficial in control of bleeding.
Topical haemostatic agents:
1- tannic acid powder.2- gel foam .
3- bone wax ( beeswax plus isopropyl palmitate).
4- surgicel (oxidized cellulose).
5-tranexamic acid (cyclocapron injectable) and epsilone aminocaproic acid EACA or amicar.
6-adrenalin 1:1000.
If bleeding don’t stop put your foot on
15- Damage to gums, lips, inferior alveolar nerve, lingual nerve ,tongue and floor of the mouth..Damage to the gum can be avoided by careful selection of the forceps and good gum separation before tooth extraction.
The lip may be injured or crushed by the forceps , or it may be burned if instrument not allowed to cool before use after being sterilized.
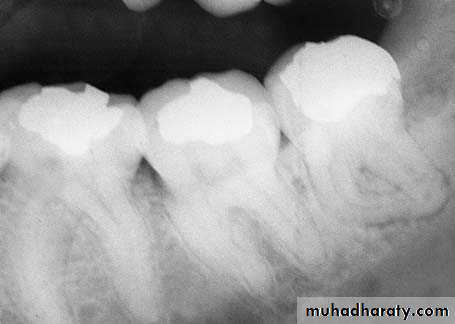
If the root or tooth is in an intimate contact to the inferior alveolar nerve, damage can be prevented or minimized only by preoperative radiographic diagnosis and surgical removal of the tooth or root.
The lingual nerve may be damaged when the lingual soft tissues are trapped in the forceps.
The tongue and floor of the mouth
If the dentist uses an elevator without proper control he may slip and drive the elevator into either the tongue or the floor of the mouth.Effective use of the non dominant hand prevents this accident.
16- post operative pain.
Dry socketDamage to the hard and soft tissues
Acute osteomyelitis of the mandible
Traumatic arthritis of the TMJ
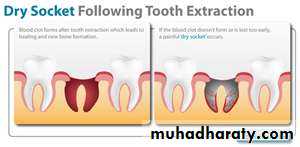
Dry socket
This clinical entity is a localized osteitis involving either the whole or a part of the condensed bone lining a tooth socket , the lamina dura . the condition is characterized by an acutely painful tooth socket containing denuded bone and broken down blood clot.Dry socket , also termed alveolar osteitis ,fibrinolytic alveolitis and alveolitis sicca dolorosa exodontias .
It is characterized by increasingly severe pain which usually starts on the 2nd or 3rd post extraction day in and around the extraction site .lasting for between 10 -14 days .
the normal post extraction blood clot is lost from the socket and its walls is denuded .
halitosis is invariably present
The aim of treatment is to relief pain and speeding of resolution
The affected socket should be gently irrigated with warmed 0.12% chlorhexidine or normal saline and all debris should be washed from the socket .
In extremely painful cases local anesthesia may be required before socket irrigation can be performed .
the socket should be lightly packed with a dressing that contains a sedative for pain relief and a non irritant antiseptic to inhibit bacterial and fungal growth .
dressing pack used in the treatment of dry socket are
1- alveogel2- iodoform pack (whitehead's varnish)
3-bipp (bismuth iodoform trinitrate paste )
4- Zink oxide eugenol paste
The dressing should prevent re- accomulation of food debris and protect the exposed bone from irritation.
Ideally the dressing should slowly dissolved without the need for its removal and should not excite a host inflammatory or foreign body response.
etiology of dry socket
1• Extraction of mandibular rather than maxillary teeth
2• Extraction of third molars, especially impacted lower third molars
3 • isolated tooth extractions
4 • “Traumatic” extractions
5 • Female sex especially if concurrently using oral contraception
6 • Patient aged between 20 and 40 years
7 • Poor oral hygiene and plaque control
8 • Active or recent history of acute ulcerative gingivitis or pericoronitis
9 • Smoking, especially if >20 cigarettes/day
Acute osteomyelitis of the mandible
It differ from dry socket in that :1- there is marked pyrexia and pain is very severe.
2- the mandible is tender on extra oral palpation.
3- there may be an onset of impairment of labial sensation some hours or even days after tooth extraction.
17- post operative swelling due to
OedemaHematoma formation
Infection
Both edema and hematoma are regress if the patient uses hot saline mouth baths frequently for 2-3 days.
infection
The patient should be cautioned against applying heat extra orally because this increase the size of the facial swelling .if fluctuation is present the pus should be evacuated before beginning antibiotic therapy.
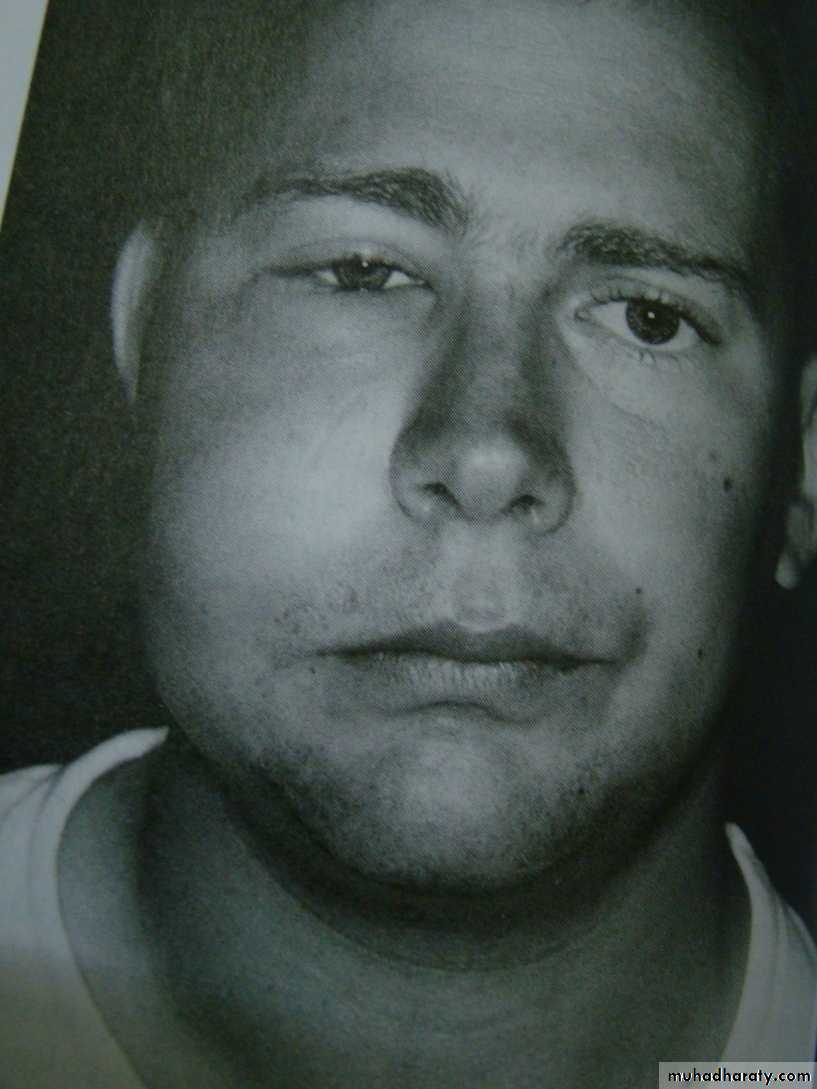
18- trismus
Trismus can be defined as inability to open the mouth due to muscle spasm and may complicate dental extractions.It may be caused by post operative edema, hematoma formation, or inflammation of the soft tissues.
The treatment of trismus consist of intra oral hot saline mouth washes and adminstration of antibiotics.
This patient has so much of limitation in opening of mouth that it is difficult to put even 2 fingers in the mouth
Patients fingers not dentist fingers
19 – Fainting or syncope
Collapse in the dental chair may occur suddenly and may or may not be accompanied by loss of consciousness.In most cases spontaneous recovery is usual.
The patient often complains of feeling dizzy, weak, and nauseated, and the skin is seen to be pale ,cold and sweating.
Treatment of fainting:
1- the patient head should be lowered by lowering the back of the dental chair .
2-any collar should be loosened.
3- ensure that the patient cannot fail out of the chair .
4- no fluid can be given by mouth until the patient is fully conscious.
5- if consciousness returns a glucose drink may be given .
Spontaneous recovery is usual and it is often possible to complete the extraction at the same visit.Have A Nice Day
TMJ dislocation : causes ,diagnosis and treatment ?
Mosul university- College of dentistry-oral & maxillofacial surgery departmentw
• Cause
• -Bleeding at wound margins
• -Bleeding at a bony foramen within the socket
• -Medical Problem
VII. Postoperative Bleeding
• Cause
• -Bleeding at wound margins
• -Bleeding at a bony foramen within the socket
• -Medical Problem