Topical antibiotic
presented by:Sura saad Sawsan kamal
Suhad saher fadia batres
Sannar mahammed Shahad ayad
Chrestien basheer Sura salim
Definition
Topical antibiotic:are medicines applied to the skin to kill or inhabit the growth of bacteria
• Topical medication include:
• Cream• gels
• Lotions
• Patches
• Ointment
• balms
Advantage of Topical administration:
• Avoids the GIT and hepatic first_pass metabolism• Reduce systemic side effect
• Higher concentration drug at site of application
• Improve compliance
• Plasma concentration of <10 compared
• To oral route
Side effect
• itching• burning
• Rash
• Allergic reaction
Indications
• Topical antibiotic help to prevent infection
• Treatment minor wound with antibiotics allows quicker healing
• Un treated infections can eventually spread and become much more serious
Topical antibiotic in medicine
1.bacitracinSpectrum of activity
Bacitracin is a broad spectrum antibiotic. It targets both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, especially those that cause skin infections.Staph. aureus
Staph.epider midis
Str.pyogenes
Mechanism of action
Bacitracin interferes with bacterial cell wall synthesis
Acts by blocking a step in the process whereby the key subunits are transferred from the cytoplasm
bactericidal
Uses for Bacitracin
1. prevent or treat superficial skin infections2. useful for preventing infection in minor skin injuries (e.g., cuts, scrapes, burns).
3. Treatment of serious or extensive skin infections usually requires systemic anti-infective therapy.
Bacitracin Dosage
Ointment: Apply amount equal to the surface area of a fingertip to the affected area 1–3 times daily
Side effect
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue); burning; redness; swelling2.Neomycin
2.Neomycin
1.Neomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic found in many topical medications such as creams, ointments, and eyedrops.2.. Neomycin is for external use only. Do not let neomycin get into your nose, or mouth, and do not swallow it..
Spectrum.
Gram-positive aerobes: e.g Staphylococcus aureusGram-negative aerobes: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella&Neisseria.
Mechanism of action
bactericidal.Appears to inhibit protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria by irreversibly binding to 30S ribosomal subunits
Neomycin Sulfate Dosage
Children ≥2 years of age& Adults : Apply amount equal to the surface area of a fingertip to the affected area 1–3 times daily.side effects
• Irritation
• burning
• Redness
• rash
• Itching
• Allergic reaction
Gramicidine
Mechanism of action
Gramicidin binds to and inserts itself into bacterial membranes (with a strong preference to gram-positive cell membranes).bactericidal
Uses
Gramicidin is particularly effective against gram-positive bacteria .It is used primarily in the treatment of infected surface wounds, and in eye, nose, and throat infections.
Side effects :
Ototoxicity risk is increased when there is a perforation of the tympanic membrane but it is rare .Gentamycin
Mechanism of action
Aminoglycosides like gentamicin "irreversibly" bind to specific 30S-subunit proteins and 16S rRNA.Spectrum
broad spectrum are useful primarily in infections involving aerobic, Gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas, & mycobacteria. Infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria..
Uses
treat minor skin infections (such as impetigo, folliculitis) or minor infections related to some skin conditions (such as eczema, psoriasis, minor burns/cuts/wounds).Gentamicin cream is usually used for wet, oozing, greasy types of skin infections.
Polymyxin B is an antibiotic derived from the bacterium Bacillus polymyxa.
Polymyxin B is a mixture of two closely related compounds, polymyxin B1 and polymyxin B2.Spectrum of activity
Polymyxin B has no activity against Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobes , but is active against a variety of Gram-negative bacilli, including most clinically relevant Enterobacteriaceae and non-fermentative species
polymyxin B
Mechanism of actionAlters bacterial outer membrane permeability by binding to a negatively charged site in the lipopolysaccharide layer, which has an electrostatic attraction for the positively charged amino groups in the cyclic peptide portion.
Uses of polymyxin b
used in the treatment of outer ear infection.Bacitracin, neomycin, and polymyxin B topical (for the skin) is a combination medicine used as a first aid antibiotic to prevent infections in minor cuts, scrapes, or burns on your skin.
Used combination with other (e.g., bacitracin, neomycin, gramicidin, trimethoprim) for treatment of superficial infections of the eye caused by susceptible bacteria
Uses of polymyxin b
Side Effect
mild Itchingskin rash
redness
swelling
signs of an allergic reaction: hives
difficult breathing
swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
• Silver sulfadiazine
• BRAND NAME: Silvadene
• Silver sulfadiazine is an antibiotic. It works by killing the bacteria or preventing its growth.
• Silver sulfadiazine cream is used to prevent and treat wound infections in patients with second- and third-degree burns.
• Mechanism of action:
• Sulfadiazine is a competitive inhibitor of the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroatesynthetase. This enzyme is needed for the proper processing of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) which is essential for folic• acid synthesis.
USES:
• prevent and treat wound infections in patients with serious burns & other skin and wound infections (such as skin ulcers).• (sepsis).
Adverse effects:
• Burning and painful sensations .• hypersensitivity
• reactions like rashes or erythema multiforme.
• Incorporation of the silver ions can lead to local discoloration of the skin .
• Generalised argyria with silver accumulation in kidneys, liver and retina .
Pharmacokinetics:
• The chemical it self is poorly soluble, and has only very limited penetration through the skin. Only when applied to large area burns or other lesions is absorption into the body a problem.
• Fusidic acid
• Type of medicine• Topical antibacterial
• Used for
• Skin infections in adults and children
• Brand names
• Fucidin; Fucibet (fusidic acid with betamethasone)
• Available as
• Cream and ointment
Fucidin cream contains the active ingredient fusidic acid, which is an antibacterial agent used to treat a number of bacterial skin infections.
• Mechanisim of action:
• Fusidic acid acts as a bacterial protein synthesis inhibitor by preventing the turnover of elongation factor G (EF-G) from the ribosome.• Without these proteins the bacteria cannot grow, replicate and increase in numbers.
Spectrum: Fusidic acid is effective primarily on gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylocccoccus species, Streptococcus species, and Corynebacterium species
Uses:
• Impetigo.
• Infected hair follicles (folliculitis).
• Skin infection around the nails (paronychia).
• Infected eczema.
• Infected wounds.
Side effects:
• Pain, stinging, burning or redness on application.
• Skin rashes.
• Contact dermatitis.
• Itching.
• Pharmacokinetics:
• Apply the cream or ointment three or four times a day
Clindamycin :
Mechanism of action :‘’bacteriostatic’’
Inhibit bacterial protien
synthesis by binding to
50s ribosomal subunit.
Spectrum of activity :
Aerobic Gram(+), including Staph. and Strep.Anaerobic Gram (-) including some Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, and Prevotella.
Uses :
Clindamycin gel most commonly used for treatmentof acne vulgaris.
Can also be used in treatment of periodontitis to decrease periodontal pocket depth.
Acne vulgaris
How acne develops ..??
Side effects :1.Dry or peeling skin 2.Itching or burning skin
3.Redness of skin 4.Oily skin
5.New pimples or blemishes 6. Head ache
Chloramphenicol :
bacteriostatic inhibit protein synthesis by binding to 50s ribosomal subunit.
broad-spectrum antibiotic effective in treating ocular infections caused by Staph.aureus, Str. pneumoniae, and E. coli
Used topically to treat bacterial conjunctivitis.
Flouroquinolones ofloxacin & ciprofloxacin
Mechanism of action : “bactericidal”Inhibit DNA replication , by inhibiting DNAgyrase (topoisomerasell) and topoisomeraselV .
Have broad spectrum of activity against gram(-)
and gram(+) bacteria including the common eye
and ear pathogens Staph. aureus and Pseudomonas. Aeruginosa.
therefore most commenly used topically for treatment of eye and ear infection.
Uses for eye infections:• Bacterial keratitis.
• Bacterial conjuctivitis.
• Redness, itching, irritation, pain, swelling or discomfort in or around the eye(s) and/or eyelids
• Accumulation of ciprofloxacin crystals on the surface of the corneal ulcer.
• conjunctival hyperemia
• chemosis
• tearing and foreign-body sensation
Side effects :
Ofloxacin eye drops
Ciprofloxacin ointmentUses for ear infections :
Otitis externa(infection of external ear canal )Otitis Media with Perforated Tympanic Membrane.
Note : They are chosen because of lack of ototoxicity.
Side effect on ear :• Headache, ear pain
• Another study reported a 35% incidence of candidal overgrowth in patients treated with ciprofloxacin
Topical antibiotic in dentistry
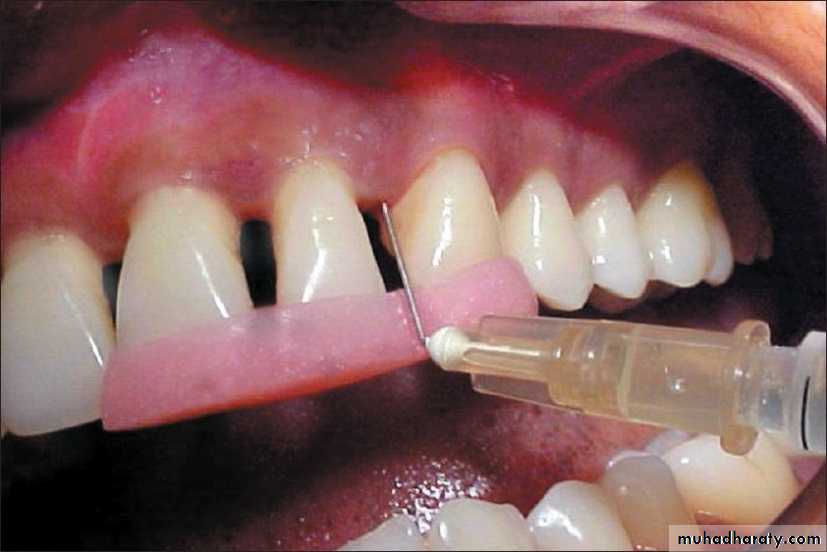
Tetracycline fibers inserted into periodontal pocket
Metronidazole gel:
metronidazole is synthetic nitromidazol effective against obligate anaerobic bacteriaMetronidazole is an antibacterial active against those organisms that are predominant in the subgingival flora in adult periodonitis
Mechanism of action :
“Bactericidal” inhibit bacterial DNA synthesisAfter metronidazole enter the cell nitro group of metronidazole is reduced and reduction products cause damage to DNA and cell death.
applied to the periodontal area twice daily.
Uses of metronidazole gel:
contraindication
Known hypersesitivity to metronidazole and chlorhexidine.
1
2
3
4
Side effects:
Side effects are local and occur directly in connection with the application such as bitter taste and temporary local tendemess headache has been reported.Some potentiation of anticoagulant such as warfarin.
InteractionsTetracycline have a “broad spectrum” of antibiotic action. Have some level of bacteriostatic activity against almost all medically relevant aerobic and anaerobic bacterial genera, both Gram-positive and Gram-negative, except Pseudomonas.aeruginosa and Proteus spp.,
2.Tetracycline
Mechanism of action:
Inhibit protein synthesis by binding to 30s ribosomal subunit. This appears to prevent access of AA-Trna to the acceptor site on the mRNA-ribosome complex
Theraputic uses:
• Acute orofacial infection• Chronic periodontitis
in the form of gel
3. The cream or topical form
Of tetracycline use to keep
Your Acne under control
Side effect: 1.pain 2.Reddness 3. Swelling 4.irritation
4. capsules, which are applied to the gums after scaling and planning. Studies report that they are more effective in reducing pocket depth and bone loss than standard periodontal maintenance3.Azithromycin:
Mechanism of action :Azithromycin inhibit bacteria protein synthesis By binding to 50s ribosomal subunit and inhibit RNA dependant protein synthesis.
Periodontitis
Azithromycin gel
Theraputic uses1.Treatement of periodontitis
2.Treatement of acne
3. Inflammatory disease of eyes
4.Treatement of blepharitis
5. Treatement of trachoma
Side effect:
1.Itching
2.Cracked dry and scaly infection.
Thank you
Forlistening