
Fifth stage
Radiology
Lec-1
د
.
زهراء
5/10/2016
Urinary tract
IMAGIMG TECHNIGUES:
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP or IVU, US, CT & radionuclide imaging
are the major modalities used in the investigations of suspected UT
disorders.
MRI, arteriography
IVU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional & anatomical
information.
US & MRI provide anatomical information.
Radionuclide scanning provides functional information only.
Intravenous Urography (IVU):
Also known as excretory urography.
It means the visualization of kidney parenchyma, calyces and pelvis after
intravenous injection of iodinated contrast medium to the patient, followed
by a series of x-ray films.
Its use has been decreased lately as it is replaced by US and Computerized
Tomography (CT).
Remains the primary modality for visualization of the pelvicalyceal system
and ureters, providing both functional and anatomical information.
Indications
When detailed demonstration of the pelvicalyceal system and ureters is
required.
The assessment of suspected acute ureteric colic.
Investigation of renal calculi (stones).
The investigation of hematuria.
Contrast medium and its excretion:
Urographic contrast media are highly concentrated solutions containing
iodine, also known as iodinated
Large volume of CM (50-100mi) is injected intravenously
passes to
glomerular filtrate concentrated in renal tubules passes to-pelvicaticeal
systems ---ureters---bladder.
The procedure of performing IVU:
A. First a plain x-ray of the abdomen is taken before the injection of the
contrast media, also known as A KUB (kidney, Ureter and Bladder).
Calcification & stones may be obscured & missed by contrast media if plain
film not taken first.
B. Films taken after injection of contrast’ medium:
A series of x-ray films are taken after injection of the contrast.
Each film is taken at a time interval determined by the radiologist who is
supervising the procedure.
1.Nephrogram phase (Immediately after injection of contrast).
2. Pyelogram Phase (l-5 minutes after injection of contrast) .
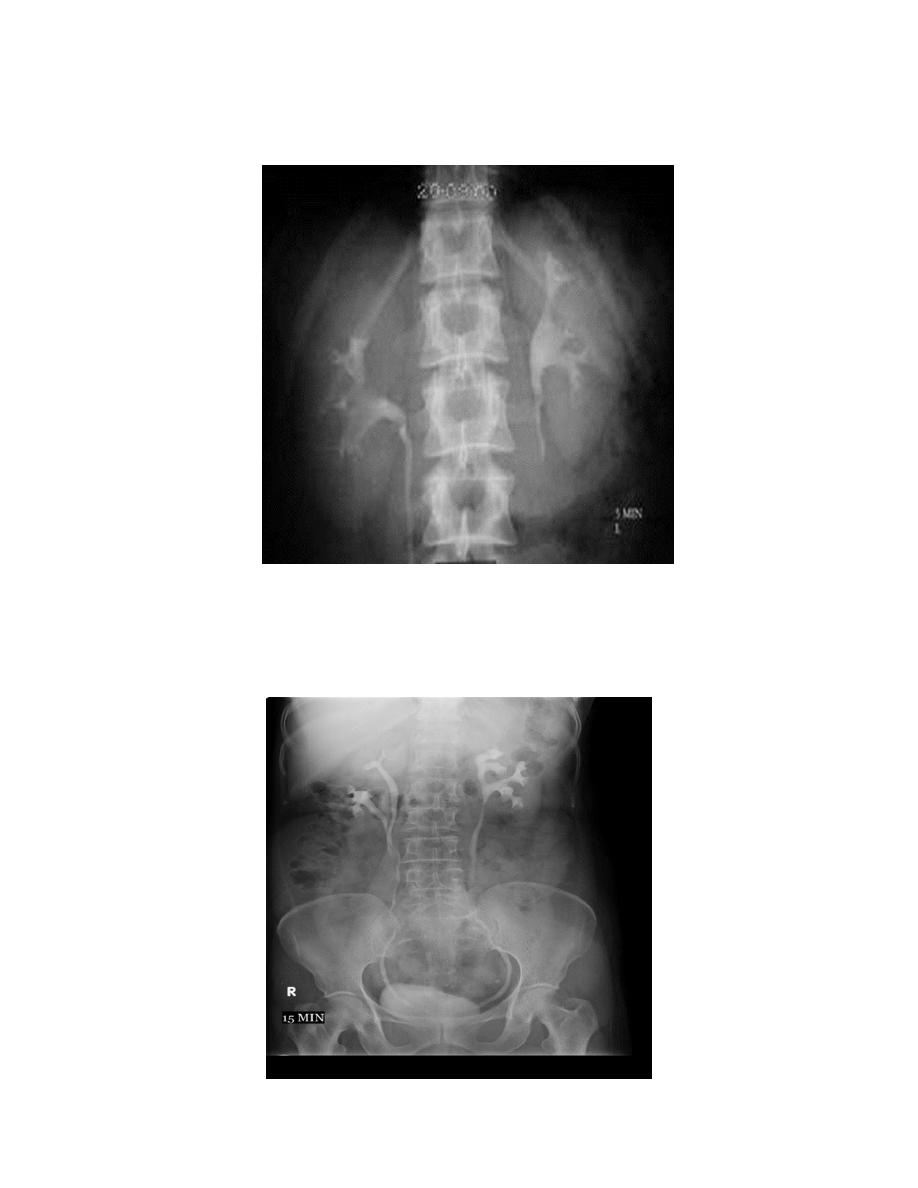
3. After 10 minutes with compression, to get better distention of the pelvis and
calyces.
4. Full length film after release of compression.
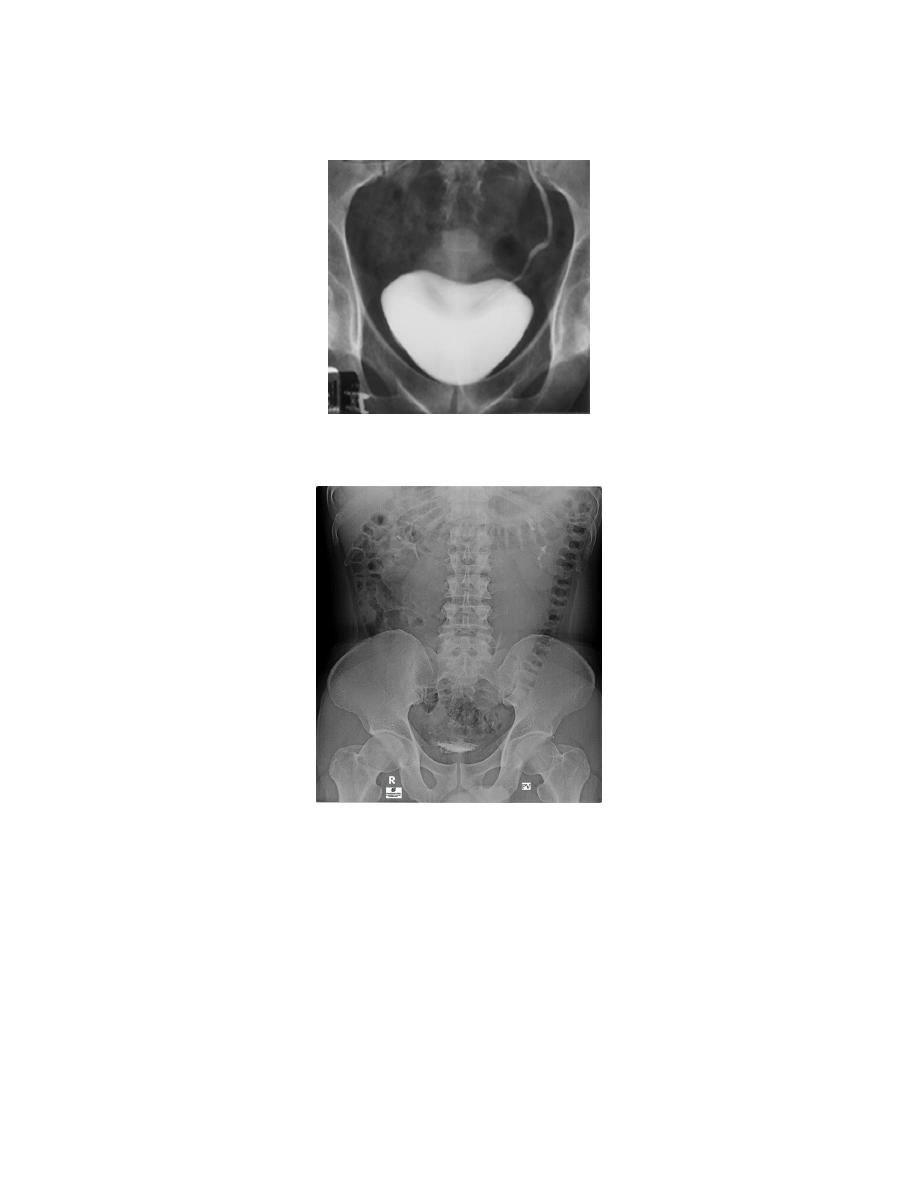
5. A full bladder film (with the urinary bladder fully distended with contrast)
6. Post voiding full length film
Interpretation of IVU films (what to look for?):
1. The kidneys:
Check their position (left kidney is usually higher).
Identify the whole of both renal outlines, look for any indentations or bulges:
Renal parenchymal width should be uniform(2-2.5cm)
measure renal lengths:
Normal length of adult kidney at IVU is 10-16cm. This is higher than in
ultrasound due to image magnification.
2.Calyces:
should be evenly distributed -symmetrical.
Cup shaped (normal shape) -Club shaped (when dilated)
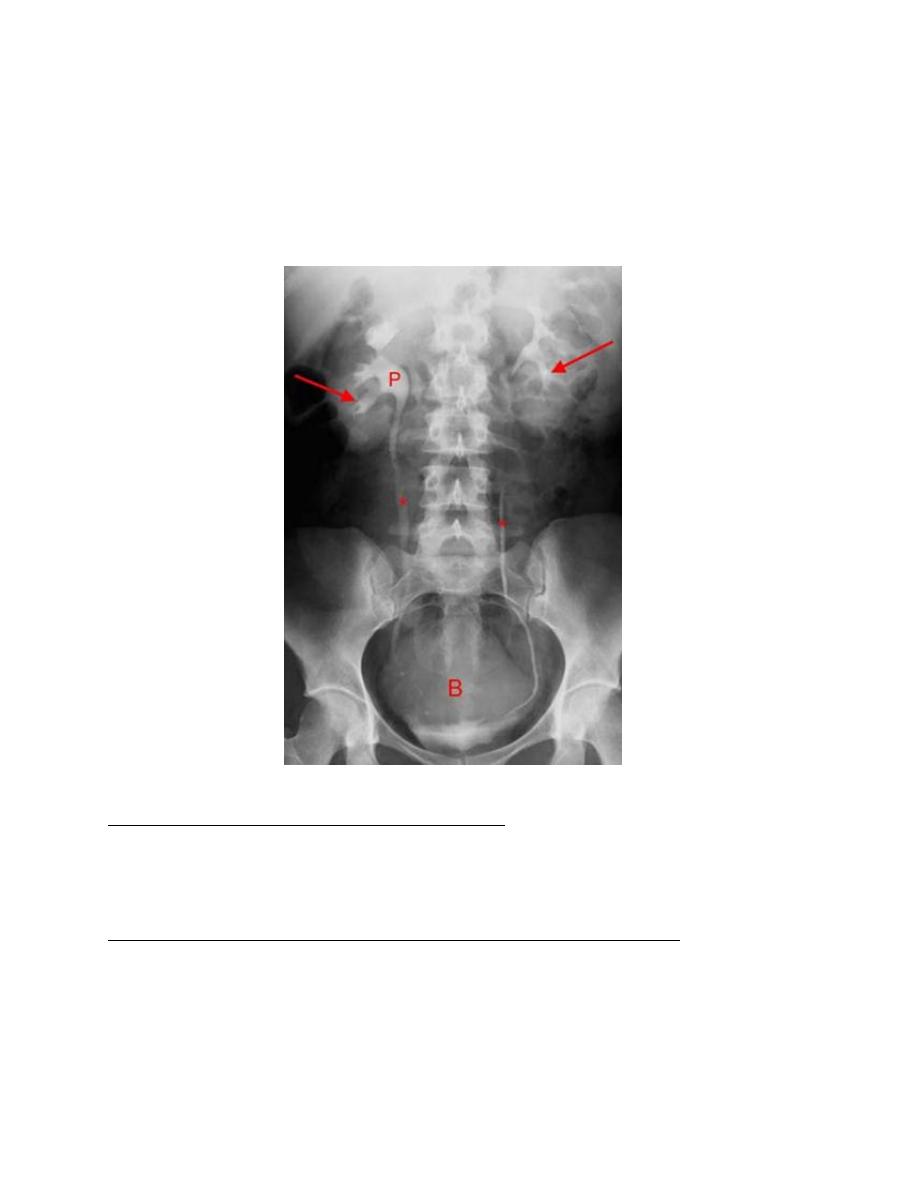
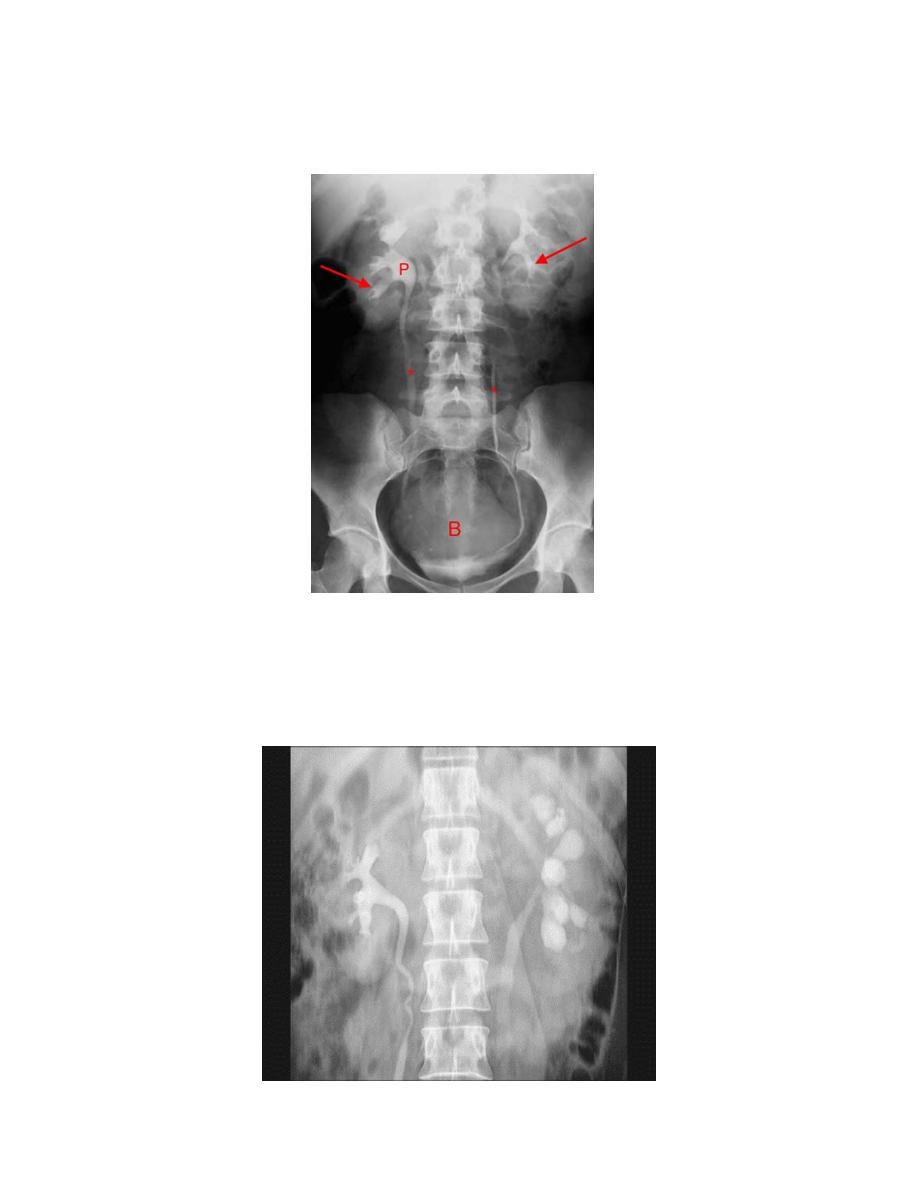
3. Renal pelvis and ureter:
-The normal renal pelvis and pelvi-ureteric junction are funnel shaped.
-Ureters are seen only in part of their length on any one film due to
obliteration by peristalsis.
Dilatation of pelvis and ureter may be due to:
-Obstruction (by stone , tumors or external compression).
-secondary to vesico-ureteric reflux
Look for filling defects which could be due to three common causes
stones
tumors.
Blood clots.
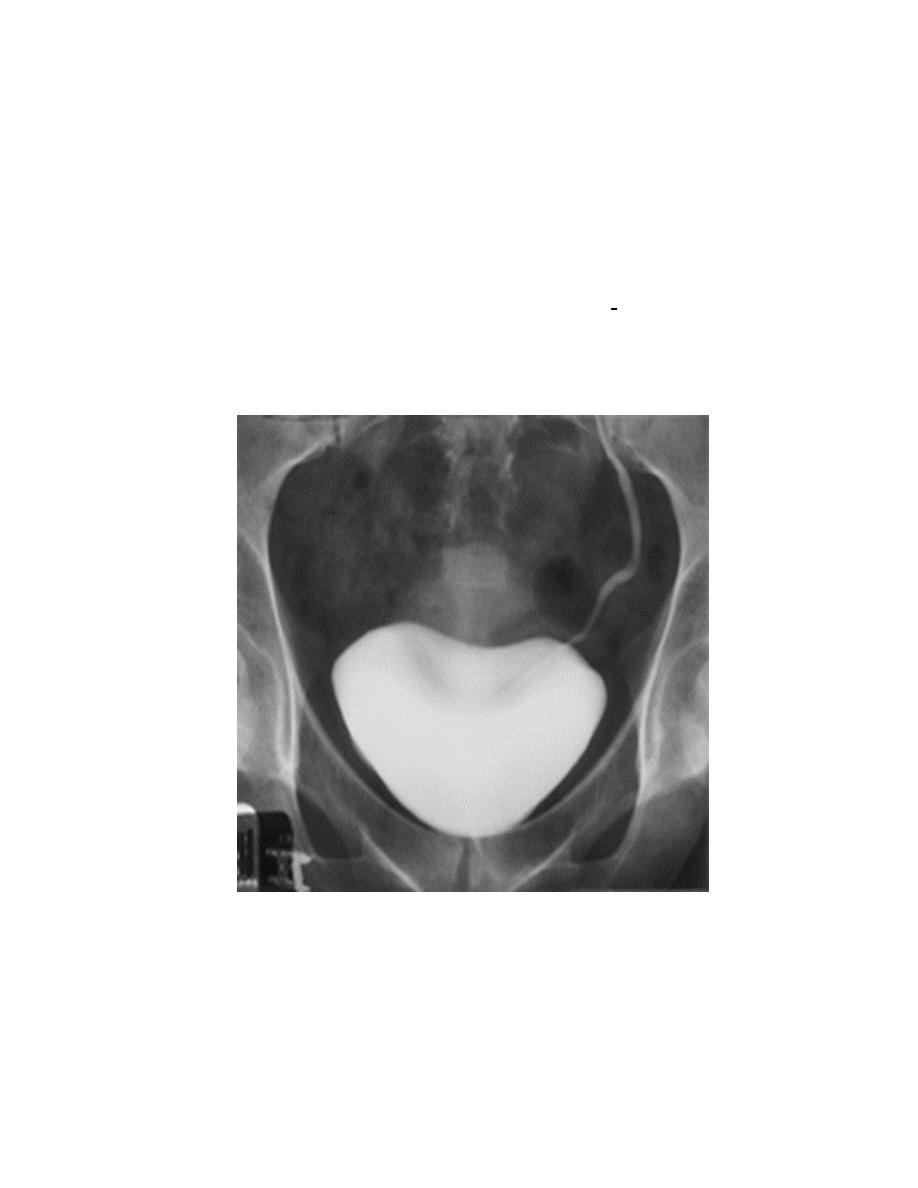
4. Bladder
The bladder is a centrally located structure.
Smooth in outline.
Smooth indentation from above by uterus on the right or sigmoid colon on
the left and from below by muscles of the pelvic floor is normal.
Other than that, any filling defect, wall irregularity or diverticula must be
carefully looked for.
