Fifth stage
MedicineLec-1
د.مثنى
11/10/2015
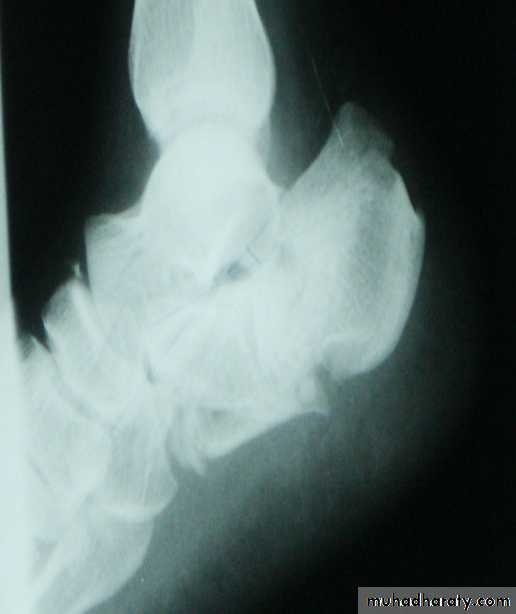
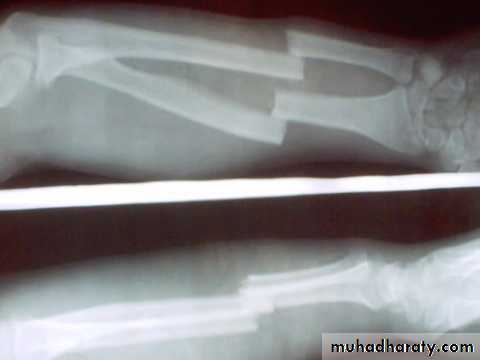
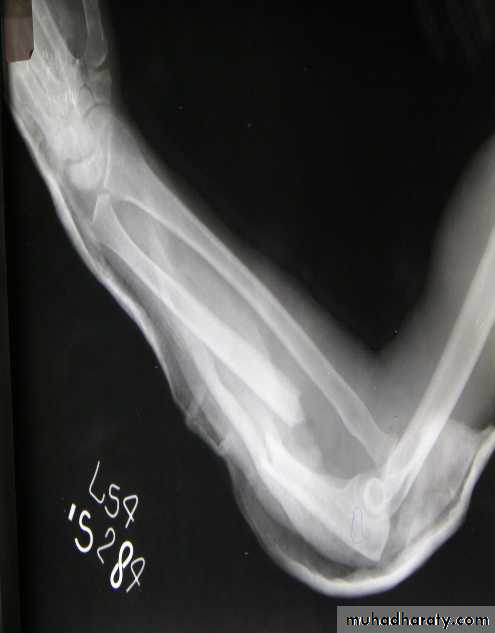
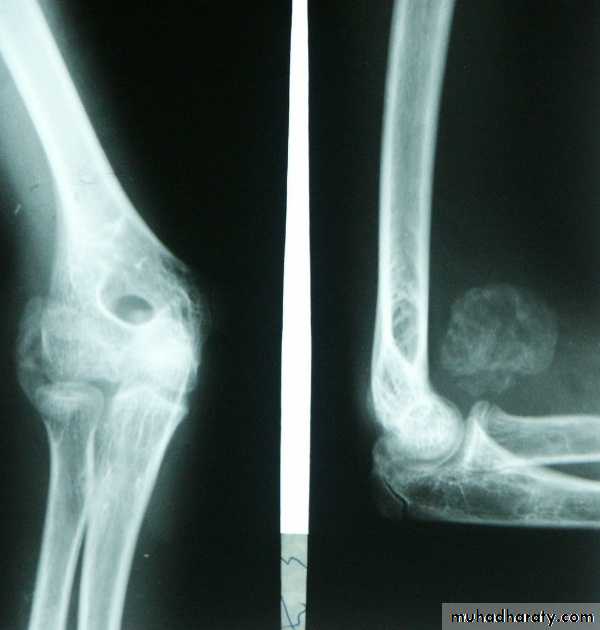
PRINCIPLE of fracturesFracture definition: It is a break in the structural continuity of bone .
How fracture happen?
1.from single traumatic incident.2.repetitive stress .
3.abnormal weakening of the bone (pathological fracture).
In cancellous bone trauma produce comminuted crush fracture.
Around joint pulling ligament and tendon produce avulsion fracture.How fracture are displaced:
By force of the injury.
Gravity.
By pull of the muscle attached to them.
How fracture heal:
Tissue destruction and haematoma formation.Inflammation and cellular proliferation occurs within 8 hours. clotted haematoma is slowely absorbed and fine capillaries grow into the area then (granulation tissues).
3. Callus formation is driven by inductive proteins.
4. Consolidation (woven bone is transformed into lamellar bone) takes several months.
5. Remodelling occurred over a period of months or even years.
Perkins’ time table
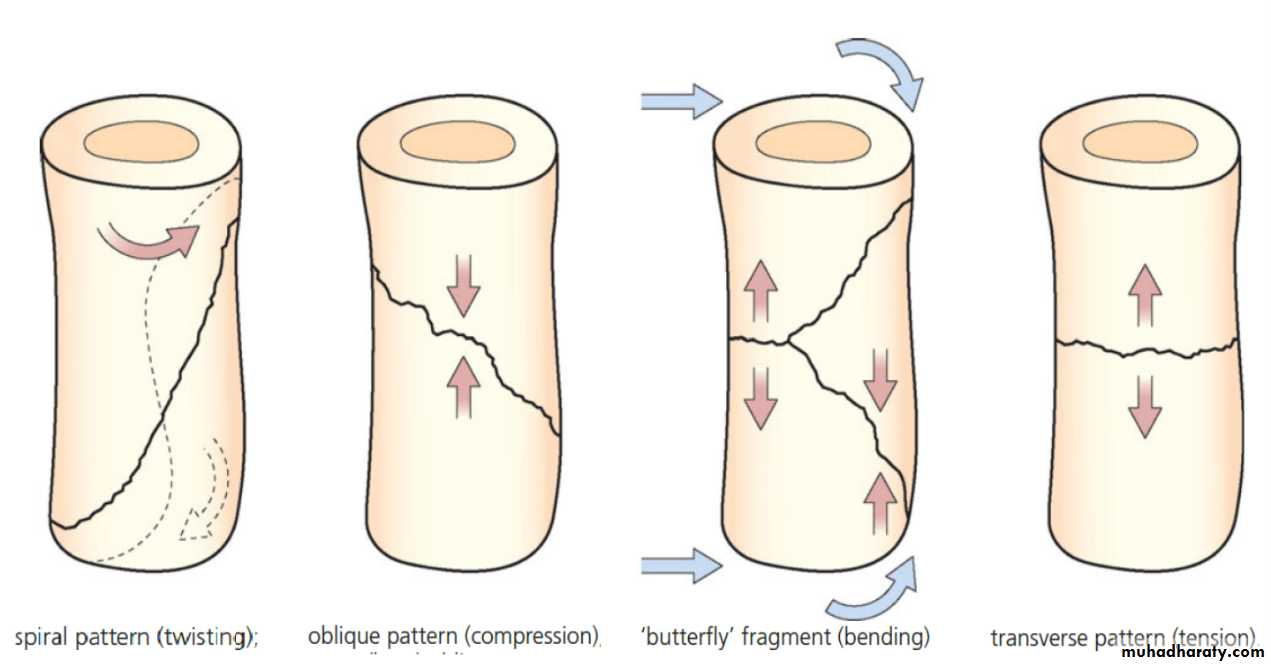
upper limb .Spiral fracture
3 weeks united * 2 consolidation.
Lower limb * 2.
Transverse fracture * 2 again.
In children the time shorter, in elderly longer
OR THERE MUST BE CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL evidence of consolidation before full stress is permitted without splintage
CLINICAL FEATURES:
History.
General sign.
Local signs.
X-ray.
Special imaging.
History:
usually a history of injury ,followed by inability to use the injured limb.BE WARE ……
The fracture is not always at the site of the injury, a blow to the knee may fracture the patella ,femoral condyle ,even the acetabulum.
Pain are common symptom.
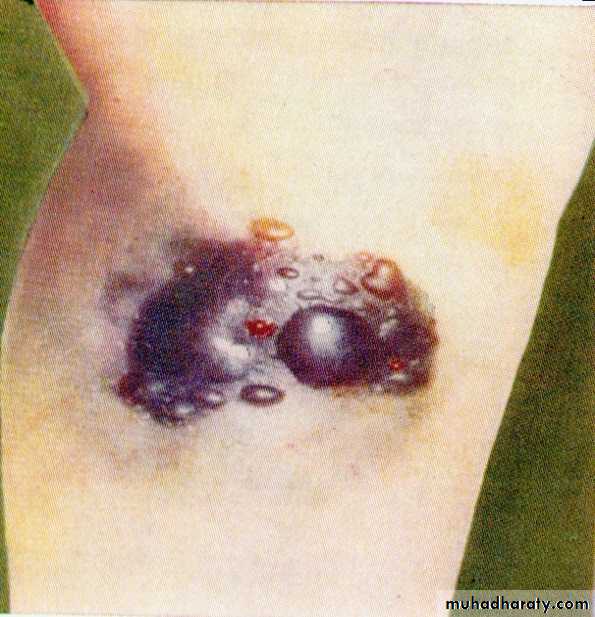
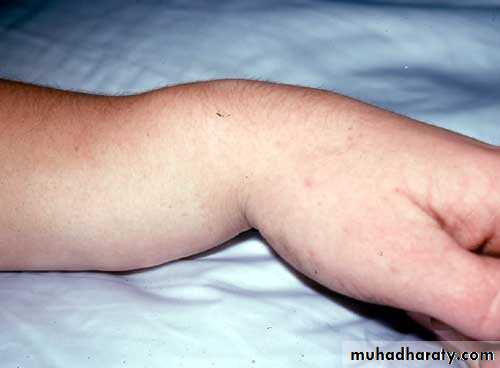
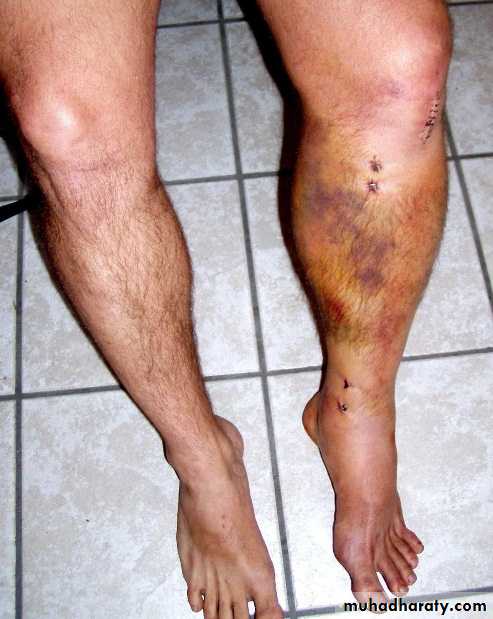
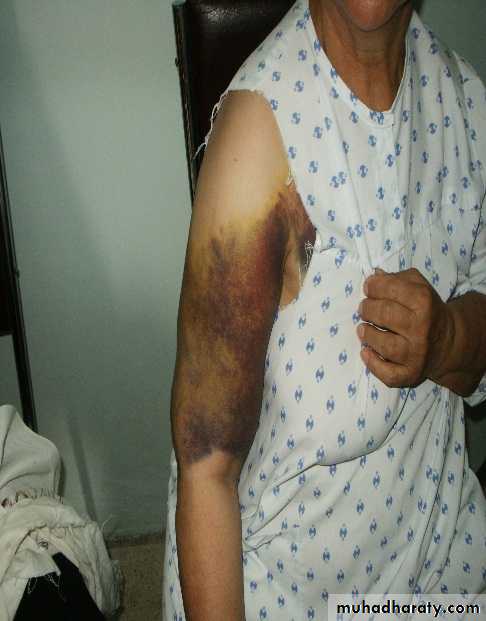
Bruising ,swelling.
Deformity.
Numbness, loss of movement.
History of previous injury.
General medical history.
General signs:
A broken bone is part of a patient so look for .Hemorrhage.
Associated damage to brain, spinal cord ,viscera.
Predisposing cause (pagets’ disease).
Local signs:
Look :
Swelling.
Bruising.
Deformity.
State of the skin.
Feel:
Tenderness.
Distal pulse.
sensation.
Move:
Crepitus.
Abnormal movement.
Movement of the joint distal to the injury.
Special imaging:
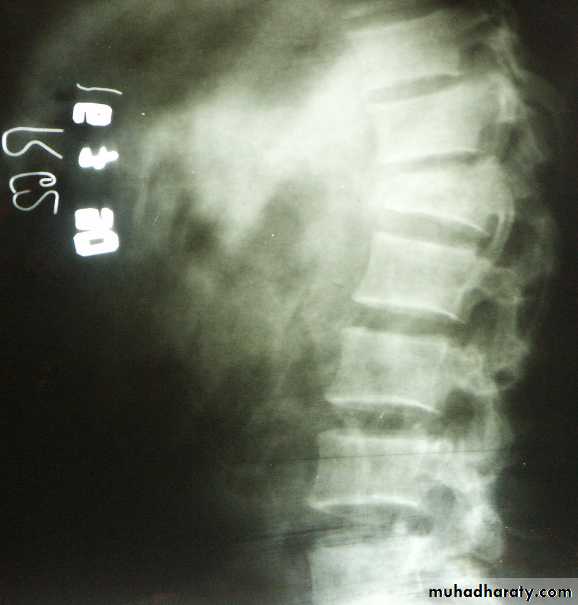
1.TOMOGRAPHY: In spine or tibia condyle injure.2. CT, MRI: In spine fracture which threatened the cord.
3-RADIO- ISOTOP scanning: In stress fracture or undisplaced fracture.
Secondary injuries:
Fracture spine cord injure.
Fracture pelvis abdominal viscera injuries (intestine, diaphragm, bladder).
Fracture ribs lung ,heart
.Fracture and dislocation around pectoral girdle: brachial plexuses& vessels.
General treatment at the accident site
Air way .Protection cervical spine.
Breathing.
Bleeding stoppage .
by direct pressure or
by tourniquets. (time)
(Circulation) Fluid replacement
Examination .
Analgesia.
Splintage to reduce pain, blood loss…
Transport by proper stretcher.
In the hospital:
Rapid survey.Constant re-evaluation.
Definitive care.
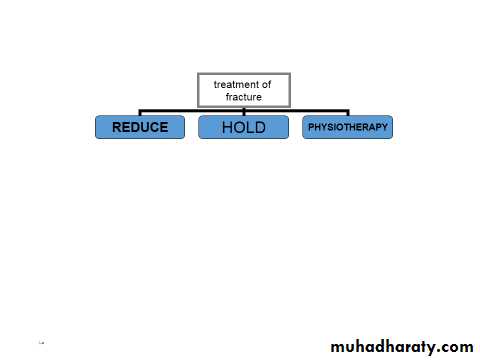
Reduction:
Conservative (closed).Operative (open).
Manipulation(reduction)
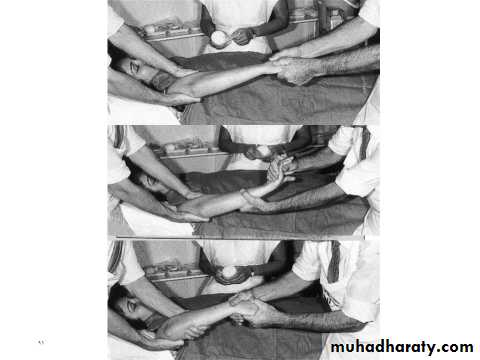
A: closed reduction:Under anesthesia, with assistant.
Used in children fracture,
Minimally displaced fracture.
Fracture not unstable after reduction.
B:Open reduction.
failure of closed reduction.Displaced intraarticular fracture.
Severely displaced avulsion fracture.
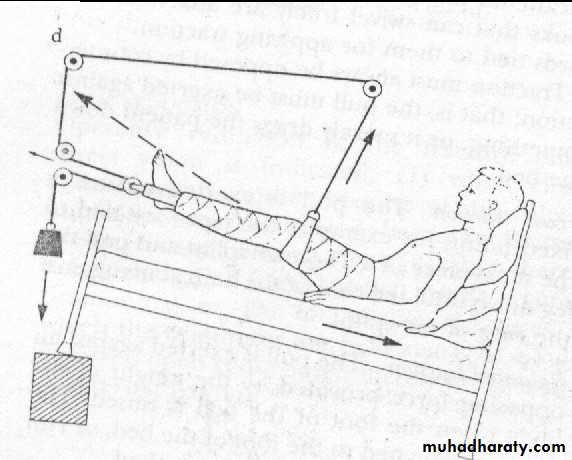
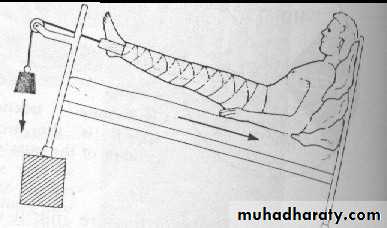
HoldI. Continuous traction
1.Traction by the gravity.
For upper limb injure.
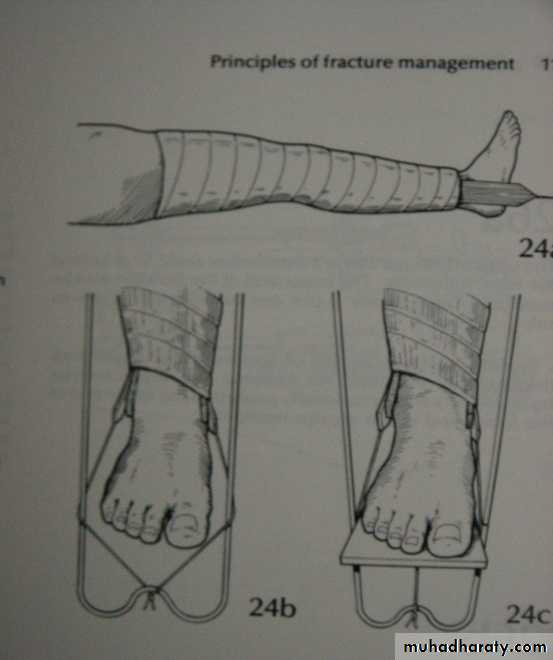
2.Skin traction:
Not more (4-5KG) e.g.
fracture in children.
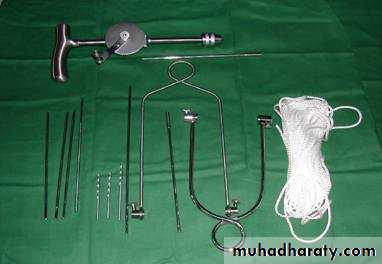
3.Skeletal traction:
By stein Mann pin or
Denham pin.
>5KG.
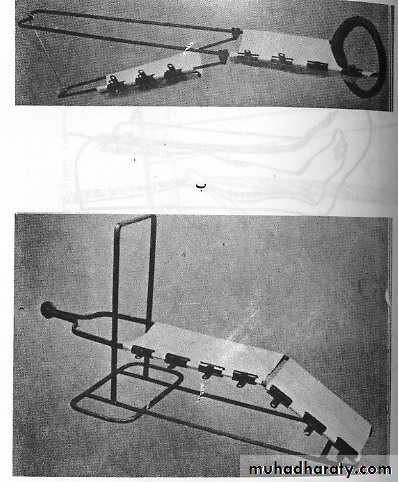
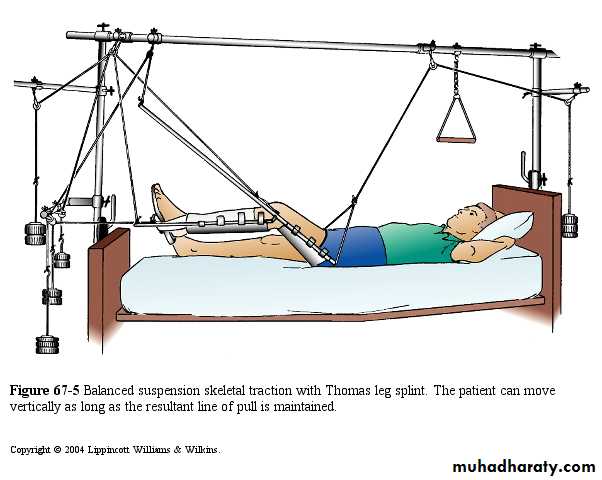
4.Fixed traction:
In Thomas splint.5.Balanced traction
Over pulleys.6.Combined traction.
COMPLICATIONS of skin and skeletal
1.may constrict circulation (gallows traction).2. Nerve injuries (peroneal).
3.compartment syndrome.
4.pin site infection.
5.skin complications.
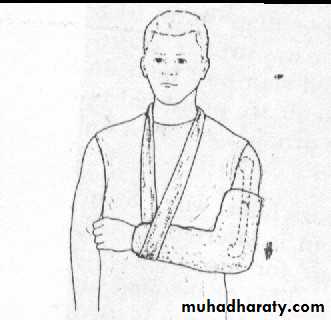
II-cast splintage
Plaster of paris(pop)Complications
1.fracture disease:stiffness, atrophy, osteoporosis,edema.2.tight cast.
3.pressure sores.
4.Skin laceration
III-Functional bracing
Is one way of preventing joint stiffness while still permitting fracture splintage and loading.E.g.(fracture femur ,fracture tibia).
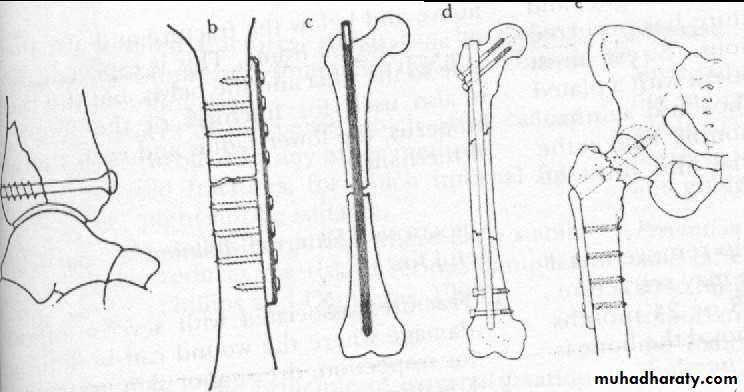
IV-internal fixation
Screw.
Plate .
Wire.
L-plate.
Compression screw.
K-nail.
Indications:
Failure conservative.Displaced intra articular fracture.
Pathological fracture.
Patients who present nursing difficulties.
Complications
Infection.Non union.
Implant failure.
Re fracture.
V.External fixation (indications)
Fracture with severe soft tissue injuries.Complicated fracture.
Infected non union.
Fracture pelvis.
Multiple injuries.
Bone lengthening.
Plastic surgery (flap).
Complications
Over distraction Reduce load transmission.
Pin tract infection.
Vascular or neurological injury during insertion.
Exercise:(physiotherapy)
Prevention of edema: by elevation.
Active exercise: So to pump edema fluid and stimulate circulation ,prevent soft tissue adhesion &promotes fracture healing.
Assisted movement:By gentle movement only.
Functional activity:By improving patient mobility.
FOR MORE:
https://www.muhadharaty.com/lectures?depth=8&&university=1&college_id=1&department_id=126&stage=5&date_from=2016-09-01&date_to=2017-08-31&material_id=29&author=%D8%AF.%D9%85%D8%AB%D9%86%D9%89&subject=PRINCIPLE%20OF%20FRACTURES