Puberty
Definitionis physiological transition from child hood to adolescence with appearance of secondary sexual charectristics
Occur
Between 8-14 yrs in girls
Between 9-14 yrs in boys
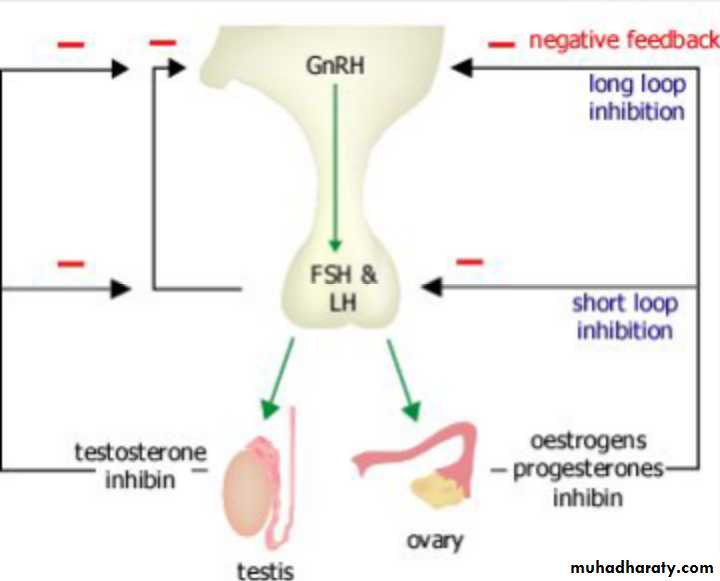
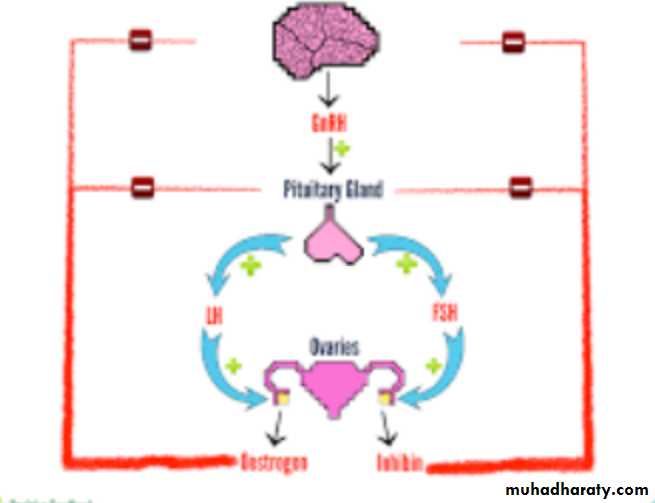
endocrine control
stages of puberty
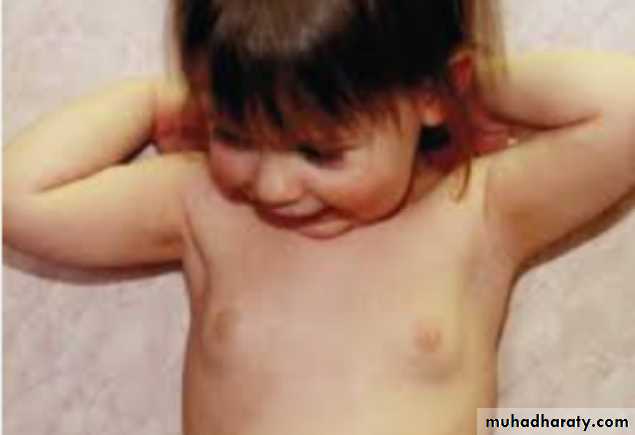
growth spurtThelarche
Pubarche
Axillary hair growth
Menarche
Influencing factors
Genetic factor
Enviromental factor
Leptin
Psychological factor
Puberty; girls
Rising level of plasma gonadotrophins....esrtadiol...development of secondary sexual characteresticsIncrease ovarian volume
1st ovulation occur 6-9 m after menarche
Uterus increase in length & thickness
Vaginal mucosa become thicker & more pink
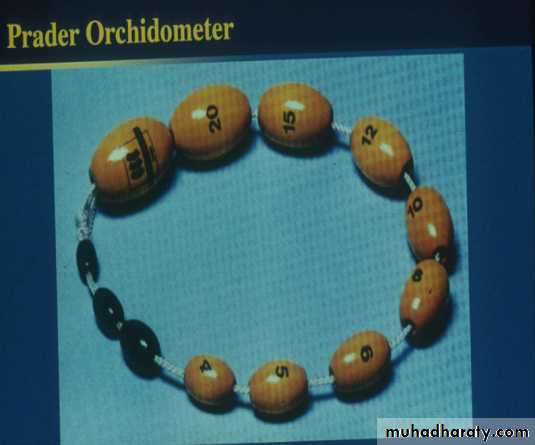
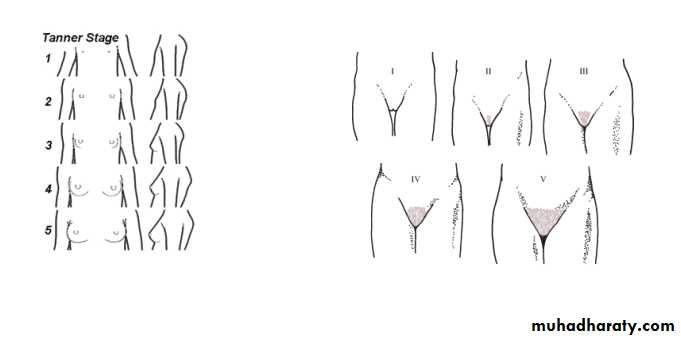
pubertal stage (Tanner )/female
P1P2
P3
P4
P5
Puberty; boys
Testicular enlargementPenil & scrotal enlargement
Pubic hair
Growth spurt
Voice changes
Precocious puberty
development of secondary sexual characteristics< 8 yrs in girls
< 9 yrs in boys
*more common in girls.
causes
gonadotrophin dependant...idiopathic 95%
...congenital (hydrocephalus)
...aquired (irradiation,surgery,sever head injury)
...tumour (glioma)
...Hypothyroidism
gonadotrophin independant
...virilization of female (CAH)...feminization of boy
...adrenal tumour
...ovarian tumour
...exogenous androgen & estrogen
...HCG secreting tumour
...Mc Cune Albright Syndrome
treatment
psychological supportGnRH aginist, leuprolide acetate 0.25-0.3mg/kg im once every 4wks.
In gonadotrophin independant
.... in girl, aromatase inhibitor or anti estrogen
.....In boy,combination of anti androgens
Treat systemic disease.
surgery to remove tumour.
delay puberty
No breast development by age of 13 in female
No mensis by age of 15Testicular size <2.5 cm or 4 ml or pubic hair is not present by age of 14 in male.
Hypogonadotrophic
idiopathicChronic illness (renal failure, crohns disese)
Malnutrition
Exercise
Tumour of pitutary/hypothalamus(cranio pharyngioma)
Hyperprolactinemia
Cushing syndrome
Isolated GnRH deficiency (kallman's syndrome)
Hypergonadotrophic
congenital (turner's, klinefelter syndrome,complete androgen insensitivity,mixed gonadal dysgenesis)
Aquired
...irradiation/ chemotherapy/ surgery
...testicular torsion, trauma
...infection
...autoimmunity
Eugonadotrophic
Congenital anatomic anomalies....imperforated hymen
...vaginal atresia.
...vaginal aplasia
**in these cases, secondary sexual characteristics are normal.
Treatmentpsychological support
Treat systemic disese
Promote puberty/growth
in male case
Low dose testosterone
HCG
In female case
Estrogen
• Assessment of puberty
History1-parents
2-body changes
3-past medical history
4-activity level
5-nutritional habits
6-growth history
7-review of systems
8-medication
examination
1-examination of growth...height
...weight
...BMI
...upper to lower segment ratios
2-pubertal assessment (Tanner staging )
3-neurological assessment
investigation
1-blood test
FBC,LFT,UREA & ELECTROLYTE,FSH,LH,E.,T.,TFT,DHEAS,HCG level.
2-karyotype
3-diagnostic imaging
4-bone age
5-brain MRI
Vaginal bleeding in infancy
Foreign bodyTrauma
Genital tumour
Vulvovaginitis
Precocious puberty
Exogenous hormone usage
Condyloma acuminata
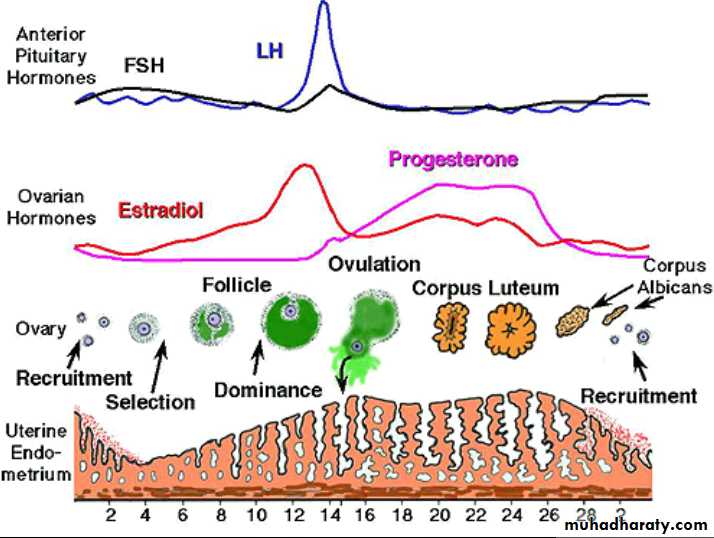
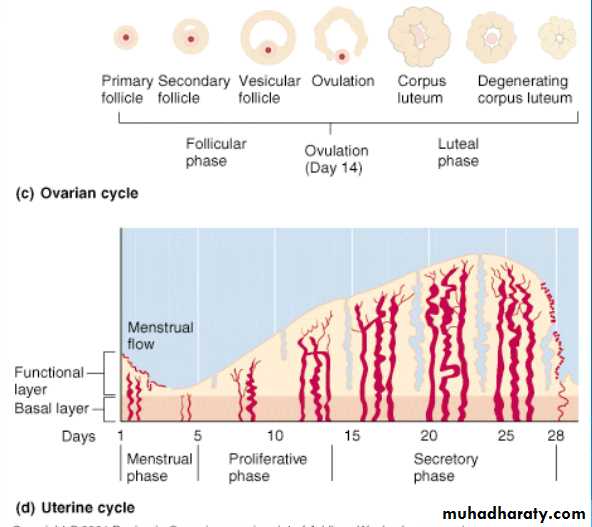
Normal menstrual cycle
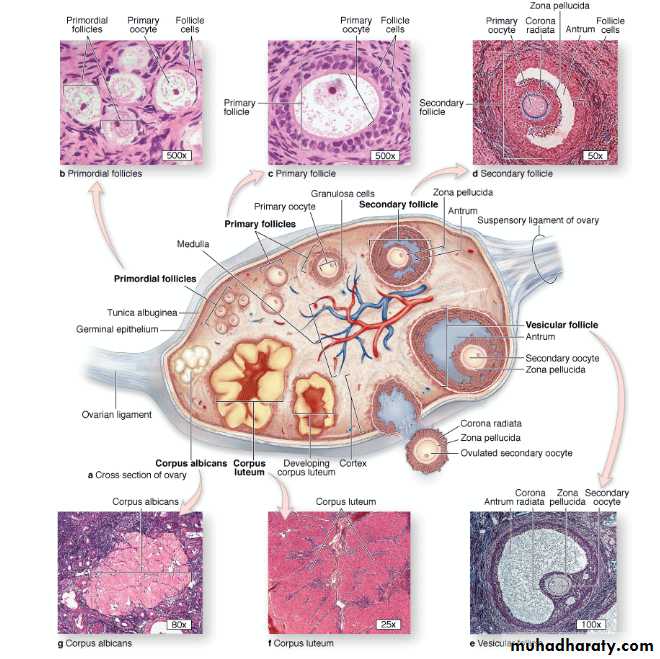
Follicular phase
ovulationLuteal phase
Menstruation
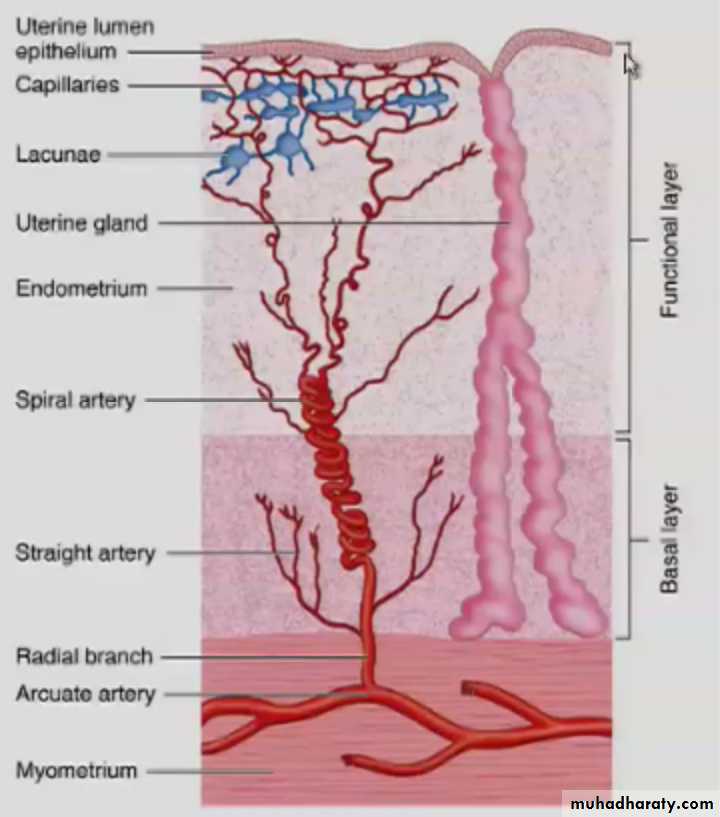
secretory endometrium
Basal layerFunctional layer
Clinical features
menarche; 12-13 yrsCycle duration; 28+-7dys
Duration of flow; 4-6 dys
Peak flow; dy1-2
Normal menstrual loss; 30-35 ml/cycle
Dysmenorrhoea