Fifth stage
Surgery-OrthoLec-4
د.مثنى
18/10/2016
Diagnosis in OrthopedicsOrthopedics
Is concerned with bone, joints, muscles, tendons and nerves, the skeletal system and all that makes it move.Describe
Write in details = introduction + pathological process + managementAll should have equal time
Diagnosis
You have to prove what it isAnatomically (what structure).
Pathology (what is wrong).
History.
Examination.
Special test.
D.D. is only referred to incidental.
Differential diagnosis
What else could be and how would you exclude the other possibilities. by
Examination , tests
We have to thing of the causes in the following
A. anatomical structure.
B. the pathological conditions either (congenital, acquired).
Give an account
Comprehensive for eachIncidence, pathology, etiology, symptoms and sign , treatment.
Discuss
Select the most important controversial aspect of the subject(compare and contrast).
References
Outline of orthopedics 14 edition 2010 adams’s.Apley's system of orthopedics & fracture.
Essential orthopaedic and trauma 2009 (david j dandy).
Landmarks of surgery in the Nineteenth Century
Fundamental advances depend upon the development of other branches of science & industry.The first ,was introduction of anaesthesia (Crawford 1842) Ether.
Louis Pasteur (1822-1895),has fundamental research on bacteria.
Joseph Lister (1867) introduce antiseptic surgical technique.
Roentgens’ in (1895) discovered X-ray
To start orthopaedic surgery encompassed by general surgeon.
Until after the first world war.
In great Britain just before twentieth century each of
(Hugh Owen Thomas &Sir Robert Jones) .
both they set the sound foundation of orthopaedic surgery that now we enjoys.
Diagnosis
History.
Examination.
Diagnostic imaging
Blood test
Synovial fluid analysis.
Bone biopsy.
Arthroscopy.
Electrodiagnosis.
History
Carefully and patiently compiled ,the history can be every bit as informative as examination or laboratory test.Patient give history e.g.
Injury.
pain.
stiffness.
Swelling .
Defomity.
instability.
Weakness .
altered sensibilty and loss function.
Each symptom is need more detail
when it begin.
suddenly or gradually.
spontaneously or after some specific events.
how it progressed.
what make it better or what it make it worse.
Symptoms
PainIs the most common symptom in orthopaedics .
Its precise location is important.
Ask the patient to point it.
Don’t forget pain might referred.
might be boring .
dramatic and bizarre .e.g.
Throbbing abcess
Aching chronic arthritis
Burning neuralgia
Stabbing ruptured tendon
Pain grading
G1(mild) :can be easily ignored.
G2 (moderate):
pain cannt’be ignored, interfer with function and need rx from time to time.
G3 (severe):
pain present most of the time ,demanding constant attention.
G4
totally incapacitating
Referred pain
Pain arising in or near the skin is usually localized accurately.
(it is due to inability of cerebral cortex to distinguish between sensory messages from embyrologically related site). E. g. sciatica.
Autonomic pain
Is much more vague ,often wide spread and accompanied by vasomotor and trophic abnormalities.Stiffness
Generalized:and regularrly in early morning as in rheumatoid arthritis.
Localized:
for a particular joint.
Regular at early morning:
as in R. A.
OR
Transient stiffness :
on or two joints after periods of inactivity is typical of osteoarthritis.
locking
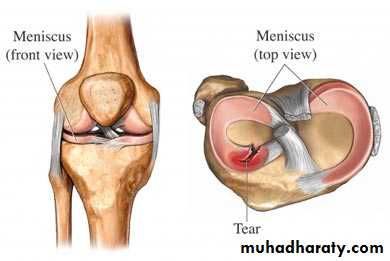
Is aspecial variety of stiffness .it is the suddenly inability to complete one particular movement and it suggests a mechanical blockE.g. torn meniscus.
Swelling
May be in soft tissue , the joint, or the bone .it occurred eitherRapidly as haematoma.
Slowly as soft tissue inflammation, joint effusion.
Painful as acute inflammation, infection.
Is it constant or continue to enlarge, or comes and goes.
Deformity
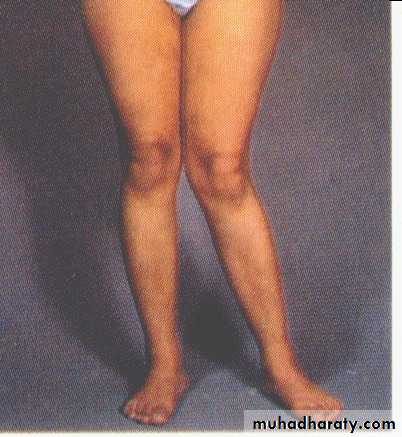
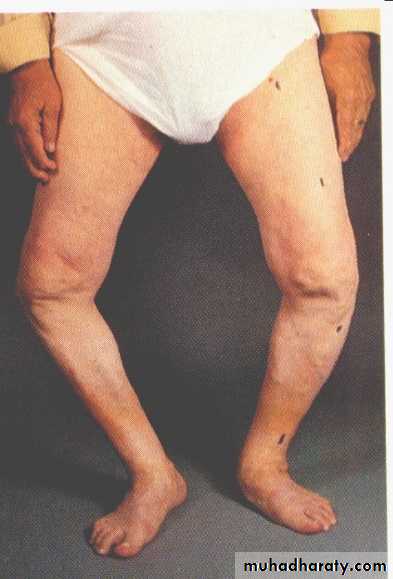
Knock knee Bow Leg
Spinal curvature changes.Kyphosis.
Scolosis.
Lordosis
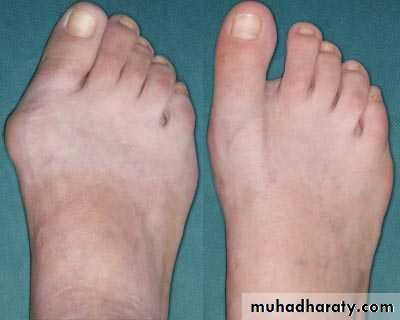
HALUX VALGUS PES PLANUS
weaknessMuscle weakness may be associated with any joint dysfunction,
It may also suggest a more specific neurological disorder as
e.g. poliomylites.
Instability
The patient complains that the joint ((( jumps out ))).Due to muscle weakness or ligamentous deficiency.
Loose body.
Changes in sensibilty
Tingling or numbness signifies interference with nerve function ,as pressure from a neighbouring structuree.g. disc prolapse.
Local ischaemia as in C.T.S in nerve entrapment.
Or peripheral neuropathy.
Loss function
e.g. patient say ‘I can't sit for long time rather than I have backache’.
Past history
It is very important e.g. history of twisted ankle many years ago may be the clue to the onset of O.A.Family history
e.g. in musculoskeletal disorder.Social background
Details about work ,travel ,recreation,home circumstances, and the level of support from family and friends.Examination
General.Local examination of the affected parts.
General
Examination begins from the moment we set eyes on the patient.We should be observing his ,her appearance, posture ,gait .
e.g. are they walking freely or do they use stick, any spinal curvature, short limb.
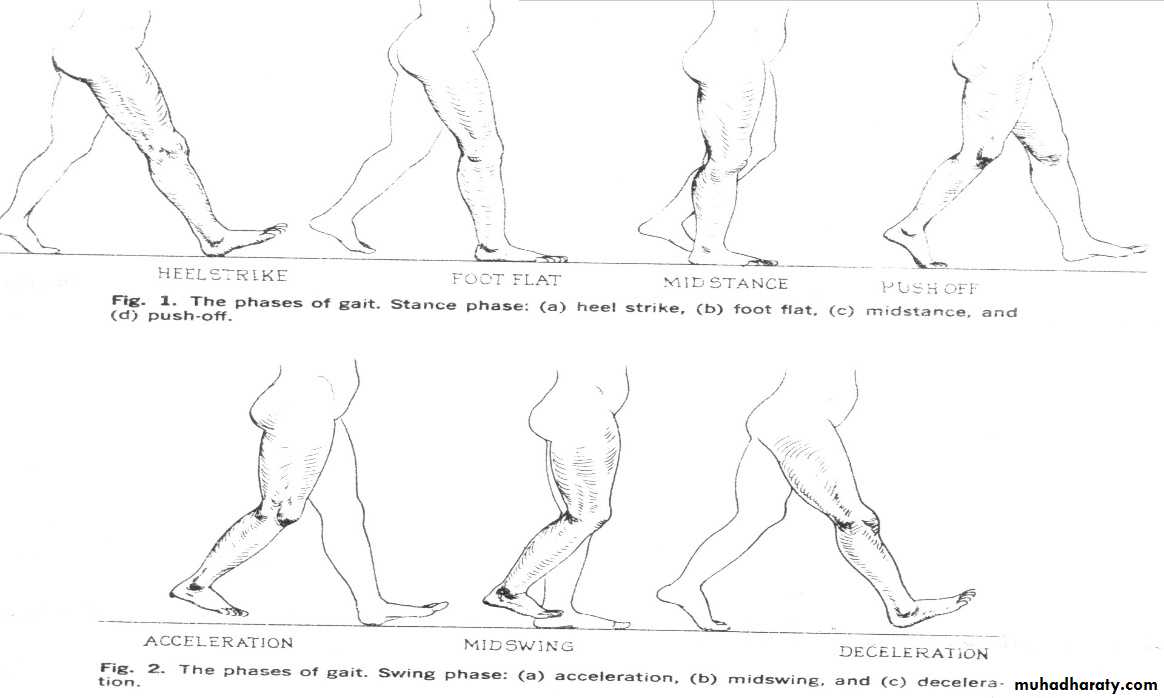
Gait consist of four parts.
Examples:
High steppage gait (foot drop)Antalgic gait in pain.
scissor gait.
Shuffling gait
Dipping gait.
Waddling gait.
Examination of the affected parts
Patient must be suitably undressed.If one limb is affected ,both must be exposed to compare.
We examine the good limb then the bad limb.
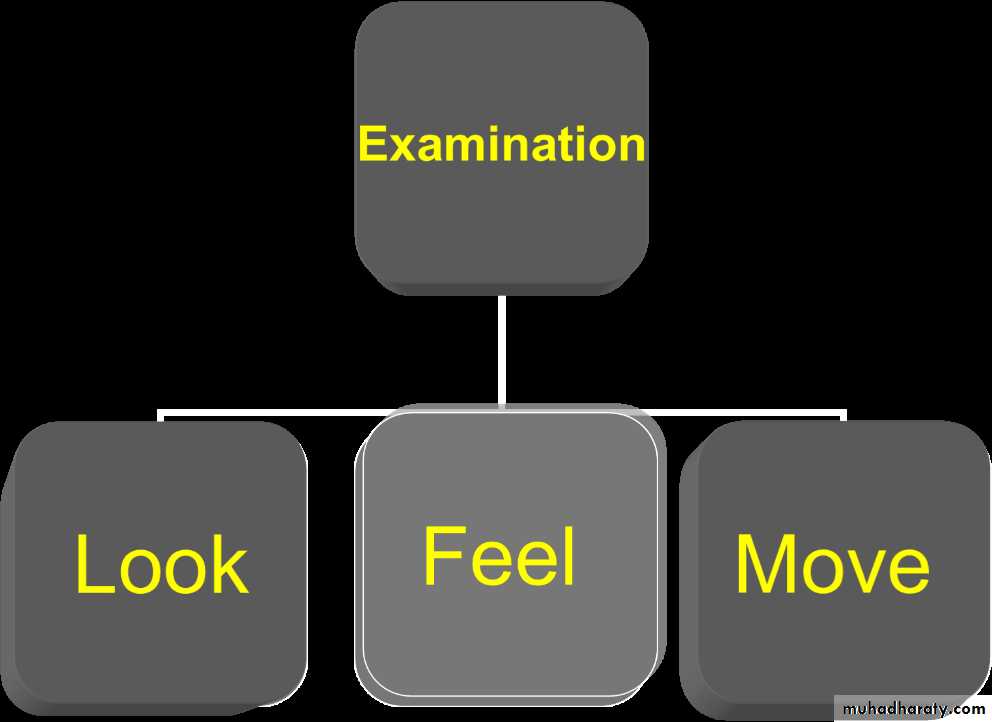
We followed the system of (look, feel, move).
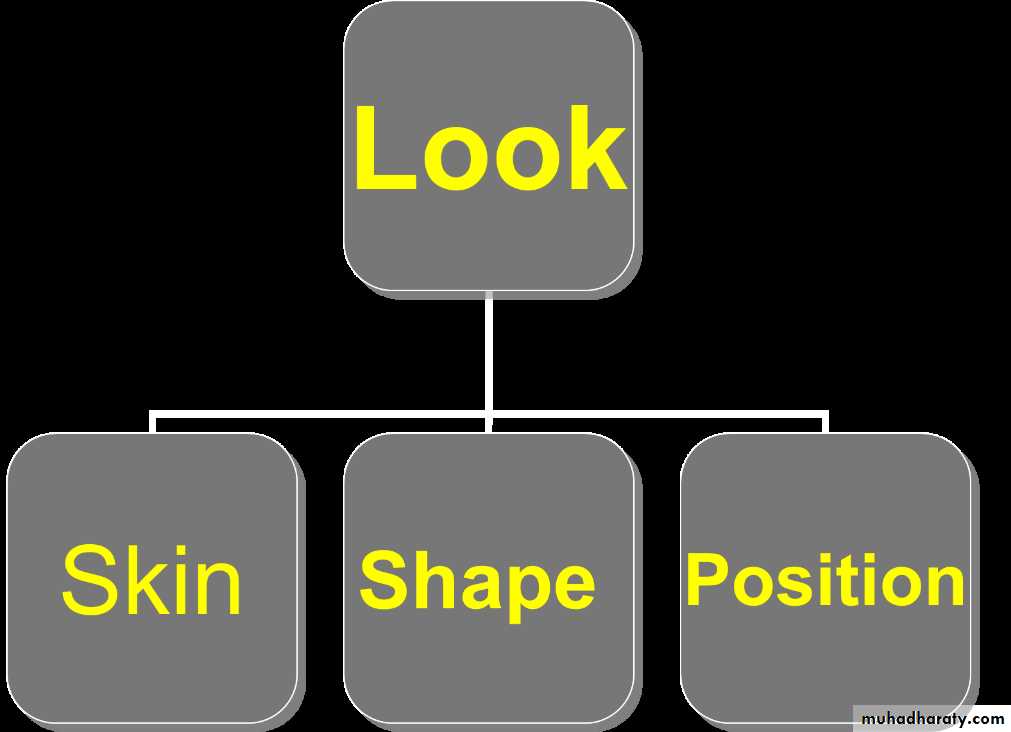
Look
Skin scar,color,creases.Shape swelling ,wasting.
Position in nerve lesion and the joint disease a limb assumes characteristic attitude.
Deformity
Deformity applied to eitherPerson shortness stature
Bone short bone.
Joint joint may be held in an unusual position. (g.varum, lordosis,
kyphosis)
Causes of bone deformity
Congenital pseudarthrosis.Bone softening, ricket.
Dysplasia, exostosis.
Plate injury.
Fracture malunion.
Pagets’ disease.
Causes of joint deformity
Skin contracture (burn).
Fascial contracure (dupuytrens’).
Muscle contracture (volkmanns’)
Muscle imbalance.
Joint instability (torn ligament).
Joint destruction (arthritis).
FEEL
Skin temp,sensation.Soft tissue lump ,pulse.
Bone and joints fluid,synovium.
Tenderness precisely WHERE.
E.G. bony lumps. (size, site, margins, consistency, tenderness, multiplicity).
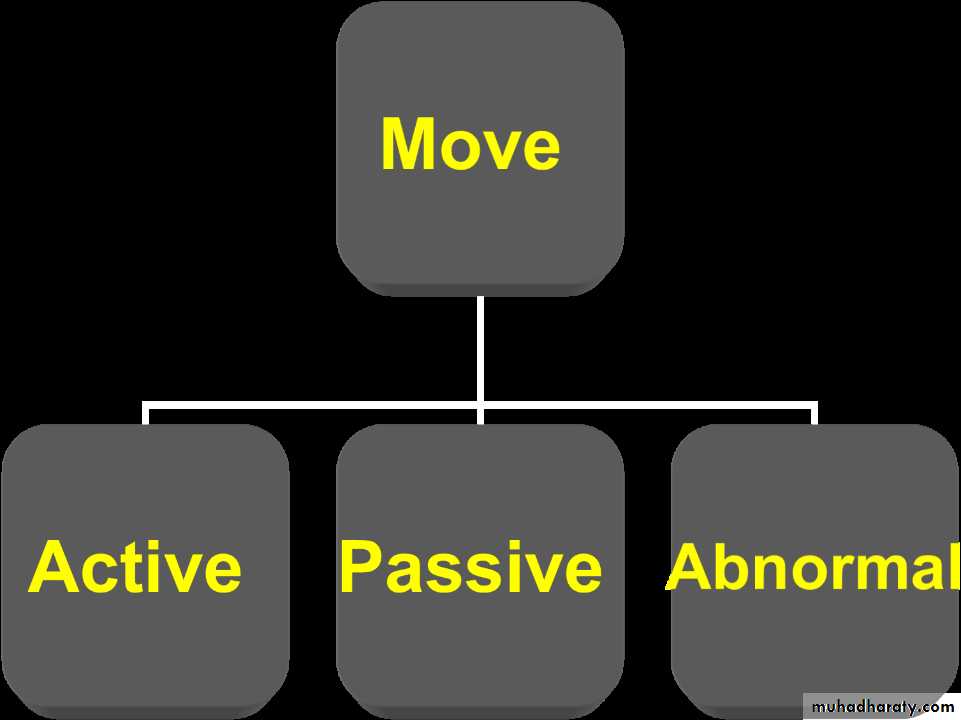
move
Active ask the patient to move the joint.Passive by the examiner.
Normal movement
The range of joint movement is recorded in degrees starting from zero.
Flexion-extension : sagittal plane.
Adduction- abduction :coronal plane.
External –internal rotation: along the longitudinal axis.
Pronation- supination: rotatory movement applied to foot and forearm.
Joint stiffness
The term stiffness covers a variety of limitation of movement .Types:
1. All movements absent.
e.g. surgical fusion. (arthrodesis).
pathological fusion (T.B.).
2. ALL MOVEMENT LIMITED
e.g. in O.A. there is active inflammation of synovium.
3. One or two movements limited
When movement in at least one direction is full and painless the cause is usually mechanical.
e.g. torn meniscus.
Neurological examination
If the symptoms include weakness or in coordination or changes in the sensibility. or if they point to any disorder of the neck or back.A complete neurological examination of the related part is mandatory.
Steps
General appearance.
Claw hand, spastic of cerebral palsy,
trophic skin changes, ulcer , muscle wasting.
Motor function:
tone(( increase tone as in CVA))
not confused with rigidity ((lead pipe….))
power ,reflexes.
flaccidity ( as in polio.).
Testing muscle power(medical research council)
G0: no movement.
G1: only a flicker of movement.
G2: movement with gravity eliminated.
G3: mov. against gravity.
G4: mov. With resistance.
G5: normal movement
Sensory function
Superficial sensationHyperasthesia (increased).
Dysaesthesia (unpleasant).
Hypoasthesia. (diminished).
Anaesthesia. (loss).
Deep sensation
vibration test,
position sense,
sense of joint posture, sterognosis the ability to recognize shape and texture
by feel alone.
Reflexes
The tendon reflexes are monosynaptic segmental reflexes that is the reflex pathway takes a short cut through the spinal cord at the segmental level.Tendon reflex.
Patellar tendon reflex.
Achilles tendon reflex.
Superficial reflexes.
e.g. abdominal reflex.
Deep reflexes.
planter reflex. ( babinski sign).
Diagnostic imaging
Plain film radiography.
Tomography.
Computed tomography T.
M .R. I .
Diagnostic ultrasound.
Radionuclide imaging.
Plain film radiography
X-ray examination is almost 100 years old .
Despite the remarkable technical advances of recent years, plain X-ray examination remains the most useful method of diagnostic imaging.
it provides information simultaneously on the .
Size.
Shape.
Tissue density.
Bone architecture.
Which is usually suggest a diagnosis or at least a range of possible diagnosis.
We should follow the principle of two in reading X –ray.
How to read an X-RAY
The process of reading x-ray films should be as methodical as clinical examination.
Systematic study is the only safeguard against missing other important signs.
The sequence as
start with identifying the part.
particular view. Then
patient : name .
age.
sex.
soft tissue study:
unless examined early ,these are liable to be forgotten.
looks for
muscular planes.
bulging around joints as in rheumatoid arthritis.
presence of calcification.
Bones
looks for deformity, irregularity.
cortex for : Periosteal surface (periosteal reaction).
Endosteal surface.
Trabecular structure.
density : increase in density (sclerosis)
Decrease as in osteoporosis.
The joint
The radiographic joint consists of the articulating bones and the space between them.
The space occupied with radiolucent cartilage.
Looks for narrowing of this space, flattening, erosion, sclerosis………..
X-ray using contrast media
The contrast media used in Orthopaedics are mostly,Iodine-based liquids. (either oily iodides or water soluble ionic variety, e.g. metrizamide.
Sinography.
Arthrography.
myelography.
Tomography
Provides an image focused on a selected plane.Computed tomography (CT)
Produce cutting image through selected tissue planes but with much greater resolution.
Is capable of recording bone and soft tissue outline in cross section.
Disadvantage irradiation.
M.R.I.
Relies upon radio frequency emission from atoms(proton) and molecules in tissues exposed to a static magnetic field.
it is with better contrast resolution and more refined differentiation of tissues.
Diagnostic ultrasound
High frequency sound waves generated by transducer can penetrate several cm into the soft tissue and reflected back and they are registered a electrical signals and displayed as images on the screen.
The equipment is simple and portable.
It has harmless side effect.
It is helpful for screening of DDH.
Radionuclide imaging
Photon emission by radionuclide taken up in specific tissue can be recorded to produce an image which reflect activity in that tissue or organ.The ideal isotope.
99m technetium methylene diphosphonate
Gallium 67.
Blood tests
Hb , differential count,ESR,c-reactive protein, gama globulin.Rheumatoid factor .
Tissue typing (HLA-AG)detected in the white blood cell and are used to characterize individual tissue types.
E.g. HLA-B27 on chromosome 6 as in seronegative.
Blood chemistry.
Synovial fluid analysis
Arthrocentesis: done aftere.g.
injures .
suspected infection .
acute synovitis in adult.
chronic synovitis .
Bone biopsy
Is often crucial means of making a diagnosis or distinguishing between local conditions that closely resemble one another.
Might open (surgery) or
closed (needle).
e.g. in bone tumor diagnosis to confirm benign or malignant.
Arthroscopy
Is commonly performed for.
Diagnostic
Therapeutic reasons.
Almost any joint can be reached,most usefully employed in .
Knee.
shoulder.
wrist.
Electro diagnosis
Nerve and muscle function can be studied by various electrical methods.Motor nerve conduction.
Sensory nerve conduction.
Electromyography.
Nerve Conduction
Conduction velocity of the nerve could be measured between 2 points.e.g. velocity could be slowed as in nerve compression.(40-60 m\ s).
Treatments
METHODS OF NON-OPERATIVE TREATMENT
REST
Since the days of H. O. Thomas , who, more than a century ago, emphasized its value in diseases of the spine and limbs, rest has been one of the mainstays of orthopaedic treatment. Complete rest demands recumbency in bedSUPPORT
. Examples in common use are spinal braces, cervical collars, wrist supports, walking calipers, knee and ankle orthoses, and devices to control drop foot
PHYSIOTHERAPY
These may be active, passive or a combination of the two.Passive approaches involve a range of different techniques carried out on the patient by the therapist.
Active approaches require active involvement by the patient, either by exercising or changing behavior
Passive intervention
Manual therapySoft tissue techniques
Traction
Electrotherapy
Ultrasound
Alternative therapies
Acupuncturemassage
LOCAL INJECTIONS
Intraarticullar
Periarticular
Drugs
Antibacterial and antibioticAnalgesics
Sedatives
Anti-inflammatory
Hormone like drug
Ant osteoporosis
Specific drugs
Cytotoxic drugs
MANIPULATION
manipulation for correction of deformitymanipulation to improve the range of movements at a stiff joint
manipulation for relief of chronic pain in or about a joint, especially in the neck or spine
RADIOTHERAPY
Operative treatment
SYNOVECTOMY
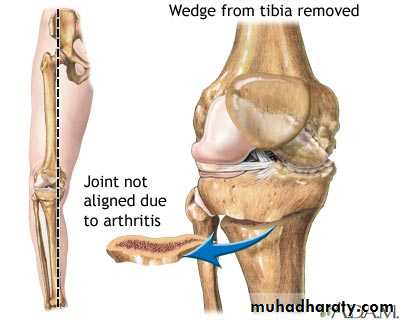
OSTEOTOMY
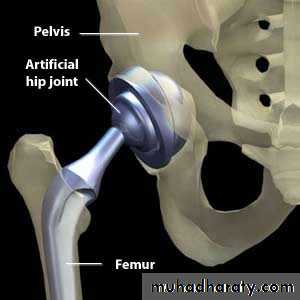
ARTHROPLASTY
Bone GRAFTING OPERATIONS
TENDON GRAFTING OPERATIONS
EQUALISATION OF LEG LENGTH
leg lengthening
leg shortening
arrest of epiphysial growth.
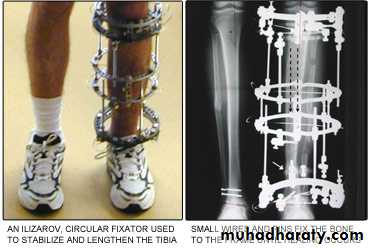
BONE FIXATION TECHNIQUES
AMPUTATION
https://www.muhadharaty.com/lectures