Removable partial prosthodontics
Dr.Shanai M. AttiaA. Definitions
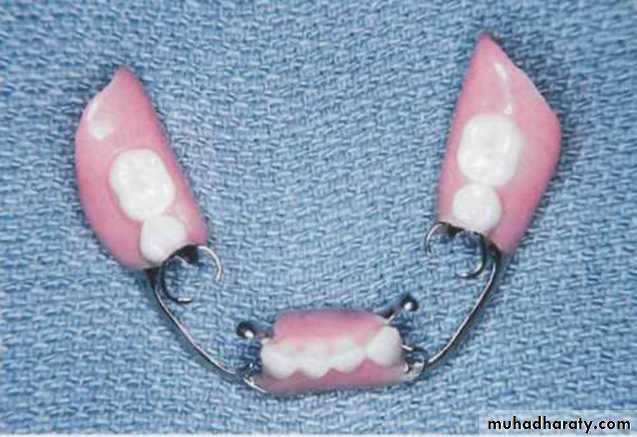
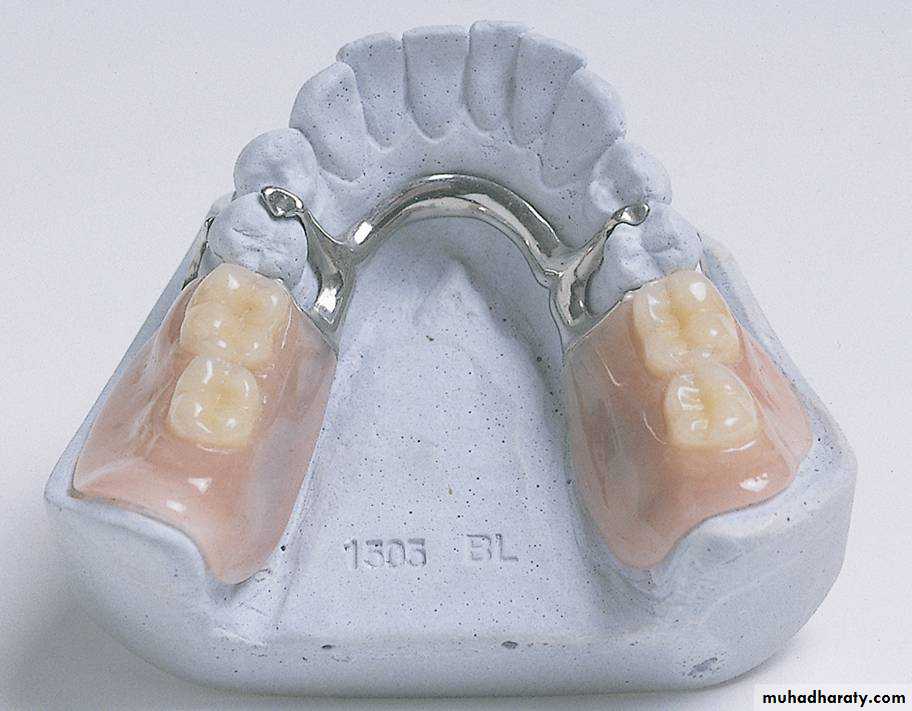
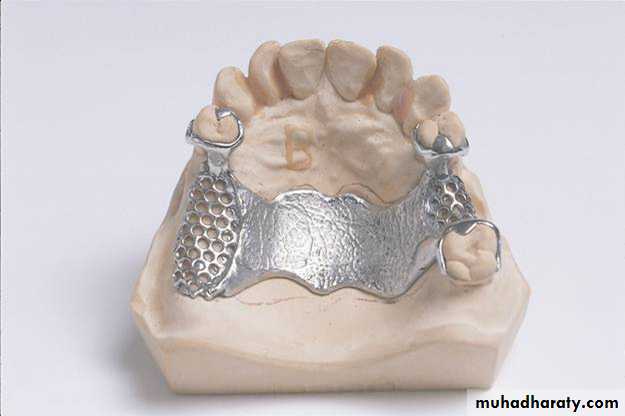
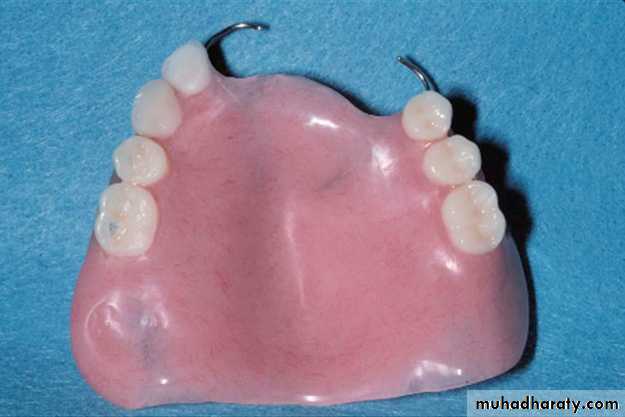
Partial denture: A prosthesis that replaces one or more, but not all of the natural teeth and supporting structures. Its supported by the teeth and/or the mucosa. It may be fixed( i.e. a bridge) or removable.Removable partial denture (RPD): A partial denture that can be removed and replaced in the mouth by patient. A partial denture being constructed from cobalt chromium alloy and considered to be as permanent treatment.
• Interim denture (provisional; temporary): A denture used for interval of time to provide:
• esthetics, mastication, occlusal support and suitability.
• Conditioning of patient to accept the final prosthesis
• Retention: resistance to removal from the tissues and teeth.
• Stability: resistance to movement in horizontal direction (anterior-posterior or medio- laterally.• Support: resistance to movement toward the tissues or teeth.
• Abutment: a natural tooth that support a partial denture.
• Retainer: a component of partial denture that provides both retention and stability for the partial denture.
• B. removable partial denture treatment objectives.
• The main objectives of removable partial denture treatment are.• Preserve remaining teeth and supporting structures
• Restore esthetics and phonetics
• Restore and/or improve mastication.
• Restore health, comfort and quality of life.
Indications of RPDs
• Long edentulous span (too long for a fixed prosthesis).• No posterior abutment for a fixed prosthesis (free end)
• Excessive alveolar bone loss (esthetic problem)
• Poor prognosis for complete denture due to residual ridge morphology.
• Reduce periodontal support of remaining teeth (wont support a fixed prosthesis).
• Cross-arch stabilization of teeth.
• Need for immediate replacement of extracted teeth.
• Cost/patient desire considerations
Alternative RPDs treatment options
• No treatment (shortened dental arch)
Most patients can function with a shortened dental arch (SDA)
RPD doesn't usually improve function if minimal occlusal unites present.
2. Fixed partial denture- requires abutments at opposite ends of edentulous space, more expensive than RPD, must grind down abutments, flexes and can fail if too long.
3. Implant supported prosthesis- most costly. Closest replacement to natural dentition.
4. Complete denture: if few teeth left, with poor prognosis.