
pg. 1
Fifth stage
Pediatric
Lec1p1
.د
فارس
2/11/2016
Respiratory diseases
Lecture note:
Respiratory disease is very commune in children and its commune
cause of hospital admission
Most of the causes of respiratory diseases in children are viral
infection (80%-90%) so not give antibiotics
Very rare bacterial infection
Commonest types of viruses are influenza, para-influenza, rubella,
RSV, measles, …
Strider:
It is harsh and high pitched sound mainly inspiratory sound (forceful
breathing against closed glottis) that result from the upper airway
obstruction
Common in winter and fall.
Causes:
Common : Croup, Acute epiglottitis, laryngeo-malasia, Foreign body
inhalation.
Rare: vocal cord paralysis, laryngeal hemangioma.
Note :
Upper respiratory tract obstruction Stridor mainly inspirotary
Middle = = = wheeze inspiratory or
expiratory
Lower = = = Expiratory
pg. 2
Acute stridor
Croup=viral Croup =
laryngotracheomalacia
Common Viral infection occur especially in winter
Its Cause :
caused mainly by Para-influenza virus ,other : rhinovirus, measles,
Very rarely bacterial.
Age of incidence :
2month to 5 years ,
Peak at 2 years of life
Male >female
Bottle >breast feed
More in crowing area
Clinical feature :
Hx of A family member has a URT infection and he got it
Begins with mild upper respiratory infection then progress in sevirty,
rhinorrhea,
sneezing ,
mild fever ,
respiratory distress,
inspiratory strider,
barking cough which is pathognomonic (start at night),
exhausted,
edema of larynx,
struggle to breathe,
child only want to sit.
It last few days and rarely recurrent (only if positive family history).
Anything disturbed the baby or make him cry will increase the
symptoms and can lead to respiratory obstruction and death.
pg. 3
Diagnosis:
clinically (always examine baby in his mother's lap) and no need for
investigations.
Investigation :no need but
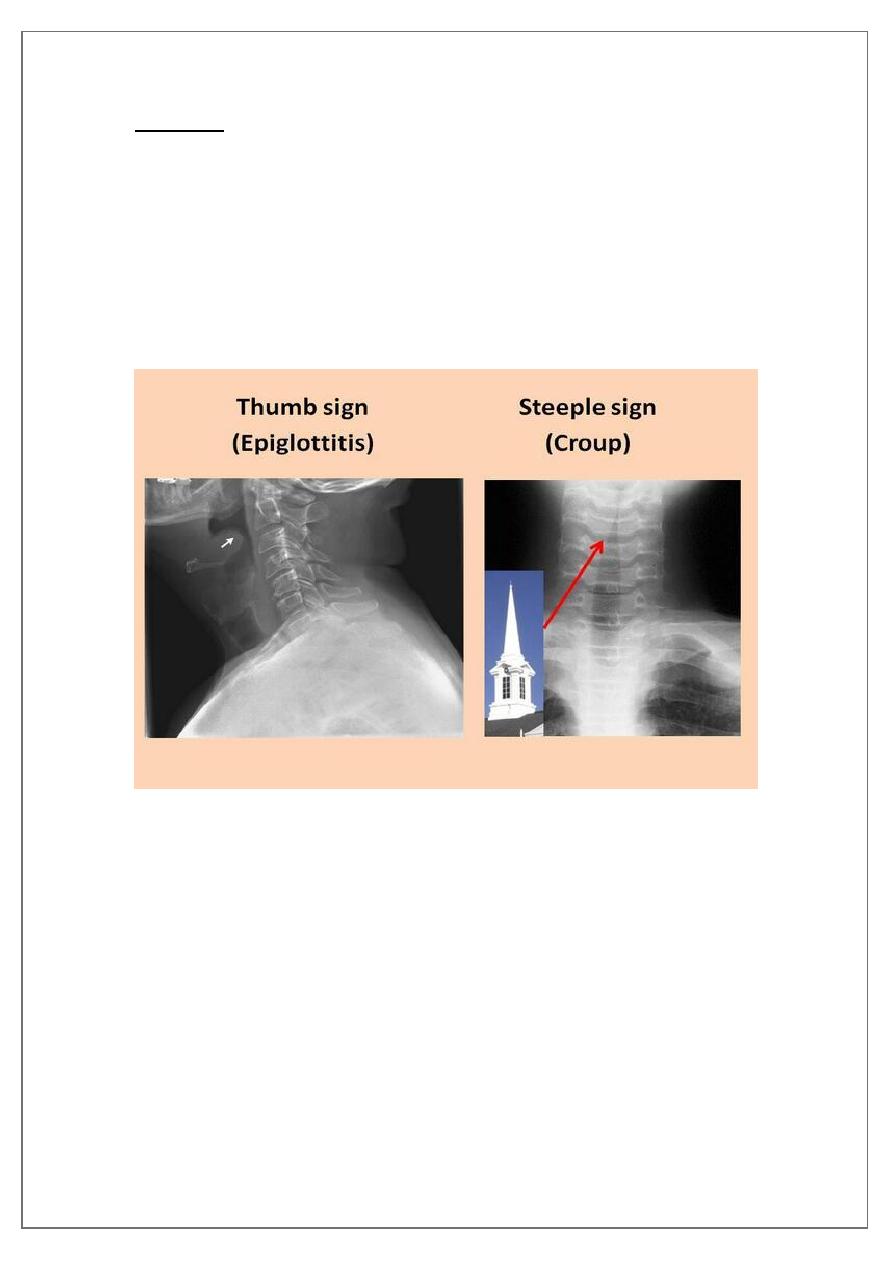
X-ray STEEPLE sign
Treatment:
Mild cases At home:
o Always try to calm the child,
o Good hydration,
o Steam inhalation,
o Anti-pyretic.

pg. 4
At hospital :
Indication of admission:
moderate to severe symptoms,
strider at rest ,
decreased level of consciousness,
cyanosis,
need O2.
Give:
humidified O2
, single dose of Dexamethasone (0.6 mg/kg orally single dose or
parenteral), Nebulized racemic epinephrine(1\3 ml epinephrine
+3ml NS)or L-epinephrine (for Broncho-dilatation),
Monitor & Observe.
Some time we give Heliox
If cyanosis or decrese mental state Intubation (only in 1% of
baby) or tracheostomy (But tracheostomy is easier because
there is edema in the airway)
Prognosis is good mortality is very rare
Some children turn to have asthma in later "source of allergy "
Spasmodic croup :
Not viral problem
Cause is unknown due to spasm ,may be psychological ,allergic
Less in severity and short coarse
Clinical feature and treatment is same as viral croup but Less in
severity and short coarse and Not cause prodromal symptom
pg. 5
Acute epiglottitis:
It is life threatening condition (Total airway obstruction).
Severe bacterial infection of epiglottis and subepiglottic fold.
Bacteria mainly Hemophilus infleunzae type b,
Strep.pyogens,strep pn. S.aurus
Age :older 3-6 year
ACUTE ONCET
SUDDEN ONCET
All children need intubation for 2-3 days.
Antibiotics for H.infleunzae (amoxicillin or ceftriaxone) for 7-10
days
Clinical Features :
sudden onset
high fever
toxic
sore throat
dysphagia
triode position
drooling of saliva
dyspnea
collapse
coma,
death (in few hours).
Any intervention is contra indicated utile airway is secure
pg. 6
Dx :
Clinical diagnosis
don't do x-ray.'during the way to x-ray department he may
develop total obstruction
(not use tongue depressor) lead to respiratory obstruction)
Any intervention is contra indicated utile airway is secure
Do examination only if you are theater room with available tools
for intubation, tracheostomy and anesthesia
Bacterial culture
Treatment :
Admission
to icu
O2
IV fluid
British school: conservative ,monitoring ,give Antibiotic
(amoxicillin or ceftriaxone
) if fill
intubation, tracheostomy
American School intubation, tracheostomy
Recently all child intubation 2to 3 day
Give rifampicin to house hold members for 2 days to prevent
meningitis due to H.infleunzae.
Note :
H.infleunzae cause :
Otitis media
Bacteremia
Arthritis
Meningitis
Pneumonia
Pulmonary edema

pg. 7
Foreign body inhalation (aspiration)
Common in infants and toddlers 1-5 year. (Infant can swallow F.B
because they explore environment by their mouth).
Inhale small things like: فستق،سمش بح ،زرخ ،لباعد
History very important, healthy baby, sudden onset, parent deny
something (social circumstances).
Cause acute strider.
Three stages of symptom :
First stage severe paroxysm of cough, cyanosis, chock, sneezing,
gagging immediately after foreign body inhalation.
Second stage Misleading "Asymptomatic" (like a recovery state).
Third stage symptoms of complications because F.B go to the right
lung and lead to atelectasis, pneumonia, tachypnea, cyanosis,
retractions, fever, and other symptoms.
Diagnosis clinically.
Investigations:
CXR
should be done in deep inhalation
see localized
hyperinflation, most are radio-lucent.
Fluoroscopic
Ct –scan
MRI
Bronchoscope
diagnostic and therapeutic
pg. 8
Treatment
:
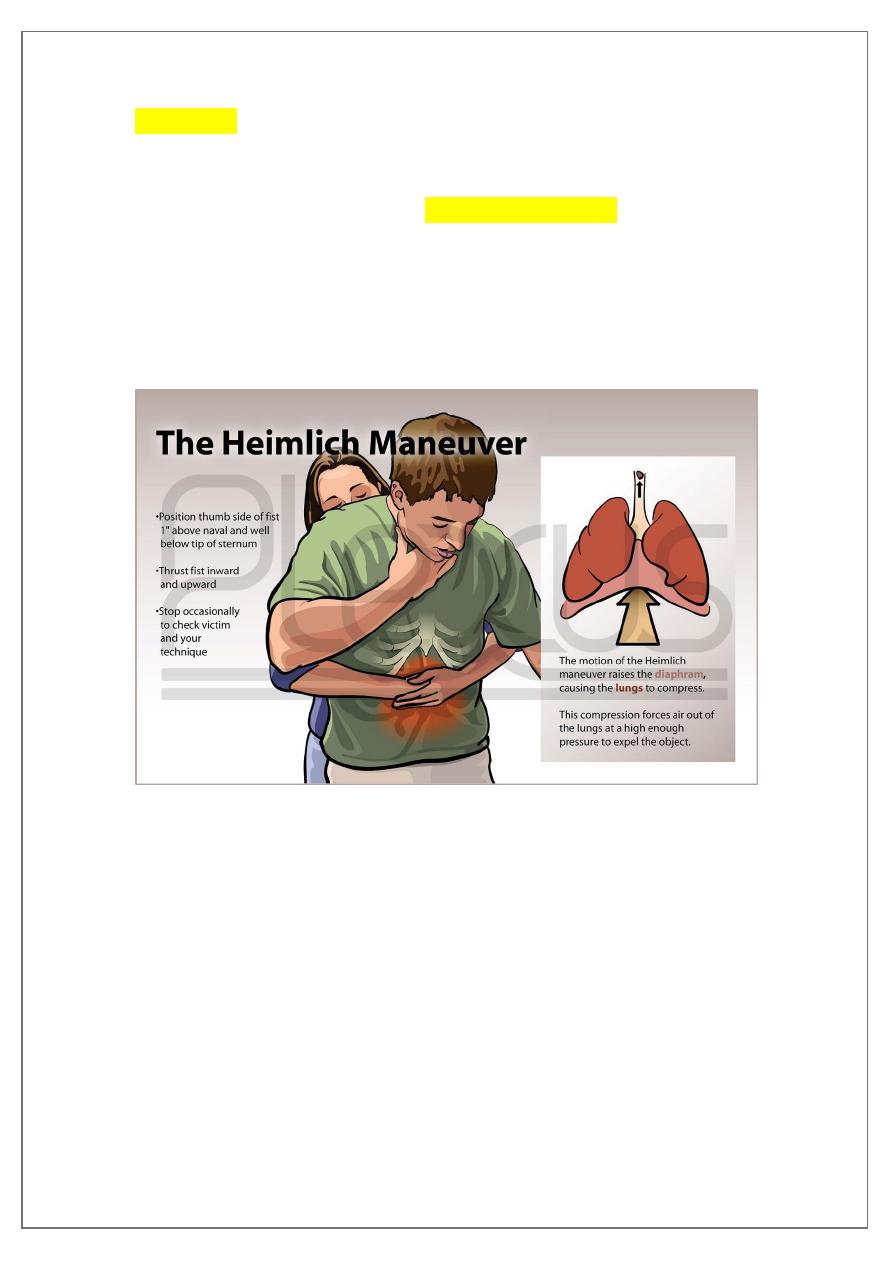
1-laryngeal F.B:a)infant held upside down &big thrust on his back
b)older children
hemleich's maneuver
c) not success laryngoscope
2-tracheal or bronchial rigid bronchoscope
NB:some time need surgery
Note :
Foreign body in:
RT main bronchus local wheeze
Carina bilateral wheeze
No wheeze mostly laryngeal stridor

pg. 9
Other cause of acute stridor :
Diphtheria
Acute laryngeal burn
Lymphoma
Leukemia
External compression of trachea by mediastina mass
Thyroid enlargement
Tetany(hypocalcemia)
Hysterical stridor
Angioedema
painless edema of hand face joint skin >>>tx :is by
anti-histamine ,steroid ,subcut.epinephrin

pg. 10
Chronic stridor
Laryngo-malacia= (floppy larynx)= (infantile larynx):
The communest cause of stridor and congenital anomaly of larynx
Exaggerated collapse of larynx in inspiration.
Common and alarming to parent
Represent 60% of strider causes.
Usually present at birth , Less than 4-6 weeks of life start. ,More than
6 weeks start
more serious condition.
Feature :
Inspiratory stridor low pitch ' Strider at rest.
Become more in excretion like crying and feeding ,disturbing the
baby, supine position and URTI
Very rare dysphagia because of laryngeal reflux
No respiratory distress (important).
INV :
Usually no need
Some time we do laryngoscope show inward collapse of
supraglotic structure during inspiration
If there is dyspnea chest X-ray ,barium swallow if there is
Dysphagia
Treatment
Explain everything to parents
Simple, recover spontaneously.
Not need admission, not need treatment, not need investigations.
Some time in more sever cases case :
Cor pulmonale ,FTT,cyanosis
need tracheostomy and supraglottoplasty

pg. 11
Chronic stridor cont.
Vocal cord paralysis :
3rd most common congenital anomalies that cause stridor
May be unilateral or bilateral
Unilateral is more common than bilateral
Unilateral Vocal cord paralysis:
More common than bilateral
Due to difficult labor
The child develop (choking ,cough, aspiration ,weak cry ,and
stridor )
It’s a salve limiting disease
Bilateral Vocal cord paralysis:
Less common than unilateral
Usually associated with CNS anomalies ,hydrocephalies, spina
bifida ,
Investigation like CT-scan MRI is done to exclude cns anomalies
Vascular ring :
One of the conginetal anomalies that cause stridor
Double Aortic arch form ring and this ring encircle trachea and
esophagus
the child has stridor ,dyspnea ,some time wheeze and dysphagia
if dysphagia barium swallow done
treatment surgry
pg. 12
Other cause of chronic stridor:
papilloma
haemingioma
https://www.muhadharaty.com/lecture/13774
