Anuria and Retention of Urine
Anuria and Acute Renal Failure (ARF)Causes of ARF
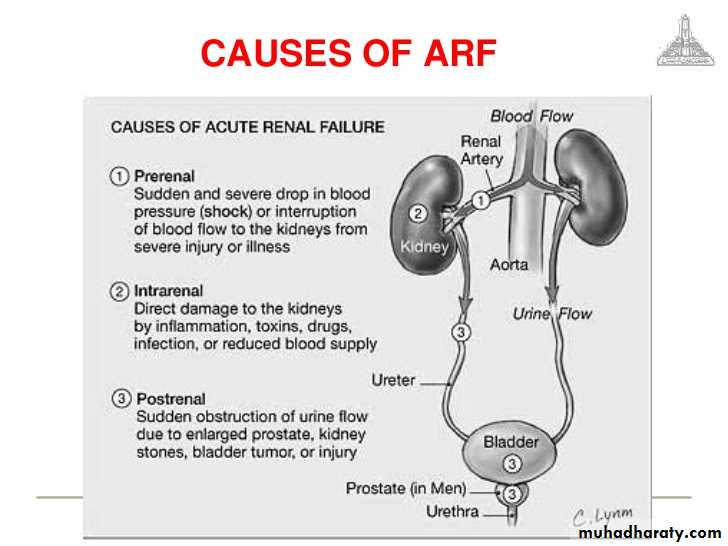
Causes of pre-renal ARF
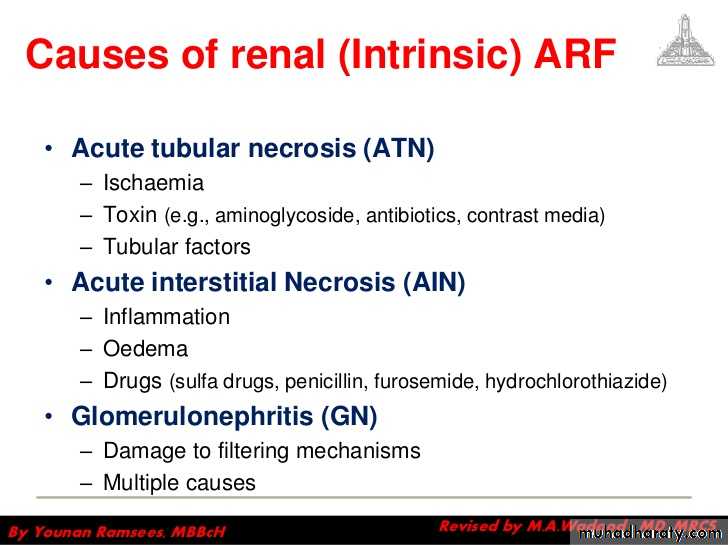
Causes of renal (intrinsic) ARF
Causes of post-renal ARF
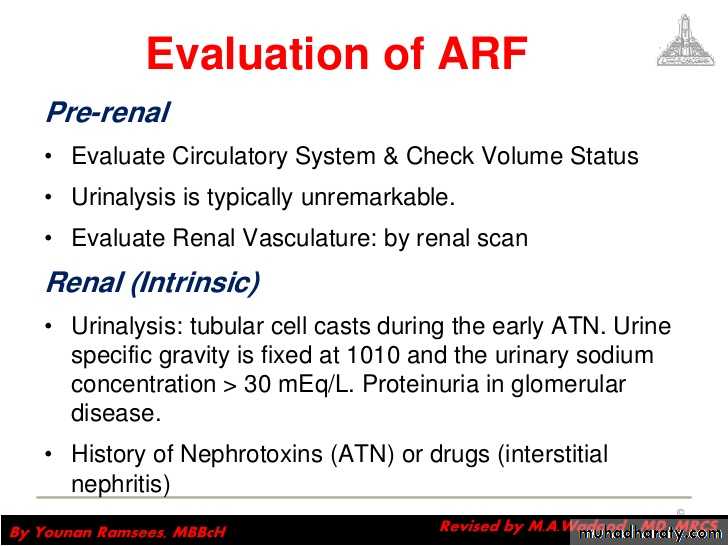
Evaluation of ARF
Evaluation of ARF
Management of ARF
Management of ARF
Indications for acute dialysis
Urinary Retention
Urinary Retention
Acute Urinary Retention (AUR)
Acute Urinary Retention (AUR)
Acute Urinary Retention (AUR)
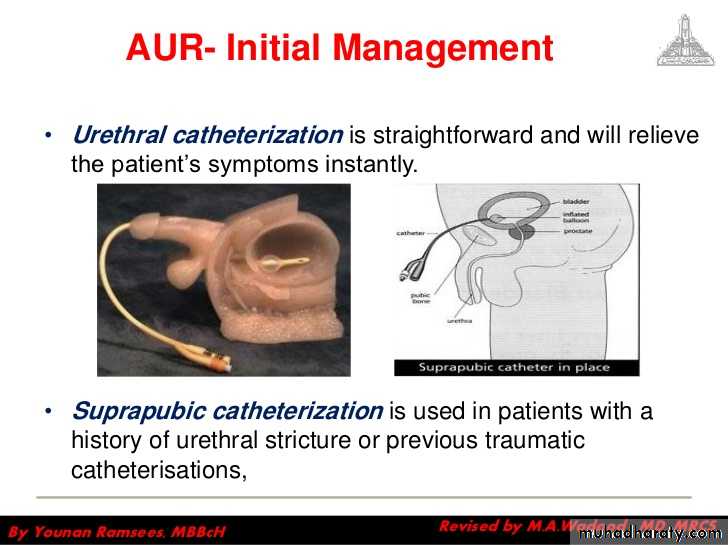
AUR-Initial Management
AUR-Further Management
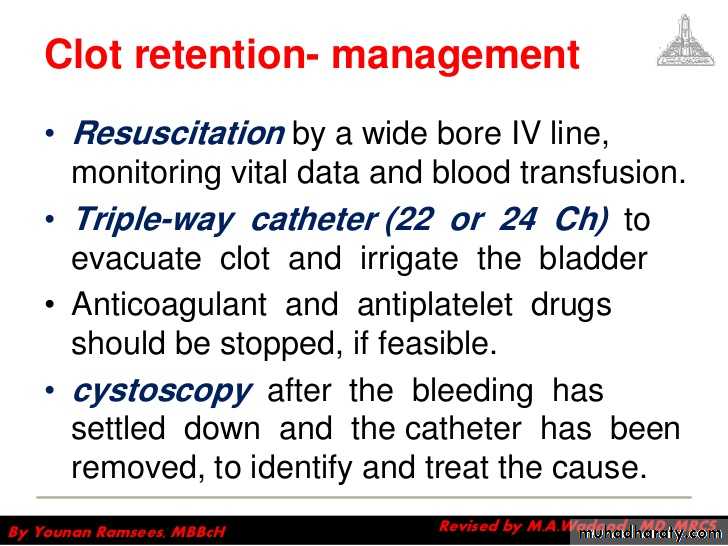
Clot retention
Clot retention-Investigations
Clot retention-Management
Chronic Retention
Large volume painless retention with overflow incontinence.Can be high pressure or low pressure chronic retention
Usually associated with hydronephrosis and uremia
Large amounts of residual urine exist, bladder volume > 800ml
When the vesical pressure exceeds the urethral resistance, the patient can pass some urine or dribble continuously. This is called false or overflow incontinence.
When the patient is suddenly unable to pass urine, acute-on-chronic retention of urine has occurred.
Chronic Retention
Causes: Long standing incomplete obstruction with:• A) Mechanical: BPH, prostate cancer
B) Functional: Neuropathic flaccid bladder.Chronic Retention
Emergency measures:Urethral catheter or Suprapubic catheter: if urethral trauma or injury are expected
Ureteric catheter or DJ stent, if failed, PCN.
Definitive trearment:
According to underlying cause---TURP
Differentiation between acute and chronic urinary retention
Chronic
Acute
+
-
Voiding
partial
Complete
• Obstruction
-
+
Pain
+/-
+
Suprapubic tenderness
>800ml
<800ml
Drainage volume
+/-
-
Uremia
+
-
Hydronephrosis
Differentiating acute and chronic retention from anuria
Anuria
Chronic retention
Acute retention
-
-
+
Desire to urinate
-
-
+
Suprapubic pain
+
-
-
Renal pain
Uremia
±Uremia
good
General exam.
Empty bladder
Full bladder
Tender full bladder
Abdominal exam.
No or <50ml
>800ml
Drainage <800ml
Catheterization
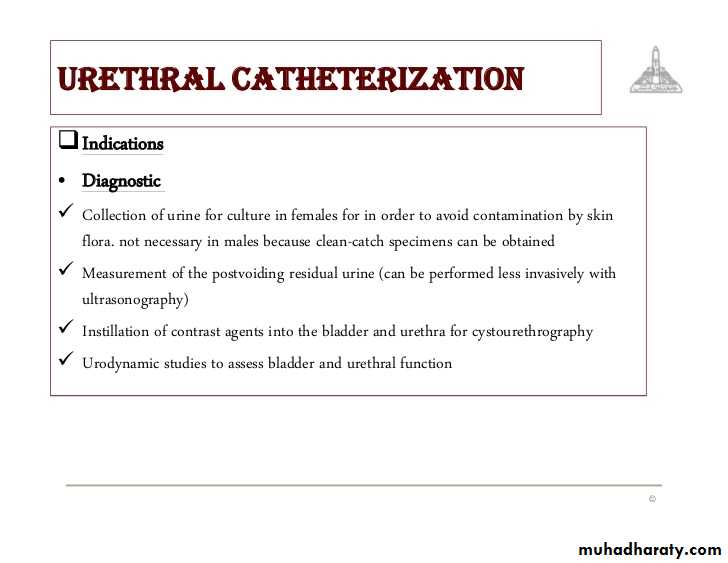
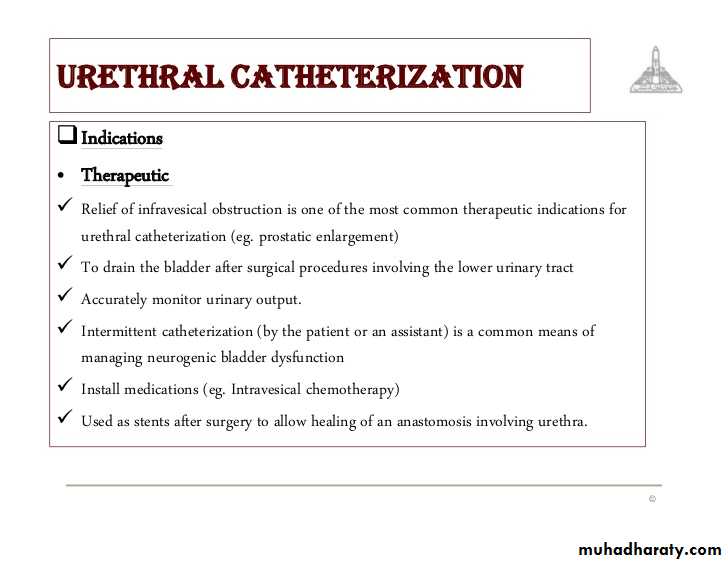
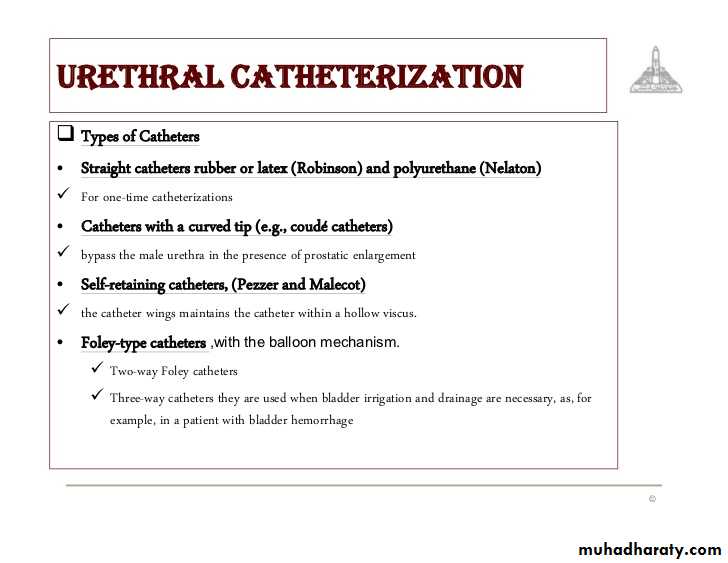
Instrumentation and Endoscopy
Instrumentation and Endoscopy
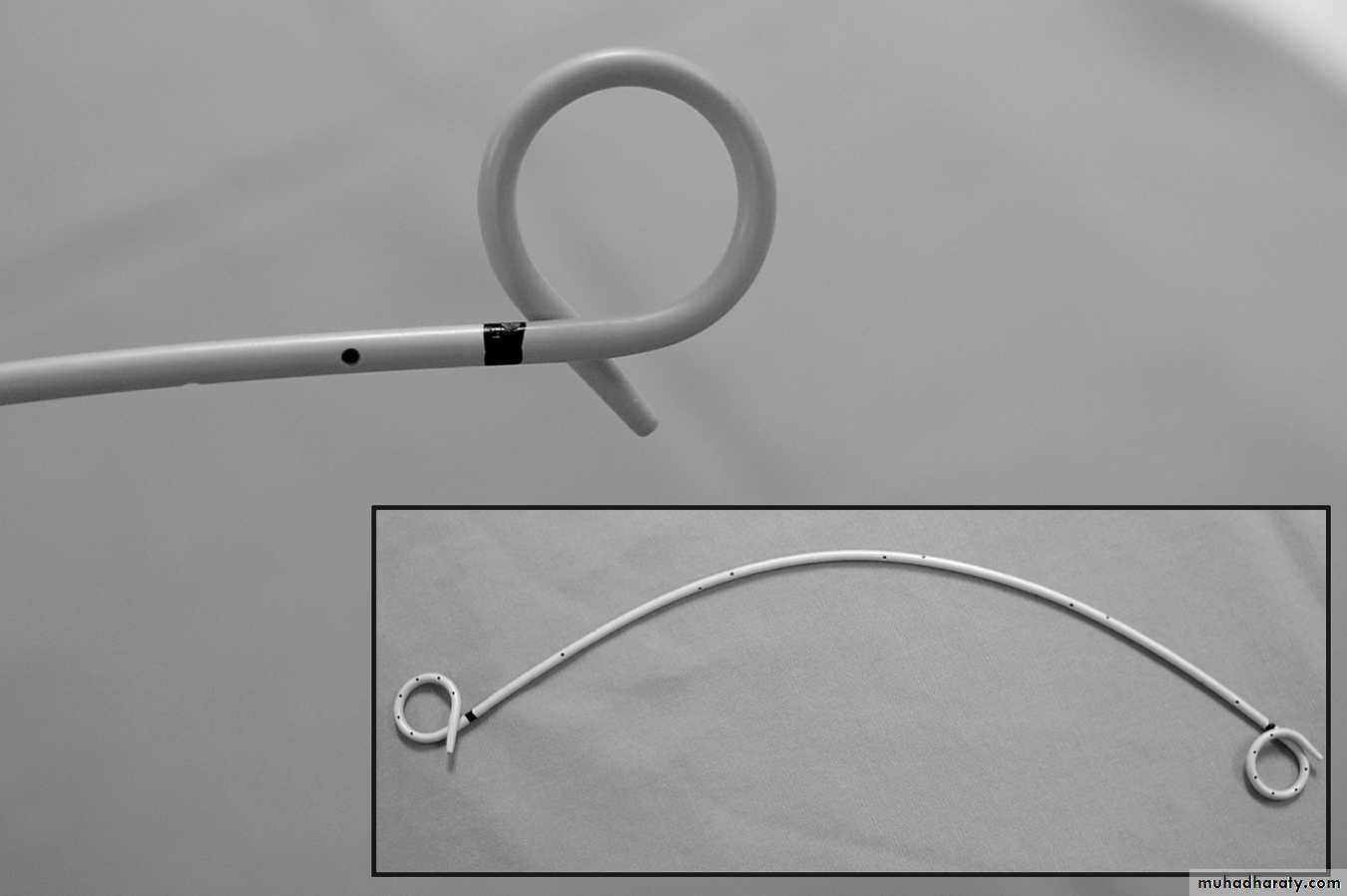
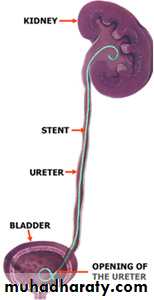
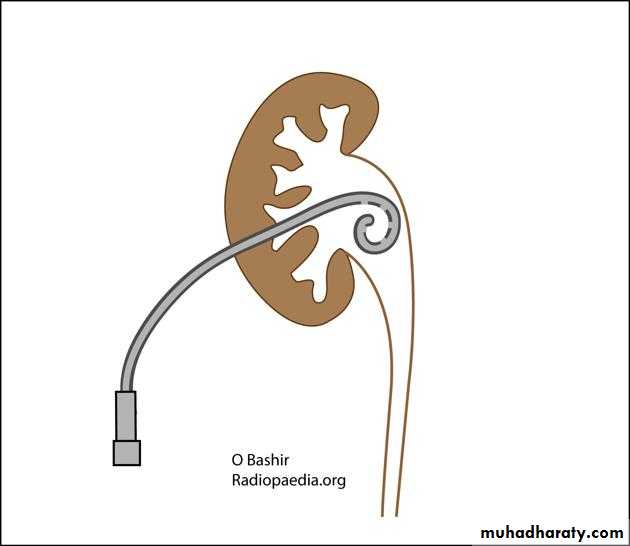
URETERAL STENTS
• Ureteral stents are a mainstay in the urological armamentarium.
• utilized in:
• treatment of urolithiasis including postureteroscopy
• preshockwave lithotripsy
• to relieve symptomatic renal colic
• to provide urinary drainage in nongenitourinary causes of ureteral obstruction, such as pregnancy and malignant ureteral obstruction
• To serve as a surgical landmark for ureteral identification in order to avoid iatrogenic ureteral injury in abdominal or pelvic surgery.
URETERAL STENTS
• Ureteral stents decrease the frequency and amplitude of ureteral contractions.• The ureter and ureteral orifice are theorized to passively dilate from the stent, thus facilitating drainage.
• Available in various sizes, designs & materials.
URETERAL STENTS
URETERAL STENTS
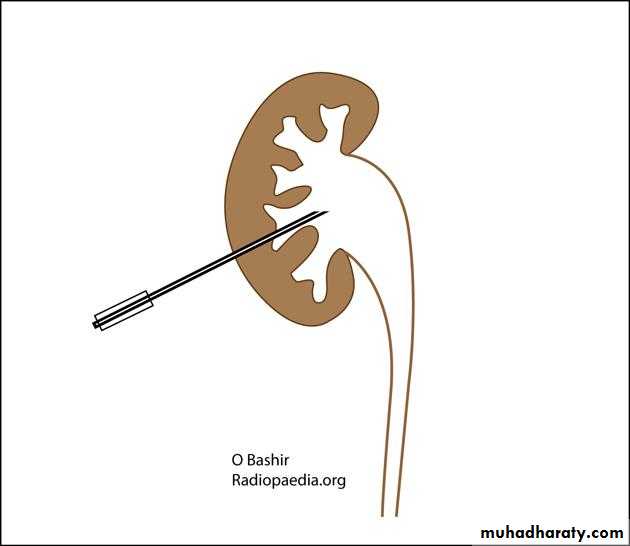
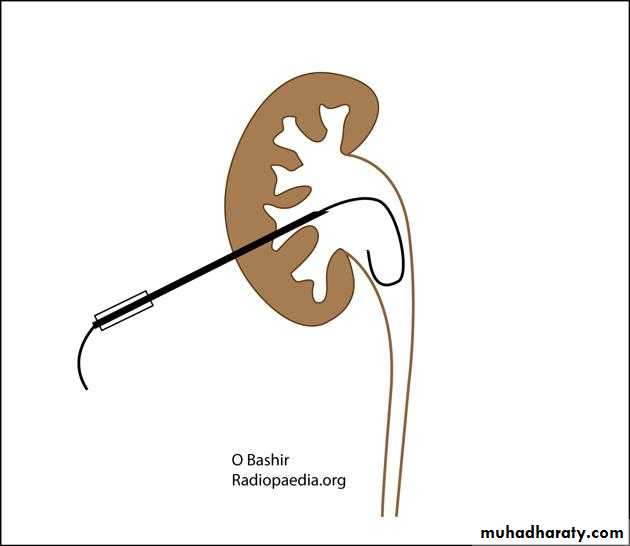
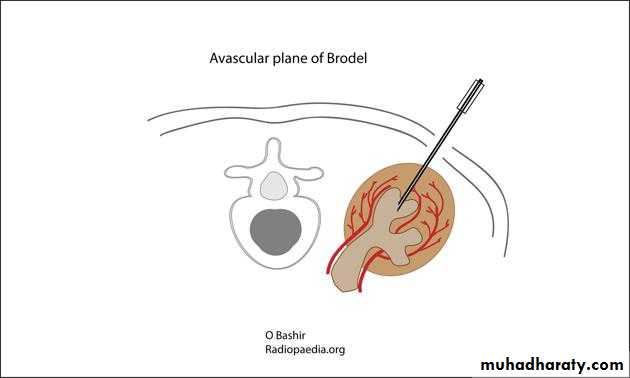
PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROSTOMY
• Primary indication- to relieve an obstructed and infected renal collecting system.Indications:
urinary tract obstruction
urinary diversion (e.g. ureteric injury; urine leak)
access for percutaneous procedures (e.g. stone treatment; ureteric stenting)
diagnostic testing (e.g. antegrade pyelography)
• MERITS:
• A wide variety of catheter sizes can be placed(8 French to 18 French) depending on the characteristics of the fluid being drained.
• Can be irrigated when the drainage is purulent or bloody, to avoid clogging.
• UOP of the kidney can be measured.
PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROSTOMY
• Excessive ureteral manipulation can be avoided, decreasing the risk for sepsis or rupture.• Can also be done under LA & under conscious sedation, which eliminates the need for an anesthesiologist and risks a/w GA.
DJ STENT Vs. PCN
• Whether urinary drainage is best accomplished via a ureteral stent or a nephrostomy tube is a subject of debate.• Both PCN catheters and retrograde internal stents have been shown to be equally effective in relieving an obstructed renal collecting system, with similar complication rates.
DJ STENT Vs. PCN
• Percutaneous nephrostomy tube easily placed in significant hydronephrosis may be even more successful than retrograde ureteral stenting when urinary drainage is required as a result of obstruction of the distal ureter.
• One theory of why nephrostomy tubes are more efficient at relieving obstruction is that because urine drains around a stent rather than through the lumen, extraluminal compression from cancer prevents ureteral peristalsis and precludes peristent urinary drainage.
DJ STENT Vs. PCN
• Percutaneous nephrostomy tubes are advantageous over ureteral stents in relieving malignant ureteral obstruction and lowering serum creatinine.• The percentage of successful retrograde stent placements is lower than nephrostomy tube insertion which is nearly always successful in a dilated system.