
1
Fifth stage
Surgery
Lec-3
د
.
مثنى الحموشي
13/12/2016
Fractures of the radius and ulna
Mechanism of injury :
Fractures of the shaft of both bones occur commonly in road traffic accidents , it can be
caused by :
1- twisting force , which cause spiral fracture in both bones in different levels .
2- direct blow , lead to transverse fractures at the same level.
Additional rotation which lead to more displacement can be caused by the pronator
muscles (pronator teres , pronator quadratus ) in the middle and the lower thirds .
And the supinator muscles (biceps , supinator ) in the upper third of the forearm.
Clinically :
Fracture is usually quite obvious but we should do checking of the nerves and arteries
(distal pulsation )distal to the site of the fracture which can be affected by compartment
syndrome .
Treatment
In children : with green stick fracture , the closed treatment is usually successful because
the thick periosteum tend to guide and control the reduction ; after reduction we put back
slab above elbow which is 90` flexed and ask the patient to elevate the limb to decrease the
edema ; after 10 days we change the slab to complete p.o.p. if the fracture is in the upper
third we put the fore arm in supination , if it in the middle third we put the fore arm in
neutral and if it in the distal third we put the fore arm in pronation . The p.o.p. should be
left for another 4 weeks . Followed by physiotherapy .
Open reduction is indicated in : 1-if the fracture can not be reduced . 2- if the reduction is
unstable .
The fixation will be by plate and screw , intramedullary nail,
In adult : closed reduction of this fracture in adult is very difficult and redisplacement in
the cast is common so most of the surgeons prefer the open reduction and fixation from
the beginning by plate and screws .
Open fracture : need external fixation because internal fixation can not be used in
compound fracture
2
Complication
Early :
1- nerve injury . It is rarely occur in this fracture but it can be caused by the surgeons e.g.
posterior interosseous nerve .
2-vascular injury . Ulnar and radial arteries .
3- compartment syndrome .
Late :
1- delayed union and nonunion .
2-malunion which lead to limitation of pronation and supination .
Fracture single fore arm bone
It is much less common than the fracture of both bones . It's importance are :
1- when one bone fractured along it's shaft , it is usually associated with dislocation of
the proximal or the distal radio - ulnar joint,so when there is one bone fracture x-ray
should be taken to the whole length of the fore arm to detect any dislocation .
2- non union is liable to occur due to intact fellow bone .
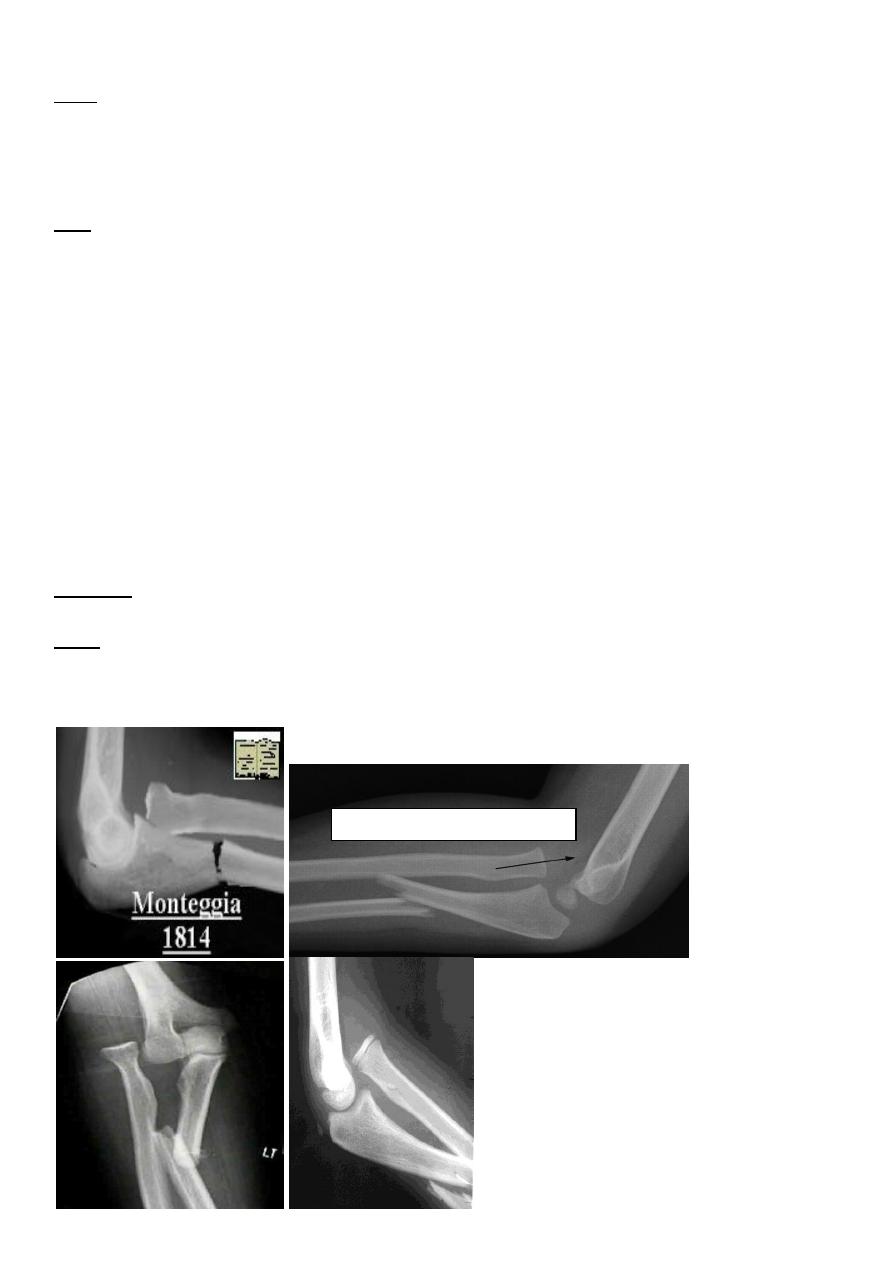
Monteggia fracture dislocation of the ulna
It is fracture of the proximal third of the ulna with dislocation or subluxation of the proximal
radio- ulnar joint .
Clinically : the ulnar deformity is usually obvious but the dislocated head of radius
is masked by the swelling .
X-ray : in isolated fracture ulna it is essential to take true a-p and lateral views of
the elbow ; the normal radial head is usually pointing to wards the capitulum in
monteggia it is not ; in addition to appearance of the fracture .
Montegia fracture dislocation
3
Treatment :
the most important point in treatment is to restore the length of the fractured ulna and
only in this case the dislocation will be reduced and remain stable ; so in adult this mean
operation (reduction and fixation by plate and screws) if the dislocation not reduced , then
open reduction of the joint .
In children if the fracture is green- stick then manipulation under anesthesia can be helpful,
but if the fracture is complete then open reduction and fixation like adult .
Complication :
1- nerve injury : which occur either due to manipulation or during surgery .
2- malunion : unless the fracture has been perfectly reduced , the radial head remain
dislocated and limiting elbow flexion , limitation of pronatiopn and supination ; if this
happened in children no treatment but if occur in adult then excision of the head of the
radius can be done .
3- non union of the ulna : the treatment by rigid internal
fixation and bone graft .
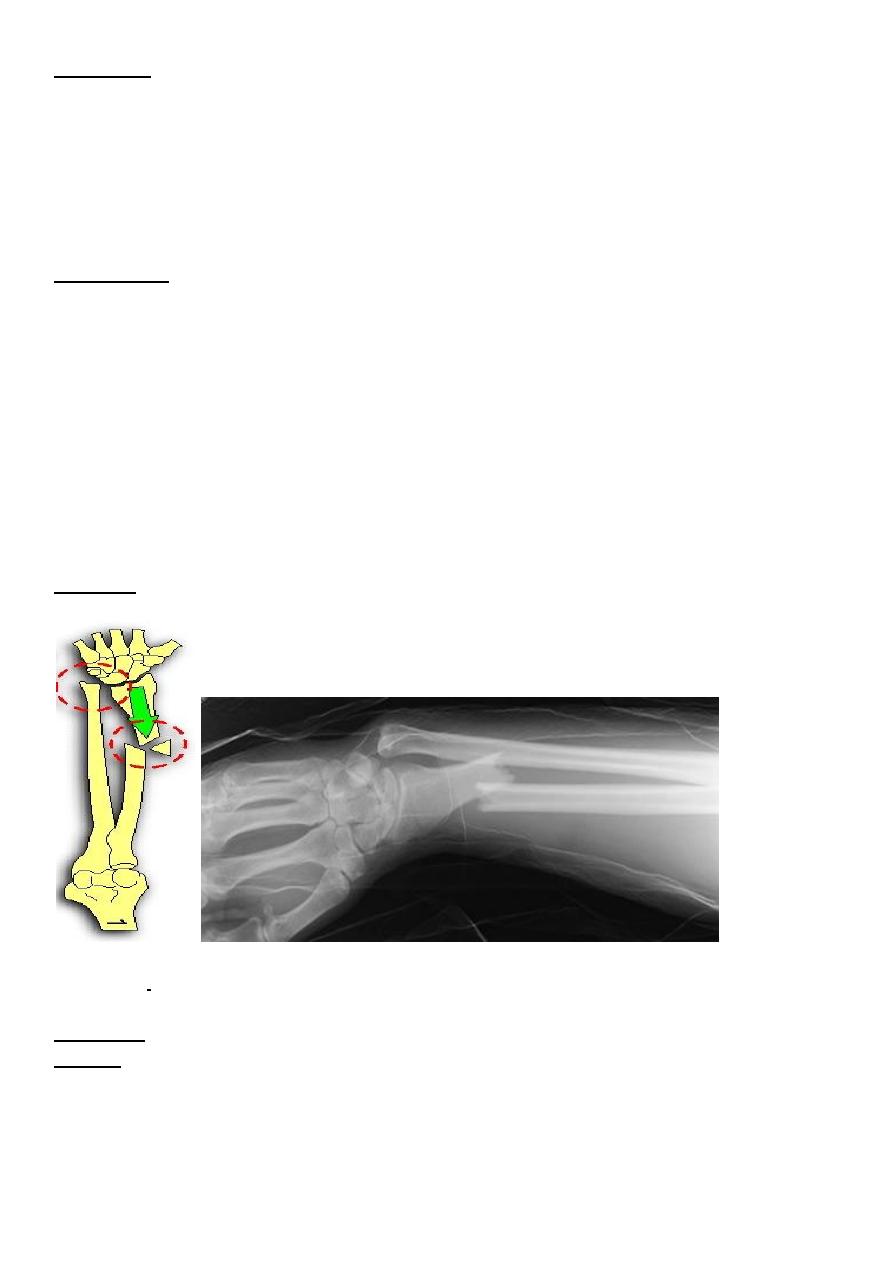
Galeazzi fracture dislocation of the radius
It is caused by fall on the hand , there is fracture in the lower third of the radius and
dislocation of the inferior radio- ulnar joint .
Clinically : it is much more common than monteggia , prominence and tenderness over the
lower end of the ulna is an important point in examination .
Treatment : the most important point is to restore the length of the fractured radius ,
other wise the dislocation will not reduced .
In children close reduction is possible but if fail , then open reduction and fixation .
In adult , the treatment will be by open reduction and internal fixation .
Complication :
The most important complication is limitation of pronation and supination .
