Fifth stage
MedicineLec-12
د.محمد حارث
6/1/2016
Multiple MyelomaMultiple Myeloma
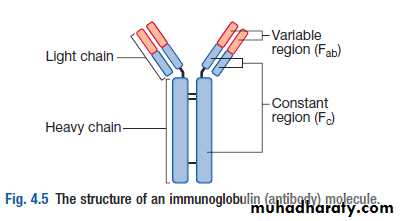
Malignant proliferation of plasma cells.Normal plasma cell form Ig which contain heavy and light chain
Normal variety of Ig polyclonal & each contain Kappa & Lambda light chain
Myeloma plasma cell : Ig of single heavy and light chain lead to monoclonal protein (para protein)
In some light chain may be only produced and appear in urine as Bence-Jones proteinuria.
Incidence : 4 new cases/100,000 peoples/year.
Sex ratio : M:F → 2:1
Age : median age 60-70 years.
Etiology : Unknown
Classification of MM
Paraprotein frequency %
IgG 55%
IgA 21%
Light chain only 22%
Other (D, E, non secretory) 2%
The diagnosis of MM requires two of the following :
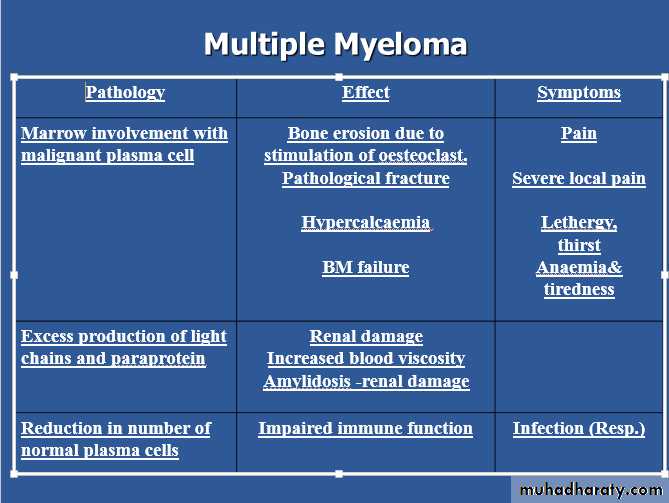
marrow plasmacytosis.
Serum and/or urinary paraprotein
+
≥ 1 of `` CRAB``
Clinical features
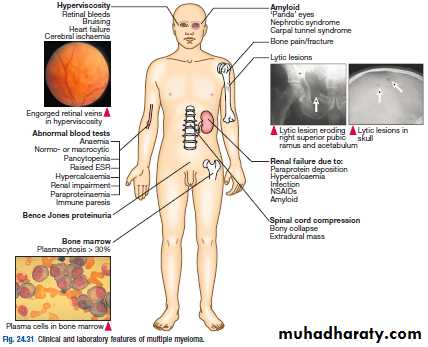
Weight loss ,malaise and fatigue.Bone pain found in 60% of cases at the back and ribs.
Anorexia , diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, polyuria, polydipsia occur with hypercalcemia in 30%,
Renal impairment due to hypercalcaemia and dehydration present in 50%
Pneumococcal, chest and urinary tract infection due to low immunoglobulin(Ig) production.
Headache , Confusion, Breathlessness, Visual Disturbance and bleeding can occur secondary to hyperviscosity (IgA).
5% present with paralysis secondary to spinal cord compression by extra-dural plasma cell mass.
Carpal-tunnel syndrome, nephrotic syndrome, cardiac failure and neuropathy secondary to amyloid deposition.
Management
Immediate support• High fluid intake to treat renal impairment and hypercalcaemia
Analgesia for bone pain.
• Bisphosphonates for hypercalcaemia and to delay other skeletal related events .
• Allopurinol to prevent urate nephropathy.
• Plasmapheresis, if necessary, for hyperviscosity
**Chemotherapy with or without HSCT
In older patients, thalidomide combined with the alkylating agent melphalan and prednisolone has increased the median overall survival to more than 4 years.
In younger, fitter patients, standard treatment includes first-in chemotherapy to maximum response and then an autologous HSCT
Management cont.
1-BORTEZOMIB(VELCADE) VTD+Z
2- Thalidomide
3-Lenalidomide(Revlimid) VRD+Z
4- Dexamethasone
5-Bisphosphonate (Zoledronate)
Treatment is administered until paraprotein levels have stopped falling. This is termed‘plateau phase’ and can last for weeks or years.
Radiotherapy; for localised bone pain and for pathological fractures.
It is also useful for the emergency treatment of spinal cord compression complicating extradural plasmacytomas
Waldenstrӧm macroglobulinaemia
This is a low-grade lymphoplasmacytoid lymphoma associated with an IgM paraprotein.
Patients classically present with features of hyperviscosity,such as nosebleeds, bruising, confusion and visual disturbance.
Anaemia, systemic symptoms, splenomegaly or lymphadenopathy
Investigation ; have an IgM paraprotein associated with a raised plasma viscosity. The bone marrow with infiltration of lymphoid cells and prominent mast cells
TREATMENT
1-Plasmapheresis for anaemia and hyperviscosity.
2- Chlorambucil
3- Fludarabine
4- Rituximab
*Monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance (MGUS);
a paraprotein is present in the blood but with no other features of myeloma, Waldenstrӧm macroglobulinaemia, lymphoma or related disease.
The bone marrow may have increased plasma cells but these usually constitute less than 10% of nucleated cells.
After follow-up of 20 years, only one-quarter of cases will progress to myeloma or a related disorder (i.e.around 1% per annum)