Childpsychiatry 2
Prof. Elham AljammasOct 2015
Emotional disorders
Important differences betweenthe disorders in adult & children:
1.Some subtypes are different (separation anxiety)
2.Medications is rarely used
3.Equal male &female ratio(1/2in adult)
4.Most affected children do not become affected adults
SEPERATION AXIETY DISORDERS
Among 5-11 yr olds 3-4%have excessive,prolonged anxiety when faced with separation
Older children may describe being harmful
that the person will be harmed & not return
can begin at the time of stress ,such as
after a death or tragedy
Some parents are noted to be very protective
Symptoms of anxiety in children:
Behavioral
Clinging to parent
Unwilling to leave house
Unwilling to go to bed
Actions designed to avoid feared events(hiding)
Psychological
Feeling worried
Nightmares
Physical
Abdominal pans
Headaches
Managements:
1.explanation& reassurance2.Identifications& resolution of stressors
3. ensuring that the parents are not reinforcing the problem
4. use specific interventions for secondary problems such as school refusal
5. applying
behavioral techniques
Somatoform disorder
Obsessive compulsive disorder
Mood disorders
School refusal
School refusal is not a psychiatric disorder, but is a common cause of child psychiatrist & frequently attributable to an emotional disorders
Not attending school
Child not at home[-----------------]child remaining at homeChild kept at home ^ child reluctant to go
To school(school refusal) social travel phobia fear of school separation anxiety social withdrawal
School refusal Truancy
Younger<11yr old older than 11yrUnderlying emotional disorders underlying conduct dis.
Good academic & behavioral record poor sch. Records
Good prognosis poor prognosis
Parents overprotective &anxious broken home
Management
Rapid return to school before avoidance is too ingrainedAddress any specific fears or stresses
Treat any associated psychiatric disorders.
Prognosis:
Younger children –good
Slightly increased risk of anxiety disorder in adulthood.
Conduct disorder
Conduct disorder is the commonest psychiatric disorder of childhood adolescence
Sex ratio=5/1(B/G) diagnosis usually made after age of 7yr
Conduct is disturbed & antisocial well beyond the range misbehavior normally observed. Clinical features of conduct disorders:
1.prschool children
Aggressive behaviour
Poor concentration
2.in mid childhood
Lying
Stealing
Disturbed & oppositional behavior bullying
3.In adolescence
StealingTruancy
Promiscuity
Substance misuse
Vandalism
Reckless behavior
Conduct disorder is associated with social deprivation,& poor parenting., individual factors Brain damage,epilepsy,specific reading disorder.
Long term prognosis is poor
Management is a mixture of punishment & treatment
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
.prevalence =2% in UK (3/4boys)
Etiology : genetic contribution, increased rate of depressive disorders ,learning difficulties, alcoholism, antisocial personality disorder,neurodevelopmental disorder . (Rare ) social deprivation ,food allergy Features : hyperactive ,poor attention & concentration,distractable & impulsive, poor planning & organization.
Associated with: learning difficulties clumsiness low self esteem, socially disinhibited,no localizing neurological signs ,50% coexist with conduct disorder.
Management:
Support for the child & the family
Specific educational approaches (attention& learning difficulties)
Behavior modification
Stimulant(methylphenidate ),careful about addiction & growth retardation
Prognosis variable---1/3 resolve completely.
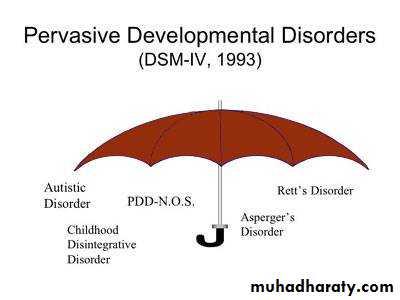
Pervasive Developmental Disorders
Group of disorders characterized by abnormalities in communication and social interaction and by restricted repetitive activities and interest.Most cases manifest before 5 years.
• Autistic DisorderChildhood autism (ICD-10)Autistic Disorder ( DSM-IV)Abnormal development apparent before the age of 3 years.3 kinds of social development:Abnormality of social development.Abnormality of communicationRestriction of interest and behavior.
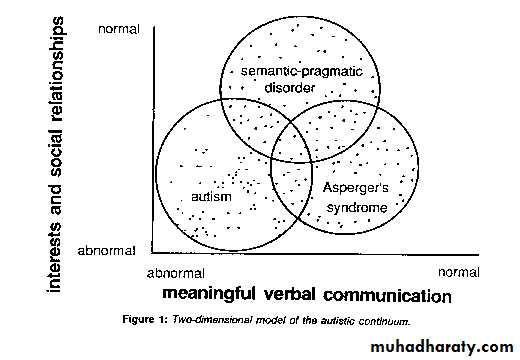
Pervasive developmental disorders(AUTISM)
Is characterized by failure to develop normal communication(social emotional).They have restricted use of language ,seems oblivious to non verbal communication& emotional expressionHave limited solitary ,repetitive behavior& resist attempts to change their routine
80% boys 1 in 2500 children age of onset <3 years autistic triad
Autistic aloneness
Impaired language & communication
Solitary repetitive behavior
Failure to develop Associated with: mannerism& rituals ,epilepsy in 25%,MR In75%
Etiology ;genetic ,no environmental risk factor
Neuropath logical involvement of the cerebellum& 0liveary nuclei has been reported
Prognosis: poor
Needs special school & residential care.
PTSD
Epidemiology
The most severe stresses resulted in the occurrence of the syndrome in more than 75% of the victims.
The lifetime prevalence ~ 8%
Among high-risk groups ~ 5 to 75%Significantly higher in women
First-responders like firemen, and police officers are at risk for PTSD-particularly when children are involved, research suggests. Likewise, journalists covering catastrophes are similarly susceptible to PTSD. Taken together, the DSM indicates about 5% of American men and 10% of American women have the disorder.
Epidemiology
The most severe stresses resulted in the occurrence of the syndrome in more than 75% of the victims.The lifetime prevalence ~ 8%
Among high-risk groups ~ 5 to 75%Significantly higher in women
First-responders like firemen, and police officers are at risk for PTSD-particularly when children are involved, research suggests. Likewise, journalists covering catastrophes are similarly susceptible to PTSD. Taken together, the DSM indicates about 5% of American men and 10% of American women have the disorder.
Comorbidity
About 2/3 have at least two other disorders like: depressive disorders, substance-related disorders, other anxiety disorders, and bipolar disorders.Etiology
• Biological• Factors
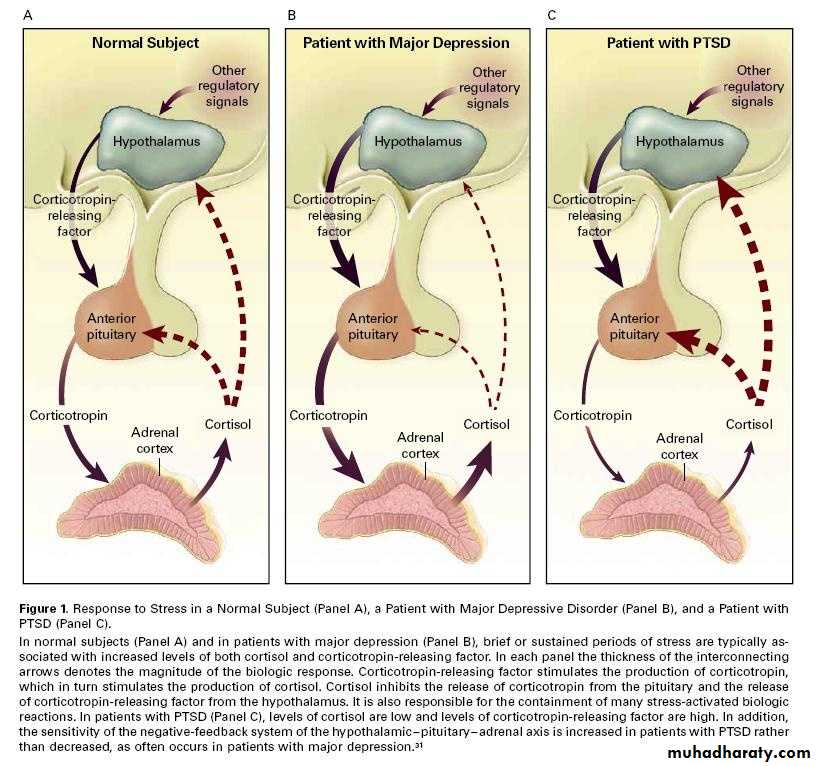
• HPA axis
Etiologybiological factors (brain imaging)
• Faced with scores of traumatized veterans of the Viet Nam war, researchers have been studying the underlying physiology of PTSD since the late 1960s. Animal studies have shown repeatedly that prolonged stress releases hormones that can damage the hippocampus, a region of the brain associated with memory. In a series of brain imaging studies conducted with humans in the mid-1990s, researchers found that the hippocampi of PTSD sufferers were smaller than average. These findings lead some to hypothesize that the damage extreme stress does to the hippocampus causes PTSD; however, a study published in the October 2002 issue of Nature Neuroscience suggests otherwise.• The hippocampus, a region of the brain associated with memory, can be damaged by the prolonged release of stress hormones
Diagnosis
• Clinical features divided into 3 groups:• Hyperarousal (persistent anxiety, irritability, insomnia, and poor concentration)
• Intrusions (intense intrusive imagery, flashbacks, and recurrent distressing dreams)
• Avoidance (difficulty in recalling stressful events at will, avoidance of reminders of the events, detachment, inability to feel emotion “numbness”, and diminished interest in activities)
Development of Drawing
3 years old 4 years old5 years old 6 years old
Test of maturity:
Eva is here.
Course and Prognosis
PTSD usually develops some time after the trauma. The delay can be as short as I week and as long as 30 years. Untreated, ~30% recover completely, 40% continue to have mild symptoms, 20% moderate, and 10% remain unchanged or become worst.After 1 year 50% recover.