Wooden tongue depressor
Used for examination of oral cavity and oro-pharynx.

Metallic tongue depressor
1. Used for examination of oral cavity and
2. oro-pharynx +
3. naso-pharynx +nasopharyngeal mirror
4. cold spatula test (mist test) for choanal atresia
5. removal of F.B +
6. in minor operations +
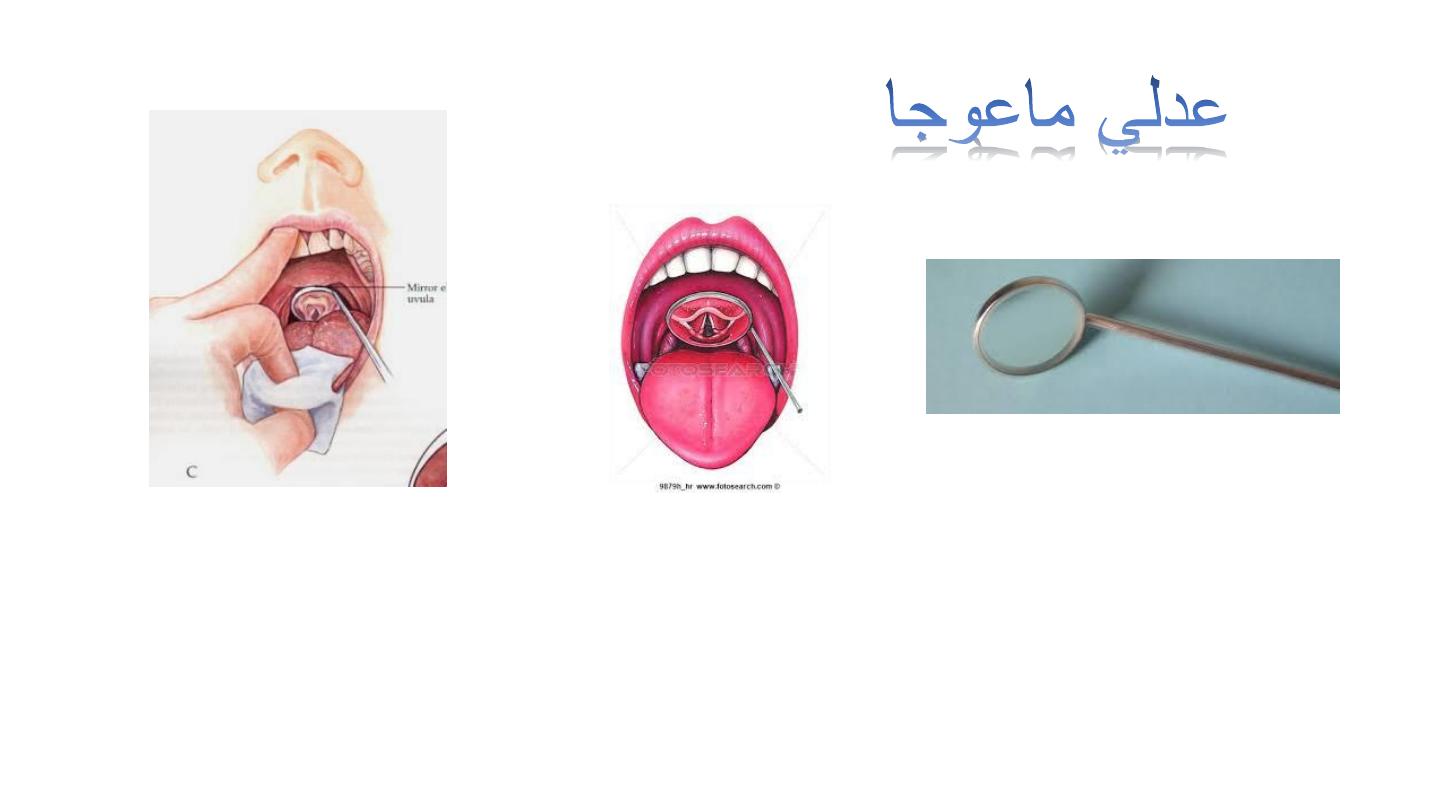
Laryngeal mirror
Don’t use it in presence of increased gag reflex more than normal.
Replaced by flexible fiberoptic endoscopy (enter from the nose).
Used to see the larynx and help in removing F.B. with other instruments
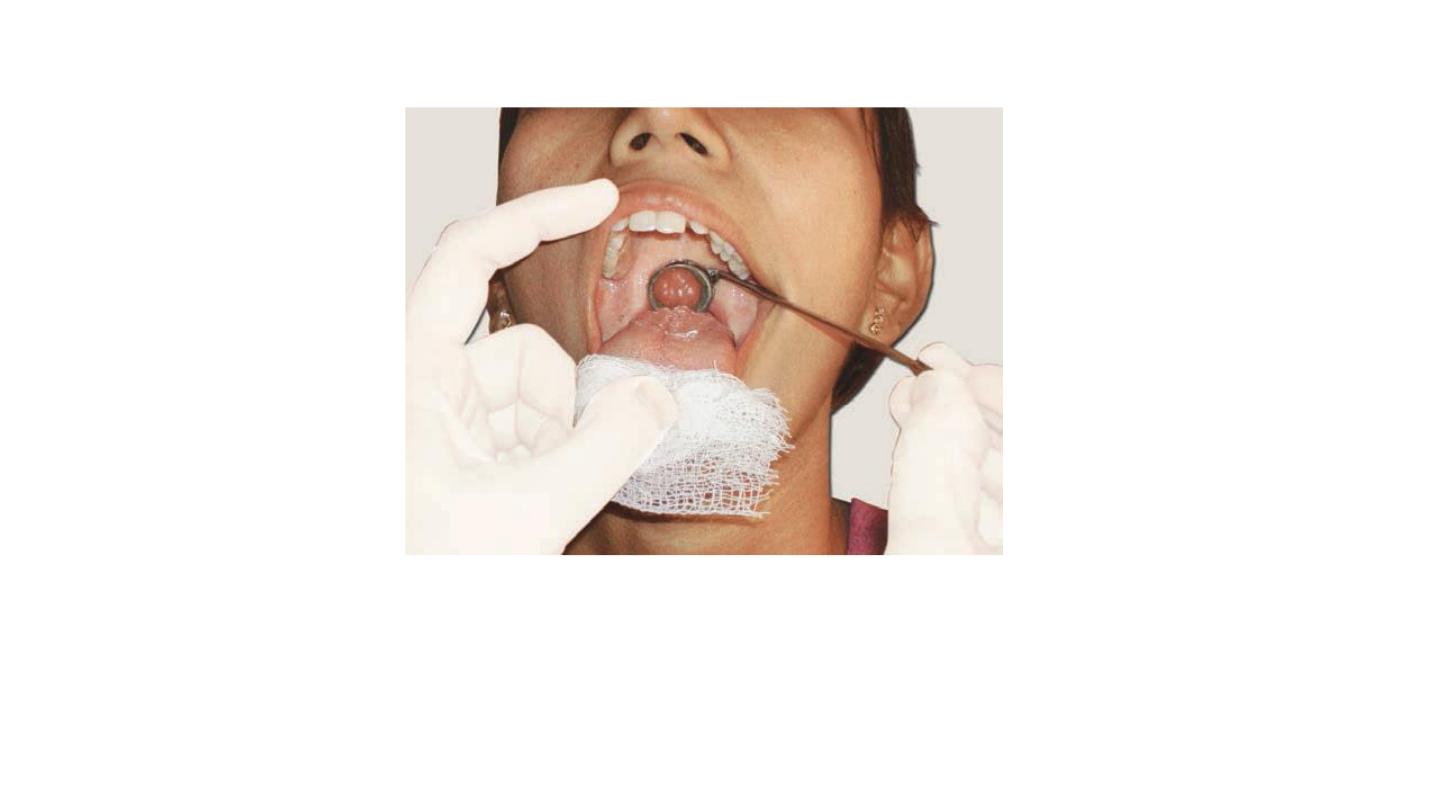
Indirect laryngoscopy.
Tongue wrapped in a piece of
gauze cloth and held by the examiner between the left thumb
and middle finger; Left index finger retracts out the upper lip.
Laryngeal mirror is firmly against the uvula and soft palate
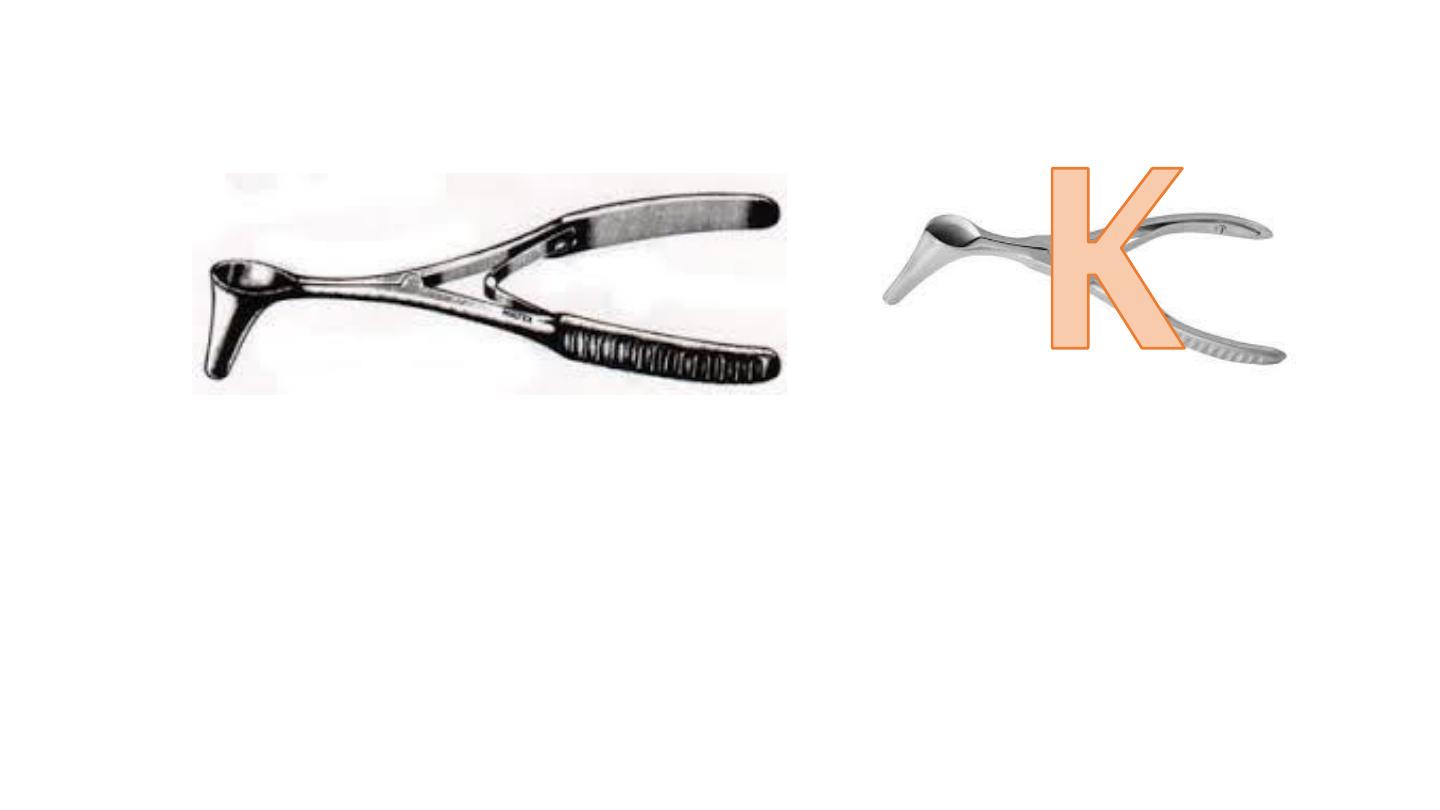
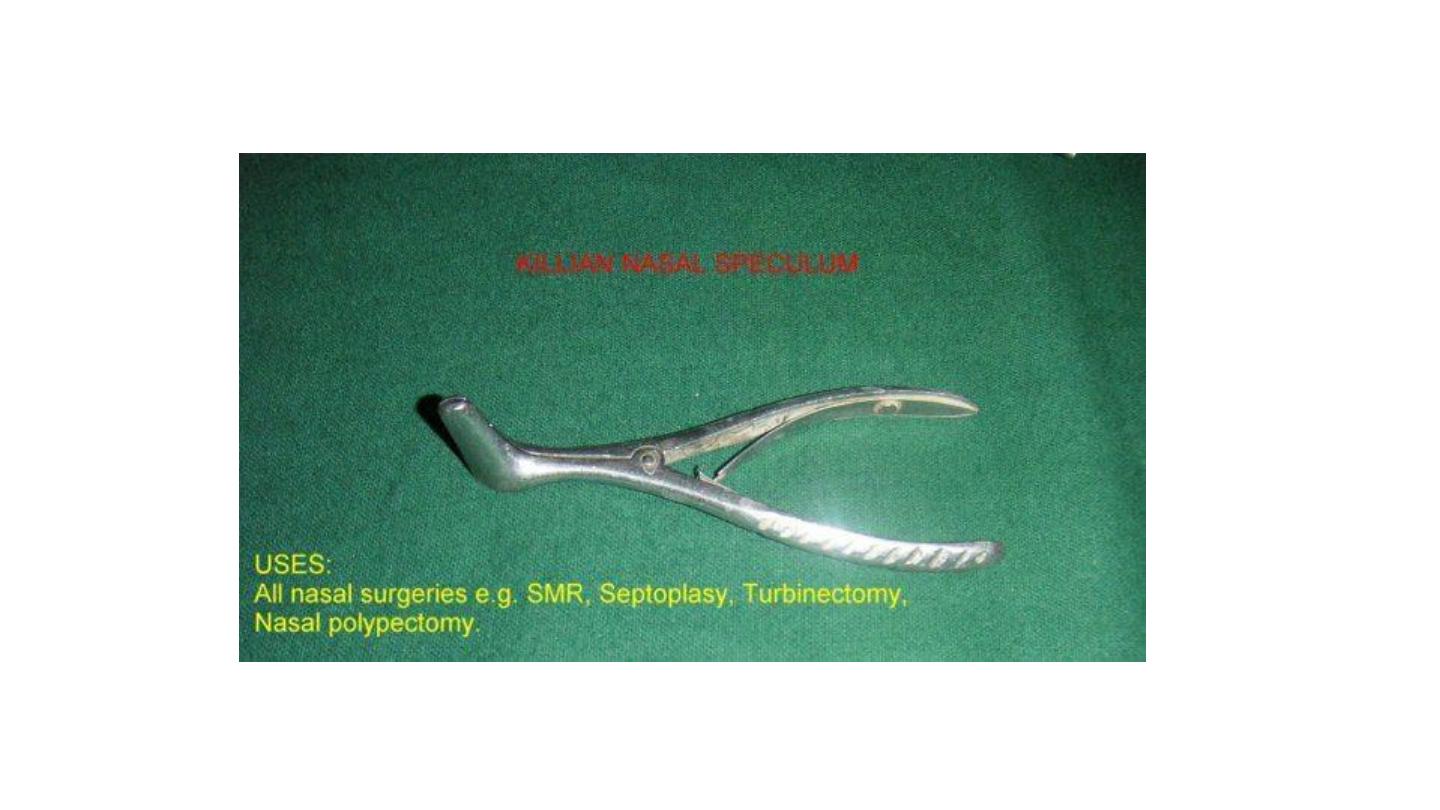
Killian nasal speculum
Non self retaining.
Used for anterior rhinoscopy examination of anterior nasal cavity.
Used to remove the F.B. – minor operation.
Thudichum
Self retaining.
Used for anterior rhinoscopy examination of anterior nasal cavity.
Used to remove the F.B. – minor operation.
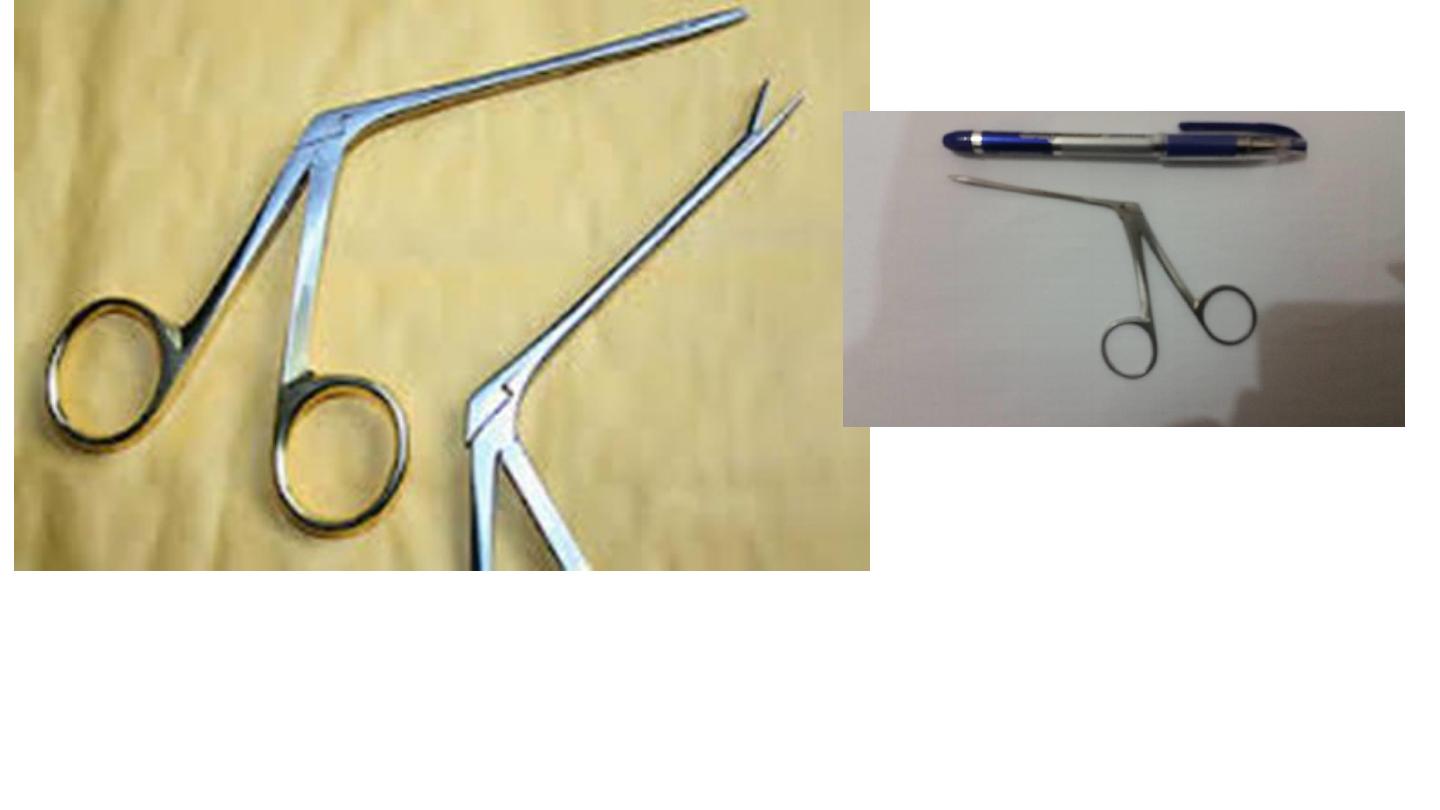
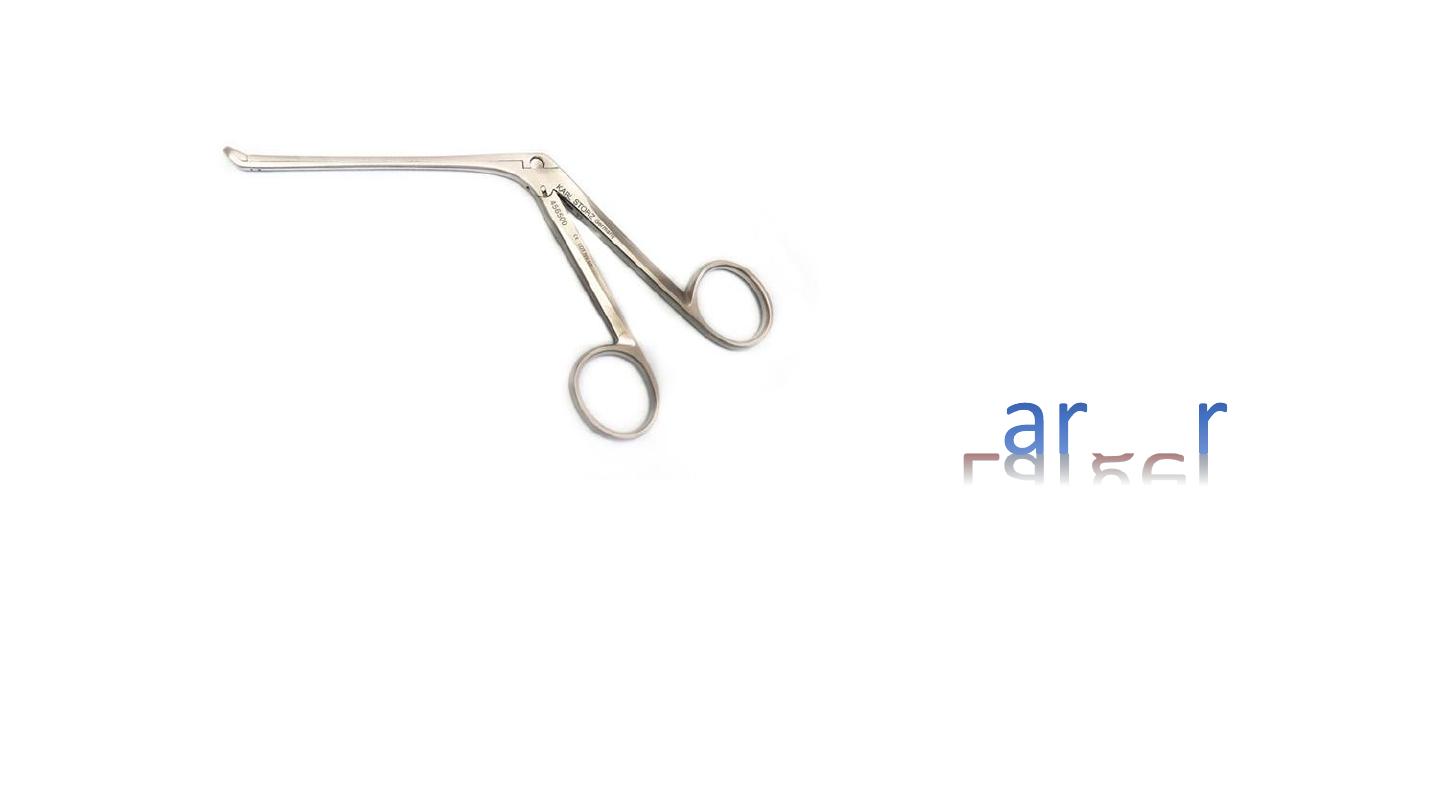
Crocodile forceps
Has distal joint. Smaller than Tilly Henkel (4 cm)
1. Grommet (ventilation tube) insertion for treatment of otitis media with effusion
2. Used to remove F.B and clots,
3. wax removal,
4. biopsy,
5. packing.
s
m
a
lle
CROCODILE FORCEPS

TILEEY–HENCKEL FORCEPS
• Nasal polyp Excisional biopsy
• Larger than Crocodile (10 cm)
L ge
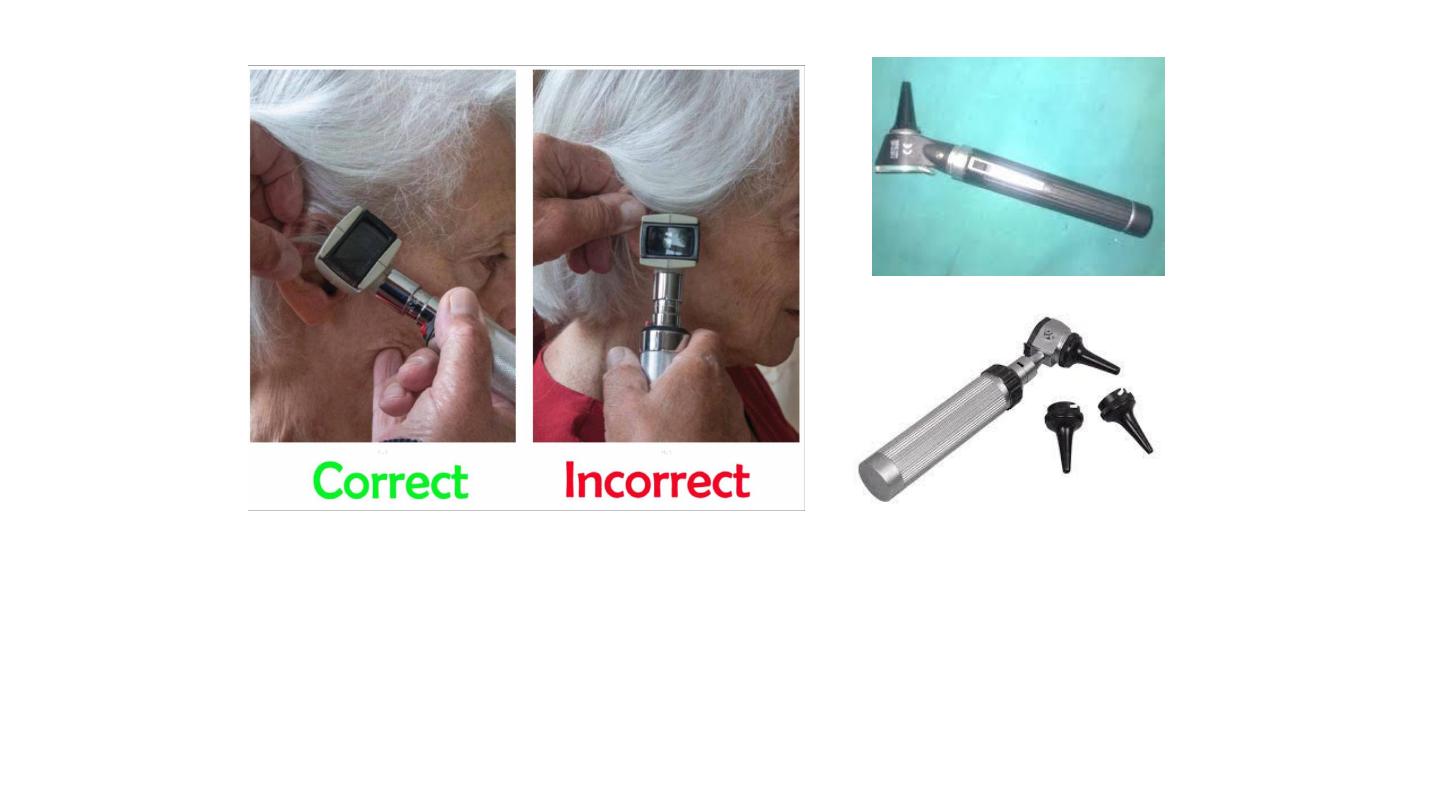

Auroscope (Otoscope)
Contain: power, light, speculum, magnification lens.
Uses: examination, suction,, drainage,
removal of F.B, minor operations.
يجب أن يمسك مثل مسكت القلم
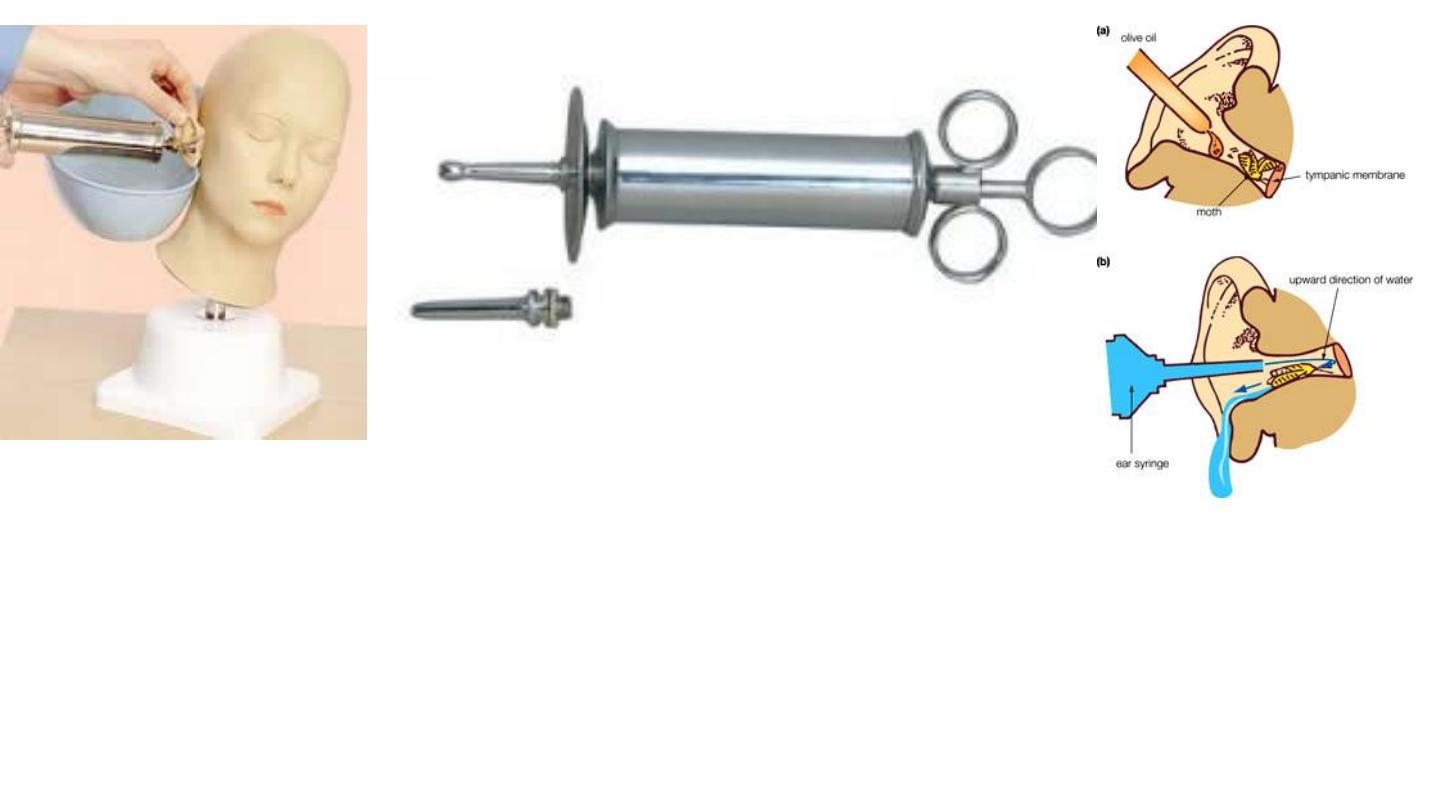
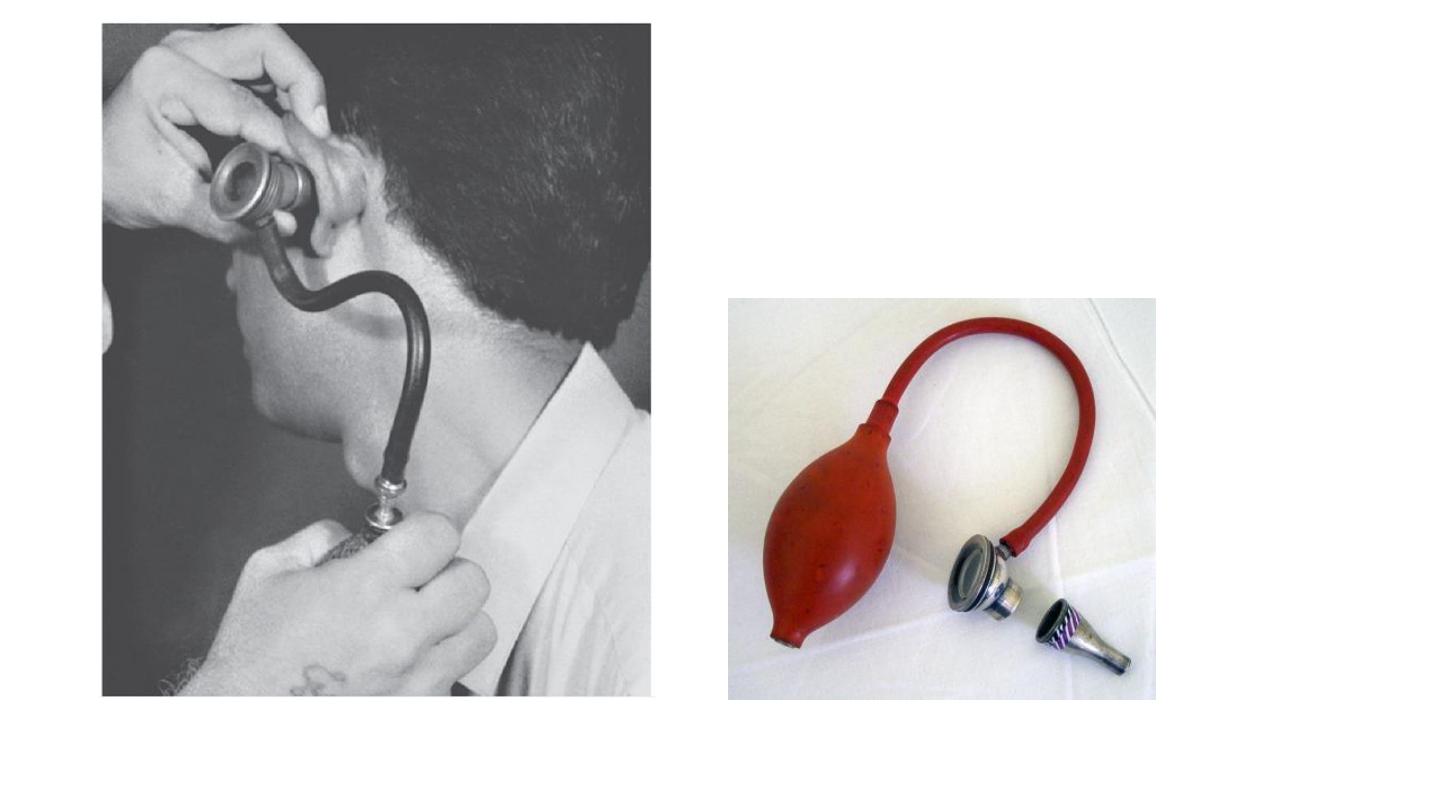
Ear (Aural) Syringe
Preparation:…The syringe has a nozzle for insertion into the external auditory canal. Water at body
temperature is loaded into the syringe. The syringe is held by inserting fingers into the rings at the
back. The third ring is on the piston that forces the water out when pushed.
• Indication:…
1.
Wax removal
2.
Foreign body removal
3.
Removal of otomycotic debris
Contraindication:…perforated tympanic membrane
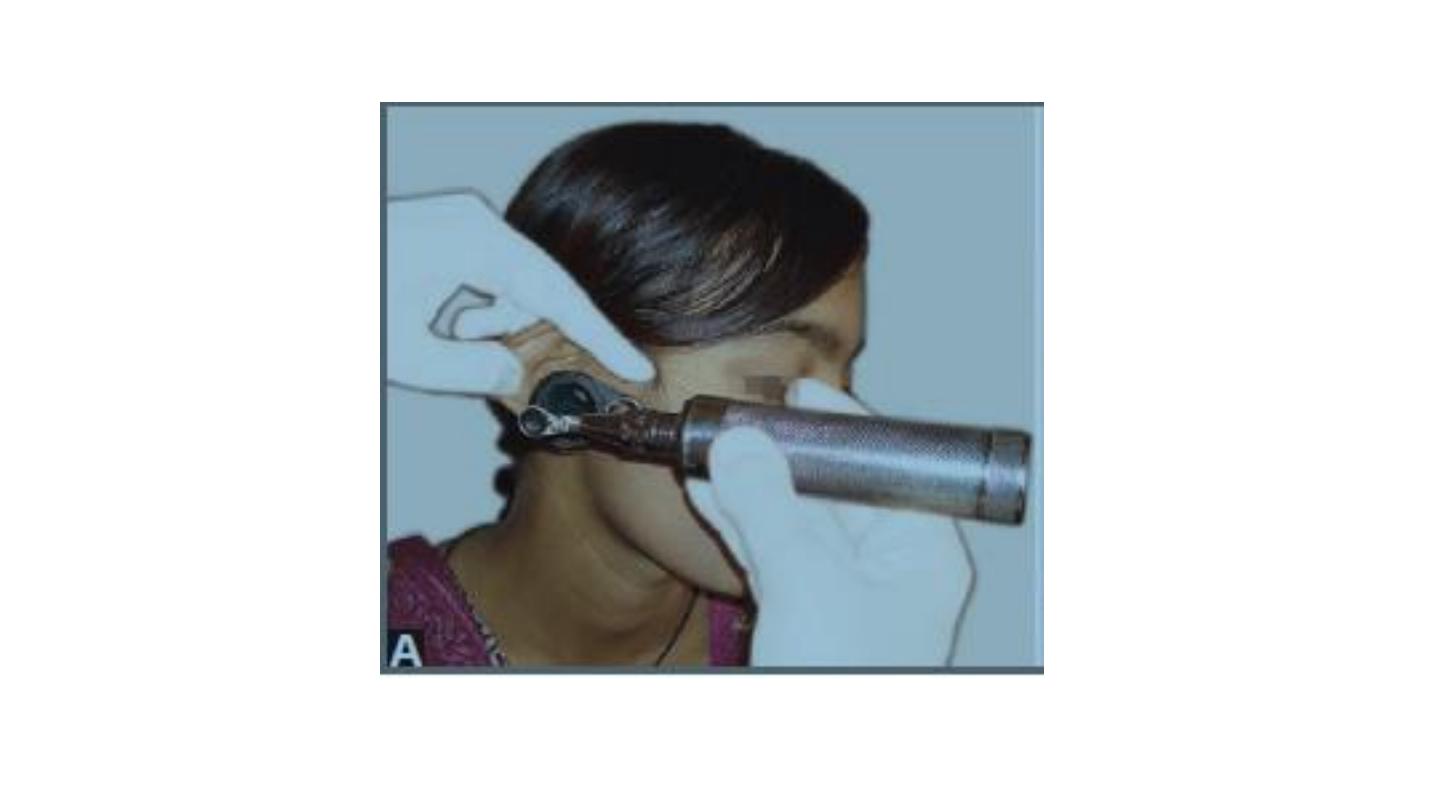
True method of auroscopy
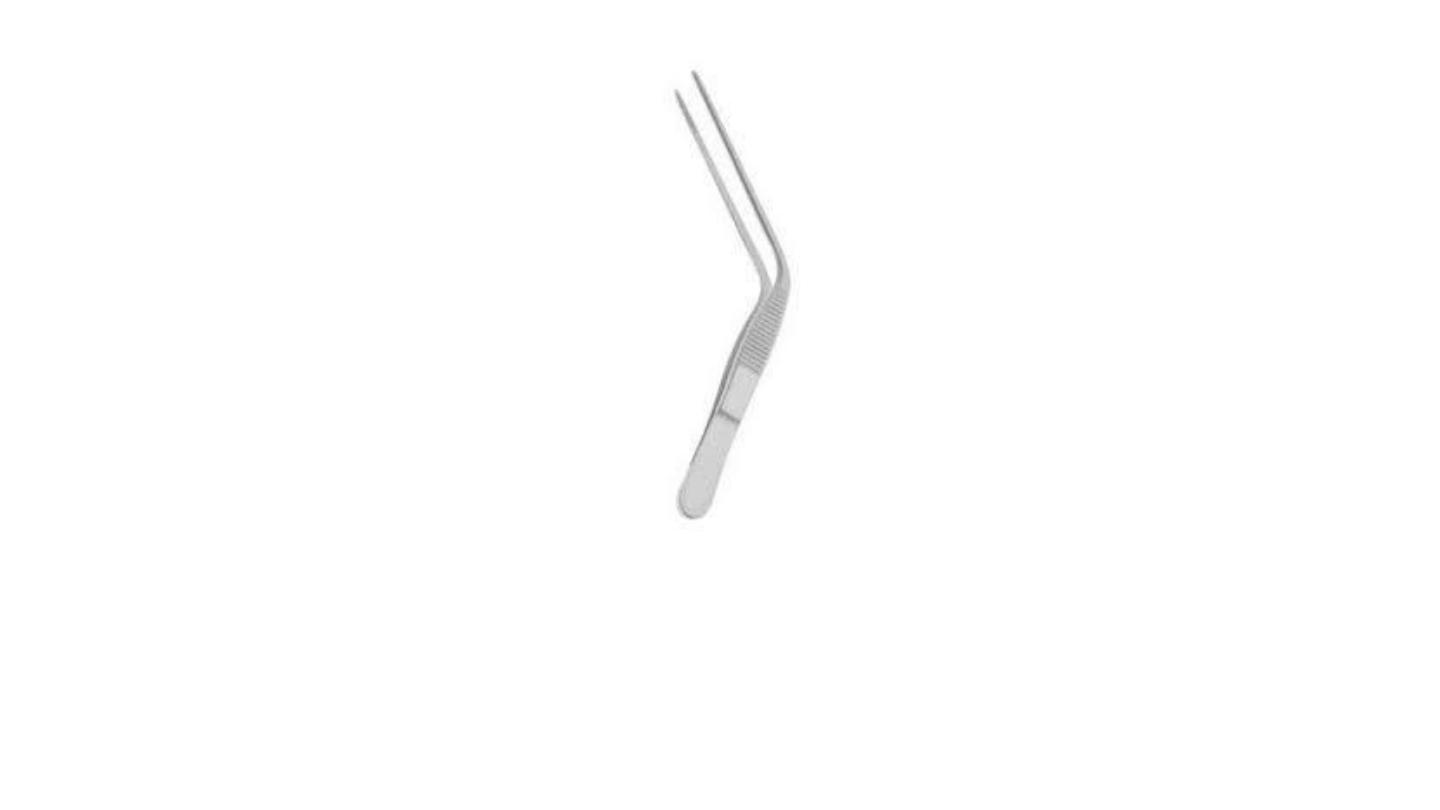

Aural dressing forceps
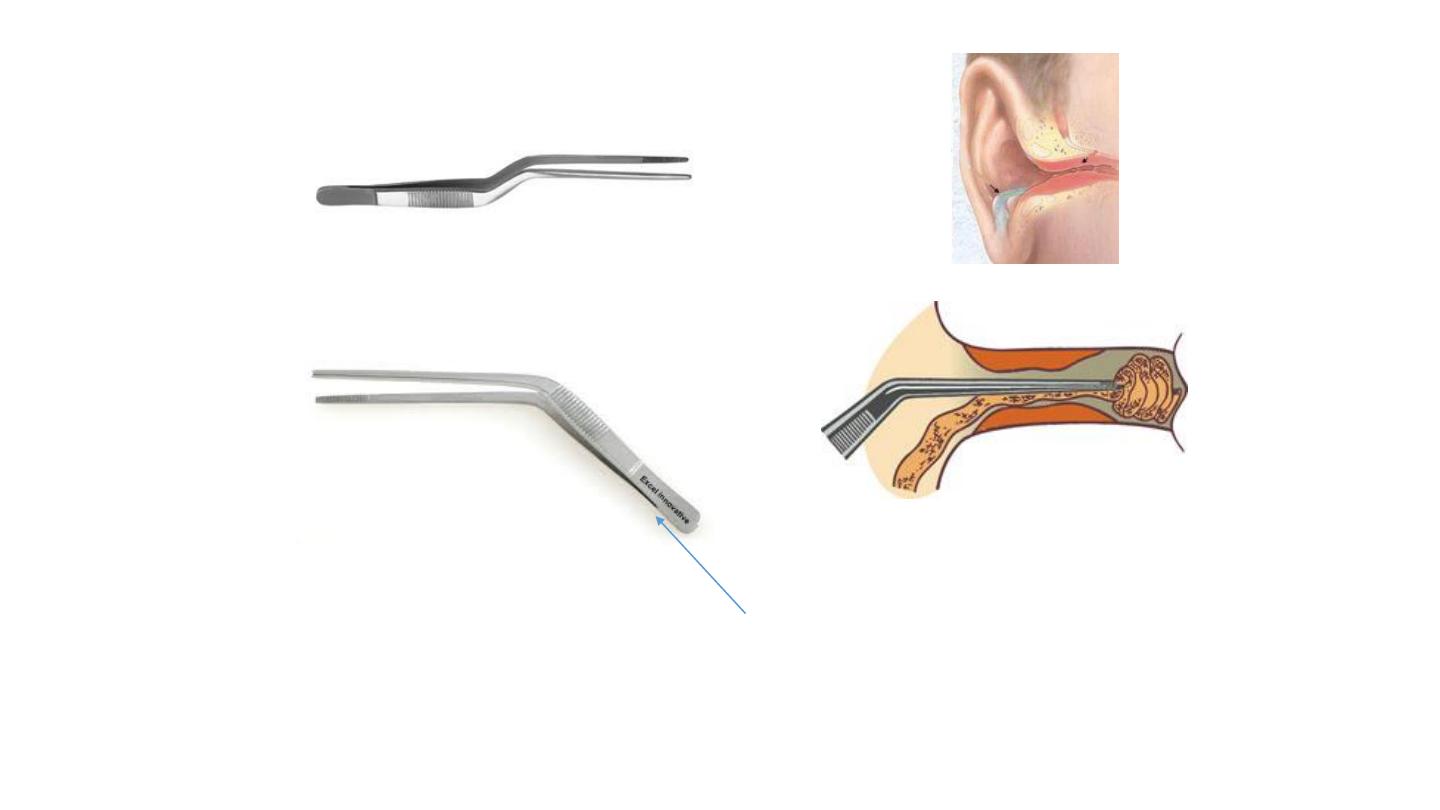
Aural Dressing Forceps
:
the joint is proximal. It is used for insertion of
wick inside the ear ( ear dressing ) in cases of
otitis externa and during ear surgery.
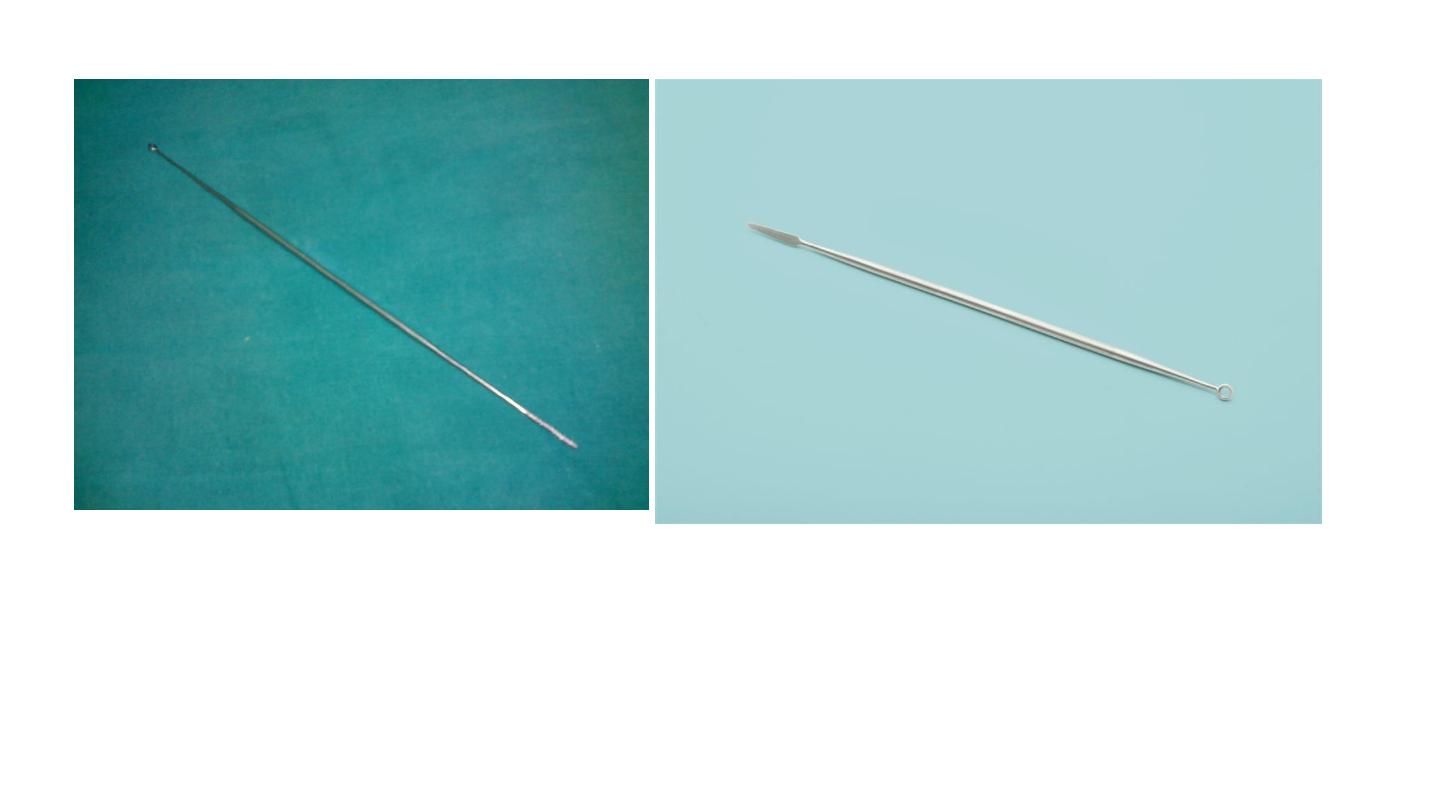
Jobson horne probe
1. Used in removal of F.B,
2.
cleaning or mobbing of nose and ear, (wax evacuation )
3. chemical cautery,
4. probing (differentiate between
hematoma
and
polyp
and
turbinate
)
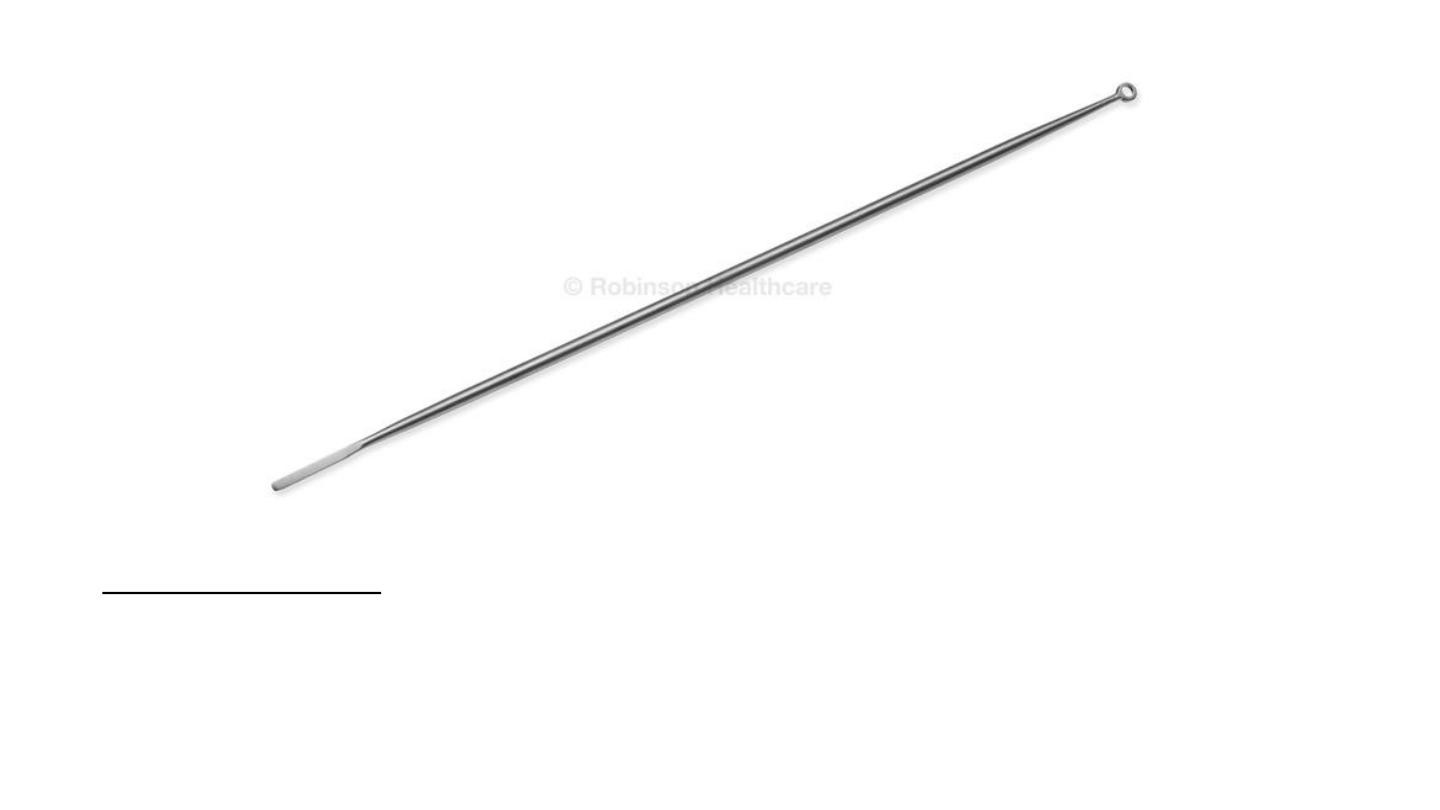
Jobson horn probe:
• Removal of the foreign body
• Wax evacuation (ear)
• Chemical cautery (nose)
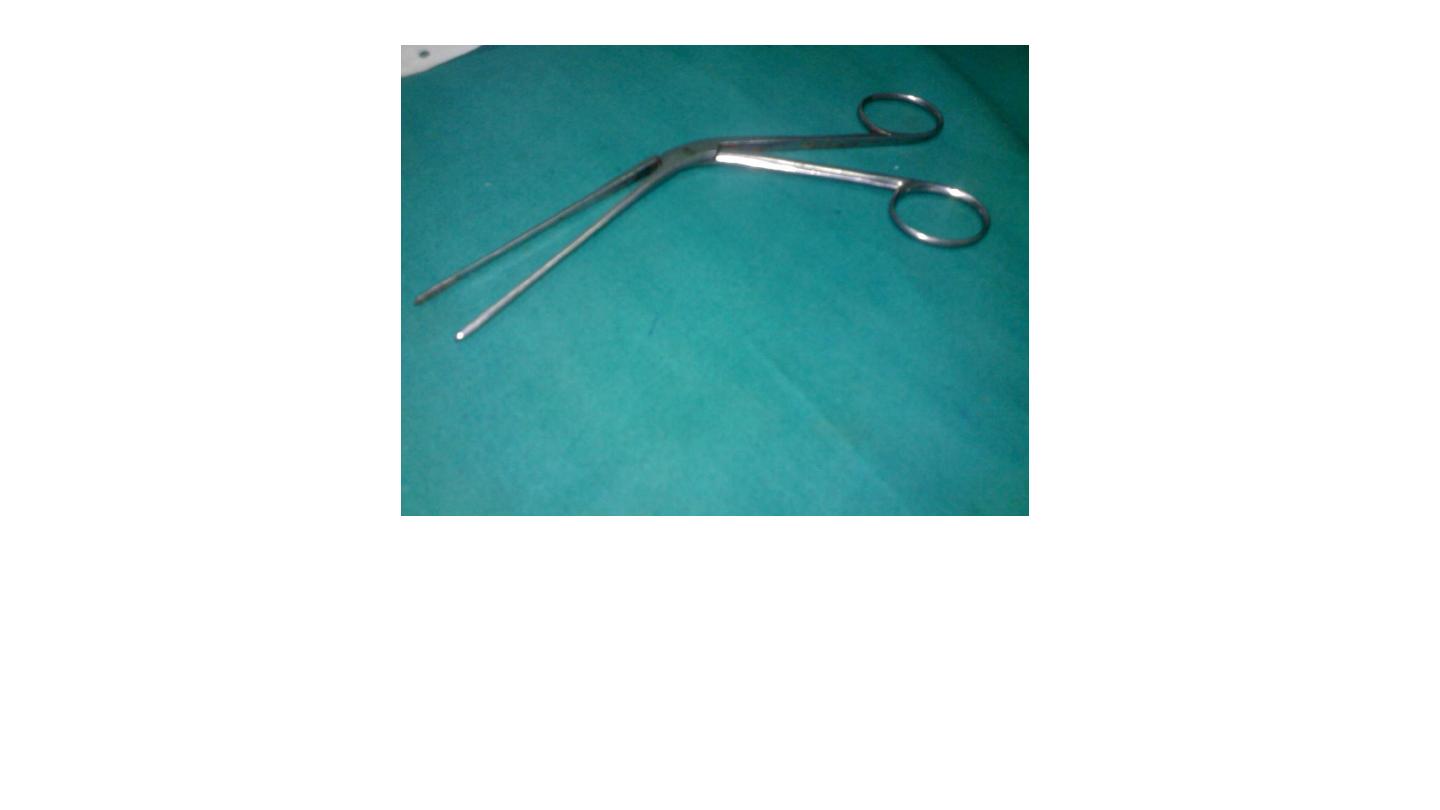
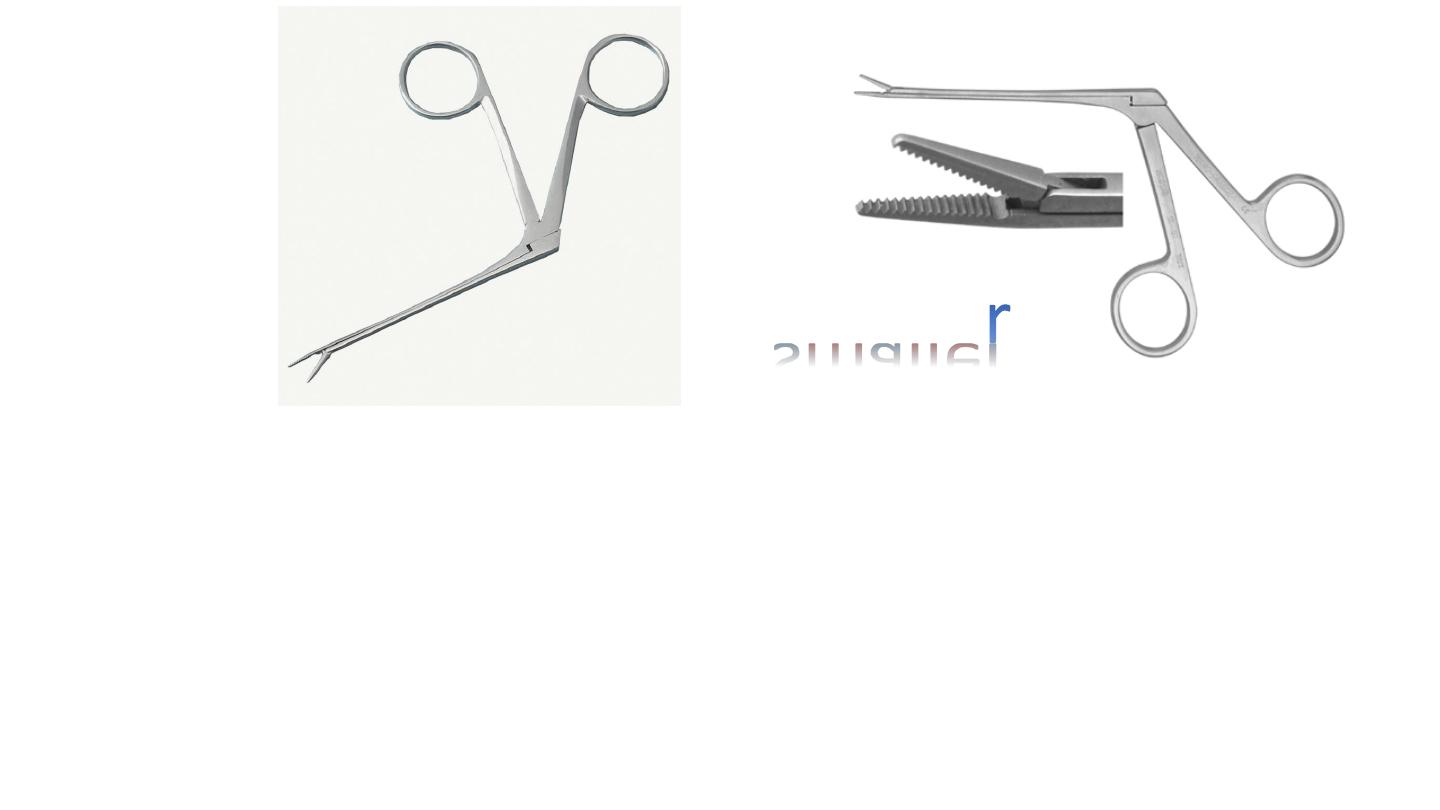
Telly’s nasal forceps
Used in removal of F.B
Arrest of bleeding (epistaxis) packing
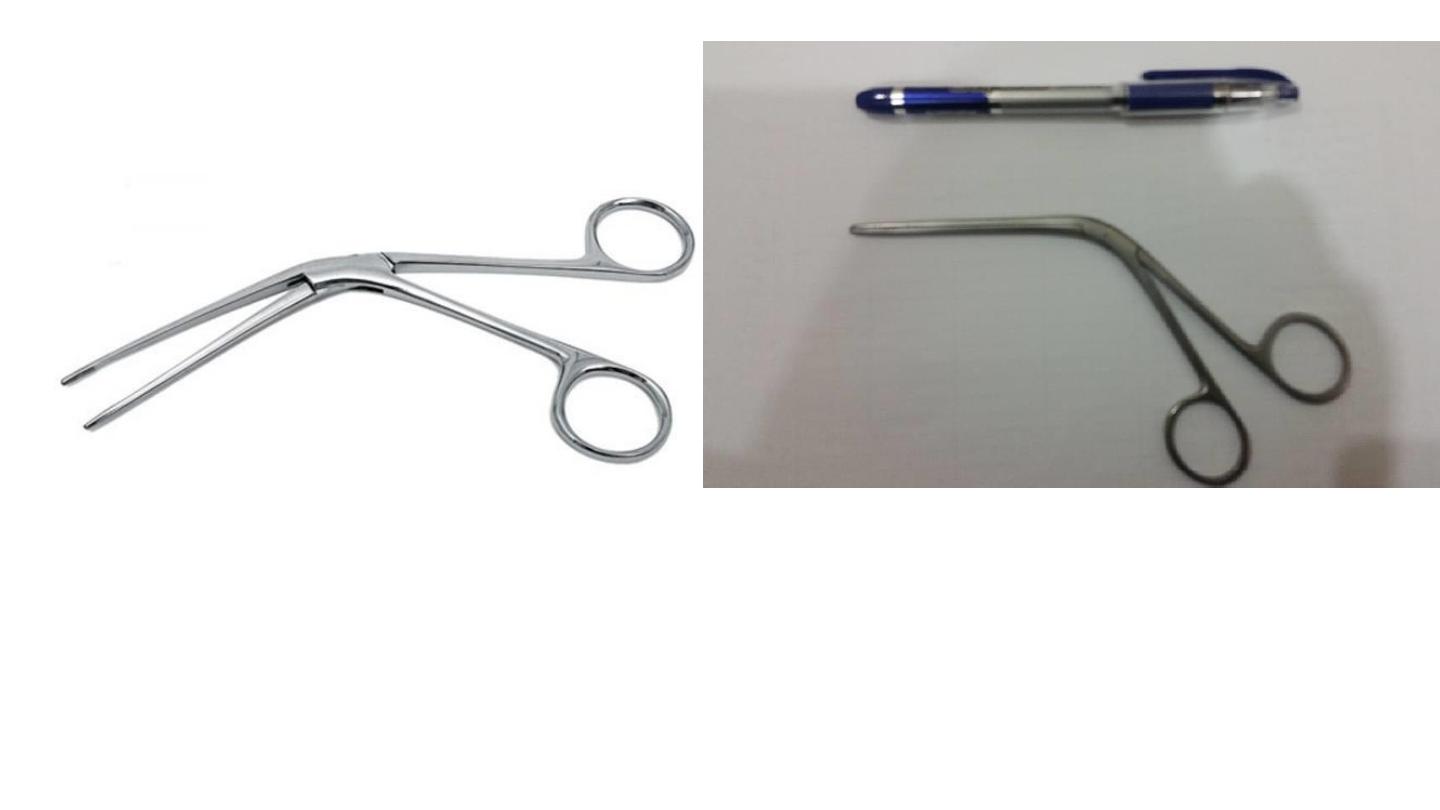
TILLEY NASAL DRESSING FORCEPS
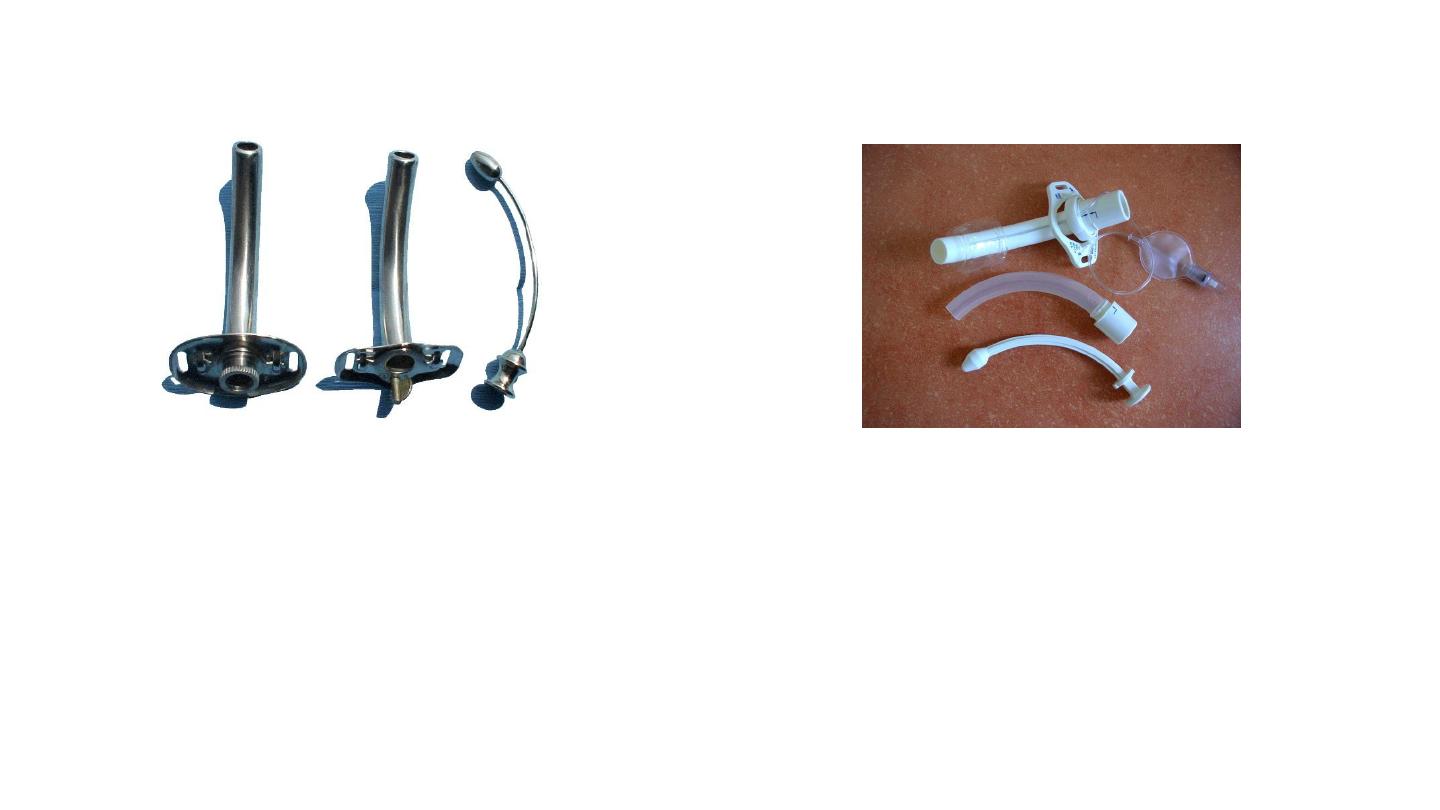

Cuffed (portex) tracheostomy tube
Used to obtain a closed circuit for
ventilation
Metal Tracheostomy Tube
Not used as frequently
anymore. Many of the patients who
received a tracheostomy years ago
still choose to continue using the
metal tracheostomy tubes.
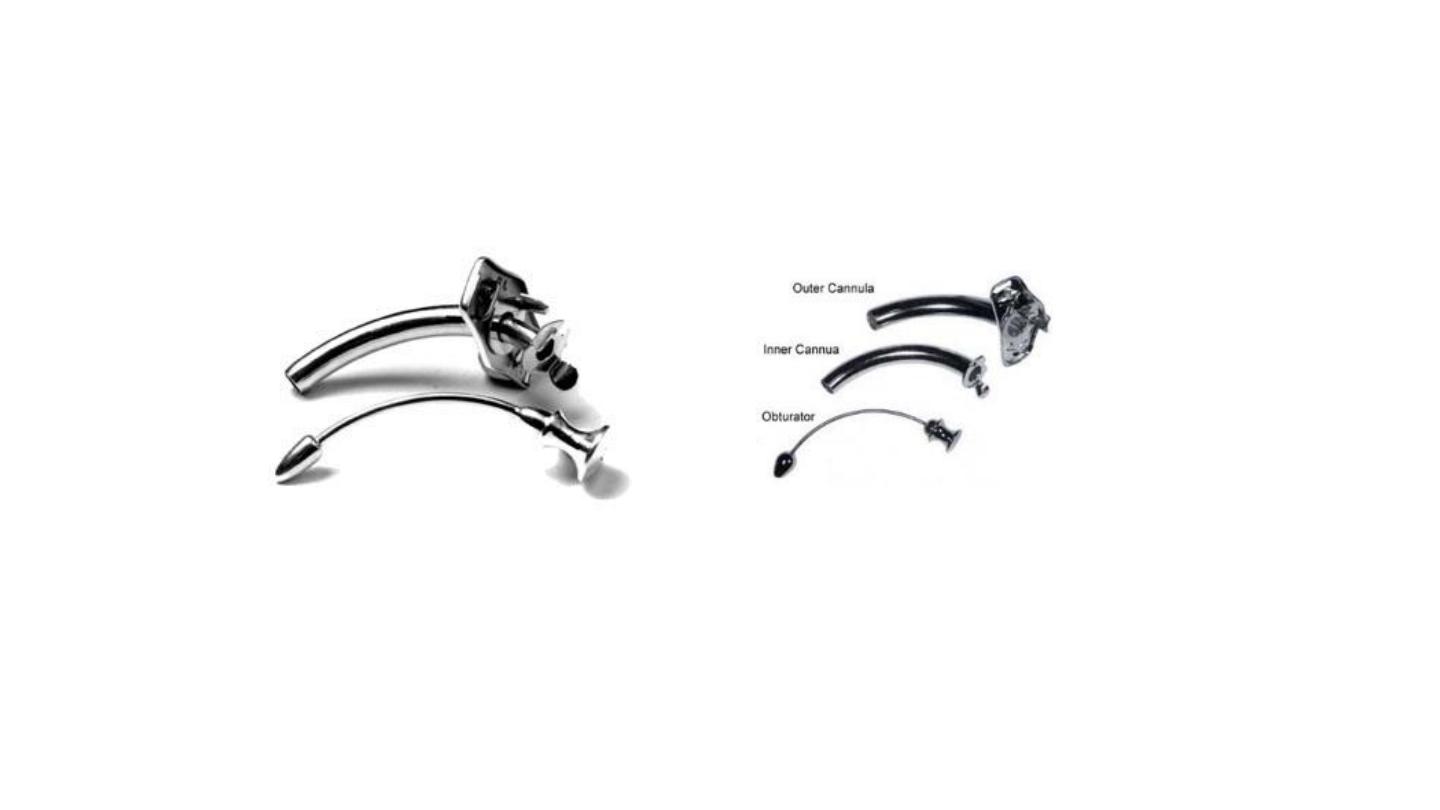

Tracheostomy Tubes
Silver Jackson tube

Uses or indication of tracheostomy
Types Emergent trchestomy –elective temporary- perminant
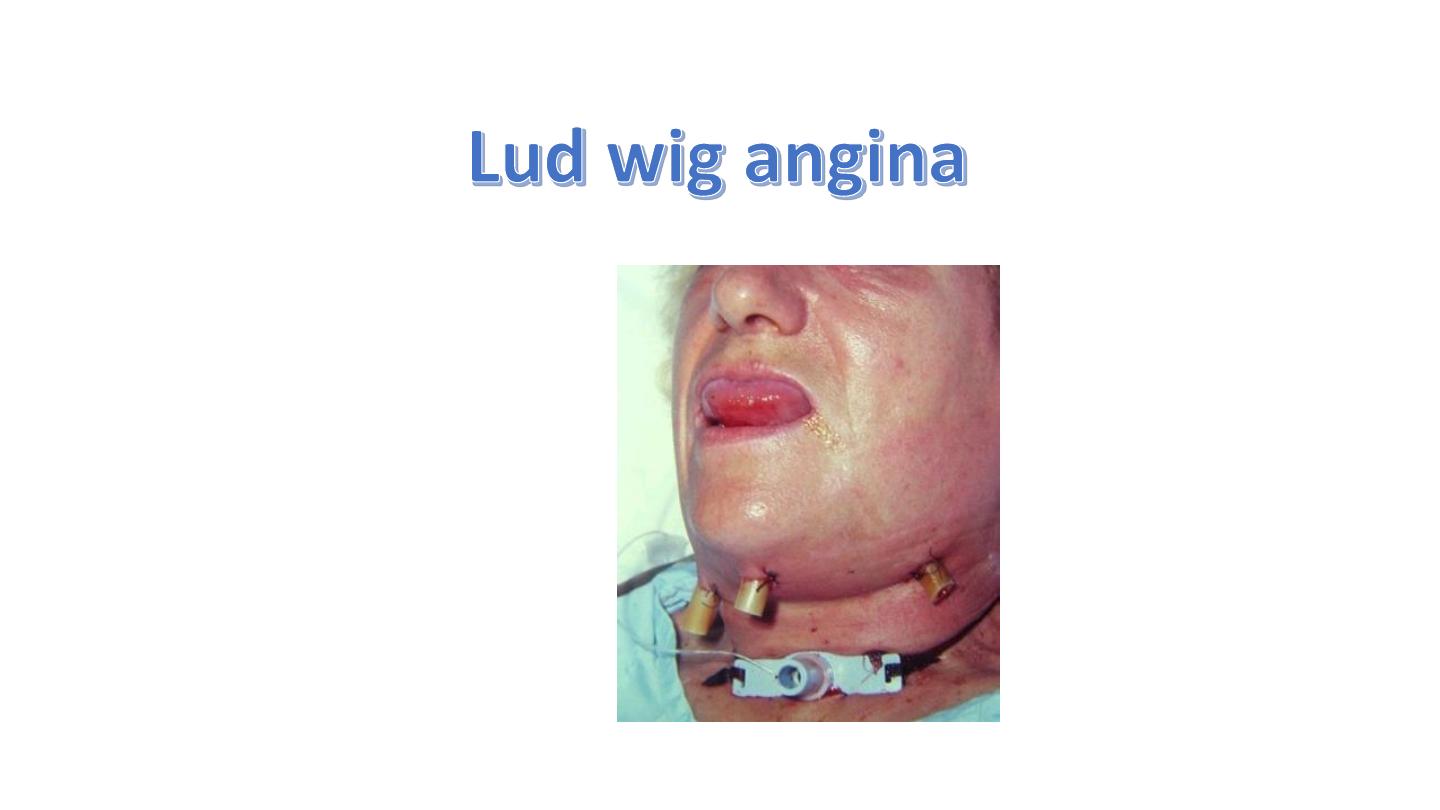
1. Relif of upper airway obstructions subglottic stenosis ,Ludwig angina , epiglottitis ,F.B
,laryngeal tumor, abductor cord paralysis
2. Respiratory inssuficincy : head injury chest injury
3. Bronchial toilet (CVA,coma )
Complication
1. Hemorrhage
2. Apnea
3. Displacement of tt
4. Obstruction of tt
5. Surgical emphysema
6. Pneumothorax
7. infection
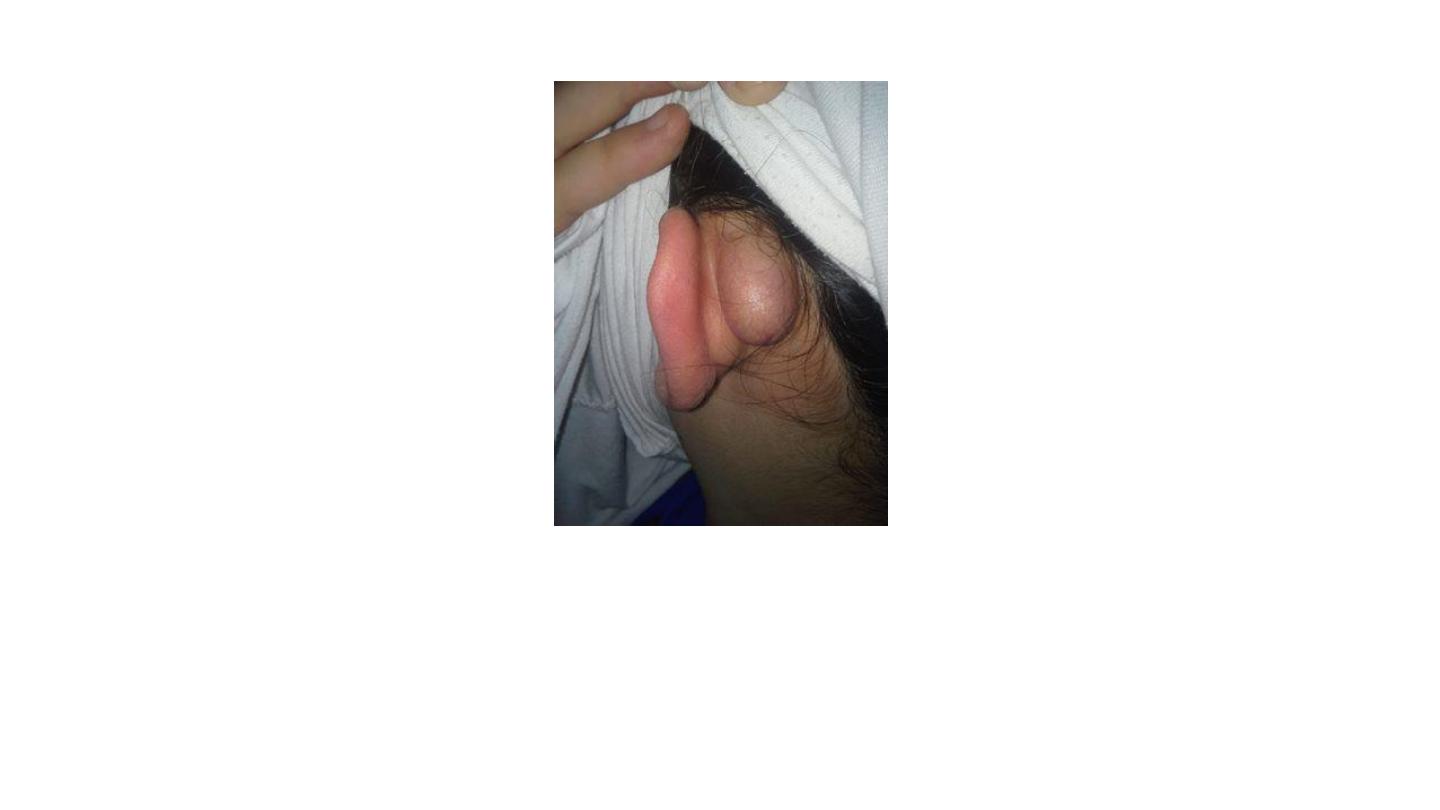
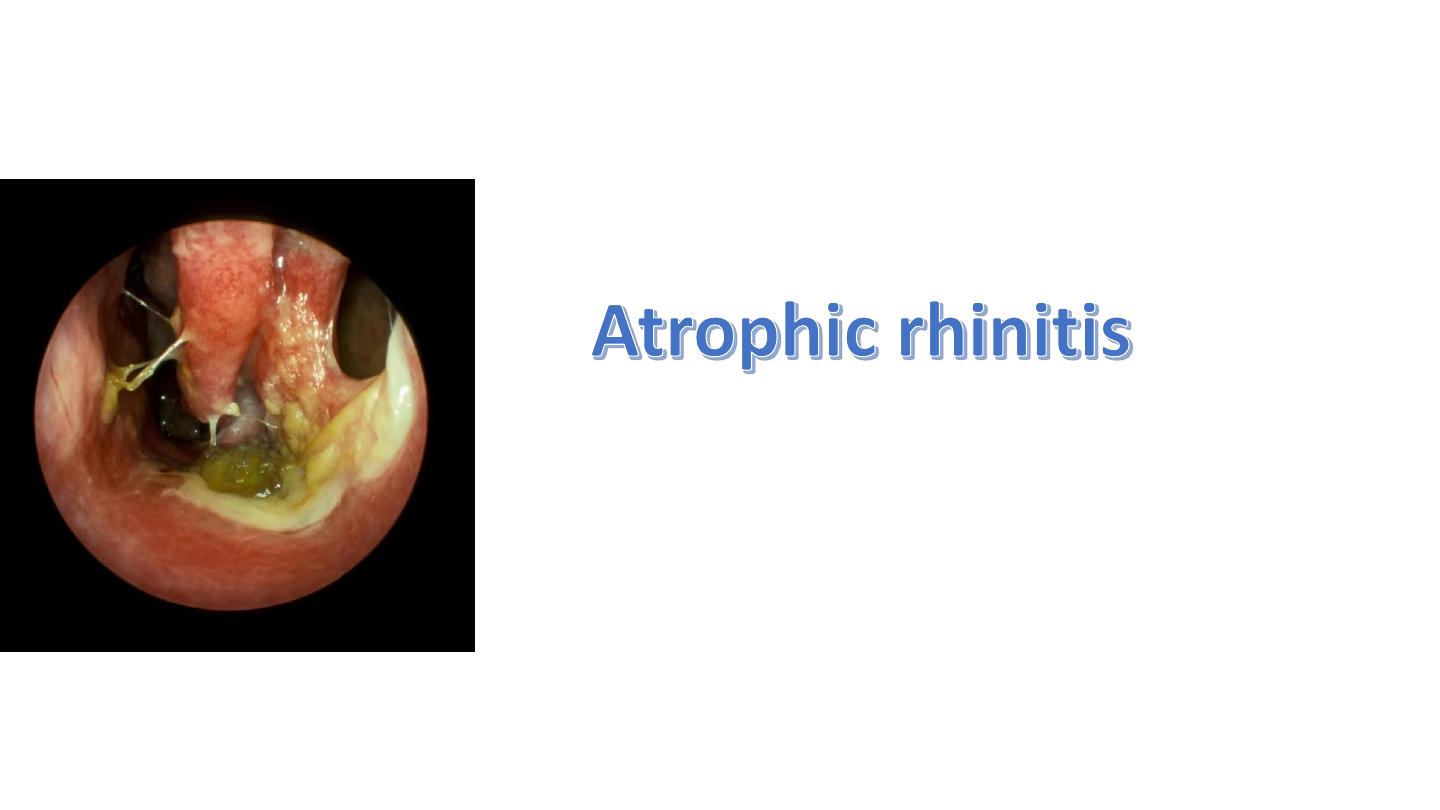
Post-auricular cyst
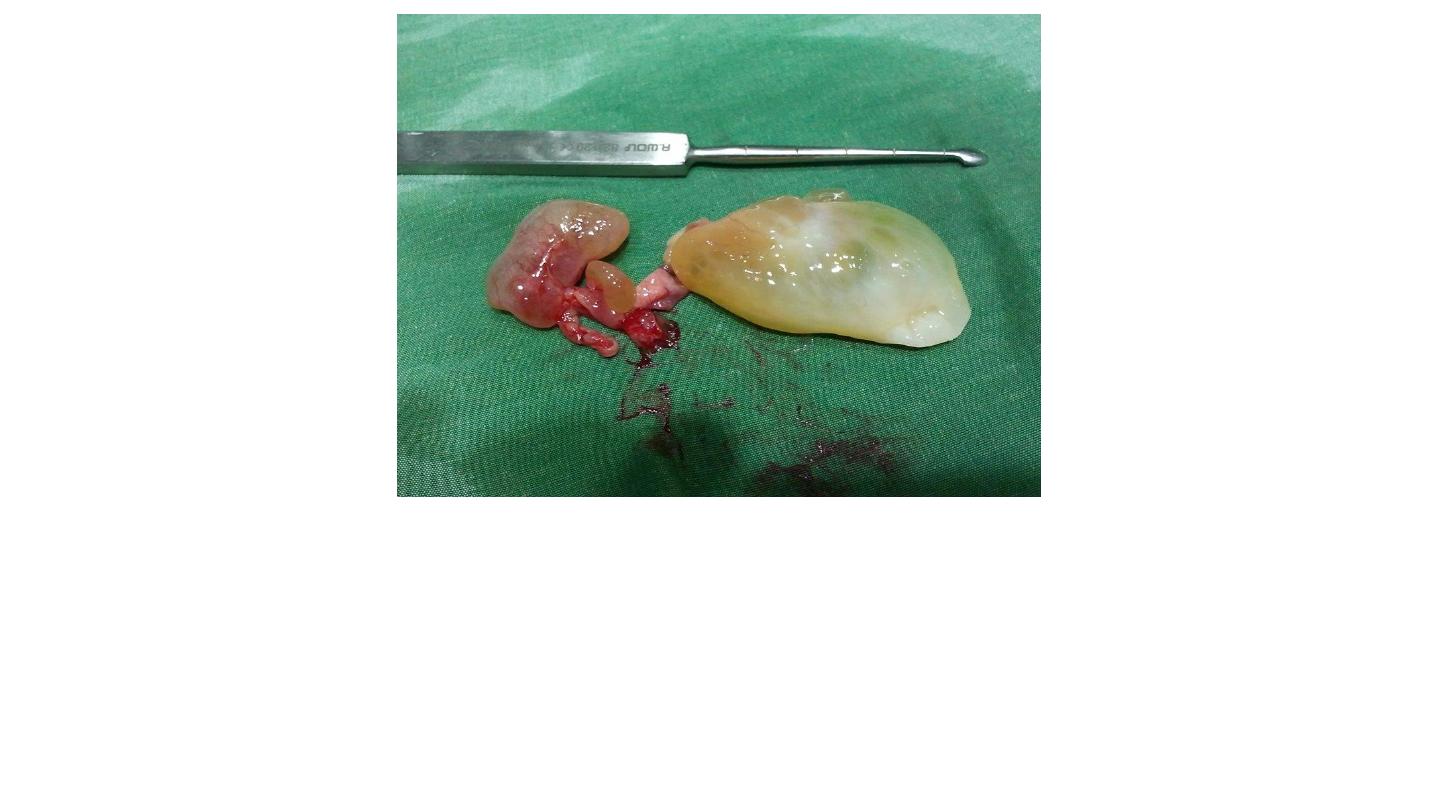
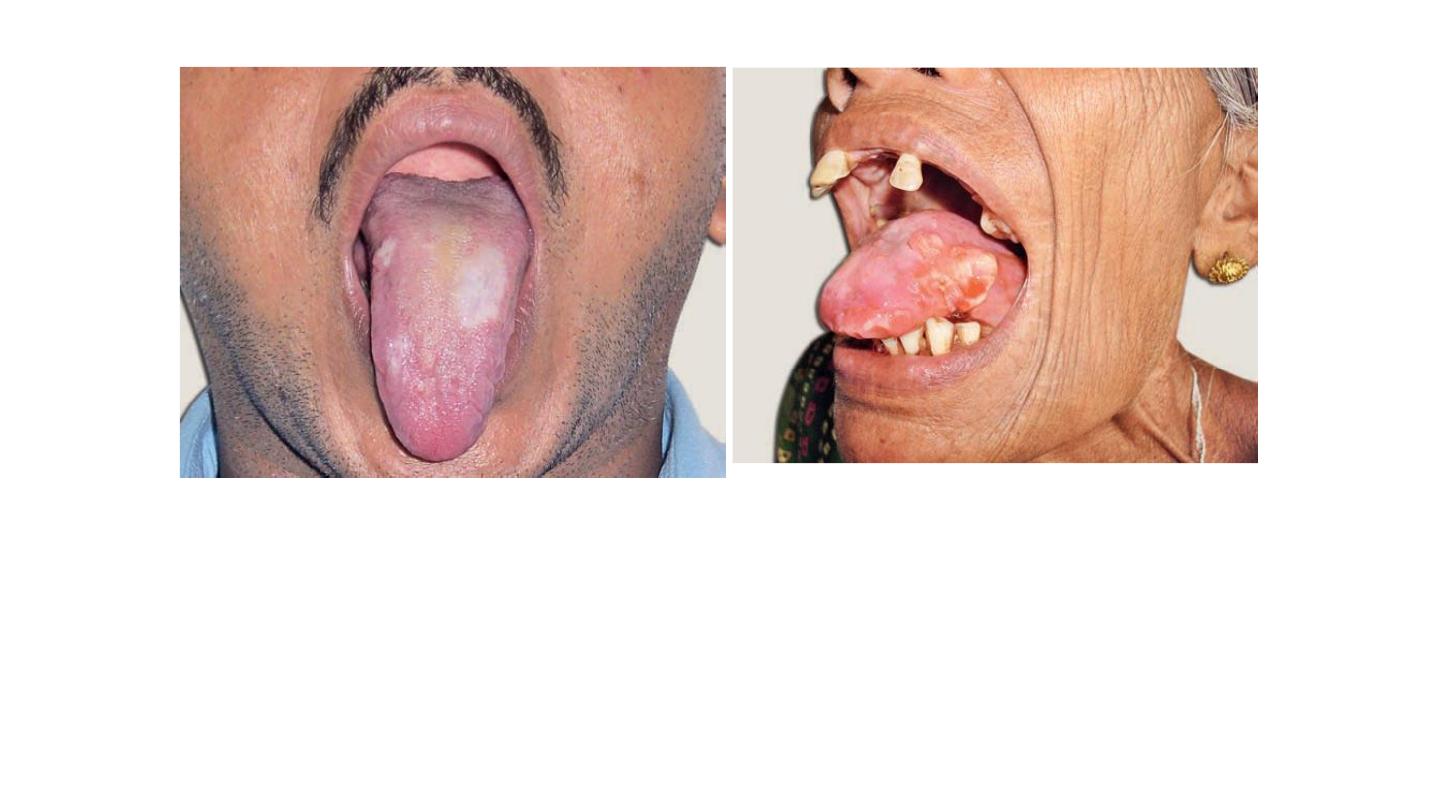
Antrochoanal polyp
Description: mass dumppell large (5-6 cm), avascular (no bleeding), pale, whitish
fibrostrak, yellowish color, gelly like appearance, with streak connected to other
small red mass.
If inside the nasal cavity it is ethemoidal polyp (treated by local or systemic
steroids)
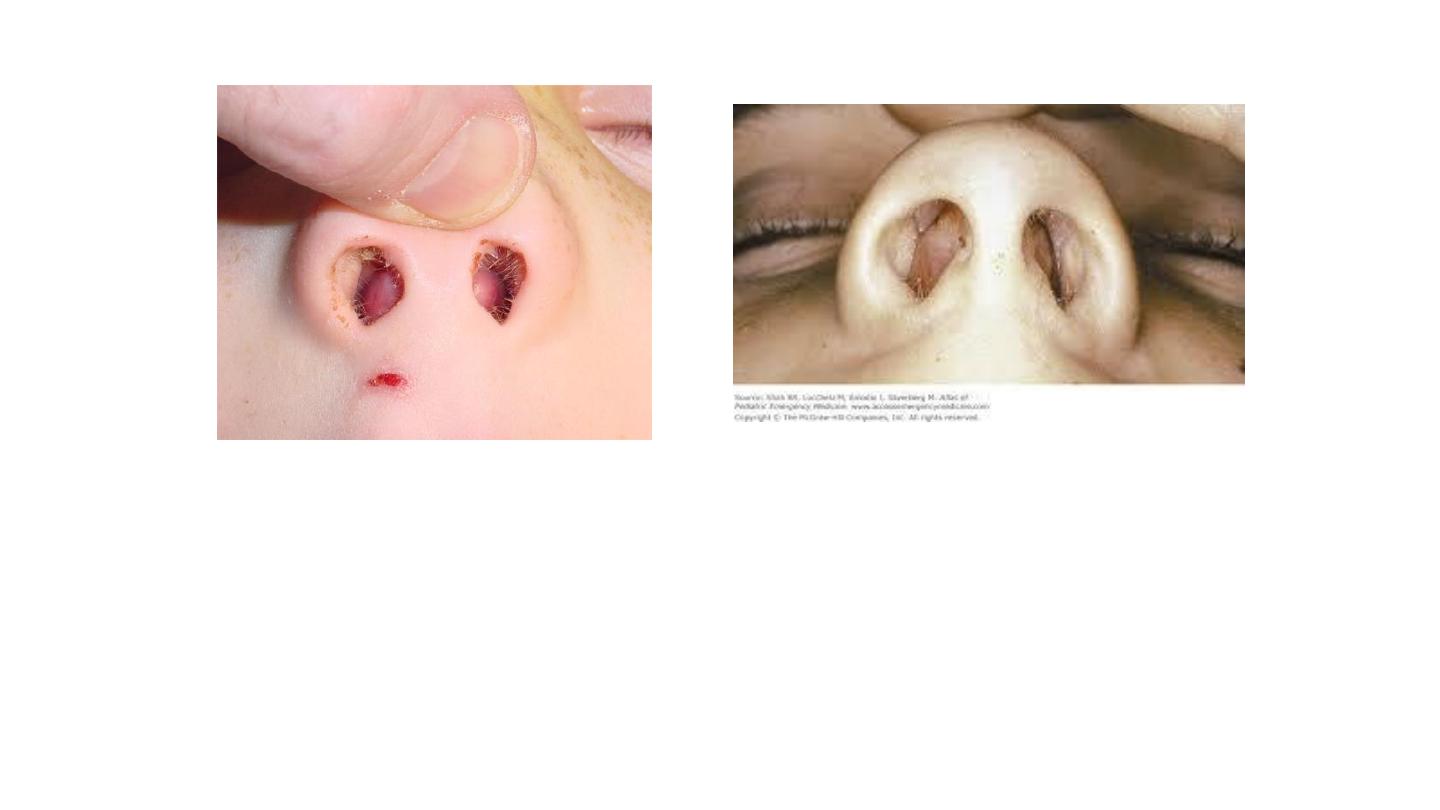
Septal hematoma
History: child – trauma.
Exam: bilateral – painful – tender – color (red, white, blue).
Treatment: emergency surgical evacuation.
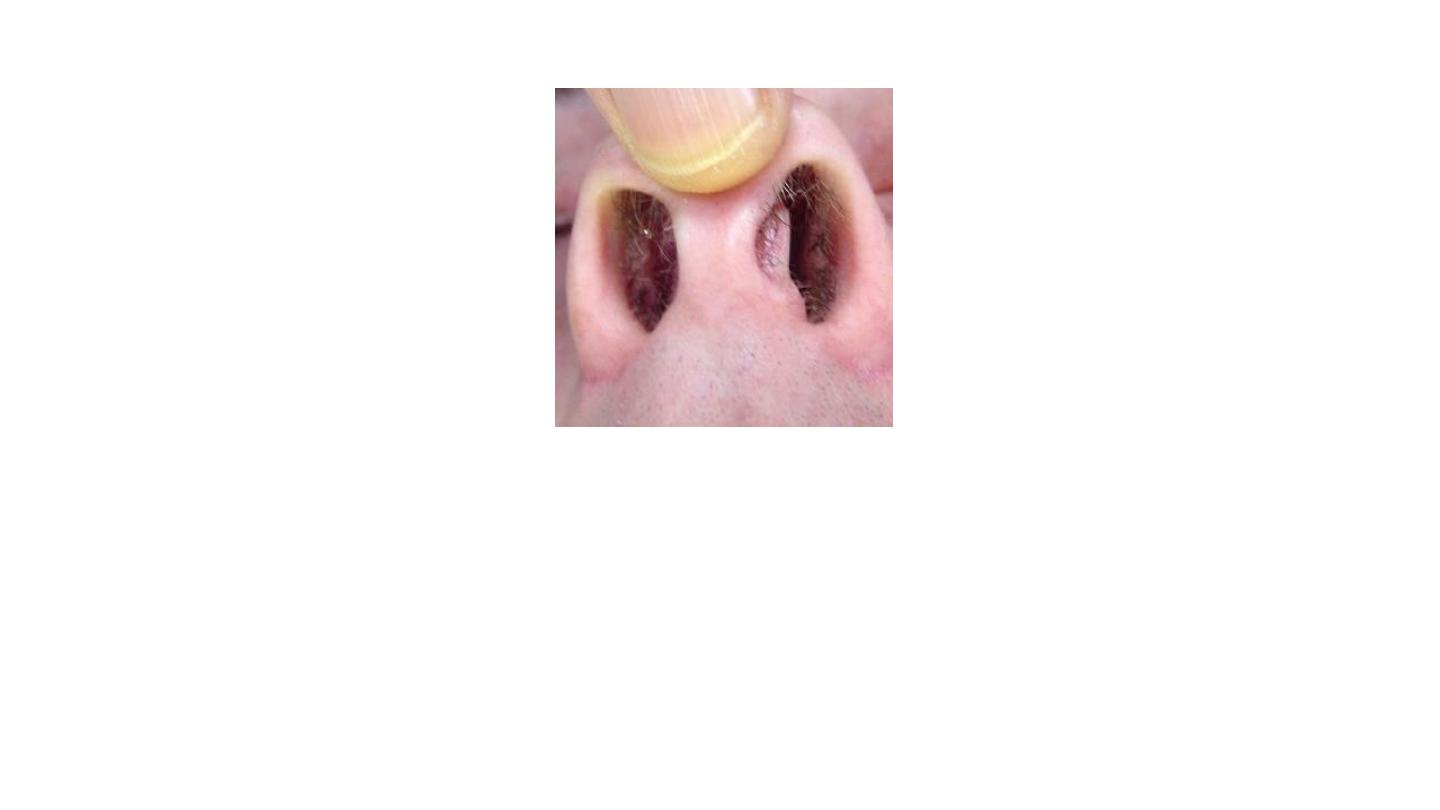
Septal deviation
History: adult – congenital or with trauma.
Exam: pale color – arise from one side only.
Management: septoplasty+/- rhinoplasty.
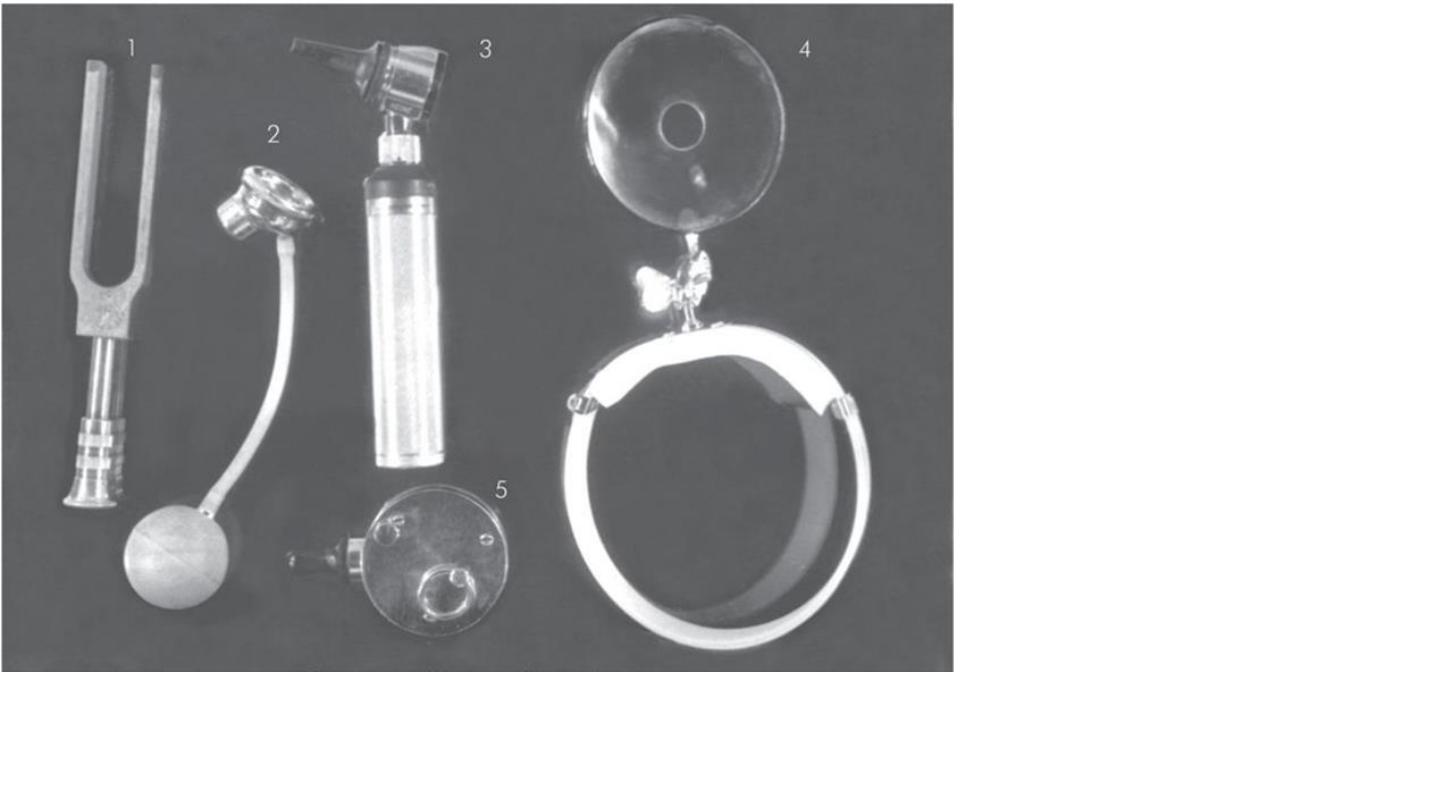
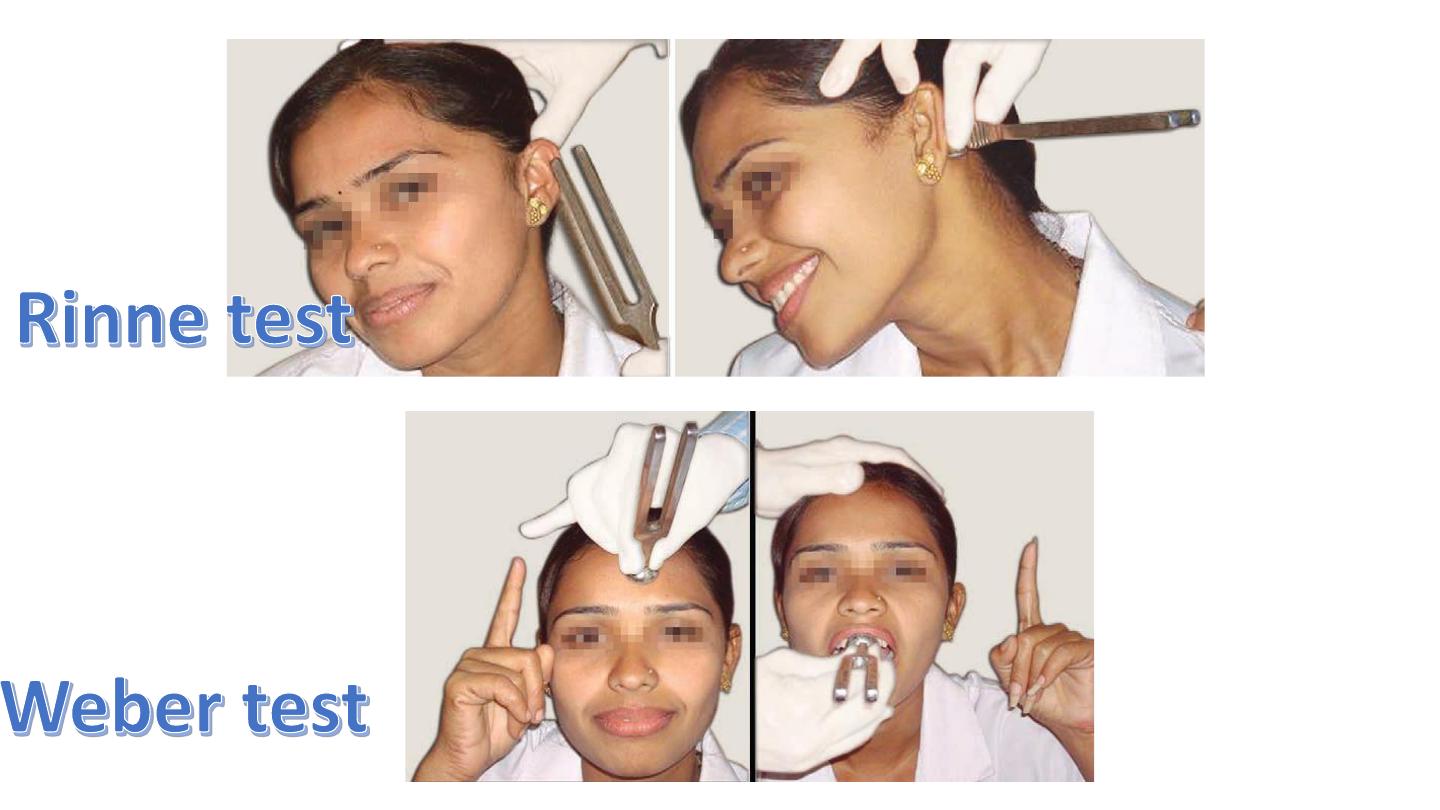
1- Tuning fork
2-Siegl’s speculum
3-Otoscope
4-Head mirror
5-barany noise box

5-barany noise box
uses
masking of non test ear
false negative Rinne test
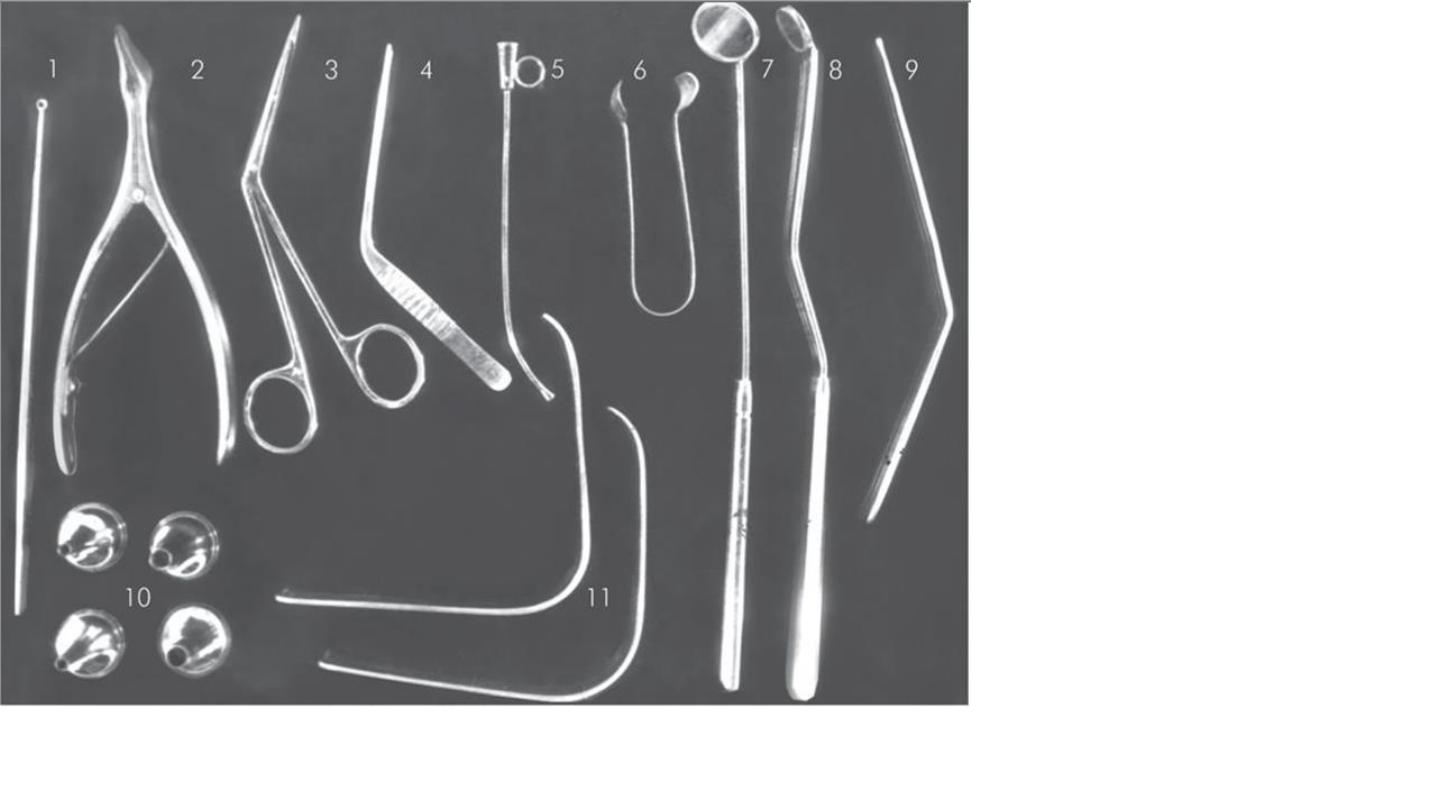
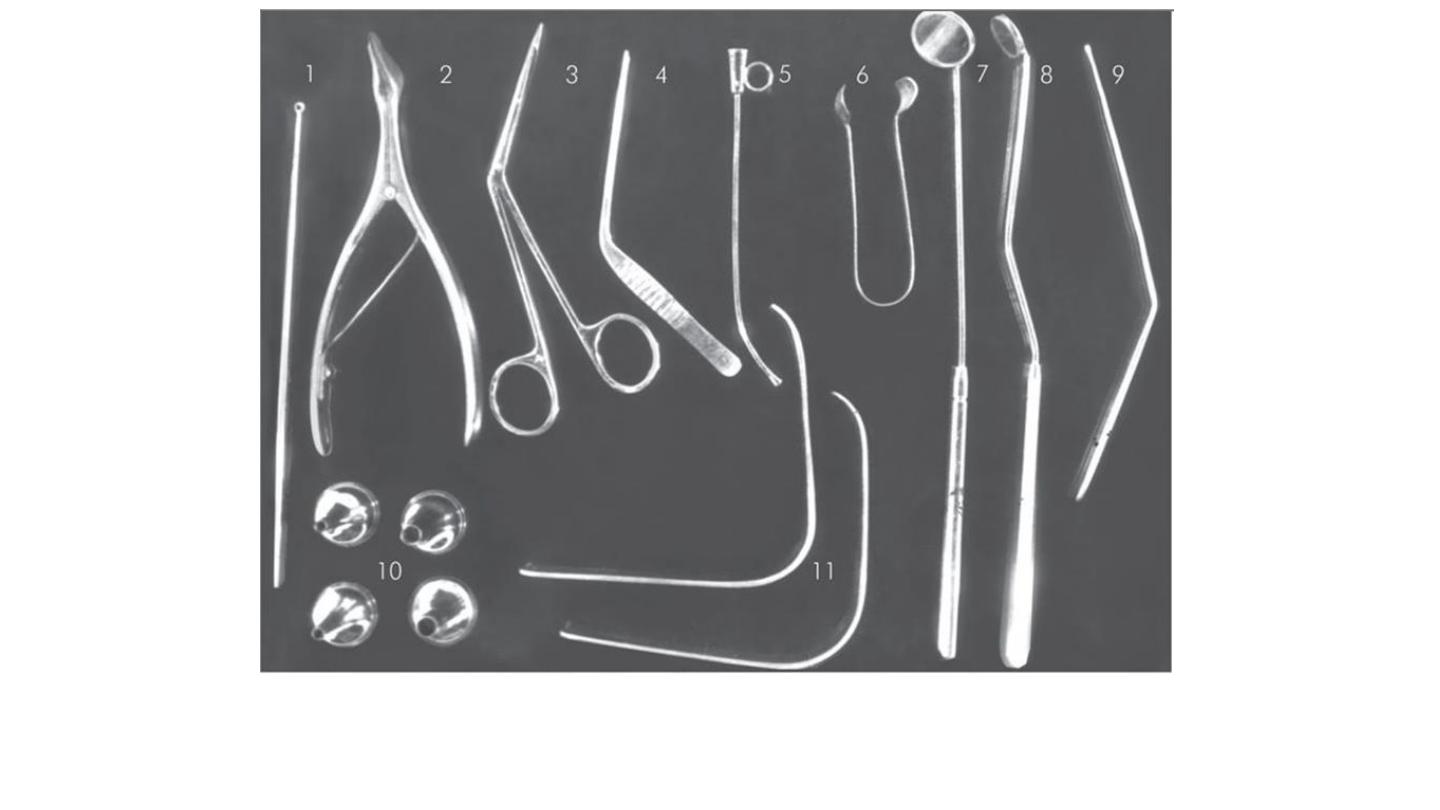
1-Jobson horn
2-Killan nasal speculum
3-telly nasal dressing
4-oooooooooo
6-thudicum nasal
speculm
7- laryngeal mirror
8-nasopharyngeal mirror
10 aural speculum
11- metallic tongue
depressor
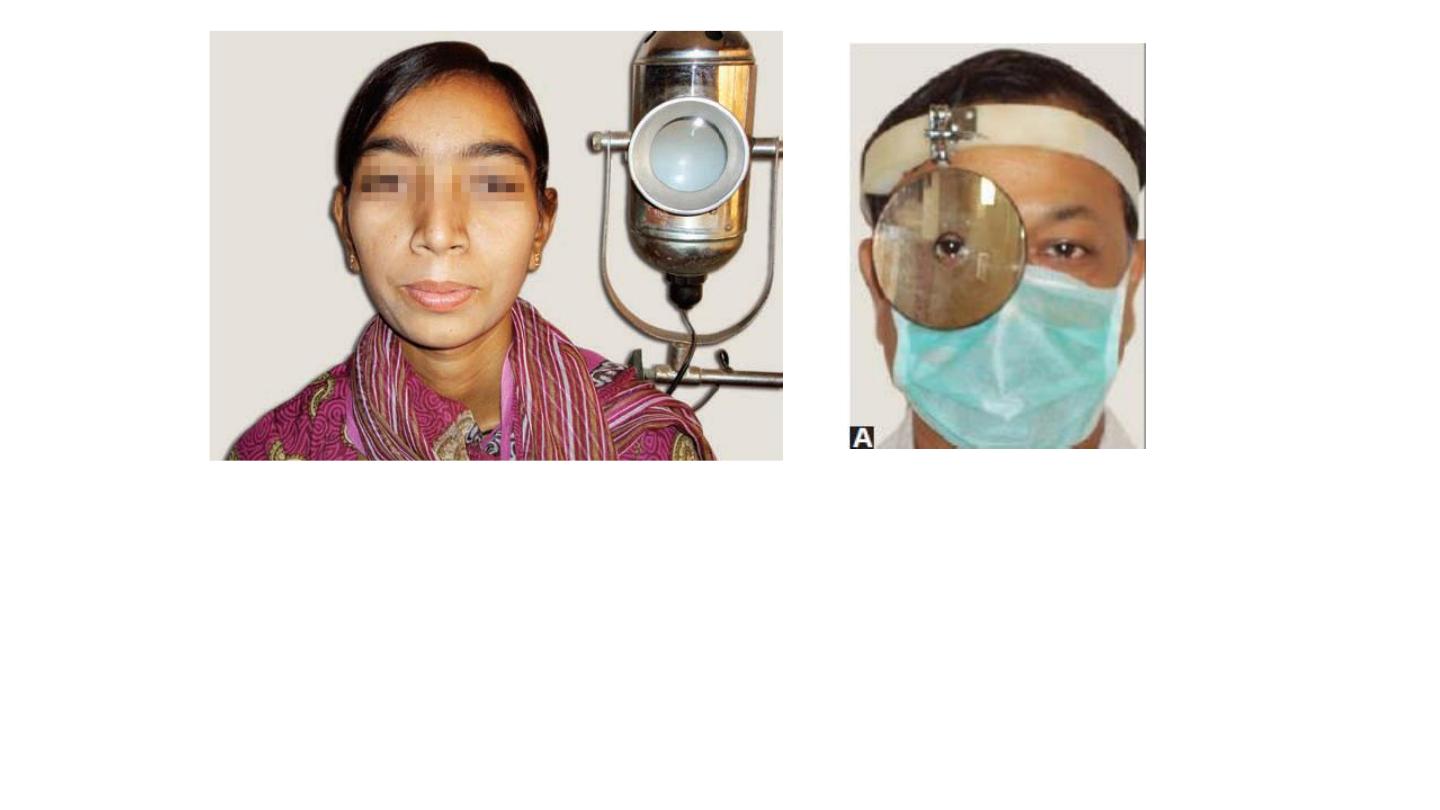
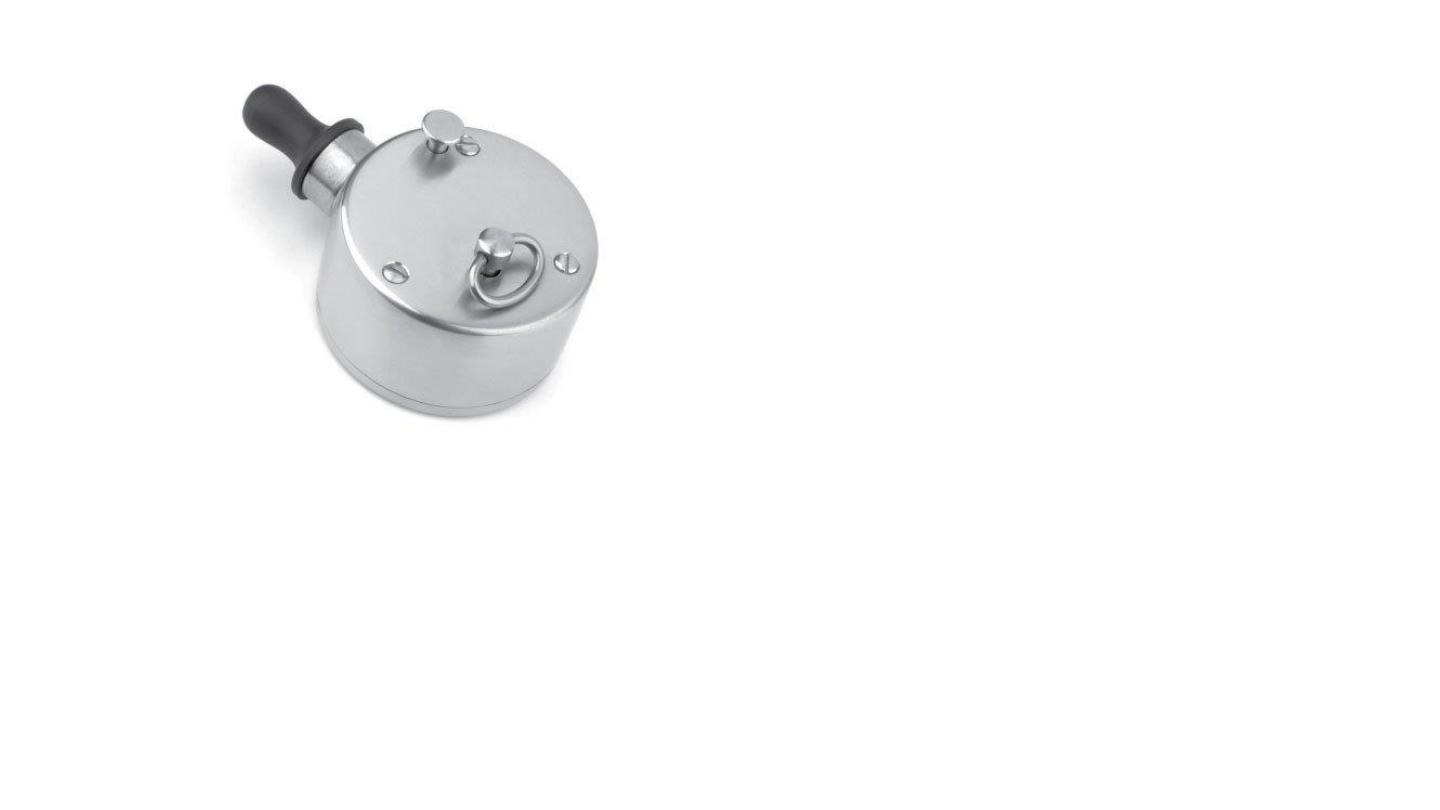
Bull’s eye lamp
placed on left side of patient at the level
of shoulder
30 cm ideal distance

Head mirror
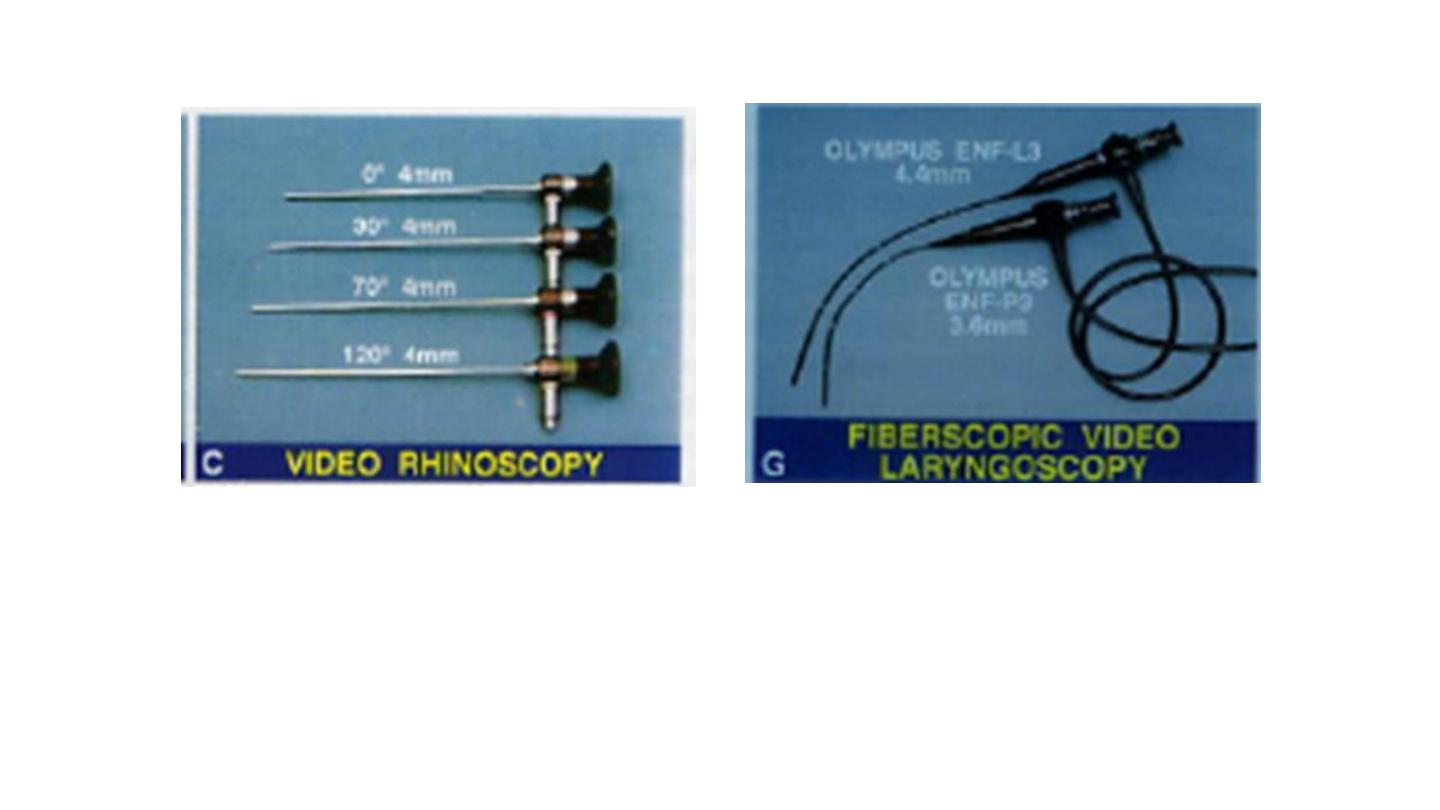
Rigid nasal endoscopes Fibreoptic nasolaryngoscope
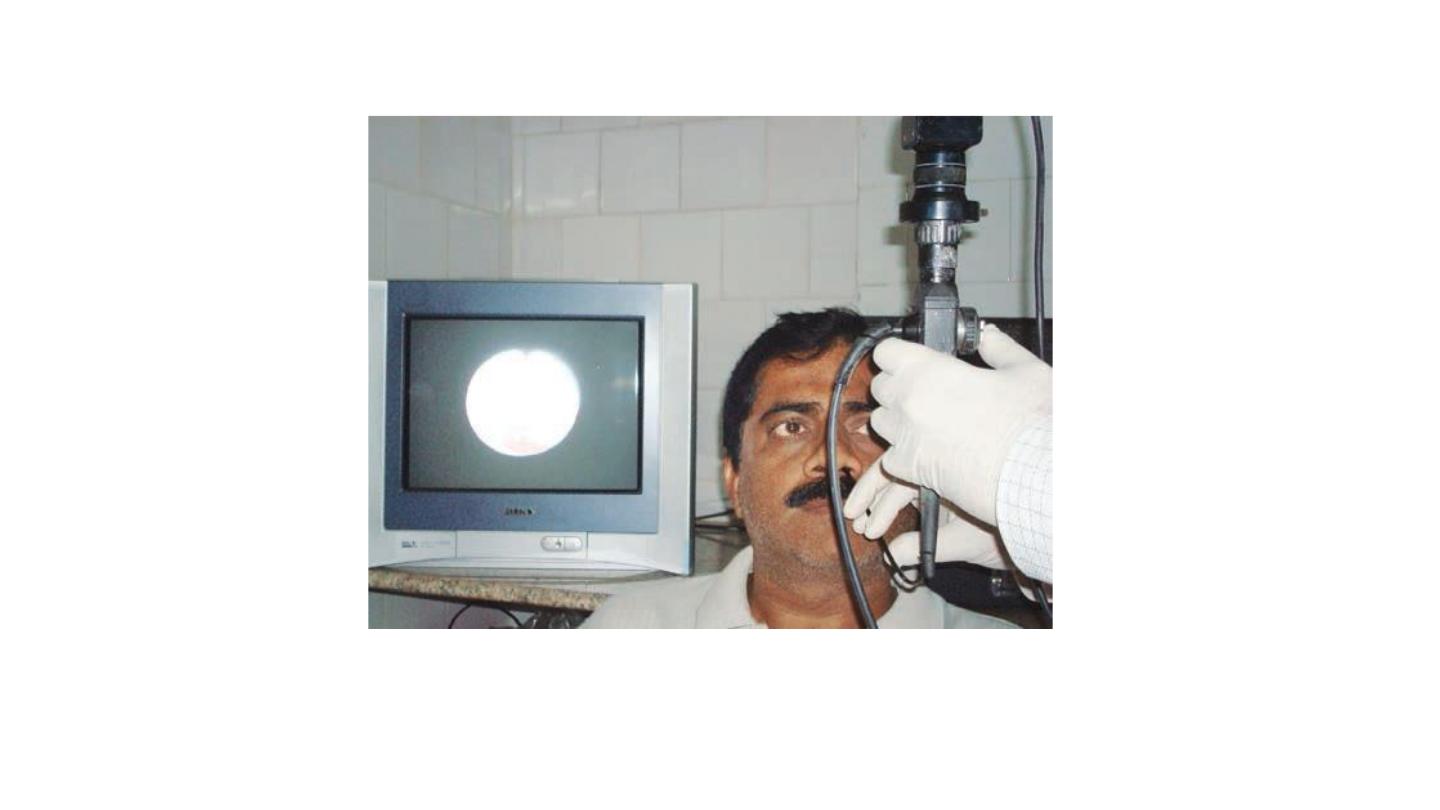
Flexible fiber optic endoscope
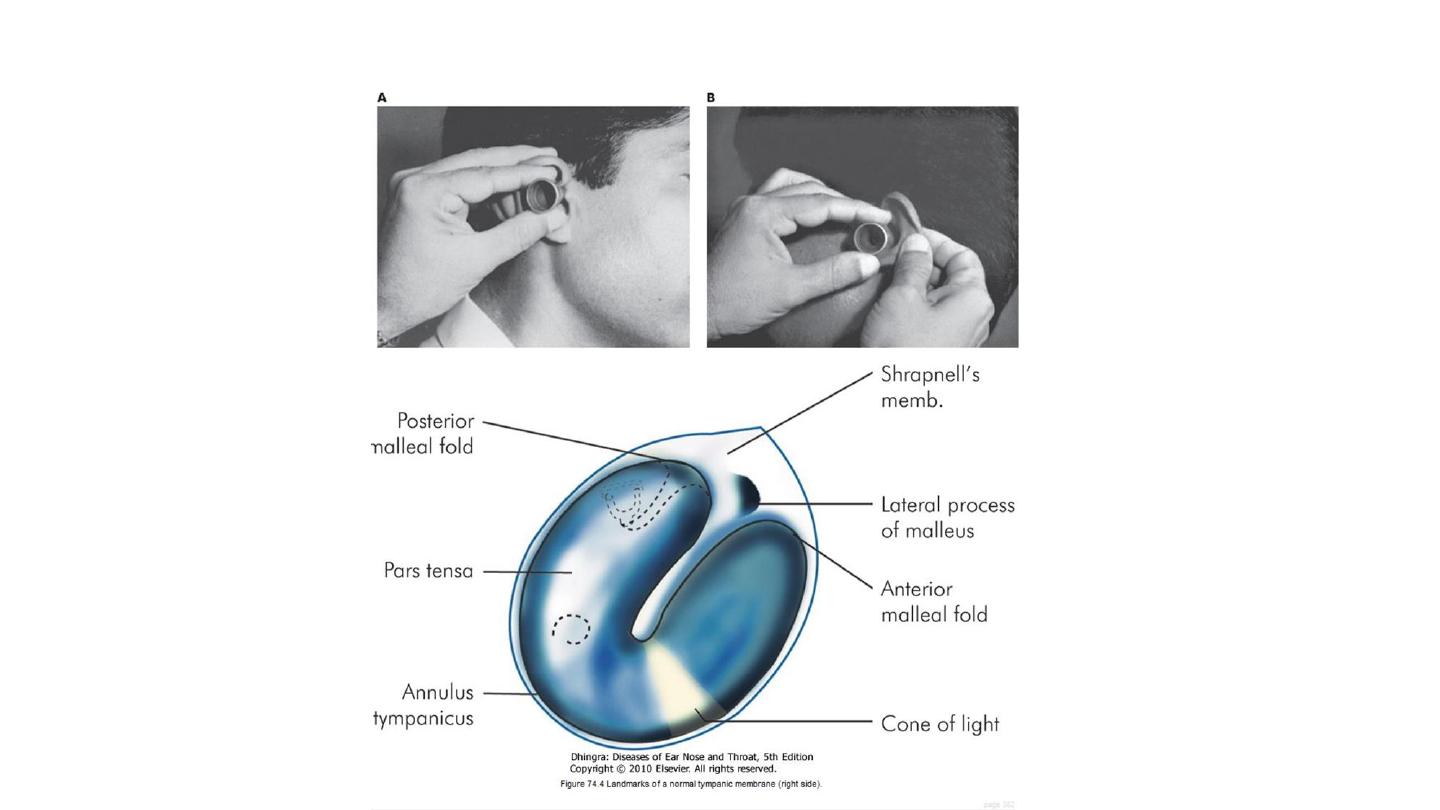
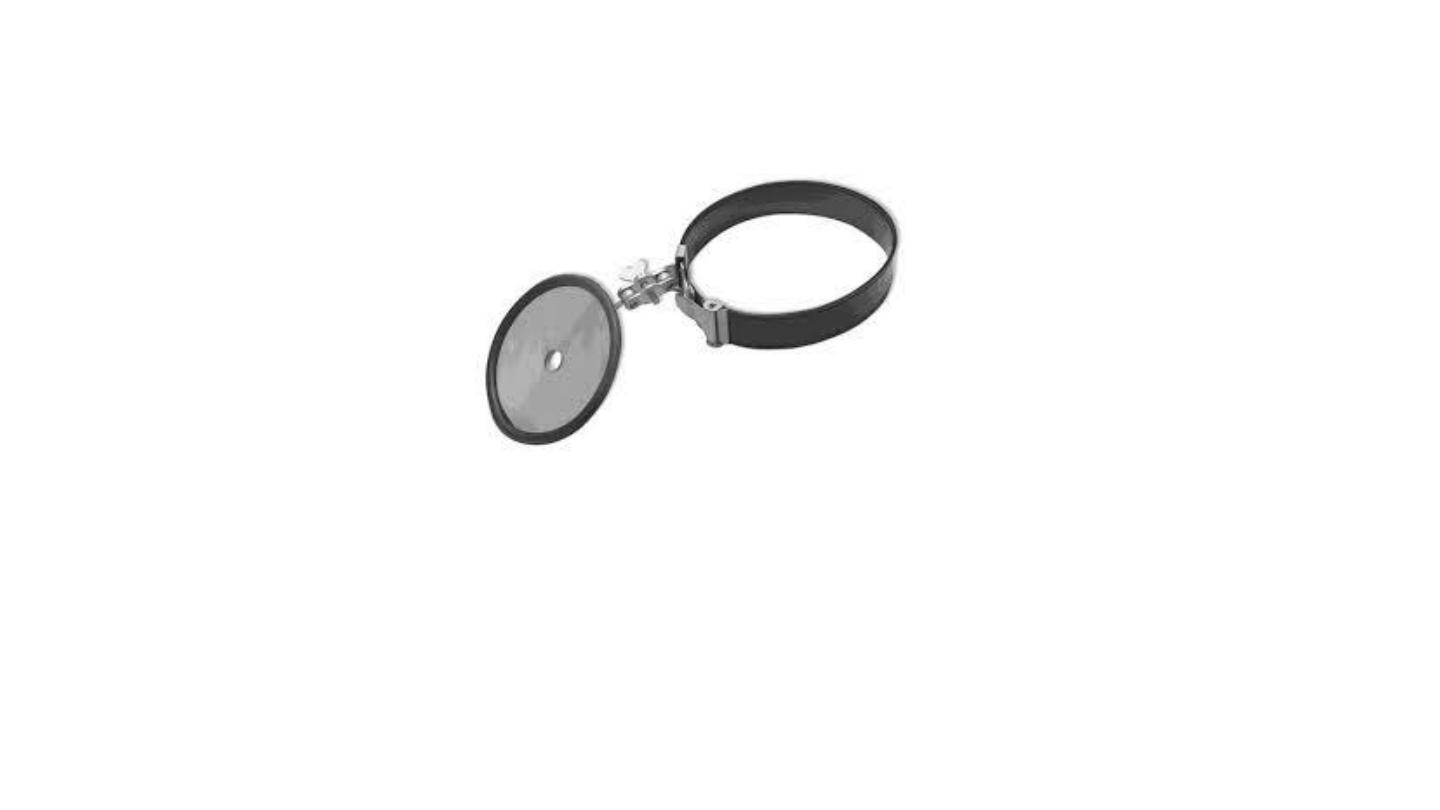
Use of seigle's pneumatic speculum to see mobility of tympanic membrane.
uses of Seigle pneumatic speculum
1. Checking tympanic membrane mobility
2. Insufflation of drugs
3. Fistula test
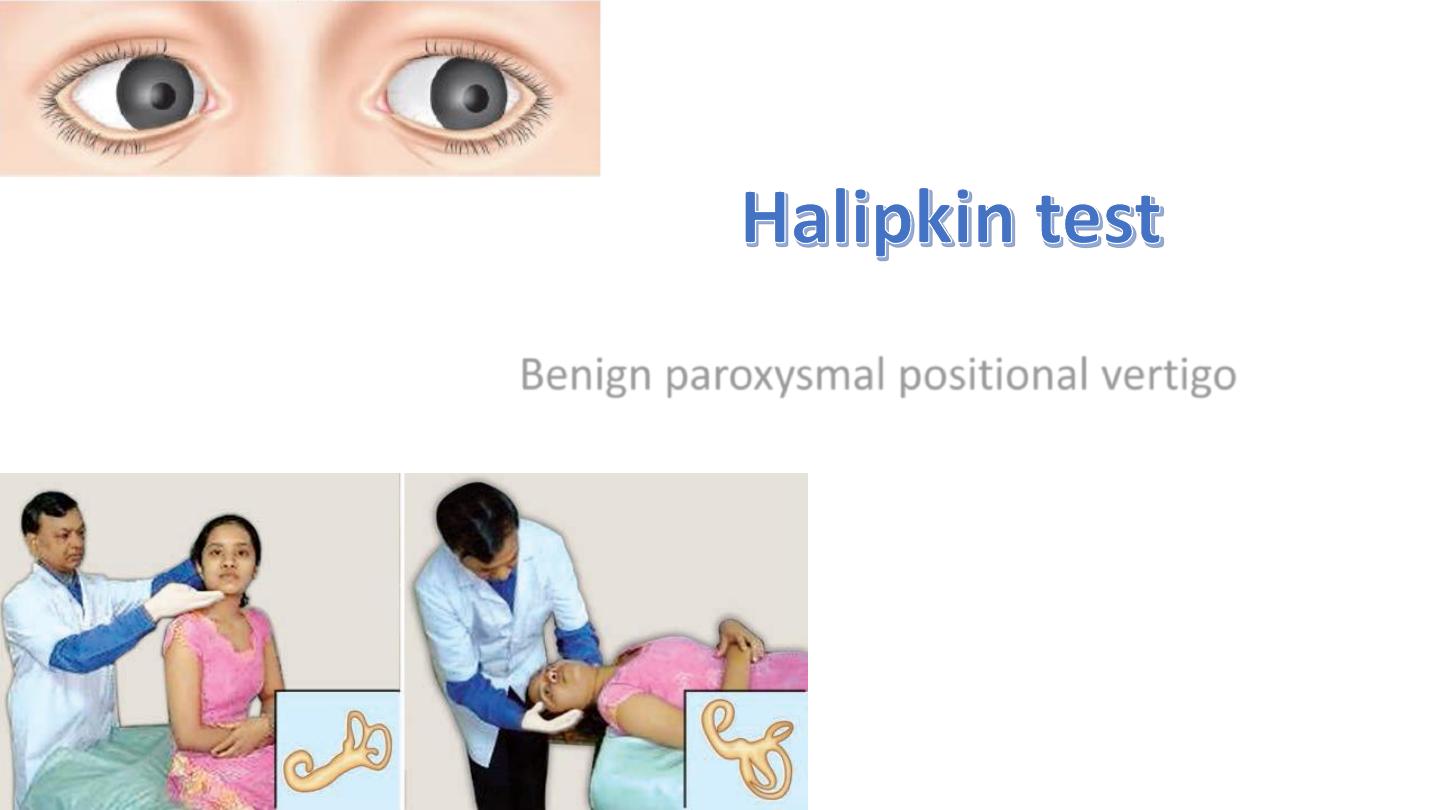
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
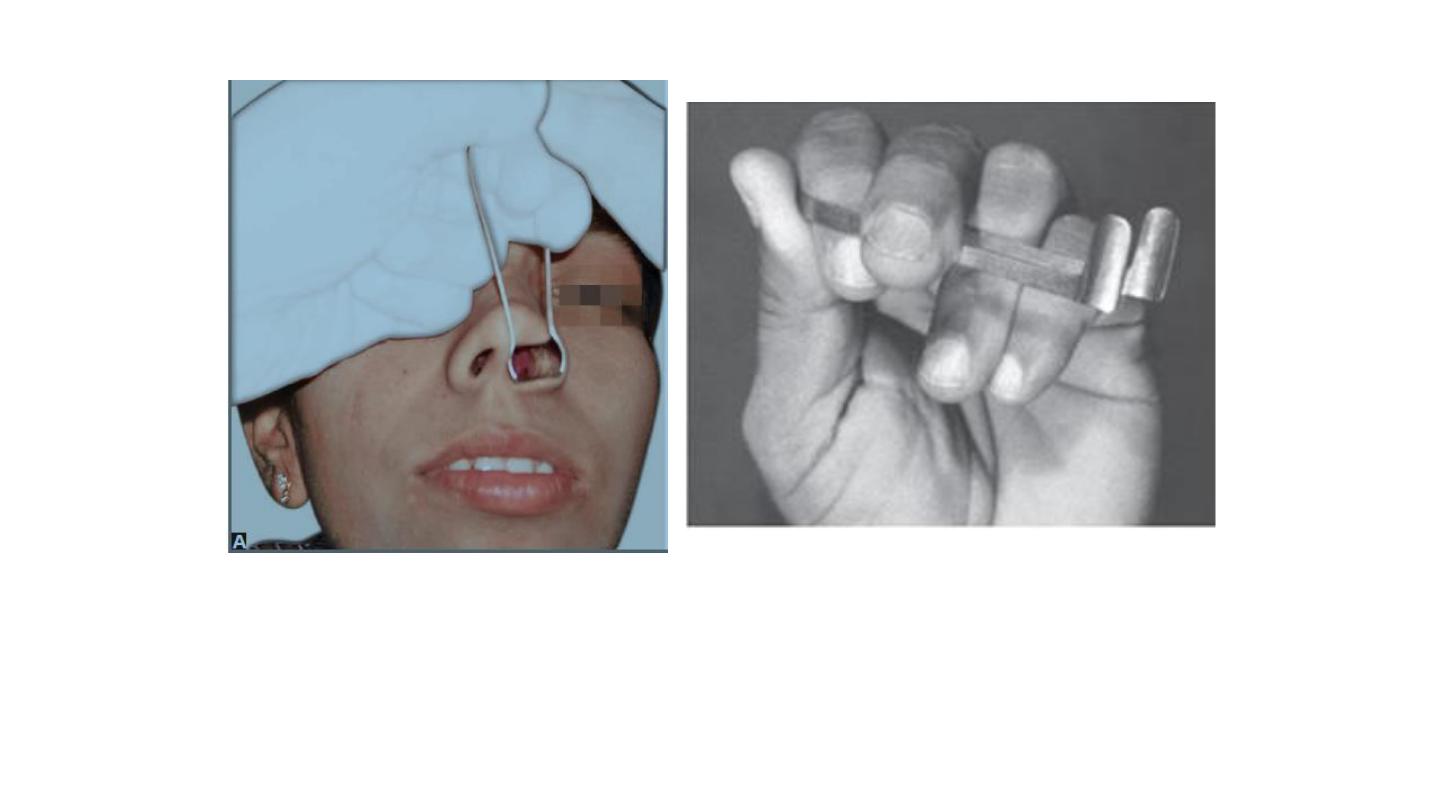
(A) Anterior rhinoscopy. (B) Technique of holding a
Thudicum nasal speculum.
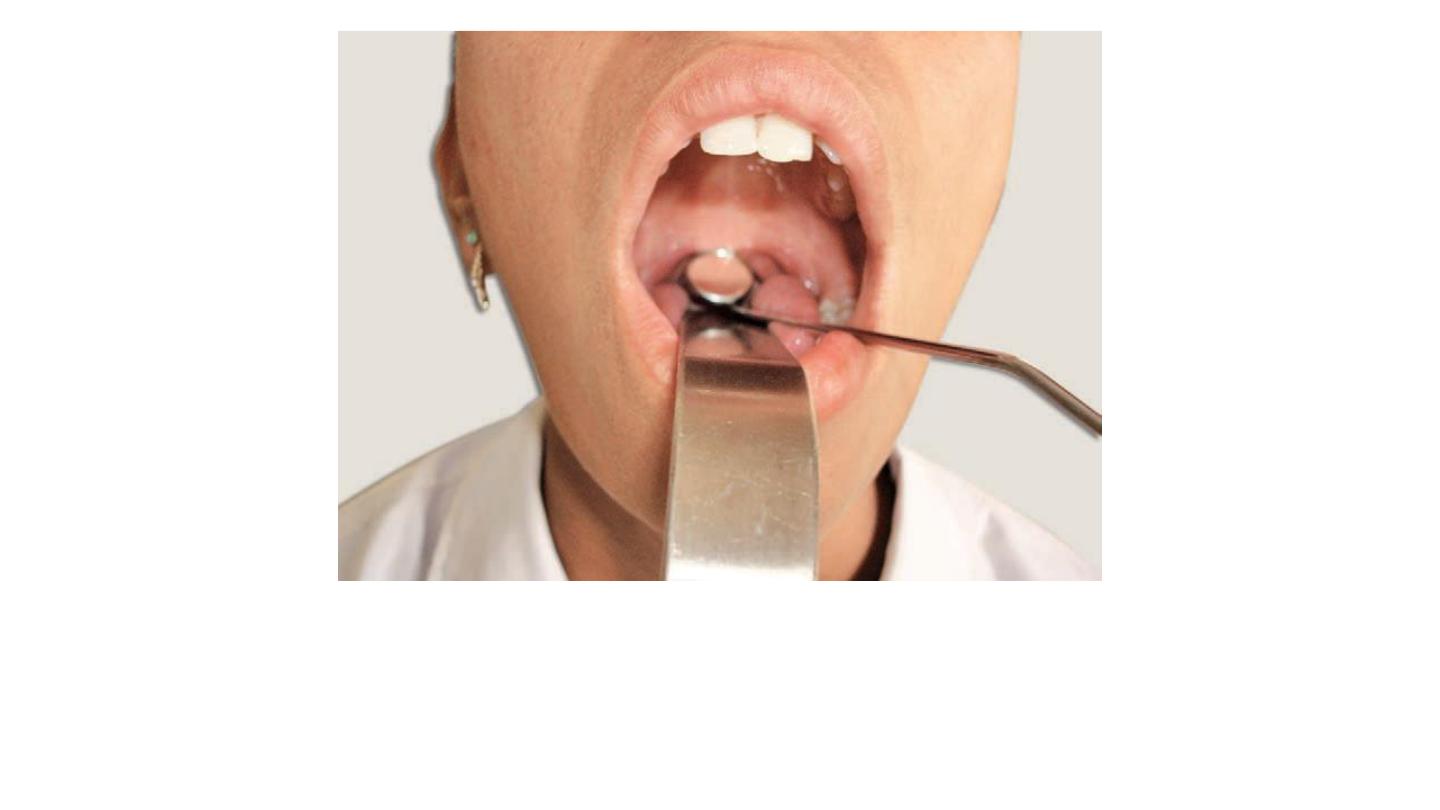
Posterior rhinoscopy. The examiner depresses the tongue
and introduces posterior rhinoscopic mirror behind the soft palate
.
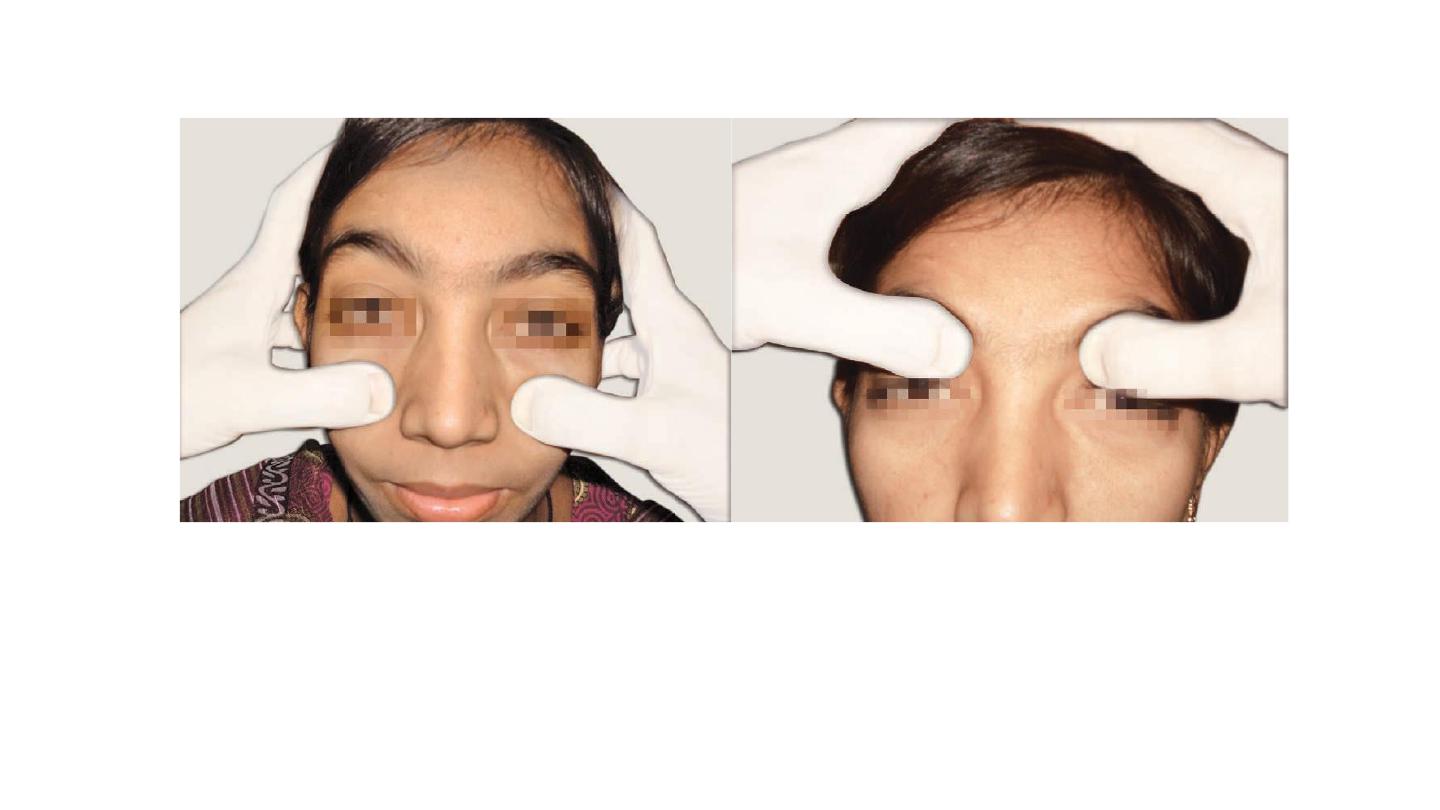
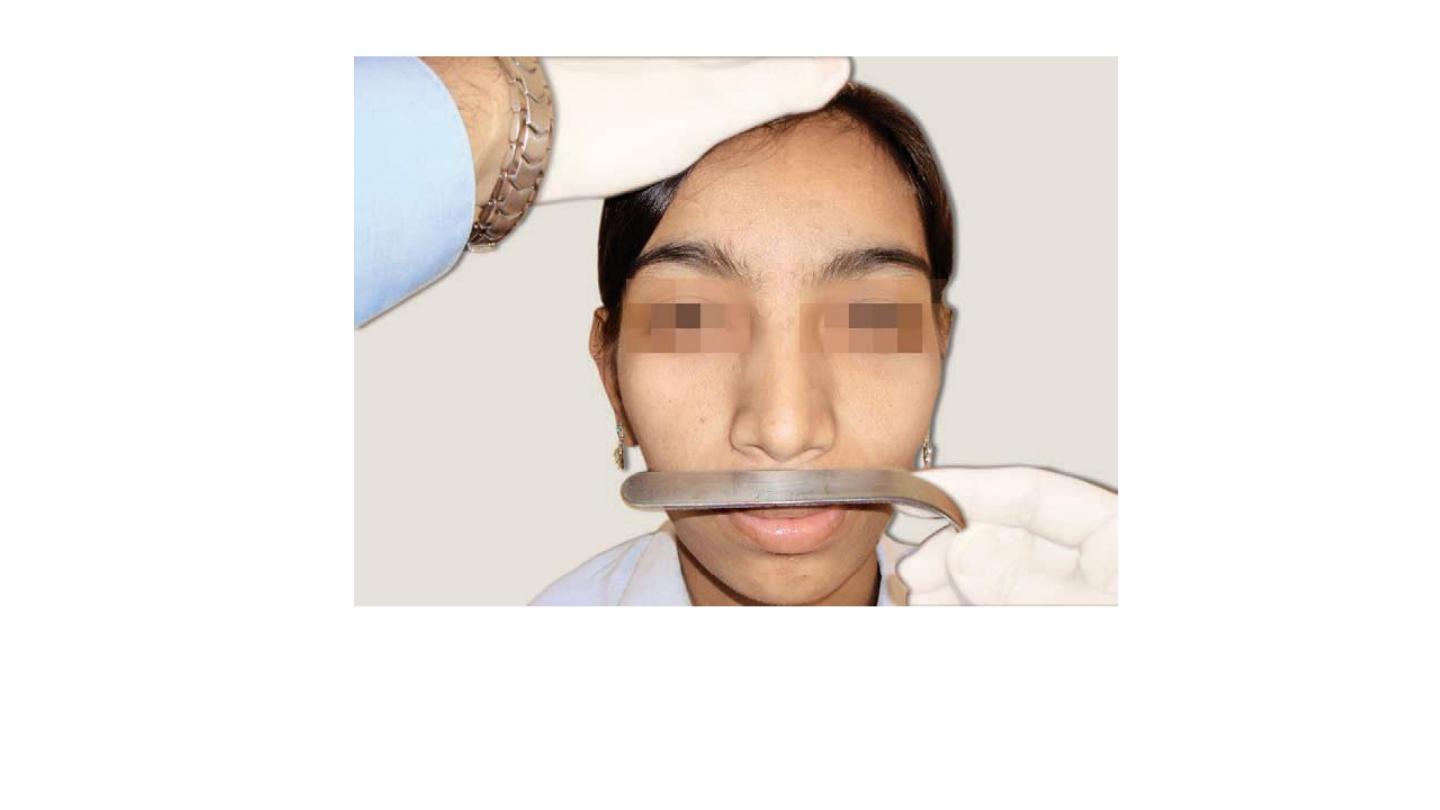
Spatula test for patency of nose. A clean cold tongue depressor
held below the nose while patient exhales. Mist formation
on either side is compared
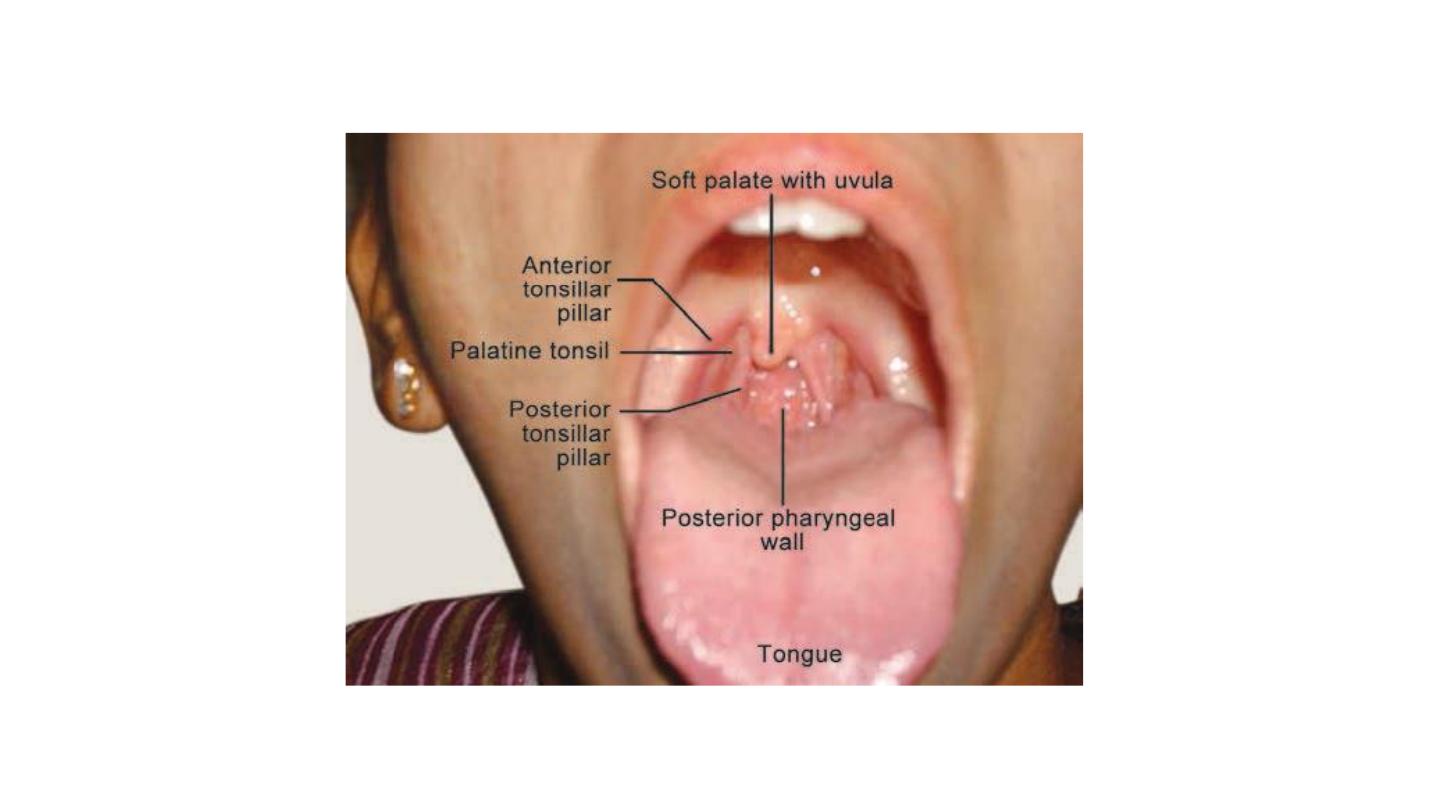
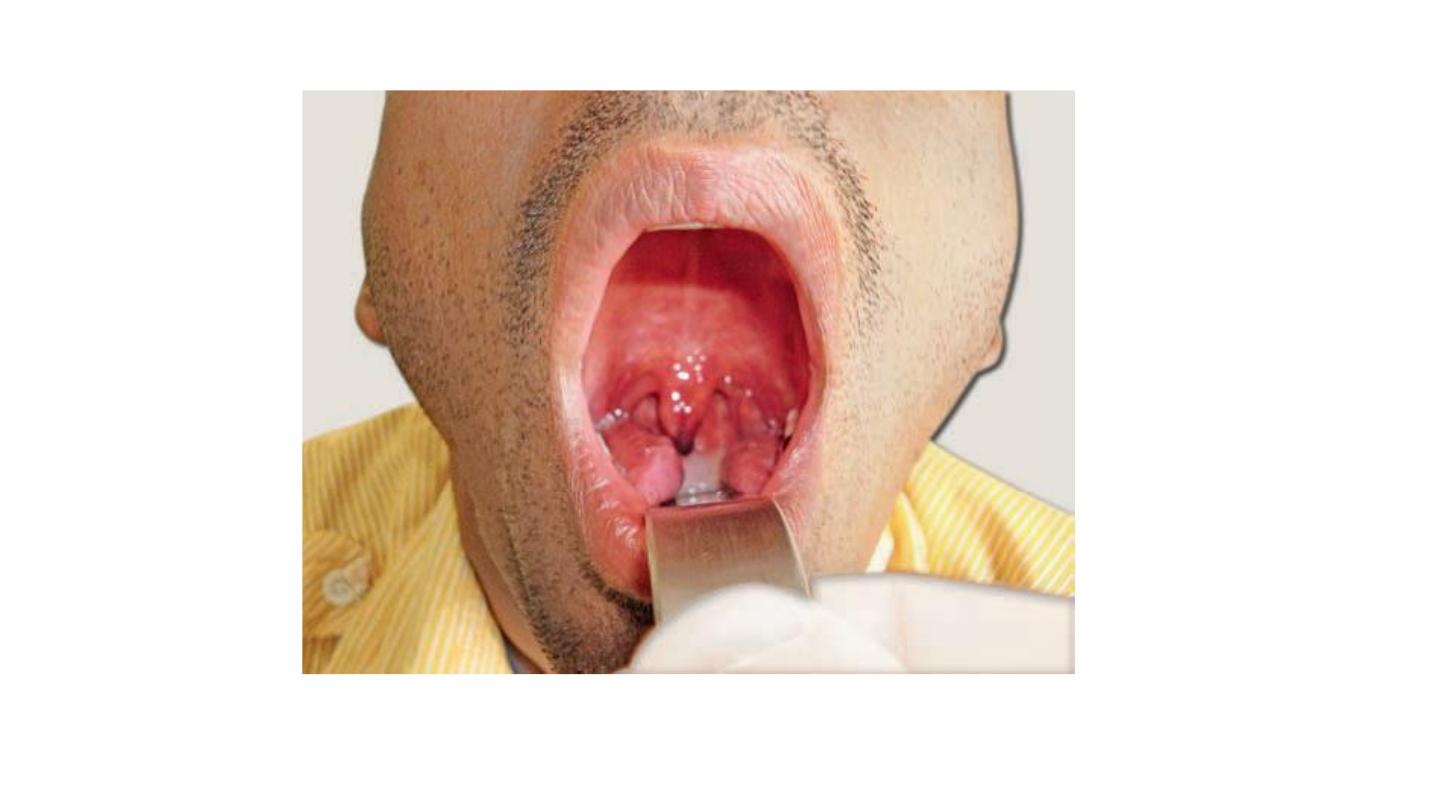
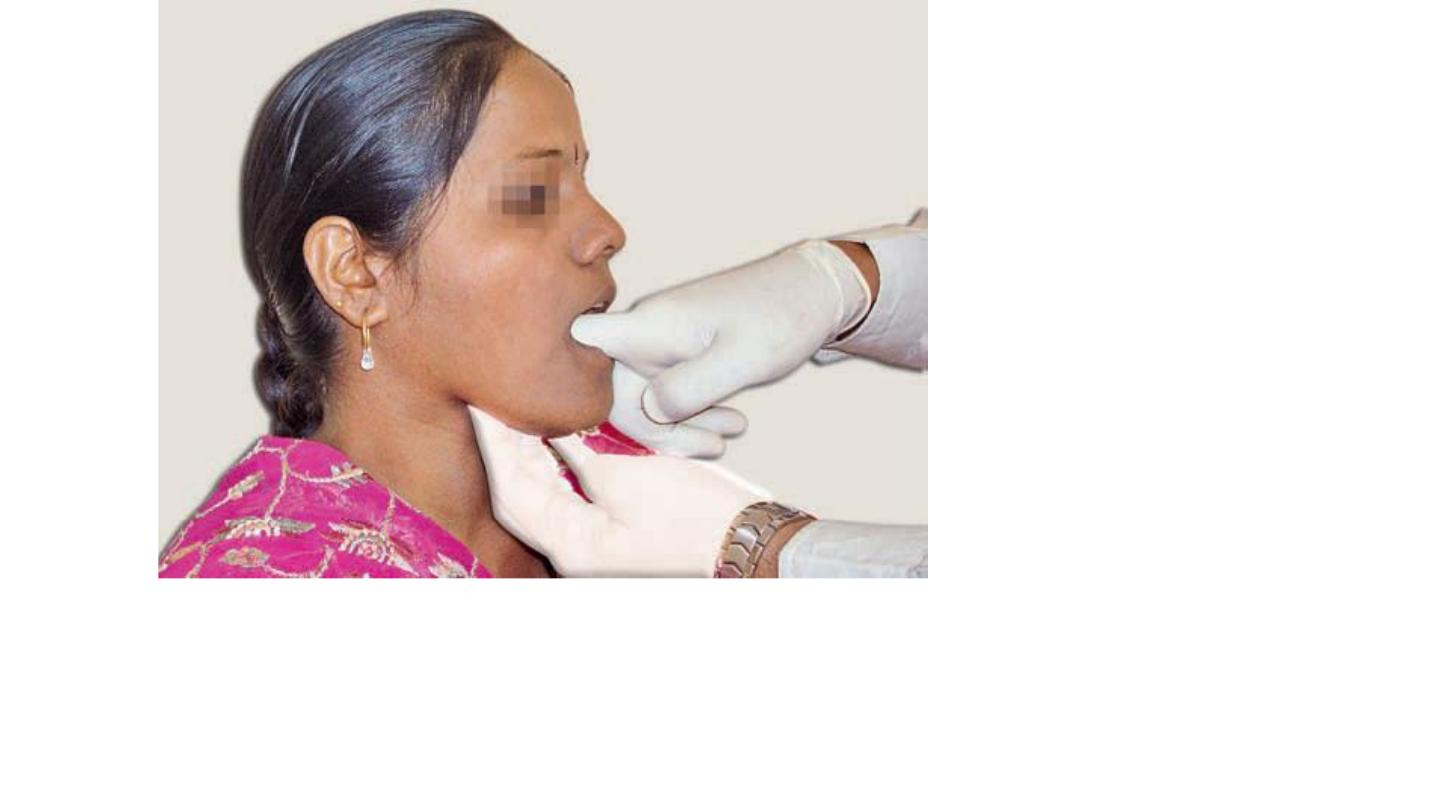
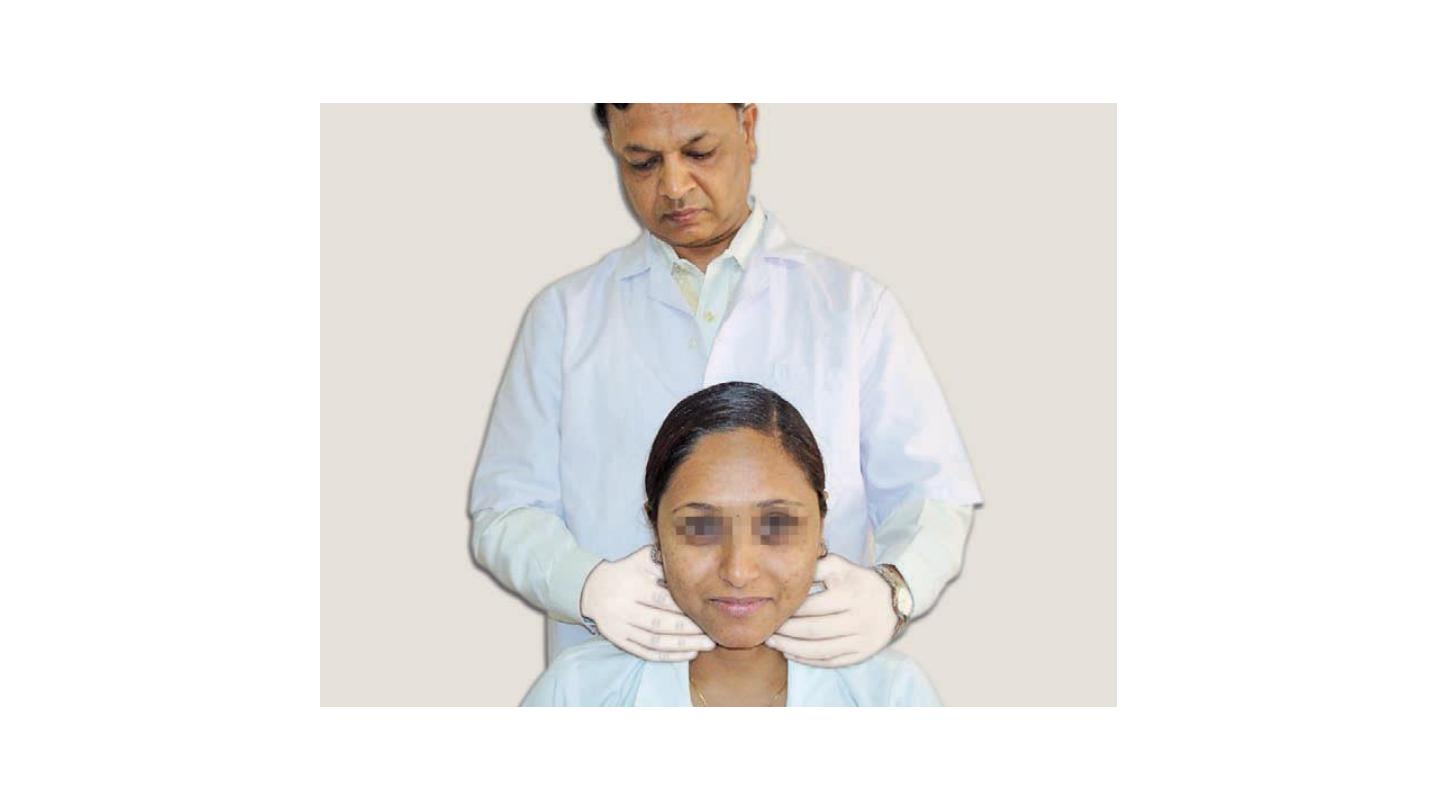
Bimanual examination of mandibular salivary gland
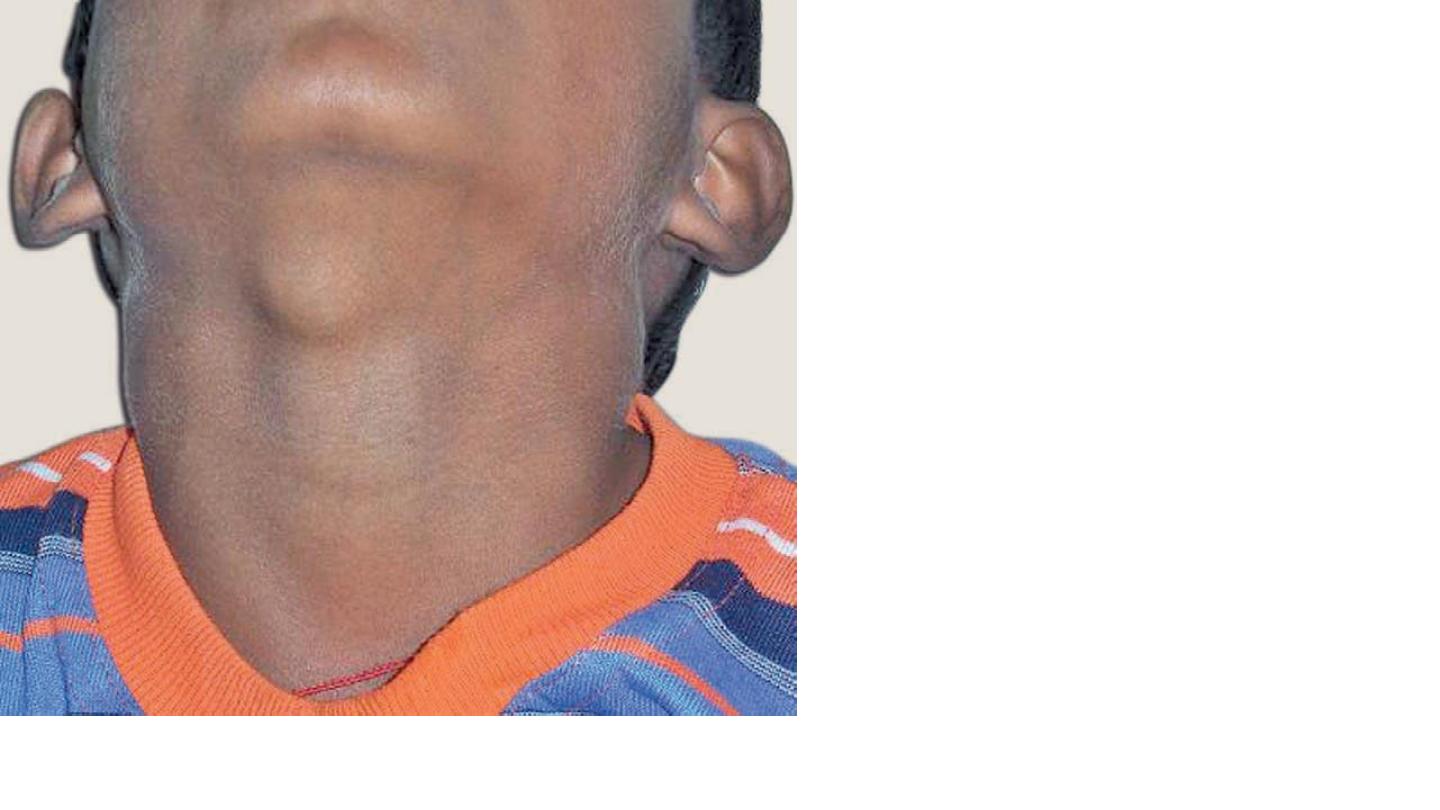
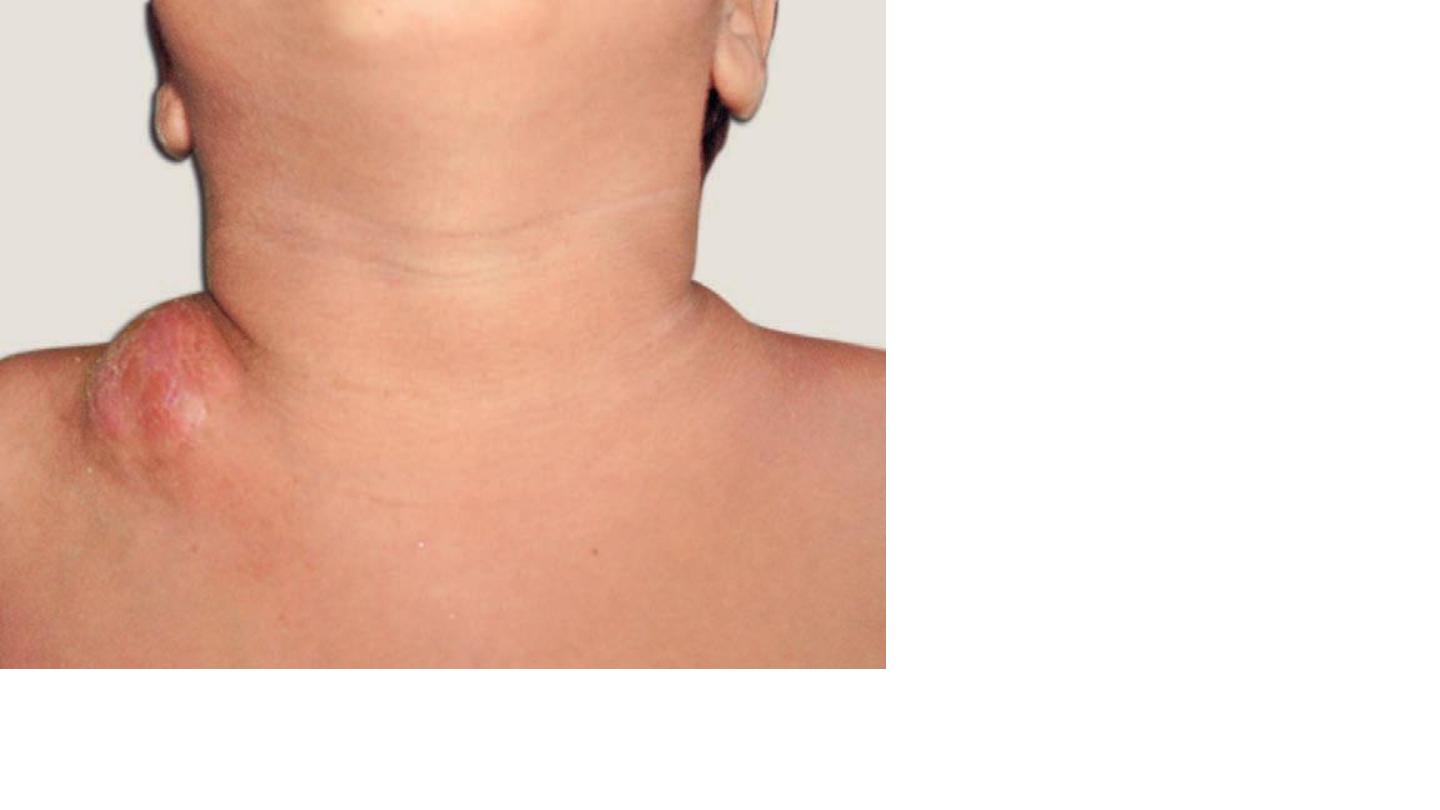
Thyroglossal cyst
Mid line is it charectecsic
Rx:
Surgery (sistrunk operation)
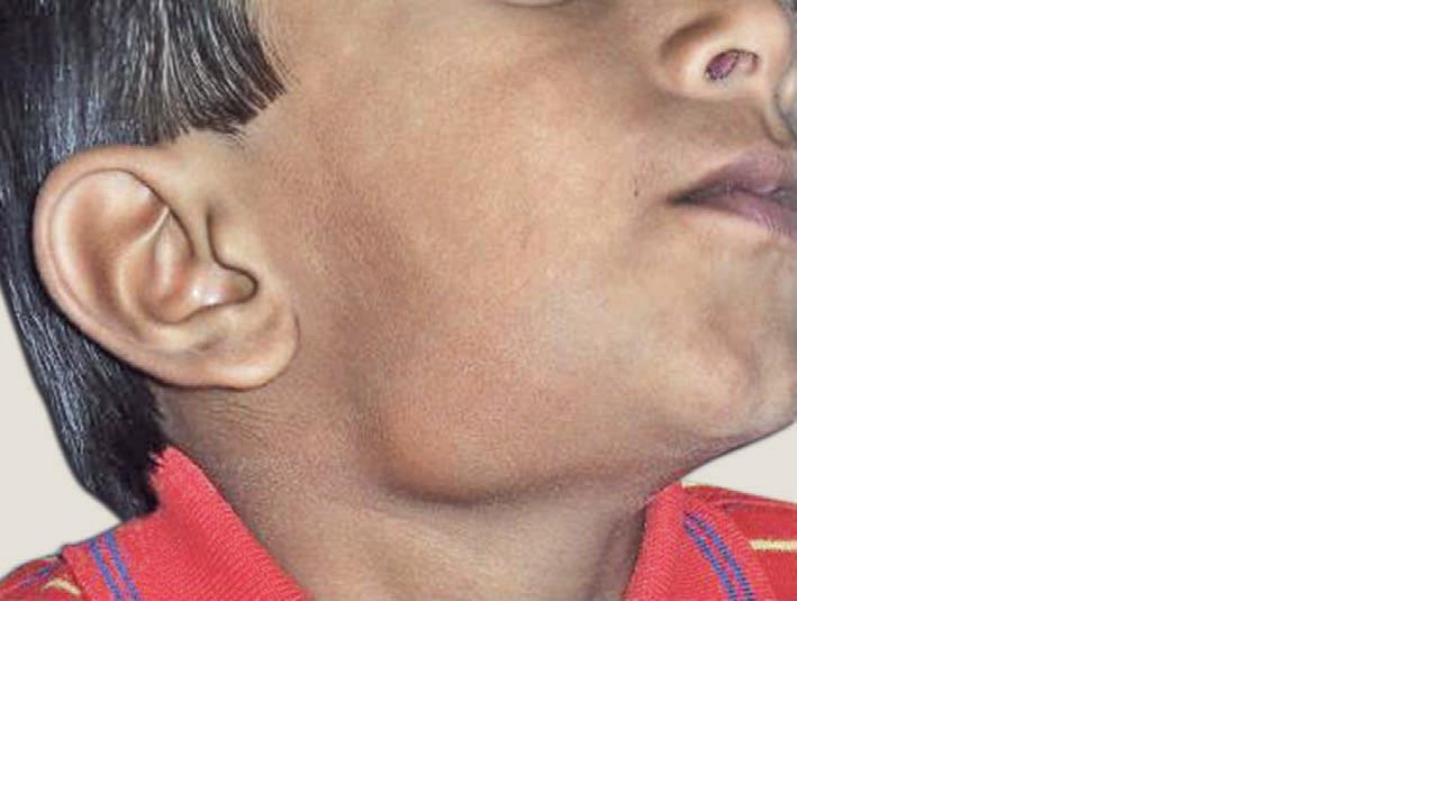
Submandibular swelling
DDx
Submandibular sailoadinitis
Parotiditis (mumps)
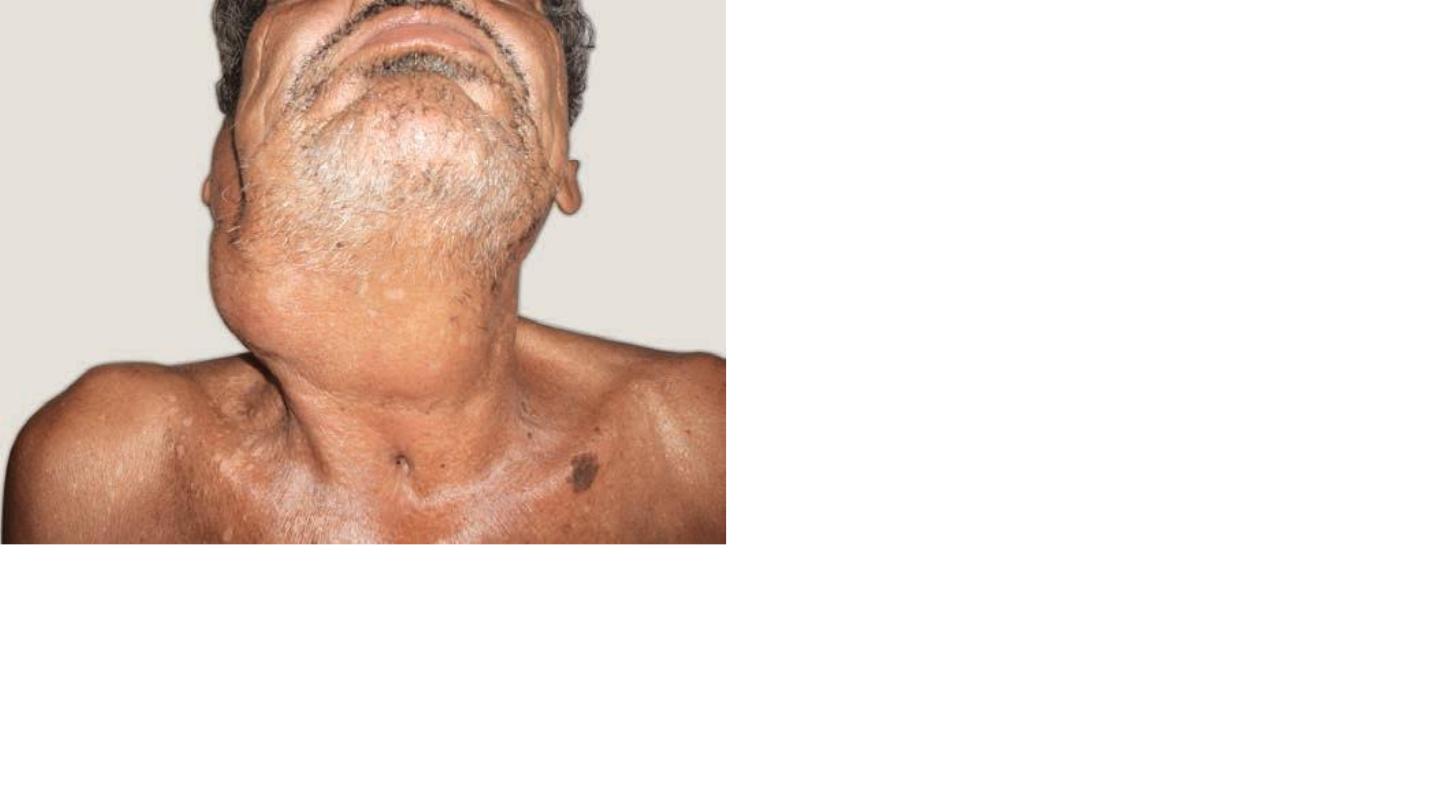
T.B
Carcinoma of the larynx
Advanced stage
Threes tracheostomy tube scar
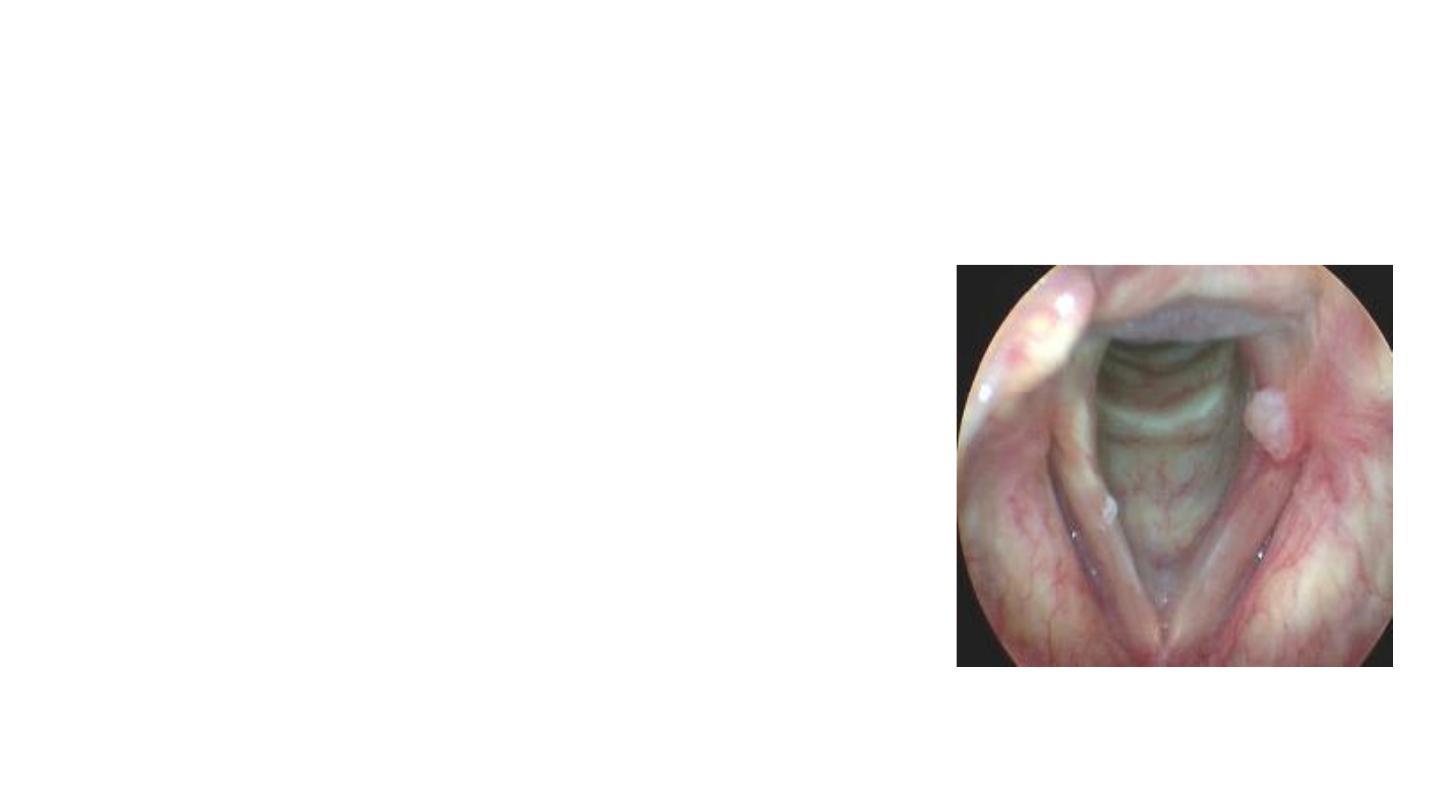
Vocal Cords Nodules
They are bilateral, small, grayish, white,
localized thickening of the vocal cords
situated at the junction of the anterior
third and posterior 2/3 of the vocal cord
Treatment
Small Voice rest and speech therapy.
Large Endoscopic excision followed by voice rest
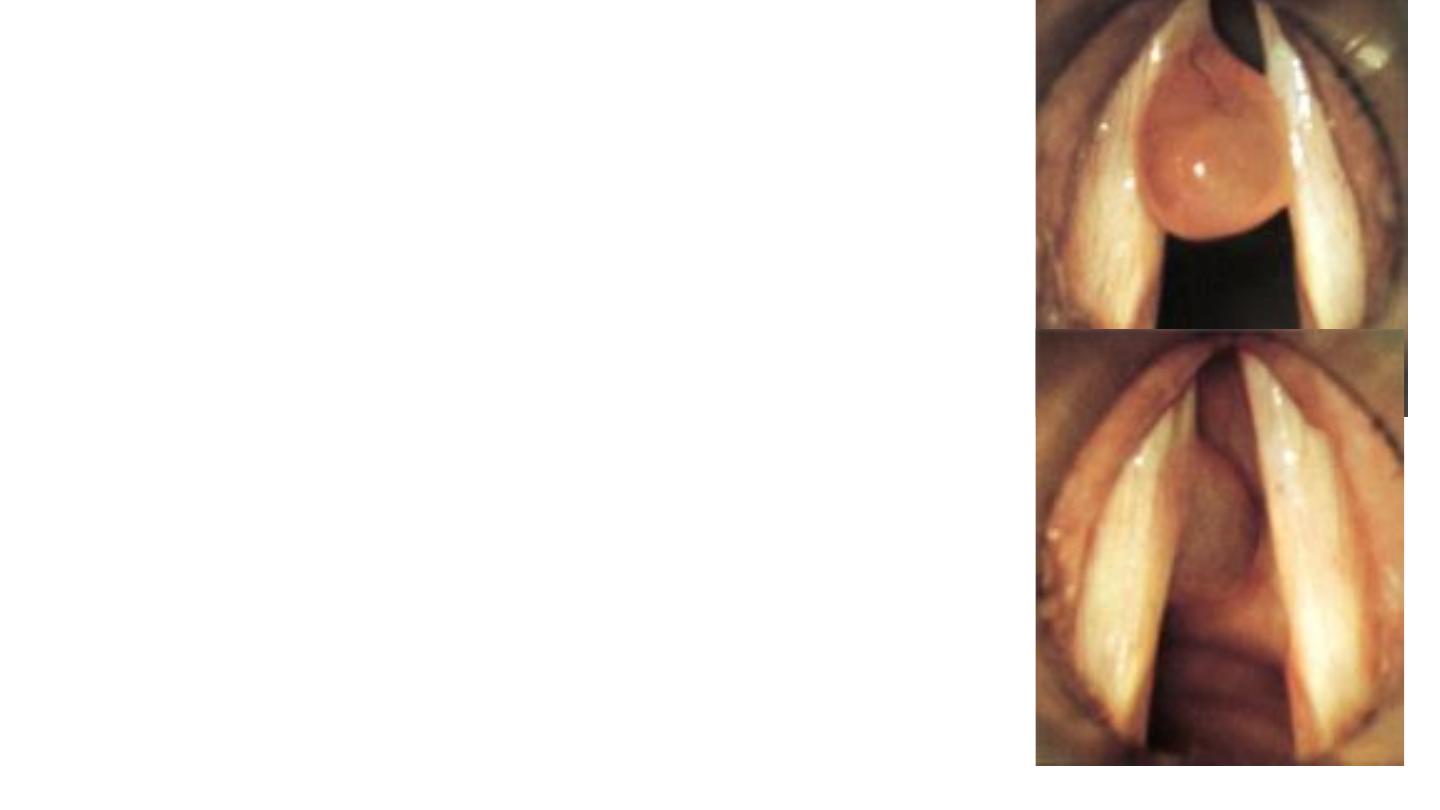

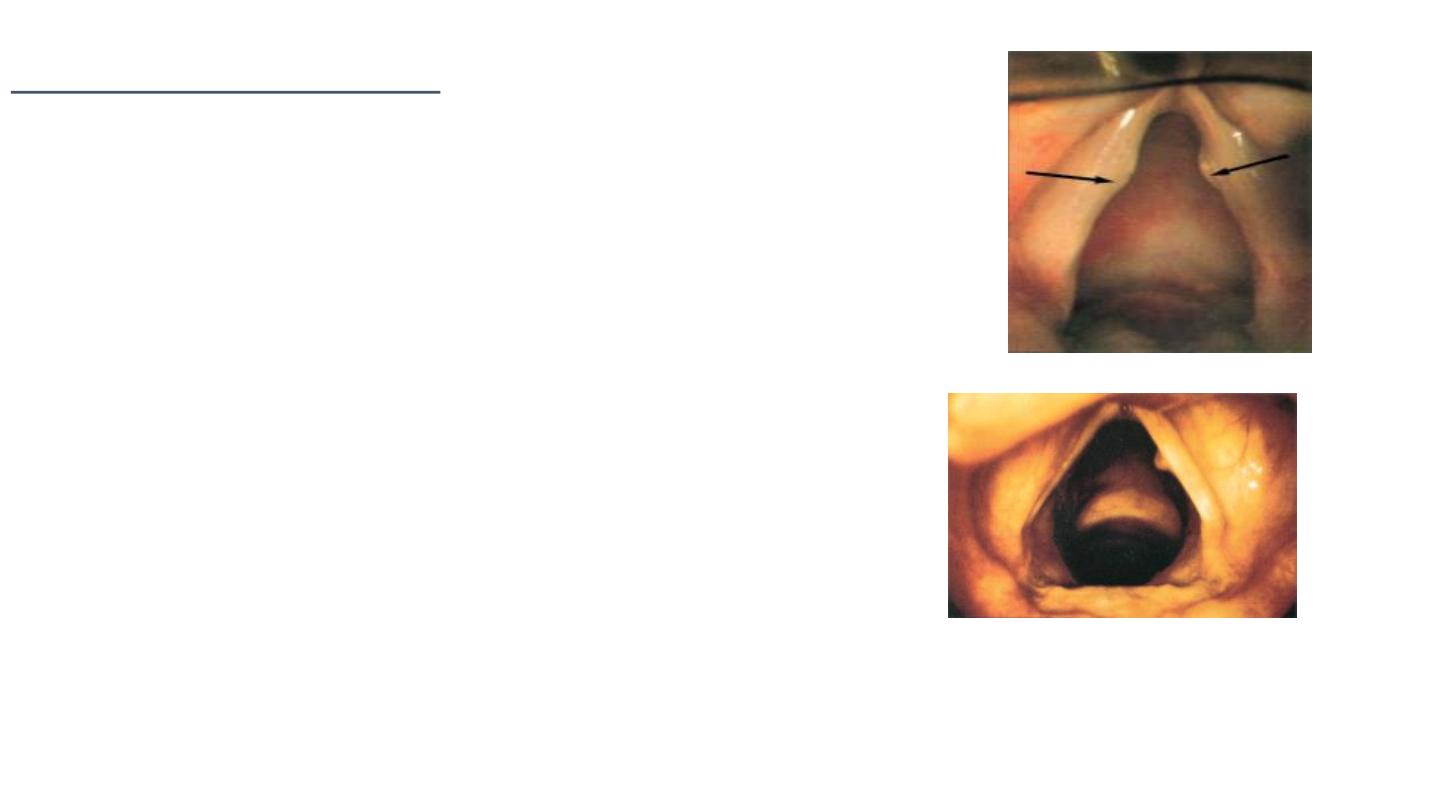
Laryngeal Polyp
Smooth unilateral glistering mass attached to the vocal
Aetiology: Vocal abuse, heavy smoking and allergy.
On Examination
:
Indirect laryngoscopy and fibroptic endoscopy:
sessile or pedunculated mass arising from the
vocal cord near the anterior commissure,
Treatment
Endoscopic excision followed by voice rest and
speech therapy. Histological examination is
exclude malignancy
Intubationa Granuloma
Aetiology
It results from injury to vocal process of
arytenoids due to rough intubation,
RX
Removal with laser endo scope +voice rest
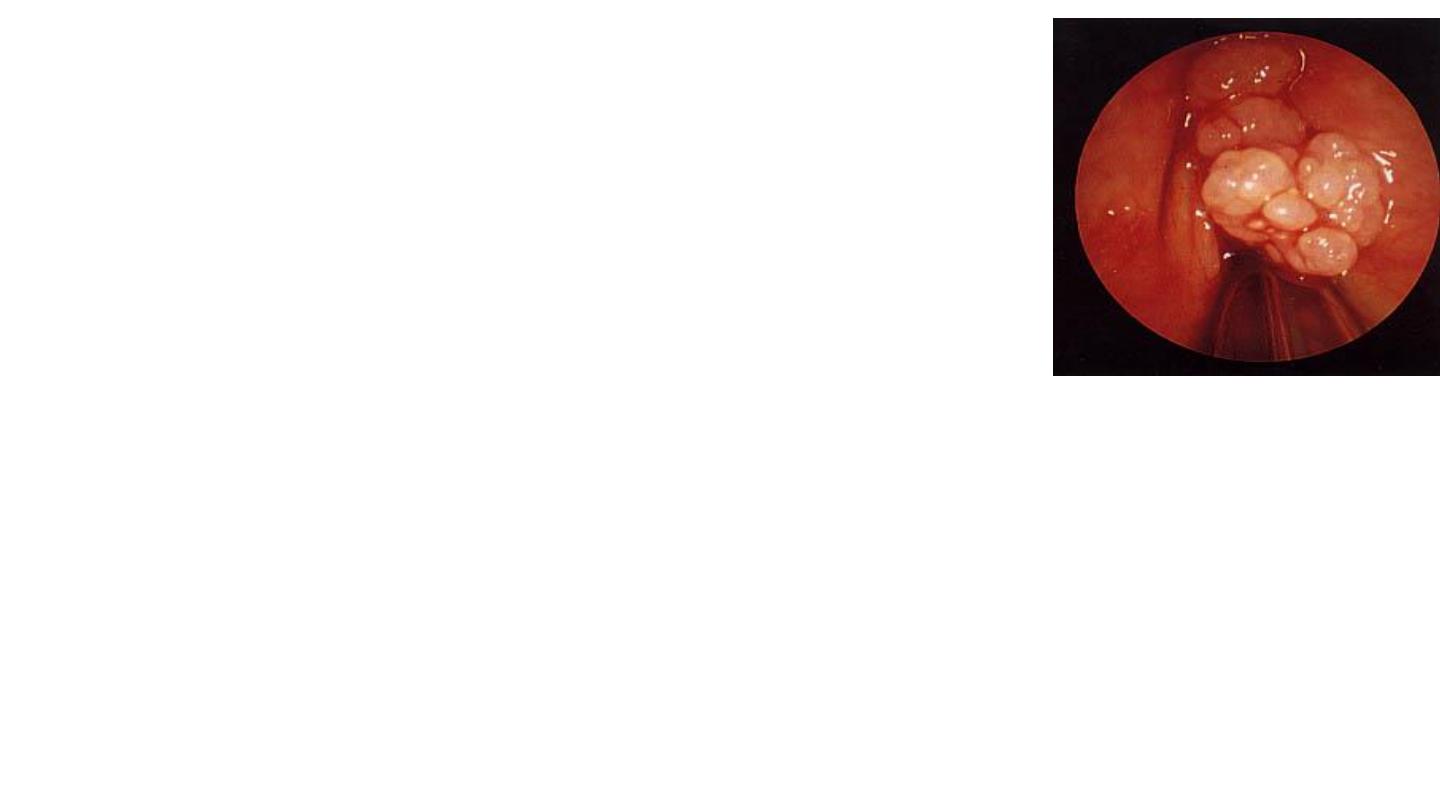

Juvenile Papilloma
Etiology: Virus HPV .
Clinical Picture:
Hoarseness of the voice.
Stridor from interference with the laryngeal intet.
On Exam.
The papillomas are commonly seen at the anterior aspect of the
vocal cords.
Endoscopic excision using LASER because
Interferon to brevent recurrence
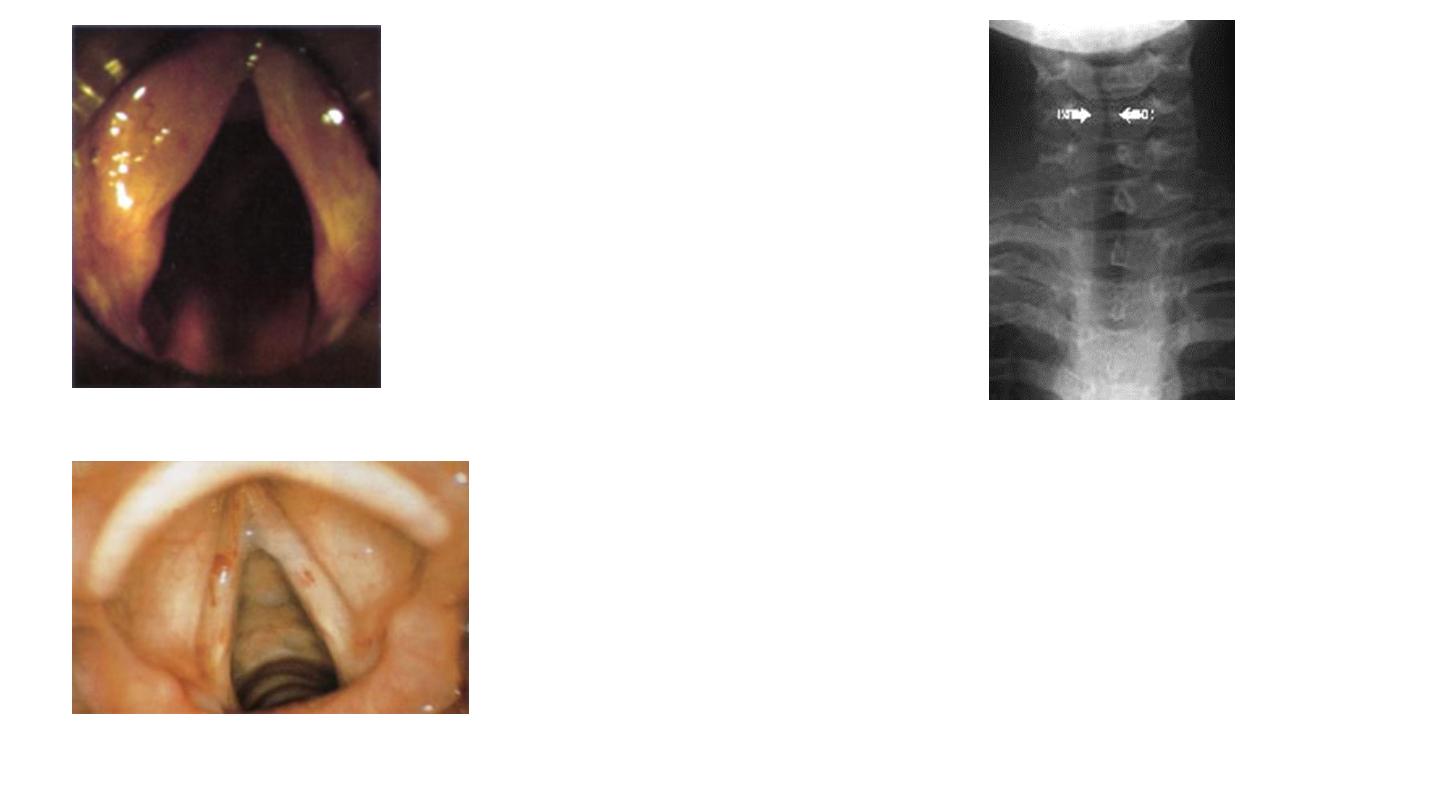
Chronic laryngitis
Acute laryngitis
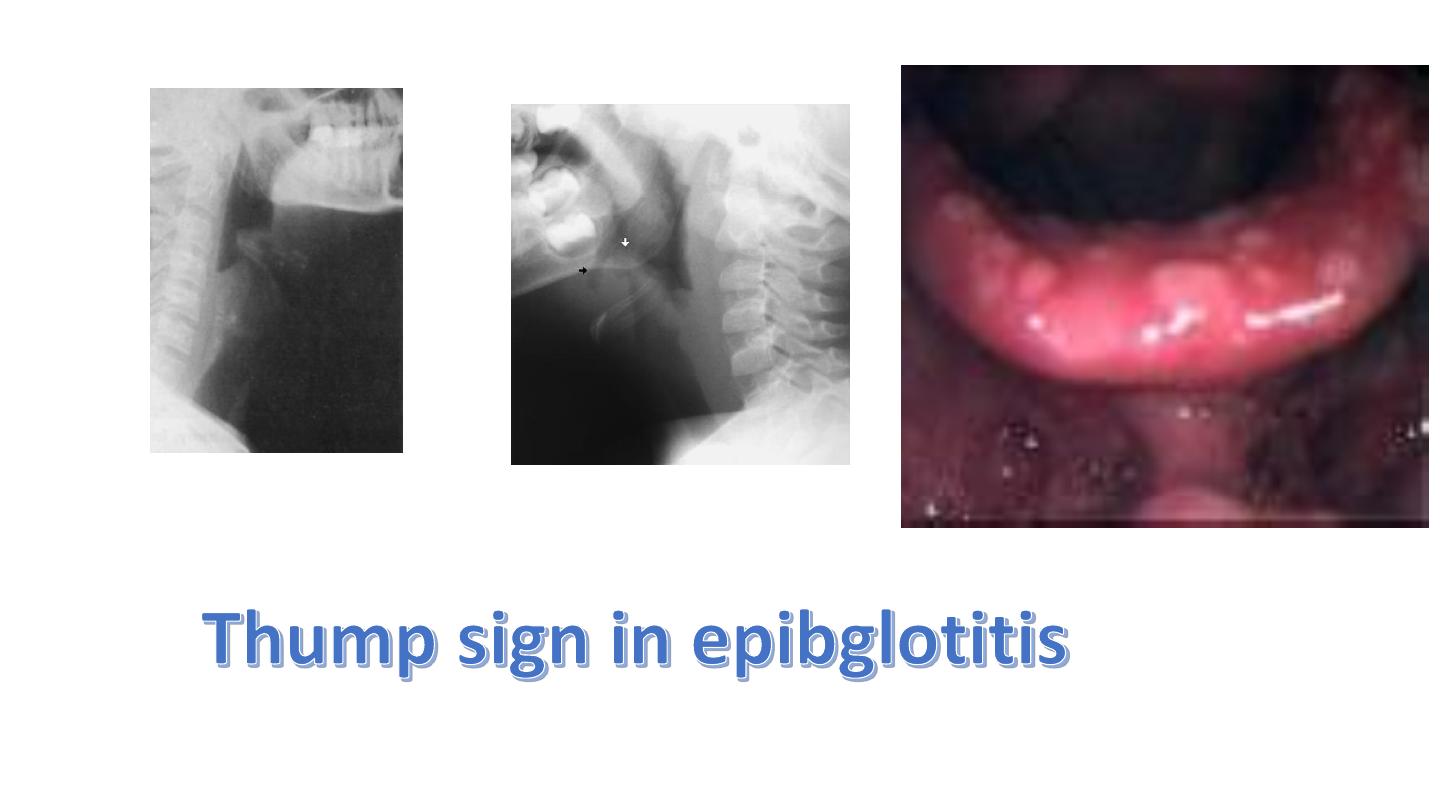
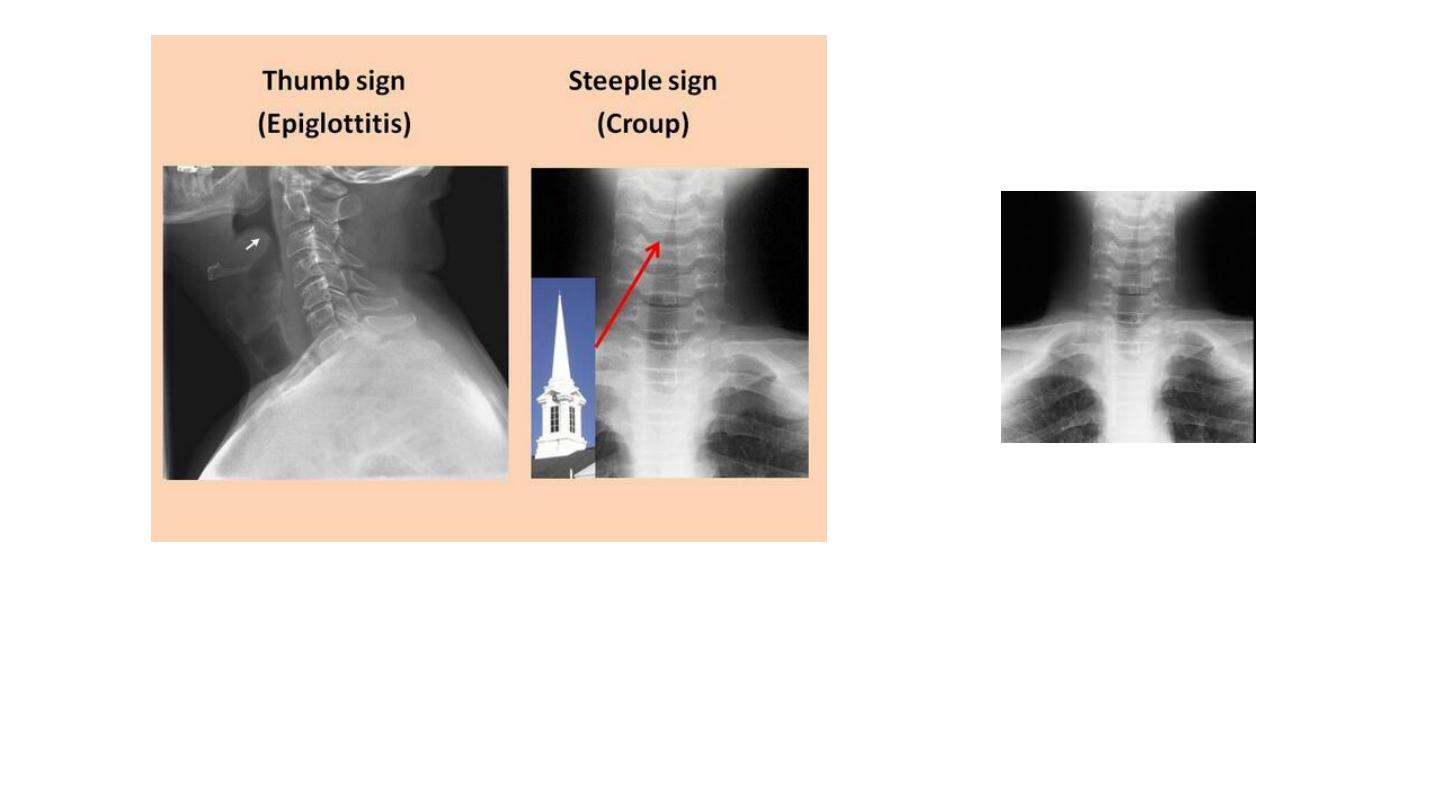
Steeple sign in croup
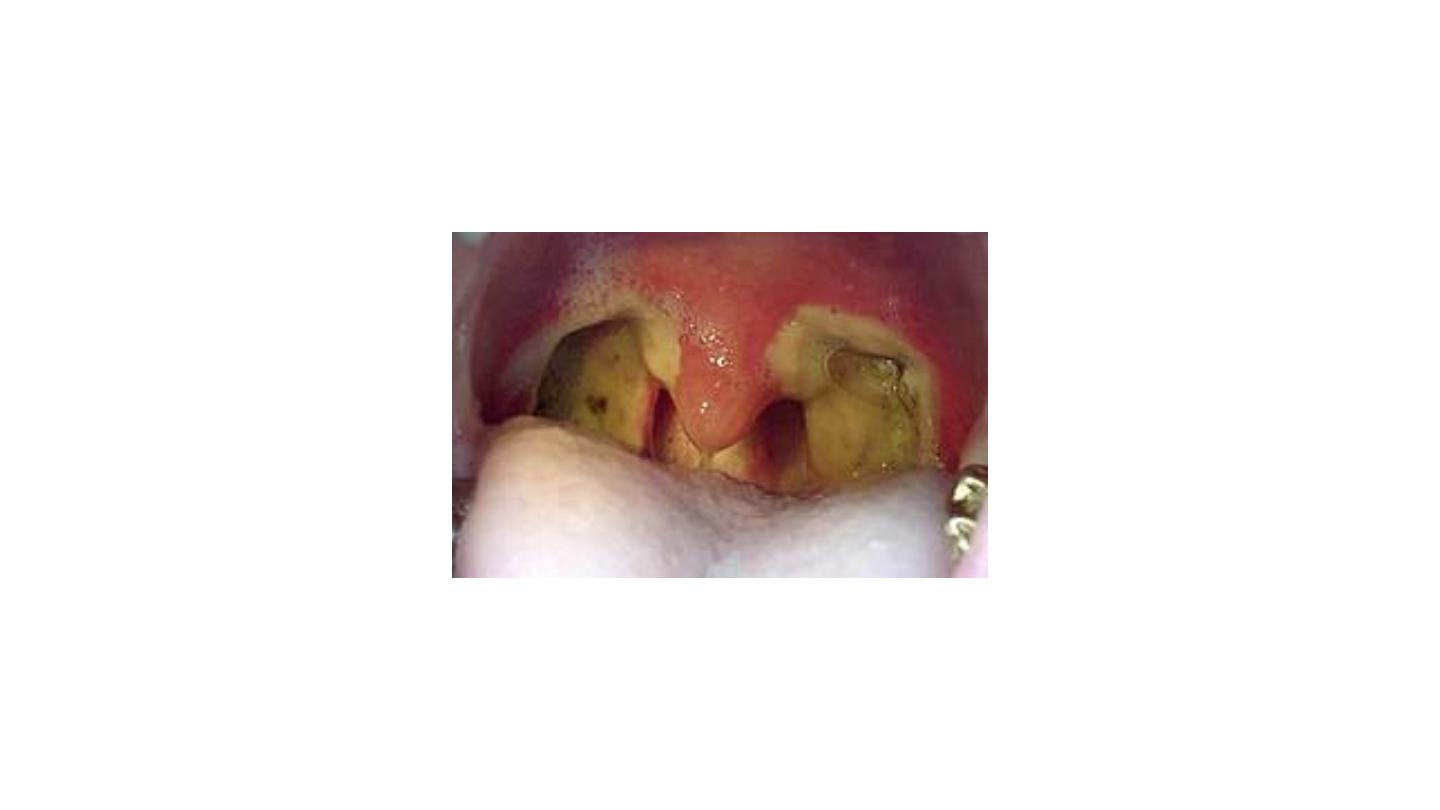
Chronic tonsillitis
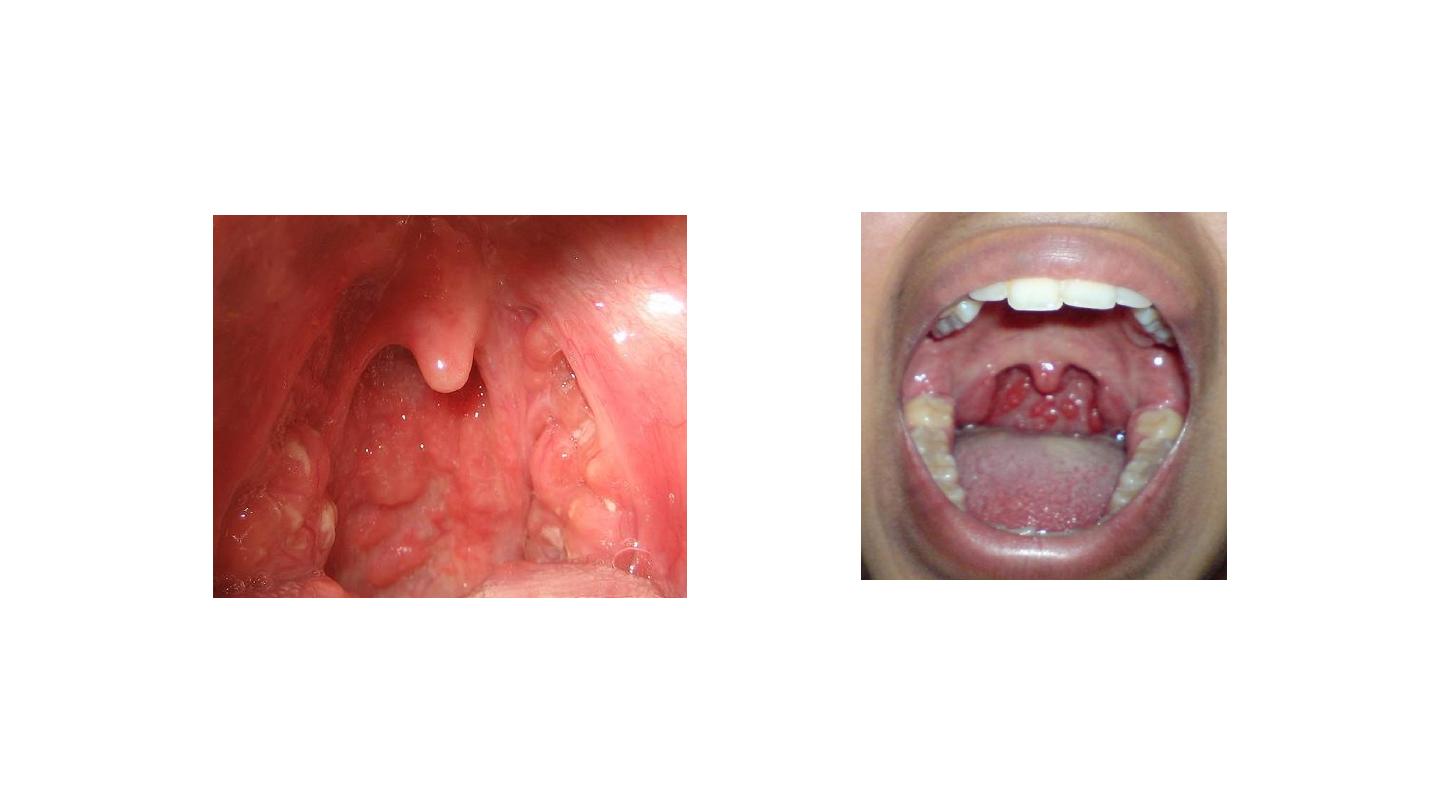
Chronic pharyngitis
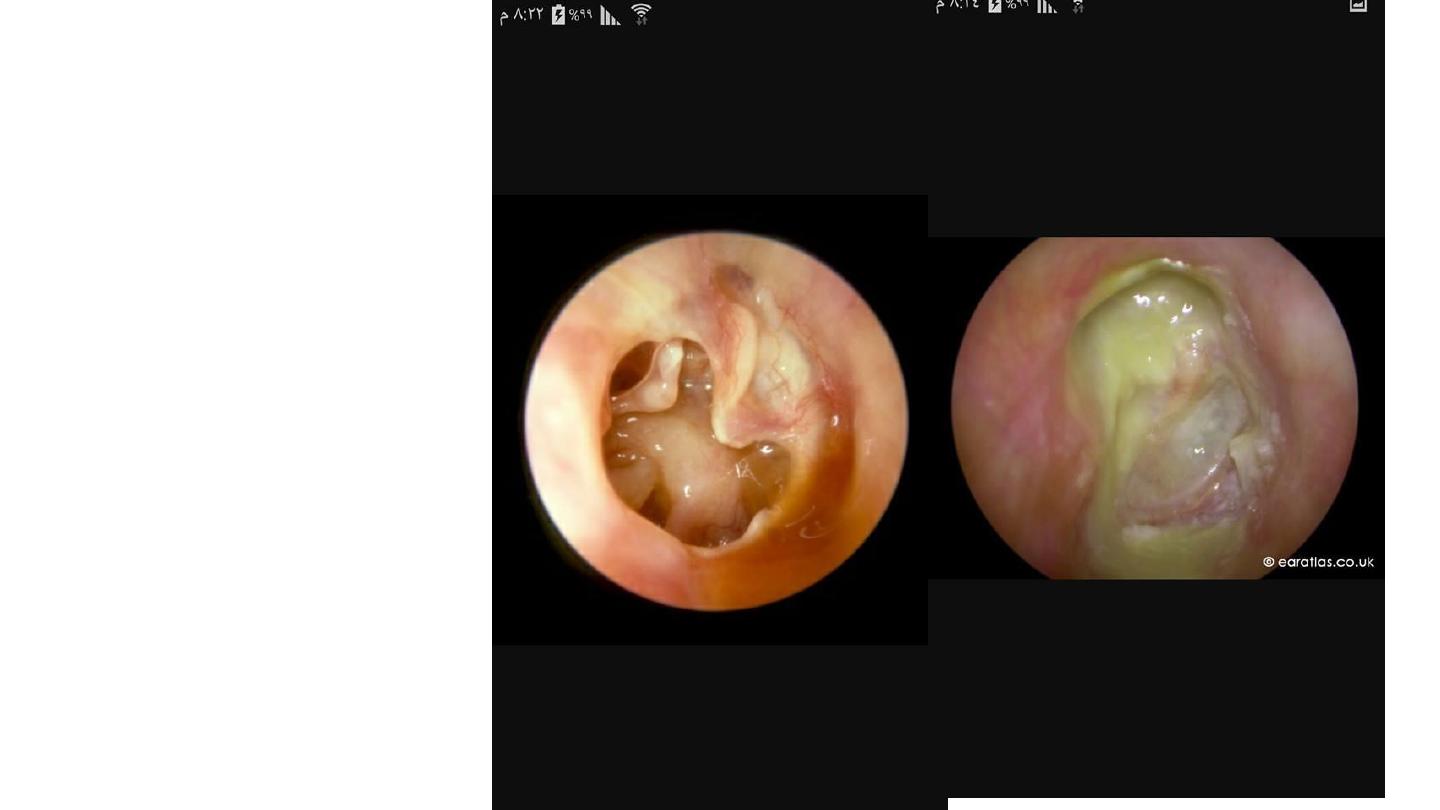
Case A in left side of the post:
Large kidney shaped TM perforation
involving pars tensa of R ear with
ossicles seen through the perforation
and some
Dx Chronic suppurative ot media
PTA will show cond H loss with air
bone gap
Case B the ear in the right side of the
pist:
Attic perforation with purulent greenish
discharge involving right ear mostly
due to cholesteatoma
C/S in case of chronic ear infections
show Gr negative bacteria and
anaerobes
In this case Pseudomonas is likely
The clue is the greenish discharge
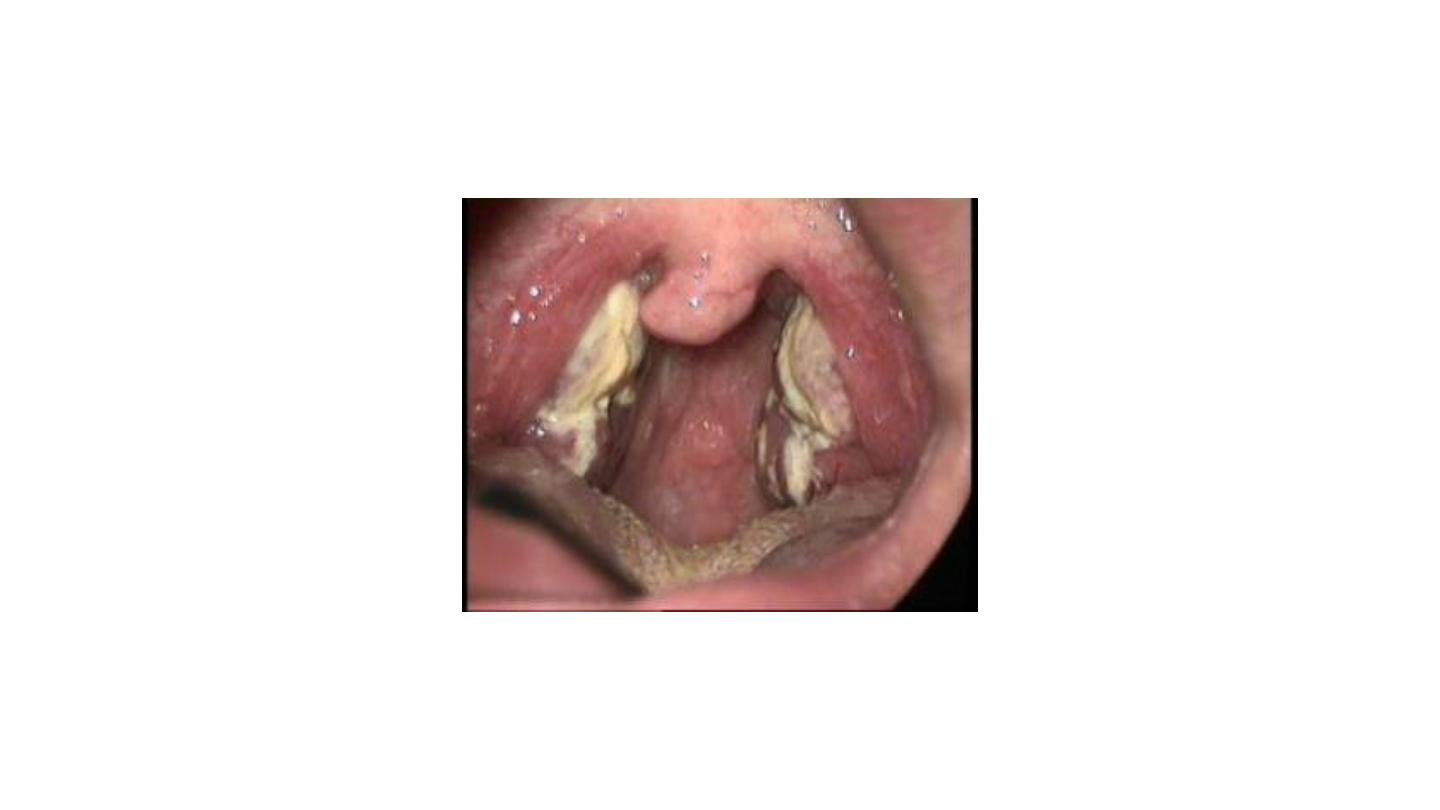
Membranous tonsillitis
Most likely infectious mononucleosis
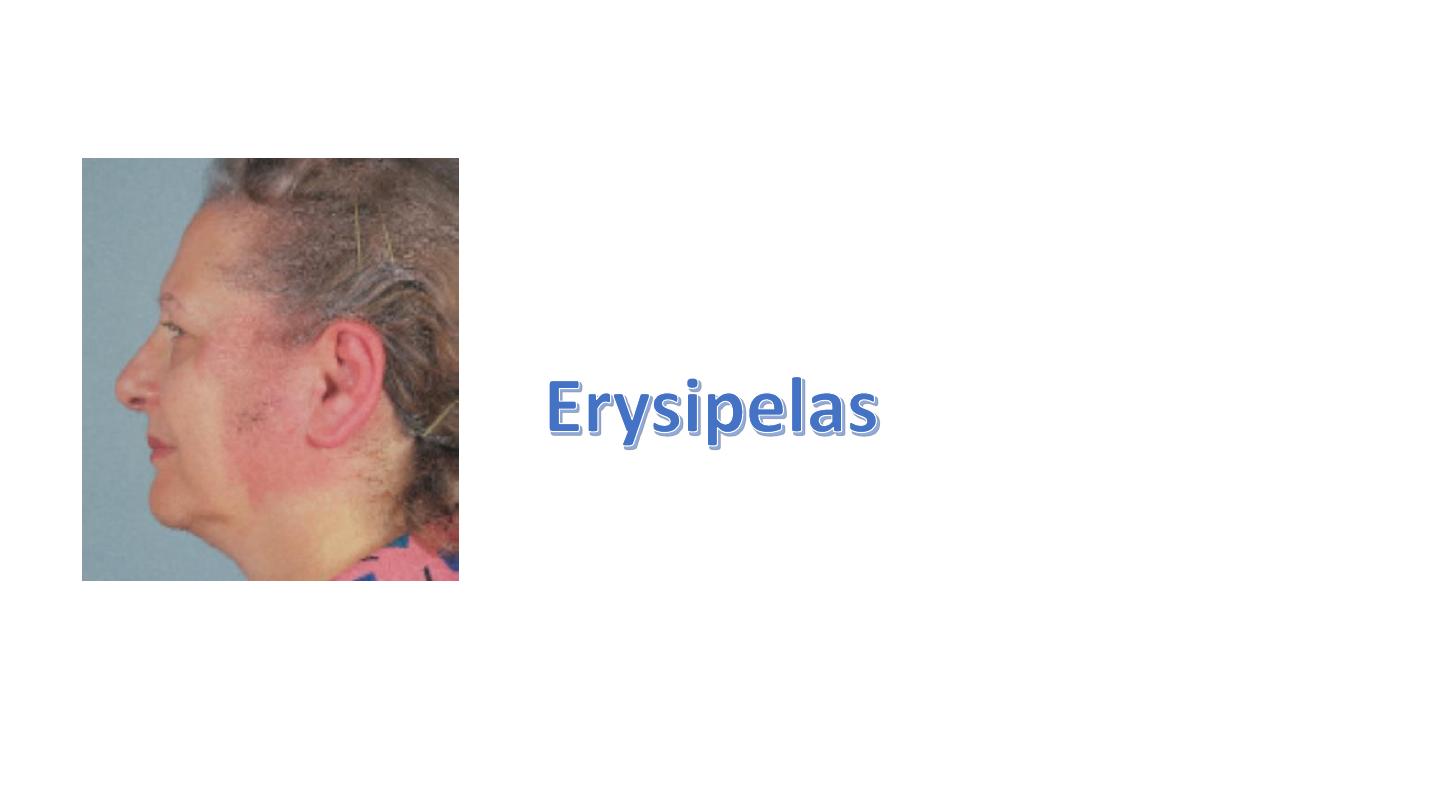
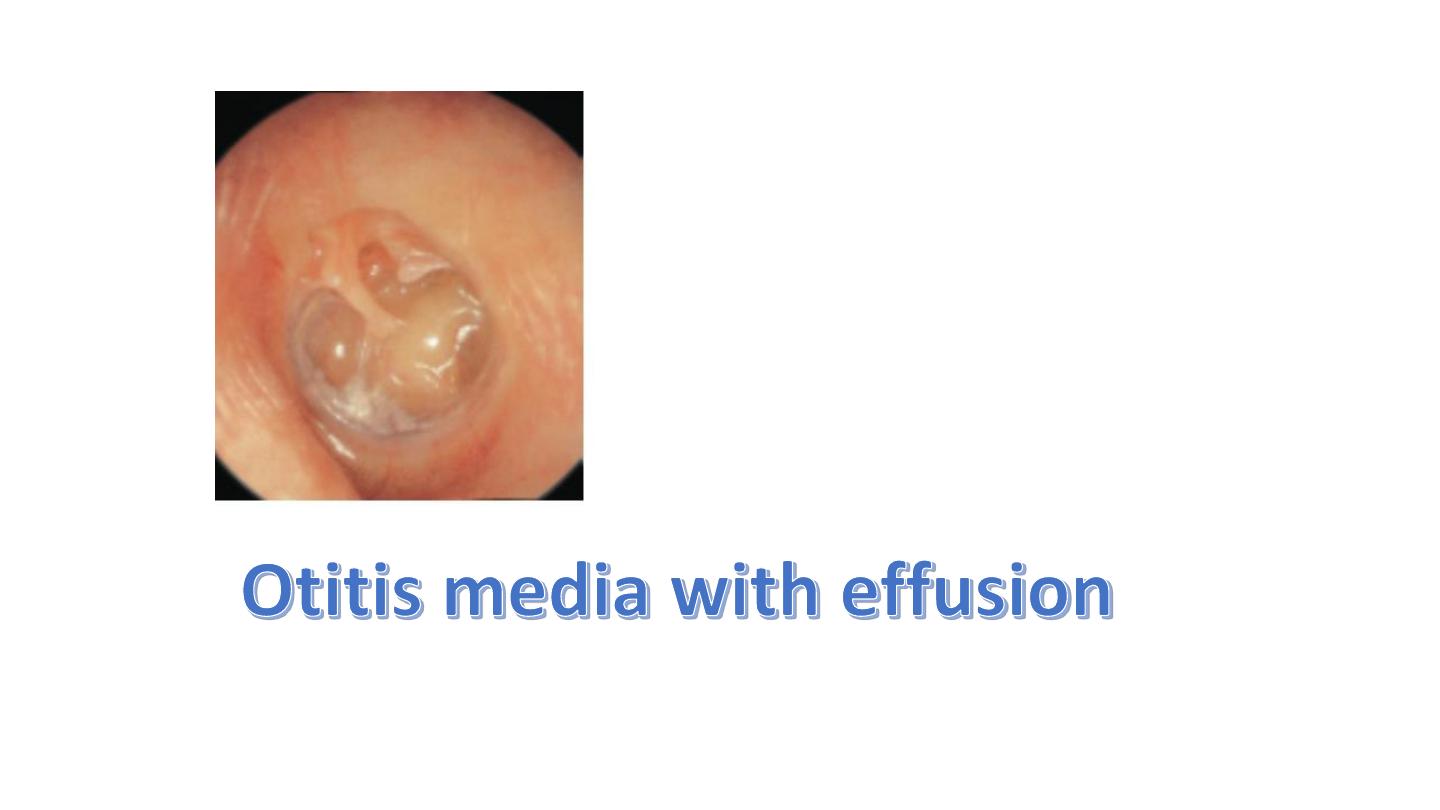
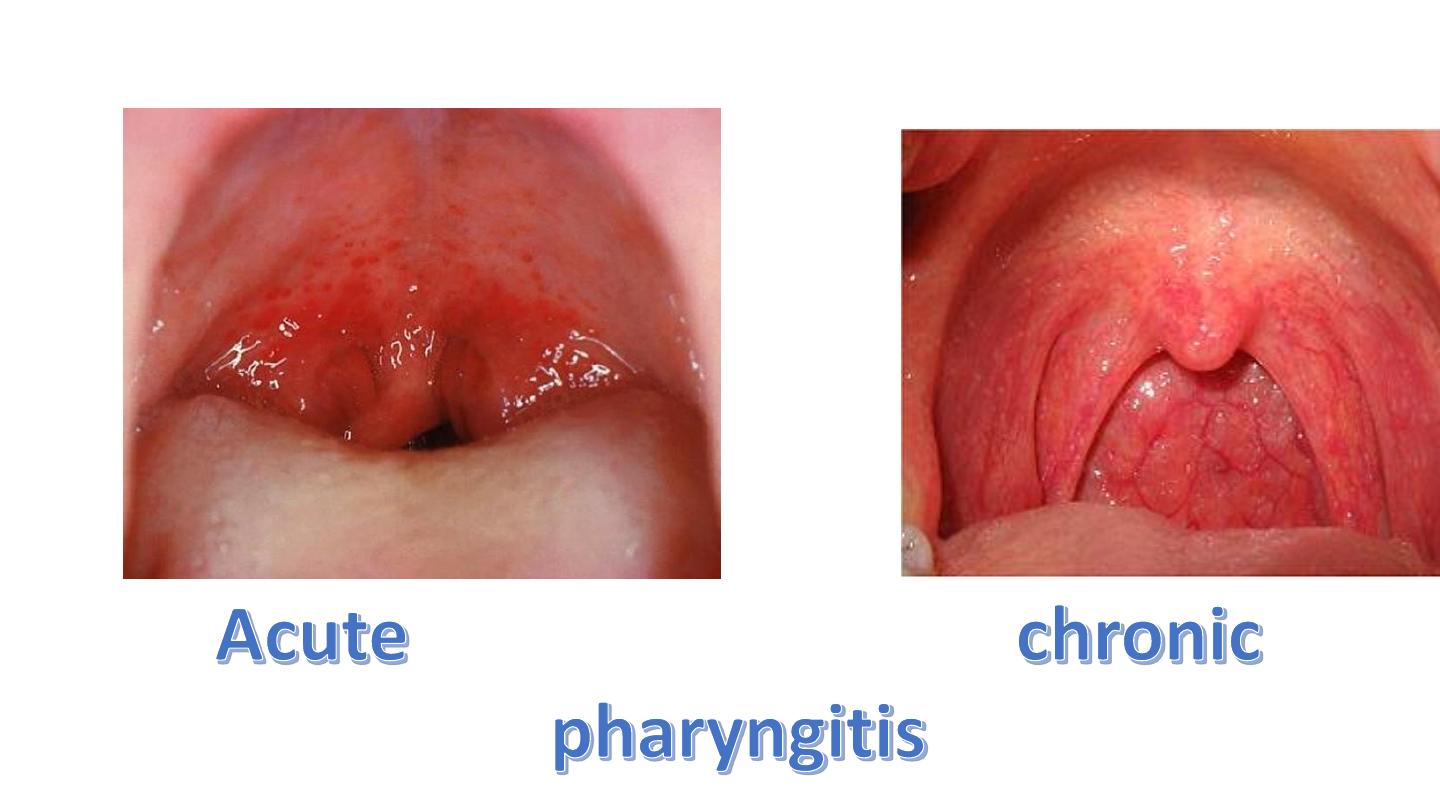
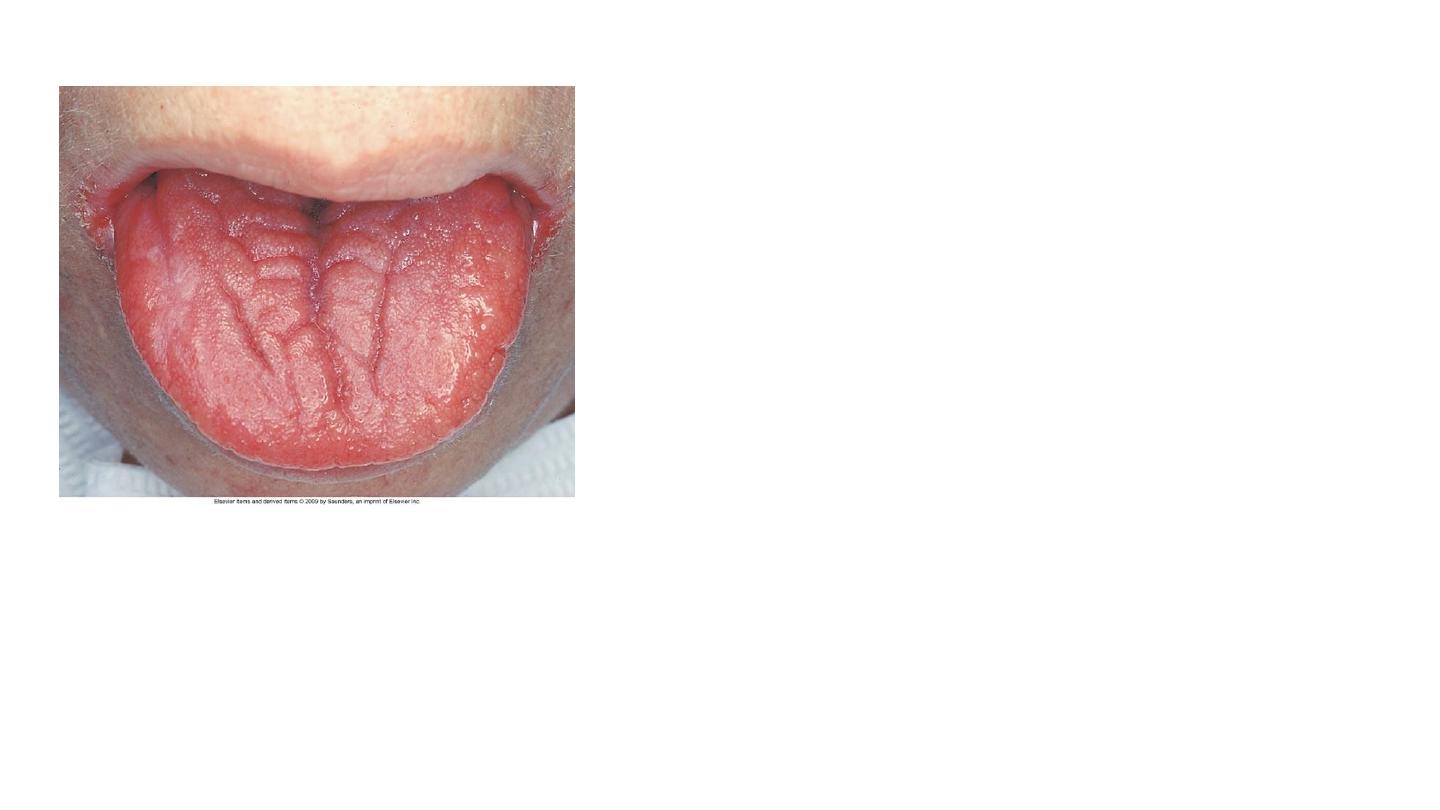
Plumer vinson syndrome
IDA
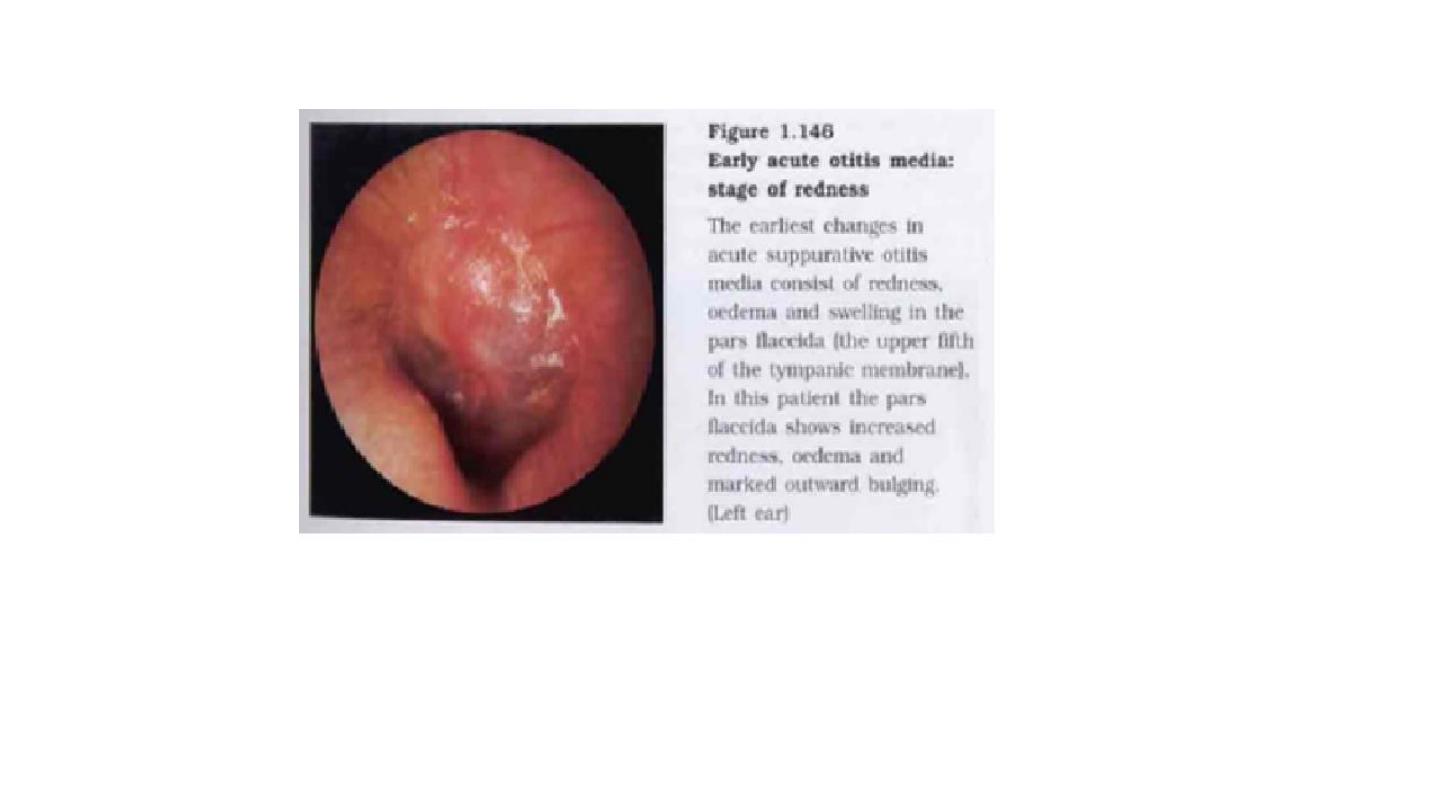
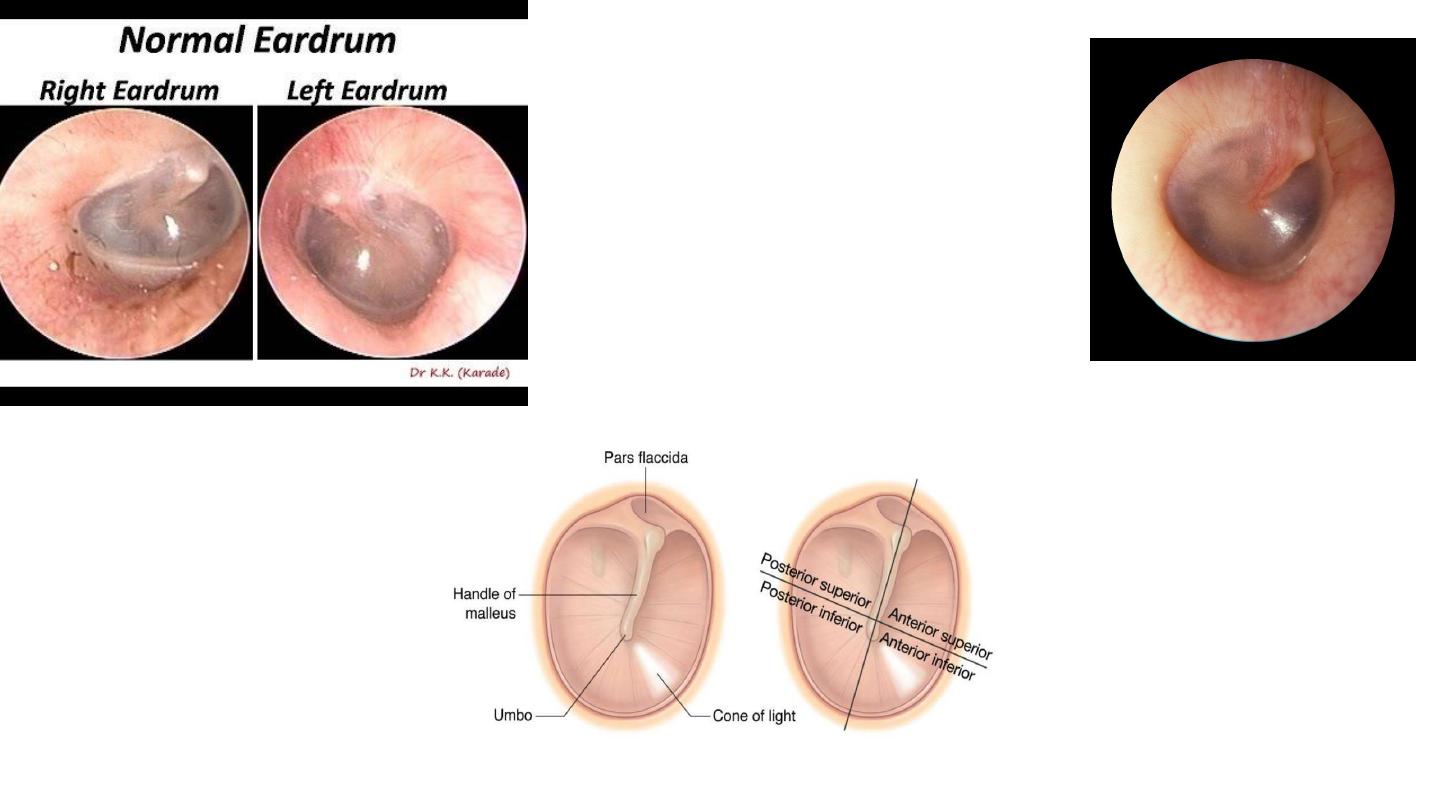
normal